Predictors of Changes in Pelvic Rotation after Surgery with or without Femoral Derotational Osteotomy in Ambulatory Children with Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
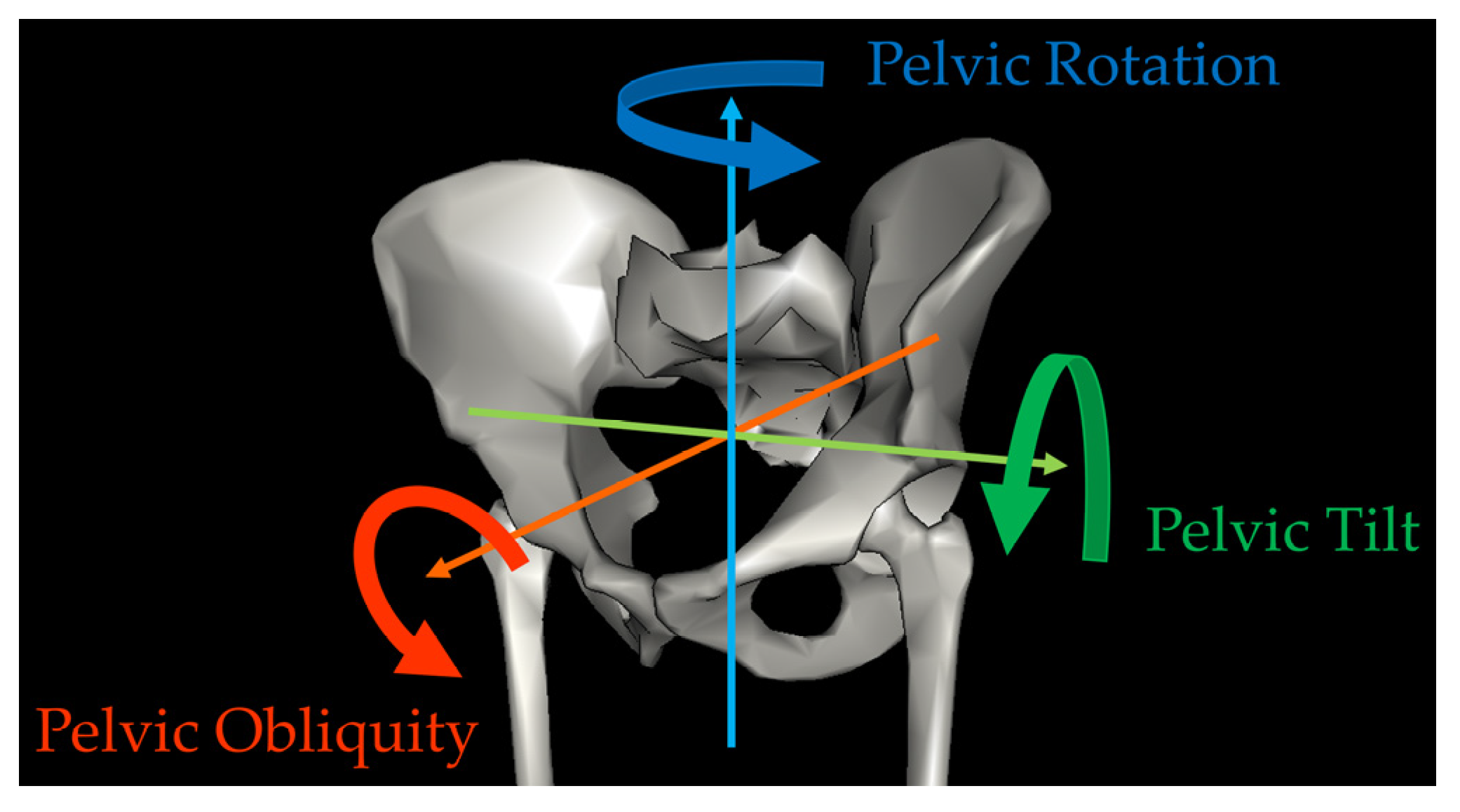
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Gait Analysis Data Collection and Processing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Leviton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Bax, M.; Damiano, D.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. Suppl. 2007, 109, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oskoui, M.; Coutinho, F.; Dykeman, J.; Jette, N.; Pringsheim, T. An update on the prevalence of cerebral palsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Meng, Q.; von Ehrenstein, O.S.; Xiao, J.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Y.W.; Ritz, B.; Liew, Z. Parental age and childhood risk for cerebral palsy in California. J. Pediatr. 2023, 255, 147–153.e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, D.; Van Naarden Braun, K.; Doernberg, N.S.; Maenner, M.J.; Arneson, C.L.; Durkin, M.S.; Benedict, R.E.; Kirby, R.S.; Wingate, M.S.; Fitzgerald, R.; et al. Prevalence of cerebral palsy, co-occurring autism spectrum disorders, and motor functioning—Autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, USA, 2008. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durkin, M.S.; Benedict, R.E.; Christensen, D.; Dubois, L.A.; Fitzgerald, R.T.; Kirby, R.S.; Maenner, M.J.; Van Naarden Braun, K.; Wingate, M.S.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M. Prevalence of cerebral palsy among 8-year-old children in 2010 and preliminary evidence of trends in its relationship to low birthweight. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2016, 30, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Naarden Braun, K.; Doernberg, N.; Schieve, L.; Christensen, D.; Goodman, A.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M. Birth prevalence of cerebral palsy: A population-based study. Pediatrics 2016, 137, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maenner, M.J.; Blumberg, S.J.; Kogan, M.D.; Christensen, D.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M.; Schieve, L.A. Prevalence of cerebral palsy and intellectual disability among children identified in two U.S. National Surveys, 2011–2013. Ann. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, D.O.; Tian, L.H.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M.; Dowling, N.F.; Christensen, D.L. Prevalence of cerebral palsy, intellectual disability, hearing loss, and blindness, national health interview survey, 2009–2016. Disabil. Health J. 2019, 12, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellier, E.; Platt, M.J.; Andersen, G.L.; Krageloh-Mann, I.; De La Cruz, J.; Cans, C.; Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy Network. Decreasing prevalence in cerebral palsy: A multi-site European population-based study, 1980 to 2003. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea, C.; McIntyre, S.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; Reid, S.M.; Gibson, C.; Delacy, M.; Watson, L.; Goldsmith, S.; Badawi, N.; Blair, E.; et al. Cerebral palsy trends in Australia (1995–2009): A population-based observational study. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2019, 61, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, J.R.; Fabian, D.; Hicks, R.; Tashman, S. Pre- and postoperative gait analysis in patients with spastic diplegia: A preliminary report. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1984, 4, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norlin, R.; Tkaczuk, H. One-session surgery for correction of lower extremity deformities in children with cerebral palsy. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1985, 5, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, G.; Smith, P. Human Motion Analysis Current Applications and Future Directions; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ounpuu, S.; Davis, R.B.; DeLuca, P.A. Joint kinetics: Methods, interpretation and treatment decision-making in children with cerebral palsy and myelomeningocele. Gait Posture 1996, 4, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, M. Gait Analysis an Introduction, 3rd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wren, T.A.; Otsuka, N.Y.; Bowen, R.E.; Scaduto, A.A.; Chan, L.S.; Sheng, M.; Hara, R.; Kay, R.M. Influence of gait analysis on decision-making for lower extremity orthopaedic surgery: Baseline data from a randomized controlled trial. Gait Posture 2011, 34, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wren, T.A.; Kalisvaart, M.M.; Ghatan, C.E.; Rethlefsen, S.A.; Hara, R.; Sheng, M.; Chan, L.S.; Kay, R.M. Effects of preoperative gait analysis on costs and amount of surgery. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2009, 29, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, P.A. Gait analysis in the treatment of the ambulatory child with cerebral palsy. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1991, 264, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, R. Modeling and Tracking of the Pelvis for Three-Dimensional Gait Analysis; University of Melbourne: Melbourne, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, R.M.; Rethlefsen, S.; Reed, M.; Do, K.P.; Skaggs, D.L.; Wren, T.A. Changes in pelvic rotation after soft tissue and bony surgery in ambulatory children with cerebral palsy. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2004, 24, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, R.; Walsh, M.; Hewart, P.; Jenkinson, A.; Ross, L.A.; O’Brien, T. Factors associated with internal hip rotation gait in patients with cerebral palsy. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2006, 26, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, R.; Walsh, M.; Jenkinson, A.; O’Brien, T. Factors associated with pelvic retraction during gait in cerebral palsy. Gait Posture 2007, 25, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais Filho, M.C.; Kawamura, C.M.; Andrade, P.H.; Dos Santos, M.B.; Pickel, M.R.; Neto, R.B. Factors associated with pelvic asymmetry in transverse plane during gait in patients with cerebral palsy. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2009, 18, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ounpuu, S.; DeLuca, P.; Davis, R.; Romness, M. Long-term effects of femoral derotation osteotomies: An evaluation using three-dimensional gait analysis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2002, 22, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohm, H.; Stief, F.; Dussa, C.U.; Doderlein, L. Predictors of pelvic retraction in children with cerebral palsy derived from gait parameters and clinical testing. Gait Posture 2012, 35, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.B.; Park, H.; Park, B.K.; Abdel-Baki, S.W.; Kim, H.W. Clinical and gait parameters related to pelvic retraction in patients with spastic hemiplegia. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carty, C.P.; Walsh, H.P.; Gillett, J.G.; Phillips, T.; Edwards, J.M.; deLacy, M.; Boyd, R.N. The effect of femoral derotation osteotomy on transverse plane hip and pelvic kinematics in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, I.H.; Cho, T.J.; Yoo, W.J.; Park, M.S. Residual pelvic rotation after single-event multilevel surgery in spastic hemiplegia. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2008, 90, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMulkin, M.L.; Gordon, A.B.; Caskey, P.M.; Tompkins, B.J.; Baird, G.O. Outcomes of orthopaedic surgery with and without an external femoral derotational osteotomy in children with cerebral palsy. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2016, 36, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lofterod, B.; Terjesen, T. Changes in lower limb rotation after soft tissue surgery in spastic diplegia. Acta Orthop. 2010, 81, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.J.; Yoon, J.Y.; Oh, M.K.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, J.H.; Eom, T.W.; Park, K.B. Effects of soft tissue surgery on pelvic and hip rotation in patients with spastic diplegia: A meta-analysis. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2016, 8, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desailly, E.; Badina, A.; Khouri, N. Kinematics after unilateral femoral derotation osteotomy in children with diplegic cerebral palsy. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2020, 106, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklasch, M.; Doderlein, L.; Klotz, M.C.; Braatz, F.; Wolf, S.I.; Dreher, T. Asymmetric pelvic and hip rotation in children with bilateral cerebral palsy: Uni- or bilateral femoral derotation osteotomy? Gait Posture 2015, 41, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perotti, L.; Church, C.; Dina, R., Jr.; Lennon, N.; Henley, J.; Sees, J.; Miller, F. The long-term outcome of pelvic asymmetry during gait in children with cerebral palsy following unilateral femoral derotation osteotomy. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2019, 28, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Cha, Y.H.; Byun, J.Y.; Chun, Y.S.; Choy, W.S. Changes in gait parameters after femoral derotational osteotomy in cerebral palsy patients with medial femoral torsion. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2018, 27, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palisano, R.; Rosenbaum, P.; Walter, S.; Russell, D.; Wood, E.; Galuppi, B. Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 1997, 39, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wren, T.A.; Do, K.P.; Hara, R.; Rethlefsen, S.A. Use of a patella marker to improve tracking of dynamic hip rotation range of motion. Gait Posture 2008, 27, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.; Sangeux, M.; Morris, M.E.; Baker, R. Determination of the optimal locations of surface-mounted markers on the tibial segment. Gait Posture 2009, 29, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazareth, A.; Mueske, N.M.; Wren, T.A. Effect of tibia marker placement on kinematics in pathological gait. J. Appl. Biomech. 2016, 32, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R. Pelvic angles: A mathematically rigorous definition which is consistent with a conventional clinical understanding of the terms. Gait Posture 2001, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacWilliams, B.A.; McMulkin, M.L.; Davis, R.B.; Westberry, D.E.; Baird, G.O.; Stevens, P.M. Biomechanical changes associated with femoral derotational osteotomy. Gait Posture 2016, 49, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebbins, J.; Harrington, M.; Thompson, N.; Zavatsky, A.; Theologis, T. Gait compensations caused by foot deformity in cerebral palsy. Gait Posture 2010, 32, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Predictive Variables | Number (%) of Patients in Each Group or Mean ± Standard Deviation (Range) |
|---|---|
| Distribution of CP | |
| Unilateral Involvement | 17 (17%) |
| Bilateral Involvement | 84 (83%) |
| Type or Surgery | |
| No FDRO | 44 (44%) |
| Unilateral FDRO | 18 (18%) |
| Bilateral FDRO | 39 (39%) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 63 (62%) |
| Female | 38 (38%) |
| GMFCS Level | |
| I | 20 (20%) |
| II | 46 (46%) |
| III | 30 (30%) |
| IV | 5 (5%) |
| Age at Surgery (years) | 10.2 ± 3.6 (4.8 – 20.7) |
| Follow-up Time (years) | 2.4 ± 2.4 (0.6 – 12.3) |
| Pre-operative Pelvic Rotation Angle (degrees) | −6.1 ± 6.2 (−35.2 – 1.1) |
| Classification of Patients | Change in Pelvic Rotation Angle (Deg) | p-Value Change in Pelvic Rotation Angle | p-Value FDRO vs. No FDRO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unilateral Involvement | 0.004 | ||
| FDRO (n = 7) | 4.1 (1.8) | 0.04 | |
| No FDRO (n = 10) | −3.7 (1.5) | 0.02 | |
| Bilateral Involvement | 0.84 | ||
| FDRO (n = 50) | 1.4 (0.8) | 0.08 | |
| No FDRO (n = 34) | 1.7 (1.0) | 0.09 |
| Predictors | p-Value Unilateral Involvement | p-Value Bilateral Involvement |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.51 | 1.00 |
| GMFCS Level | 0.73 | 0.07 |
| Age at Surgery | 0.33 | 0.66 |
| Follow-up Time | 1.00 | 0.82 |
| Pre-operative Pelvic Rotation Angle | 0.69 | 0.03 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hara, R.; Rethlefsen, S.A.; Wren, T.A.L.; Kay, R.M. Predictors of Changes in Pelvic Rotation after Surgery with or without Femoral Derotational Osteotomy in Ambulatory Children with Cerebral Palsy. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101214
Hara R, Rethlefsen SA, Wren TAL, Kay RM. Predictors of Changes in Pelvic Rotation after Surgery with or without Femoral Derotational Osteotomy in Ambulatory Children with Cerebral Palsy. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(10):1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101214
Chicago/Turabian StyleHara, Reiko, Susan A. Rethlefsen, Tishya A. L. Wren, and Robert M. Kay. 2023. "Predictors of Changes in Pelvic Rotation after Surgery with or without Femoral Derotational Osteotomy in Ambulatory Children with Cerebral Palsy" Bioengineering 10, no. 10: 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101214
APA StyleHara, R., Rethlefsen, S. A., Wren, T. A. L., & Kay, R. M. (2023). Predictors of Changes in Pelvic Rotation after Surgery with or without Femoral Derotational Osteotomy in Ambulatory Children with Cerebral Palsy. Bioengineering, 10(10), 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101214






