Balancing Hydrological Sustainability and Heritage Conservation: A Decadal Analysis of Water-Yield Dynamics in the Honghe Hani Rice Terraces
Abstract
1. Introduction
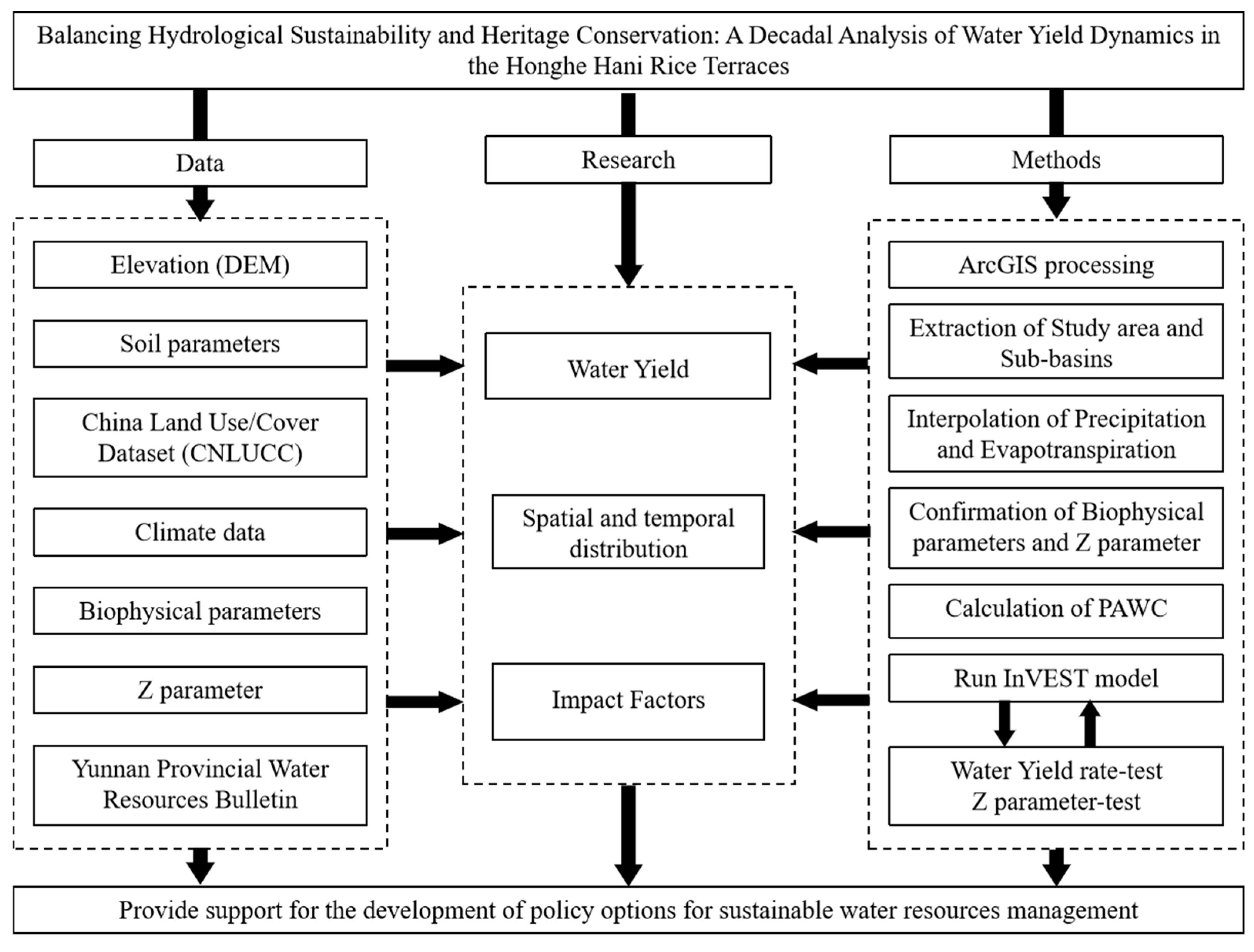
2. Materials and Methods
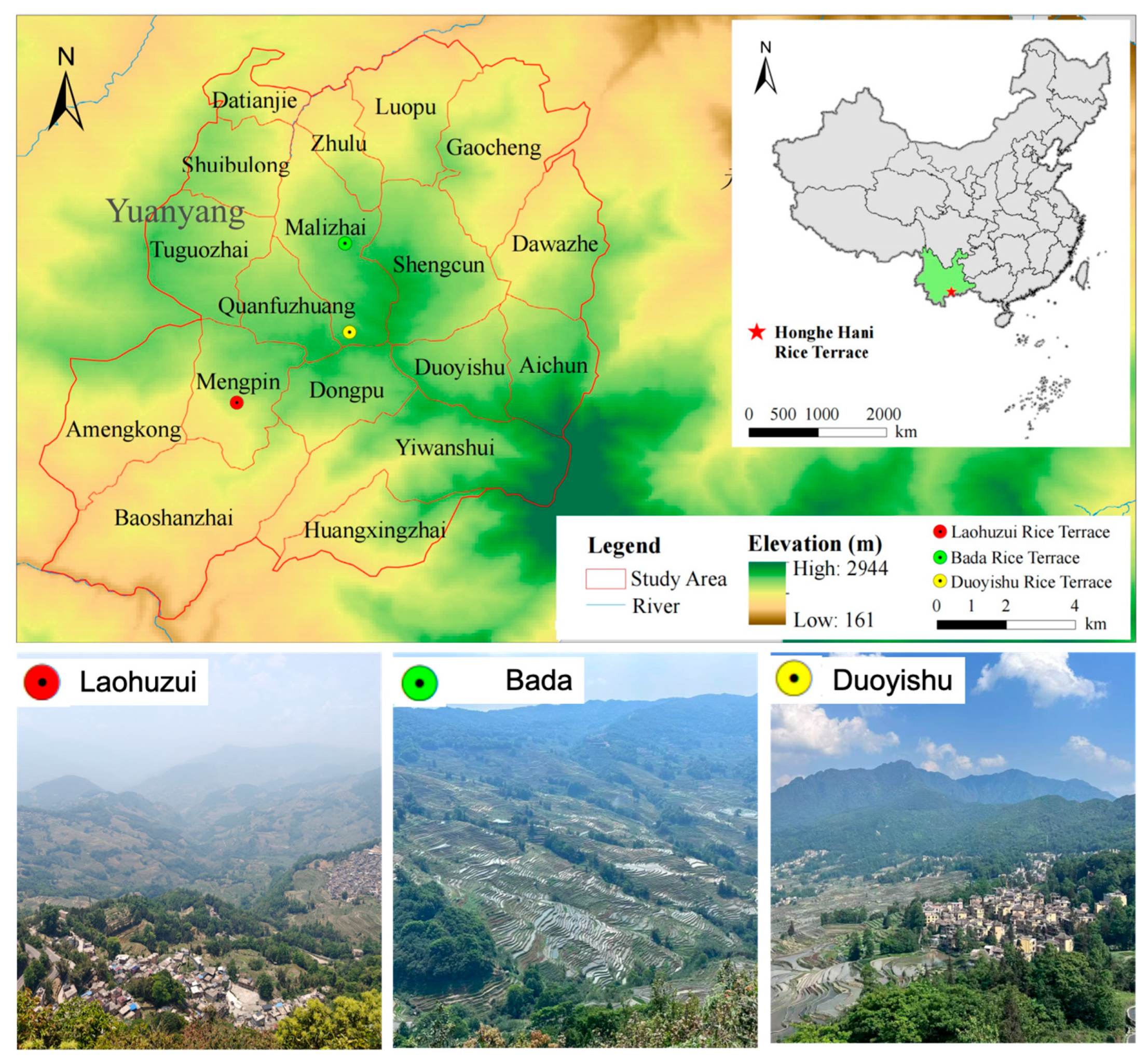
2.1. Study Area and Research Design
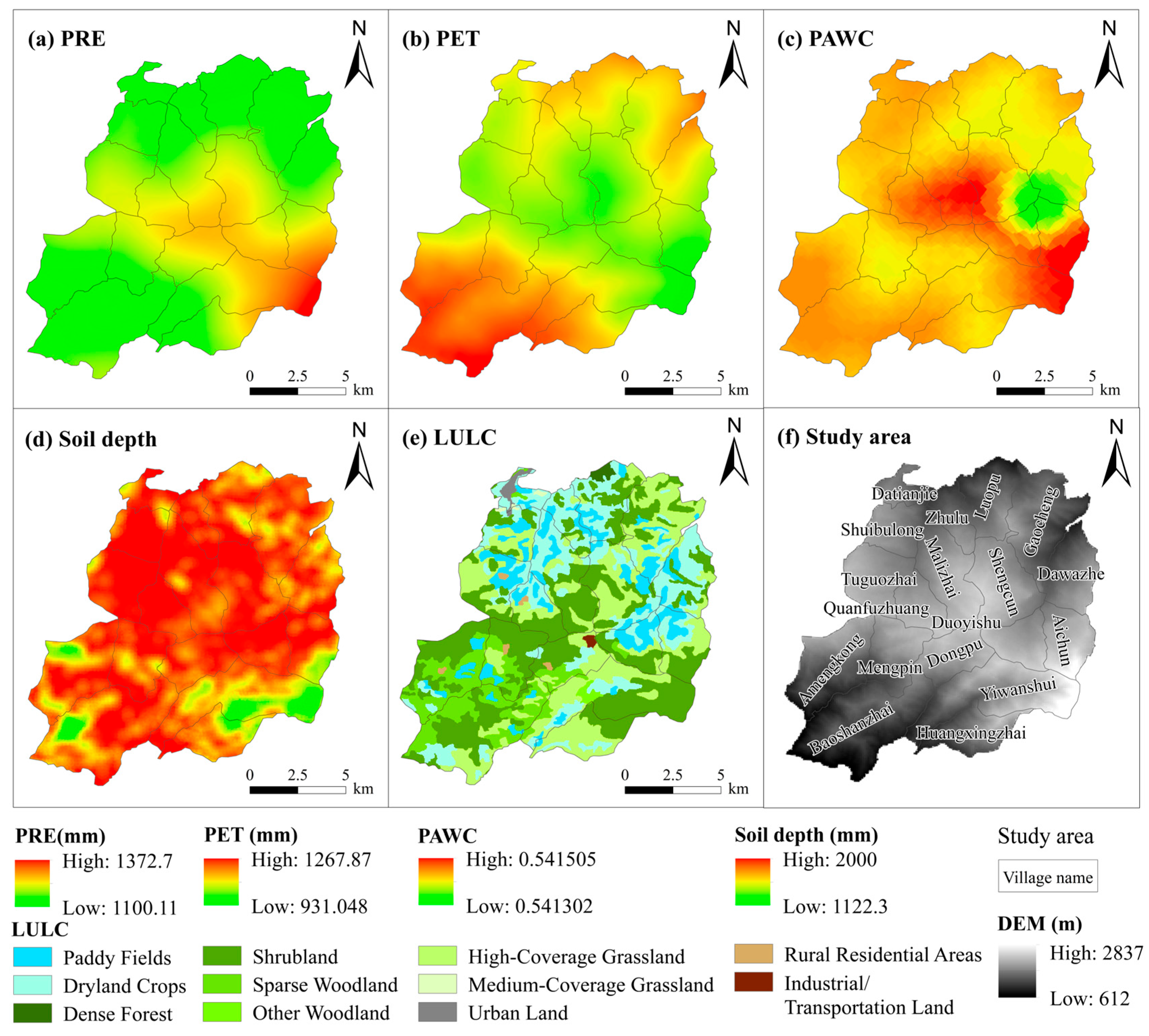
2.2. Data Collection and Preprocessing
2.3. Water-Yield Modeling Using the InVEST Model with Validation
2.4. Spatial Analysis of Water-Yield Patterns
2.5. Driver and Interaction Analysis Using the Geographic Detector Model
3. Results
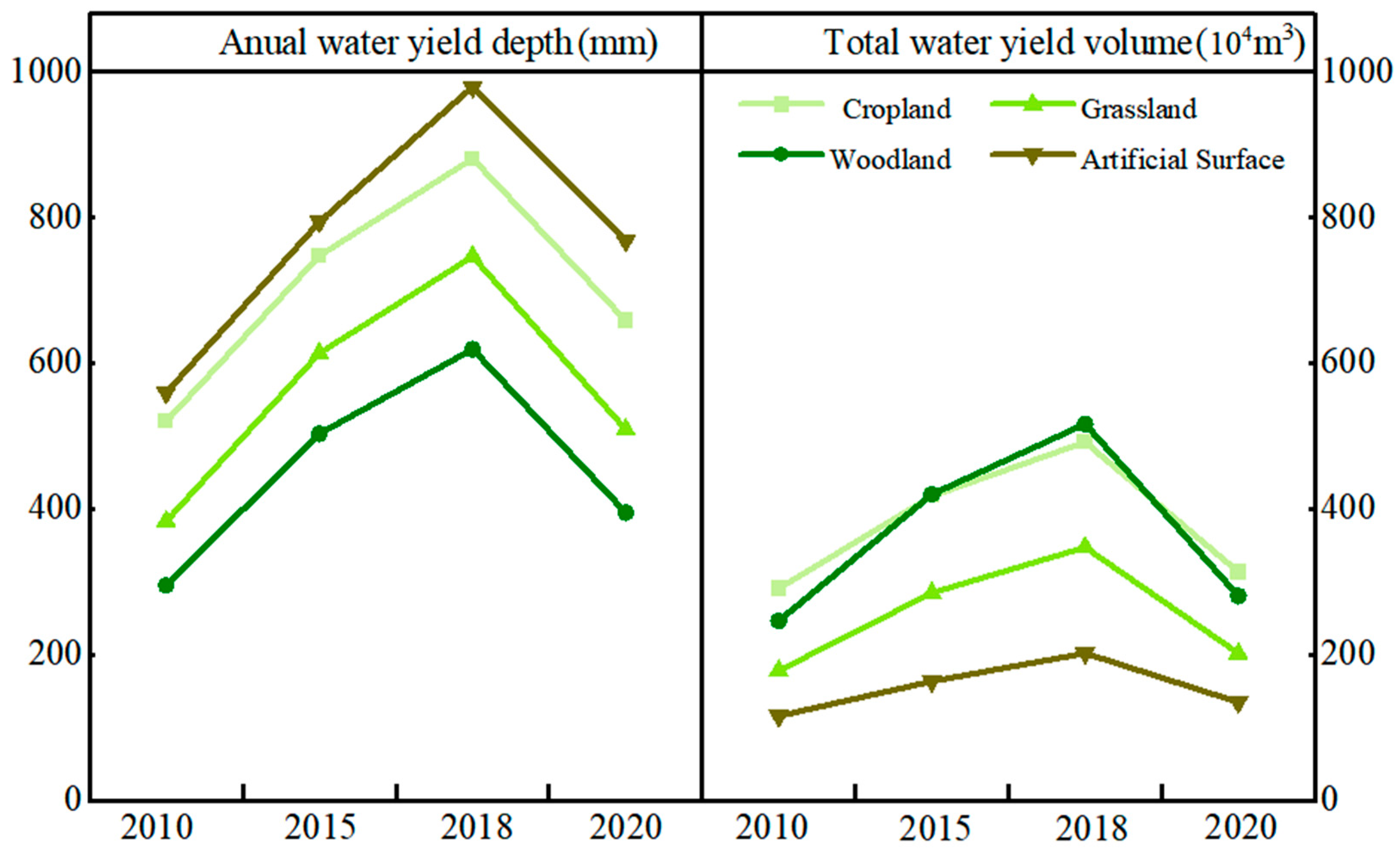
3.1. Rising and Falling Water Yields in the Hani Terraces
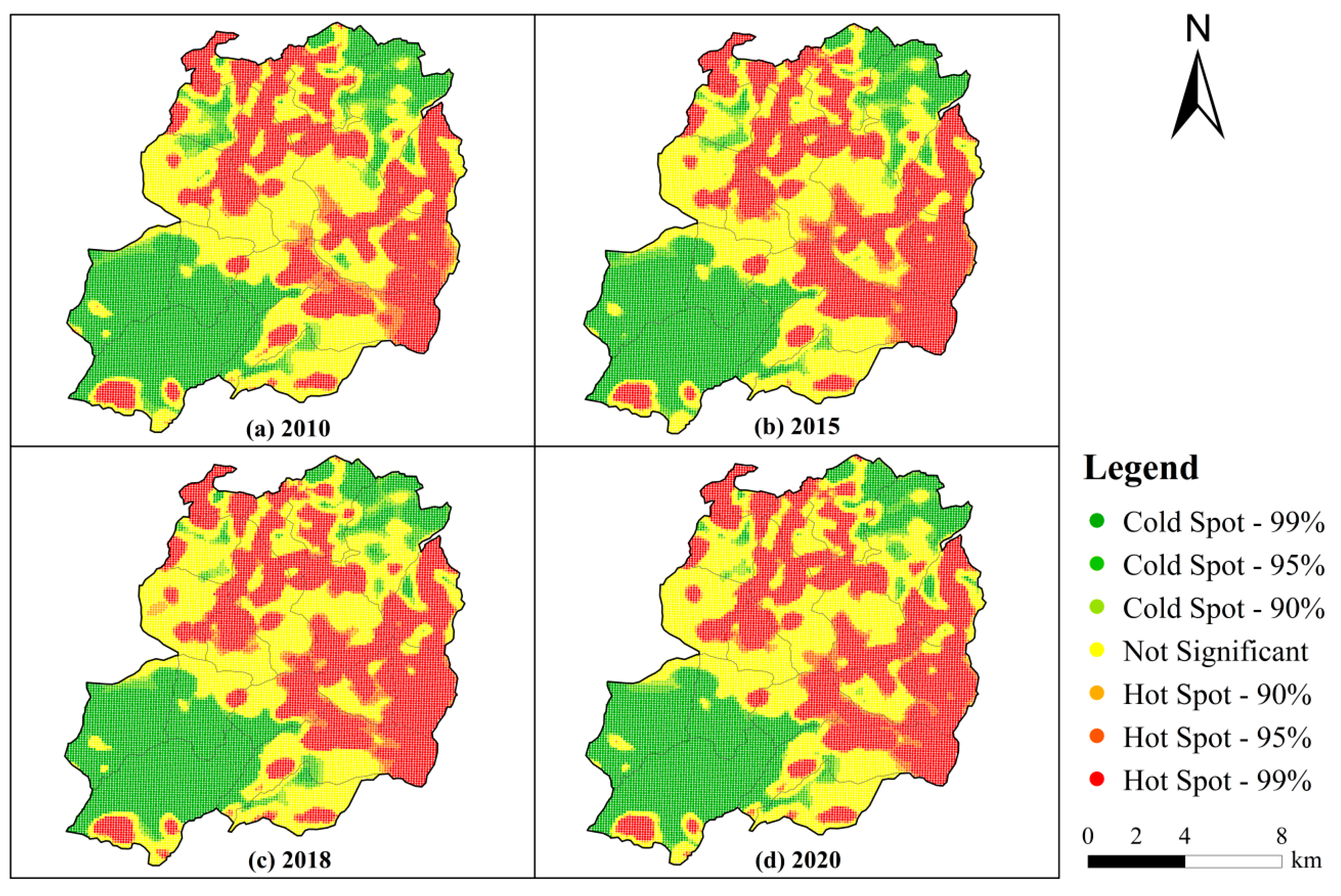
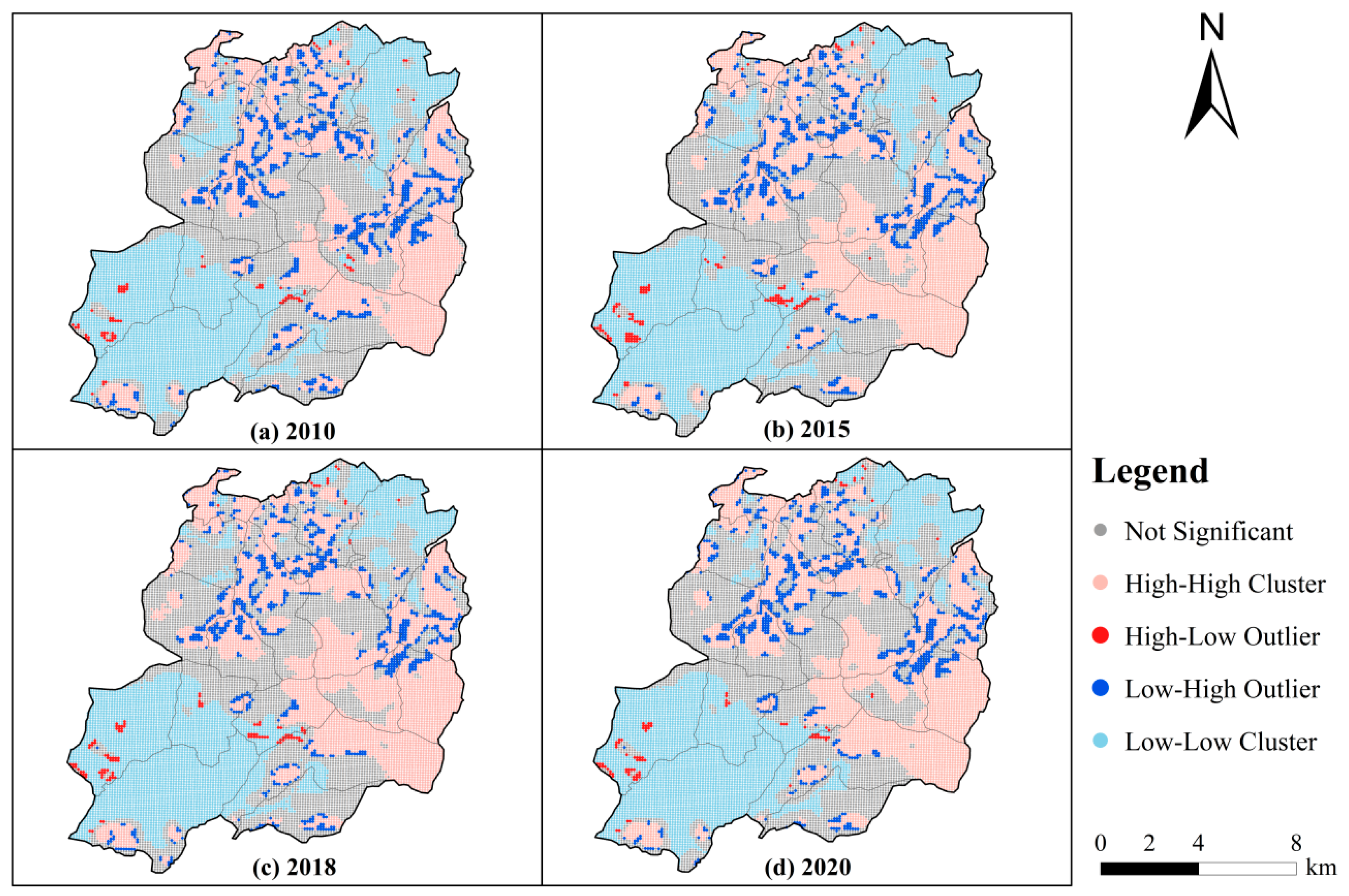
3.2. Growing High-Yield and Shrinking Low-Yield Zones
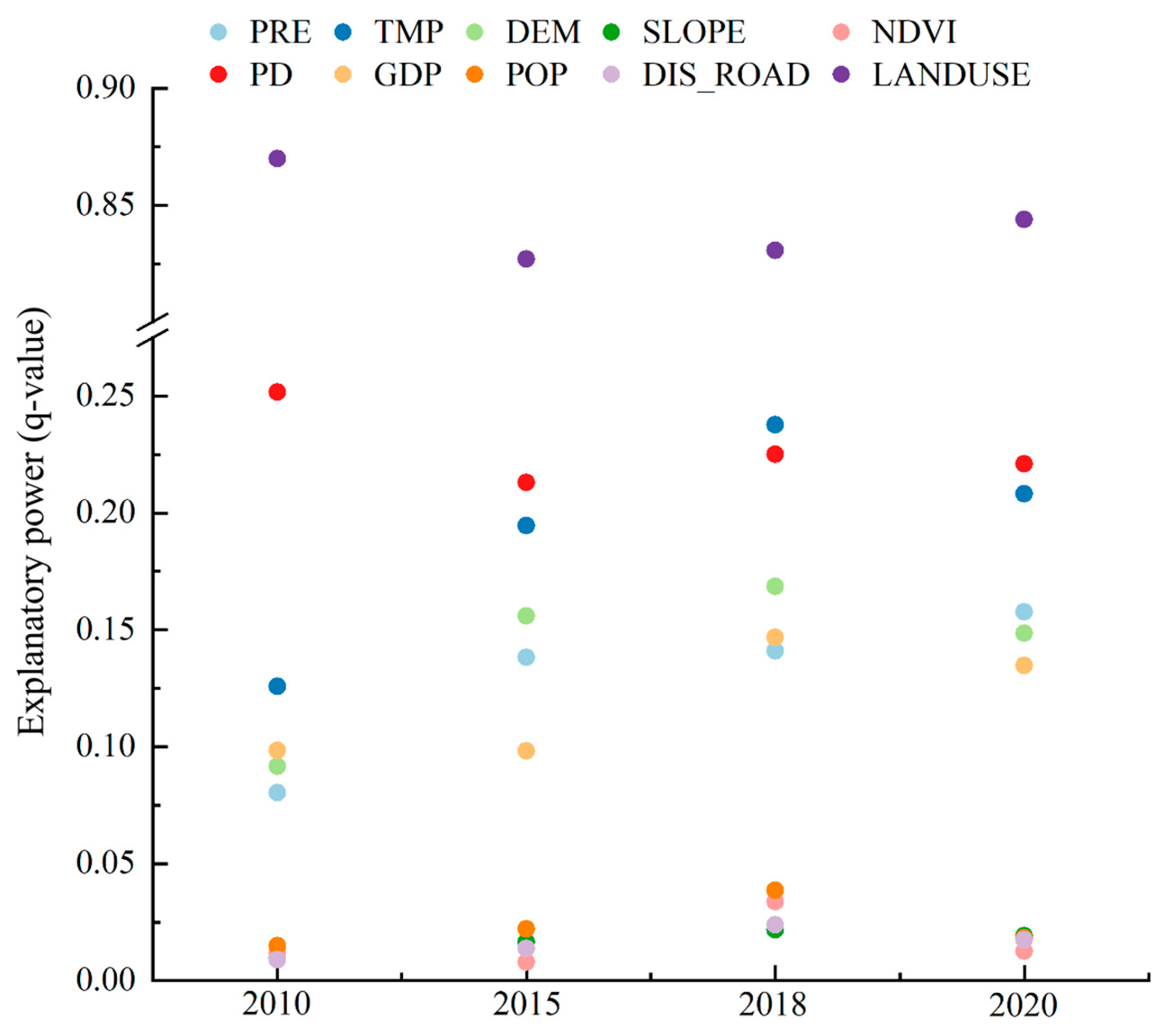
3.3. Land-Use Leads and Climate Enhances Water-Yield Changes
4. Discussion
4.1. Land-Use and Climate Synergies
4.2. Spatial Mismatches in Water Provisioning
4.3. Policy Implications for Heritage Landscapes
4.4. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Z.; Song, W.; Ma, J.; Ma, J.; He, X. Dynamic change characteristics of soil moisture and its relationship with precipitation in Hani Rice Terraces water source area. Water 2022, 14, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.L.; Zhou, S.Y. Human-environment system boundaries: A case study of the Honghe Hani Rice Terraces as a world heritage cultural landscape. Sustainability 2015, 7, 10733–10755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, G.; Jin, Z. Hani Rice Terraces of Honghe-the harmonious landscape of nature and humans. Landsc. Res. 2015, 40, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.F.; Gao, J.C.; Xu, Y.; Nie, Z.J.; Fang, J.H.; Zhou, Q.L.; Xu, G.C.; Shao, N.L.; Xu, D.P.; Xu, P.; et al. Biodiversity and sustainability of the integrated rice-fish system in Hani terraces, Yunnan province, China. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xu, G.; Shen, N.; Nie, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Y.; He, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Valuation of ecosystem services for the sustainable development of Hani Terraces: A Rice-Fish-Duck integrated farming model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.Z.; Ding, Y.X.; Wen, Z.M.; Chen, Y.M.; Cao, Y.; Ren, J.Y. Spatiotemporal change and trend analysis of potential evapotranspiration over the Loess Plateau of China during 2011–2100. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Z.-Q.; Jiao, Y.-M.; Liu, Z.-L.; Liu, C.-J.; Gao, X.; Ding, Y.-P.; Zhao, D.-M. Evaluation on water eutrophication and retention effect in wetland landscape of Hani Rice Terraces. Chin. J. Ecol. 2018, 37, 3413–3421. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.M.; Zhao, D.M.; Ding, Y.P.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Q.E.; Qiu, Y.M.; Liv, C.J.; Liv, Z.L.; Zha, Z.Q.; Li, R. Performance evaluation for four GIS-based models purposed to predict and map landslide susceptibility: A case study at a World Heritage site in Southwest China. Catena 2019, 183, 104221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.H.; Iankova, K.; Zhang, Y.; McDonald, T.; Qi, X.G. The role of self-gentrification in sustainable tourism: Indigenous entrepreneurship at Honghe Hani Rice Terraces World Heritage Site, China. J. Sustain. Tour. 2016, 24, 1262–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Song, Y.X.; Sun, Y.H. Response relationship between tourism disturbance and community resilience in agricultural heritage site: A case study of Honghe Hani Rice Terraced System. J. Mt. Sci. 2025, 22, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.M.; Wang, M.H.; Yu, J.J.; Wall, G.; Jin, M. Measuring tourism impacts on community well-being at the Hani Rice Terraces GIAHS Site, Yunnan Province of China. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2023, 36, 796–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Mao, Z.; Chen, X.; Yi, C. Resilience measurement of rural settlement in Hani terrace field heritage in Yuanyang and its optimization strategy: A case study of Duoyishu village. Econ. Geogr. 2023, 43, 220–228. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Lin, H.; Zhang, C. Locally situated rights and the ‘doing’ of responsibility for heritage conservation and tourism development at the cultural landscape of Honghe Hani Rice Terraces, China. J. Sustain. Tour. 2021, 29, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.M.; Zhao, D.M.; Xu, Q.E.; Liu, Z.L.; Ding, Z.Q.; Ding, Y.P.; Liu, C.J.; Zha, Z.Q. Mapping lateral and longitudinal hydrological connectivity to identify conservation priority areas in the water-holding forest in Honghe Hani Rice Terraces World Heritage Site. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.Y.; Jiao, Y.M.; Liang, L.H. Strengthening the socio-ecological resilience of forest-dependent communities: The case of the Hani Rice Terraces in Yunnan, China. For. Policy Econ. 2012, 22, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Min, Q.W.; Zhang, C.Q.; He, L.L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; Tian, M.; Xiong, Y. Traditional culture as an important power for maintaining agricultural landscapes in cultural heritage sites: A case study of the Hani terraces. J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 25, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.D. Effects of terracing practices on water erosion control in China: A meta analysis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.Q.; Dong, N.; Wu, H.J.; Li, S. The projected futures of water resources vulnerability under climate and socioeconomic change in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.S.; Long, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, D.S.; Wu, H.J.; Li, S. Identifying the drivers of water yield ecosystem service: A case study in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G.; Li, Z. Estimation of soil erosion and evaluation of soil and water conservation benefit in terraces under extreme precipitation. Water 2022, 14, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Nie, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhu, D. Advantages and disadvantages of terracing: A comprehensive review. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, M.A.; Herath, S. Quantifying the role of traditional rice terraces in regulating water resources: Implications for management and conservation efforts. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 42, 885–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Liu, C.; Gao, X.; Xu, Q.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Z. Impacts of moisture sources on the isotopic inverse altitude effect and amount of precipitation in the Hani Rice Terraces region of the Ailao Mountains. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D. Beneficial Water Resources and Harmonious Relationship: A Study on Irrigation Order and Ethnic Relations in Hani Rice Terraces. Ph.D. Thesis, Yunan University, Kunming, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.B.; Xu, J.C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhai, D.L.; Chen, H.F.; Li, Q.; Zhao, G.J. Paddy rice phenological mapping throughout 30-years satellite images in the Honghe Hani Rice Terraces. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; Wu, S. China Multi-Period Land Use Remote Sensing Monitoring Dataset (CNLUCC). Data Registration and Publication System for Resources and Environmental Sciences. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, G.; Pan, J.; Feng, X. Distribution of available soil water capacity in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2005, 15, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Yang, J.; Qiu, M.; Liu, Z. Spatial-temporal distribution and the influencing factors of water conservation function in Yunnan, China. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Using InVEST to evaluate water yield services in Shangri-La, Northwestern Yunnan, China. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Lun, F.; He, L.; Cao, Z.; Min, Q.W.; Bai, Y.Y.; Liu, M.C.; Cheng, S.K.; Li, W.H.; Fuller, A.M. Exploring the state of retention of traditional ecological knowledge (TEK) in a Hani Rice Terrace village, Southwest China. Sustainability 2014, 6, 4497–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhou, S.; Yu, B.; Song, J. Deforestation-induced runoff changes dominated by forest-climate feedbacks. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadp3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.X.; Huang, G.X.; Tong, S.C.; Chen, W.; Song, Y.H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.H.; Jiang, P.F. Assessing the impacts of rice terraces and ponds on the sediment and phosphorus loads in a typical hilly watershed of three gorge reservoir, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 459, 142560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, J.R.; Vincent, J.R.; Auffhammer, M.; Moya, P.F.; Dobermann, A.; Dawe, D. Rice yields in tropical/subtropical Asia exhibit large but opposing sensitivities to minimum and maximum temperatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14562–14567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Mcdermid, S.S.; Valdivia, R.O.; Sundaram, P. Climate change mitigation and adaptation for rice-based farming systems in the Red River Delta, Vietnam. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2024, 5, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldscheider, N. A holistic approach to groundwater protection and ecosystem services in karst terrains. Carbonates Evaporites 2019, 34, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangash, R.F.; Passuello, A.; Sanchez-Canales, M.; Terrado, M.; Lopez, A.; Elorza, F.J.; Ziv, G.; Acuna, V.; Schuhmacher, M. Ecosystem services in Mediterranean river basin: Climate change impact on water provisioning and erosion control. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Preti, F.; Romano, N. Terraced landscapes: From an old best practice to a potential hazard for soil degradation due to land abandonment. Anthropocene 2014, 6, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folke, C.; Polasky, S.; Rockstrom, J.; Galaz, V.; Westley, F.; Lamont, M.; Scheffer, M.; Osterblom, H.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S., 3rd; et al. Our future in the Anthropocene biosphere. Ambio 2021, 50, 834–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leimona, B.; van Noordwijk, M.; de Groot, R.; Leemans, R. Fairly efficient, efficiently fair: Lessons from designing and testing payment schemes for ecosystem services in Asia. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 12, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElwee, P.; Nghiem, T.; Le, H.; Vu, H.; Tran, N. Payments for environmental services and contested neoliberalisation in developing countries: A case study from Vietnam. J. Rural. Stud. 2014, 36, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, M.M.; Bantayan, N.C.; Dizon, J.T.; Sajise, A.J.U.; Codilan, A.L.; Canceran, M.S. Community-based resource assessment and management planning for the rice terraces of Hungduan, Ifugao, Philippines. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2015, 18, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, K.L.; Gonzalvo, C.M.; Baggo, J.C. Balancing tradition and innovation: The role of environmental conservation agriculture in the sustainability of the Ifugao Rice Terraces. Agriculture 2025, 15, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carollo, M.; Butera, I.; Revelli, R. Water savings and urban storm water management: Evaluation of the potentiality of rainwater harvesting systems from the building to the city scale. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adade Williams, P.; Sikutshwa, L.; Shackleton, S. Acknowledging indigenous and local knowledge to facilitate collaboration in landscape approaches—Lessons from a systematic review. Land 2020, 9, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.S.; Hewitt, R.J. Understanding climate risks to world cultural heritage: A systematic analysis and assessment framework for the case of Spain. Heritage Science 2024, 12, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honey, M. Ecotourism and Sustainable Development. Who Owns Paradise? Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Berkes, F. Advanced Introduction to Community-Based Conservation; Edward Elgar Publishing: Northampton, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, N.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.B.; Huang, B.; Zhang, L.Q.; Mathiopoulos, P.T. Land-use mapping for high-spatial resolution remote sensing image via deep learning: A review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 5372–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bretz, M.; Dewan, M.A.A.; Delavar, M.A. Machine learning in modelling land-use and land cover-change (LULCC): Current status, challenges and prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.B.; Scheiner, S.M.; Schoolmaster, D.R., Jr. Structural Equation Modeling: Building and Evaluating Causal Models. In Ecological Statistics: Contemporary Theory and Application; Oxford University Press: Cary, NC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Takahashi, Y.; Strosnider, W.H.J.; Kogure, T.; Wang, B.; Wu, P.; Zhu, L.; Dong, Z. Identification and quantification of contributions to karst groundwater using a triple stable isotope labeling and mass balance model. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Land-Use/Land-Cover Categories | Land-Use/Land-Cover Type | Vegetation Cover (1 = Yes, 0 = No) | Crop Coefficient (Kc) | Maximum Root Depth (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cropland | Paddy fields | 1 | 0.7 | 2000 |
| Dryland crops | 1 | 0.5 | 300 | |
| Woodland | Dense forest | 1 | 1 | 3000 |
| Shrubland | 1 | 0.85 | 1000 | |
| Sparse woodland | 1 | 1 | 3000 | |
| Other woodland | 1 | 0.85 | 1000 | |
| Grassland | High-coverage grassland | 1 | 0.65 | 1700 |
| Medium-coverage grassland | 1 | 0.5 | 1300 | |
| Artificial surface | Urban land | 0 | 0.3 | 1 |
| Rural residential areas | 0 | 0.5 | 100 | |
| Industrial/transportation land | 0 | 0.3 | 1 |
| Primary Category | Secondary Category | Factors | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural environment | Climate factors | Annual precipitation (PRE) | National Earth System Science Data Center (https://www.geodata.cn, accessed on 1 May 2024) |
| Annual mean temperature (TMP) | |||
| Topographic factors | Elevation (DEM) | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/) | |
| Slope (P) | |||
| Socio-economics | Ecological factors | Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | Resource and Environmental Science Data Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 1 May 2024) |
| Economic level | Gross domestic product (GDP) | ||
| Social development | Population density (POP) | WorldPop dataset (https://www.worldpop.org, accessed on 1 May 2024) | |
| Transportation and location | Distance to roads (DIS_ROAD) | OpenStreetMap data (https://www.geofabrik.de); Euclidean distance calculated using ArcGIS | |
| Land use | Land-use types (LANDUSE) | Resource and Environmental Science Data Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 1 May 2024) | |
| Cropland fragmentation (PD) | Calculated from land-use/land-cover data using ArcGIS and Fragstats | ||
| Land-use diversity (SHDI) |
| Interaction | q-Value | Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 2015 | 2018 | 2020 | ||
| PRE and LANDUSE | 0.977 | 0.974 | 0.964 | 0.977 | NE (2010, 2015), BE (2018, 2020) |
| TMP and LANDUSE | 0.969 | 0.969 | 0.972 | 0.969 | BE |
| DEM and LANDUSE | 0.966 | 0.96 | 0.964 | 0.966 | BE |
| GDP and LANDUSE | 0.861 | 0.862 | 0.845 | 0.859 | BE |
| DIS_ROAD and LANDUSE | 0.859 | 0.844 | 0.848 | 0.858 | NE (2010, 2015), BE (2018, 2020) |
| SLOPE and LANDUSE | 0.858 | 0.838 | 0.843 | 0.856 | BE |
| NDVI and LANDUSE | 0.856 | 0.834 | 0.839 | 0.861 | BE (2010–2018), NE (2020) |
| POP and LANDUSE | 0.847 | 0.831 | 0.834 | 0.847 | BE |
| PD and LANDUSE | 0.846 | 0.829 | 0.833 | 0.846 | BE |
| TMP and PD | 0.428 | 0.472 | 0.5 | 0.466 | NE |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, L.; Lyu, Y.; Miao, L.; Li, S. Balancing Hydrological Sustainability and Heritage Conservation: A Decadal Analysis of Water-Yield Dynamics in the Honghe Hani Rice Terraces. Hydrology 2025, 12, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060135
Huang L, Lyu Y, Miao L, Li S. Balancing Hydrological Sustainability and Heritage Conservation: A Decadal Analysis of Water-Yield Dynamics in the Honghe Hani Rice Terraces. Hydrology. 2025; 12(6):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060135
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Linlin, Yunting Lyu, Linxuan Miao, and Sen Li. 2025. "Balancing Hydrological Sustainability and Heritage Conservation: A Decadal Analysis of Water-Yield Dynamics in the Honghe Hani Rice Terraces" Hydrology 12, no. 6: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060135
APA StyleHuang, L., Lyu, Y., Miao, L., & Li, S. (2025). Balancing Hydrological Sustainability and Heritage Conservation: A Decadal Analysis of Water-Yield Dynamics in the Honghe Hani Rice Terraces. Hydrology, 12(6), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12060135








