Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources and Crop Production in Western Nepal: Implications and Adaptation Strategies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
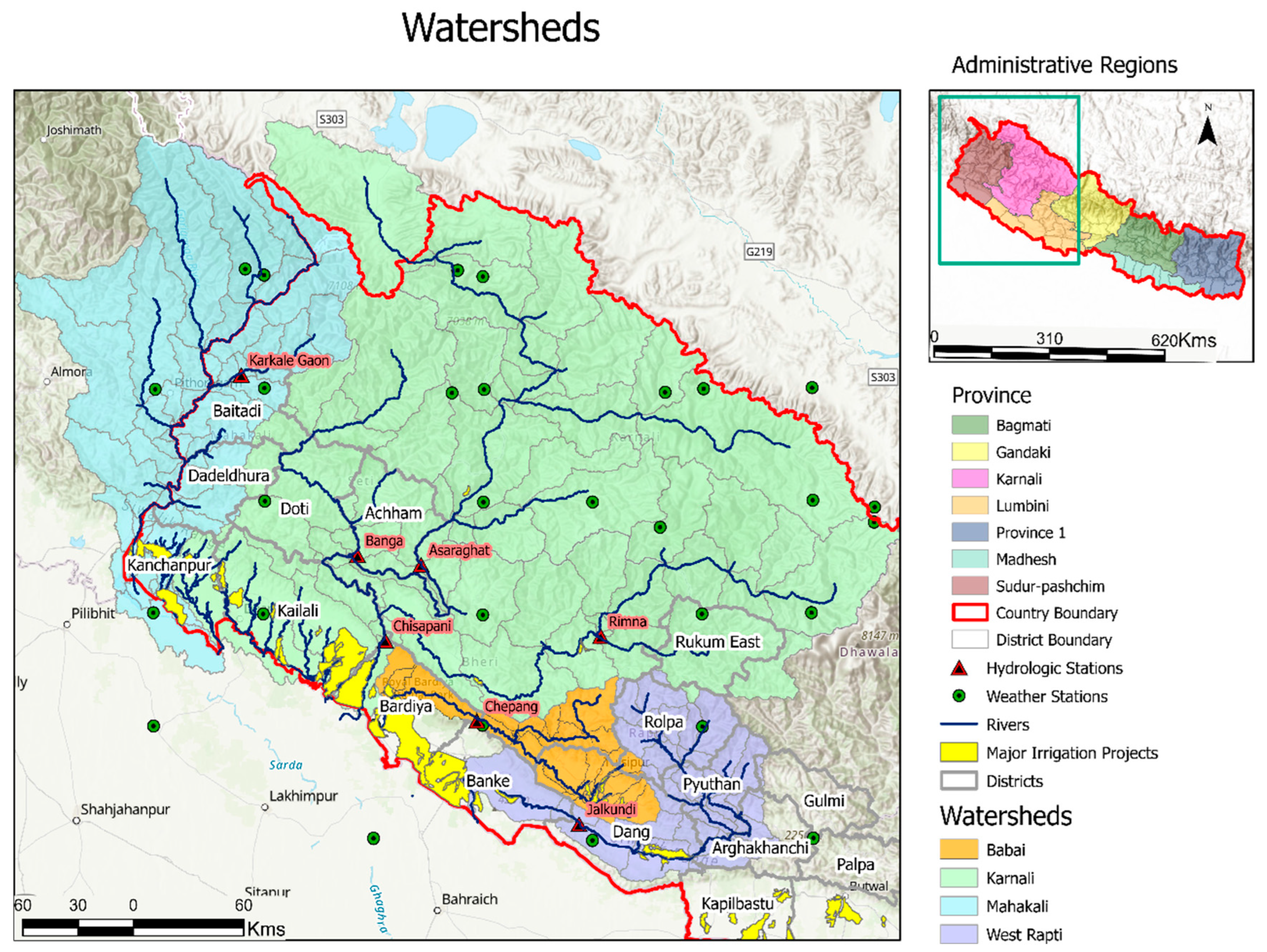
2.1. Study Area
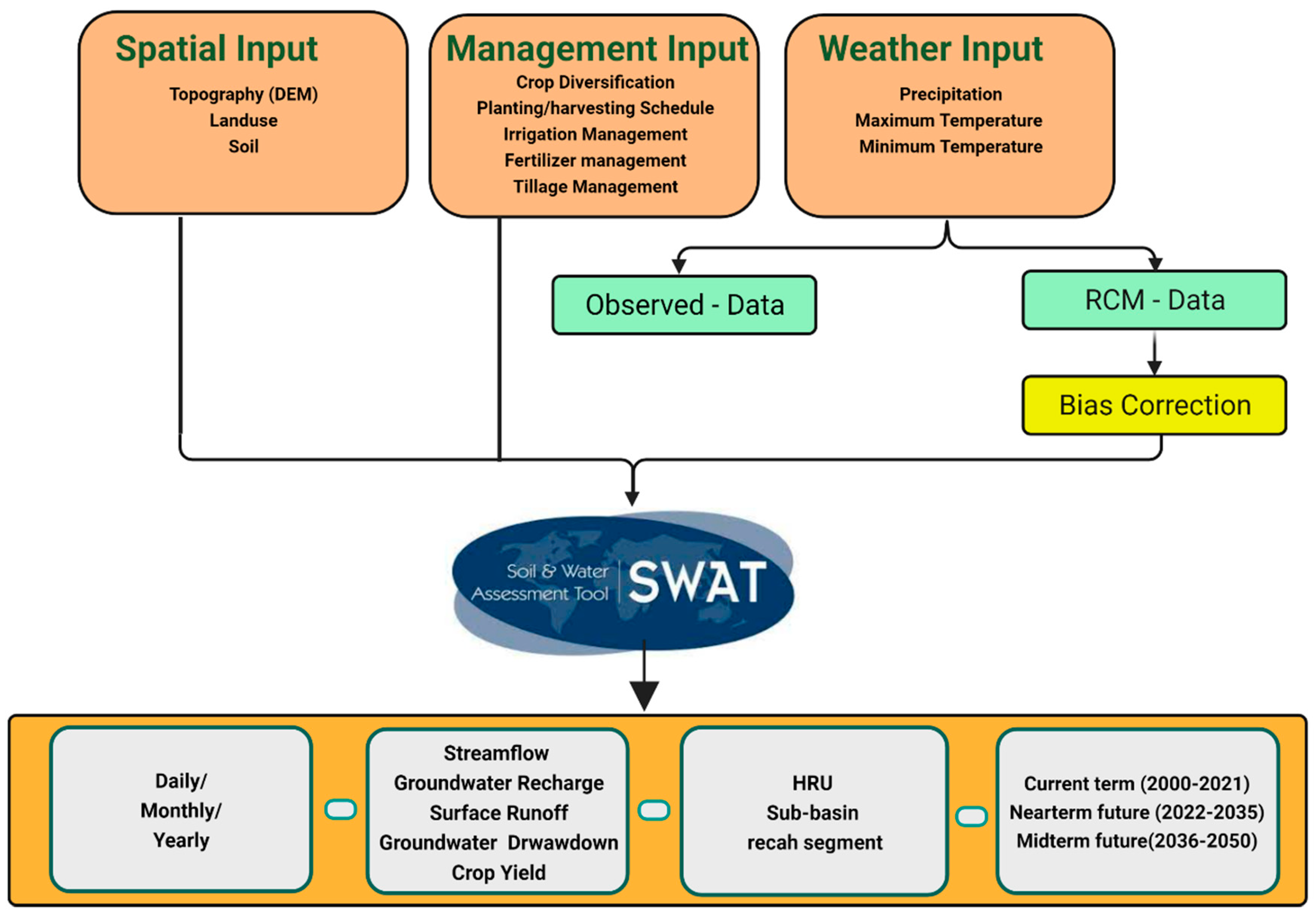
2.2. Hydrological Model and Data
2.3. Climate Model
2.4. Modelling Scenarios
3. Results and Discussion
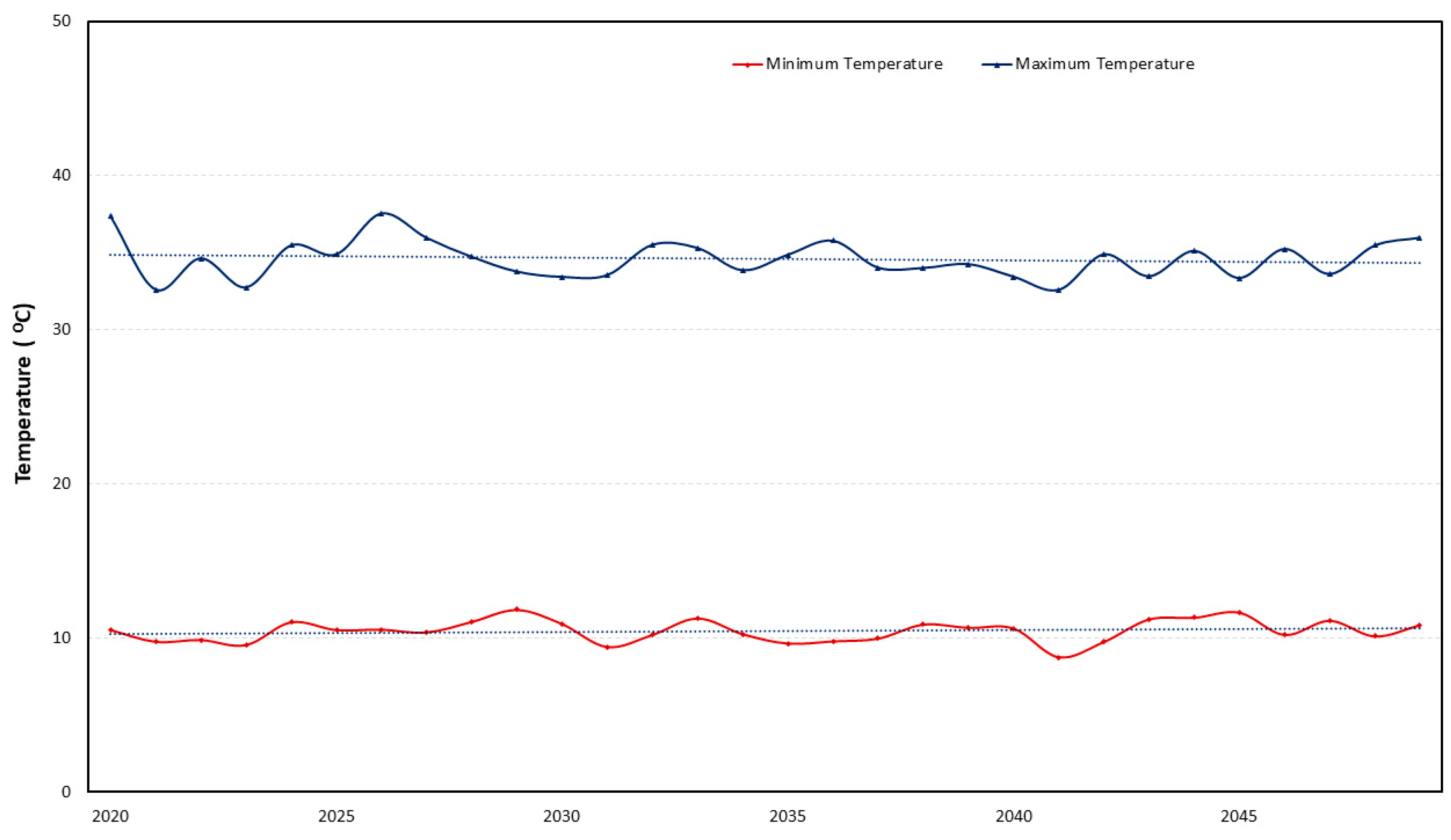
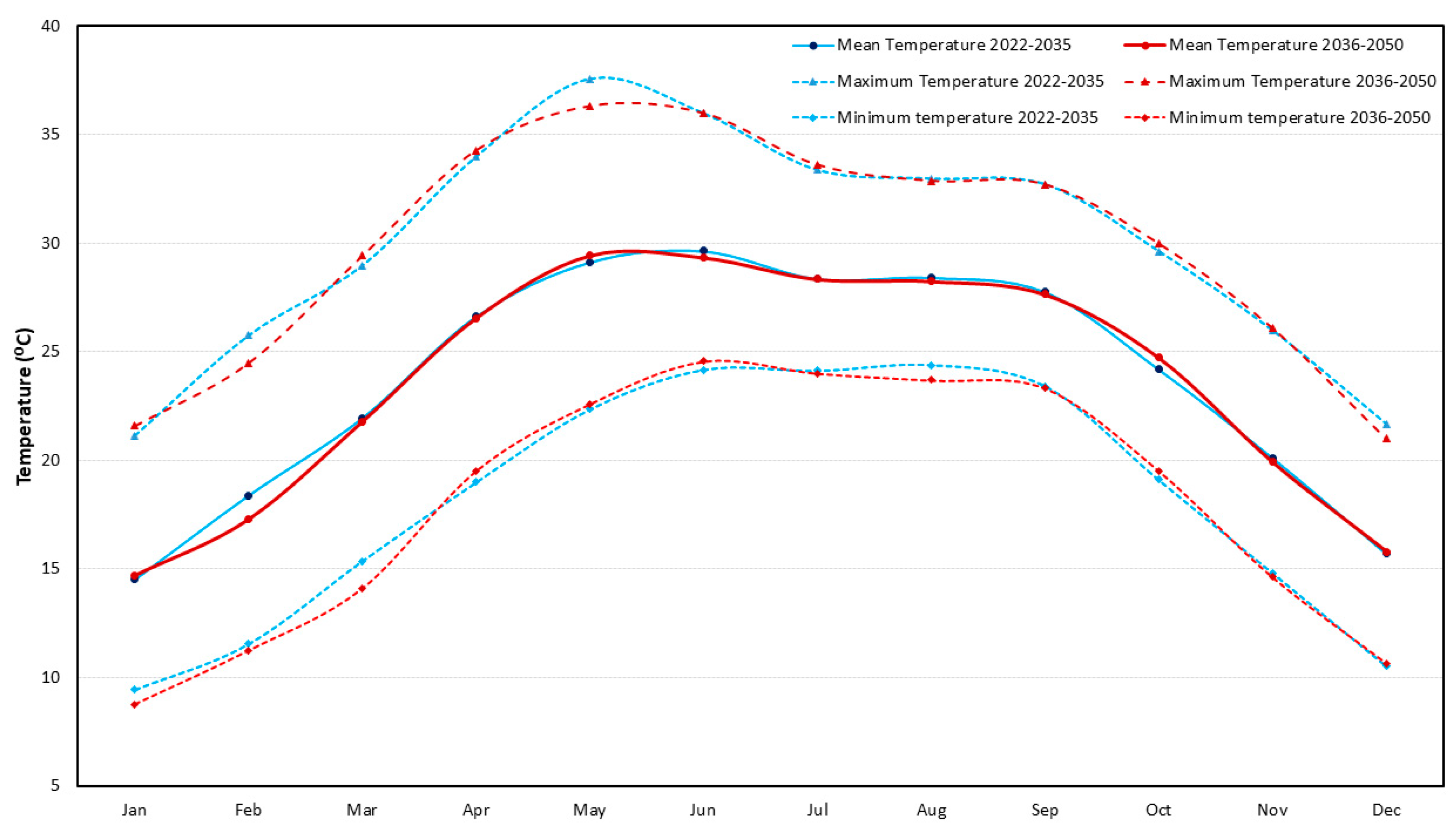
3.1. Projected Change in Average Precipitation and Temperature
3.2. Impact of Climate Change on River and Streamflow
3.3. Impact of Climate Change and Scenarios Implemented at Upstream Subbasins
3.4. Impact on Groundwater Recharge and Groundwater Sustainability
3.5. Impacts on Groundwater Reserves
3.6. Impact on Crop Yields
3.7. Impact on Rice Equivalent Yield
4. Study Assumptions and Limitations
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urfels, A.; Khadka, M.; Shrestha, N.; Pavelic, P.; Risal, A.; Uprety, L.; Shrestha, G.; Dile, Y.; McDonald, A.J.; Pandey, V.P.; et al. A Framework for Sustainable and Inclusive Irrigation Development in Western Nepal; The Cereal Systems Initiative for South Asia (CSISA): Kathmandu, Nepal, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Urfels, A.; McDonald, A.J.; Krupnik, T.J.; van Oel, P.R. Drivers of Groundwater Utilization in Water-Limited Rice Production Systems in Nepal. Water Int. 2020, 45, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- IMP. Irrigation Master Plan Preparation through Integrated River Basin Planning, 2019; Water Resources Project Preparatory Facility Department of Irrigation Ministry of Irrigation Nepal: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nepal, S.; Neupane, N.; Belbase, D.; Pandey, V.P.; Mukherji, A. Achieving Water Security in Nepal through Unravelling the Water-Energy-Agriculture Nexus. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2021, 37, 67–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, X.; Zhang, J.; Bao, Z.; Liu, C.; Jin, J.; Wang, G. Past Variations and Future Projection of Runoff in Typical Basins in 10 Water Zones, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teklay, A.; Dile, Y.T.; Asfaw, D.H.; Bayabil, H.K.; Sisay, K.; Ayalew, A. Modeling the Impact of Climate Change on Hydrological Responses in the Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2022, 97, 101278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Yang, Q.-L.; Bao, Z.-X.; Guan, X.-X.; Guan, T.-S.; Chen, X.; Wang, G.-Q. Impact of Environmental Change on Runoff in a Transitional Basin: Tao River Basin from the Tibetan Plateau to the Loess Plateau, China. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2019, 10, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, P.B.; Risal, A. Evaluation of Climate Change on Streamflow, Sediment, and Nutrient Load at Watershed Scale. Climate 2021, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H.; Nie, N. Climate Change and Anthropogenic Impacts on Wetland and Agriculture in the Songnen and Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–151. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, J.; Daoud, M.; Oates, N.; Few, R.; Conway, D.; Mtisi, S.; Matheson, S. Social Vulnerability in Three High-Poverty Climate Change Hot Spots: What Does the Climate Change Literature Tell Us? Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 15, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, A.B.; Aryal, R. Climate Change in Nepal and Its Impact on Himalayan Glaciers. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.P.; Nepal, N. An Assessment by Subsistence Farmers of the Risks to Food Security Attributable to Climate Change in Makwanpur, Nepal. Food Secur. 2016, 8, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, J.; Pricope, N.G. High-Resolution Spatial Assessment of Population Vulnerability to Climate Change in Nepal. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 82, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, Y.; Babel, M.S.; Nakamura, T.; Mishra, B. Impacts of Climate Change on Irrigation Water Management in the Babai River Basin, Nepal. Hydrology 2021, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, C.K.B.; Lall, U.; Kwon, H.-H. Changing Frequency and Intensity of Rainfall Extremes over India from 1951 to 2003. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 4737–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Babel, M.S.; Ninsawat, S.; Ochi, S. Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources of the Bheri River Basin, Nepal. Water 2018, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babel, M.S.; Bhusal, S.P.; Wahid, S.M.; Agarwal, A. Climate Change and Water Resources in the Bagmati River Basin, Nepal. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, D.K.; Dulal, K. Determination of Threshold Runoff for Flood Early Warning in Nepalese Rivers. IDRiM J. 2013, 3, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castillo, C.; Robines, L.; Poudel, A.; MacNair, K.L.; Gajewski, C. Impact of Climate Change on Forests and Biodiversity and Current Adaptation Practices-A Case Study of Nepal. Samriddhi J. Dev. Stud. 2014, 7, 5–12. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/288357872_Impact_of_Climate_Change_on_Forests_and_Biodiversity_and_Current_Adaptation_Practices_-_A_Case_Study_of_Nepal (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Ratha, D.K.; De, S.; Schuettler, K.; Seshan, G.K.; Yameogo, N.D. Migration and Remittances: Recent Developments and Outlook-Transit Migration; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Poudel, S.; Shaw, R. The Relationships between Climate Variability and Crop Yield in a Mountainous Environment: A Case Study in Lamjung District, Nepal. Climate 2016, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheikh, M.M.; Manzoor, N.; Ashraf, J.; Adnan, M.; Collins, D.; Hameed, S.; Manton, M.J.; Ahmed, A.U.; Baidya, S.K.; Borgaonkar, H.P. Trends in Extreme Daily Rainfall and Temperature Indices over South Asia. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmann, R.; Jagadish, S.V.K.; Sumfleth, K.; Pathak, H.; Howell, G.; Ismail, A.; Serraj, R.; Redona, E.; Singh, R.K.; Heuer, S. Regional Vulnerability of Climate Change Impacts on Asian Rice Production and Scope for Adaptation. Adv. Agron. 2009, 102, 91–133. [Google Scholar]
- Poudel, S.; Shaw, R. Demographic Changes, Economic Changes and Livelihood Changes in the HKH Region. In Mountain Hazards and Disaster Risk Reduction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 105–123. [Google Scholar]
- Poudel, A. Migration, Youth Workshops and Forestry: Case Studies from Nepal. Trees For. People 2021, 3, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, A.; Kennedy, J.; Basnet, S.M.S.; Pokhrel, P. Federalism and Environment in Nepal: Issues and Challenges. J. Dev. Stud. 2019, 5, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Karki, R.; Talchabhadel, R.; Aalto, J.; Baidya, S.K. New Climatic Classification of Nepal. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 125, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.B.; Wake, C.P.; Mayewski, P.A.; Dibb, J.E. Precipitation Fluctuations in the Himalaya and Its Vicinity: An Analysis Based on Temperature Records from Nepal. Int. J. Clim. 2000, 20, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, S.A.; Jeelani, G.; Deshpande, R.D.; Mukherjee, A.; Jasechko, S.; Lone, A. Meltwaters Dominate Groundwater Recharge in Cold Arid Desert of Upper Indus River Basin (UIRB), Western Himalayas. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, G.; Deshpande, R.D.; Shah, R.A.; Hassan, W. Influence of Southwest Monsoons in the Kashmir Valley, Western Himalayas. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2017, 53, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapri, K.; Ghimire, S. Migration, Remittance, and Agricultural Productivity: Evidence from the Nepal Living Standard Survey. World Dev. Perspect. 2020, 19, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.R.; Tripathi, G.N.; Laudari, D. Groundwater Resources of Nepal: An Overview. Groundw. South Asia. 2018, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, A. Water Security in Nepal—Analysis of Groundwater Resource and Governance. In WaterAid Multi-Country Research on Water Security: HSBC Water Program; Global Synthesis Report; WaterAid: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, P.; Neilson, R.P.; Lenihan, J.M.; Drapek, R.J. Global Patterns in the Vulnerability of Ecosystems to Vegetation Shifts Due to Climate Change. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flato, G.; Marotzke, J.; Abiodun, B.; Braconnot, P.; Chou, S.C.; Collins, W.; Cox, P.; Driouech, F.; Emori, S.; Eyring, V. Evaluation of Climate Models. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 741–866. [Google Scholar]
- Emami, F.; Koch, M. Sustainability Assessment of the Water Management System for the Boukan Dam, Iran, Using CORDEX-South Asia Climate Projections. Water 2018, 10, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, V.P.; Shrestha, D.; Adhikari, M. Characterizing Natural Drivers of Water-Induced Disasters in a Rain-Fed Watershed: Hydro-Climatic Extremes in the Extended East Rapti Watershed, Nepal. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaubanjar, S.; Prasad Pandey, V.; Bharati, L. Climate Futures for Western Nepal Based on Regional Climate Models in the CORDEX-SA. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 2201–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.P.; Dhaubanjar, S.; Bharati, L.; Thapa, B.R. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Water Availability in Karnali-Mohana Basin, Western Nepal: Hydrological Model Development Using Multi-Site Calibration Approach (Part-A). J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 29, 100690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Johnston, C.A. Hydrologic Response to Climatic Variability in a Great Lakes Watershed: A Case Study with the SWAT Model. J. Hydrol. 2007, 337, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Shrestha, M.; Shrestha, P.K. Evaluation of the SWAT Model Performance for Simulating River Discharge in the Himalayan and Tropical Basins of Asia. Hydrol. Res. 2018, 49, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahal, V.; Shakya, N.M.; Bhattarai, R. Estimating the Impact of Climate Change on Water Availability in Bagmati Basin, Nepal. Environ. Process. 2016, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, L.P.; Gyawali, D.R. Impacts of Climate Change on Hydrological Regime and Water Resources Management of the Koshi River Basin, Nepal. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 4, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahal, P.; Shrestha, M.L.; Panthi, J.; Pradhananga, D. Modeling the Future Impacts of Climate Change on Water Availability in the Karnali River Basin of Nepal Himalaya. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, B.; Shrestha, S.; Shrestha, P.K.; Talchabhadel, R. Evaluation and Application of a SWAT Model to Assess the Climate Change Impact on the Hydrology of the Himalayan River Basin. Catena 2019, 181, 104082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhathoki, A.; Babel, M.S.; Shrestha, S.; Meon, G.; Kamalamma, A.G. Climate Change Impact on Water Balance and Hydrological Extremes in Different Physiographic Regions of the West Seti River Basin, Nepal. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2021, 21, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute: College Station, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gashaw, T.; Dile, Y.T.; Worqlul, A.W.; Bantider, A.; Zeleke, G.; Bewket, W.; Alamirew, T. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Best Management Practices on Soil Erosion Reduction Using the SWAT Model: For the Case of Gumara Watershed, Abbay (Upper Blue Nile) Basin. Environ. Manag. 2021, 68, 240–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharjan, G.R.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, N.W.; Shin, D.S.; Choi, J.W.; Hyun, G.W.; Jeon, J.-H.; Ok, Y.S.; Lim, K.J. Evaluation of SWAT Sub-Daily Runoff Estimation at Small Agricultural Watershed in Korea. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Yuan, Y.; Kepner, W.; Nash, M.S.; Jackson, M.; Erickson, C. Assessing Impacts of Landuse and Landcover Changes on Hydrology for the Upper San Pedro Watershed. J. Hydrol. 2011, 407, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risal, A.; Parajuli, P.B.; Ouyang, Y. Impact of BMPs on Water Quality: A Case Study in Big Sunflower River Watershed, Mississippi. Int. J. River Basin Management. 2021, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. United States Geological Survey, Global Visualization (GLOVIS) Portal. Available online: http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 7 February 2021).
- CIMMYT. International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT). Available online: https://www.cimmyt.org/resources/data/ (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- ICIMOD. Land Cover of Nepal. 2010. Available online: http://rds.icimod.org/Home/DataDetail?metadataId=9224 (accessed on 20 June 2021).
- ISRIC. International Soil Reference and Information Centre (ISRIC) Soil Data Hub. Available online: https://www.isric.org/explore/isric-soil-data-hub (accessed on 18 June 2021).
- DHM. Department of Hydrology and Meteorology, Kathmandu Nepal. Available online: https://www.dhm.gov.np/ (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Michaelsen, J. The Climate Hazards Infrared Precipitation with Stations—A New Environmental Record for Monitoring Extremes. Sci Data. 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ESGF. The Earth System Grid Federation. Available online: https://esgf-node.llnl.gov/search/esgf-llnl/ (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Van Vuuren, D.P.; Edmonds, J.; Kainuma, M.; Riahi, K.; Thomson, A.; Hibbard, K.; Hurtt, G.C.; Kram, T.; Krey, V.; Lamarque, J.-F. The Representative Concentration Pathways: An Overview. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathjens, H.; Bieger, K.; Srinivasan, R.; Chaubey, I.; Arnold, J.G. CMhyd User Manual. Documentation for Preparing Simulated Climate Change Data for Hydrologic Impact Studies. 2016. Available online: https://swat.tamu.edu/media/115265/bias_cor_man.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2021).
- Wang, X.; Folberth, C.; Skalsky, R.; Wang, S.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Balkovic, J. Crop Calendar Optimization for Climate Change Adaptation in Rice-Based Multiple Cropping Systems of India and Bangladesh. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 315, 108830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, B.; Gautam, P.; Panda, B.B.; Raja, R.; Singh, T.; Tripathi, R.; Shahid, M.; Nayak, A.K. Crop and Varietal Diversification of Rainfed Rice Based Cropping Systems for Higher Productivity and Profitability in Eastern India. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175709. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.; Min, S.-K.; Lee, D.; Cha, D.-H.; Suh, M.-S.; Kang, H.-S.; Hong, S.-Y.; Lee, D.-K.; Baek, H.-J.; Boo, K.-O.; et al. Evaluation of Multiple Regional Climate Models for Summer Climate Extremes over East Asia. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 2469–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legg, S. IPCC, 2021: Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science basis. Interaction 2021, 49, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjay, J.; Krishnan, R.; Shrestha, A.B.; Rajbhandari, R.; Ren, G.Y. Downscaled climate change projections for the Hindu Kush Himalayan region using CORDEX South Asia regional climate models. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2017, 8, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Han, D.; Wang, L.; Jin, Z.F. Changes in Photosynthetic Parameters and Antioxidant Enzymatic Activity of Four Tea Varieties during a Cold Wave. Acta Ecol. Sin 2016, 36, 629–641. [Google Scholar]


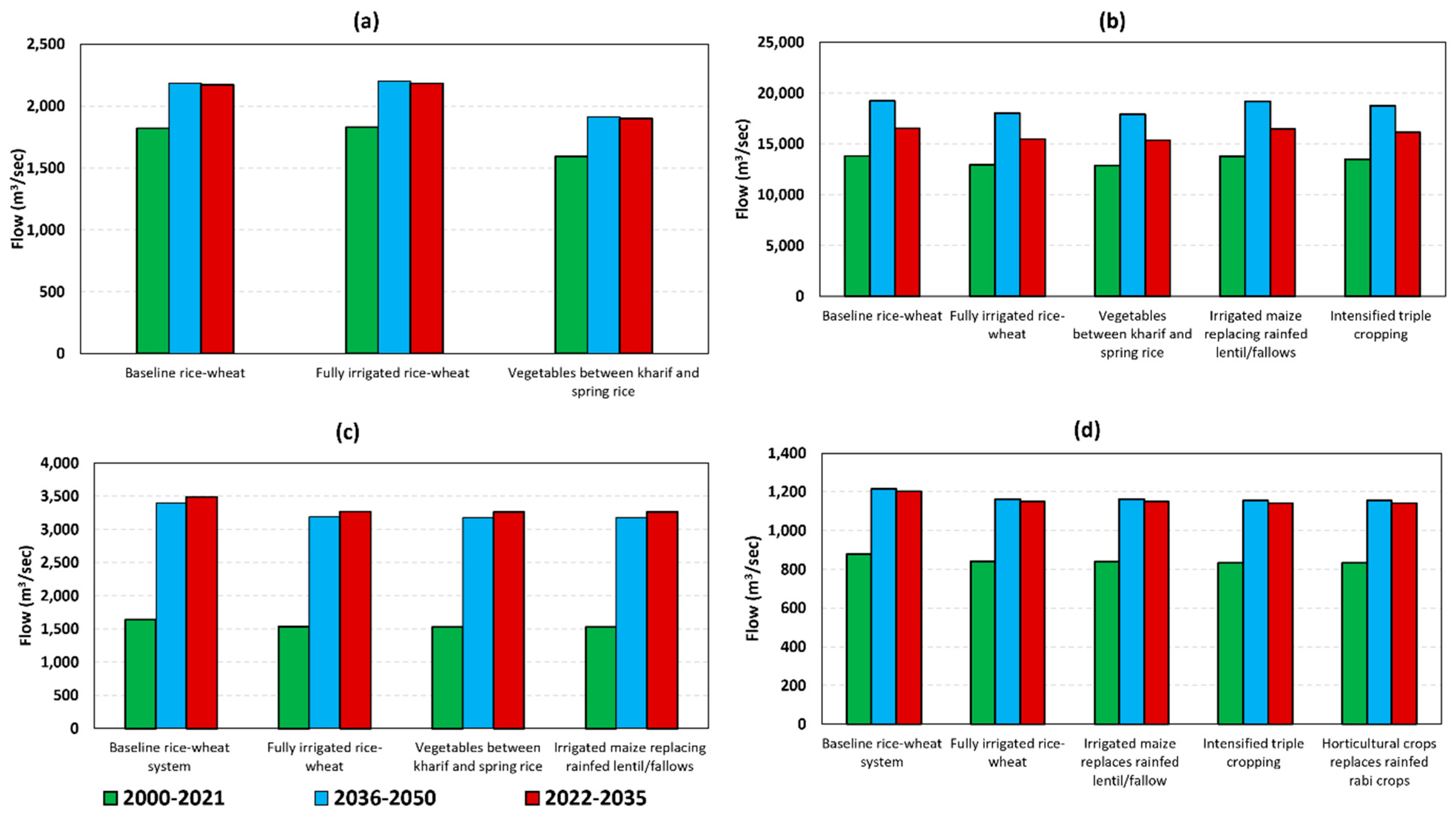
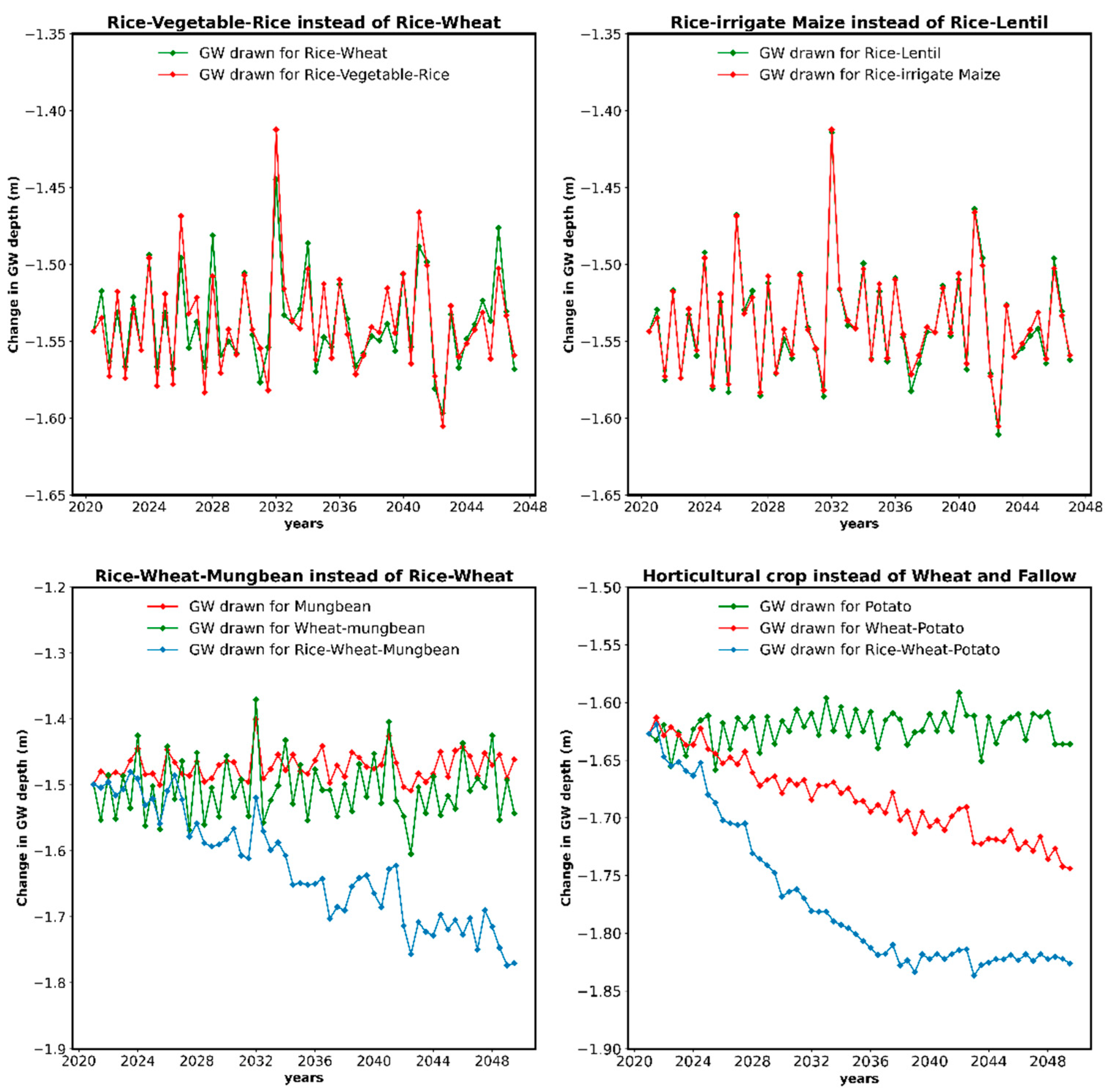
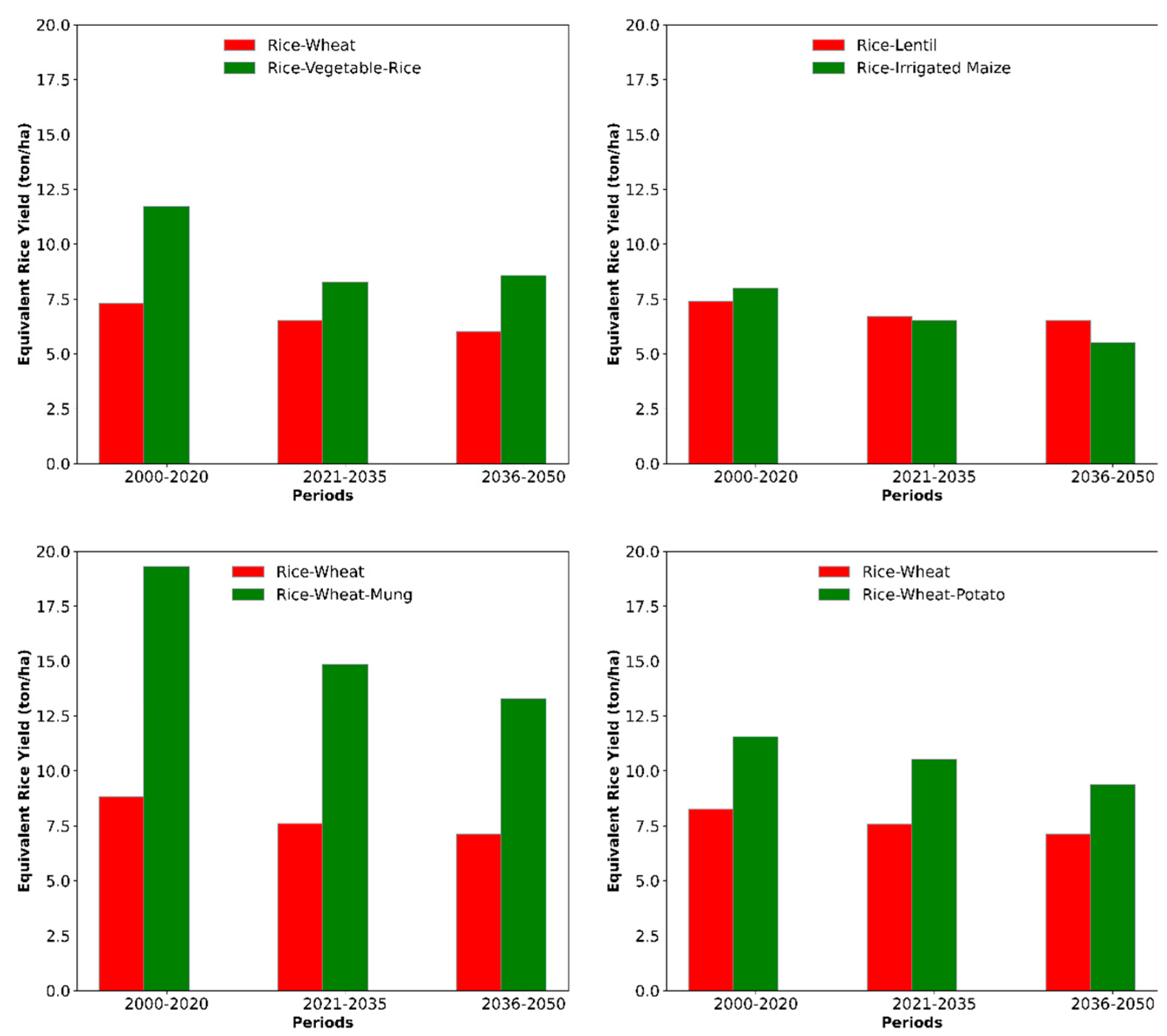
| Watershed | Time Period | Rice–Wheat (%) | Rice–Vegetable–Rice (%) | Rice–Rainfed Lentil (%) | Rice–Irrigated Maize (%) | Rice–Wheat–Mung (%) | Rice–Potato (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mahakali | 2000–2020 | 92 | 69 | — | — | — | — |
| 2021–2035 | 89 | 72 | — | — | — | — | |
| 2035–2050 | 96 | 73 | — | — | — | — | |
| Karnali | 2000–2020 | 39 | 45 | 63 | 31 | 27 | — |
| 2021–2035 | 44 | 61 | 93 | 35 | 42 | — | |
| 2035–2050 | 36 | 47 | 76 | 40 | 39 | — | |
| Babai | 2000–2020 | 64 | 48 | 139 | 61 | — | — |
| 2021–2035 | 64 | 51 | 195 | 81 | — | — | |
| 2035–2050 | 62 | 52 | 183 | 77 | — | — | |
| West Rapti | 2000–2020 | 35 | — | 59 | 31 | 36 | 33 |
| 2021–2035 | 53 | — | 90 | 49 | 44 | 43 | |
| 2035–2050 | 55 | — | 92 | 49 | 44 | 46 |
| Rice–Wheat | Rice–Tomato–Rice | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Rice Yield (t/ha) | Wheat Yield (t/ha) | Rice Yield (t/ha) | Tomato Yield (t/ha) | Spring Rice Yield (t/ha) |
| 2000–20 | 4.2 | 2.8 | 4.2 | 1.3 | 5.3 |
| 2021–35 | 3.7 | 2.5 | 3.7 | 0.7 | 3.4 |
| 2035–50 | 3.7 | 2 | 3.8 | 0.6 | 3.7 |
| Rice–Lentil | Rice–Maize | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Rice Yield (t/ha) | Lentil Yield (t/ha) | Rice Yield (t/ha) | Maize Yield (t/ha) |
| 2000–20 | 4.0 | 1.3 | 4.0 | 3.9 |
| 2021–35 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 2.9 | 3.5 |
| 2035–50 | 3.1 | 1.3 | 3.1 | 2.4 |
| Rice–Wheat | Rice–Wheat–Mungbean | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Rice Yield (t/ha) | Wheat Yield (t/ha) | Rice Yield (t/ha) | Wheat Yield (t/ha) | Mungbean Yield (t/ha) |
| 2000–20 | 4.0 | 4.3 | 4.0 | 4.7 | 2.9 |
| 2021–35 | 3.0 | 4.1 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 2 |
| 2035–50 | 3.1 | 3.6 | 3.1 | 2.1 | 1.7 |
| Rice–Wheat | Rice–Potato | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Rice Yield (t/ha) | Wheat Yield (t/ha) | Rice Yield (t/ha) | Potato Yield (t/ha) |
| 2000–20 | 2.5 | 3.3 | 3.4 | 3.2 |
| 2021–35 | 2.1 | 3 | 3 | 2.9 |
| 2035–50 | 2.2 | 3 | 3 | 2.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Risal, A.; Urfels, A.; Srinivasan, R.; Bayissa, Y.; Shrestha, N.; Paudel, G.P.; Krupnik, T.J. Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources and Crop Production in Western Nepal: Implications and Adaptation Strategies. Hydrology 2022, 9, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9080132
Risal A, Urfels A, Srinivasan R, Bayissa Y, Shrestha N, Paudel GP, Krupnik TJ. Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources and Crop Production in Western Nepal: Implications and Adaptation Strategies. Hydrology. 2022; 9(8):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9080132
Chicago/Turabian StyleRisal, Avay, Anton Urfels, Raghavan Srinivasan, Yared Bayissa, Nirman Shrestha, Gokul P. Paudel, and Timothy J. Krupnik. 2022. "Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources and Crop Production in Western Nepal: Implications and Adaptation Strategies" Hydrology 9, no. 8: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9080132
APA StyleRisal, A., Urfels, A., Srinivasan, R., Bayissa, Y., Shrestha, N., Paudel, G. P., & Krupnik, T. J. (2022). Impact of Climate Change on Water Resources and Crop Production in Western Nepal: Implications and Adaptation Strategies. Hydrology, 9(8), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology9080132








