Fully Automatic Liver and Tumor Segmentation from CT Image Using an AIM-Unet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
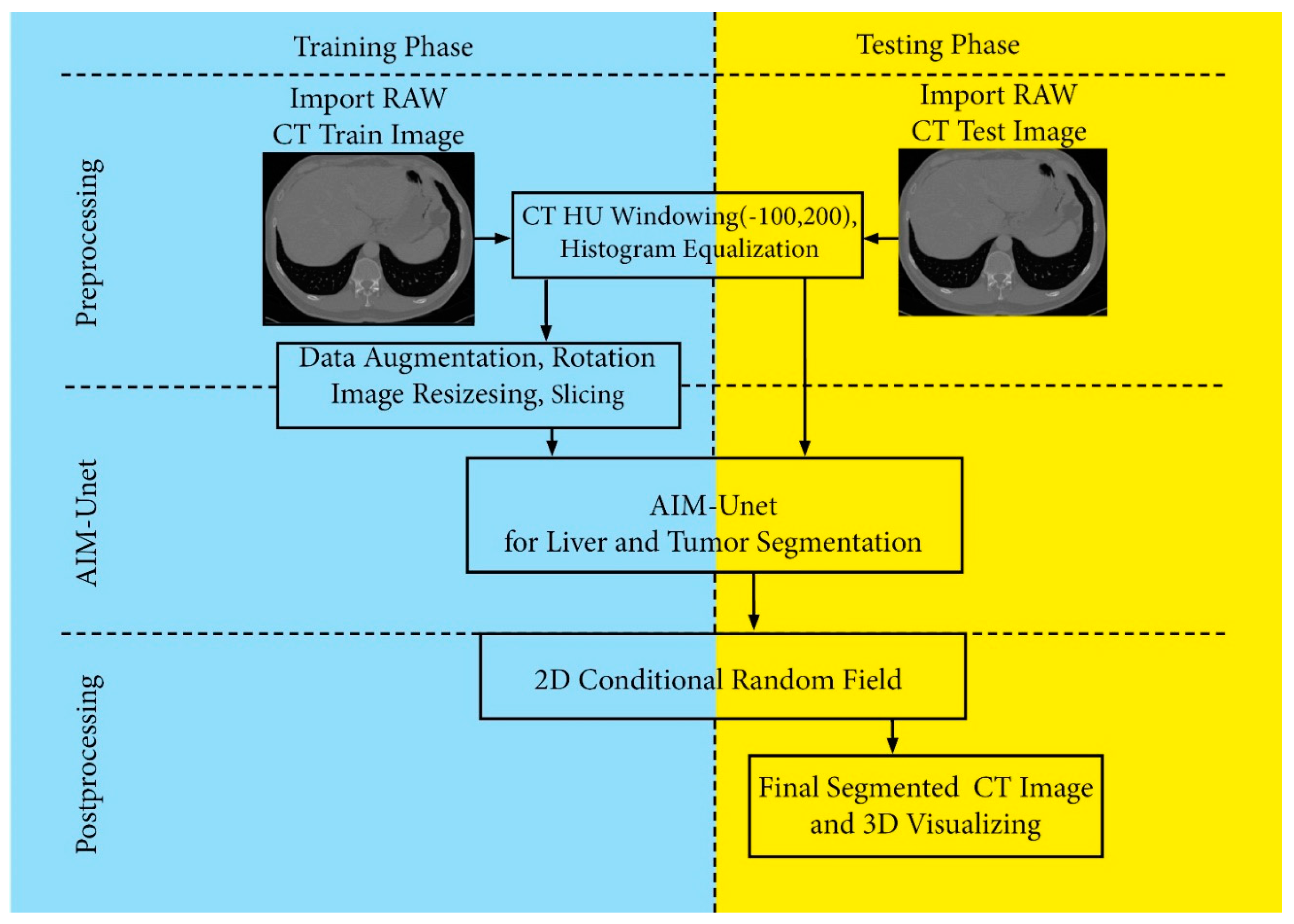
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Deep Learning Model Development
3.2. Inception Module Part (IMP)
4. Experiments
- CPU: Intel Core i7-10875H 2.3 GHZ
- GPU: 8 GB NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Super with Max-Q Design.
- Memory: 16,384 Mb RAM
4.1. Datasets
4.1.1. Patients and Data Acquisition Protocol
4.1.2. Creating the Dataset (Our Dataset)
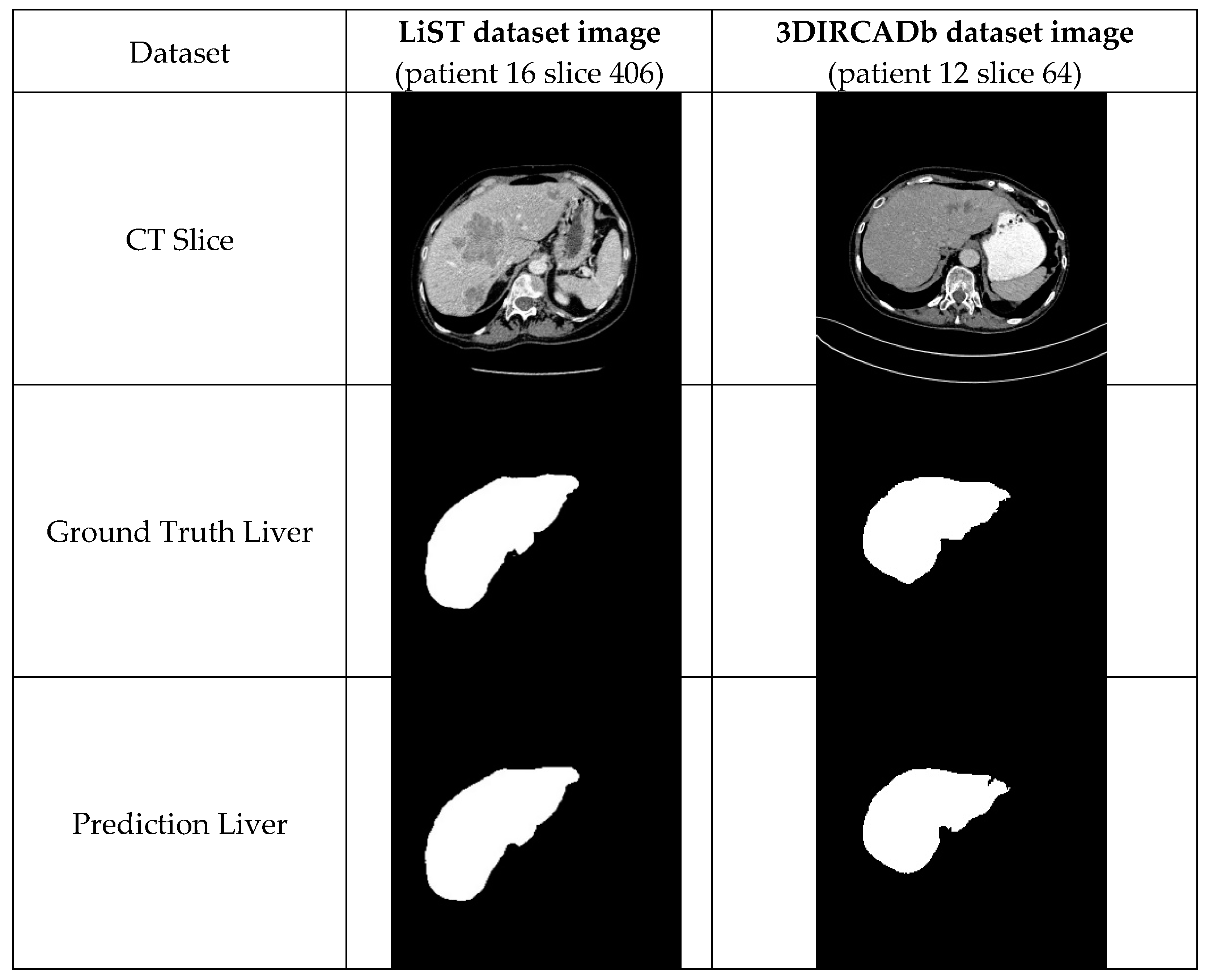
4.1.3. The LiTS Image Dataset
4.1.4. CHAOS Dataset
4.1.5. 3DIRCADb Dataset
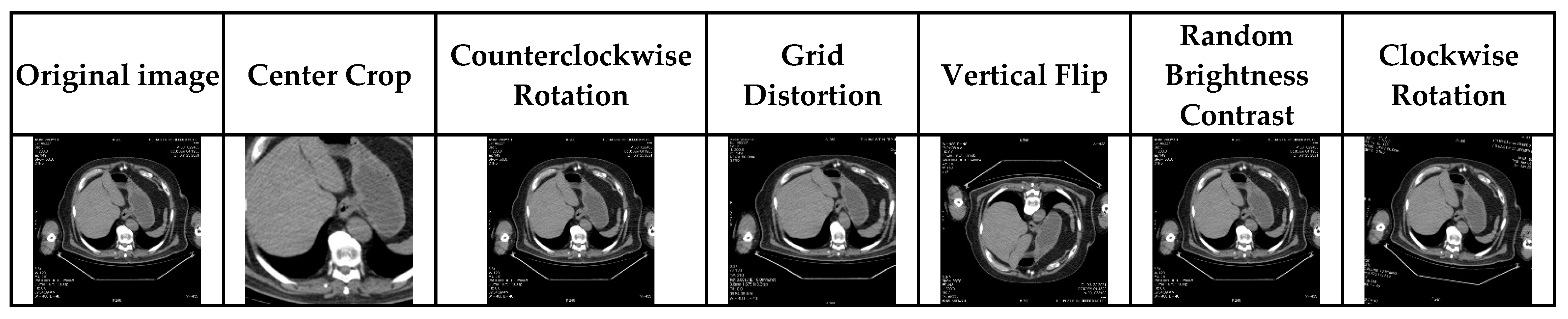
4.2. Data Preparation and Processing
4.3. Post-Processing
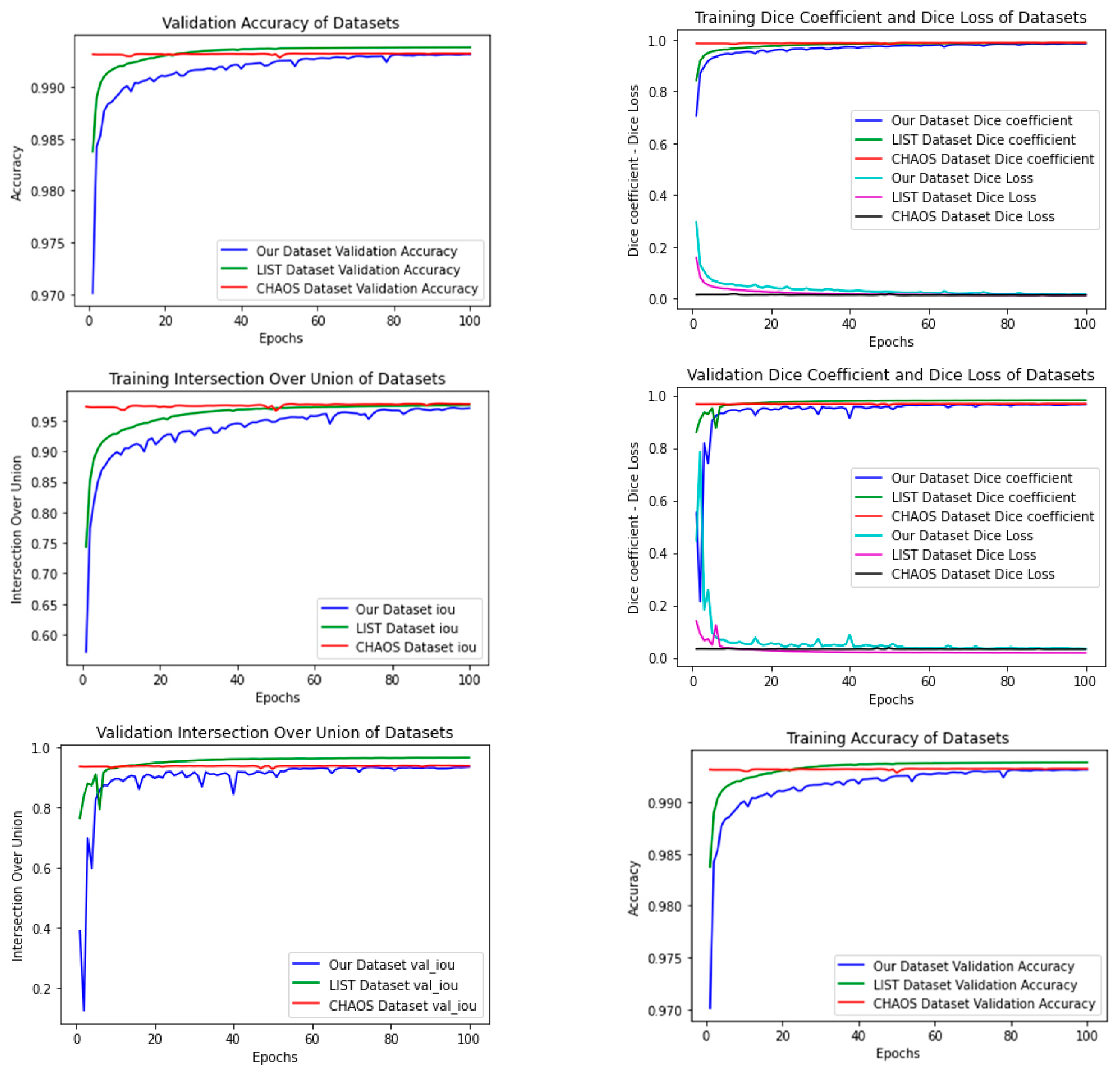
4.4. Metrics
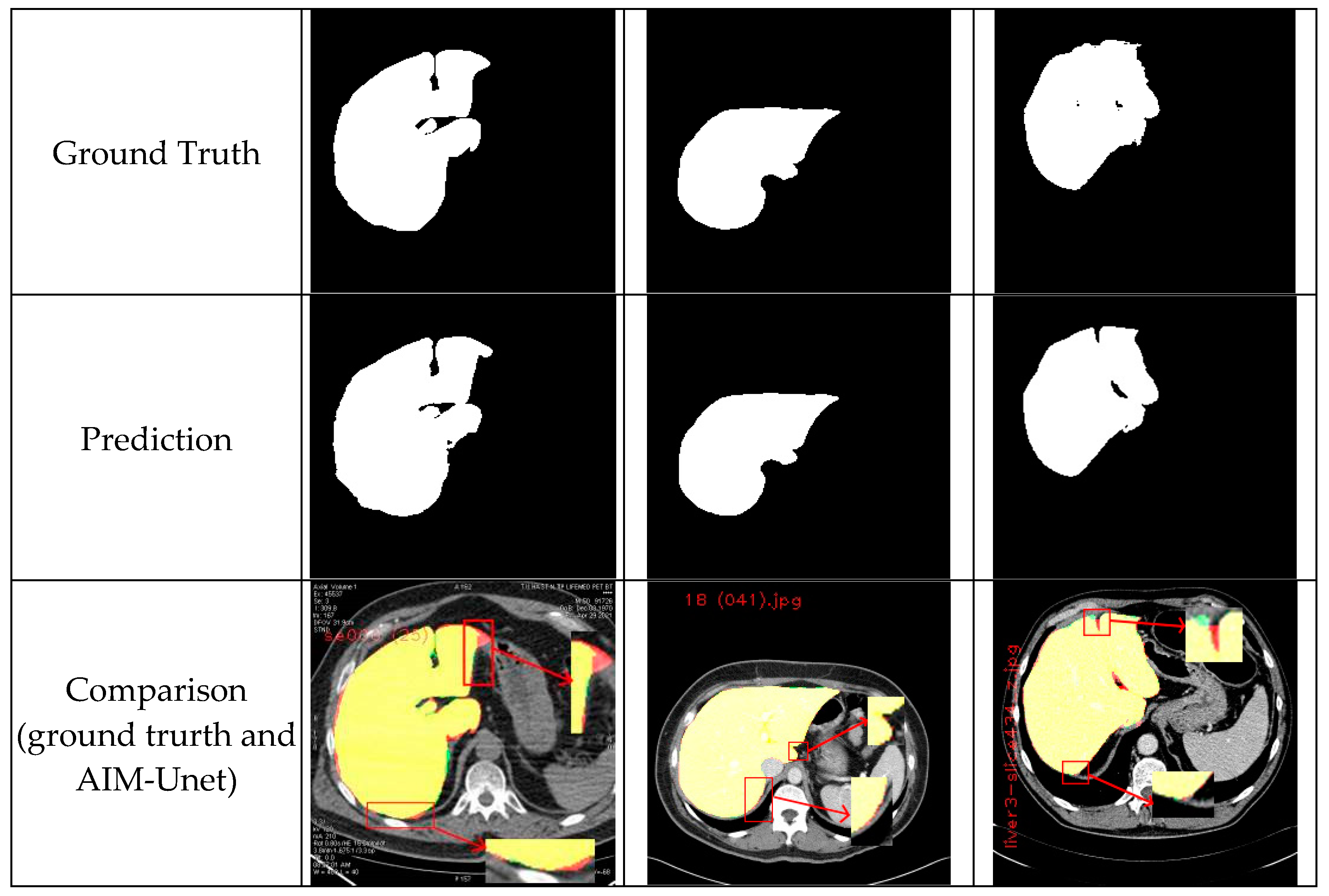
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bogovic, J.A.; Prince, J.L.; Bazin, P.-L. A multiple object geometric deformable model for image segmentation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2013, 117, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.H.; Yeo, A.U.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, C.; Goh, Y.; Cho, S.; Lee, S.B.; Lim, Y.K.; Kim, H.; Shin, D.; et al. Comparative clinical evaluation of atlas and deep-learning-based auto-segmentation of organ structures in liver cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Landesberger, T.; Bremm, S.; Kirschner, M.; Wesarg, S.; Kuijper, A. Visual Analytics for model-based medical image segmentation: Opportunities and challenges. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 4934–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Ding, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G. Fully automatic liver segmentation in CT images using modified graph cuts and feature detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 95, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotra, A.; Sivakumaran, L.; Chartrand, G.; Vu, K.-N.; Vandenbroucke-Menu, F.; Kauffmann, C.; Kadoury, S.; Gallix, B.; de Guise, J.A.; Tang, A. Liver segmentation: Indications, techniques and future directions. Insights Into Imaging 2017, 8, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Xiong, W.; Leow, W.K.; Tian, Q.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Han, T.; Venkatesh, S.; Wang, S.-C. Semi-automatic Segmentation of Liver Tumors from CT Scans Using Bayesian Rule-based 3D Region Growing. MIDAS J. 2008, 41, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Prince, J.L. Snakes, shapes, and gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1998, 7, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Meng, H.; Nandi, A.K. Significantly Fast and Robust Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Algorithm Based on Morphological Reconstruction and Membership Filtering. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 26, 3027–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Bischof, L. Seeded region growing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1994, 16, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, T.; Wolf, I.; Meinzer, H.-P. Active shape models for a fully automated 3D segmentation of the liver—An evaluation on clinical data. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2006, 4191, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, J.; Deng, K.; Wu, Y.; Li, X. Automatic Liver Segmentation Using a Statistical Shape Model with Optimal Surface Detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 2622–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomoshige, S.; Oost, E.; Shimizu, A.; Watanabe, H.; Nawano, S. A conditional statistical shape model with integrated error estimation of the conditions; Application to liver segmentation in non-contrast CT images. Med. Image Anal. 2014, 18, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambino, O.; Vitabile, S.; Re, G.L.; La Tona, G.; Librizzi, S.; Pirrone, R.; Ardizzone, E.; Midiri, M. Automatic volumetric liver segmentation using texture based region growing. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Complex, Intelligent and Software Intensive Systems, Krakow, Poland, 15–18 February 2010; pp. 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; He, J.; Yang, X.; Deklerck, R.; Cornelis, J. ACM-Based Automatic Liver Segmentation From 3-D CT Images by Combining Multiple Atlases and Improved Mean-Shift Techniques. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2013, 17, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremers, D.; Rousson, M.; Deriche, R. A Review of Statistical Approaches to Level Set Segmentation: Integrating Color, Texture, Motion and Shape. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2006, 72, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, L.; Hu, H.; Yu, H.; Jin, C.; Wang, J.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.-W. Combined density, texture and shape features of multi-phase contrast-enhanced CT images for CBIR of focal liver lesions: A preliminary study. Smart Innov. Syst. Technol. 2016, 45, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Chi, Y.; Liu, J.; Venkatesh, S.K.; Brown, M.S. Three-Dimensional Spatiotemporal Features for Fast Content-Based Retrieval of Focal Liver Lesions. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lu, Z.; Yu, M.; Huang, M.; Feng, Q.; Chen, W. Content-Based Retrieval of Focal Liver Lesions Using Bag-of-Visual-Words Representations of Single- and Multiphase Contrast-Enhanced CT Images. J. Digit. Imaging 2012, 25, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamant, I.; Goldberger, J.; Klang, E.; Amitai, M.; Greenspan, H. Multi-phase liver lesions classification using relevant visual words based on mutual information. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 12th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Brooklyn, NY, USA, 16–19 April 2015; pp. 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDiamant, I.; Hoogi, A.; Beaulieu, C.F.; Safdari, M.; Klang, E.; Amitai, M.; Greenspan, H.; Rubin, D.L. Improved Patch-Based Automated Liver Lesion Classification by Separate Analysis of the Interior and Boundary Regions. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRida, I.; Al-Maadeed, N.; Al-Maadeed, S.; Bakshi, S. Automatic Liver and Lesion Segmentation in CT Using Cascaded Fully Convolutional Neural Networks and 3D Conditional Random Fields. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2016), Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2016; pp. 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamnitsas, K.; Ledig, C.; Newcombe, V.F.; Simpson, J.P.; Kane, A.D.; Menon, D.K.; Rueckert, D.; Glocker, B. Efficient multi-scale 3D CNN with fully connected CRF for accurate brain lesion segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 36, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YZeng, Y.-Z.; Liao, S.-H.; Tang, P.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Liao, M.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Y. Automatic liver vessel segmentation using 3D region growing and hybrid active contour model. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 97, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moltz, J.H.; Bornemann, L.; Dicken, V.; Peitgen, H.-O. Segmentation of Liver Metastases in CT Scans by Adaptive Thresholding and Morphological Processing. MIDAS J. 2008, 41, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.; Liu, J.; Yin, F.; Tian, Q.; Xiong, W.; Zhou, J.; Yingyi, Q.; Han, T.; Venkatesh, S.; Wang, S.-C. A semi-automated method for liver tumor segmentation based on 2D region growing with knowledge-based constraints. MIDAS J. 2008, 41, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiman, M.; Eliassaf, O.; Taieb, Y.; Joskowicz, L.; Azraq, Y.; Sosna, J. An iterative Bayesian approach for nearly automatic liver segmentation: Algorithm and validation. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2008, 3, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawiaski, J.; Decenciere, E.; Bidault, F. Interactive Liver Tumor Segmentation Using Graph-cuts and Watershed. In Proceedings of the 11th international conference on medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (MICCAI 2008), New York, NY, USA, 6–10 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cornelio, L.K.S.; del Castillo, M.A.V.; Naval, P.C. U-ISLES: Ischemic Stroke Lesion Segmentation Using U-Net. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 869, pp. 326–336. [Google Scholar]
- VVi, V.T.T.; Oh, A.-R.; Lee, G.-S.; Yang, H.-J.; Kim, S.-H. Automatic Extraction of Liver Region from Medical Images by Using an MFUnet. Korean Inst. Smart Media 2020, 9, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, R.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Rajalakshmi, R.; Raymann, J. Delineation of ischemic lesion from brain MRI using attention gated fully convolutional network. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2021, 11, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hille, G.; Agrawal, S.; Wybranski, C.; Pech, M.; Surov, A.; Saalfeld, S. Joint Liver and Hepatic Lesion Segmentation using a Hybrid CNN with Transformer Layers. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.10981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Liu, S.; Sharan, R.V.; Coiera, E.; Berkovsky, S. Weak label based Bayesian U-Net for optic disc segmentation in fundus images. Artif. Intell. Med. 2022, 126, 102261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, C.E.; Yang, J.; Anderson, B.M.; Court, L.E.; Brock, K.B. Advances in Auto-Segmentation. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 29, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, S.; Cheng, M.; Tao, Y.-B.; Wang, Y.-F.; Juengpanich, S.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-K.; Yan, Y.-Y.; Lu, W.; Lue, J.-M.; et al. Deep Learning for Accurate Diagnosis of Liver Tumor Based on Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Clinical Data. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A.; Liu, W.; et al. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halawa, L.J.; Wibowo, A.; Ernawan, F. Face Recognition Using Faster R-CNN with Inception-V2 Architecture for CCTV Camera. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Informatics and Computational Sciences (ICICoS), Semarang, Indonesia, 29–30 October 2019; pp. 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Li, L.; Luo, W.; Wang, K.C.P.; Guo, J. Transfer Learning Based Traffic Sign Recognition Using Inception-v3 Model. Period. Polytech. Transp. Eng. 2019, 47, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xu, C.; Nan, B. Inception-v3 for flower classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd international conference on image, vision and computing (ICIVC), Chengdu, China, 2–4 June 2017; pp. 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Längkvist, M.; Karlsson, L.; Loutfi, A. Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2016, 42, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, V.; Prasad, K.J.R. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition Kaiming carbaldehydes. Indian J. Chem. 2006, 45, 1951–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, C.; Liu, L.; Dai, H. MIRD-Net for Medical Image Segmentation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2020, 12085, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention U-Net: Learning Where to Look for the Pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Szemenyei, M.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, W.; Yi, Y. Channel Attention Residual U-Net for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Cananda, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, H.; Qi, X.; Dou, Q.; Fu, C.-W.; Heng, P.-A. H-DenseUNet: Hybrid Densely Connected UNet for Liver and Tumor Segmentation from CT Volumes. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 2663–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavur, A.E.; Gezer, N.S.; Barış, M.; Aslan, S.; Conze, P.-H.; Groza, V.; Pham, D.D.; Chatterjee, S.; Ernst, P.; Özkan, S.; et al. CHAOS Challenge - combined (CT-MR) healthy abdominal organ segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 69, 101950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalew, Y.A.; Fante, K.A.; Mohammed, M.A. Modified U-Net for liver cancer segmentation from computed tomography images with a new class balancing method. BMC Biomed. Eng. 2021, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H.; Bukht, T.F.N.; Imran, A.; Tariq, J.; Tu, S.; Alzahrani, A. A Deep Learning Approach for Liver and Tumor Segmentation in CT Images Using ResUNet. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, S.F.; Shen, L.; Ahmad, M.; Qadri, S.; Zareen, S.S.; Khan, S. OP-convNet: A Patch Classification-Based Framework for CT Vertebrae Segmentation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 158227–158240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiak, B.; Tarasiuk, P.; Michalska, I.; Tomczyk, A. Application of convolutional neural networks with anatomical knowledge for brain MRI analysis in MS patients. Bull. Polish Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2018, 66, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y. Hierarchical Convolutional-Deconvolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Liver and Tumor Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.04540. [Google Scholar]
- Mourya, G.K.; Paul, S.; Handique, A.; Baid, U.; Dutande, P.V.; Talbar, S.N. Modified U-Net for fully automatic liver segmentation from abdominal CT-image. Int. J. Biomed. Eng. Technol. 2022, 40, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Song, H.; Zhang, W.; Fan, J.; Ai, D.; Lin, Y.; Yang, J. CC-DenseUNet: Densely Connected U-Net with Criss-Cross Attention for Liver and Tumor Segmentation in CT Volumes. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Houston, TX, USA, 9–12 December 2021; pp. 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- lirr, O.I. Deep learning and level set approach for liver and tumor segmentation from CT scans. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2020, 21, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, P.F.; Ettlinger, F.; Grün, F.; Elshaera, M.E.A.; Lipkova, J.; Schlecht, S.; Ahmaddy, F.; Tatavarty, S.; Bickel, M.; Bilic, P.; et al. Automatic Liver and Tumor Segmentation of CT and MRI Volumes using Cascaded Fully Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.05970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 833–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorontsov, E.; Tang, A.; Pal, C.; Kadoury, S. Liver lesion segmentation informed by joint liver segmentation. Proc. Int. Symp. Biomed. Imaging 2018, 2018, 1332–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Kim, J.; Kumar, A.; Feng, D. Automatic Liver Lesion Detection using Cascaded Deep Residual Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.02703. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Xu, D.; Zhou, S.K.; Pauly, O.; Grbic, S.; Mertelmeier, T.; Wicklein, J.; Jerebko, A.; Cai, W.; Comaniciu, D. 3D anisotropic hybrid network: Transferring convolutional features from 2D images to 3D anisotropic volumes. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2018, 11071, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Wang, S.; Zhong, C.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z. Decoupled pyramid correlation network for liver tumor segmentation from CT images. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 7207–7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, T.; Futakami, N.; Kunieda, E.; Yagi, M.; Takeda, A.; Akiba, T.; Mutu, E.; Shigematsu, N. Effects of sample size and data augmentation on U-Net-based automatic segmentation of various organs. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2021, 14, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Fong, A.; McVicar, N.; Smith, S.; Giambattista, J.; Wells, D.; Kolbeck, C.; Giambattista, J.; Gondara, L.; Alexander, A. Comparing deep learning-based auto-segmentation of organs at risk and clinical target volumes to expert inter-observer variability in radiotherapy planning. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 144, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, M.; Adapa, K.; Das, S.K.; Mazur, L.; Dooley, J.; Marks, L.B.; Thompson, R.F.; Chera, B.S. Using Artificial Intelligence to Improve the Quality and Safety of Radiation Therapy. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2019, 16, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
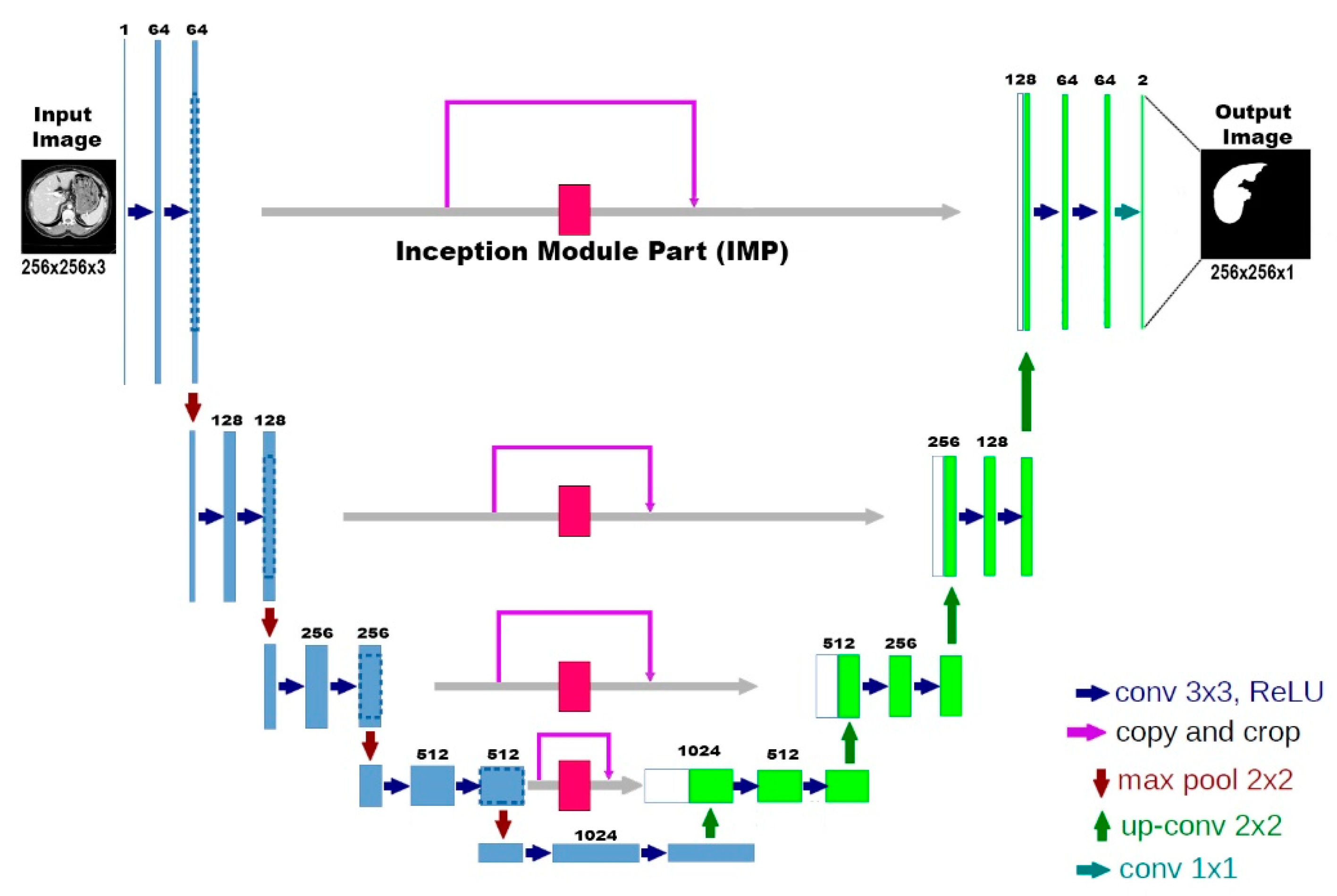
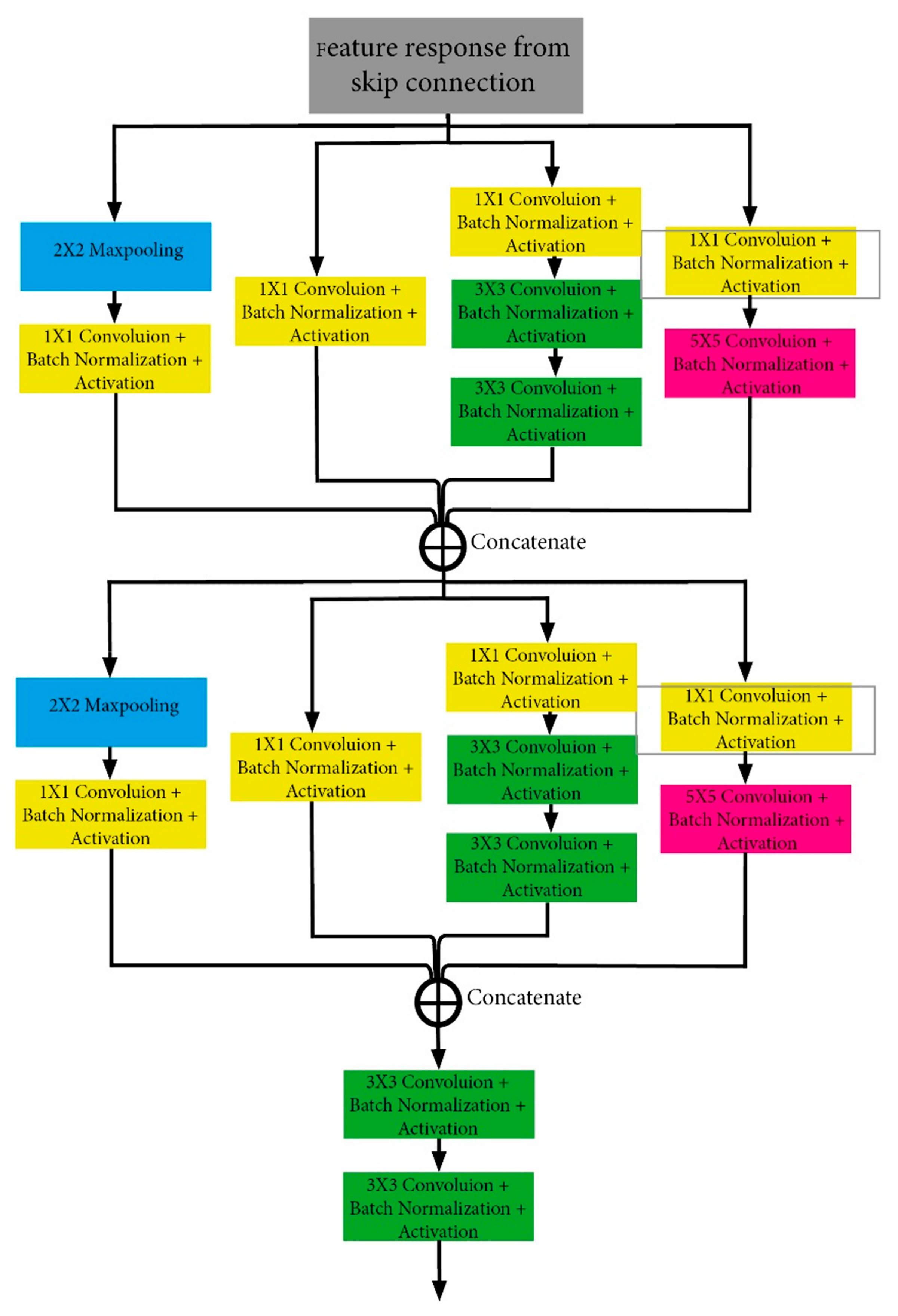




| Encoder Part | Inception Module Part | Decoder Part | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Block | Input | Layer (Filter Size) | Output | Filters | Block | Input | Layer | Output | Filters | Block | Input | Layer (Filter Size) | Output | Filters |
| Encoder 1 | (256,256) | Conv2D (3,3) | (128,128) | 64 | Skip Connection 1 | (256,256) | IMP 1 | (256,256) | 128 | Decoder 1 | (128,128) | Conv2D (3,3) | (256,256) | 64 |
| Conv2D (3,3) | Conv2D (3,3) | |||||||||||||
| Encoder 2 | (128,128) | Conv2D (3,3) | (64,64) | 128 | Skip Connection 2 | (128,128) | IMP 2 | (128,128) | 256 | Decoder 2 | (64,64) | Conv2D (3,3) | (128,128) | 128 |
| Conv2D (3,3) | Conv2D (3,3) | |||||||||||||
| Encoder 3 | (64,64) | Conv2D (3,3) | (32,32) | 256 | Skip Connection 3 | (64,64) | IMP 3 | (64,64) | 512 | Decoder 3 | (32,32) | Conv2D (3,3) | (64,64) | 256 |
| Conv2D (3,3) | Conv2D (3,3) | |||||||||||||
| Encoder 4 | (32,32) | Conv2D(3,3) | (16,16) | 512 | Skip Connection 4 | (32,32) | IMP4 | (32,32) | 1024 | Decoder 4 | (16,16) | Conv2D (3,3) | (32,32) | 512 |
| Conv2D (3,3) | Conv2D (3,3) | |||||||||||||
| Base | (16,16) | Conv2D (3,3) | (16,16) | 1024 | Base | (16,16) | Conv2D (3,3) | (16,16) | 1024 | |||||
| Dataset | Training Slices | Validation Slices | Test Slices | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHAOS | 1935 | 828 | 212 | 2975 |
| LiST | 13171 | 5644 | 618 | 19433 |
| Our Dataset | 2362 | 1011 | 254 | 3627 |
| Dataset | Accuracy (%) | Recall (%) | Precision (%) | Mean IoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our Dataset | 99.54 ± 0.27 | 96.35 ± 2.64 | 98.47 ± 1.23 | 97.21 ± 1.46 |
| CHAOS | 99.75 ± 0.10 | 96.39 ± 6.23 | 99.69 ± 0.55 | 97.91 ± 3.13 |
| LiST | 99.48 ± 0.48 | 95.12 ± 6.15 | 96.78 ± 3.78 | 95.82 ± 3.52 |
| Model Name | Train Dataset | Test Dataset | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our Dataset | LiST | CHAOS | |||||
| Dice (%) | Jaccard (%) | Dice (%) | Jaccard (%) | Dice (%) | Jaccard (%) | ||
| AIM-Unet | Our Dataset | 97.38 ± 1.63 | 94.95 ± 3.00 | 93.60 ± 7.49 | 88.60 ± 9.10 | 97.64 ± 6.74 | 95.91 ± 7.81 |
| LiST | 77.43 ± 27.60 | 69.61 ± 28.96 | 95.77 ± 5.16 | 92.22 ± 6.90 | 94.12 ± 5.97 | 89.38 ± 8.70 | |
| CHAOS | 97.06 ± 3.89 | 94.53 ± 6.02 | 93.46 ± 9.46 | 88.64 ± 10.49 | 97.86 ± 4.65 | 96.10 ± 6.21 | |
| Model | Dataset | Dice (%) | Jaccard (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ronneberger et al. [25] * | LiST | 95.2 | 90.8 |
| Lin et al. * | LiST | 90.9 | 86.7 |
| Li et al. [46] | LiST | 96.5 | 92.6 * |
| Yuan et al. [52] | LiST | 96.7 | 92.9 * |
| Thi et al. [31] | LiST | 96.0 | 90.4 |
| Unet | LiST | 87.86 ± 20.28 | 82.10 ± 21.05 |
| AIM-Unet | LiST | 95.77 ± 5.16 | 92.22 ± 6.90 |
| Ronneberger et al. [25] * | CHAOS | 74.75 | |
| Thi et al. [31] | CHAOS | 94.92 | |
| Mourya et al. [53] | CHAOS | 97.0 ± 0.03 | |
| Unet | CHAOS | 68.30 ± 33.96 | 60.35 ± 33.24 |
| AIM-Unet | CHAOS | 97.86 ± 4.65 | 96.10 ± 6.21 |
| Unet | Our Dataset | 46.64 ± 35.52 | 37.69 ± 31.72 |
| AIM-Unet | Our Dataset | 97.38 ± 1.63 | 94.95 ± 3.00 |
| Model | Dataset | Dice (%) |
|---|---|---|
| AIM-Unet | 3DIRCADb | 65.5 ± 12.9 |
| Li et al. [54] | 3DIRCADb | 66.3 |
| Omar et al. [55] | 3DIRCADb | 75.0 |
| Christ et al. [56] | 3DIRCADb | 56.0 |
| Chen et al. [57] | LiST | 66.6 |
| Vorontsov et al. [58] | LiST | 66.1 |
| Bi et al. [59] | LiST | 64.5 |
| Liu et al. [60] | LiST | 63.4 |
| Zhang et al. [61] | LiST | 58.7 ± 28.3 |
| Li et al. [54] | LiST | 74.1 |
| AIM-Unet | LiST | 75.6 ± 13.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Özcan, F.; Uçan, O.N.; Karaçam, S.; Tunçman, D. Fully Automatic Liver and Tumor Segmentation from CT Image Using an AIM-Unet. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020215
Özcan F, Uçan ON, Karaçam S, Tunçman D. Fully Automatic Liver and Tumor Segmentation from CT Image Using an AIM-Unet. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(2):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020215
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖzcan, Fırat, Osman Nuri Uçan, Songül Karaçam, and Duygu Tunçman. 2023. "Fully Automatic Liver and Tumor Segmentation from CT Image Using an AIM-Unet" Bioengineering 10, no. 2: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020215
APA StyleÖzcan, F., Uçan, O. N., Karaçam, S., & Tunçman, D. (2023). Fully Automatic Liver and Tumor Segmentation from CT Image Using an AIM-Unet. Bioengineering, 10(2), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020215





