The Effectiveness of an Artificial Floating Wetland to Remove Nutrients in an Urban Stream: A Pilot-Study in the Chicago River, Chicago, IL USA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Location
2.2. Water Chemistry
3. Results
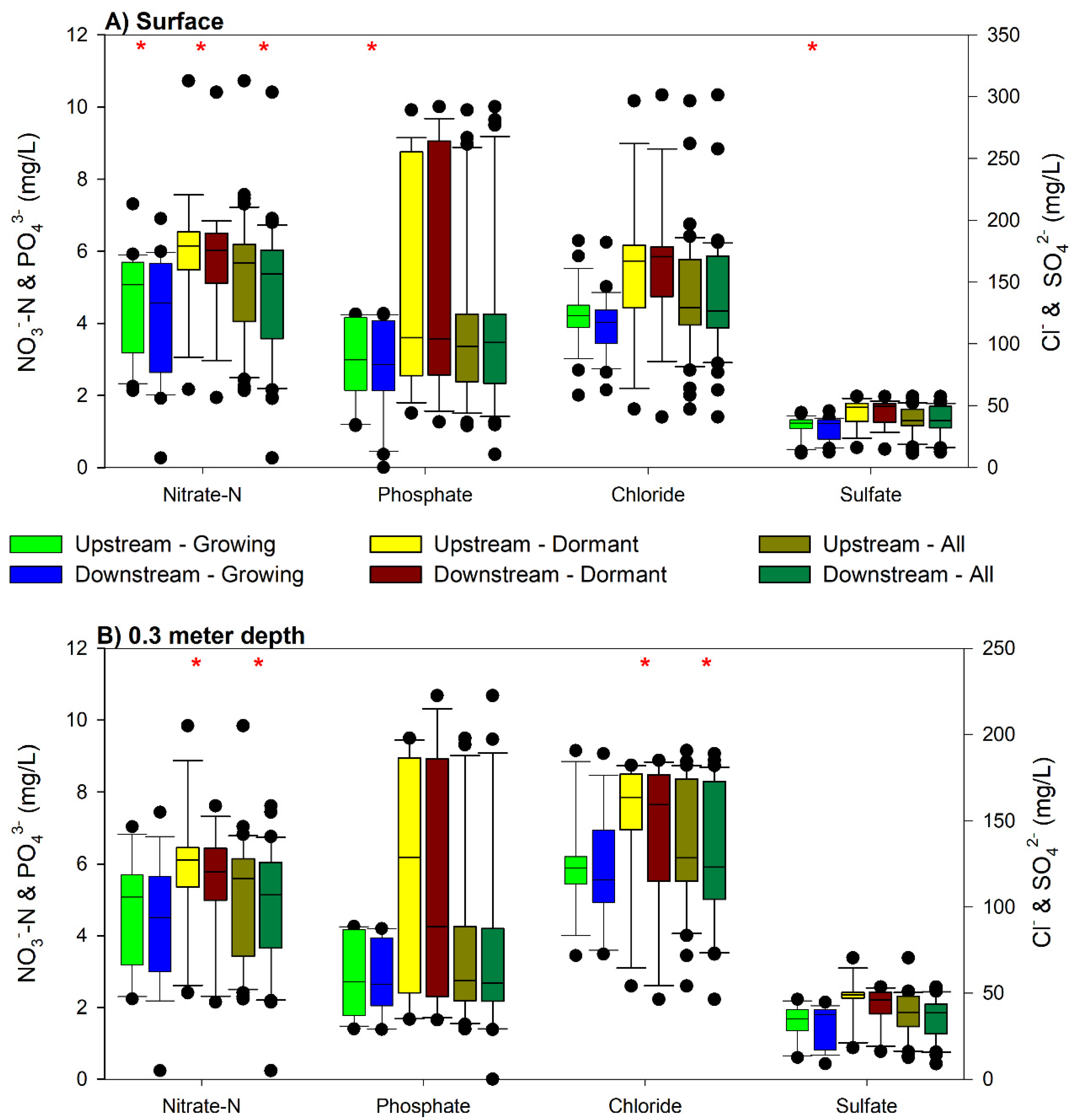
3.1. Nutrients
3.2. Chloride
3.3. Heavy Metals
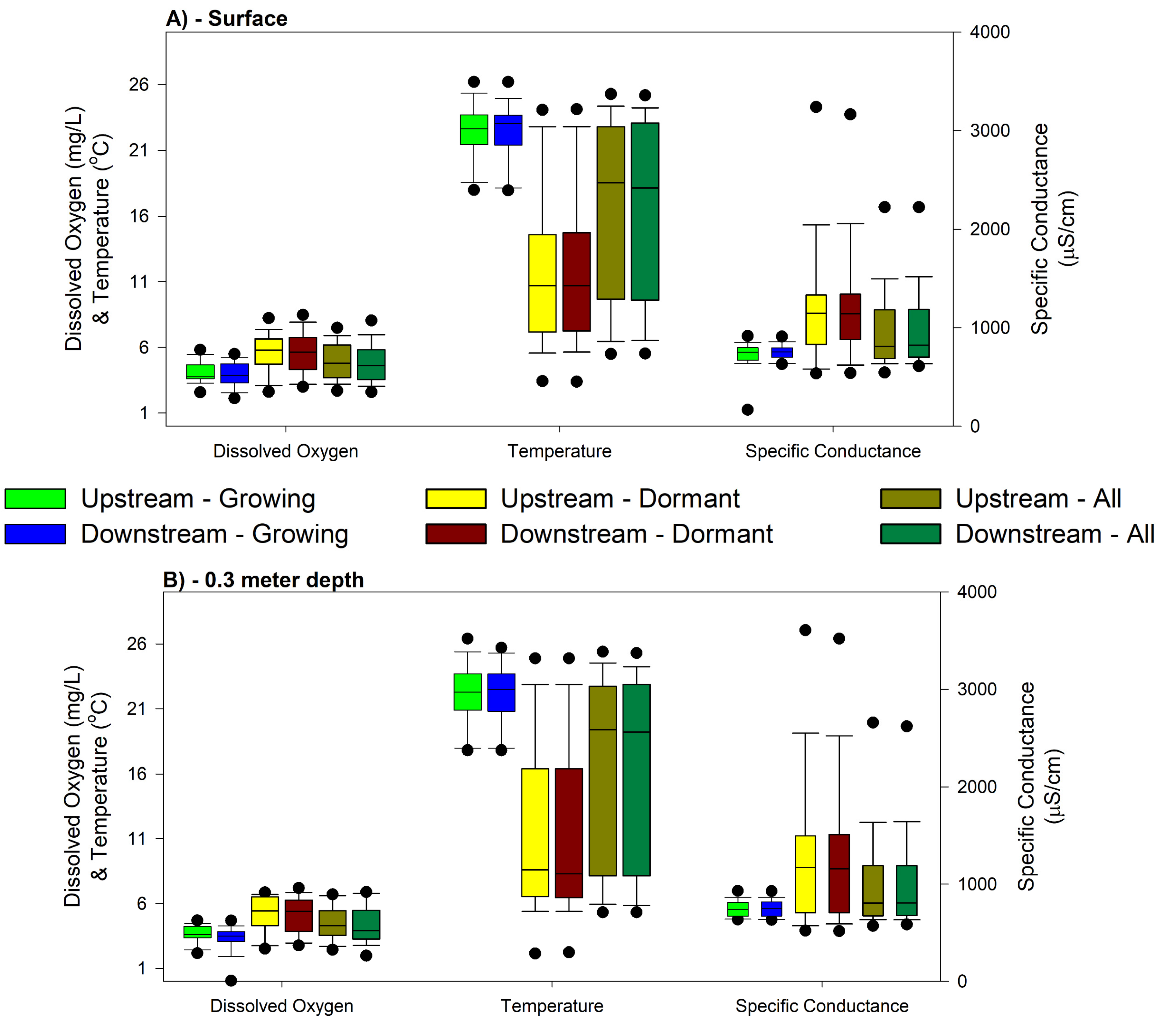
3.4. Dissolved Oxygen
3.5. Temperature
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walsh, C.J.; Roy, A.H.; Feminella, J.W.; Cottingham, P.D.; Groffman, P.M.; Morgan, R.P. The urban stream syndrome: Current knowledge and the search for a cure. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 706–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisi, P.J.; Childress, E.S.; Gagne, R.B.; Hain, E.F.; Lamphere, B.A.; Walter, R.P.; Hogan, J.D.; Gilliam, J.F.; Blum, M.J.; McIntyre, P.B. Overcoming urban stream syndrome: Trophic flexibility confers resilience in a Hawaiian stream fish. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 63, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.L.; Paul, M.J.; Taulbee, W.K. Stream ecosystem function in urbanizing landscapes. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, I.A.; Davies, P.J.; Findlay, S.J.; Jonasson, O.J. A new type of water pollution: Concrete drainage infrastructure and geochemical contamination of urban waters. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, S.J.; Roy, A.H.; Jackson, C.R.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Carter, T.L.; Filoso, S.; Gibson, C.A.; Hession, W.C.; Kaushal, S.S.; Martí, E.; et al. Twenty-six key research questions in urban stream ecology: An assessment of the state of the science. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2009, 28, 1080–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halstead, J.A.; Kliman, S.; Berheide, C.W.; Chaucer, A.; Cock-Esteb, A. Urban stream syndrome in a small, lightly developed watershed: A statistical analysis of water chemistry parameters, land use patterns, and natural sources. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 3391–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somers, K.A.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Grace, J.B.; Hassett, B.A.; Sudduth, E.B.; Wang, S.Y.; Urban, D.L. Streams in the urban heat island: Spatial and temporal variability in temperature. Freshw. Sci. 2013, 32, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, W.; Zhang, Y. Removal of nitrogen (N) from hypereutrophic waters by ecological floating beds (EFBs) with various substrates. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 62, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.O.; Hochmuth, G.J.; Martinez, C.J.; Boyer, T.H.; Dukes, M.D.; Toor, G.S.; Cisar, J.L. Evaluating nutrient impacts in urban watersheds: Challenges and research opportunities. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Andrieu, H.; Hamel, P. Understanding, management and modelling of urban hydrology and its consequences for receiving waters: A state of the art. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.X.; Bowling, L.C.; Cherkauer, K.A.; Pijanowski, B.C. The impact of urban development on hydrologic regime from catchment to basin scales. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 103, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Groffman, P.M.; Likens, G.E.; Belt, K.T.; Stack, W.P.; Kelly, V.R.; Band, L.E.; Fisher, G.T. Increased salinization of fresh water in the northeastern United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13517–13520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lax, S.M.; Peterson, E.W.; Van der Hoven, S.J. Stream chloride concentrations as a function of land use: A comparison of an agricultural watershed to an urban agricultural watershed. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, W.R. Long-term trends in chloride concentrations in shallow aquifers near Chicago. Ground Water 2008, 46, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, M.; Clinton, S.; Jefferson, A.; Manda, A.; McMillan, S. Urbanization Effects on Watershed Hydrology and In-Stream Processes in the Southern United States. Water 2010, 2, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.E.; Streeter, M.T.; Seeman, A.; Jones, C.S.; Wolter, C.F. Total phosphorus export from Iowa agricultural watersheds: Quantifying the scope and scale of a regional condition. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierp, M.T.; Qin, J.G.; Recknagel, F. Biomanipulation: A review of biological control measures in eutrophic waters and the potential for Murray cod Maccullochella peelii peelii to promote water quality in temperate Australia. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2009, 19, 143–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Sondergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Liu, Z.W. Nitrogen, macrophytes, shallow lakes and nutrient limitation: Resolution of a current controversy? Hydrobiologia 2013, 710, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.B.; Miller, C.; Arhonditsis, G.; Boyer, G.L.; Carmichael, W.; Charlton, M.N.; Confesor, R.; Depew, D.C.; Hook, T.O.; Ludsin, S.A.; et al. The re-eutrophication of Lake Erie: Harmful algal blooms and hypoxia. Harmful Algae 2016, 56, 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macintosh, K.A.; Mayer, B.K.; McDowell, R.W.; Powers, S.M.; Baker, L.A.; Boyer, T.H.; Rittmann, B.E. Managing Diffuse Phosphorus at the Source versus at the Sink. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11995–12009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thin, M.M.; Sacchi, E.; Setti, M.; Re, V. A Dual Source of Phosphorus to Lake Sediments Indicated by Distribution, Content, and Speciation: Inle Lake (Southern Shan State, Myanmar). Water 2020, 12, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, S.R.; Graczyk, D.J.; Geis, S.W.; Booth, N.L.; Richards, K.D. A Fresh Look at Road Salt: Aquatic Toxicity and Water-Quality Impacts on Local, Regional, and National Scales. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7376–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Rahman, M.S.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Industrial metal pollution in water and probabilistic assessment of human health risk. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 185, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobielska, P.A.; Howarth, A.J.; Farha, O.K.; Nayak, S. Metal-organic frameworks for heavy metal removal from water. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 358, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavcar, P.; Sofuoglu, A.; Sofuoglu, S.C. A health risk assessment for exposure to trace metals via drinking water ingestion pathway. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2009, 212, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, N.; Zaman, M. Evaluation of possible health risks of heavy metals by consumption of foodstuffs available in the central market of Rajshahi City, Bangladesh. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 3867–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armendáriz, C.R.; Garcia, T.; Soler, A.; Fernández, Á.J.G.; Glez-Weller, D.; González, G.L.; de la Torre, A.H.; Gironés, C.R. Heavy metals in cigarettes for sale in Spain. Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illinois Environmental Protection Agency. Illinois Integrated Water Quality Report and Section 303(d) List; Illinois Environmental Protection Agency: Springfield, IL, USA, 2018.
- Shore, D. From waste treatment to resource recovery: A Chicago sustainability story. MRS Energy Sustain. Rev. J. 2017, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hnatukova, P.; Benesova, L.; Kominkova, D. Impact of urban drainage on metal distribution in sediments of urban streams. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, R.S. Water Quality Trends of the Illinois Waterway System Upstream of Peoria Including the Chicago Metropolitan Area; Illinois State Water Survey: Champaign, IL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdi, N.; Elhadi, H.; Pagilla, K.R. Case study of the Chicago River Watershed: Physical modeling vs data-driven modeling of an urban watershed. J. Water Manag. Model. 2017, 26, C431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, W.; Panno, S.; Hackley, K. The Sources, Distribution, and Trends of Chloride in Waters of Illinois; Bulletin (Illinois State Water Survey) no. 74; Illinois State Water Survey: Champaign, IL, USA, 2012; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2142/90994 (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Friederici, P. Salt on earth. Chic. Wilderness Mag. 2004, 25–31. Available online: https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.chicagowilderness.org/resource/collection/0625B160-07C5-482A-8BDF-D86381B9FC77/2004-Winter.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Kelly, W.R.; Panno, S.V.; Hackley, K.C. Impacts of road salt on water resources in the Chicago region. In Proceedings of the 2009 UCOWR Conference; Southern Illinois University: Carbondale, IL, USA; Available online: https://opensiuc.lib.siu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1004&context=ucowrconfs_2009 (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Jackson, P.R.; García, C.M.; Oberg, K.A.; Johnson, K.K.; García, M.H. Density currents in the Chicago River: Characterization, effects on water quality, and potential sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 401, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Illinois Environmental Protection Agency. Illinois 2004 Section 303(d) List; Illinois Environmental Protection Agency: Springfield, IL, USA, 2004.
- Bradl, H.B. Heavy Metals in the Environment Preface. Interface Sci. Techno. 2005, 6, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy metals in contaminated soils: A review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2011, 2011, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trujillo-Gonzalez, J.M.; Torres-Mora, M.A.; Keesstra, S.; Brevik, E.C.; Jimenez-Ballesta, R. Heavy metal accumulation related to population density in road dust samples taken from urban sites under different land uses. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAndrew, B.; Ahn, C. Developing an ecosystem model of a floating wetland for water quality improvement on a stormwater pond. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-N.; Song, H.-L.; Li, W.; Lu, X.-W.; Nishimura, O. An integrated ecological floating-bed employing plant, freshwater clam and biofilm carrier for purification of eutrophic water. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, Z.; Ketola, T. Biomass accumulations and nutrient uptake of plants cultivated on artificial floating beds in China’s rural area. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.X.; Zhang, L.M.; Chua, H.; Li, X.D.; Xia, M.F.; Pu, P.M. A mosaic community of macrophytes for the ecological remediation of eutrophic shallow lakes. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henny, C.; Jasalesmana, T.; Kurniawan, R.; Melati, I.; Suryono, T.; Susanti, E.; Yoga, G.; Sudiono, B. The effectiveness of integrated floating treatment wetlands (FTWs) and lake fountain aeration systems (LFAS) in improving the landscape ecology and water quality of a eutrophic lake in Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 535, 012018. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/535/1/012018 (accessed on 1 April 2021). [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, G. Nutrient concentration variations during Oenanthe javanica growth and decay in the ecological floating bed system. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headley, T.R.; Tanner, C.C. Constructed Wetlands with Floating Emergent Macrophytes: An Innovative Stormwater Treatment Technology. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 2261–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlineri, N.; Skoulikidis, N.T.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Constructed Floating Wetlands: A review of research, design, operation and management aspects, and data meta-analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Sample, D.J. Assessment of the nutrient removal effectiveness of floating treatment wetlands applied to urban retention ponds. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 137, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wei, C.-Z.; Zhao, J.-C.; Sun, L.-Q. Effect of a strengthened ecological floating bed on the purification of urban landscape water supplied with reclaimed water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Jin, H. Nitrogen removal from polluted river by enhanced floating bed grown canna. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, K.; Kar, S.; Trivedi, S. Ecological floating bed (EFB) for decontamination of polluted water bodies: Design, mechanism and performance. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, R.; Zhou, C.; Jia, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, P.; Reichwaldt, E.S.; Liu, W. Giving waterbodies the treatment they need: A critical review of the application of constructed floating wetlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Wallace, S.D. Introduction to Treatment Wetlands, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; Volume 1, p. 1000. [Google Scholar]
- Osem, Y.; Chen, Y.; Levinson, D.; Hadar, Y. The effects of plant roots on microbial community structure in aerated wastewater-treatment reactors. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Li, S.; Peng, S.; Zhao, H. Microbial mechanisms of using enhanced ecological floating beds for eutrophic water improvement. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.J.; Hunt, W.F.; Kennedy, S.G.; Merriman, L.S.; Chandler, J.; Brown, D. Evaluation of floating treatment wetlands as retrofits to existing stormwater retention ponds. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 54, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borne, K.E.; Fassman-Beck, E.A.; Winston, R.J.; Hunt, W.F.; Tanner, C.C. Implementation and Maintenance of Floating Treatment Wetlands for Urban Stormwater Management. J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 141, 04015030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, Y.-J.; Yu, Z.-L.; Sheng, G.-P.; Yu, H.-Q. Enhanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal from eutrophic lake water by Ipomoea aquatica with low-energy ion implantation. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; He, Z.L.; Graetz, D.A.; Stoffella, P.J.; Yang, X.; Research, P. Phytoremediation to remove nutrients and improve eutrophic stormwaters using water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.; Peterson, E.W.; Budikova, D. Diurnal and seasonal variation in nitrate-nitrogen concentrations of groundwater in a saturated buffer zone. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 27, 1373–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Chai, X. Removal of water nutrients by different aquatic plant species: An alternative way to remediate polluted rural rivers. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 110, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautman, D.P.; Munch, D.J. Method 300.1: Determination of Inorganic Anions in Drinking Water by Ion Chromatography; US Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1997.
- Peterson, E.W.; Nicodemus, P.; Spooner, E.A. Supporting data—Floating Gardens, Chicago River, 29 April 2018 to 19 November 2019. In Faculty Publications—Geography, Geology, and the Environment. 2021, Volume 3. Available online: https://ir.library.illinoisstate.edu/fpgeo/3 (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. National Primary Drinking Water Regulations; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Komínková, D.; Nábělková, J.; Vitvar, T. Effects of combined sewer overflows and storm water drains on metal bioavailability in small urban streams (Prague metropolitan area, Czech Republic). J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 1569–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbarino, J.R.; Antweiler, R.C.; Brinton, T.; Roth, D.; Taylor, H.E. Concentration and transport data for selected dissolved inorganic constituents and dissolved organic carbon in water collected from the Mississippi River and some of its tributaries, July 1991–May 1992. US Geol. Surv. Open. File. Rep. 1995, 149, 95–149. [Google Scholar]
- Körner, S.; Vermaat, J.E. The relative importance of Lemna gibba L., bacteria and algae for the nitrogen and phosphorus removal in duckweed-covered domestic wastewater. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3651–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmo, O.R.; Van Der Steen, N.P.; Gijzen, H.J. Quantification of nitrification and denitrification rates in algae and duckweed based wastewater treatment systems. Environ. Technol. 2004, 25, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, P.B.; Nielsen, L.P.; Sorensen, J.; Revsbech, N.P. Denitrification in nitrate-rich streams: Diurnal and seasonal variation related to benthic oxygen metabolism. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, R.S.; Bartsch, L.A.; Richardson, W.B.; Strauss, E.A. The dark side of the hyporheic zone: Depth profiles of nitrogen and its processing in stream sediments. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 2021–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschall, N.; Boutin, C.; Crolla, A.; Kinsley, C.; Champagne, P. The role of plants in the removal of nutrients at a constructed wetland treating agricultural (dairy) wastewater, Ontario, Canada. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.M.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.Z.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xie, H.J.; Zhang, B. Nutrient removal in constructed microcosm wetlands for treating polluted river water in northern China. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, J.J.; Mayer, P.M.; Kaushal, S.S.; Pennino, M.J.; Arango, C.P.; Balz, D.A.; Canfield, T.J.; Elonen, C.M.; Fritz, K.M.; Hill, B.H.; et al. Effects of urban stream burial on organic matter dynamics and reach scale nitrate retention. Biogeochemistry 2014, 121, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groffman, P.M.; Gold, A.J.; Simmons, R.C. Nitrate dynamics in riparian forests: Microbial studies. J. Environ. Qual. 1992, 21, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simmons, R.C.; Gold, A.J.; Groffman, P.M. Nitrate Dynamics in Riparian Forests: Groundwater Studies. J. Environ. Qual. 1992, 21, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer, P.M.; Reynolds, S.K.; McCutchen, M.D.; Canfield, T.J. Meta-Analysis of nitrogen removal in riparian buffers. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosompemaa, P.; Peterson, E.W.; Perry, W.; Seyoum, W.M. Recycling of nitrate and organic matter by plants in the vadose zone of a saturated riparian buffer. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-H.; Scholz, M. What is the role of Phragmites australis in experimental constructed wetland filters treating urban runoff? Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, L.; Mench, M.; Jacob, D.; Otte, M. Metal and metalloid removal in constructed wetlands, with emphasis on the importance of plants and standardized measurements: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3447–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Xi, S.; Yang, X.; Yang, W.; Li, J.; Gu, B.; He, Z. Purifying eutrophic river waters with integrated floating island systems. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollheim, W.M.; Harms, T.K.; Peterson, B.J.; Morkeski, K.; Hopkinson, C.S.; Stewart, R.J.; Gooseff, M.N.; Briggs, M.A. Nitrate uptake dynamics of surface transient storage in stream channels and fluvial wetlands. Biogeochemistry 2014, 120, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, P.J.; Helton, A.M.; Poole, G.C.; Hall, R.O.; Hamilton, S.K.; Peterson, B.J.; Tank, J.L.; Ashkenas, L.R.; Cooper, L.W.; Dahm, C.N.; et al. Stream denitrification across biomes and its response to anthropogenic nitrate loading. Nature 2008, 452, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Wu, B.-Y.; Lai, C.-F. A study of the ecological benefits of the green energy landscape fountain. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 75, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haycock, N.; Pinay, G. Groundwater nitrate dynamics in grass and poplar vegetated riparian buffer strips during the winter. J. Environ. Qual. 1993, 22, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, S.; Butturini, A.; Clement, J.-C.; Burt, T.; Dowrick, D.; Hefting, M.; Matre, V.; Pinay, G.; Postolache, C.; Rzepecki, M.; et al. Nitrogen Removal by Riparian Buffers along a European Climatic Gradient: Patterns and Factors of Variation. Ecosystems 2003, 6, 0020–0030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.M.; Dodds, W.K.; Wilson, K.C.; Murdock, J.N.; Eichmiller, J. The saturation of N cycling in Central Plains streams: 15N experiments across a broad gradient of nitrate concentrations. Biogeochemistry 2007, 84, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kent, R.; Belitz, K.; Burton, C.A. Algal productivity and nitrate assimilation in an effluent dominated concrete lined stream. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2005, 41, 1109–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, G.; Dzienia, S.; Vander Pol, R.A. Effect of Temperature on Denitrification Rate in Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1975, 39, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, P.V.; Dennett, K.E.; Marchand, E.A.; Spurkland, L.E. Potential of constructed wetland in reducing total nitrogen loading into the Truckee River. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 16, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacks, G.; Joelsson, A.; Fleischer, S. Nitrogen retention in forest wetlands. Ambio 1994, 23, 358–362. [Google Scholar]
- Pinay, G.; Roques, L.; Fabre, A. Spatial and temporal patterns of denitrification in a riparian forest. J. Appl. Ecol. 1993, 30, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, G.N. Chloride (Cl−) Uptake. In Regulation of Nutrient Uptake by Plants: A Biochemical and Molecular Approach; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; pp. 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
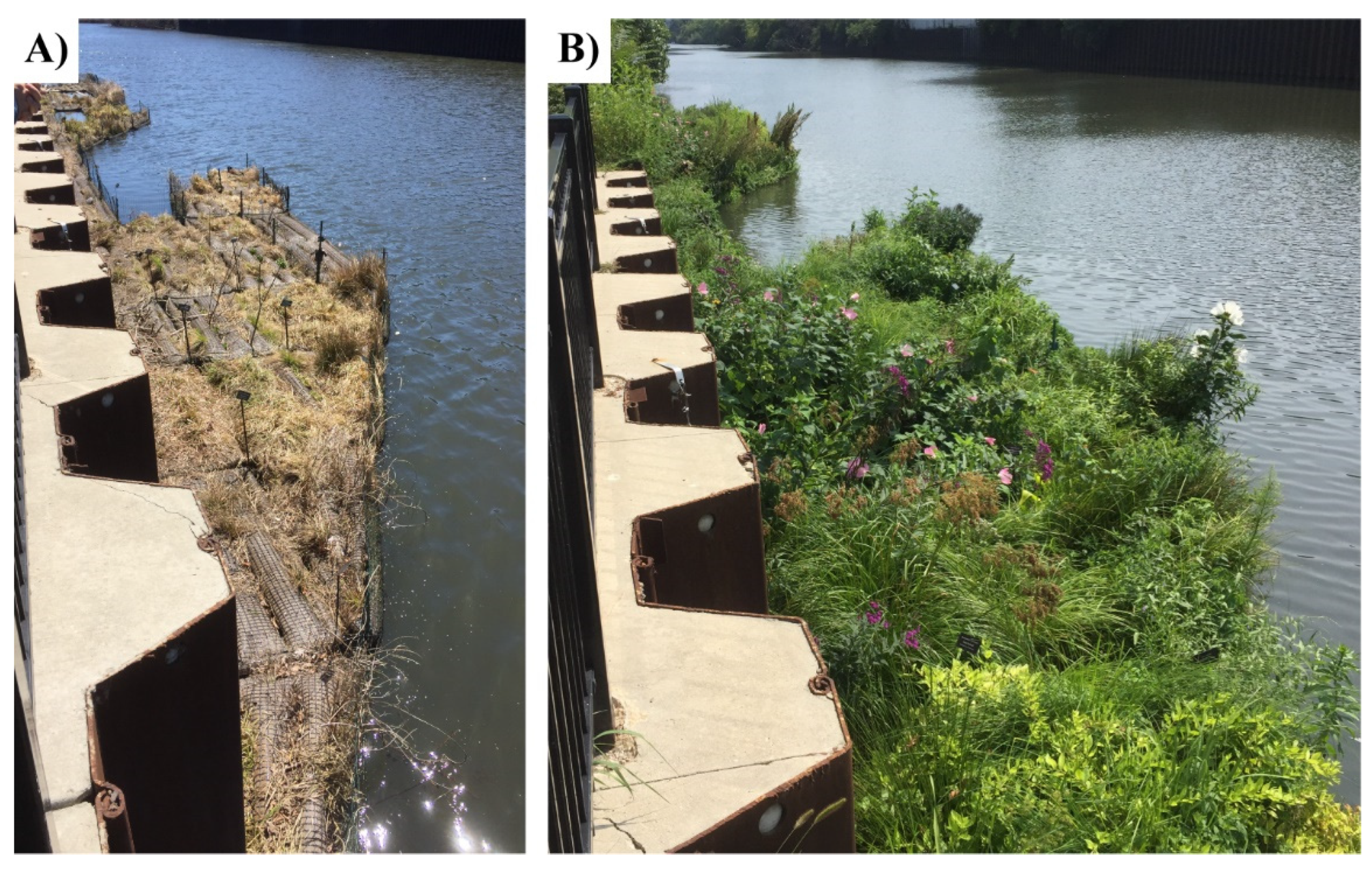


| Species Name | Common Name |
|---|---|
| Acorus calamus | Sweet flag |
| Caltha palustris | Marsh-marigold |
| Carex bromoides | Brome sedge |
| Carex comosa | Bristly sedge |
| Carex stricta | Tussock sedge |
| Decodon verticillatus | Waterwillow |
| Filipendula rubra | Queen of the prairie |
| Hibiscus moscheutos | Rose mallow |
| Iris virginica var. shrevei | Southern blue flag |
| Juncus effusus | Common rush |
| Justicia americana | American water-willow |
| Rumex altissimus | Pale dock |
| Saururus cernuus | Lizards tail |
| Scirpus cyperinus | Woolgrass |
| Verbena hastata | Blue vervain |
| Analyte | ICP-AES Detection Limit | MCL | SMCL |
|---|---|---|---|
| μg/L | μg/L | μg/L | |
| Al | 1 | 50 | |
| As | 1 | 10 | |
| Be | 0.09 | 4 | |
| Cd | 0.1 | 5 | |
| Cr | 0.2 | 100 | |
| Cu | 0.4 | 1300 * | |
| Mn | 0.1 | 50 | |
| Pb | 1 | 0 | 15 * |
| Se | 2 | 50 | |
| Zn | 0.2 | 500 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peterson, E.W.; Nicodemus, P.; Spooner, E.; Heath, A. The Effectiveness of an Artificial Floating Wetland to Remove Nutrients in an Urban Stream: A Pilot-Study in the Chicago River, Chicago, IL USA. Hydrology 2021, 8, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology8030115
Peterson EW, Nicodemus P, Spooner E, Heath A. The Effectiveness of an Artificial Floating Wetland to Remove Nutrients in an Urban Stream: A Pilot-Study in the Chicago River, Chicago, IL USA. Hydrology. 2021; 8(3):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology8030115
Chicago/Turabian StylePeterson, Eric W., Phil Nicodemus, Emmett Spooner, and Abigail Heath. 2021. "The Effectiveness of an Artificial Floating Wetland to Remove Nutrients in an Urban Stream: A Pilot-Study in the Chicago River, Chicago, IL USA" Hydrology 8, no. 3: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology8030115
APA StylePeterson, E. W., Nicodemus, P., Spooner, E., & Heath, A. (2021). The Effectiveness of an Artificial Floating Wetland to Remove Nutrients in an Urban Stream: A Pilot-Study in the Chicago River, Chicago, IL USA. Hydrology, 8(3), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology8030115






