Estimating Aquifer Storage and Recovery (ASR) Regional and Local Suitability: A Case Study in Washington State, USA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
2.1. Water Rights in Washington
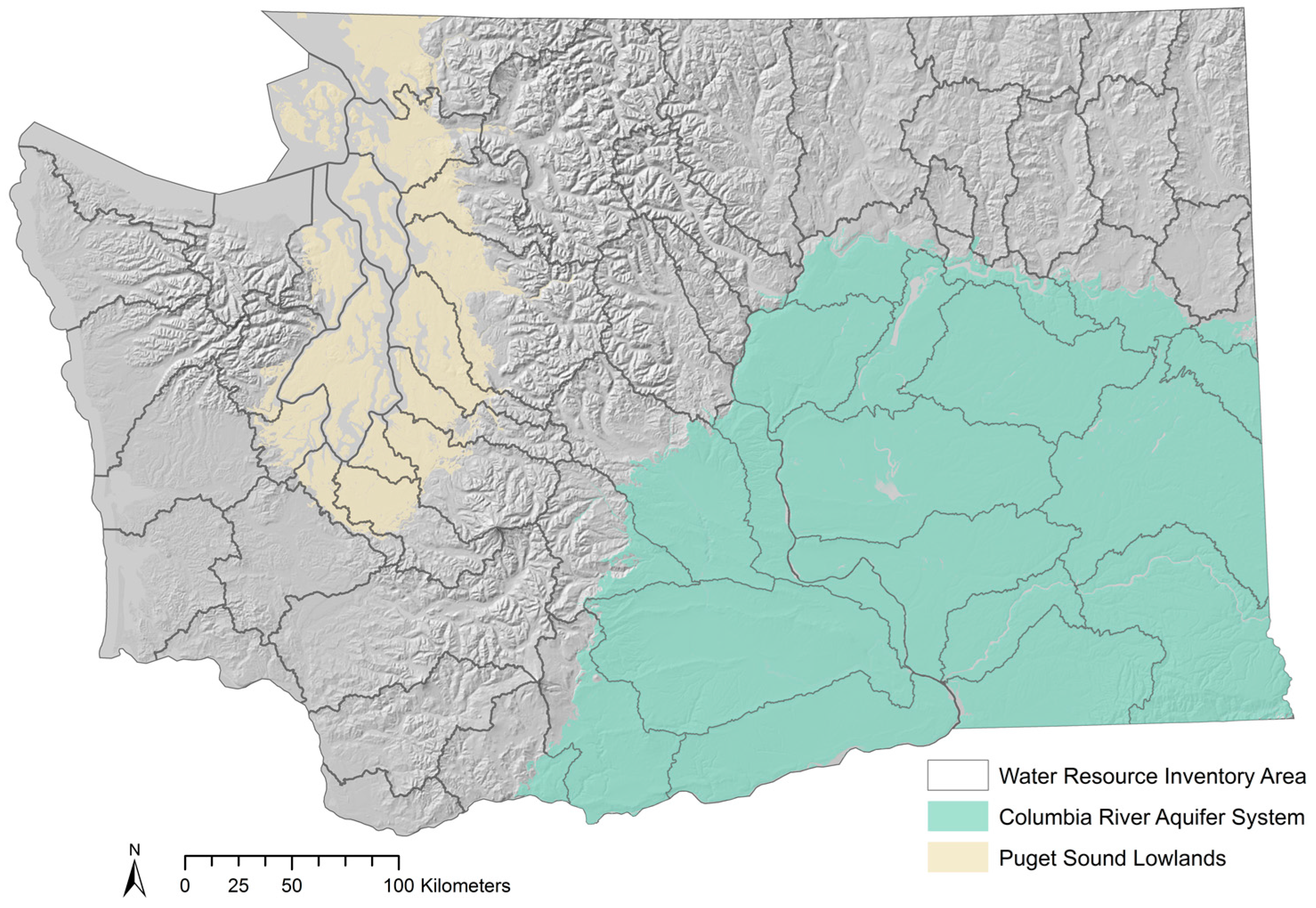
2.2. Washington Watershed Boundaries
2.3. Washington ASR Regulatory Framework
2.3.1. Reservoir Application Process
2.3.2. ASR Authorization and Process
2.3.3. Water Quality Requirements
3. Methods
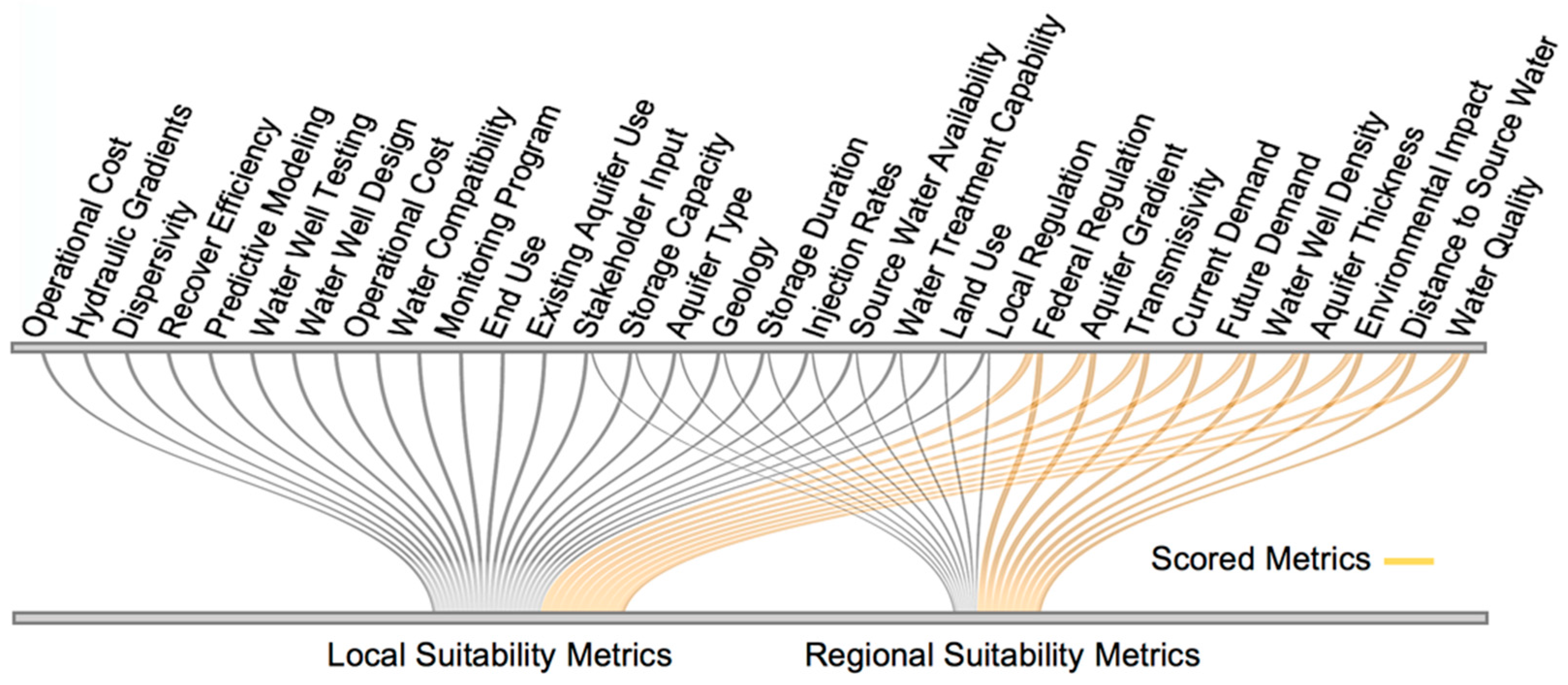
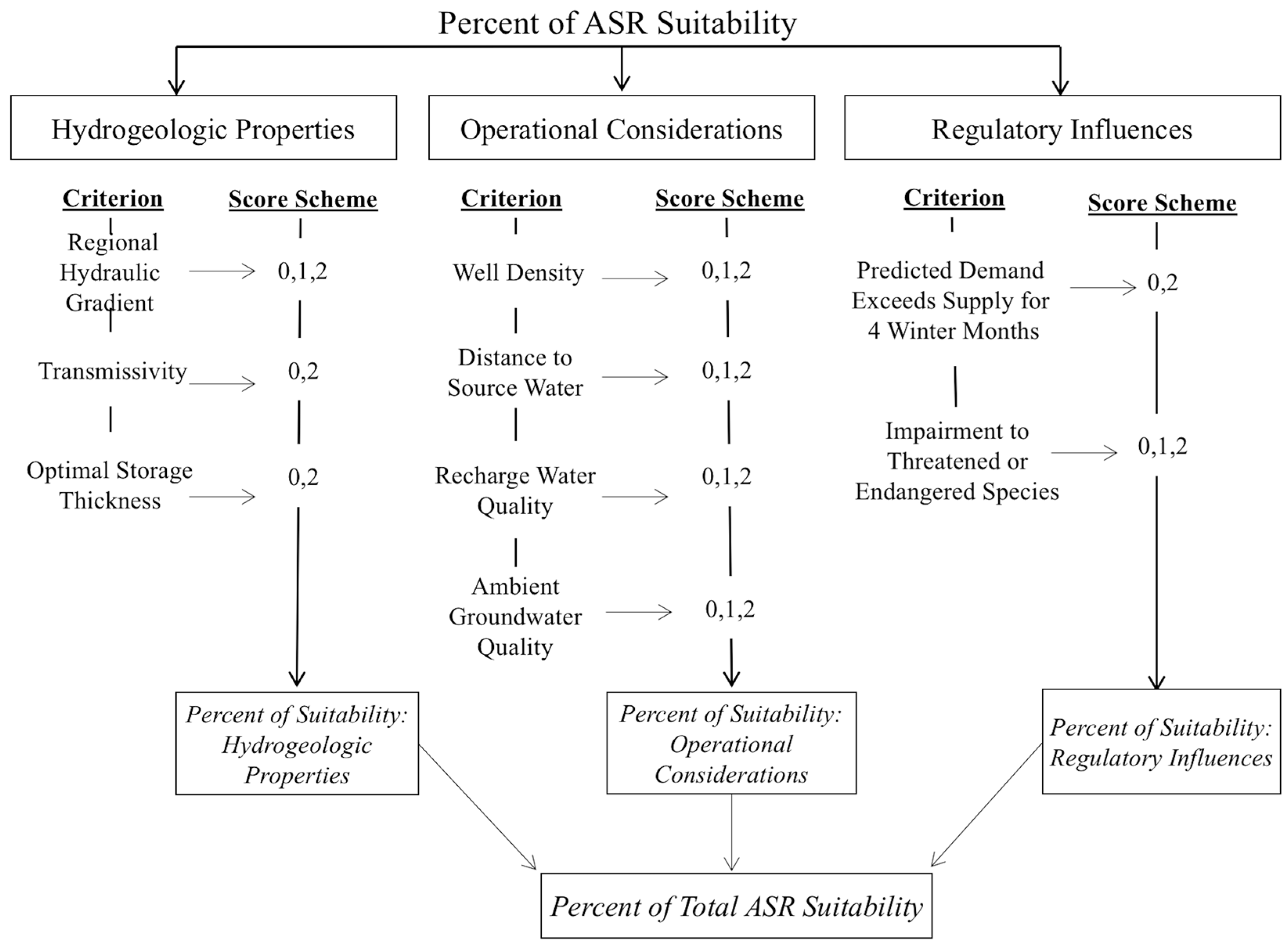
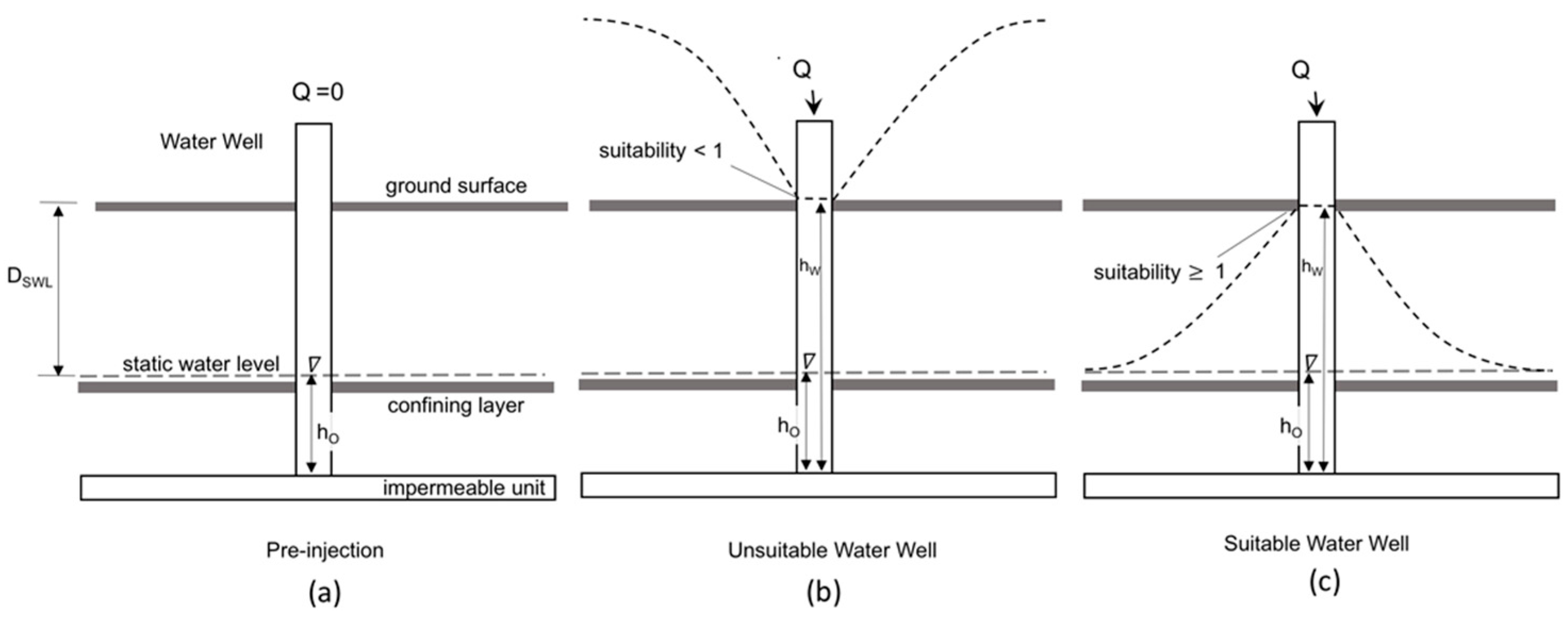
3.1. Site Scoring System
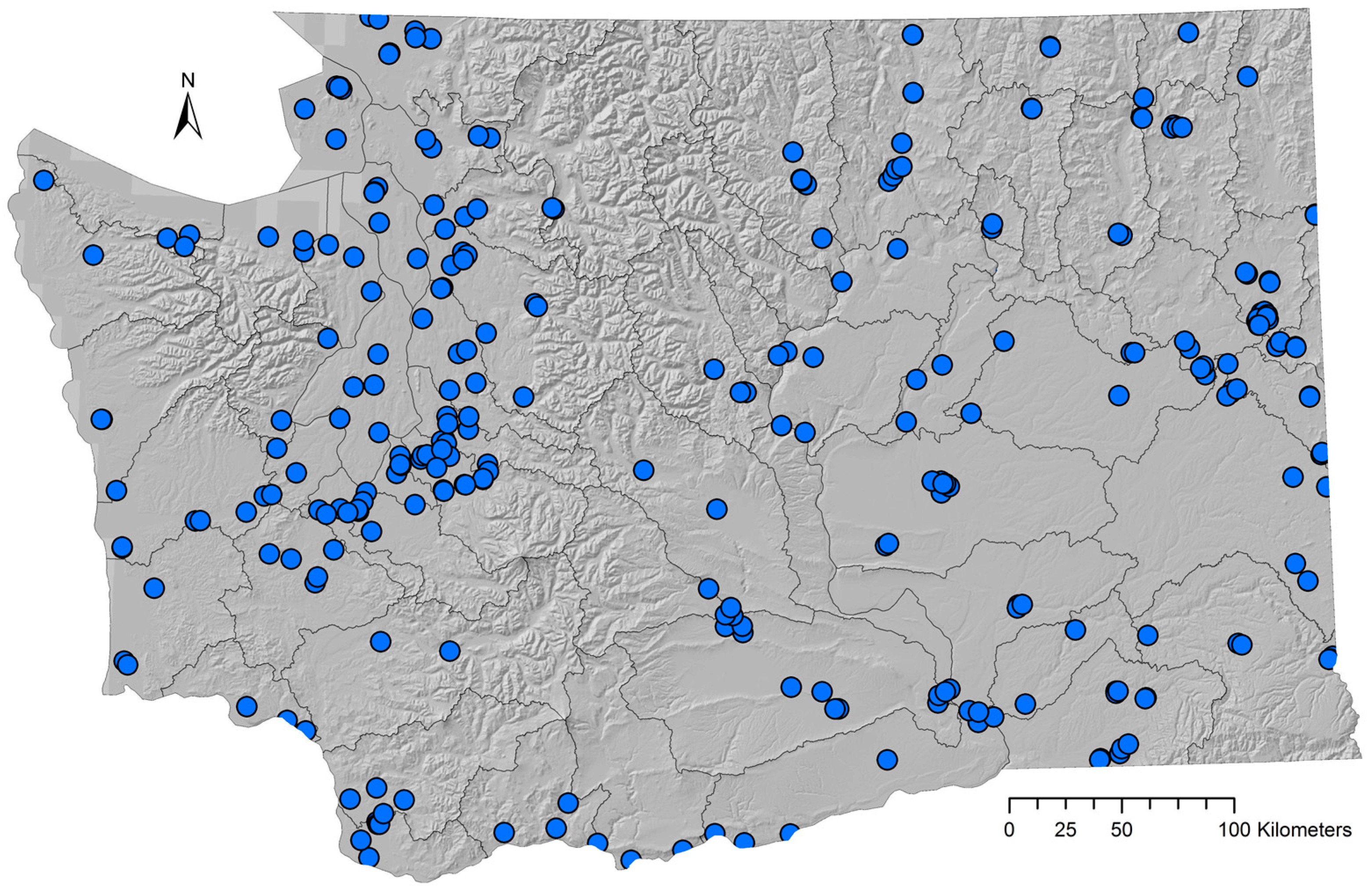
3.1.1. Water Well Selection Process
3.1.2. Hydrogeologic Properties
3.1.3. Operational Considerations
3.1.4. Regulatory Influences
3.2. Water Well Suitability
4. Results and Discussion
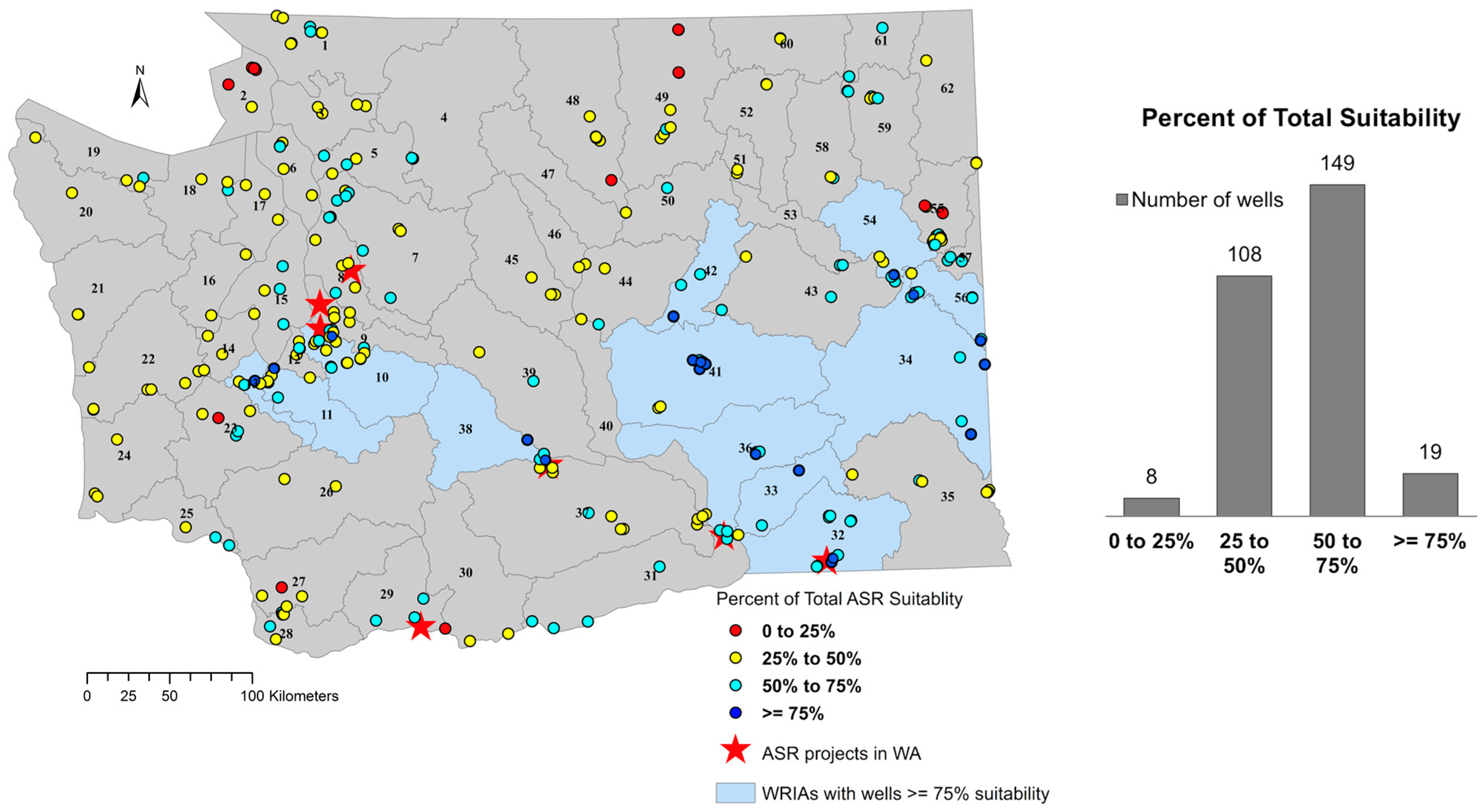
4.1. Site Scoring System
Subcatagory Results
4.2. Water Well Suitability
4.2.1. Desired Injection Rate
4.2.2. Potential Injection Capacity
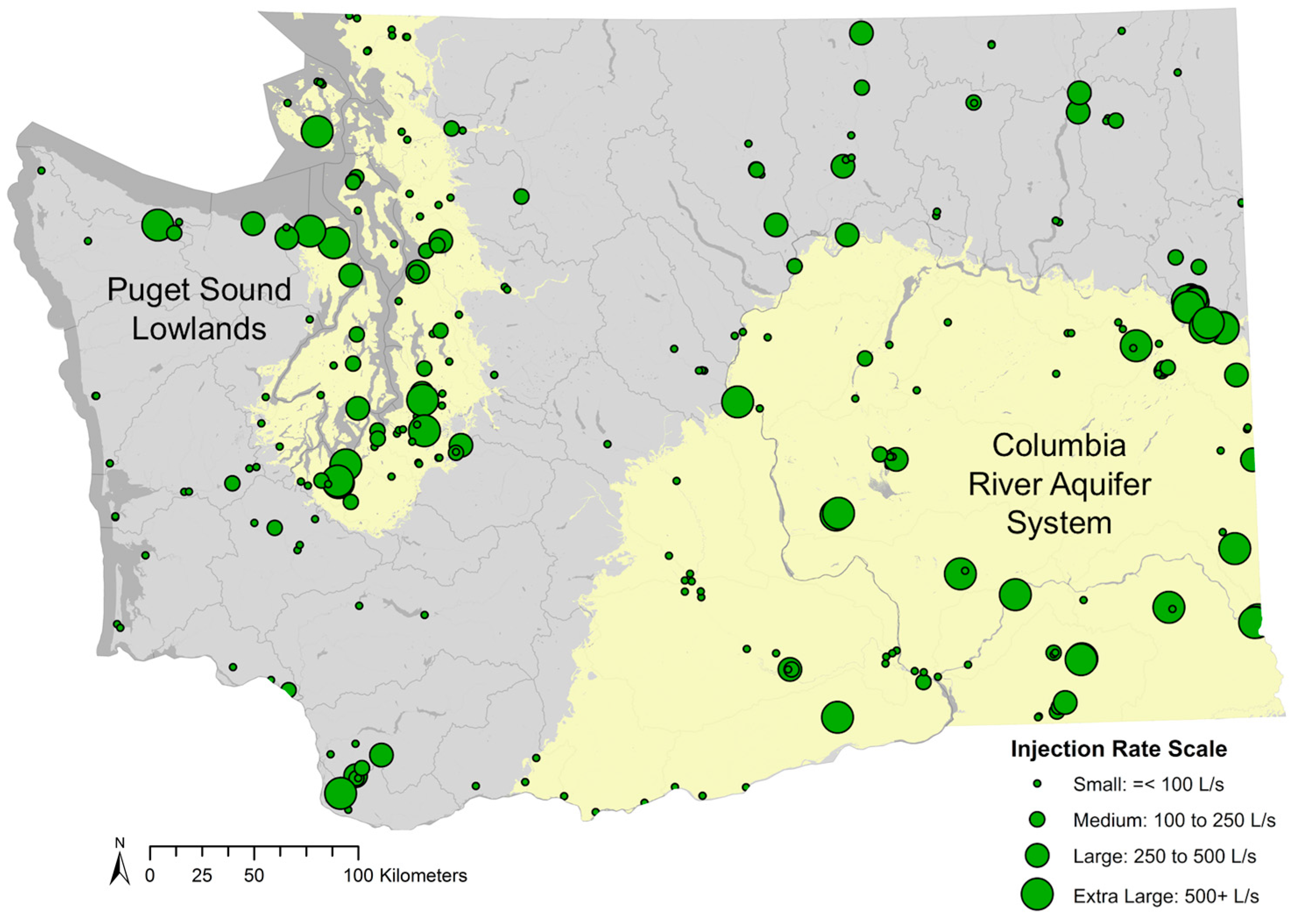
4.2.3. Assessment of Principal Aquifers in Washington
4.2.4. Watershed Scale Assessment
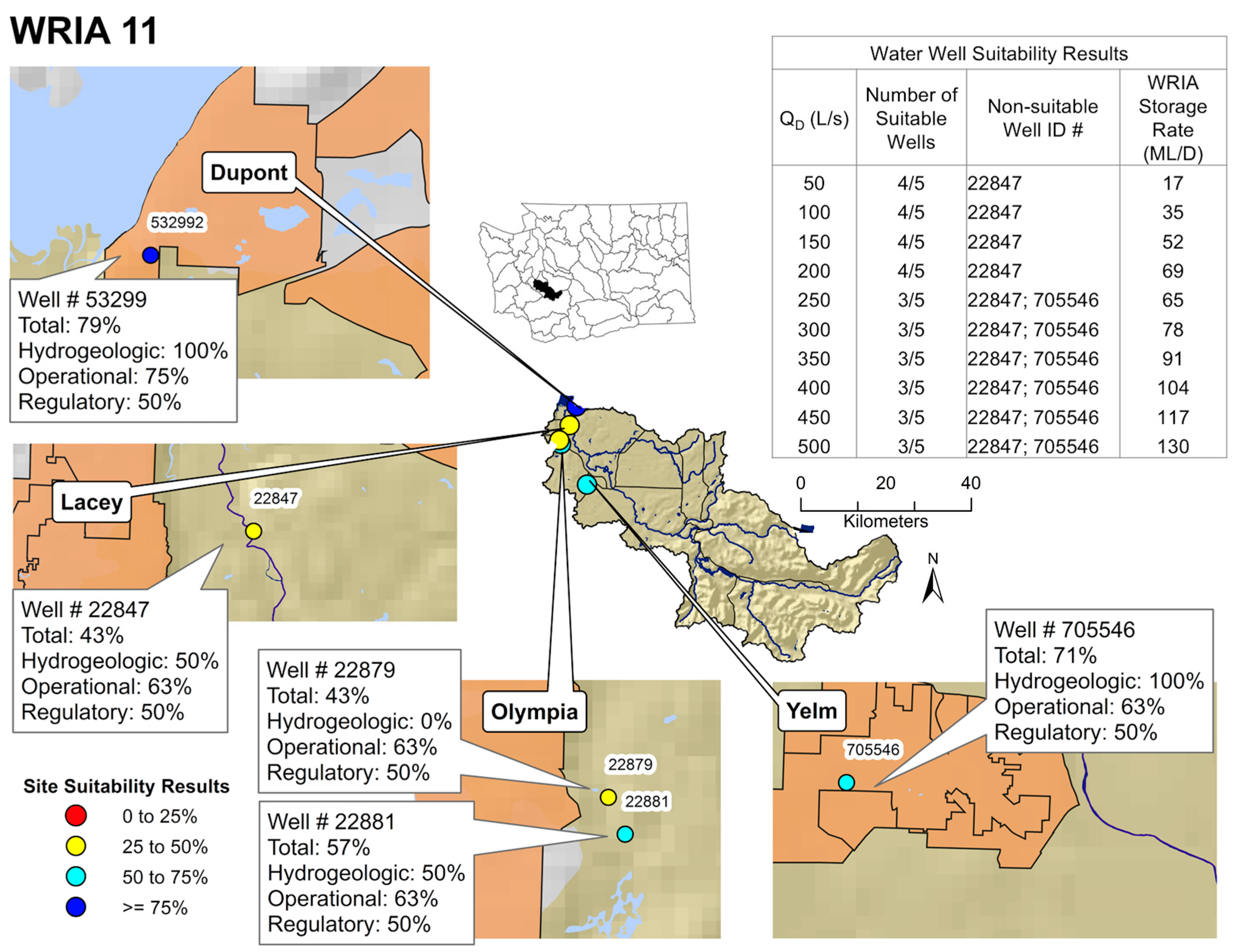
4.3. Local Scale Assessment and Application
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alley, W.M.; Healy, R.W.; LaBaugh, J.W.; Reilly, T.E. Flow and storage in groundwater systems. Science 2002, 296, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harden, B. A River Lost: The Life and Death of the Columbia; W.W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1996; ISBN 9780393316902. [Google Scholar]
- Castle, S.L; Thomas, B.F; Reager, J.T; Rodell, M.; Swenson, S.C; Famiglietti, J.S. Groundwater depletion during drought threatens future water security of the Colorado River Basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 5904–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, D.K. Groundwater Hydrology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, T. Artificial Recharge of Groundwater; Butterworth Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; ISBN 0-250-40549-0. [Google Scholar]
- Pyne, D.R. Artificial Recharge and Wells; Lewis Publishers: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1995; ISBN 10.1566700973. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Mushtaq, S.; Hanjra, M.A.; Schaeffer, J. Estimating potential costs and gains from an aquifer storage and recovery program in Australia. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliva, R.; Missimer, T. Aquifer storage and recovery: Developing sustainable water supplies. IDA J. Desalin. Water Reuse 2010, 2, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliva, R.; Missimer, T. Aquifer Storage and Recovery and Managed AQUIFER Recharge Using Wells: Planning, Design, and Operation. Methods in Water Resources Evaluation; Schlumberger Publisher: Sugarland, TX, USA, 2010; ISBN 0978853067. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchelson, A.; Muckel, D. Spreading Water for Storage Underground; US Dept. of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1937; Volume 578, p. 80.
- Babcock, H.M.; Cushing, E.M. Recharge to ground-water from floods in a typical desert wash, Pinal County, Arizona. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1942, 23, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinzer, O.E. General principles of artificial ground-water recharge. Econ. Geol. 1946, 41, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapuram, S.; Kumar, G.V.; Krishna, I.M.; Kahya, E.; Demirel, M.C. Mapping of groundwater potential zones in the Musi basin using remote sensing data and GIS. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2009, 40, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Jha, M.K.; Chowdary, V.M. Delineation of groundwater recharge zones and identification of artificial recharge sites in West Medinipur district, West Bengal, using RS, GIS and MCDM techniques. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, I.; Sankar, K.; Dar, M. Remote sensing technology and geographic information system modeling: An integrated approach towards the mapping of groundwater potential zones in Hardrock terrain, Mamundiyar basin. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, J.K.; Park, E.; Lee, S. GIS mapping of regional probabilistic groundwater potential in the area of Pohang City, Korea. J. Hydrol. 2011, 399, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, A. GIS-based groundwater spring potential mapping in the Sultan Mountains (Konya, Turkey) using frequency ratio, weights of evidence and logistic regression methods and their comparison. J. Hydrol. 2011, 411, 290–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, F. Mapping of groundwater prospective zones using remote sensing and GIS techniques: A case study from the Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2012, 70, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Oh, H.J. Application of a weights-of-evidence method and GIS to regional groundwater productivity potential mapping. J. Eviron. Manag. 2012, 96, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Rusteberg, B.; Gogu, R.C.; Ferreira, J.L.; Sauter, M. A new spatial multi-criteria decision support tool for site selection for implementation of managed aquifer recharge. J. Eviron. Manag. 2012, 99, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Garg, P.; Garg, R. Remote sensing and GIS based approach for identification of artificial recharge sites. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2671–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, H.; Boloorani, A.D.; Sabokbar, H.A.F.; Jafari, H.R.; Hamzeh, M.; Rafii, Y. Determining the most suitable areas for artificial groundwater recharge via an integrated PROMETHEE II-AHP method in GIS environment (case study: Garabaygan Basin, Iran). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Panda, S.; Kumar, K.; Sharma, C. Artificial groundwater recharge zones mapping using remote sensing and GIS: A case study in Indian Punjab. Environ. Manag. 2013, 52, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, N.; Krishna, A.P. Geospatial techniques based assessment of groundwater recharge site suitability. Int. J. Adv. Remote Sens. GIS 2013, 2, 96–109. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, S.; Alazba, A.; Amin, T. Identification of potential sites for groundwater recharge using a GIS-based decision support system in Jazan region, Saudi Arabia. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 3319–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.; Gautam, A.; Jhariya, D. Multi-criteria decision analysis for planning and management of groundwater resources in Balod District, India. Envrion. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, I.; Dissanayake, D.; Myadunna, B.; Weerasekera, W. An approach to delineate groundwater recharge potential sites in Ambalantota, Sri Lanka using GIS techniques. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.; Cheng, Y.; Lin, H.; Lee, C. Mapping groundwater recharge potential zone using a GIS approach in Hualian River, Taiwan. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2016, 26, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topper, R.; Barkmann, P.; Bird, D.; Sares, M. Artificial groundwater recharge and management. In State of the Art Water Supply Practices; Technical Report; Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission: Waukesha, WI, USA, 2004; Available online: http://www.sewrpc.org/SEWRPCFiles/Publications/TechRep/tr-043_water_supply_practices.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2016).
- Woody, J. A Preliminary Assessment of Hydrogeologic Suitability for Aquifer Storage and Recovery (ASR) in Oregon. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, C.; Ward, J.; Mirecki, J. A revised brackish water aquifer storage and recovery (ASR) site selection index for water resources management. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2465–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amineh, Z.B.; Hashemian, S.J.; Magholi, A. Integrating spatial multi criteria decision making (SMCDM) with geographic information system (GIS) for delineation of the most suitable areas for aquifer storage and recovery (ASR). J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C. Water Supply Needs and Sources Assessment Alternative Water Supply Strategies Investigation: A Tool for Assessing the Feasibility of Aquifer Storage and Recovery; Special Publication SJ; St. Johns River Water Management District: Palatka, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, C. Planning Decision Framework for Brackish Water Aquifer, Storage and Recovery (ASR) Projects. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, C.J.; Weiss, R.; Verrastro, R.; Shulbert, S. Development of an aquifer storage and recovery (ASR) site selection suitability index in support of the comprehensive everglades restoration project. J. Hydrol. 2005, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, S.; Dillon, P.; Irvine, E.; Holland, G.; Kaufman, C. Progress in Managed Aquifer Recharge in Australia; Waterlines Report Series No. 73; National Water Commission: Canberra, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, C.S.; Anderson, M.P. An assessment of aquifer storage recovery using ground water flow models. Groundwater 2006, 44, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.J.; Pollock, D.W. Assessment of managed aquifer recharge potential using ensembles of local models. Groundwater 2012, 50, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.D.; Simmons, C.T.; Dillon, P.J.; Pavelic, P. Integrated assessment of lateral flow, density effects and dispersion in aquifer storage and recovery. J. Hydrol. 2009, 370, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M. Radial Dupuit interface flow to assess the aquifer storage and recovery potential of saltwater aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanudjaja, E.H.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; De Jong, S.M.; van Geer, F.C.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Large-scale groundwater modeling using global datasets: A test case for the Rhine-Meuse basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2913–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, R.C. Water Use Trends in Washington, 1985–2005: U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet 2010-3057. 2010; p. 4. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/2010/3057/ (accessed on 11 August 2017).
- Kimbrough, R.A.; Ruppert, G.P.; Wiggins, W.D.; Smith, R.R.; Kresch, D.L. U.S. Geological Survey Water Data Report WA-05-1: Water Resources Data-Washington Water Year 2005; U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/wdr/2005/wdr-wa-05-1/ (accessed on 10 June 2017).
- Cohen, S.J.; Miller, K.A.; Hamlet, A.F.; Avis, W. Climate change and resource management in the Columbia River Basin. Water Int. 2000, 25, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, M.M.; Cuo, L.; Voisin, N.; Deems, J.S.; Hamlet, A.F.; Vano, J.A.; Mickelson, K.E.; Lee, S.Y.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Implications of 21st century climate change for the hydrology of Washington State. Clim. Chang. 2010, 102, 225–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snover, A.K.; Mote, P.W.; Whitely Binder, L.C.; Hamlet, A.F.; Mantua, N.J. Uncertain Future: Climate Change and Its Effects on Puget Sound, 2005. Available online: https://digital.lib.washington.edu/researchworks/handle/1773/38383 (accessed on 2 October 2017).
- Dalton, M.; Mote, P.; Snover, A. Climate Change in the Northwest: Implications for our Landscapes, Waters, and Communities; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vaccaro, J.J.; Hansen, A.J.; Jones, M.A. Hydrogeologic framework of the Puget Sound aquifer system, Washington and British Columbia (No. 1424); U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. Available online: https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/pp1424D (accessed on 15 February 2017).
- Brocher, T.M.; Parsons, T.; Blakely, R.J.; Christensen, N.I.; Fisher, M.A.; Wells, R.E. Upper crustal structure in Puget Lowland, Washington: Results from the 1998 seismic hazards investigation in Puget Sound. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2001, 106, 13541–13564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolan, T.L.; Reidel, S.P.; Beeson, M.H.; Anderson, J.L.; Fecht, K.R.; Swanson, D.A. Revisions to the estimates of the areal extent and volume of the Columbia River Basalt Group. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap. 1989, 239, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Washington State Legislature. Chapter WAC 173–200 WAC. Water Quality Standards for Groundwaters of the State of Washington. Available online: http://apps.leg.wa.gov/wac/default.aspx?cite=173-200 (accessed on 7 August 2017).
- Washington State Legislature. Water Resources Act of 1971. Chapter 90.54. RCW. Available online: http://app.leg.wa.gov/rcw/default.aspx?cite=90.54 (accessed on 7 August 2017).
- Washington State Legislature. Chapter 173–175 WAC. Underground Artificial Storage and Recovery. Available online: http://apps.leg.wa.gov/wac/default.aspx?cite=173-157 (accessed on 5 August 2017).
- Washington State Department of Ecology. Water Resources Explorer. 2012. Available online: https://fortress.wa.gov/ecy/waterresources/map/WaterResourcesExplorer.aspx (accessed on 7 April 2017).
- Bear, J.; Jacobs, M. On the movement of water bodies injected into aquifers. J. Hydrol. 1965, 3, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razack, M.; Huntley, D. Assessing transmissivity from specific capacity in a large and heterogeneous alluvial aquifer. Groundwater 1991, 29, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, M.L. Recovering fresh water stored in saline limestone aquifers. Groundwater 1986, 24, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington State Department of Health. Division of Environmental Health Office of Drinking Water. Available online: https://fortress.wa.gov/doh/eh/portal/odw/si/Intro.aspx (accessed on 9 May 2014).
- Washington State Department of Ecology. Map of 16 Fish-Critical Basins. Available online: http://www.ecy.wa.gov/programs/wr/instream-flows/Images/pdfs/16fishbasins.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2014).
- Joint Natural Resources Cabinet. Statewide Strategy to Recover Salmon. Extinction Is not an Option; State of Washington, Governor’s Salmon Recovery Office: Olympia, WA, USA, 1999; p. 396.
- Quinn, T.P. The Behavior and Ecology of Pacific Salmon and Trout; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Washington State University. Columbia River Basin: Long-Term Water Supply and Demand Forecast; Publication No. 12-12-001; Washington State Department of Ecology: Olympia, WA, USA, 2011; p. 452.
- Theis, C. The relation between the lowering of the peizometric surface and the rate and duration of discharge of a well using groundwater storage. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1935, 16, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.; Jacob, C. A generalized graphical method for evaluating formation constants and summarizing well-field history. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1946, 27, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloetscher, F. Manual of Water Supply Practices—M63 Aquifer Storage and Recovery, 1st ed.; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA, 2015; p. 146. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, D.; Jones, J. Geological Survey Open-File Report: Numerical Model Analysis of the Effects of Ground-Water Withdraws on Discharge to Streams and Springs in Small Basins Typical of the Puget Sound Lowland; U.S. Dept. of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; p. 81.
- United States Census Bureau. Washington State and County Quick Facts. Available online: https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/WA (accessed on 16 October 2017).



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gibson, M.T.; Campana, M.E.; Nazy, D. Estimating Aquifer Storage and Recovery (ASR) Regional and Local Suitability: A Case Study in Washington State, USA. Hydrology 2018, 5, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology5010007
Gibson MT, Campana ME, Nazy D. Estimating Aquifer Storage and Recovery (ASR) Regional and Local Suitability: A Case Study in Washington State, USA. Hydrology. 2018; 5(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology5010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleGibson, Maria T., Michael E. Campana, and Dave Nazy. 2018. "Estimating Aquifer Storage and Recovery (ASR) Regional and Local Suitability: A Case Study in Washington State, USA" Hydrology 5, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology5010007
APA StyleGibson, M. T., Campana, M. E., & Nazy, D. (2018). Estimating Aquifer Storage and Recovery (ASR) Regional and Local Suitability: A Case Study in Washington State, USA. Hydrology, 5(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology5010007




