Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Modulates EEG Microstates in Low-Functioning Autism: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. tDCS Treatment
2.4. EEG Acquisition and Data Preprocessing
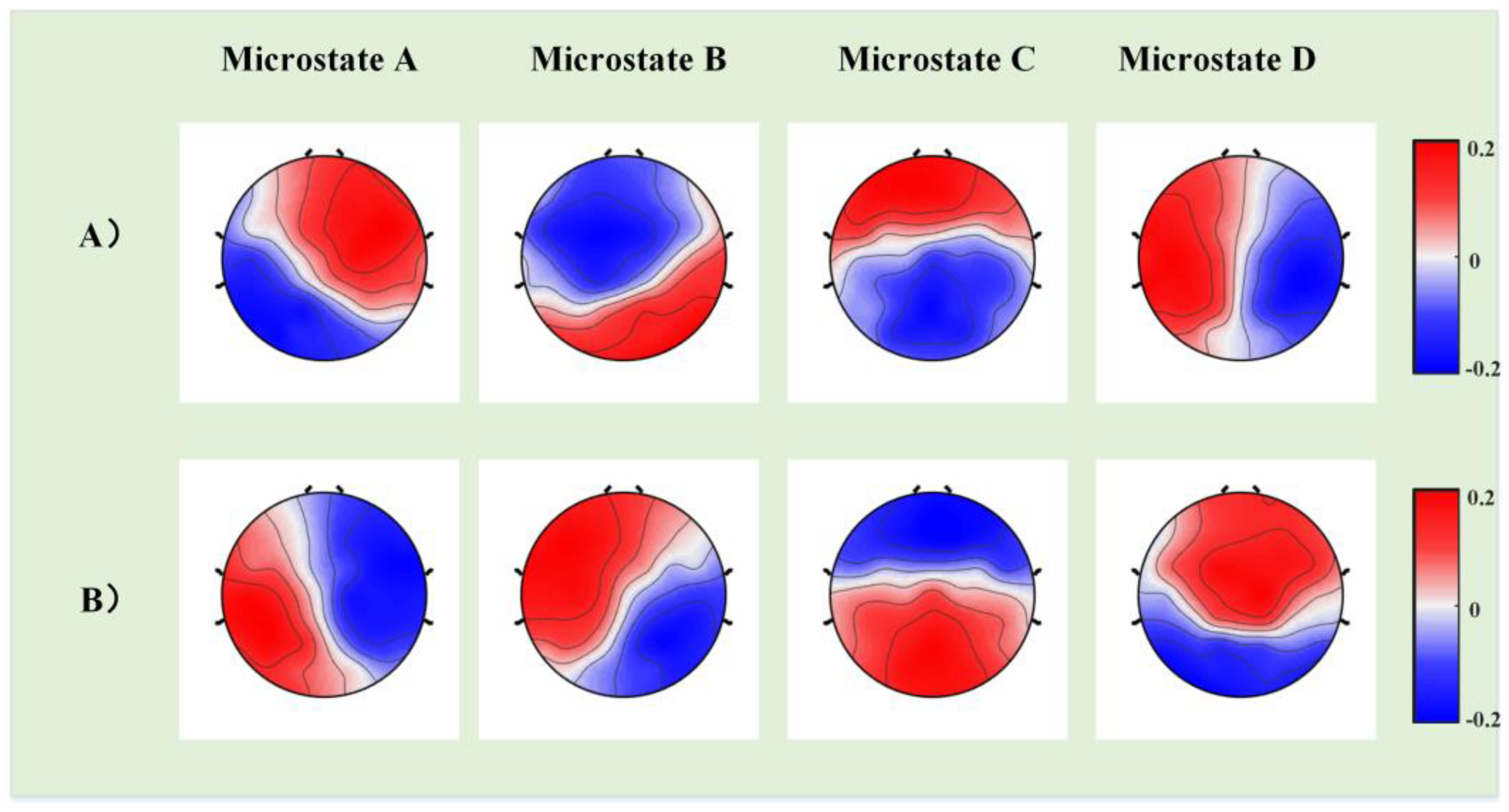
2.5. Microstate Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
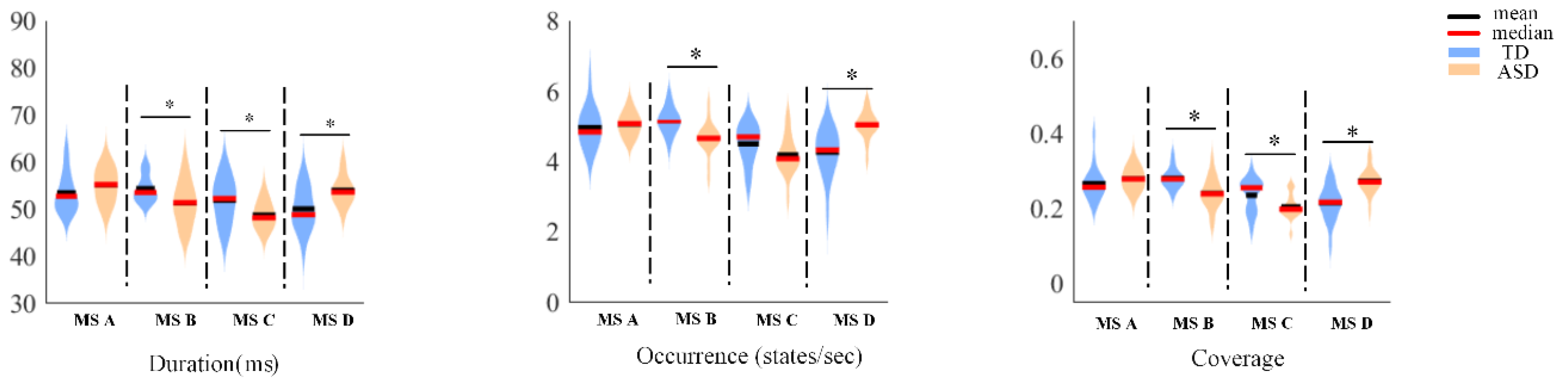
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mottron, L.; Bzdok, D. Autism spectrum heterogeneity: Fact or artifact? Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 3178–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trottier, G.; Srivastava, L.; Walker, C.D. Etiology of infantile autism: A review of recent advances in genetic and neurobiological research. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 1999, 24, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, C.; Pasquier, L.; Cohen, D.; Fradin, M.; Canitano, R.; Damaj, L.; Odent, S.; Tordjman, S. Role of genetics in the etiology of autistic spectrum disorder: Towards a hierarchical diagnostic strategy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehr, B. American Psychiatric Association explains DSM-5. BMJ 2013, 346, f3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Parayil, R.; Mishra, S.; Nongthomba, U.; Clement, J.P. Epilepsy Characteristics in Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Research from Patient Cohorts and Animal Models Focusing on Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, D.M.; Veltman, E.; Sellbom, M. Surviving Senior Psychopathy: Informant Reports of Deceit and Antisocial Behavior in Multiple Types of Relationships. Int. J. Offender Ther. Comp. Criminol. 2022, 66, 1703–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, K.A.; Maenner, M.J.; Baio, J.; Washington, A.; Christensen, D.L.; Wiggins, L.D.; Pettygrove, S.; Andrews, J.G.; White, T.; Rosenberg, C.R.; et al. Early Identification of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 4 Years—Early Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, Six Sites, United States, 2016. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2020, 69, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSouza, A.A.; Akers, J.S.; Fisher, W.W. Empirical Application of Skinner’s Verbal Behavior to Interventions for Children with Autism: A Review. Anal. Verbal. Behav. 2017, 33, 229–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundberg, C.T.; Sundberg, M.L. Jack Michael’s Contributions to the Treatment of Autism. Behav. Anal. Pract. 2021, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, F.; Jamil, A.; Mosayebi Samani, M.; Vidor, L.P.; Nitsche, M.A. Basic and functional effects of transcranial Electrical Stimulation (tES)-An introduction. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 85, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Vliet, R.; Jonker, Z.D.; Louwen, S.C.; Heuvelman, M.; de Vreede, L.; Ribbers, G.M.; De Zeeuw, C.I.; Donchin, O.; Selles, R.W.; van der Geest, J.N.; et al. Cerebellar transcranial direct current stimulation interacts with BDNF Val66Met in motor learning. Brain. Stimul. 2018, 11, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knotkova, H.; Nitsche, M.A.; Tronnier, V. Neurostimulation. Neural. Plast. 2016, 2016, 1830405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, H.; Chen, Y.; Zuo, L.; Xia, X.; Zhang, X. Corrigendum: Thinking on Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) in Reading Interventions: Recommendations for Future Research Directions. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 814964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padrón, I.; García-Marco, E.; Moreno, I.; Birba, A.; Silvestri, V.; León, I.; Álvarez, C.; López, J.; de Vega, M. Multisession Anodal tDCS on the Right Temporo-Parietal Junction Improves Mentalizing Processes in Adults with Autistic Traits. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunoni, A.R.; Nitsche, M.A.; Bolognini, N.; Bikson, M.; Wagner, T.; Merabet, L.; Edwards, D.J.; Valero-Cabre, A.; Rotenberg, A.; Pascual-Leone, A.; et al. Clinical research with transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS): Challenges and future directions. Brain Stimul. 2012, 5, 175–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, E.; Mori, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Harada, M.; Kagami, S. Function of the frontal lobe in autistic individuals: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic study. J. Med. Invest. 2010, 57, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vega, M.; Padrón, I.; Moreno, I.; García-Marco, E.; Domínguez, A.; Marrero, H.; Hernández, S. Both the mirror and the affordance systems might be impaired in adults with high autistic traits. Evidence from EEG mu and beta rhythms. Autism Res. 2019, 12, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auvichayapat, N.; Patjanasoontorn, N.; Phuttharak, W.; Suphakunpinyo, C.; Keeratitanont, K.; Tunkamnerdthai, O.; Aneksan, B.; Klomjai, W.; Boonphongsathian, W.; Sinkueakunkit, A.; et al. Brain Metabolite Changes After Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S.C.; Hoy, K.E.; Enticott, P.G.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Fitzgerald, P.B. Improving working memory: The effect of combining cognitive activity and anodal transcranial direct current stimulation to the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Brain Stimul. 2011, 4, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehinejad, M.A.; Paknia, N.; Hosseinpour, A.H.; Yavari, F.; Vicario, C.M.; Nitsche, M.A.; Nejati, V. Contribution of the right temporoparietal junction and ventromedial prefrontal cortex to theory of mind in autism: A randomized, sham-controlled tDCS study. Autism. Res. 2021, 14, 1572–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimland, B.; Edelson, S. Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist (ATEC); Autism Research Institute: San Diego, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Amatachaya, A.; Jensen, M.P.; Patjanasoontorn, N.; Auvichayapat, N.; Suphakunpinyo, C.; Janjarasjitt, S.; Ngernyam, N.; Aree-uea, B.; Auvichayapat, P. The short-term effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on electroencephalography in children with autism: A randomized crossover controlled trial. Behav. Neurol. 2015, 2015, 928631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodifar, E.; Sotoodeh, M.S. Combined Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation and Selective Motor Training Enhances Balance in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Percept. Mot. Skills 2020, 127, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckhardt, C.; Schütz, M.; Mühlherr, A.; Mössinger, H.; Boxhoorn, S.; Dempfle, A.; Salvador, R.; Ruffini, G.; Pereira, H.C.; Castelo-Branco, M.; et al. Phase-IIa randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled, parallel group trial on anodal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) over the left and right tempo-parietal junction in autism spectrum disorder-StimAT: Study protocol for a clinical trial. Trials 2021, 22, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Steenburgh, J.J.; Varvaris, M.; Schretlen, D.J.; Vannorsdall, T.D.; Gordon, B. Balanced bifrontal transcranial direct current stimulation enhances working memory in adults with high-functioning autism: A sham-controlled crossover study. Mol. Autism. 2017, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadoush, H.; Nazzal, M.; Almasri, N.A.; Khalil, H.; Alafeef, M. Therapeutic Effects of Bilateral Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Prefrontal and Motor Cortical Areas in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Pilot Study. Autism Res. 2020, 13, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymaekers, R.; Wiersema, J.R.; Roeyers, H. EEG study of the mirror neuron system in children with high functioning autism. Brain Res. 2009, 1304, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, K.A.; Badran, B.W.; DeVries, W.H.; Summers, P.M.; Kofmehl, E.; Li, X.; Borckardt, J.J.; Bikson, M.; George, M.S. Transcranial electrical stimulation motor threshold can estimate individualized tDCS dosage from reverse-calculation electric-field modeling. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanesco, A.P. EEG Electric Field Topography is Stable During Moments of High Field Strength. Brain Topogr. 2020, 33, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Zou, G.; He, Y.; Zou, Q.; Gao, J.H. Reliability and Individual Specificity of EEG Microstate Characteristics. Brain Topogr. 2020, 33, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquelet, N.; De Tiège, X.; Roshchupkina, L.; Peigneux, P.; Goldman, S.; Woolrich, M.; Wens, V. Microstates and power envelope hidden Markov modeling probe bursting brain activity at different timescales. Neuroimage 2022, 247, 118850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.M.; Koenig, T. EEG microstates as a tool for studying the temporal dynamics of whole-brain neuronal networks: A review. Neuroimage 2018, 180, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keinänen, T.; Rytky, S.; Korhonen, V.; Huotari, N.; Nikkinen, J.; Tervonen, O.; Palva, J.M.; Kiviniemi, V. Fluctuations of the EEG-fMRI correlation reflect intrinsic strength of functional connectivity in default mode network. J. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 96, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubega, M.; Carboni, M.; Seeber, M.; Pascucci, D.; Tourbier, S.; Toscano, G.; Van Mierlo, P.; Hagmann, P.; Plomp, G.; Vulliemoz, S.; et al. Estimating EEG Source Dipole Orientation Based on Singular-value Decomposition for Connectivity Analysis. Brain Topogr. 2019, 32, 704–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baradits, M.; Bitter, I.; Czobor, P. Multivariate patterns of EEG microstate parameters and their role in the discrimination of patients with schizophrenia from healthy controls. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 288, 112938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.J.; Kendall, P.C.; Wood, K.S.; Kerns, C.M.; Seltzer, M.; Small, B.J.; Lewin, A.B.; Storch, E.A. Cognitive Behavioral Treatments for Anxiety in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescorla, L.A.; Ghassabian, A.; Ivanova, M.Y.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Verhulst, F.C.; Tiemeier, H. Structure, longitudinal invariance, and stability of the Child Behavior Checklist 1½-5’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-Autism Spectrum Disorder scale: Findings from Generation R (Rotterdam). Autism 2019, 23, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, B.; Sellbom, M.; Skjernov, M.; Simonsen, E. ICD-11 and DSM-5 personality trait domains capture categorical personality disorders: Finding a common ground. Aust N Z J. Psychiatry 2018, 52, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myslobodsky, M.S.; Coppola, R.; Bar-Ziv, J.; Weinberger, D.R. Adequacy of the International 10-20 electrode system for computed neurophysiologic topography. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1990, 7, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, D.; Skrandies, W. Reference-free identification of components of checkerboard-evoked multichannel potential fields. Electroencephalogr Clin. Neurophysiol. 1980, 48, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.M.; Brunet, D.; Michel, C.M. Topographic ERP analyses: A step-by-step tutorial review. Brain Topogr. 2008, 20, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, L.E.; Austin, K.L. The Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) as an adjunct to pharmacokinetic analysis. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1983, 4, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Datta, S. Rank-based inference for covariate and group effects in clustered data in presence of informative intra-cluster group size. Stat. Med. 2018, 37, 4807–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunet, D.; Murray, M.M.; Michel, C.M. Spatiotemporal analysis of multichannel EEG: CARTOOL. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 813870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, V.; Coffman, B.; Trumbo, M.; Gasparovic, C. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) produces localized and specific alterations in neurochemistry: A (1)H magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 500, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.N.; Cai, E.J.; Han, J.X.; Tong, Z.; Li, X.; Sokhadze, E.M.; Casanova, M.F.; Ouyang, G.X.; Li, X.L. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) Can Modulate EEG Complexity of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zoubi, O.; Mayeli, A.; Misaki, M.; Tsuchiyagaito, A.; Zotev, V.; Refai, H.; Paulus, M.; Bodurka, J. Canonical EEG microstates transitions reflect switching among BOLD resting state networks and predict fMRI signal. J. Neural. Eng. 2022, 18, 066051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, F.; Mottron, L.; Soulières, I.; Zeffiro, T.A. Enhanced visual functioning in autism: An ALE meta-analysis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2012, 33, 1553–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, A.S.; Grummett, T.S.; Bakhshayesh, H.; Lewis, T.W.; DeLosAngeles, D.; Whitham, E.M.; Willoughby, J.O.; Pope, K.J. Fast and effective removal of contamination from scalp electrical recordings. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadak, M.T.; Demirel, O.F.; Yavuz, M.; Demir, T. Recognition of emotional facial expressions and broad autism phenotype in parents of children diagnosed with autistic spectrum disorder. Compr. Psychiatry 2014, 55, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avraam, R.; Binur, N.; Hadad, B.S. Typical perceptual organization in autism: Perceptual grouping and spatial distortion. Autism Res. 2019, 12, 1623–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Yu, D. Aberrant Intrinsic Brain Activity in Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Insights from EEG Microstates. Brain Topogr. 2019, 32, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, G.L.; Pope, D.L.; Astafiev, S.V.; McAvoy, M.P.; Snyder, A.Z.; Corbetta, M. Right hemisphere dominance during spatial selective attention and target detection occurs outside the dorsal frontoparietal network. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 3640–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delbruck, E.; Yang, M.; Yassine, A.; Grossman, E.D. Functional connectivity in ASD: Atypical pathways in brain networks supporting action observation and joint attention. Brain Res. 2019, 1706, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadone, S.; Wyczesany, M.; Della Penna, S.; Corbetta, M.; Capotosto, P. Directed Flow of Beta Band Communication During Reorienting of Attention Within the Dorsal Attention Network. Brain Connect. 2021, 11, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, A.; Varcin, K.J.; Sahin, M.; Nelson, C.A., 3rd; Jeste, S.S. Early patterns of functional brain development associated with autism spectrum disorder in tuberous sclerosis complex. Autism Res. 2019, 12, 1758–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, F.; Bauer, S.; Rosenow, F.; Triesch, J.; Laufs, H. EEG microstate periodicity explained by rotating phase patterns of resting-state alpha oscillations. Neuroimage 2021, 224, 117372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Jia, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Scale-free dynamics of microstate sequence in negative schizophrenia and depressive disorder. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 143, 105287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| ABC Scale | Pre-tDCS (Mean ± SD) | Post-tDCS (Mean ± SD) | p-Value | z-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S R B L S | 13.31 ± 6.76 16.13 ± 4.52 14.45 ± 3.08 13.75 ± 5.50 11.88 ± 4.01 | 11.94 ± 6.38 11.80 ± 4.89 11.91 ± 3.08 9.31 ± 4.72 11.13 ± 3.76 | 0.12 0.002 * 0.113 0.019 * 0.589 | 1.555 3.090 1.585 2.346 0.540 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.; Fan, X.; Zhong, Y.; Casanova, M.F.; Sokhadze, E.M.; Li, X.; Niu, Z.; Geng, X. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Modulates EEG Microstates in Low-Functioning Autism: A Pilot Study. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010098
Kang J, Fan X, Zhong Y, Casanova MF, Sokhadze EM, Li X, Niu Z, Geng X. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Modulates EEG Microstates in Low-Functioning Autism: A Pilot Study. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(1):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010098
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Jiannan, Xiwang Fan, Yiwen Zhong, Manuel F. Casanova, Estate M. Sokhadze, Xiaoli Li, Zikang Niu, and Xinling Geng. 2023. "Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Modulates EEG Microstates in Low-Functioning Autism: A Pilot Study" Bioengineering 10, no. 1: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010098
APA StyleKang, J., Fan, X., Zhong, Y., Casanova, M. F., Sokhadze, E. M., Li, X., Niu, Z., & Geng, X. (2023). Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Modulates EEG Microstates in Low-Functioning Autism: A Pilot Study. Bioengineering, 10(1), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10010098







