Diagnostic Accuracy and Performance Analysis of a Scanner-Integrated Artificial Intelligence Model for the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhages in a Traumatology Emergency Department
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. CT Technique
2.3. Clinical Report
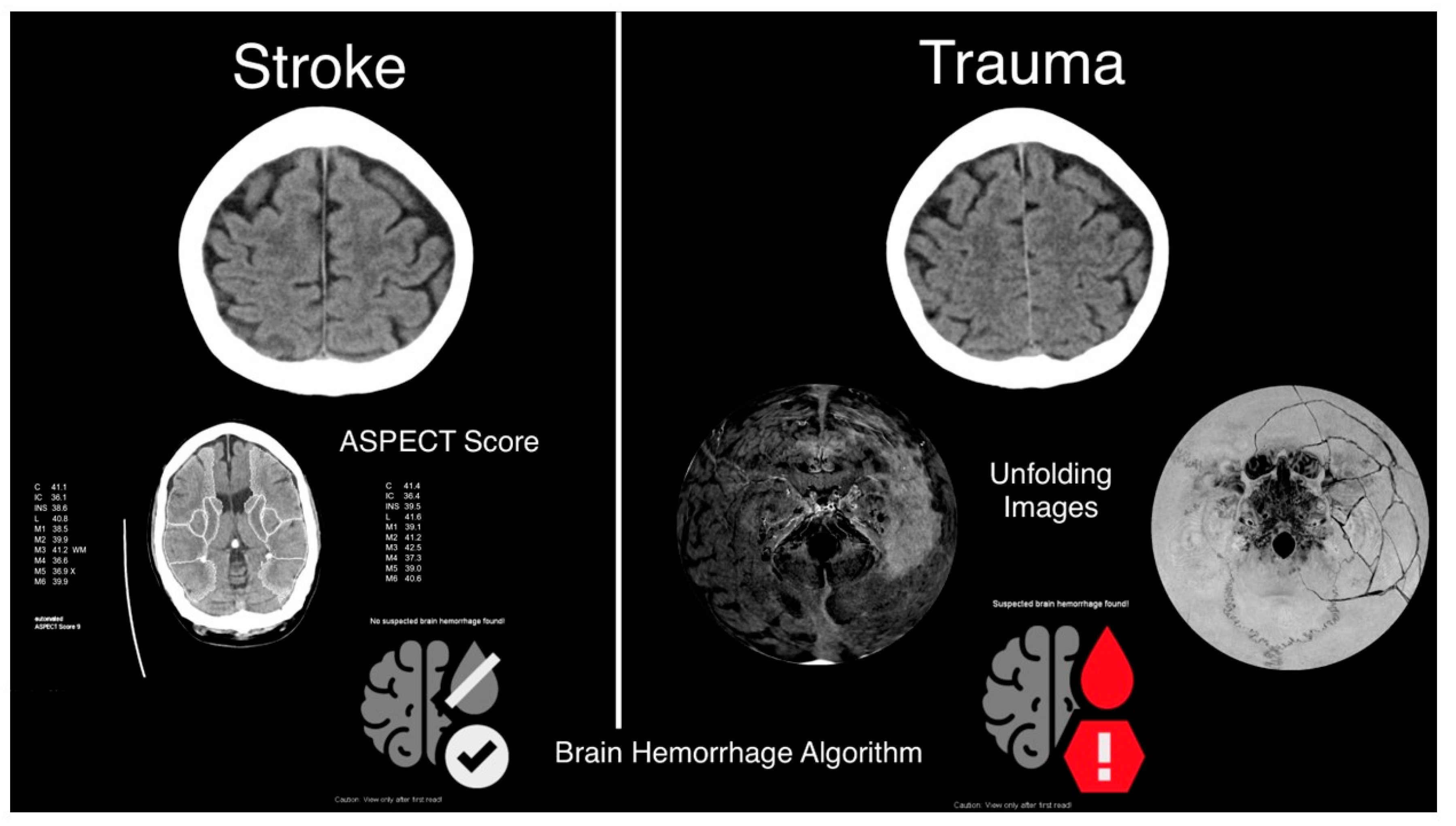
2.4. Automatic Brain Hemorrhage Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
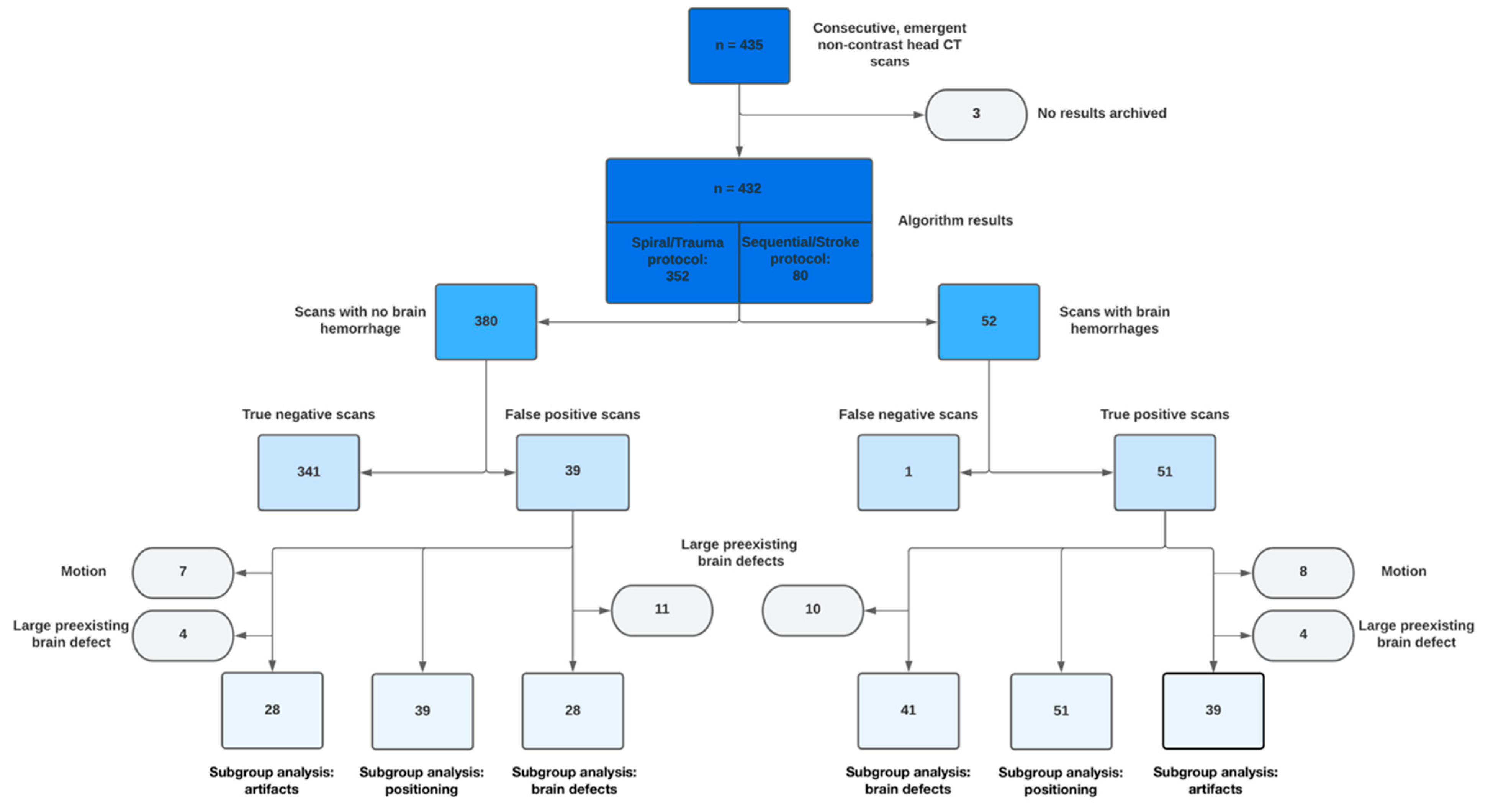
3.1. Patients
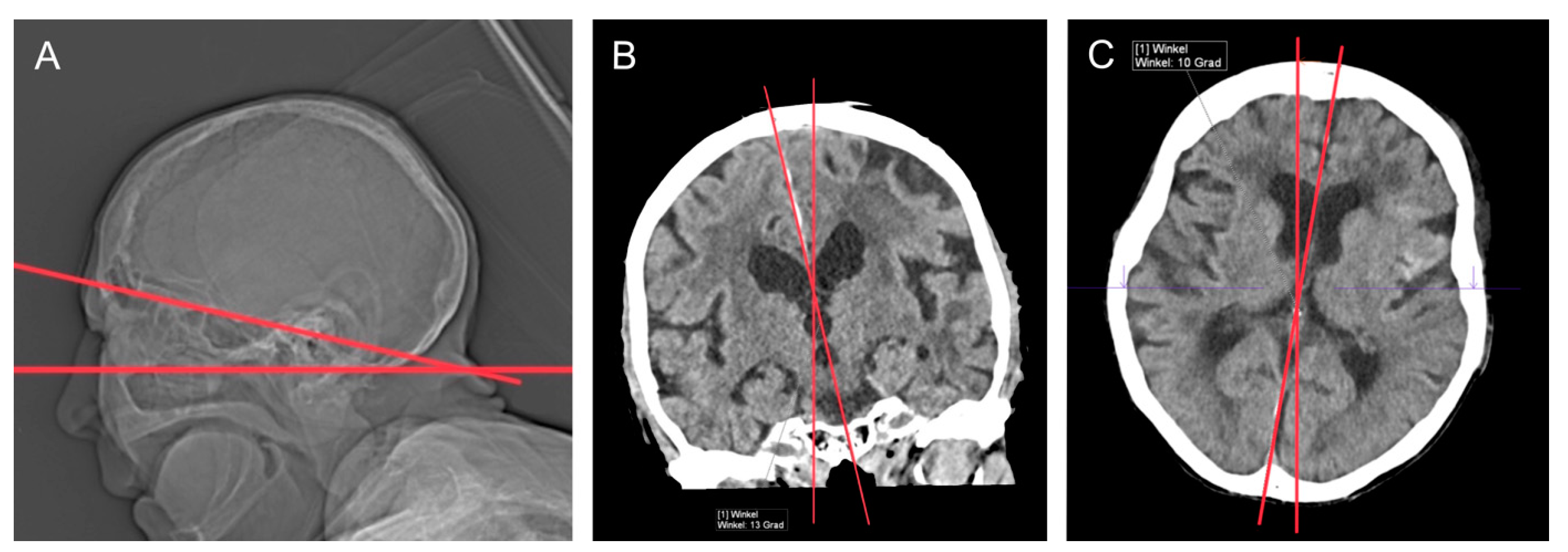
3.2. CT Technique
3.3. Clinical Reports
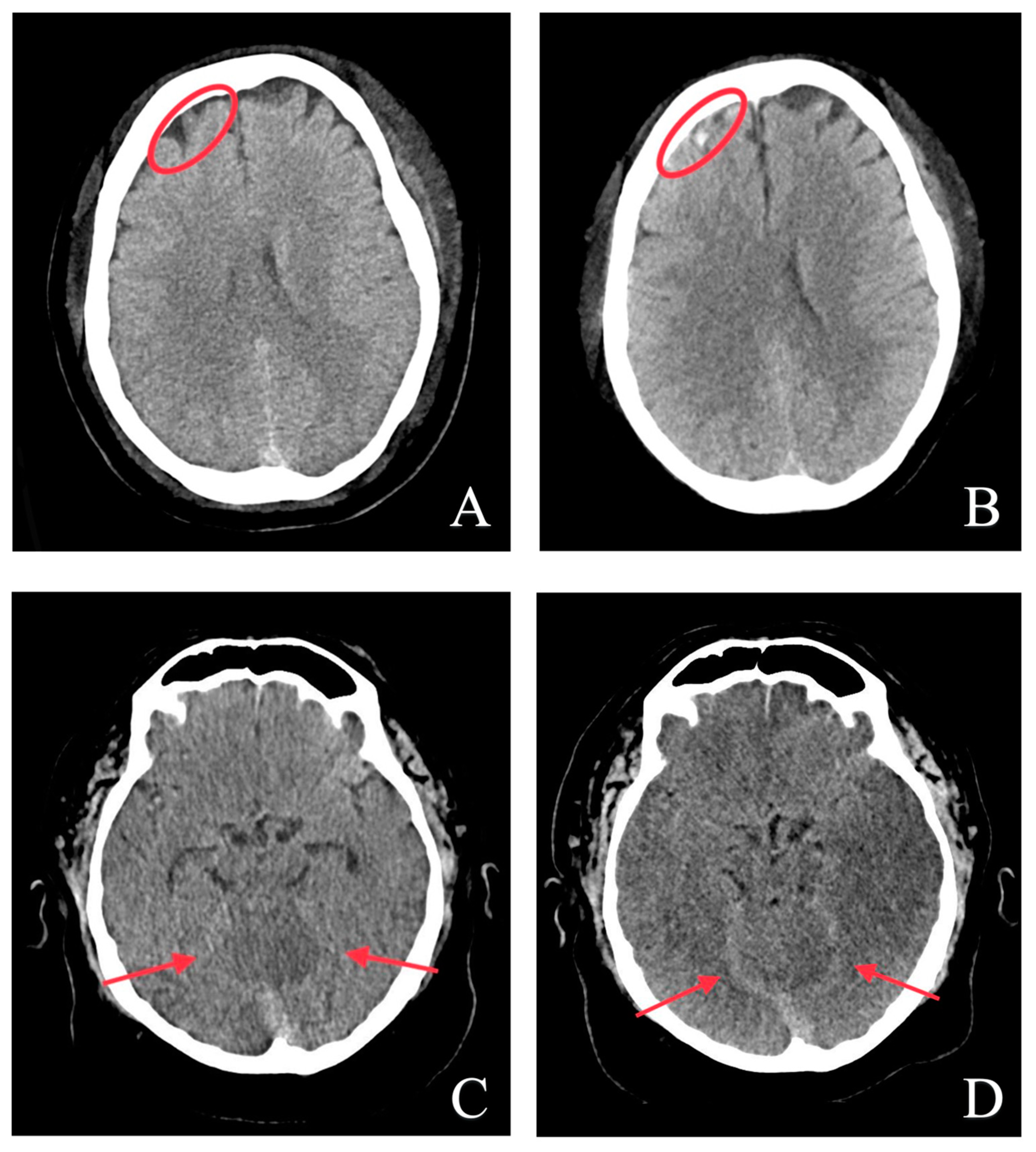
3.4. Automatic Brain Hemorrhage Analysis
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vella, M.A.; Crandall, M.L.; Patel, M.B. Acute Management of Traumatic Brain Injury. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 97, 1015–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajashekar, D.; Liang, J.W. Intracerebral Hemorrhage. In StatPearls; Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2022; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Mendelow, A.D.; Hanley, D.F. Intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet 2009, 373, 1632–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, T.N.; Zygmont, M.E.; Peterson, R.; Theriot, D.; Shekhani, H.; Johnson, J.-O.; Krupinski, E.A. The Effects of Fatigue From Overnight Shifts on Radiology Search Patterns and Diagnostic Performance. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2018, 15, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, R.J.; Schwartz, K.M.; Eckel, L.J.; Diehn, F.E.; Hunt, C.H.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Erickson, B.J.; Kallmes, D.F. The effects of changes in utilization and technological advancements of cross-sectional imaging on radiologist workload. Acad. Radiol. 2015, 22, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzi, A.; Cè, M.; De Padova, G.; Libri, D.; Caldarelli, N.; Zucconi, F.; Oliva, G.; Cellina, M. Deep Learning-Based Versus Iterative Image Reconstruction for Unenhanced Brain CT: A Quantitative Comparison of Image Quality. Tomography 2023, 9, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-D.; Hou, X.-X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, M.; Yang, J.; Wang, S.-H. Voxelwise detection of cerebral microbleed in CADASIL patients by leaky rectified linear unit and early stopping. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 21825–21845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.D.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, X.X.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.H. Seven-layer deep neural network based on sparse autoencoder for voxelwise detection of cerebral microbleed. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 10521–10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Mehmood, I.; Pan, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Cerebral micro-bleeding identification based on a nine-layer convolutional neural network with stochastic pooling. Concurr. Comput. Pr. Exp. 2019, 32, e5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirri, S.; Delnevo, G.; Roccetti, M. Is a COVID-19 Second Wave Possible in Emilia-Romagna (Italy)? Forecasting a Future Out-break with Particulate Pollution and Machine Learning. Computation 2020, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellina, M.; Cé, M.; Irmici, G.; Ascenti, V.; Caloro, E.; Bianchi, L.; Pellegrino, G.; D’Amico, N.; Papa, S.; Carrafiello, G. Artificial Intelligence in Emergency Radiology: Where Are We Going? Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, Y.S. Detection and classification of intracranial haemorrhage on CT images using a novel deep-learning algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, I.; Zarb, F. A comparison of sequential and spiral scanning techniques in brain CT. Radiol. Technol. 2015, 86, 373–378. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, E.J.; Brenner, D.J. Cancer risks from diagnostic radiology. Br. J. Radiol. 2008, 81, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalender, W.A. Computed Tomography: Fundamentals, System Technology, Image Quality, Applications, 3rd ed.; Publicis Publishing: Er-langen, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- van Straten, M.; Venema, H.; Majoie, C.; Freling, N.; Grimbergen, C.; Heeten, G.D. Image quality of multisection CT of the brain: Thickly collimated sequential scanning versus thinly collimated spiral scanning with image combining. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- GmbH, S.H. Syngo.CT Brain Hemorrhage Manual VB60; GmbH, S.H., Ed.; Siemens Healthcare GmbH: Munich, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ghesu, F.-C.; Georgescu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Grbic, S.; Maier, A.; Hornegger, J.; Comaniciu, D. Multi-Scale Deep Reinforcement Learning for Real-Time 3D-Landmark Detection in CT Scans. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Xu, D.; Zhou, S.K.; Georgescu, B.; Chen, M.; Grbic, S.; Metaxas, D.N.; Comaniciu, D. Automatic Liver Segmentation Using an Adversarial Image-to-Image Network; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 507–515. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, E.; Georgescu, B.; Ceccaldi, P.; Trigan, P.-H.; Yoo, Y.; Das, J.; Re, T.J.; Rs, V.; Balachandran, A.; Eibenberger, E.; et al. Artificial Intelligence with Statistical Confidence Scores for Detection of Acute or Subacute Hemorrhage on Noncontrast CT Head Scans. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2022, 4, e210115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Bonney, P.; Briggs, A.; Briggs, R.G.; A Jarvis, C.; Attenello, F.; Giannotta, S.L. Rate of Intracranial Hemorrhage After Minor Head Injury. Cureus 2020, 12, e10653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, H.R.; Graves, J.A.; Rohatgi, S.; Vakil, M.; McCarty, J.; Van Hemert, R.L.; Geppert, S.; Peterson, R.B. Skull Base-related Lesions at Routine Head CT from the Emergency Department: Pearls, Pitfalls, and Lessons Learned. Radiographics 2019, 39, 1161–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundisch, A.; Hönning, A.; Mutze, S.; Kreissl, L.; Spohn, F.; Lemcke, J.; Sitz, M.; Sparenberg, P.; Goelz, L. Deep learning algorithm in detecting intracranial hemorrhages on emergency com-puted tomographies. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food & Drug Administratio. 510(K) Summary for SYNGO.CT Brain Hemorrhage K203260 [FDA.GOV Web Site]. January 28, 2022. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf20/K203260.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Saade, C.; Najem, E.; Asmar, K.; Salman, R.; El Achkar, B.; Naffaa, L. Intracranial calcifications on CT: An updated review. J. Radiol. Case Rep. 2019, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilamkurthy, S.; Ghosh, R.; Tanamala, S.; Biviji, M.; Campeau, N.G.; Venugopal, V.K.; Mahajan, V.; Rao, P.; Warier, P. Deep learning algorithms for detection of critical findings in head CT scans: A retrospective study. Lancet 2018, 392, 2388–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruschwitz, P.; Grunz, J.P.; Kuhl, P.J.; Kosmala, A.; Bley, T.A.; Petritsch, B.; Heidenreich, J.F. Performance testing of a novel deep learning algorithm for the detection of intracranial hemorrhage and first trial under clinical conditions. Neurosci. Inform. 2021, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, P.; Zawaideh, M.; Mossa-Basha, M.; Haynor, D.R. The utility of deep learning: Evaluation of a convolutional neural net-work for detection of intracranial bleeds on non-contrast head computed tomography studies. In Proceedings of the Volume 10949, Medical Imaging 2019: Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–21 February 2019; p. 109493J. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voter, A.F.; Meram, E.; Garrett, J.W.; Yu, J.-P.J. Diagnostic Accuracy and Failure Mode Analysis of a Deep Learning Algorithm for the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhage. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2021, 18, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amann, J.; Blasimme, A.; Vayena, E.; Frey, D.; Madai, V.I. Explainability for artificial intelligence in healthcare: A multidisciplinary perspective. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2020, 20, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wei, M.; Liu, B.; Atchaneeyasakul, K.; Zhou, F.; Pan, Z.; Kumar, S.A.; Zhang, J.Y.; Pu, Y.; Liebeskind, D.S.; et al. Deep Learning for Hemorrhagic Lesion Detection and Segmentation on Brain CT Images. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 1646–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Gu, X.; Wu, D.; Hang, W.; Xue, J.; Qiu, S.; Chin-Teng, L. A Novel Negative-Transfer-Resistant Fuzzy Clustering Model with a Shared Cross-Domain Transfer Latent Space and its Application to Brain CT Image Segmentation. IEEE ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2021, 18, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Protocol Selection | Stroke | Trauma |
|---|---|---|
| Collimation | 128 × 0.6 mm | 128 × 0.6 mm |
| Mode | Sequential | Spiral |
| Rotation time | 0.5 s | 0.5 s |
| Inline results | ASPECT score Brain Hemorrhage | Brain Hemorrhage Brain unfolding Skull unfolding |
| kV | 120 | 120 |
| IQ Level | 282 | 282 |
| Average scan length | 16.5 cm | 17.3 cm |
| CTDI | 48.9 ± 6.6 mGy | 43.0 ± 4.8 mGy |
| DLP | 808.9 ± 146.7 mGy × cm | 743.3 ± 107.8 mGy × cm |
| Gold standard: Positive | Gold standard: Negative | |||
| AI: Positive | True Positives: 51 | False Positives: 39 | 90 | PPV: 56.7% |
| AI: Negative | False Negatives: 1 | True Negatives: 341 | 342 | NPV: 99.7% |
| 52 | 380 | 432 | ||
| Sensitivity: 98.1% | Specificity: 89.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiefer, J.; Kopp, M.; Ruettinger, T.; Heiss, R.; Wuest, W.; Amarteifio, P.; Stroebel, A.; Uder, M.; May, M.S. Diagnostic Accuracy and Performance Analysis of a Scanner-Integrated Artificial Intelligence Model for the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhages in a Traumatology Emergency Department. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121362
Kiefer J, Kopp M, Ruettinger T, Heiss R, Wuest W, Amarteifio P, Stroebel A, Uder M, May MS. Diagnostic Accuracy and Performance Analysis of a Scanner-Integrated Artificial Intelligence Model for the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhages in a Traumatology Emergency Department. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(12):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121362
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiefer, Jonas, Markus Kopp, Theresa Ruettinger, Rafael Heiss, Wolfgang Wuest, Patrick Amarteifio, Armin Stroebel, Michael Uder, and Matthias Stefan May. 2023. "Diagnostic Accuracy and Performance Analysis of a Scanner-Integrated Artificial Intelligence Model for the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhages in a Traumatology Emergency Department" Bioengineering 10, no. 12: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121362
APA StyleKiefer, J., Kopp, M., Ruettinger, T., Heiss, R., Wuest, W., Amarteifio, P., Stroebel, A., Uder, M., & May, M. S. (2023). Diagnostic Accuracy and Performance Analysis of a Scanner-Integrated Artificial Intelligence Model for the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhages in a Traumatology Emergency Department. Bioengineering, 10(12), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121362








