Abstract
Kuttara Volcano, Hokkaido, Japan, consists of temperate Lake Kuttara and the western Noboribetsu geothermal area. In order to explore geothermal relations between Lake Kuttara and the geothermal area, the heat budget of a hydrothermal pond, Okunoyu, was evaluated, and the heat storage change in the lower layer of Lake Kuttara was calculated by monitoring the water temperature at the deepest point. The lake water temperature consistently increased during the thermal stratification in June–November of 2013–2016. The heat flux QB at lake bottom was then calculated at a range of 4.1–10.9 W/m2, which is probably due to the leakage from a hydrothermal reservoir below the lake bottom. Meanwhile, the heat flux HGin by geothermal groundwater input in Okunoyu was evaluated at 3.5–8.5 kW/m2, which is rapidly supplied through faults from underlying hydrothermal reservoirs. With a time lag of 5 months to monthly mean QB values in Lake Kuttara, the correlation with monthly mean HGin in Okunoyu was significant (R2 = 0.586; p < 0.01). Applying Darcy’s law to the leakage from the hydrothermal reservoir at 260–310 m below the lake bottom, the time needed for groundwater’s passage through the media 260–310 m thick was evaluated at 148–149 days (ca. 5 months). These findings suggest that the hydrothermal reservoir below lake bottom and the underlying hydrothermal reservoirs in the western geothermal area are both connected to a unique geothermal source in the deeper zone as a geothermal flow system of Kuttara Volcano.
1. Introduction
There are many volcanic lakes that are geothermally affected by magmatic activity of volcanoes or their eruptions throughout the world, as typified by Lake Nyos, Cameroon, with the lower magma’s pocket [1]. For Crater Lake, Oregon, USA, the US Geological Survey has provided a volcano hazards program for a possible future eruption [2], though the volcano at present seems to be undergoing stable magmatic activity. In New Zealand, the activity of Ruapehu Volcano is explored by using acoustic and seismic signals and estimating the water and heat budgets of Ruapehu Crator Lake [3,4,5,6]. Geothermal and hydrothermal systems of volcanic origin are proposed by White and Brannock [7] and Fukutomi et al. [8] from a geophysical viewpoint and by White [9] from a geological viewpoint. Terada and Hashimoto [10] proposed a numerical model for a thermal response of a crater lake to lower geothermal activity. As for other studies for volcanic activity, there are many geochemical investigations about interrelations between hydrothermal lakes and lower magmatic activity [11,12,13,14,15]. However, there are few field studies on estimates of water and heat budgets of hydrothermal lakes or ponds [3,16]. This is because high water temperature at more than 50 °C and volcanic heated gases such as water vapor, SO2 and CO2 could damage instruments for monitoring water level and water properties such as pH, electric conductivity and water temperature. The water, heat and chemical budgets of Ruapehu Crator Lake (water temperature of less than about 50 °C) were estimated for 25 years [3]. However, spatial distributions of water temperatures in the lake are not shown, and groundwater input and output in the water budget are not estimated. In a volcanic caldera lake, Lake Kussharo, Japan, Chikita et al. [17] evaluated groundwater outflow and groundwater inflow including the input of geothermal water by estimating the water and chemical budgets of the lake. In the present study, the heat budget of a hydrothermal pond with water temperature of mostly 50–70 °C is estimated over four years. Such a long-term estimate under heated conditions is very rare in the world. Kuttara Volcano, Hokkaido, Japan, consists of the western Noboribetsu geothermal area and eastern Lake Kuttara (Figure 1 and Figure 2). In the Noboribetsu geothermal area, in order to watch volcanic activity, seismographs, clinometers, infrasound meters, GNSS and video cameras have been set by the Japan Meteorological Agency. Kuttara Volcano is currently at the first level for the five volcanic alert levels (the Japan Meteorological Agency: URL http://www.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vois/data/tokyo/STOCK/kaisetsu/English/level.html) [18]. Thus, the volcanic activity present is relatively stable. Fukutomi et al. [16] numerically obtained the heat flux HGin (W/m2) by groundwater input in a hydrothermal pond, Ohyunuma, in the Noboribetsu area by estimating the water and heat budgets. Boehrer et al. [19] estimated the bottom geothermal heat flux at the deepest points of four Japanese volcanic lakes, Shikotsu, Kuttara, Towada and Tazawa, at 0.29 W/m2, 1.0 W/m2, 18.6 W/m2 and 0.27 W/m2, respectively. This suggests that of the four lakes, Kuttara and Towada are affected by relatively high volcanic geothermal activity. A magneto-telluric (MT) survey for internal structure of Kuttara Volcano by Goto and Johmori [20] indicates that the zone of relatively low specific resistivity underlying the bottom at the deepest point of Lake Kuttara may be a hydrothermal reservoir. Goto and Johmori [20] also pointed out that there is a geothermally active zone just below the western Noboribetsu geothermal area. In this study, the heat budget of a hydrothermal pond in the Noboribetsu area is continually estimated over four years, and then the question of how the evaluated heat flux by geothermal groundwater input is related to the bottom geothermal heat flux in Lake Kuttara is discussed.
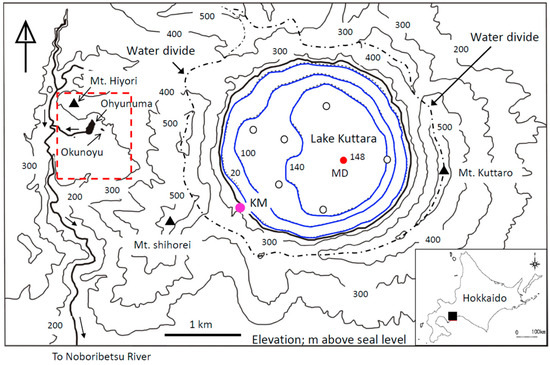
Figure 1.
Location of Kuttara Volcano in Hokkaido (inserted), Lake Kuttara with the bathymetry (blue isopleths of 20 m, 100 m and 140 m in water depth) and hydrothermal ponds, Ohyunuma and Okunoyu, in the geothermal area (red dotted line). The deepest point of Kuttara is located at site MD (148 m in depth), and a meteorological station at site KM on the lake shore.
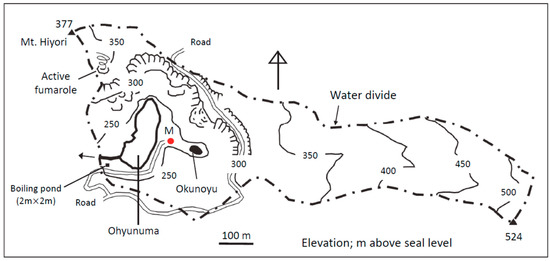
Figure 2.
Location of two hydrothermal ponds, Ohyunuma and Okunoyu, and a meteorological station (site M) in the catchment, upstream of the small boiling pond of a square shape (2 m × 2 m). There is an active fumarole with rising steam and smokes near the summit of Mt. Hiyori.
2. Methodology
2.1. Field Observations
Locations of Lake Kuttara, hydrothermal ponds in the Noboribetsu geothermal area and observation sites are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2. Lake Kuttara (42°29′57″ N, 141°10′55″ E) has a surface area of 4.68 km2 and mean water depth of 104.9 m with lake level at ca. 258 m above sea level abbreviated as “asl”. Vertical profiles of water temperature and electric conductivity were obtained about twice per month at the deepest point (site MD; 148 m depth) and at the other 6 sites (white circles in Figure 1). The vertical measurements were performed by using a TCTD (temperature- conductivity-turbidity-depth) profiler (model ASTD102, JFE Advantec, Inc., Japan; accuracies, ±0.01 °C for 0–35 °C, ±0.1 mS/m for 0–200 mS/m, ±0.3 FTU for 0–1000 FTU, and ±1.8 m for 0–600 m, respectively) in 2013–2016. In order to know a temporal change of water temperature in the bottom layer, eleven temperature loggers (HOBO TidbiT v2, Onset Computer, Inc., USA; accuracy, ±0.2 °C) were fixed at 45 m, 35 m, 25 m, 15 m, 10 m, 5 m, 4 m, 3 m, 2 m, 1 m and 0 m above the bottom of site MD by a mooring buoy system [21]. In order to improve the accuracy from ±0.2 °C to ±0.1 °C, the loggers’ values were calibrated by water temperature from the TCTD profiler by using high correlations (R2 = 0.920–0.998, p < 0.01) at a range of 3.6–6.0 °C. At site MD, a sediment core 0.2 m long was sampled by a portable gravity core sampler to determine sedimentary facies and measure the hydraulic conductivity using the falling head test in laboratory. A sediment core 1.39 m long was also sampled at site MD in 2009 by Dr. Okamura, Kochi University, Japan, and the group “Water and Cep in Lake Shikotsu”, Sapporo, Japan [22]. Ochiai [22] pointed out that the sediment core mostly contains deposits from the eruptions of the western volcano (at present, Noboribetsu geothermal area) and Usu Volcano at 29.4 km west of Lake Kuttara.
The Noboribetsu geothermal area consists of Mt. Hiyori, four hydrothermal ponds, Ohyunuma, Okunoyu, Taisho-jigoku and a small boiling pond (square shape of 2 m × 2 m), the southern geothermal valley, called “Jigoku-dani” (Hell’s Valley) and the Noboribetsu Spa Town with spring points of geothermal water. Figure 2 shows a catchment area upstream of the small boiling pond, including the northern part of the Noboribetsu geothermal area. In Ohyunuma (42°30′9″ N, 141°8′50″ E; surface elevation 240 m asl, water surface area 1.60 × 104 m2, mean depth 5.7 m) and Okunoyu, (42°30′8″ N, 141°8′57″ E; surface elevation 243 m asl, water surface area 9.6 × 102 m2, mean depth 1.8 m), the water temperature was recorded every 1 h at 0.2 m depth by using sheath type thermocouples (temperature allowance, ±1.5 °C for a range of −40–+333 °C). The thermocouple sensor in Okunoyu was set at ca. 10 m distant from one of geothermally bubbled regions with more than 80 °C at the surface. In Ohyunuma, which has no noticeably bubbled region at the surface but two rising steam areas near the western shore, the thermocouple sensor was fixed near the outlet. The temperature data are managed and supplied by Noboribetsu On-sen Co., Ltd. Okunoyu normally has no outlet, because the water level is dominantly controlled by the water’s intake (ca. 0.023 m3/s) using pipelines. The hot water by the uptake is supplied to the Noboribetsu Spa Town. The data of intake volume and water temperature are also managed and supplied by Noboribetsu On-sen Co., Ltd. In order to estimate the heat budget of Okunoyu, surface inflow, its water temperature and the water level were frequently measured.
Meteorology (solar radiation, air temperature, relative humidity, rainfall and wind velocity) was observed at 1 h intervals at site M between Ohyunuma and Okunoyu (Figure 2), and at site KM on the shore of Lake Kuttara (Figure 1), which are both set at 3 m above ground surface. The missing data were complemented by significant correlations with data of the Noboribetsu AMeDAS station at a distance of 5.4 km south-southwest of site M. Snowfall at site M was assumed to be equal to that at the Noboribetsu station.
2.2. Heat Budget and Geothermal Heat Flux in a Hydrothermal Pond
In order to evaluate the geothermal heat flux at the bottom of hydrothermal Okunoyu, the heat budget was estimated by the following equation:
where ΔG is heat storage change (J/m) of a lake for a budget period Δt (s), ρw and cp are water density (kg/m3) and specific heat of water (J/kg/K) at temperature T (K) at z (m), vertical coordinate, h is water depth (m) at deepest point, A(z) is the area at z (surface area, A0 at z = 0), Rn is net radiation (W/m2), QH is sensible heat flux (W/m2), QE is latent heat flux (W/m2), QP is heat flux (W/m2) by direct precipitation onto the lake, HR is heat flux (W/m2) by net river inflow, HG is heat flux (W/m2) by net groundwater inflow, and Hs is heat flux (W/m2) by heat conduction at bottom. Net radiation Rn in Equation (1) consists of net shortwave radiation K* and net longwave radiation L*, as given by the following:
where K is downward shortwave radiation, α is albedo, Ld and Lup are downward and upward longwave radiations, respectively, ε is emissivity (here, 0.97 for water and 1.0 for air), σ is Stefan-Boltzmann constant (=5.67 × 10−8 W/m2/K4) and Ts is pond surface temperature (K). Considering observational results of Brandt and Warren [23], α value of water was given as constant of 0.05. Downward longwave radiation Ld was numerically obtained as a function of air temperature, total amount of effective water vapor content and relative sunshine duration [24]. HR, HG and QP in Equation (1) are given as follows:
where Rin and Rout are surface inflow and artificial intake (m3/s), HRin and HRout are heat fluxes (W/m2) by surface inflow and intake, TRin and TRout are water temperatures (K) for surface inflow and intake, respectively, Gin and Gout are groundwater inflow and outflow (m3/s), HGin and HGout are heat fluxes (W/m2) by groundwater inflow and outflow, respectively, TGin and TGout are temperatures (K) of inflowing and outflowing groundwaters, T0 is standard temperature (K), P is precipitation (m/s) onto lake surface, TP is temperature (K) of precipitation (here assumed to be equal to the wet-bulb temperature). Daily mean values of the meteorological factors and temperatures were utilized for a budget period, Δt = 86,400 s. In case of snowfall onto the pond, latent heat of ice from the negative air temperature to 0 °C and fusion heat of the 0 °C ice in water are reduced from Equation (5). Here, T0 = 281.05 K (7.9 °C), being equal to the annual mean air temperature at site M, is given, which corresponds to the temperature of unconfined groundwater under non-geothermal condition in the catchment (Figure 1). Heat flux HGin by groundwater input in Equation (4) is here defined as the bottom input of geothermal heat ascending through many faults and fractures, containing liquid water and volcanic gases mainly composed of water vapor [25]. Hence, the heat flux Hs by heat conduction in Equation (1) is supposed to be negligibly small, compared with HGin. Unconfined groundwater inflow from the surrounding catchment slope in Equation (4) could also be negligibly small because of the muddy bottom deposits [16].
HR = HRin − HRout = ρwCp{Rin(TRin − T0) − Rout(TRout − T0)}/A0
HG = HGin − HGout = ρwCp{Gin(TGin − T0) − Gout(TGout − T0)}/A0
Sensible heat flux QH and latent heat flux QE in Equation (1) were numerically obtained by the following bulk transfer method:
where ρa is air density (=1.2 kg/m3), c is specific heat (J/Kg/K) of air under constant pressure, β is ratio of water vapor density to dry air density (=0.622), aH and aE are dimensionless bulk transfer coefficients for sensible heat and latent heat, respectively, uz is wind speed (m/s) at z above ground surface, Tz is air temperature (K) at z, Ts is water temperature (K) at surface, l is latent heat (J/kg) for evaporation, p is air pressure (Pa) at z, ez is vapor pressure (Pa) at z, and e0 is saturated vapor pressure (Pa) at Ts. Here z = 3 m, and assuming the atmospheric condition to be neutral at any time, aH = aE ~ 1.5 × 10−3 was given for 1~ < u3 < ~10 m/s [24].
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 3 shows time series of daily mean water temperature in Ohyunuma and Okunoyu, and daily mean air temperature and daily precipitation at site M in 2013–2016. Water temperature in Ohyunuma varied at a range of 36.9–55.6 °C (mean, 46.6 °C), being in phase with air temperature. The temperature in Okunoyu ranged over 42.3–72.2 °C (mean, 63.0 °C) and exhibited a small response only to large rainfalls of more than 100 mm/day. The relatively high temperature in Okunoyu is due to relatively high geothermal activity. In fact, the geothermally bubbled region in Okunoyu occupies ca. 35% area at the surface, but there is no noticeably bubbled region in Ohyunuma except at the near shore. The water level of Okunoyu temporally varied with the amplitude of ca. 0.25 m, which means that the surface area and volume were approximately constant (9.6 × 102 m2 and 1.7 × 103 m3, respectively).
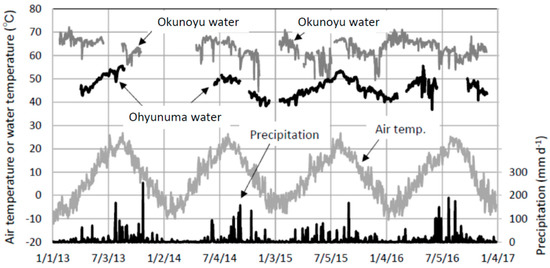
Figure 3.
Daily mean water temperature in Ohyunuma and Okunoyu, and daily mean air temperature and daily precipitation at site M in 2013–2016. The date labels show “month/day/year”.
Figure 4 shows vertical profiles of water temperature and electric conductivity at 25 °C (EC25) at site MD of Lake Kuttara in 2014. The EC25 data were missed on 20 September. After the vertical whole circulation in April, when water temperature is nearest to the Tmd line, the lake is thermally stratified in May–November [21]. Then, both water temperature and EC25 temporally increased at 0–45 m above bottom, especially at 0–22 m above bottom. Under water pressure of 148 m, pure water has the maximum density at 3.688 °C. The increase in water temperature in Figure 4a should produce pycnal instability, if it is pure water. However, the increase in EC25 (i.e., increase in ionic concentration) increases water bulk density, which can keep the lake water pycnally stable [19]. The increase in both water temperature and EC25 in Figure 4 suggests that the geothermal heat input occurs by the heat supply from the underlying zone. The MT survey of Goto and Johmori [20] indicates that a reservoir of low specific resistivity lies at 260–310 m below the lake basin, and that such a reservoir is horizontally limited to the deepest point and its surrounding area. The increase in water temperature and EC25 was not noticeably observed at the other six sites (white circles in Figure 1). Hence, the geothermal heat is probably supplied from the hydrothermal reservoir underlying the deepest area.
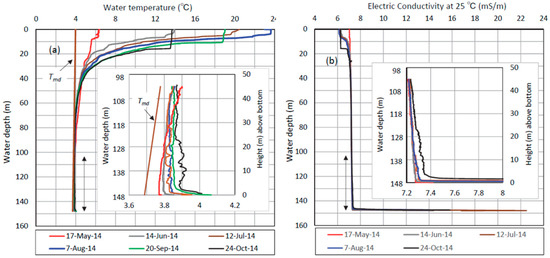
Figure 4.
Vertical distributions of (a) water temperature and (b) electric conductivity at 25 °C at site MD. Their distributions at 0–45 m (two-way arrows) above the bottom are deployed in more detail (inserted). The Tmd line indicates a vertical distribution of water temperatures, giving the maximum density of pure water.
The geothermal heat flux at bottom of Lake Kuttara is calculated as that averaged over the period between two profiles by using the temperature profiles in Figure 4a. The geothermal heat flux QB is then given as follows:
where h is height (m) above bottom (here, = 45 m). Boehrer et al. [19] estimated QB at about 1 W/m2, which is much larger than that in geothermally inactive volcanic lakes such as Tazawa and Shikotsu (0.1 W/m2 order) [19] or in ocean (less than 0.1 W/m2) [26,27]. Similarly, the QB values were obtained by using the loggers’ data at 0−45 m above the bottom, after the calibration of loggers’ temperature by the profiler’s temperature.
Figure 5 shows time series of (a) daily mean water temperature averaged at 0–45 m above bottom, and (b) calculated daily mean (gray line) and monthly mean (black plotted line) heat flux QB at the deepest point of Lake Kuttara. In June–December, when the lake is thermally stratified, the temperature increase is seen. Two vertical circulations in late December–early January and late April–early May abruptly decrease and increase the temperature, respectively. The weak stratification in the ice-covered periods (red arrows in Figure 5a; 82 days in 2013, 57 days in 2014 and 31 days in 2016) does not induce a noticeable temperature increase. In the winter of 2015, when the lake was not completely ice-covered, the vertical mixing under long weak stratification decreased water temperature. The monthly mean heat flux QB was evaluated at 2.8–10.7 W/m2 for the periods of the noticeable increase in water temperature. The daily mean QB exhibits large fluctuations, and thus the monthly mean values are here related to monthly mean geothermal heat flux in Okunoyu from the heat budget estimate.
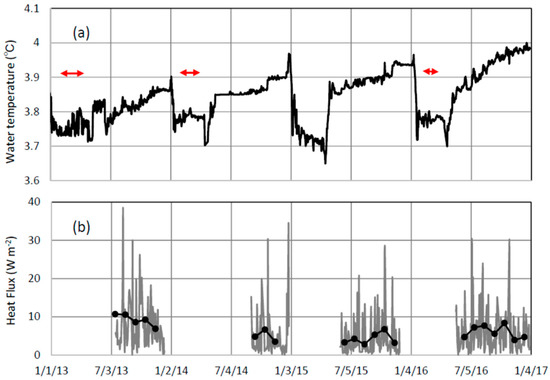
Figure 5.
Temporal variations of (a) daily mean water temperature averaged over 0–45 m above bottom at site MD and (b) calculated daily mean (gray line) and monthly mean (black plotted line) heat flux QB. Red arrows indicate completely ice-covered periods in Lake Kuttara.
Figure 6 shows daily mean heat fluxes at water surface of Okunoyu in Equation (1), and evaluated heat flux HGin by groundwater input in Equation (4). In the calculation of HGin, ∆G/∆t in Equation (1) was approximately given as ρw cp∙V∙(∆Tav/∆t)/A0, where V is water volume (m3), A0 is surface area (m2) and Tav is water temperature (K) averaged over the pond. Here, the measured water temperature was assumed to represent Tav. This is based the fact that the measuring point is located near one of the geothermally bubbled regions and an airborne IR survey of Terada et al. [28] above Okunoyu deployed nearly a uniform surface water temperature. At the water surface, upward longwave radiation Lup and latent heat flux QE are remarkably large, reflecting the high water temperature in Figure 3. Heat flux by river inflow HRin in Equation (3) was then neglected because the magnitude HRin = 100–300 W/m2 is much smaller than HRout = 3–6 kW/m2 by the intake. The heat flux HGout by groundwater outflow in Equation (4) was also neglected, because muddy deposits at bottom is impermeable [16]. Geothermal heat flux HGin by groundwater inflow was evaluated at a range of 3.5–8.5 kW/m2, which completely corresponds to 3.4–8.2 MJ/day.
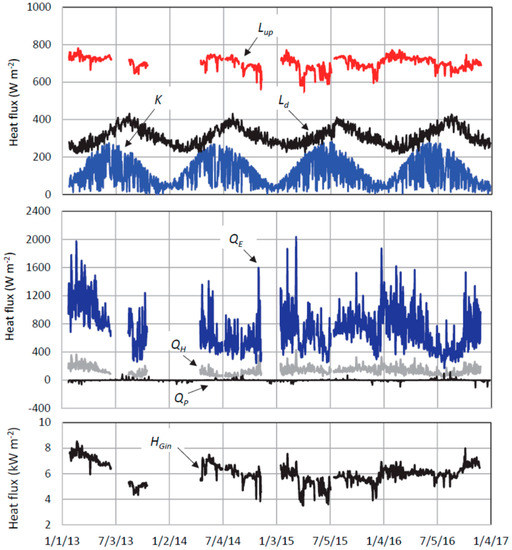
Figure 6.
Daily mean heat fluxes calculated for Okunoyu in 2013–2016. See the text for the symbols.
Figure 7 shows a relation between monthly mean QB (Kuttara) delayed by 5 months and monthly mean HGin (Okunoyu). Giving a time lag of 5 months) to QB, there exists a significant correlation (R2 = 0.586, p < 0.01) between QB and HGin. There was no correlation (R2 = 0.013) between the two, if there is no time lag to QB, and low correlation of R2 = 0.374 and 0.390 for time lags of 6 months and 4 months, respectively. The MT survey of Goto and Johmori [20] suggests that in Kuttara Volcano, the western hydrothermal regions and the hydrothermal reservoir underlying the bottom of Lake Kuttara are each linked through faults and fractures to a deeper hydrothermal zone. Hence, the time lag of 5 months is considered to be the time necessary for leakage from the hydrothermal reservoir to the lake bottom. Here, it is supposed that a porous media 260–310 m thick exists between lake bottom and the hydrothermal reservoir. A laboratory test indicated that the sediment core 20 cm thick (sandy silt) at site MD has a mean hydraulic conductivity of 1.10× 10−5 m/s and mean specific weight at 1.97. Here, supposedly giving the effective porosity at 0.25 for the sandy silt [29] and lake bottom pressure at 14.5 atm, and assuming the hydraulic quantity to be equal in the whole porous media, the application of Darcy’s law under static sediment pressure allows us to numerically obtain the time of 148–149 days as the time necessary for geothermal groundwater flow’s reaching to the bottom. This value is agreeable to the time lag of 5 months between QB and HGin. Hence, the geothermal heat flux at the bottom of Lake Kuttara may be an indicator of volcanic activity accompanied by an underground hydrothermal system. The hydraulic conductivity 1.10 × 10−5 m/s given in a laboratory is a mean value for the sandy-silt core 0.2 m long. However, the sediment core 1.39 m long sampled at site MD also contains the thick sandy-silt tephra from the eruption of the western volcano. Thus, the hydraulic conductivity value could be representative as that of the porous media between the lake bottom and the underlying hydrothermal reservoir.
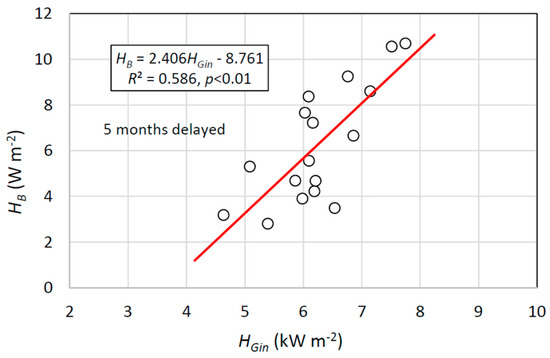
Figure 7.
Relation between monthly mean QB in Lake Kuttara and monthly mean HGin in Okunoyu. The QB values are delayed by 5 months for HGin.
4. Conclusions
Kuttara Volcano, Hokkaido, Japan, consists of the western geothermal area and eastern Lake Kuttara. The heat flux by geothermal groundwater input was evaluated from the heat budget estimate for a hydrothermal pond, Okunoyu, in the geothermal area, and compared with geothermal heat flux at the bottom of Lake Kuttara. During the thermal stratification of the lake, the lower layer increased both the water temperature and electric conductivity at 25 °C (EC25). By using the MT method, Goto and Johmori [20] pointed out that a hydrothermal reservoir lies at 260–310 m below the lake bottom and hydrothermal reservoirs are just below the western geothermal area as the zone of relatively low specific resistivity. Hence, the increase in both water temperature and EC25 in Lake Kuttara suggests that geothermal heat is supplied from a hydrothermal reservoir underlying the bottom. Giving a time lag of 5 months to the geothermal heat flux QB at lake bottom calculated monthly by monitored water temperature, the heat flux HGin by geothermal groundwater input in Okunoyu is significantly correlated with QB. A supposed calculation by means of the Darcy’s law gives 148–149 days as a time necessary for the passage of geothermal water in the media between the lake bottom and the underlying hydrothermal reservoir. The geothermal leakage in Lake Kuttara could thus be connected to the western geothermal area by the deeper geothermal zone of Kuttara Volcano, and the magnitude and variation of QB may become an indicator for volcanic activity.
Author Contributions
K.C., Y.O. and Y.S. participated in all the filed surveys to set and manage field instruments; H.O. set some instrument at Lake Kuttara and supplied many data; K.C. conceived and designed the Kuttara Volcano research project, and wrote the paper.
Funding
Part of this research was funded by the Earthquake Research Institute, the University of Tokyo Joint Usage/Research Program.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express gratitude to graduate students of Laboratory of Physical Hydrology, Division of Natural History Sciences, Graduate School of Science, Hokkaido University, for their great help in the field surveys. We are also indebted to Noboribetsu On-sen, Co., Ltd. and members of the group “Water and Cep in Lake Shikotsu” for their welcome data supply.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rouwet, D.; Tanyileke, G.; Costa, A. Cameroon’s Lake Nyos gas burst: 30 years later. Meeting report on 9th Workshop of the IAVCEI-Commission on Volcanic Lakes (CVL9); Cameroon, 14–24 March 2016. Eos 2016, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, S.P.; Doelger, S.; Bacon, C.R.; Mastin, L.G.; Scott, K.; Nathenson, M. Digital data for volcano hazards in the Crater Lake region, Oregon (data to accompany USGS Open-File Report 97-487). Open-File Report; U.S. Geological Survey, 2008. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2007/1223/index.html (accessed on 29 June 2018).
- Hurst, A.W.; Bibby, H.M.; Scott, B.J.; McGuinness, M.J. The heat source of Ruapehu Crater Lake; deductions from the energy and mass balances. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1991, 46, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, A.W. Stochastic simulation of volcanic tremor from Ruapehu. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1992, 51, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, A.W.; Vandemeulebrouck, J. Acoustic noise and temperature monitoring of the crater lake of Mount Ruapehu Volcano. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1991, 71, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, T.; Christenson, B.; Cole-Baker, J. Use of a weather buoy to derive improved heat and mass balance parameters for Ruapehu Crater Lake. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2012, 235–236, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.E.; Brannock, W.W. The sources of heat and water supply of thermal springs, with particular reference to Steamboat Springs, Nevada. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1950, 31, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukutomi, T.; Sugawa, A.; Fujiki, T. A Geophysical study on the hot spring of Kawayu, Hokkaido. Geophys. Bull. Hokkaido Univ. 1956, 4, 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- White, D.E. Thermal waters of volcanic origin. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 1957, 68, 1637–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, A.; Hashimoto, T. Variety and sustainability of volcanic lakes: Response to subaqueous thermal activity predicted by a numerical model. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murozumi, M.; Abiko, T.; Nakamura, S. Geochemical Investigation of the Noboribetsu Oyunuma Explosion Crater Lake. J. Volcanol. Soc. Japan 1964, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ohba, T.; Hirabayashi, H.; Nogami, K. Temporal changes in the chemistry of lake water within Yugama Crater, Kusatsu-Shirane Volcano, Japan: Implications for the evolution of the magmatic hydrothermal system. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2008, 178, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouwet, D.; Tassi, F.; Mora-Amador, R.; Sandri, L.; Chiarini, V. Past, present and future of volcanic lake monitoring. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2014, 272, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucker, V.K.; de Ronde, C.E.J.; Scott, B.J.; Wilson, N.J.; Walker, S.L.; Lupton, J.E. Subaerial and sublacustrine hydrothermal activity at Lake Rotomahana. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2016, 314, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudron, C.; Ohba, T.; Capaccini, B. Geochemistry and geophysics of active volcanic lakes: An introduction. Geol. Soc. London 2017, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukutomi, K.; Nakao, K.; Miyoshi, H.; Tanoue, R. Studies of water balance and heat budget at Ohyunuma Hot Lake in Noboribetsu, Hokkaido. Geophys. Bull. Hokkaido Univ. 1968, 19, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chikita, K.A.; Nishi, M.; Fukuyama, R.; Hamahara, K. Hydrological and chemical budgets in a volcanic caldera lake: Lake Kussharo, Hokkaido, Japan. J. Hydrol. 2004, 291, 91–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Japan Meteorological Agency. Volcanic Alert Levels in Volcanic Forecasts/Warnings. Available online: http://www.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vois/data/tokyo/STOCK/kaisetsu/English/level.html (accessed on 28 November 2018).
- Boehrer, B.; Fukuyama, R.; Chikita, K.A. Geothermal heat flux into deep caldera lakes Shikotsu, Kuttara, Tazawa and Towada. Limnology 2013, 14, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, Y.; Johmori, A. Internal structure of Kuttara Caldera, Hokkaido, Japan. Bull. Volcanol. Soc. Japan 2015, 60, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Chikita, K.A.; Oyagi, H.; Aiyama, T.; Okada, M.; Sakamoto, H.; Itaya, T. Thermal regime of a deep temperate lake and its response to climate change: Lake Kuttara, Japan. Hydrology 2018, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, Y. Water and Heat Budgets of Hydrothermal Area and Thermal Influence on Surrounding Water Area - Kuttara Volcano, Hokkaido. Master’s Thesis, Hokkaido University, Hokkaido, Japan, 2014; 45p. [Google Scholar]
- Brandt, R.E.; Warren, S.G. Surface albedo of the Antarctic sea ice zone. J Clim. 2005, 18, 3606–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, J. Meteorology in Aquatic Environments; Asakura Publishing Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 1994; 350p. [Google Scholar]
- Shigeno, H. Geochemical characteristics and sources of spring water in Shiraoi and three surrounding regions, Iburi. Hokkaido Inst. Hokkaido Geol. Surv. Rep. 2011, 62, 143–176. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, J.H.; Davies, D.R. Earth’s surface heat flux. Solid Earth 2010, 1, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.H. Global map of solid Earth surface heat flow. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2013, 14, 4608–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, A.; Yoshikawa, S.; Oshima, H.; Maekawa, T.; Matsushima, N. Airborne IR surveys of Usu, Noboribetsu and Hokkaido-Komagatake volcanoes: Evaluation of heat discharge ratios from steaming grounds and hot crater lakes. Geophys. Bull. Hokkaido Univ. 2012, 75, 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, D.K. Groundwater Hydrology, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980; 556p. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).