Implicit HbA1c Achieving 87% Accuracy within 90 Days in Non-Invasive Fasting Blood Glucose Measurements Using Photoplethysmography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Non-Invasive Blood Glucose (NIBG) Measurements
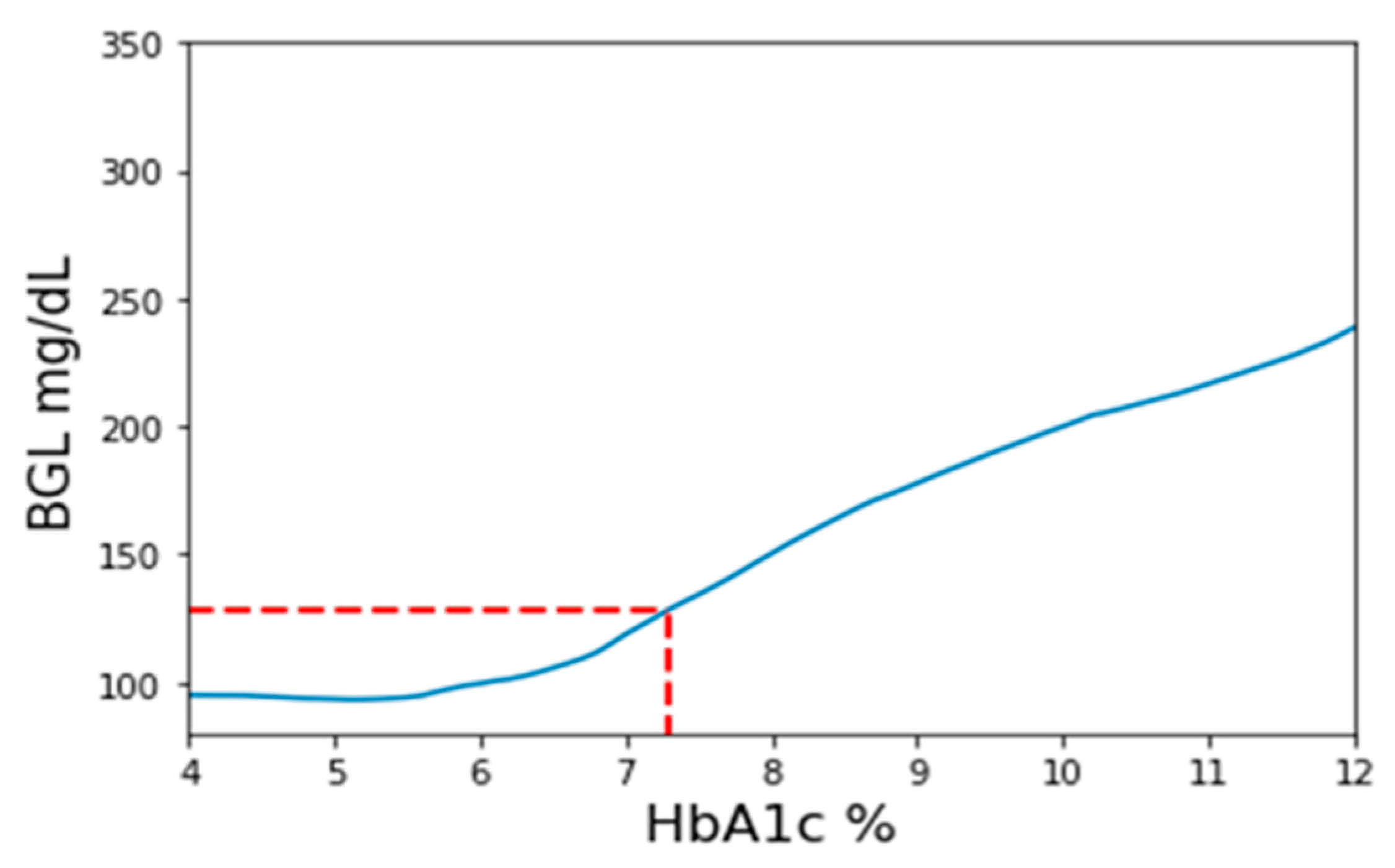
1.2. From Measured HbA1c to Implicit HbA1c
2. Experiments and Method
2.1. Experimental Set-Up
2.2. Method
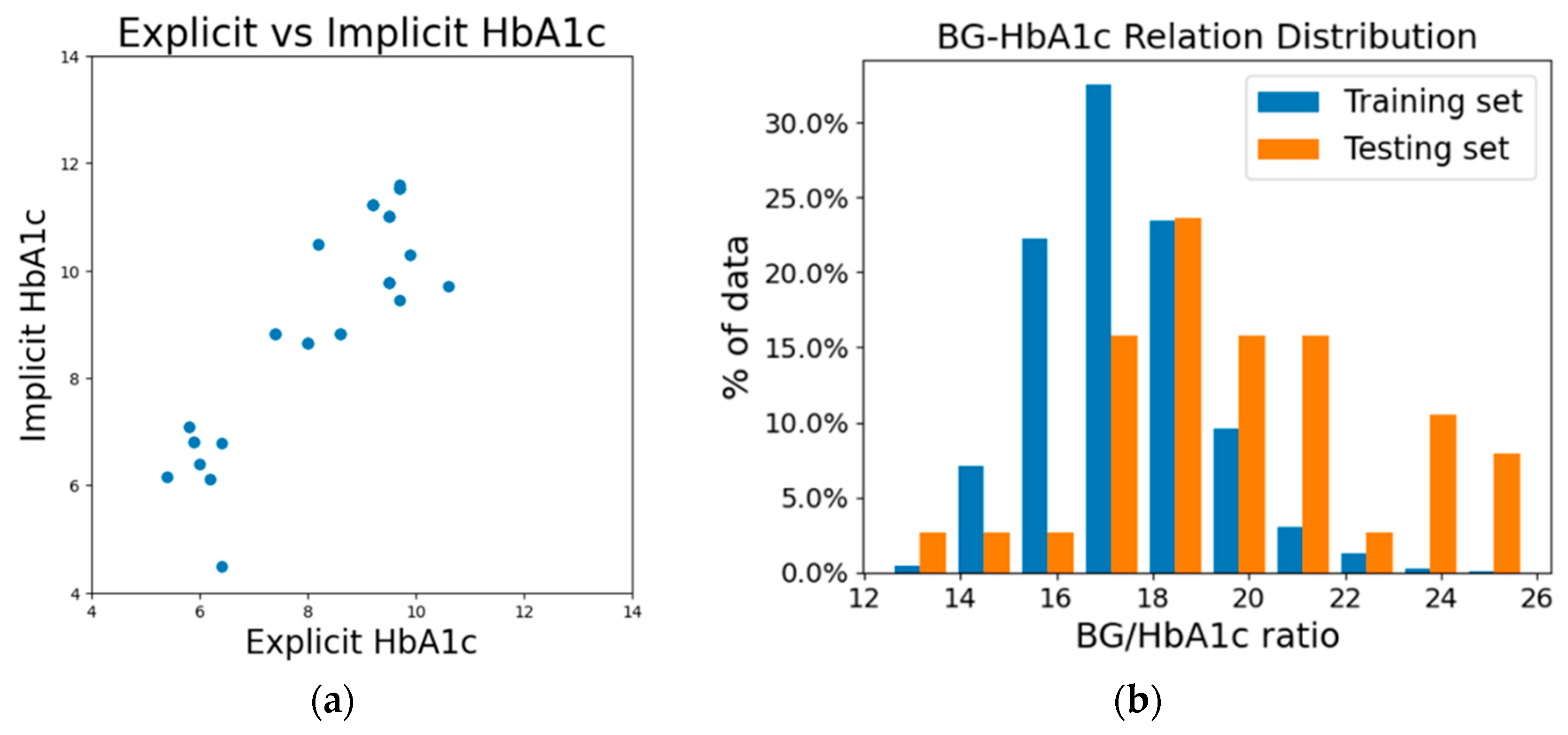
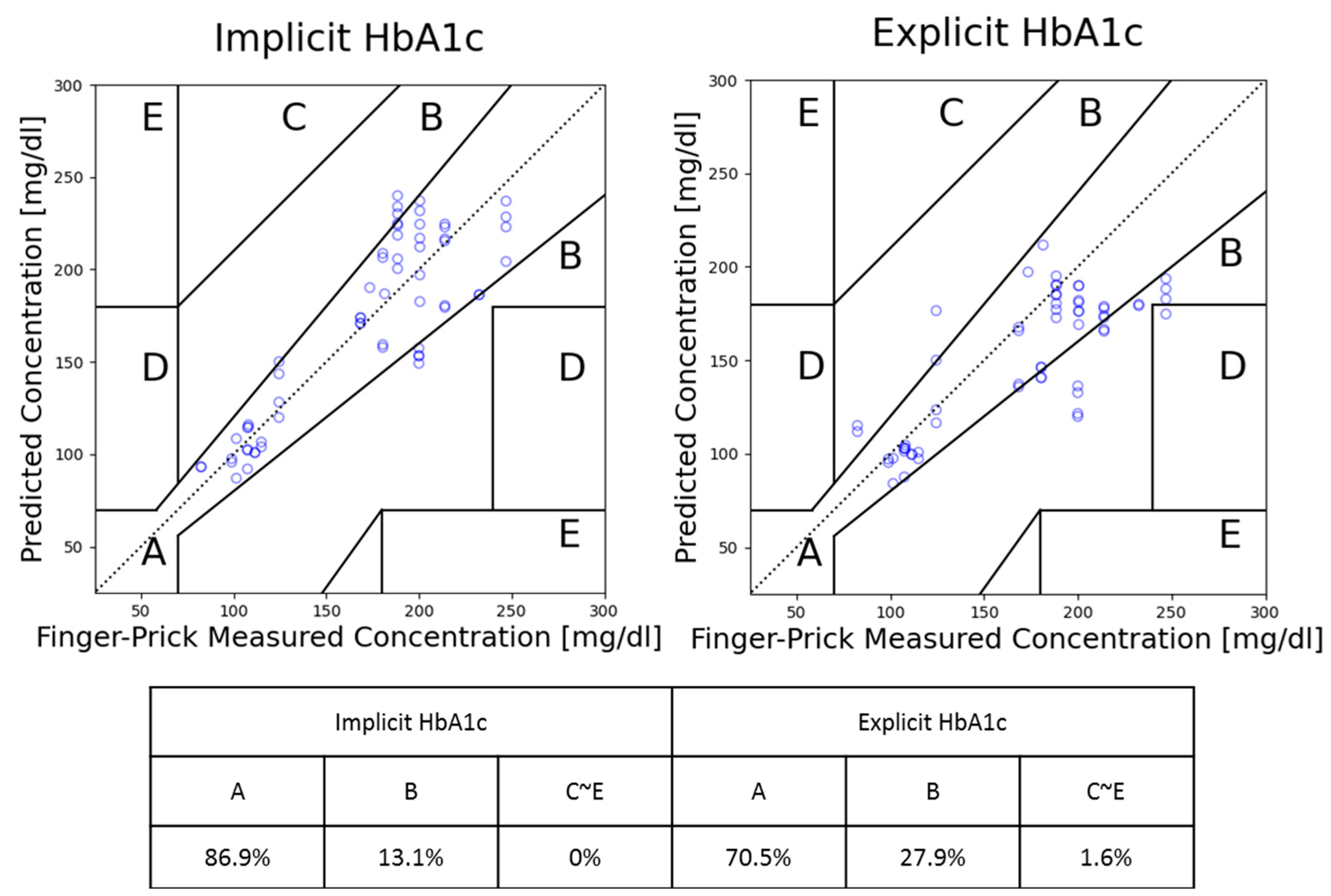
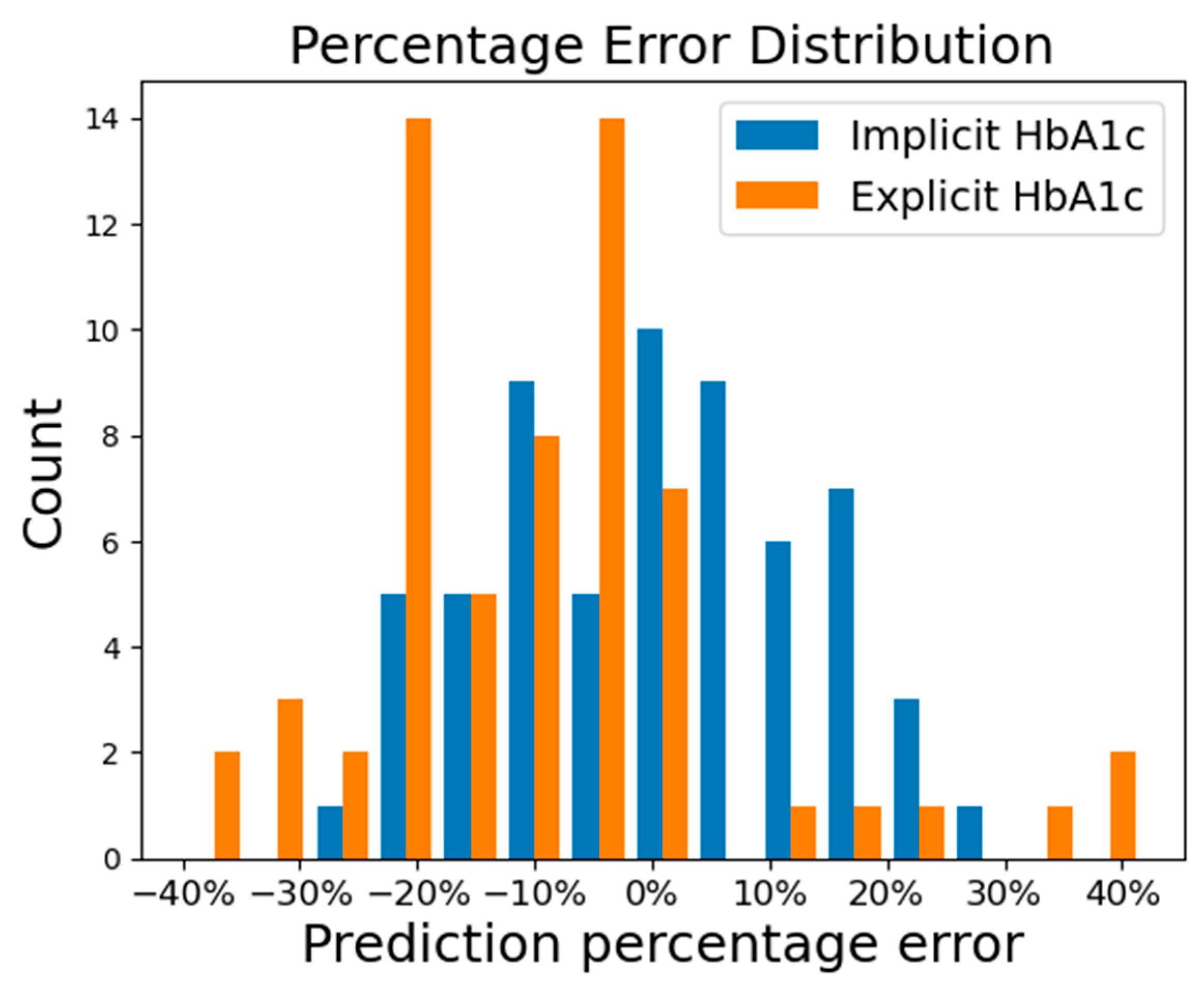
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National and State Diabetes Trends. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/library/reports/reportcard/national-state-diabetes-trends.html (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes around the World in 2021. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/ (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, M.; Kubota, N.; Minami, T.; Shirakawa, R.; Sakurai, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Iwamoto, M.; Takamoto, I.; Kubota, T.; Suzuki, R.; et al. Association between tear and blood glucose concentrations: Random intercept model adjusted with confounders in tear samples negative for occult blood. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, H.; Channa, A.; Jeoti, V.; Stojanovic, G.M. Comprehensive Review on Wearable Sweat-Glucose Sensors for Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Sensors 2022, 22, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Du, Y.; Wang, M.L. Noninvasive glucose monitoring using saliva nano-biosensor. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2015, 4, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte-Moreno, E. Non-invasive estimate of blood glucose and blood pressure from a photoplethysmograph by means of machine learning techniques. Artif. Intell. Med. 2011, 53, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachim, V.P.; Chung, W.-Y. Wearable-band type visible-near infrared optical biosensor for non-invasive blood glucose monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 286, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.; Rani, A.; Singh, V.; Murari, B.M. Prospects and limitations of non-invasive blood glucose monitoring using near-infrared spectroscopy. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2015, 18, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, B.G.; Marcondes, D.W.C.; Bertemes-Filho, P. Analytical Model for Blood Glucose Detection Using Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy. Sensors 2020, 20, 6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alian, A.A.; Shelley, K.H. Photoplethysmography. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2014, 28, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Brinker, A.C.; Wang, W. Chapter 3—Model-based camera-PPG: Pulse-rate monitoring in fitness. In Contactless Vital Signs Monitoring; Wang, W., Wang, X., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 51–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hina, A.; Saadeh, W. Noninvasive Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems Using Near-Infrared Technology-A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benichou, T.; Pereira, B.; Mermillod, M.; Tauveron, I.; Pfabigan, D.; Maqdasy, S.; Dutheil, F. Heart rate variability in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paneni, F.; Beckman, J.A.; Creager, M.A.; Cosentino, F. Diabetes and vascular disease: Pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: Part I. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2436–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hina, A.; Saadeh, W. A Noninvasive Glucose Monitoring SoC Based on Single Wavelength Photoplethysmography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2020, 14, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.; Yang, W.T.; Lu, W.R.; Chang, Y.T.; Hsieh, T.H.; Yang, F.L. 90% Accuracy for Photoplethysmography-Based Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Prediction by Deep Learning with Cohort Arrangement and Quarterly Measured HbA1c. Sensors 2021, 21, 7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Use of Glycated Haemoglobin (HbA1c) in the Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus: Abbreviated Report of a WHO Consultation; World Health Organization CTI—WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- International Organization for Standardization. In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems—Requirements for Blood-Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Testing in Managing Diabetes Mellitus; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, W.L.; Cox, D.; Gonder-Frederick, L.A.; Carter, W.; Pohl, S.L. Evaluating clinical accuracy of systems for self-monitoring of blood glucose. Diabetes Care 1987, 10, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.R.; Yang, W.T.; Chu, J.; Hsieh, T.H.; Yang, F.L. Deduction learning for precise noninvasive measurements of blood glucose with a dozen rounds of data for model training. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettiarachchi, C.; Chitraranjan, C. A Machine Learning Approach to Predict Diabetes Using Short Recorded Photoplethysmography and Physiological Characteristics. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, Poznan, Poland, 26–29 June 2019; pp. 322–327. [Google Scholar]
- International Diabetes Federation Clinical Guidelines Task Force. Guideline on Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose in Non-Insulin Treated Type 2 Diabetes. Int. Diabetes Fed. 2009, 17, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, D.M.; Genuth, S.; Lachin, J.; Cleary, P.; Crofford, O.; Davis, M.; Rand, L.; Siebert, C. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sia, H.K.; Kor, C.T.; Tu, S.T.; Liao, P.Y.; Wang, J.Y. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in association with glycemic control in newly diagnosed non-insulin-treated diabetes patients: A retrospective cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Molfetta, S.; Bosi, E.; Ceriello, A.; Cucinotta, D.; Tiengo, A.; Scavini, M.; Piccolo, C.; Bonizzoni, E.; Acmet, E.; Giorgino, F.; et al. Structured self-monitoring of blood glucose is associated with more appropriate therapeutic interventions than unstructured self-monitoring: A novel analysis of data from the PRISMA trial. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 181, 109070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Model training | User | |||
| Featuring HbA1c (Pretest) | Interval up to 90 days | Testing | ||
| Required Input |
| PPG signal Reference BGL | PPG signal Implicit HbA1c | |
| Outcome |
| Implicit HbA1c | Predicted BGL | |
| Dataset | Interval between Test and Pretest | BG (mg/dL) | HbA1c (%) | Age (Years) | BMI (kg/m2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total 856 entries | Training (747 entries) | No pretest | 99.9 ± 12.9 | 5.7 ± 0.53 | 57.9 ± 9.7 | 23.4 ± 3.2 |
| Testing (61 pairs) | 45 ± 19 days | 154.9 ± 50.8 | 7.7 ± 1.76 | 62.7 ± 3.95 | 28.4 ± 4.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, J.; Chang, Y.-T.; Liaw, S.-K.; Yang, F.-L. Implicit HbA1c Achieving 87% Accuracy within 90 Days in Non-Invasive Fasting Blood Glucose Measurements Using Photoplethysmography. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101207
Chu J, Chang Y-T, Liaw S-K, Yang F-L. Implicit HbA1c Achieving 87% Accuracy within 90 Days in Non-Invasive Fasting Blood Glucose Measurements Using Photoplethysmography. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(10):1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101207
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Justin, Yao-Ting Chang, Shien-Kuei Liaw, and Fu-Liang Yang. 2023. "Implicit HbA1c Achieving 87% Accuracy within 90 Days in Non-Invasive Fasting Blood Glucose Measurements Using Photoplethysmography" Bioengineering 10, no. 10: 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101207
APA StyleChu, J., Chang, Y.-T., Liaw, S.-K., & Yang, F.-L. (2023). Implicit HbA1c Achieving 87% Accuracy within 90 Days in Non-Invasive Fasting Blood Glucose Measurements Using Photoplethysmography. Bioengineering, 10(10), 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101207










