Optimizing Platelet-Rich Plasma: Spin Time and Sample Source
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
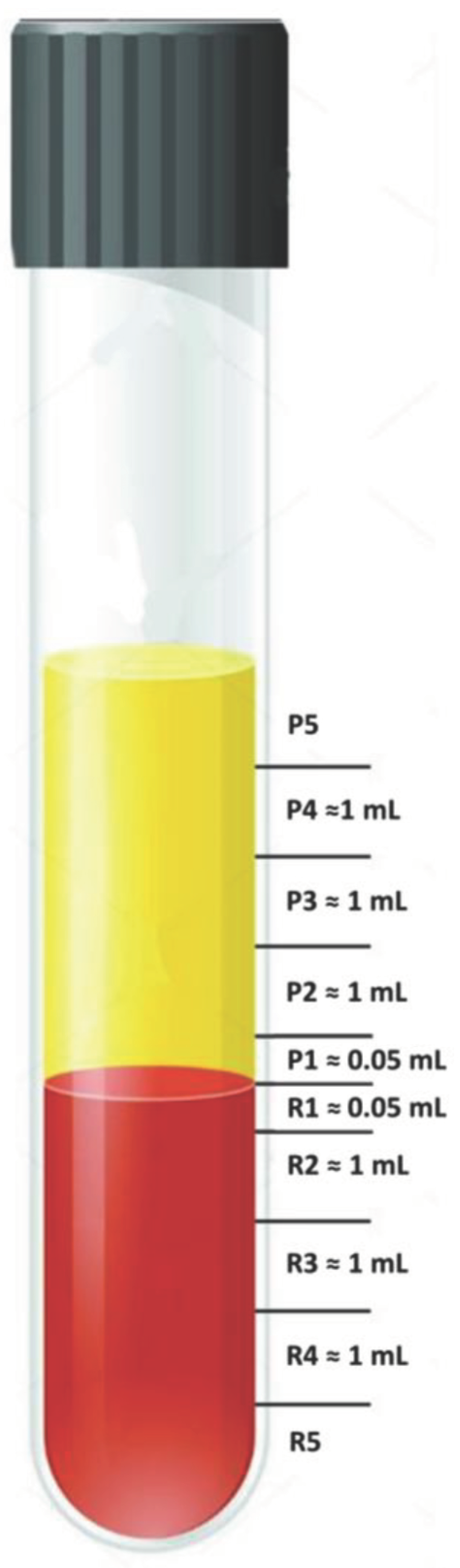
2.1. Practical Guidance for Aspiration of 0.5 mL below and above the Plasma/RBC Junction
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
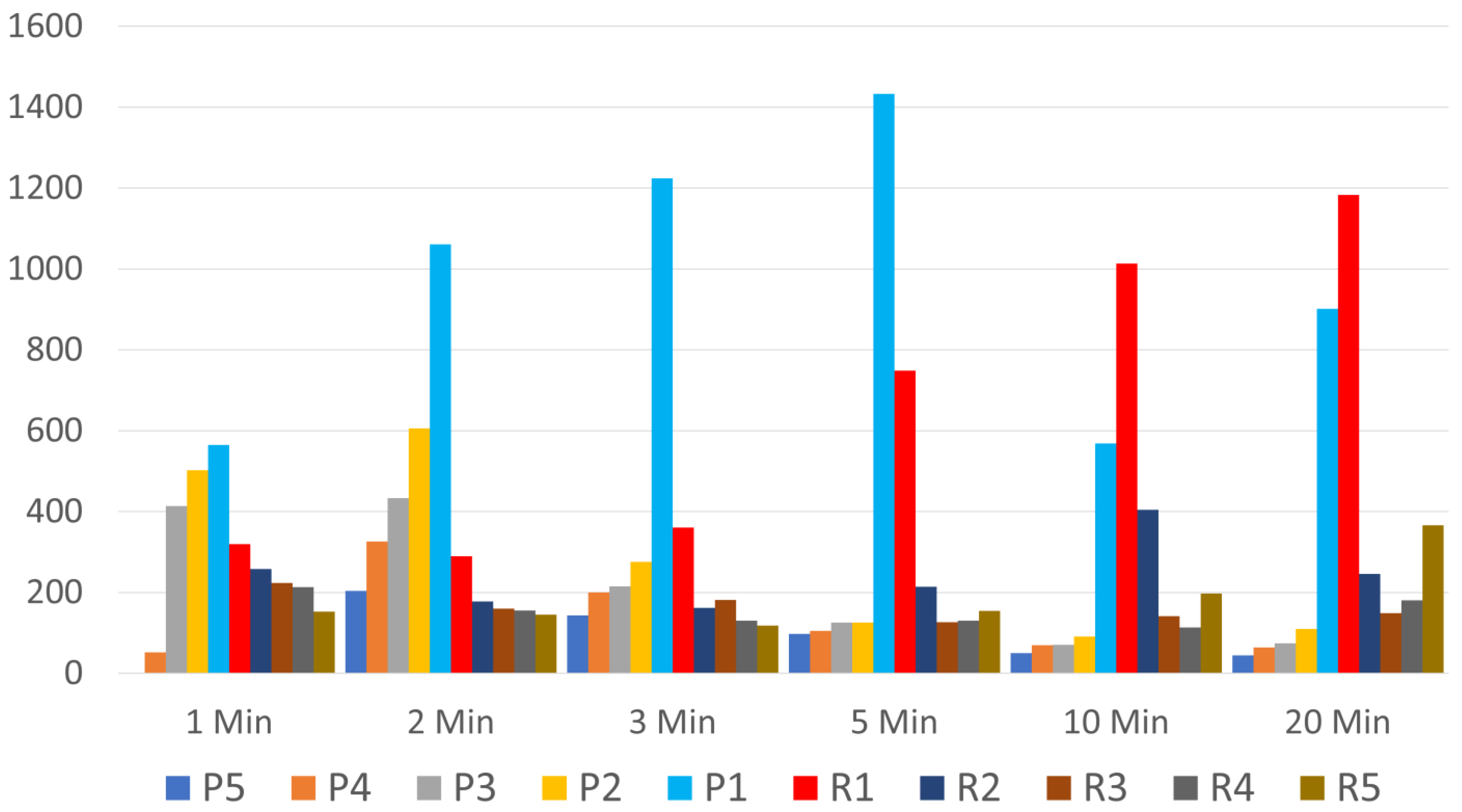
3.1. Which Layers Have the Most Platelets?
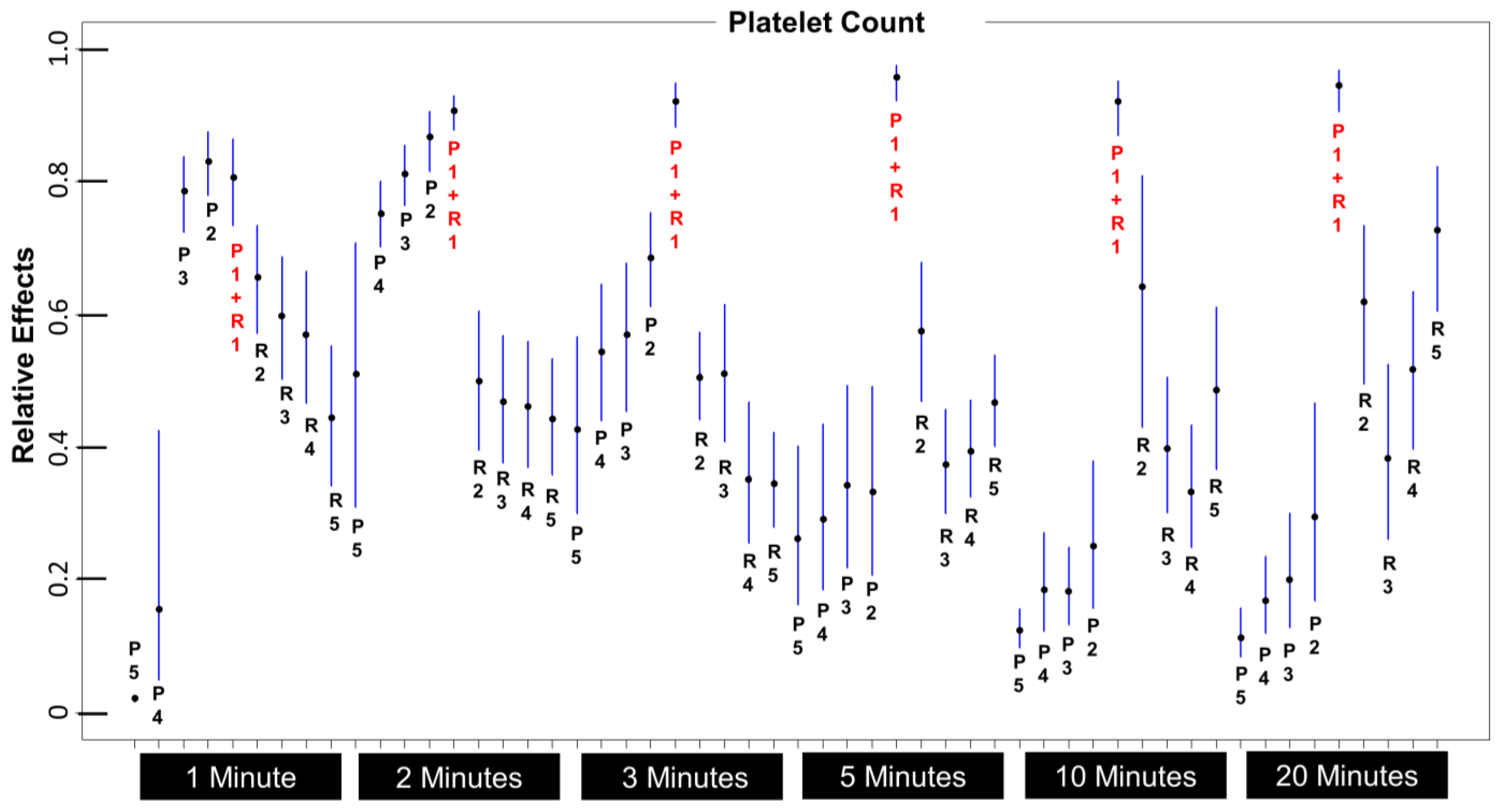
3.2. Which 1 mL Layer Has the Highest Platelet Count, and Is It Significantly Higher Than Any Other Layer?
3.3. What Is the Optimum Centrifugation Time?
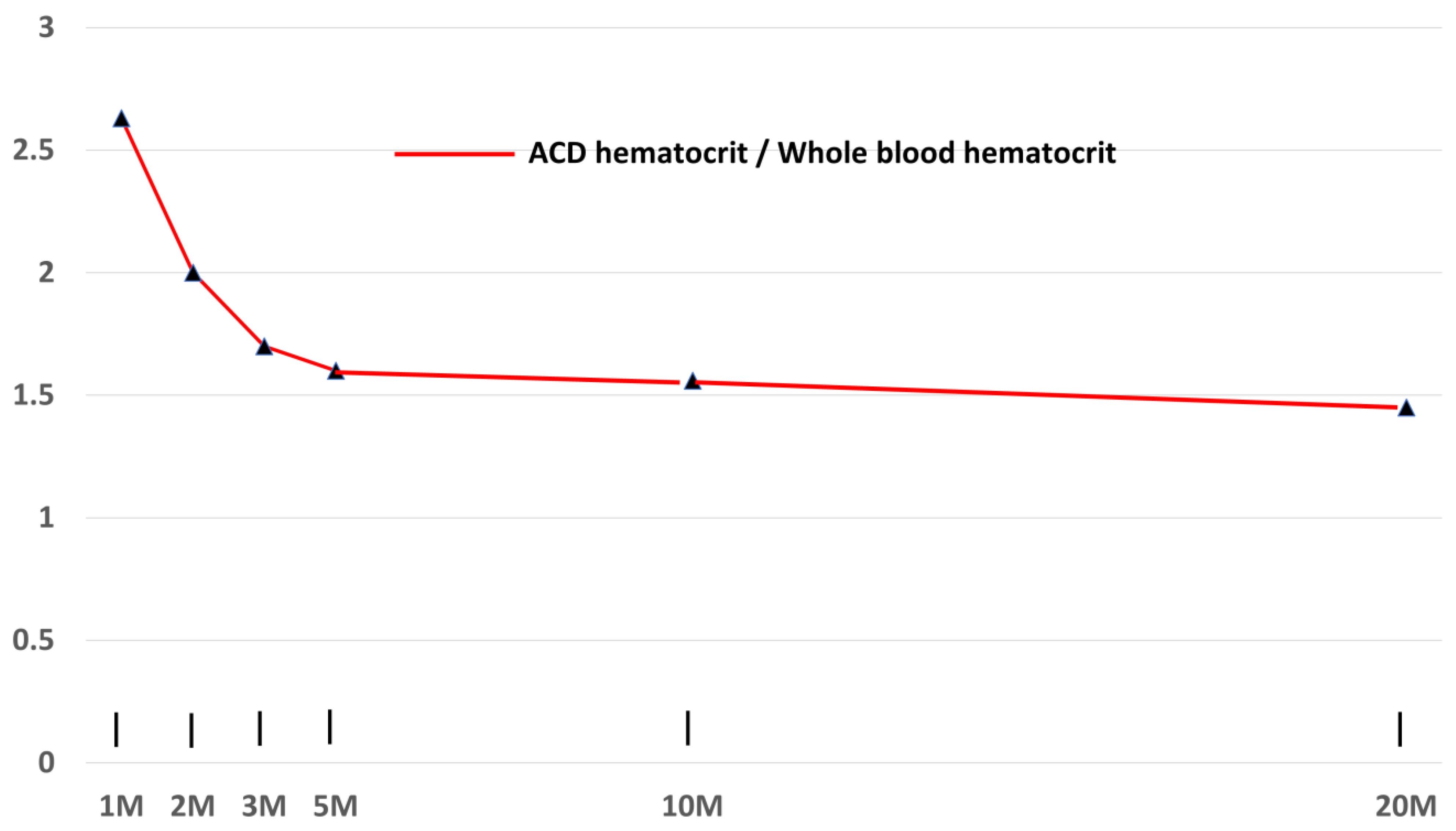
3.4. Effects on Centrifugation Time on Hematocrit
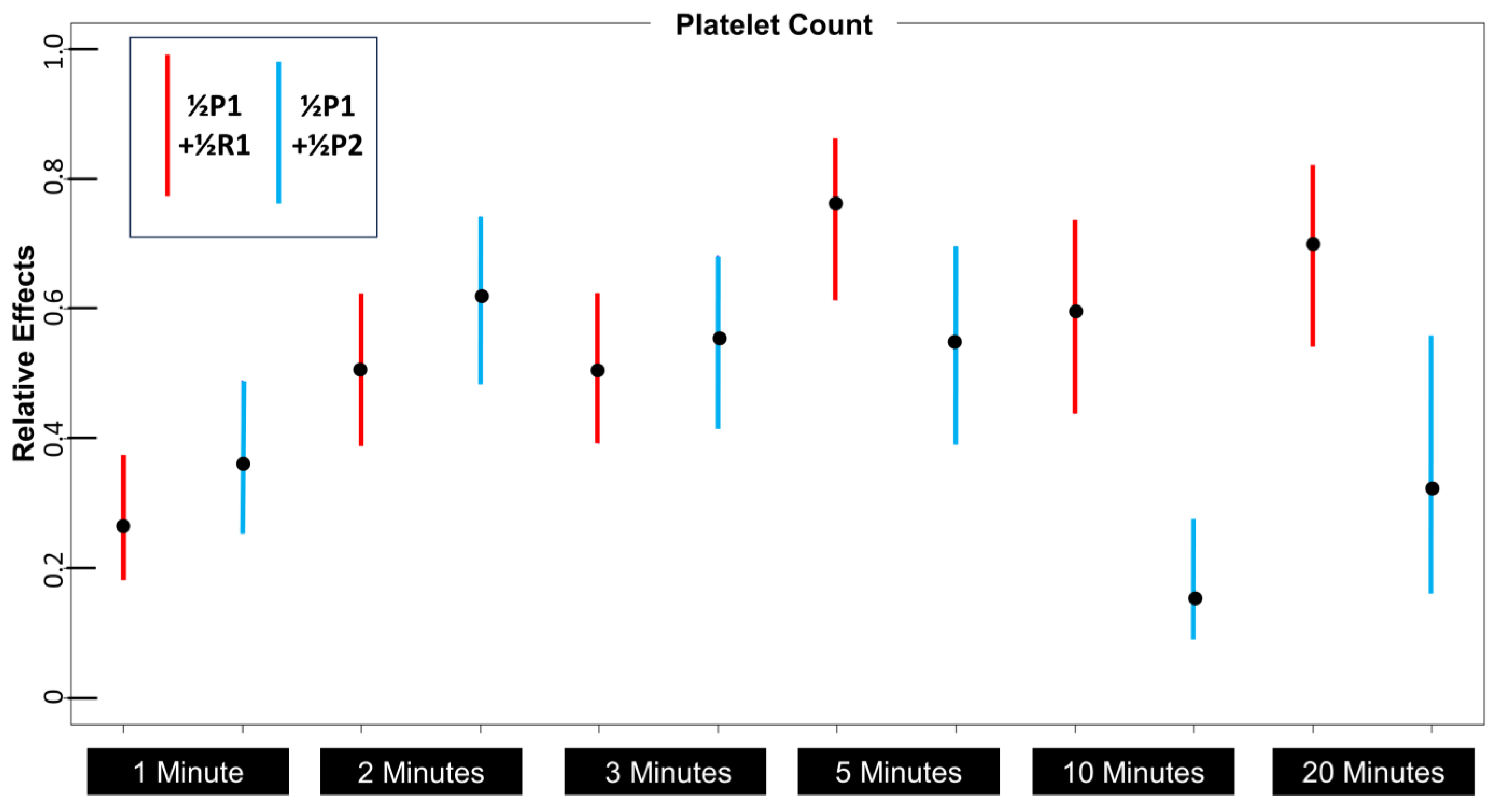
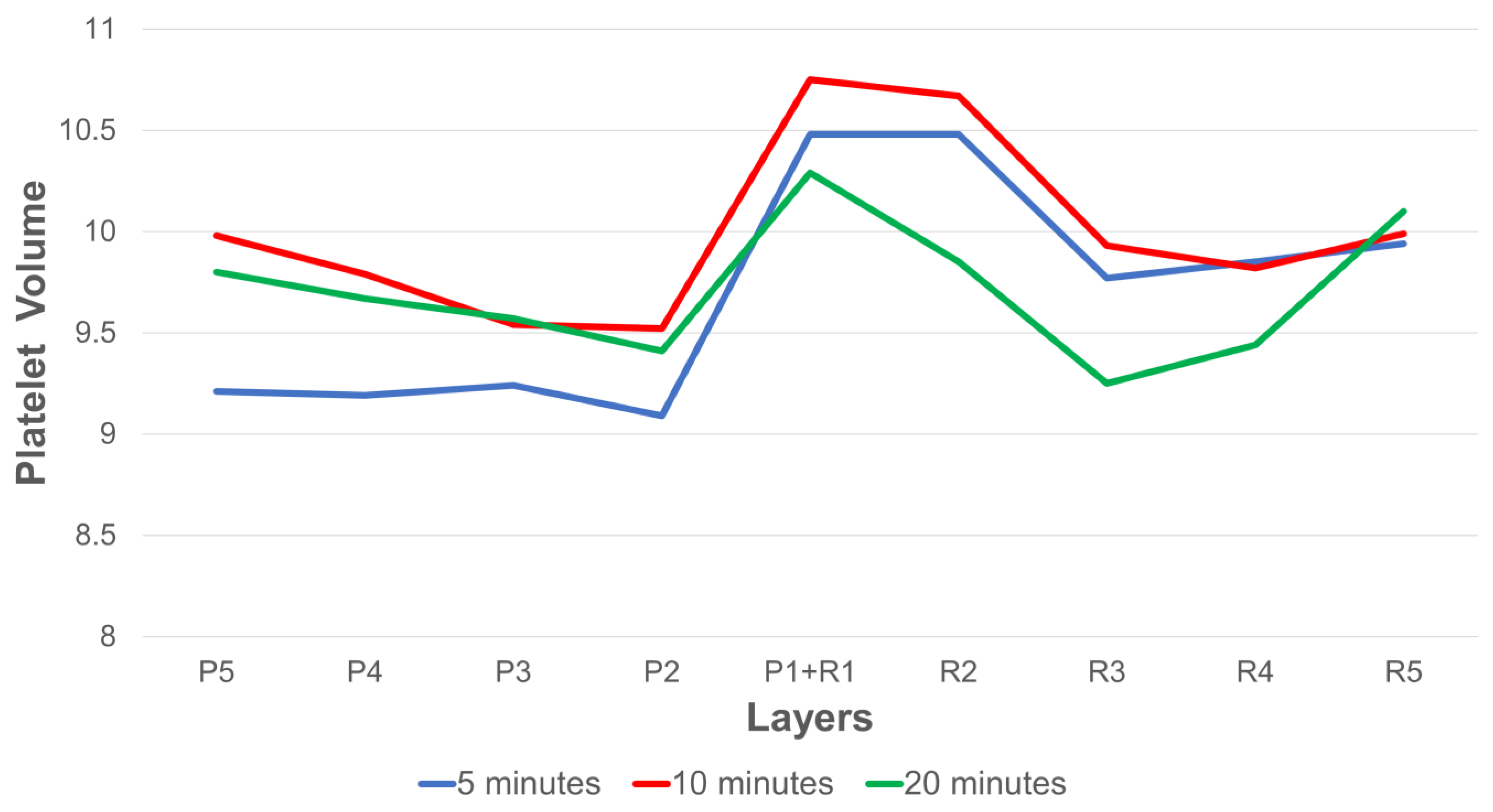
3.5. Effects of Platelet Volume on Platelet Distribution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Powell, M.E. Formation and morphology of the ‘buffy coat’ and measurement of density of blood and tumour cells. Nature 1962, 193, 1047–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, R. Cell separation by gradient centrifugation. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1974, 38, 369–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meer, P.F.; Reesink, H.W.; de Korte, D.; Loos, J.A.; Klei, T.R.L. The history of buffy coat platelet concentrates: The Dutch story. Vox Sang. 2022, 117, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CS, K. Blood coagulation; evidence of an antagonist to factor VI in platelet-rich human plasma. Nature 1954, 173, 723–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, E.B.; Kingsley, H.D.; Howland, J.W. The Therapeutic Value of Preserved Blood Plasma: A Summary of One Hundred and Ten Cases. Ann. Surg. 1941, 113, 969–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, R.E. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): What Is PRP and What Is Not PRP? Implant. Dent. 2001, 10, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, K.; Shope, B. Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Dentistry and Oral Surgery: Introduction and Review of the Literature. J. Vet. Dent. 2019, 36, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Guo, S.C.; Han, P.; Zhang, C.Q.; Zeng, B.F. Applications of leukocyte- and platelet-rich plasma (L-PRP) in trauma surgery. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.; Delgado, D.; Sanchez, P.; Fiz, N.; Azofra, J.; Orive, G.; Anitua, E.; Padilla, S. Platelet rich plasma and knee surgery. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 890630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Ghname, A.; Perdanasari, A.T.; Davis, M.J.; Reece, E.M. Platelet-Rich Plasma: Principles and Applications in Plastic Surgery. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2019, 33, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanez-Castillo, Y.M.; Arrabal-Polo, M.A. Applications of Platelet Rich Plasma in Urology. Arch. Esp. Urol. 2022, 75, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnalich, F.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Luque-Rio, A.; Alio, J.L. Solid Platelet Rich Plasma in Corneal Surgery. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2016, 5, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emer, J. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Current Applications in Dermatology. Skin. Ther. Lett. 2019, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, T.E. Regenerative Medicine: Building a Better, Healthier Body; Rejuvacare PC: Port Angeles, WA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nasiek, D. PRP Platelet Rich Plasma: A New Paradigm of Regenerative Medicine; Master Printing USA: Carlstadt, NJ, USA, 2012; p. 116. [Google Scholar]
- Rout, A.T.K.; Choubey, A.K. Subcutaneous Platelet-rich Plasma Therapy for Management of Hyperalgesia in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Indian J. Pain. 2023, 37, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubrova, E.; Martinez Alvarez, G.A.; Her, Y.F.; Pagan-Rosado, R.; Qu, W.; D’Souza, R.S. Platelet Rich Plasma and Platelet-Related Products in the Treatment of Radiculopathy-A Systematic Review of the Literature. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, C.; Tuan, R.S. Biology of platelet-rich plasma and its clinical application in cartilage repair. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolber, M.J.; Purita, J.; Paulus, C.; Carreno, J.A.; Hanney, W.J. Platelet-Rich Plasma: Basic Science and Biological Effects. Strength Cond. J. 2018, 40, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.; Onishi, K.; Jayaram, P.; Lana, J.F.; Mautner, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denfors, I.; Jacobsson, S.; Kutti, J.; Lindholm, A.; Wadenvik, H. The Effect of Centrifugation Time and Gravitational Force on Platelet Yield and Platelet Volume Distribution in Platelet-rich Plasma (PRP) Obtained by Differential Centrifugation. Thromb. Res. 1991, 61, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibrich, G.; Kleis, W.K.; Kunz-Kostomanolakis, M.; Loos, A.H.; Wagner, W. Correlation of platelet concentration in platelet-rich plasma to the extraction method, age, sex, and platelet count of the donor. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 2001, 16, 693–699. [Google Scholar]
- Marlovits, S.; Mousavi, M.; Gabler, C.; Erdos, J.; Vecsei, V. A new simplified technique for producing platelet-rich plasma: A short technical note. Eur. Spine J. 2004, 13 (Suppl. S1), S102–S106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagataa, M.J.H.; Messora, M.R.; Furlanetoa, F.A.C.; Fucinia, S.E.; Boscoa, A.F.; Garcia, V.G.; Deliberadorc, T.M.; de Melod, L.G.N. Effectiveness of Two Methods for Preparation of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma: An Experimental Study in Rabbits. Eur. J. Dent. 2010, 4, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, J.; Jona, M.; Eto, H.; Aoi, N.; Kato, H.; Suga, H.; Doi, K.; Yatomi, Y.; Yoshimura, K. Optimized preparation method of platelet-concentrated plasma and noncoagulating platelet-derived factor concentrates: Maximization of platelet concentration and removal of fibrinogen. Tissue Eng. Part. C Methods 2012, 18, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amable, P.R.; Carias, R.B.; Teixeira, M.V.; da Cruz Pacheco, I.; Corrêa do Amaral, R.J.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Borojevic, R. Platelet-rich plasma preparation for regenerative medicine: Optimization and quantification of cytokines and growth factors. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, C.H.; Roh, Y.H.; Kim, J.E.; Shin, S.; Yoon, K.S. Optimizing platelet-rich plasma gel formation by varying time and gravitational forces during centrifugation. J. Oral Implantol. 2013, 39, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalon, J.; Bausset, O.; Serratrice, N.; Giraudo, L.; Aboudou, H.; Veran, J.; Magalon, G.; Dignat-Georges, F.; Sabatier, F. Characterization and comparison of 5 platelet-rich plasma preparations in a single-donor model. Arthroscopy 2014, 30, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Doda, V.; Kotwal, U.; Dogra, M. Quantification of platelets and platelet derived growth factors from platelet-rich-plasma (PRP) prepared at different centrifugal force (g) and time. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2016, 54, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Miao, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, P.; Hu, Z. A Novel and Convenient Method for the Preparation and Activation of PRP without Any Additives: Temperature Controlled PRP. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1761865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etulain, J.; Mena, H.A.; Meiss, R.P.; Frechtel, G.; Gutt, S.; Negrotto, S.; Schattner, M. An optimised protocol for platelet-rich plasma preparation to improve its angiogenic and regenerative properties. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, T.N.; Pouliot, M.A.; Kim, H.J.; Dragoo, J.L. Comparison of growth factor and platelet concentration from commercial platelet-rich plasma separation systems. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushida, S.; Kakudo, N.; Morimoto, N.; Hara, T.; Ogawa, T.; Mitsui, T.; Kusumoto, K. Platelet and growth factor concentrations in activated platelet-rich plasma: A comparison of seven commercial separation systems. J. Artif. Organs 2014, 17, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudelaar, B.W.; Peerbooms, J.C.; Huis In’t Veld, R.; Vochteloo, A.J.H. Concentrations of Blood Components in Commercial Platelet-Rich Plasma Separation Systems: A Review of the Literature. Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 47, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, J.; Bulsara, M.K.; McCrory, P.R.; Richardson, M.D.; Zheng, M.H. Analysis of Platelet-Rich Plasma Extraction: Variations in Platelet and Blood Components Between 4 Common Commercial Kits. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2017, 5, 2325967116675272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, J.M.; Russell, R.P.; Mazzocca, A.D. Platelet-rich plasma: The PAW classification system. Arthroscopy 2012, 28, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahla, J.; Cinque, M.E.; Piuzzi, N.S.; Mannava, S.; Geeslin, A.G.; Murray, I.R.; Dornan, G.J.; Muschler, G.F.; LaPrade, R.F. A Call for Standardization in Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparation Protocols and Composition Reporting: A Systematic Review of the Clinical Orthopaedic Literature. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2017, 99, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadadu, P.P.; Mazzola, A.J.; Hunter, C.W.; Davis, T.T. Review of concentration yields in commercially available platelet-rich plasma (PRP) systems: A call for PRP standardization. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2019, 44, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderstrom, A.C.; Nybo, M.; Nielsen, C.; Vinholt, P.J. The effect of centrifugation speed and time on pre-analytical platelet activation. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochini, A.C.; Antonioli, E.; Bucci, D.Z.; Sardinha, L.R.; Andreoli, C.V.; Ferretti, M.; Ejnisman, B.; Goldberg, A.C.; Cohen, M. Analysis of cytokine profile and growth factors in platelet-rich plasma obtained by open systems and commercial columns. Einstein 2016, 14, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, T.E.; Bowler, J.; Levins, T.N.; Cheng, A.L.; Reeves, K.D. Platelet yield and yield consistency for six single-spin methods of platelet rich plasma preparation. Platelets 2020, 31, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachito, D.V.; Bagattini, A.M.; de Almeida, A.M.; Mendrone-Junior, A.; Riera, R. Technical Procedures for Preparation and Administration of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Related Products: A Scoping Review. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 598816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.D.K.; Enweze, L.; DeBaun, M.R.; Dragoo, J.L. Current Clinical Recommendations for Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2018, 11, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, T.E.; Bowler, J.; Levins, T.N.; Reeves, K.D. PRPCalc2: An App for Platelet-Rich Plasma Preparation. Cureus 2023, 15, e36099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, E.; Domhof, S.; Langer, F. Nonparametric Analysis of Longitudinal Data in Factorial Experiments; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.H.; Rau, C.S.; Zeng, W.H.; Lu, T.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Chiu, Y.H.; Wu, K.M.; Tsai, C.W.; Lin, C.W.; Wu, C.J.; et al. A new technique for separating platelet-rich plasma by a copolymer device—Without a centrifugation process. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miron, R.J.; Chai, J.; Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Sculean, A.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of 24 protocols for the production of platelet-rich fibrin. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalon, J.; Chateau, A.L.; Bertrand, B.; Louis, M.L.; Silvestre, A.; Giraudo, L.; Veran, J.; Sabatier, F. DEPA classification: A proposal for standardising PRP use and a retrospective application of available devices. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2016, 2, e000060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqlain, N.; Mazher, N.; Fateen, T.; Siddique, A. Comparison of single and double centrifugation methods for preparation of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP). Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 39, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Layer | Means (SDs) According to Time in Minutes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 20 | |
| P5PLT | 0 (0) | 204 (49) | 143 (25) | 97 (22) | 50 (6) | 44 (10) |
| P4PLT | 52 (35) | 326 (32) | 200 (34) | 105 (23) | 69 (13) | 64 (12) |
| P3PLT | 414 (63) | 433 (54) | 215 (34) | 125 (29) | 70 (11) | 74 (15) |
| P2PLT | 502 (71) | 606 (103) | 276 (38) | 125 (30) | 91 (19) | 110 (32) |
| P1PLT | 565 (73) | 1061 (107) | 1224 (163) | 1433 (239) | 568 (86) | 901 (250) |
| R1Cell | 319 (45) | 290 (41) | 360 (78) | 748 (176) | 1013 (190) | 1183 (143) |
| R2 Cell | 258 (34) | 178 (24) | 162 (11) | 214 (30) | 404 (119) | 246 (38) |
| R3 Cell | 223 (31) | 160 (17) | 181 (29) | 126 (10) | 141 (18) | 149 (35) |
| R4 Cell | 213 (34) | 155 (16) | 130 (22) | 130 (8) | 113 (12) | 180 (25) |
| R5 Cell | 152 (18) | 145 (12) | 118 (8) | 154 (15) | 197 (46) | 366 (66) |
| Layer | Medians (IQRs) according to time in minutes | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 20 | |
| P5PLT | 0 (0) | 232 (353) | 152 (101) | 81 (100) | 45 (25) | 40 (57) |
| P4PLT | 0 (55) | 316 (142) | 158 (119) | 77 (96) | 55 (64) | 61 (75) |
| P3PLT | 357 (357) | 410 (231) | 187 (150) | 109 (148) | 51 (76) | 57 (59) |
| P2PLT | 407 (404) | 501 (424) | 242 (76) | 110 (129) | 79 (89) | 71 (114) |
| P1PLT | 517 (309) | 1099 (653) | 1287 (923) | 1147 (1224) | 471 (309) | 526 (1315) |
| R1Cell | 313 (212) | 272 (246) | 281 (363) | 504 (748) | 779 (1036) | 1298 (606) |
| R2 Cell | 226 (211) | 157 (139) | 154 (38) | 192 (159) | 273 (459) | 235 (125) |
| R3 Cell | 188 (192) | 146 (104) | 162 (72) | 127 (47) | 116 (71) | 118 (86) |
| R4 Cell | 175 (165) | 142 (84) | 110 (45) | 130 (28) | 114 (67) | 157 (121) |
| P5PLT | 149 (95) | 154 (67) | 121 (41) | 139 (26) | 135 (103) | 366 (299) |
| P4PLT | 0 (0) | 232 (353) | 152 (101) | 81 (100) | 45 (25) | 40 (57) |
| Layer | Means (SDs) According to Time in Minutes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 20 | |
| 1/2P1 + 1/2R1 PLT | 442 (58) | 676 (65) | 792 (92) | 1090 (122) | 790 (87) | 1042 (153) |
| Medians (IQRs) according to time in minutes | ||||||
| 1/2P1 + 1/2R1 PLT | 418 (269) | 682 (434) | 774 (448) | 1063 (749) | 786 (446) | 888 (799) |
| Layer | Means (SDs) According to Time in Minutes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 20 | |
| 1/2P1 + 1/2R1 PLT | 442 (58) | 676 (65) | 792 (92) | 1090 (122) | 790 (87) | 1042 (153) |
| 1/2P1 + 1/2P2 PLT | 533 (69) | 834 (98) | 750 (92) | 779 (120) | 330 (49) | 506 (126) |
| Layer | Medians (IQRs) according to time in minutes | |||||
| 1/2P1 + 1/2R1 PLT | 418 (269) | 682 (434) | 774 (448) | 1063 (749) | 786 (446) | 888 (799) |
| 1/2P1 + 1/2P2 PLT | 513 (366) | 817 (594) | 759 (447) | 657 (682) | 298 (151) | 307 (745) |
| Time | Layer | Mean | Std. Error | 95% C.I. Lower Bound | 95% C.I. Upper Bound |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | P5 | 9.210 | 0.190 | 8.829 | 9.591 |
| P4 | 9.190 | 0.228 | 8.733 | 9.647 | |
| P3 | 9.240 | 0.227 | 8.784 | 9.696 | |
| P2 | 9.090 | 0.219 | 8.650 | 9.530 | |
| P1 + R1 | 10.480 | 0.224 | 10.032 | 10.928 | |
| R2 | 10.475 | 0.277 | 9.919 | 11.031 | |
| R3 | 9.770 | 0.202 | 9.365 | 10.175 | |
| 8 | 9.850 | 0.220 | 9.409 | 10.291 | |
| 9 | 9.940 | 0.189 | 9.561 | 10.319 | |
| 10 | P5 | 9.980 | 0.190 | 9.599 | 10.361 |
| P4 | 9.790 | 0.228 | 9.333 | 10.247 | |
| P3 | 9.540 | 0.227 | 9.084 | 9.996 | |
| P2 | 9.520 | 0.219 | 9.080 | 9.960 | |
| P1 + R1 | 10.750 | 0.224 | 10.302 | 11.198 | |
| R2 | 10.670 | 0.277 | 10.114 | 11.226 | |
| R3 | 9.930 | 0.202 | 9.525 | 10.335 | |
| 8 | 9.820 | 0.220 | 9.379 | 10.261 | |
| 9 | 9.990 | 0.189 | 9.611 | 10.369 | |
| 20 | P5 | 9.800 | 0.190 | 9.419 | 10.181 |
| P4 | 9.670 | 0.228 | 9.213 | 10.127 | |
| P3 | 9.570 | 0.227 | 9.114 | 10.026 | |
| P2 | 9.410 | 0.219 | 8.970 | 9.850 | |
| P1 + R1 | 10.290 | 0.224 | 9.842 | 10.738 | |
| R2 | 9.850 | 0.277 | 9.294 | 10.406 | |
| R3 | 9.250 | 0.202 | 8.845 | 9.655 | |
| 8 | 9.440 | 0.220 | 8.999 | 9.881 | |
| 9 | 10.100 | 0.189 | 9.721 | 10.479 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harrison, T.E.; Bowler, J.; Cheng, C.-I.; Reeves, K.D. Optimizing Platelet-Rich Plasma: Spin Time and Sample Source. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111270
Harrison TE, Bowler J, Cheng C-I, Reeves KD. Optimizing Platelet-Rich Plasma: Spin Time and Sample Source. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(11):1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111270
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarrison, Theodore E., Jannice Bowler, Chin-I Cheng, and Kenneth Dean Reeves. 2023. "Optimizing Platelet-Rich Plasma: Spin Time and Sample Source" Bioengineering 10, no. 11: 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111270
APA StyleHarrison, T. E., Bowler, J., Cheng, C.-I., & Reeves, K. D. (2023). Optimizing Platelet-Rich Plasma: Spin Time and Sample Source. Bioengineering, 10(11), 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10111270





