An Improved Microaneurysm Detection Model Based on SwinIR and YOLOv8
Abstract
:1. Introduction
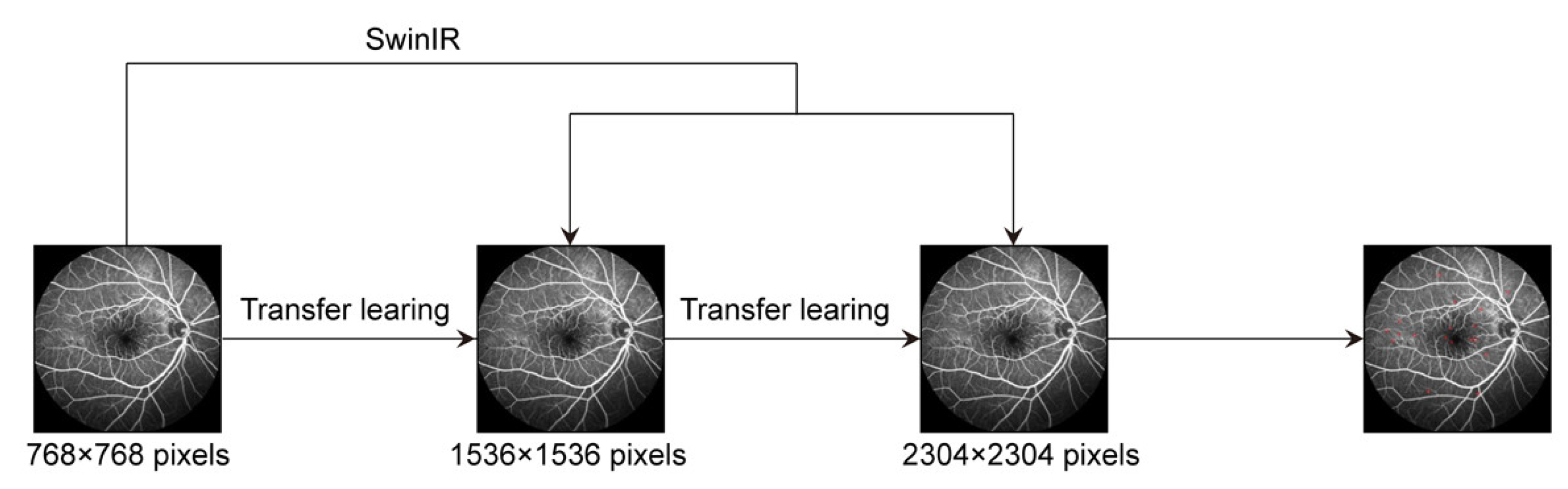
- SwinIR was used to reconstruct high-resolution FFA images, which could enhance the visibility and discriminability of MAs in FFA images.
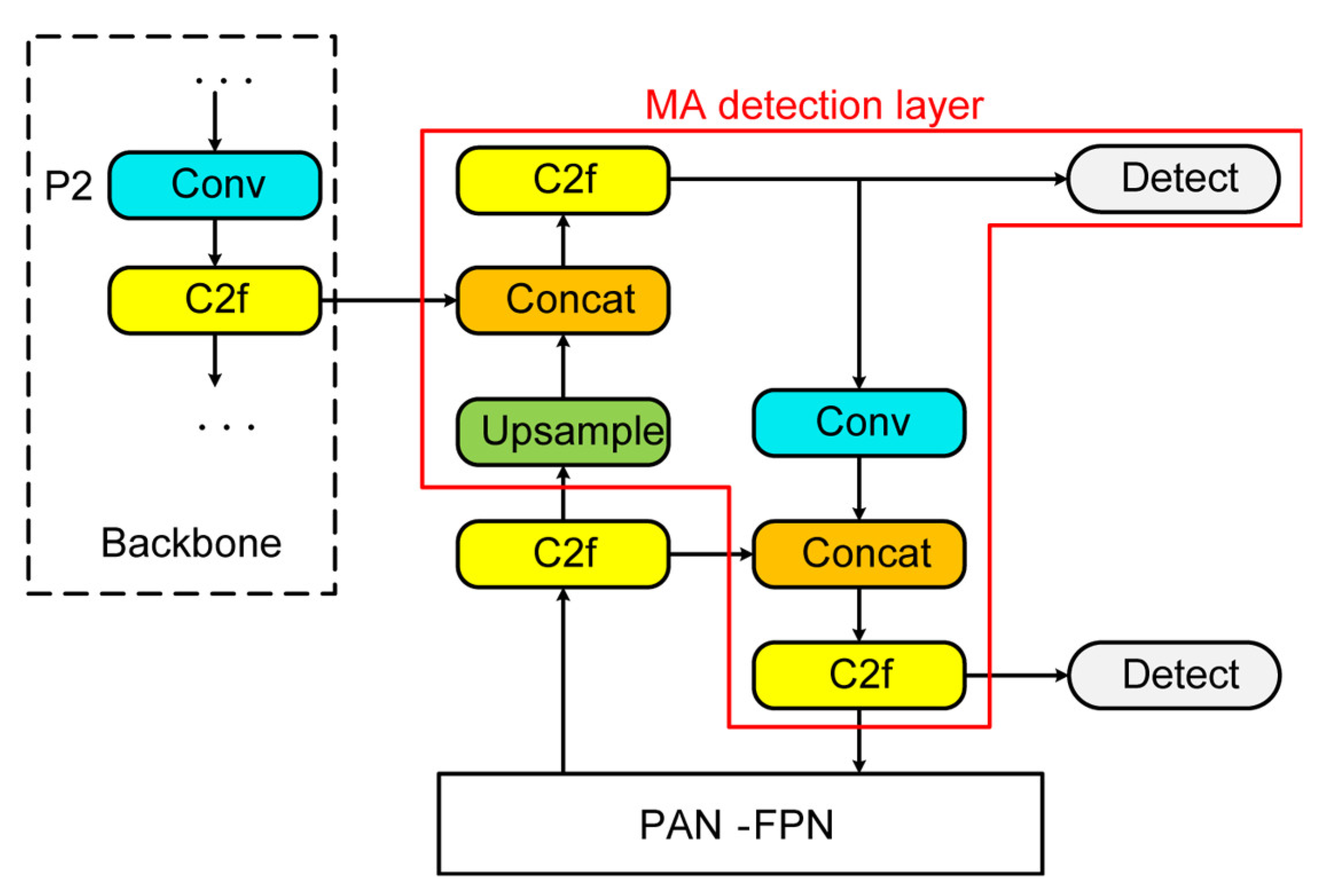
- A detection layer was added to the YOLOv8 model, which could avoid feature information loss in shallow layers and improve the performance of MA detection.
- Transfer learning was utilized between high- and low-resolution images to expand the data samples and improve the generalization ability.
- Taking Wise-IoU as the bounding box regression loss, the loss function of MA-YOLO was improved, which could relieve the sample distribution imbalance problem and enhance the generalization performance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Datasets
2.1.2. Implementation
2.1.3. Evaluation Metrics
2.2. Methods
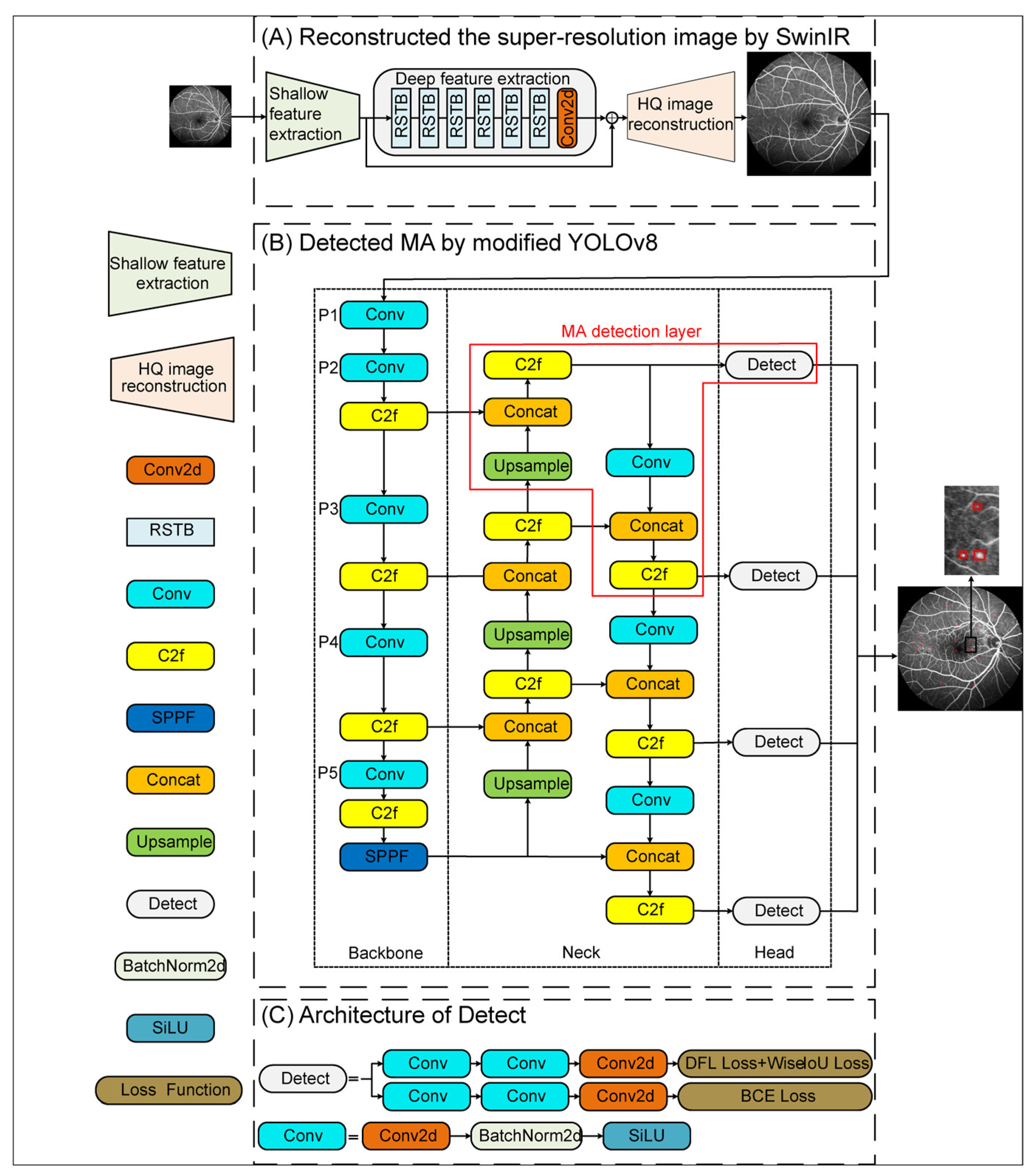
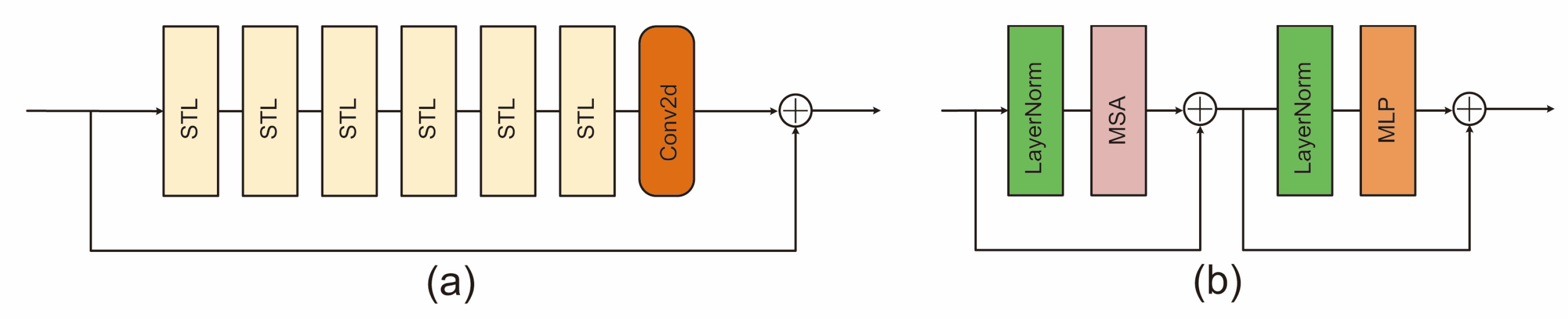
2.2.1. Super-Resolution FFA Image Reconstruction Based on SwinIR
2.2.2. YOLOv8 Modified by MA Detection Layer and Transfer Learning
2.2.3. Loss Function Optimization Based on Wise-IoU
3. Results
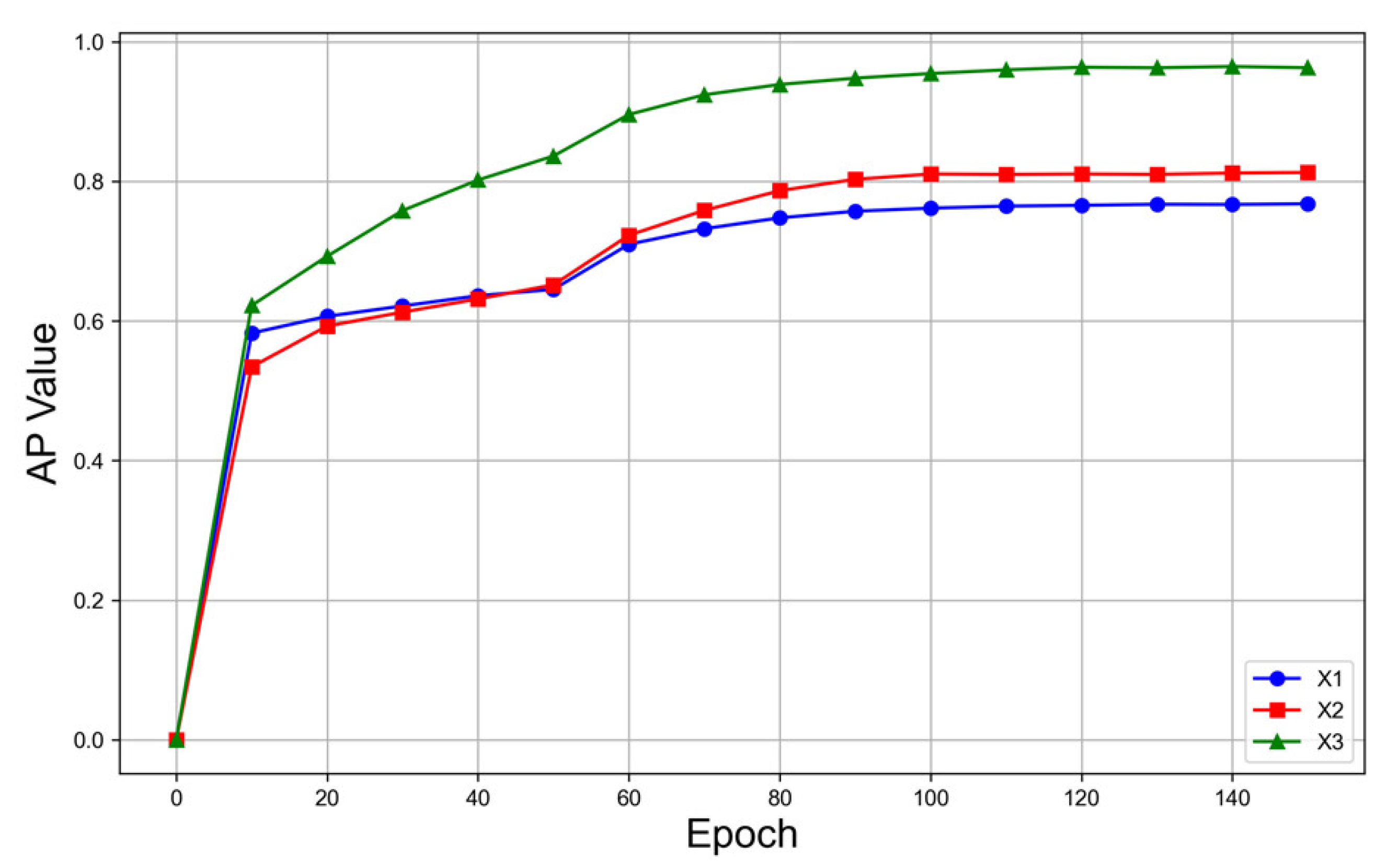
3.1. Ablation Experiment
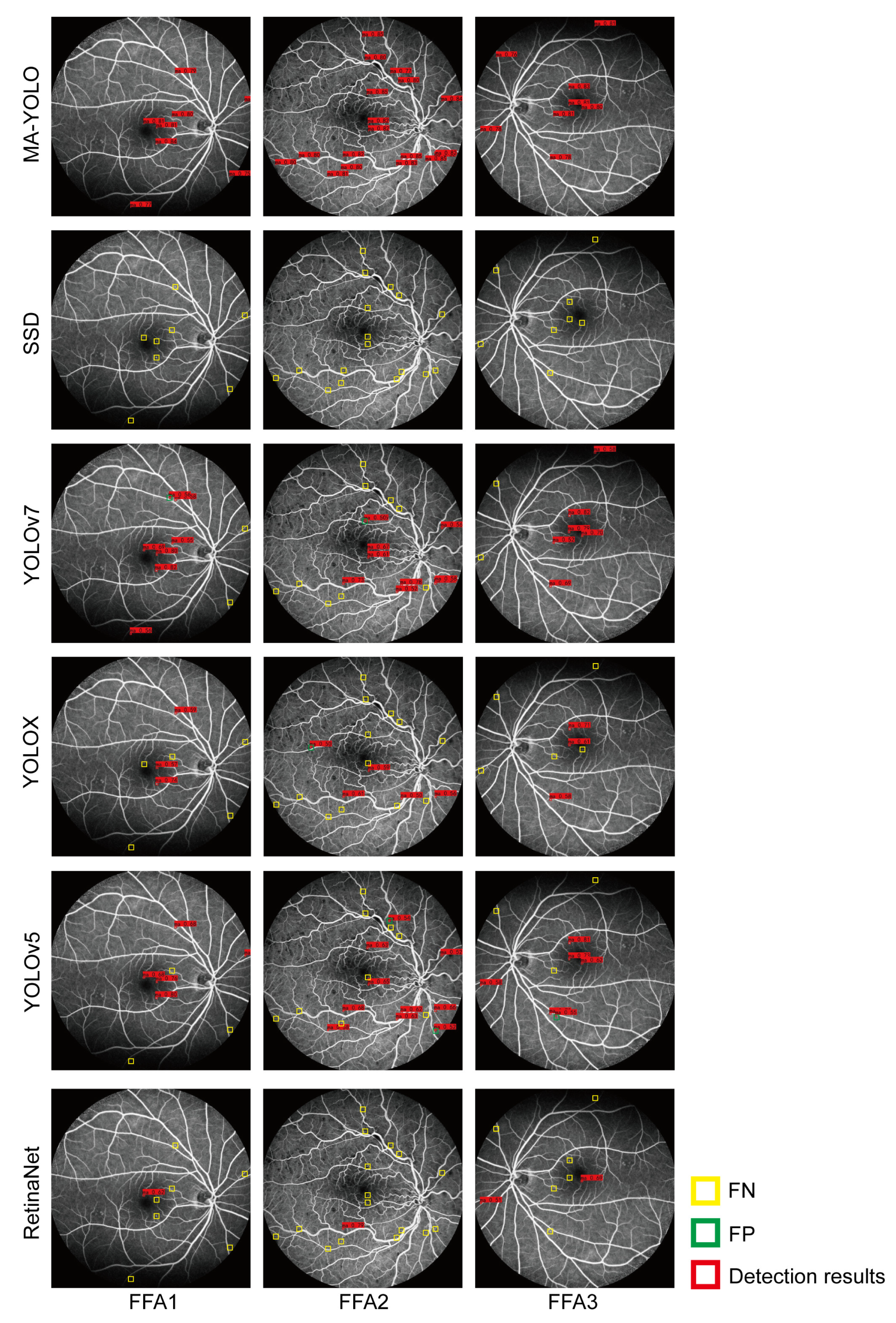
3.2. Comparison Experiment
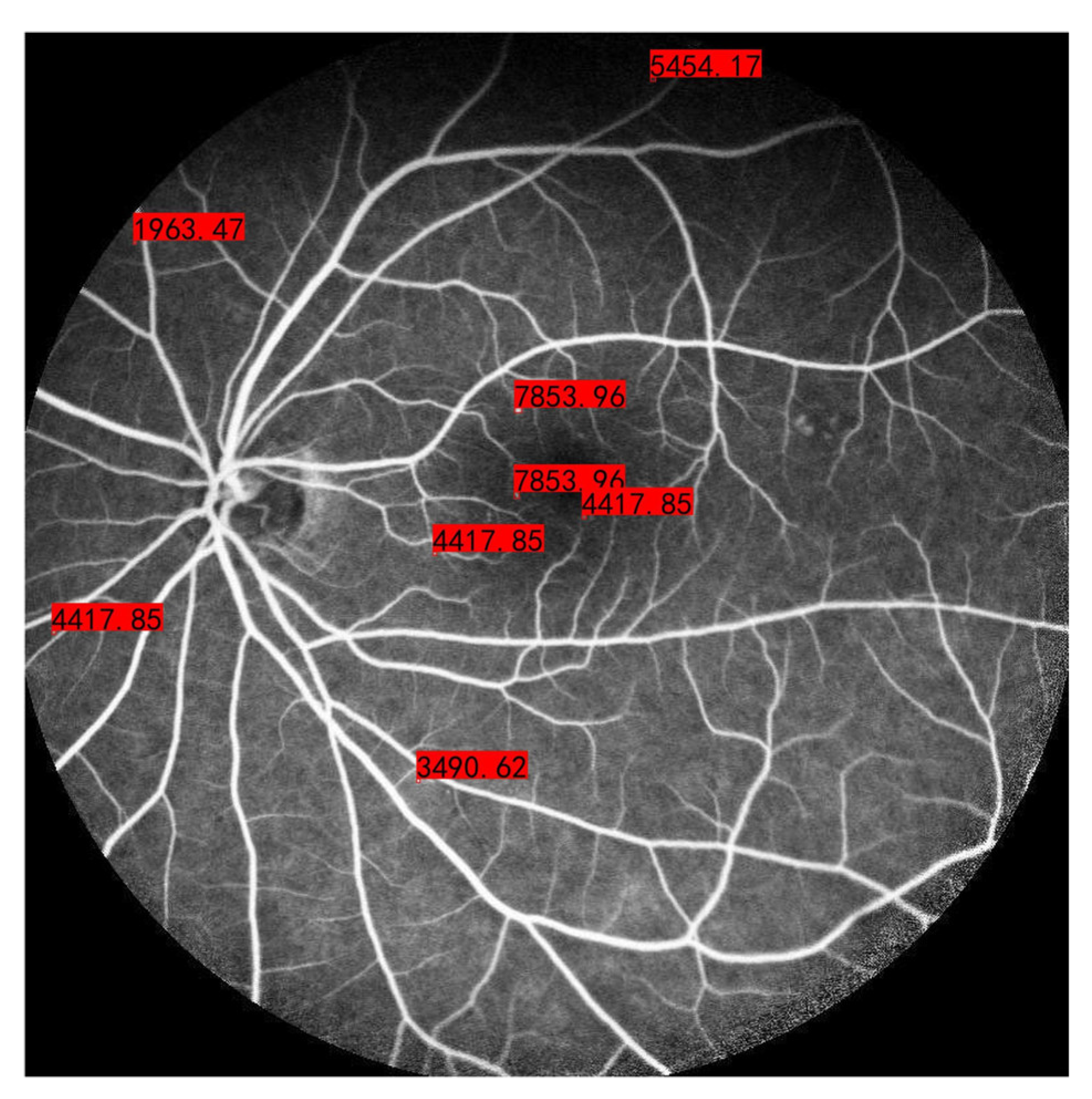
3.3. Calculation of the MA Region
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alifanov, I.; Sakovych, V. Prognostic risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 6, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, J.W.; Rogers, S.L.; Kawasaki, R.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Kowalski, J.W.; Bek, T.; Chen, S.-J.; Dekker, J.M.; Fletcher, A.; Grauslund, J. Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, T.; Massin, P.; Erginay, A.; Ordonez, R.; Jeulin, C.; Klein, J.-C. Automatic detection of microaneurysms in color fundus images. Med. Image Anal. 2007, 11, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couturier, A.; Mané, V.; Bonnin, S.; Erginay, A.; Massin, P.; Gaudric, A.; Tadayoni, R. Capillary plexus anomalies in diabetic retinopathy on optical coherence tomography angiography. Retina 2015, 35, 2384–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zhu, W.; Shi, F.; Zhu, S.; Chen, X. Automatic detection of microaneurysms in retinal fundus images. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2017, 55, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part 14. pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Xia, H.; Song, S.; Li, H. Microaneurysm detection in fundus images based on a novel end-to-end convolutional neural network. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Lan, Y.; Song, S.; Li, H. A multi-scale segmentation-to-classification network for tiny microaneurysm detection in fundus images. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 226, 107140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudzik, P.; Majumdar, S.; Calivá, F.; Al-Diri, B.; Hunter, A. Microaneurysm detection using fully convolutional neural networks. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 158, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhu, F.; Cui, S.; Shao, L. Collaborative learning of semi-supervised segmentation and classification for medical images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2079–2088. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, H.; Shen, C.; Xia, Y. SESV: Accurate medical image segmentation by predicting and correcting errors. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 40, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Liu, B.; Feng, R.; Lu, L.; Zou, H. Automated diabetic retinopathy grading and lesion detection based on the modified R-FCN object-detection algorithm. IET Comput. Vis. 2020, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, T.; Kang, H.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K. L-Seg: An end-to-end unified framework for multi-lesion segmentation of fundus images. Neurocomputing 2019, 349, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateen, M.; Malik, T.S.; Hayat, S.; Hameed, M.; Sun, S.; Wen, J. Deep Learning Approach for Automatic Microaneurysms Detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Adarsh, A.; Kumar, B.; Singh, A.K. An automated early diabetic retinopathy detection through improved blood vessel and optic disc segmentation. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 121, 105815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Cao, J.; Sun, G.; Zhang, K.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. Swinir: Image restoration using swin transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 1833–1844. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Hajeb Mohammad Alipour, S.; Rabbani, H.; Akhlaghi, M. A new combined method based on curvelet transform and morphological operators for automatic detection of foveal avascular zone. Signal Image Video Process. 2014, 8, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Shan, M.; Song, N.; Fan, B.; Fang, Y. Detection of microaneurysms in fundus images based on improved YOLOv4 with SENet embedded. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi = J. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 39, 713–720. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Caballero, J.; Huszár, F.; Totz, J.; Aitken, A.P.; Bishop, R.; Rueckert, D.; Wang, Z. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1874–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2009, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, L.; Chen, S.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Yang, J. Generalized focal loss: Learning qualified and distributed bounding boxes for dense object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 21002–21012. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 12993–13000. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yu, R. Wise-IoU: Bounding Box Regression Loss with Dynamic Focusing Mechanism. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10051. [Google Scholar]
- Akut, R.R. FILM: Finding the location of microaneurysms on the retina. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2019, 9, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdar, M.; Pourpanah, F.; Hussain, S.; Rezazadegan, D.; Liu, L.; Ghavamzadeh, M.; Fieguth, P.; Cao, X.; Khosravi, A.; Acharya, U.R. A review of uncertainty quantification in deep learning: Techniques, applications and challenges. Inf. Fusion 2021, 76, 243–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoni, S.; Jahmunah, V.; Salvi, M.; Barua, P.D.; Molinari, F.; Acharya, U.R. Application of uncertainty quantification to artificial intelligence in healthcare: A review of last decade (2013–2023). Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 165, 107441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, S.K.; Acharya, U.R. Adazd-Net: Automated adaptive and explainable Alzheimer’s disease detection system using EEG signals. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 278, 110858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, S.K.; Blanes-Vidal, V.; Nadimi, E.S.; Acharya, U.R. Emotion recognition and artificial intelligence: A systematic review (2014–2023) and research recommendations. Inf. Fusion 2023, 102, 102019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, S.K.; March, S.; Barua, P.D.; Gadre, V.M.; Acharya, U.R. Application of data fusion for automated detection of children with developmental and mental disorders: A systematic review of the last decade. Inf. Fusion 2023, 99, 101898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
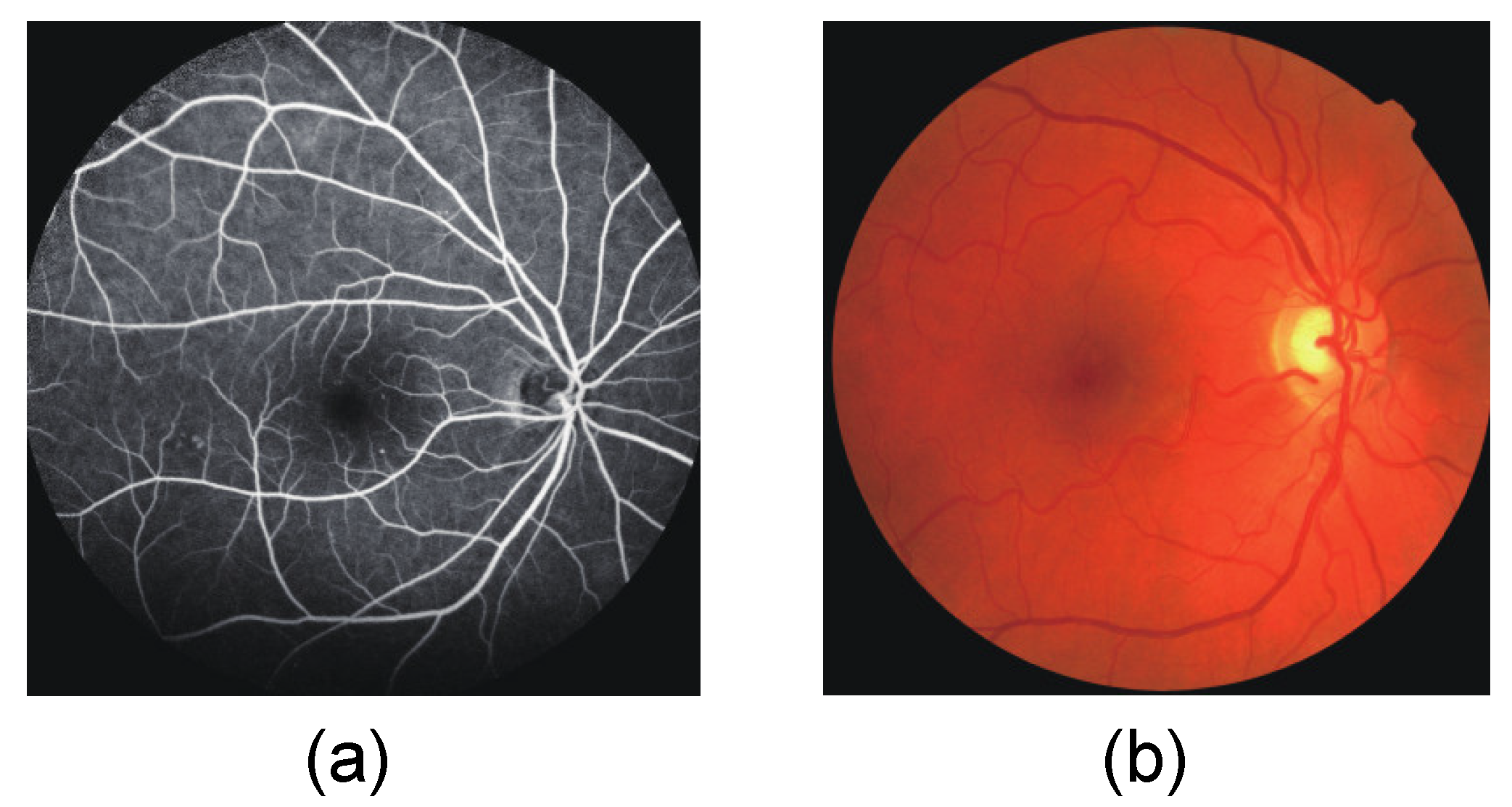
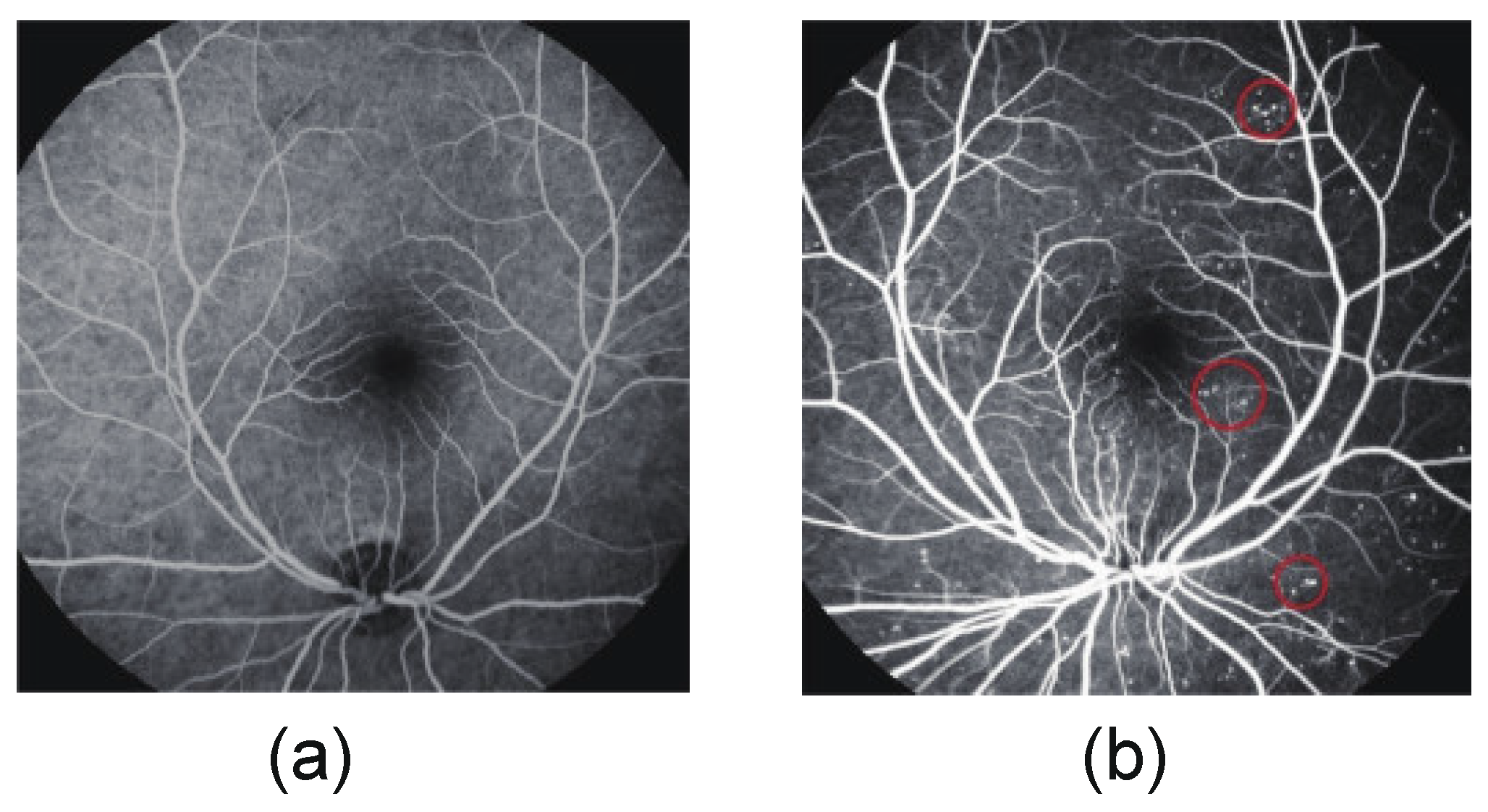


| Model | Strength | Weakness |
|---|---|---|
| U-net + DiceLoss + Activation function with long tail [10] | Increasing discrimination ability of probability maps | Missed detection of low-contrast MAs |
| U-net + residual learning + EfficientNet [11] | Improving segmentation performance by adding a classification network | Structural complexity and time-consuming calculation |
| U-net + BN layers + Dice coefficient function [12] | Simplifying MA extraction using a three-stage method | Presence of a large number of patches and inefficient detection |
| U-net + semi-supervised learning [13] | Reduction of the reliance on data labeling | Weak learning performance for MA features |
| SESV framework + DeepLabv3+ [14] | Presenting a high level of versatility, could be extended to other networks | High spatial and computational complexity and high cost of training time |
| R-FCN [15] | Improving the ability to detect objects at different scales | MA detection was compromised by the absence of annotated images |
| L-Seg [16] | Prevention of information loss by multi-scale feature fusion | Serious misclassification problem in MA detection |
| VGG-19 + Inception-v3 [17] | Obtaining data correlation in original feature space using feature embedding | Sample distribution imbalance was neglected |
| Radial basis function neural network [18] | Enhancement of MA extraction by removing morphological structures inside the retinas | Morphological structure removal made MA extraction cumbersome |
| Model | Improvement Strategy | Re (%) | Pre (%) | F1 (%) | AP (%) | FPS (It/s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SwinIR | Transfer Learning | Wise-IoU | MA Detection Layer | ||||||
| YOLOv8 | 80.81 ± 0.03 | 86.07 ± 0.03 | 83.36 ± 0.03 | 82.09 ± 0.03 | 16.11 ± 0.02 | ||||
| YOLOv8-A | ✓ | 83.44 ± 0.01 | 85.50 ± 0.04 | 84.46 ± 0.04 | 83.46 ± 0.09 | 1.99 ± 0.05 | |||
| YOLOv8-B | ✓ | ✓ | 85.22 ± 0.12 | 88.07 ± 0.14 | 86.62 ± 0.11 | 84.13 ± 0.10 | 1.99 ± 0.04 | ||
| YOLOv8-C | ✓ | 84.65 ± 0.07 | 86.73 ± 0.06 | 85.68 ± 0.08 | 87.29 ± 0.12 | 16.11 ± 0.01 | |||
| YOLOv8-D | ✓ | 86.15 ± 0.05 | 93.19 ± 0.09 | 89.53 ± 0.06 | 88.67 ± 0.03 | 12.79 ± 0.04 | |||
| MA-YOLO | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 88.23 ± 0.11 | 97.98 ± 0.06 | 92.85 ± 0.09 | 94.62 ± 0.06 | 1.51 ± 0.03 |
| Model | Re (%) | Pre (%) | F1 (%) | AP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD | 32.77 ± 0.05 | 76.30 ± 0.07 | 45.85 ± 0.16 | 51.53 ± 0.06 |
| RetinaNet | 71.32 ± 0.03 | 70.99 ± 0.14 | 71.15 ± 0.09 | 72.04 ± 0.05 |
| YOLOv5 | 69.62 ± 0.05 | 71.53 ± 0.15 | 70.56 ± 0.02 | 71.57 ± 0.07 |
| YOLOX | 60.72 ± 0.12 | 67.04 ± 0.06 | 63.72 ± 0.13 | 63.33 ± 0.05 |
| YOLOv7 | 68.18 ± 0.02 | 77.78 ± 0.07 | 72.66 ± 0.08 | 76.48 ± 0.02 |
| MA-YOLO | 88.23 ± 0.11 | 97.98 ± 0.06 | 92.85 ± 0.09 | 94.62 ± 0.06 |
| Model | Epochs | Freeze Backbone Epochs | UnFreeze Epochs | Batch Size | Optimizer | Initial Learning Rate | Learning Rate Decay | FPS (it/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD | 150 | 50 | 100 | 4 | SGD | 0.01 | cosine annealing | 22.93 ± 0.02 |
| RetinaNet | 150 | 50 | 100 | 4 | SGD | 0.01 | cosine annealing | 0.53 ± 0.02 |
| YOLOv5 | 150 | 50 | 100 | 4 | SGD | 0.01 | cosine annealing | 16.85 ± 0.04 |
| YOLOX | 150 | 50 | 100 | 4 | SGD | 0.01 | cosine annealing | 13.74 ± 0.02 |
| YOLOv7 | 150 | 50 | 100 | 4 | SGD | 0.01 | cosine annealing | 33.86 ± 0.04 |
| MA-YOLO | 150 | 50 | 100 | 4 | SGD | 0.01 | cosine annealing | 1.51 ± 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Bai, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yan, B.; Wang, Z. An Improved Microaneurysm Detection Model Based on SwinIR and YOLOv8. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121405
Zhang B, Li J, Bai Y, Jiang Q, Yan B, Wang Z. An Improved Microaneurysm Detection Model Based on SwinIR and YOLOv8. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(12):1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121405
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bowei, Jing Li, Yun Bai, Qing Jiang, Biao Yan, and Zhenhua Wang. 2023. "An Improved Microaneurysm Detection Model Based on SwinIR and YOLOv8" Bioengineering 10, no. 12: 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121405
APA StyleZhang, B., Li, J., Bai, Y., Jiang, Q., Yan, B., & Wang, Z. (2023). An Improved Microaneurysm Detection Model Based on SwinIR and YOLOv8. Bioengineering, 10(12), 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121405







