Leaky Dams as Nature-Based Solutions in Flood Management Part I: Introduction and Comparative Efficacy with Conventional Flood Control Infrastructure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Natural and Man-Made Flood Control Methods
3. NBSs vs. Traditional Engineering Solutions
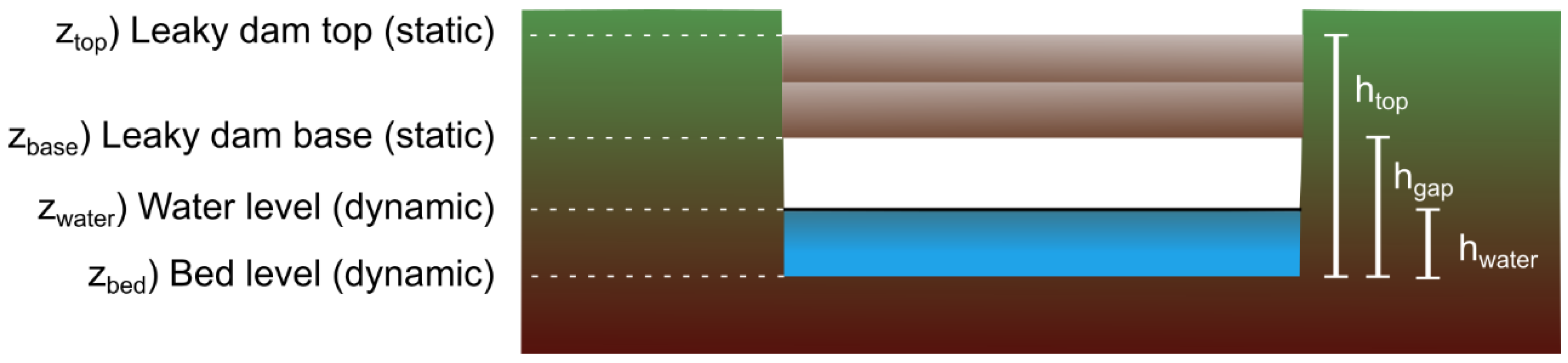
4. Overview of Leaky Dams
4.1. Historical Context and Evolution
4.2. Types of Leaky Dams
4.2.1. Natural Leaky Dams
Natural Woody Debris Dams
Brushwood Dams
4.2.2. Engineered Leaky Dams
Wooden Board Dams
Rock and Boulder Dams
4.2.3. Hybrid Leaky Dams
Wood–Rock Hybrid Dams
Geotextile-Assisted Dams
4.2.4. Temporary and Movable Leaky Dams
Seasonal Leaky Dams
Mobile Leaky Dams
4.3. Distinction Between Leaky Dams and Traditional Engineered Dams
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allaire, M. Socio-economic impacts of flooding: A review of the empirical literature. Water Secur. 2018, 3, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, Y. Economic impact of floods in the Indian states. Environ. Dev. Econ. 2019, 25, 267–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentschler, J.; Salhab, M.; Jafino, B.A. Flood Exposure and Poverty in 188 Countries. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, Z.; Wang, C. Cost of high-level flooding as a consequence of climate change driver?: A case study of China’s flood-prone regions. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrawi, J.; Ewea, H.; Kamis, A.; Elhag, M. Potential flood risk due to urbanization expansion in arid environments, Saudi Arabia. Nat. Hazards 2020, 104, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Week, D.A.; Wizor, C.H. Effects of Flood on Food Security, Livelihood and Socio-economic Characteristics in the Flood-prone Areas of the Core Niger Delta, Nigeria. Asian J. Geogr. Res. 2020, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hussein, A.A.M.; Khan, S.; Ncibi, K.; Hamdi, N.; Hamed, Y. Flood Analysis Using HEC-RAS and HEC-HMS: A Case Study of Khazir River (Middle East—Northern Iraq). Water 2022, 14, 3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrich, C.T.; Tate, E.; Larson, S.E.; Zhou, Y. Measuring social equity in flood recovery funding. Environ. Hazards 2019, 19, 228–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar Reaños, M.A. Floods, flood policies and changes in welfare and inequality: Evidence from Germany. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 180, 106879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tota-Maharaj, K.; Karunanayake, C.; Cheddie, D.; Azamathulla, H.M.; Rathnayake, U. Exploring Granular Filter Media in Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS) for Stormwater Pollutant Adsorption: A Pilot Study. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 210, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srishantha, U.; Rathnayke, U. Sustainable urban drainage systems (SUDS)—What it is and where do we stand today? Eng. Appl. Sci. Res. 2017, 44, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Ren, B.; He, B.; Nover, D. Influence assessment of new Inner Tube Porous Brick with absorbent concrete on urban floods control. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, M.; Ellingwood, B.R.; Mahmoud, H.N. The Role of Urban Growth in Resilience of Communities Under Flood Risk. Earth’s Future 2020, 8, e2019EF001382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, W.; Kim, J.-H.; Li, M.-H.; Brown, R.D.; Jaber, F.H. How does increasing impervious surfaces affect urban flooding in response to climate variability? Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Bourke, R. Urbanization impacts on flood risks based on urban growth data and coupled flood models. Nat. Hazards 2021, 106, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makumbura, R.K.; Samarasinghe, J.; Rathnayake, U. Multidecadal Land Use Patterns and Land Surface Temperature Variation in Sri Lanka. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2022, 2022, 2796637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarasinghe, J.T.; Gunathilake, M.B.; Makubura, R.K.; Arachchi, S.M.; Rathnayake, U. Impact of Climate Change and Variability on Spatiotemporal Variation of Forest Cover; World Heritage Sinharaja Rainforest, Sri Lanka. For. Soc. 2022, 6, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuller, M.; Schoenholzer, K.; Lienert, J. Creating effective flood warnings: A framework from a critical review. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, L.J.; Cranston, M.D.; White, C.J.; Kelly, L. Operational and emerging capabilities for surface water flood forecasting. WIREs Water 2021, 8, e1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostriker, A.; Russo, A. The Effects of Floodplain Regulation on Housing Markets. 2024. Available online: https://ostriker.github.io/papers/Ostriker-Russo_floodplain-regulations.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Boulange, J.; Hanasaki, N.; Yamazaki, D.; Pokhrel, Y. Role of dams in reducing global flood exposure under climate change. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, M. Reservoir regulation affects droughts and floods at local and regional scales. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 124016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, R.L.; Wohl, E.E.; Morrison, R.R. Levees don’t protect, they disconnect: A critical review of how artificial levees impact floodplain functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Feng, L.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, D. Economic growth dominates rising potential flood risk in the Yangtze River and benefits of raising dikes from 1991 to 2015. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 34046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasandara, M.; Ernst, R.; Kulatunga, U.; Rathnasiri, P. Investigation of Issues in Structural Flood Management Measures in Sri Lanka. J. Constr. Dev. Ctries. 2022, 27, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovis, M.; Hollinger, J.C.; Cubbage, F.; Shear, T.; Doll, B.; Kurki-Fox, J.J.; Line, D.; Fox, A.; Baldwin, M.; Klondike, T.; et al. Natural Infrastructure Practices as Potential Flood Storage and Reduction for Farms and Rural Communities in the North Carolina Coastal Plain. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, H.S. Flood Disaster Management. In Machine Vision Inspection Systems; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 115–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, L. Flood Control Through Structural and Non-Structural Amplification Approaches. J. Tek. Sipil 2022, 11, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.A.R.; Rahman, A.; Chowdhury, S.H. Challenges for achieving sustainable flood risk management. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2015, 11, S352–S358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagat, J.; Bett, H.; Shilisia, R.W. Impact of Non-structural Flood Control Measures on Household Welfare in Bunyala Sub-County, Kenya. In Crisis Management—Principles, Roles and Application; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.S.; Mourato, S.; Kasanin-Grubin, M.; Ferreira, A.J.D.; Destouni, G.; Kalantari, Z. Effectiveness of Nature-Based Solutions in Mitigating Flood Hazard in a Mediterranean Peri-Urban Catchment. Water 2020, 12, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.S.S.; Potočki, K.; Kapović-Solomun, M.; Kalantari, Z. Nature-Based Solutions for Flood Mitigation and Resilience in Urban Areas. In Nature-Based Solutions for Flood Mitigation; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, Z.R.; Klaar, M.; Smith, M.W.; Brown, L.E. Quantifying the Natural Flood Management Potential of Leaky Dams in Upland catchments, Part II: Leaky Dam Impacts on Flood Peak Magnitude. J. Hydrol. 2023, 628, 130449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.S.S.; Kašanin-Grubin, M.; Solomun, M.K.; Sushkova, S.; Minkina, T.; Zhao, W.; Kalantari, Z. Wetlands as nature-based solutions for water management in different environments. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2023, 33, 100476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallecillo, S.; Kakoulaki, G.; La Notte, A.; Feyen, L.; Dottori, F.; Maes, J. Accounting for changes in flood control delivered by ecosystems at the EU level. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 44, 101142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, M.M.D.; Patil, S.D.; Nisbet, T.R.; Thomas, H.; Smith, A.R.; McDonald, M.A. Role of forested land for natural flood management in the UK: A review. WIREs Water 2021, 8, e1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-Y.; Raina, N.; Chen, H.-E. Evolution of Flood Defense Strategies: Toward Nature-Based Solutions. Environments 2021, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfreda, S.; Miglino, D.; Albertini, C. Impact of detention dams on the probability distribution of floods. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 4231–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Agarwal, A.; Villuri, V.G.K.; Pasupuleti, S.; Kumar, D.; Kaushal, D.R.; Gosain, A.K.; Bronstert, A.; Sivakumar, B. Constructed wetland management in urban catchments for mitigating floods. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2021, 35, 2105–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Chan, F.K.S.; Thorne, C.; O’Donnell, E.; Quagliolo, C.; Comino, E.; Pezzoli, A.; Li, L.; Griffiths, J.; Sang, Y.; et al. Addressing Challenges of Urban Water Management in Chinese Sponge Cities via Nature-Based Solutions. Water 2020, 12, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.; O’Donnell, E.; Johnson, M.; Slater, L.; Thorne, C.; Zheng, S.; Stirling, R.; Chan, F.K.S.; Li, L.; Boothroyd, R.J. Green infrastructure: The future of urban flood risk management? WIREs Water 2021, 8, e21560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, K.V.; Caloiero, T.; Mehta, D.J.; Singh, K.P. Comprehensive Overview of Flood Modeling Approaches: A Review of Recent Advances. Hydrology 2023, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Li, F. Ecosystem restoration and management based on Nature-based Solutions in China: Research progress and representative practices. Nat.-Based Solut. 2024, 6, 100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balwan, W.K.; Kour, S. Wetland- An Ecological Boon for the Environment. East Afr. Sch. J. Agric. Life Sci. 2021, 4, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Llobet, A.; Jähnig, S.C.; Geist, J.; Kondolf, G.M.; Damm, C.; Scholz, M.; Lund, J.; Opperman, J.J.; Yarnell, S.M.; Pawley, A.; et al. Restoring Rivers and Floodplains for Habitat and Flood Risk Reduction: Experiences in Multi-Benefit Floodplain Management From California and Germany. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 9, 778568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkelboom, F.; Demeyer, R.; Vranken, L.; De Becker, P.; Raymaekers, F.; De Smet, L. How does a nature-based solution for flood control compare to a technical solution? Case study evidence from Belgium. AMBIO 2021, 50, 1431–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferk, M.; Ciglič, R.; Komac, B.; Loczy, D. Management of small retention ponds and their impact on flood hazard prevention in the Slovenske Gorice Hills. Acta Geogr. Slov. 2020, 60, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadisharaf, E.; Alamdari, N.; Tajrishy, M.; Ghanbari, S. Effectiveness of Retention Ponds for Sustainable Urban Flood Mitigation across Range of Storm Depths in Northern Tehran, Iran. J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. 2021, 7, 5021003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkinshaw, S.J.; Kilsby, C.; O’Donnell, G.; Quinn, P.; Adams, R.; Wilkinson, M.E. Stormwater Detention Ponds in Urban Catchments—Analysis and Validation of Performance of Ponds in the Ouseburn Catchment, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK. Water 2021, 13, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, J.B.; Winston, R.J.; Hunt, W.F. Evaluating the hydrologic and water quality performance of novel infiltrating wet retention ponds. Blue-Green Syst. 2020, 2, 282–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, S.; Eslamian, F.A. Flood Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, B.B.; Kawasaki, A. Quantitative assessment of flood risk with evaluation of the effectiveness of dam operation for flood control: A case of the Bago River Basin of Myanmar. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 50, 101707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamizar, M.L.; Stoate, C.; Biggs, J.; Szczur, J.; Williams, P.; Brown, C.D. A model for quantifying the effectiveness of leaky barriers as a flood mitigation intervention in an agricultural landscape. River Res. Appl. 2024, 40, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brattgård, N. Sustainable Stormwater Management in Stockholm’s Inner City. 2021. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2:1579050 (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Adamo, N.; Al-Ansari, N.; Sissakian, V.; Laue, J.; Knutsson, S. Dam Safety and Overtopping. J. Earth Sci. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 10, 41–78. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2:1443995 (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Angelakιs, A.N.; Capodaglio, A.G.; Valipour, M.; Krasilnikoff, J.A.; Ahmed, A.T.; Mandi, L.; Tzanakakis, V.A.; Baba, A.; Kumar, R.; Zheng, X.; et al. Evolution of Floods: From Ancient Times to the Present Times (ca 7600 BC to the Present) and the Future. Land 2023, 12, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conitz, F.; Zingraff-Hamed, A.; Lupp, G.; Pauleit, S. Non-Structural Flood Management in European Rural Mountain Areas—Are Scientists Supporting Implementation? Hydrology 2021, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dazzi, S.; Vacondio, R.; Mignosa, P.; Aureli, F. Assessment of pre-simulated scenarios as a non-structural measure for flood management in case of levee-breach inundations. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 74, 102926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabbussum, R.; Dar, A.Q. Performance evaluation of artificial intelligence paradigms—Artificial neural networks, fuzzy logic, and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for flood prediction. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 25265–25282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, N.; Chausson, A.; Berry, P.; Girardin, C.A.J.; Smith, A.; Turner, B. Understanding the Value and Limits of Nature-Based Solutions to Climate Change and Other Global Challenges. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaler, T.; Hudson, P.; Viavattene, C.; Green, C. Natural flood management: Opportunities to implement nature-based solutions on privately owned land. WIREs Water 2023, 10, e1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inácio, M.; Karnauskaitė, D.; Mikša, K.; Gomes, E.; Kalinauskas, M.; Pereira, P. Nature-Based Solutions to Mitigate Coastal Floods and Associated Socioecological Impacts. In Nature-Based Solutions for Flood Mitigation; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, C.; Cottet, M.; Rivière-Honegger, A.; François, A.; Evette, A. Nature-based solutions (NbS): A management paradigm shift in practitioners’ perspectives on riverbank soil bioengineering. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Bulkeley, H. Nature-based solutions for urban biodiversity governance. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 110, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneghan, E.; Collier, M.; Kelly-Quinn, M. An evaluation of the potential applications of nature-based solutions for water quality protection: Ireland as a case study. Biol. Environ. 2021, 121B, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.-W.; Thedy, J.; Tai, C.-C. Fluvial flood adaptation using nature-based solutions: A comprehensive and effective assessment of hydro-meteorological risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarina, L. This River Is a Model. Places J. 2024, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penning, E.; Burgos, R.P.; Mens, M.; Dahm, R.; de Bruijn, K. Nature-based solutions for floods AND droughts AND biodiversity: Do we have sufficient proof of their functioning? Camb. Prism. Water 2023, 1, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massam, A.; Smith, H.; Filipova, V.; Waller, S.; Muhamad, N.; Pereira, J.J. Flood risk in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: A consideration of flood defences in a broadscale hydraulic model. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2023, 16, e12907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, D.; Wang, K.; Yan, Y.; Smith, H.; Massam, A.; Filipova, V.; Pereira, J.J. Flood vulnerability and risk assessment of urban traditional buildings in a heritage district of Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 2221–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, Q.P.; Lim, S.Y.; Rusli, N.; Chong, K.H.; Lim, D.W.G.; Lim, H.-S.; Yun, Z.; Iskander, M.F. Propagation Measurement of a Pedestrian Tunnel at 24 GHz for 5G Communications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 149934–149942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, H.P.; von der Thannen, M.; Raymond, P.; Mira, E.; Evette, A. Ecological challenges* for the use of soil and water bioengineering techniques in river and coastal engineering projects. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 176, 106539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, A.G.; Mul, M.; van der Zaag, P.; Slinger, J. Re-operating dams for environmental flows: From recommendation to practice. River Res. Appl. 2020, 37, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. A review of the flood management: From flood control to flood resilience. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, B.; Srivast, P.K.; Boruah, A. Quantifying Soil Erosion Dynamics in Subansiri river, Assam, India using RUSLE Model. Res. Sq. 2024, 10, 173–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.J.; Berkowitz, J.F. Wetland Functional Responses to Prolonged Inundation in the Active Mississippi River Floodplain. Wetlands 2020, 40, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, N. Muddy Thinking in the Mississippi River Delta: A Call for Reclamation; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arneth, A.; Olsson, L.; Cowie, A.; Erb, K.-H.; Hurlbert, M.; Kurz, W.A.; Mirzabaev, A.; Rounsevell, M.D.A. Restoring Degraded Lands. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2021, 46, 569–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, L.M.; Lal, R.; Wohl, E.; Fairfax, E.; Gellis, A.C.; Pollock, M.M. Natural infrastructure in dryland streams (NIDS) can establish regenerative wetland sinks that reverse desertification and strengthen climate resilience. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puttock, A.; Graham, H.A.; Ashe, J.; Luscombe, D.J.; Brazier, R.E. Beaver Dams Attenuate flow: A Multi-site Study. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 35, e14017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H. A Comparison of Nature Based Solutions: Beaver Dams versus Timber Flood Storage Bunds at Cropton Forest, N Yorks. 2024. Available online: https://cdn.forestresearch.gov.uk/2024/07/Beaver-Dam-vs-Timber-Bund-Storage-Analysis-FR-May-2024.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Juárez, A.; Alfredsen, K.; Stickler, M.; Adeva-Bustos, A.; Suárez, R.; Seguín-García, S.; Hansen, B. A Conflict between Traditional Flood Measures and Maintaining River Ecosystems? A Case Study Based upon the River Lærdal, Norway. Water 2021, 13, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Fang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liang, Z. Cost-Benefit Analysis of the Wuxikou Integrated Flood Management Project Considering the Effects of Flood Risk Reduction and Resettlement. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2023, 14, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, J.C.J.H. A Review of Cost Estimates for Flood Adaptation. Water 2018, 10, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.; Bathurst, J.C.; Lewis, E.; Quinn, P. Leaky dams augment afforestation to mitigate catchment scale flooding. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e14920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, B.; Bandh, S.A.; Shafi, S. Management of Natural Resources. In Environmental Management; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 185–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronnquist, A.L.; Westbrook, C.J. Beaver dams: How structure, flow state, and landscape setting regulate water storage and release. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakιs, A.N.; Zaccaria, D.; Krasilnikoff, J.; Salgot, M.; Bazza, M.; Roccaro, P.; Jimenez, B.; Kumar, A.; Yinghua, W.; Baba, A.; et al. Irrigation of World Agricultural Lands: Evolution through the Millennia. Water 2020, 12, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Burns, M.J.; Russell, K.L.; Hamel, P.; Duchesne, S.; Cherqui, F.; Roy, A.H. Concepts and evolution of urban hydrology. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radcliffe, J.C. Chapter 1—History of Water Sensitive Urban Design/Low Impact Development Adoption in Australia and Internationally. In Approaches to Water Sensitive Urban Design; Sharma, A.K., Gardner, T., Begbie, D., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 1–24. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128128435000010 (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Konrad, C.P. Effects of Urban Development on Floods. 2016. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/fs07603/ (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Miller, J.D.; Hutchins, M. The impacts of urbanisation and climate change on urban flooding and urban water quality: A review of the evidence concerning the United Kingdom. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 12, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiedrzyńska, E.; Kiedrzyński, M.; Zalewski, M. Sustainable floodplain management for flood prevention and water quality improvement. Nat. Hazards 2014, 76, 955–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Baba, A.; Valipour, M.; Dietrich, J.; Fallah-Mehdipour, E.; Krasilnikoff, J.; Bilgic, E.; Passchier, C.; Tzanakakis, V.A.; Kumar, R.; et al. Water Dams: From Ancient to Present Times and into the Future. Water 2024, 16, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, N.; Al-Ansari, N.; Sissakian, V.; Laue, J.; Knutsson, S. Dam Safety: Use of Seismic Monitoring Instrumentation in Dams. J. Earth Sci. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 11, 203–247. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2:1471297 (accessed on 1 November 2024). [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.D. How Boulder Canyon Dam Ended Up in Black Canyon as Hoover Dam. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2020, Henderson, NV, USA, 17–20 May 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randle, T.J.; Morris, G.L.; Tullos, D.D.; Weirich, F.H.; Kondolf, G.M.; Moriasi, D.N.; Annandale, G.W.; Fripp, J.; Minear, J.T.; Wegner, D.L. Sustaining United States reservoir storage capacity: Need for a new paradigm. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.K. Land-Use Changes: Floodplains, Dams, and Reservoirs—Integrated River Basins Management. Riverine Ecol. 2021, 2, 531–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Chen, H.; Hou, Y.; Finlayson, B.; Li, M.; Chen, J. Lowering water level of Dongting lake of the Mid-Yangtze River in response to large-scale dam construction: A 60-year analysis. Geomorphology 2021, 391, 107894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loire, R.; Piégay, H.; Malavoi, J.-R.; Kondolf, G.M.; Bêche, L.A. From flushing flows to (eco)morphogenic releases: Evolving terminology, practice, and integration into river management. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 213, 103475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roni, P.; Beechie, T.; Pess, G.; Hanson, K. Wood placement in river restoration: Fact, fiction, and future direction. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, J.M.; Skinner, C.J.; Milan, D.J.; Thomas, R.E.; Parsons, D.R. Localised Geomorphic Response to Channel-Spanning Leaky Wooden Dams; EGUsphere: Munich, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashbrook, J.D. Assessing the effectiveness of Leaky Dams at Crimsworth Dean, Hebden Bridge. Bachelor’s Thesis, Edge Hill University, Ormskirk, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankin, B.; Hewitt, I.; Sander, G.; Danieli, F.; Formetta, G.; Kamilova, A.; Kretzschmar, A.; Kiradjiev, K.; Wong, C.; Pegler, S.; et al. A risk-based network analysis of distributed in-stream leaky barriers for flood risk management. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 2567–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, T.L.; Majerova, M.; Neilson, B.T. Impacts of beaver dams on channel hydraulics and substrate characteristics in a mountain stream. Ecohydrology 2016, 10, e1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D. Dianne Edwards. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R685–R686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katyal, A.K.; Petrisor, I.G. Flood Management Strategies for a Holistic Sustainable Development. Environ. Forensics 2011, 12, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarah. “Flood Busting” Leaky Dams Installed on Crompton Moor in Oldham—Natural Course. 2020. Available online: https://naturalcourse.co.uk/2020/10/15/flood-busting-leaky-dams-installed-on-crompton-moor-in-oldham/ (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Cao, Y. Dam Siting: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, J.M.; Skinner, C.J.; Milan, D.; Thomas, R.E.; Parsons, D.R. Hydro-geomorphological modelling of leaky wooden dam efficacy from reach to catchment scale with CAESAR-Lisflood 1.9j. Geosci. Model Dev. 2025, 18, 1395–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, C.E.; Warren, D.R. Development of spatial pattern in large woody debris and debris dams in streams. Geomorphology 2003, 51, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.W.; van Leeuwen, Z.; Klaar, M.; Woulds, C.; Smith, M. Geomorphic effects of natural flood management woody dams in upland streams. River Res. Appl. 2022, 38, 1787–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhari, M.A.; Lotfalian, M.; Hosseini, A.; Khaledi Darvishan, A. Using Wood-Shred, Rice-Straw and Brush-Wood-Dams with Planting Seedlings to Runoff and Erosion Control in a Forest Road Fill Slope. Croat. J. For. Eng. 2019, 40, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankl, A.; Nyssen, J.; Vanmaercke, M.; Poesen, J. Gully prevention and control: Techniques, failures and effectiveness. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 46, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotherham, I.; Harrison, K. South Yorkshire Fens Past, Present and Future: Ecology and Economics as Drivers for Re-wilding and Restoration? In Greening History: The Presence of the Past in Environmental Restoration; Routledge Publishing: London, UK, 2009; Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=e998049ad2844d43c581e61121a7cc8c48108755 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Tahy, A.; Bogardi, I.; Matic, B.B.; Simonffy, Z.; Perger, L.; Nachtnebel, H.P.; Kuschnig, G.; Stevanovic, Z.; Vica, P.; Zambetoglou, K.; et al. CC-WARE Mitigating Vulnerability of Water Resources under Climate Change, Framework of National/Regional Action Plans Guidance for Facilitating Development of Action Plans to Mitigate Vulnerability of Water Resources under Climate Change, Report WP5.2, SOUTHEAST EUROPE Transitional Cooperation Programme. 2014. Available online: https://m2.mtmt.hu/gui2/?mode=browse¶ms=publication;34762835 (accessed on 10 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Adamo, N.; Al-Ansari, N.; Sissakian, V.; Laue, J.; Knutsson, S. Dams Safety: Inspections, Safety Reviews, and Legislations. J. Earth Sci. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 11, 109–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piton, G.; Horiguchi, T.; Marchal, L.; Lambert, S. Open check dams and large wood: Head losses and release conditions. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 3293–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timber, D. Hardwood vs. Softwood: Differences, Uses, Species & Examples. 2021. Available online: https://duffieldtimber.com/the-workbench/timber-trends/hardwood-vs-softwood-what-are-the-differences (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Crane, J. Protesting Monuments to Progress: A Comparative Study of Protests against Four Dams, 1838–1955. Or. Hist. Q. 2002, 103, 294–319. [Google Scholar]
- Degerman, T. The Development of Landscape Design Principles Based upon Ecosystem Aesthetics, and Their Application in Rehabilitating Diablo Lake Overlook, Ross Lake National Recreation Area, Washington. 2007. Available online: http://www.dissertations.wsu.edu/thesis/spring2007/t_degerman_050307.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2024).
- Lenzi, M.A. Stream bed stabilization using boulder check dams that mimic step-pool morphology features in Northern Italy. Geomorphology 2002, 45, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ruzouq, R.; Shanableh, A.; Yilmaz, A.G.; Idris, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Khalil, M.A.; Gibril, M.B.A. Dam Site Suitability Mapping and Analysis Using an Integrated GIS and Machine Learning Approach. Water 2019, 11, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, G.; Roy, A.N.; Sanyal, P.; Mitra, K.; Mishra, L.; Ghosh, S.K. Bioengineering of river earth embankment using natural fibre-based composite-structured geotextiles. Geotext. Geomembr. 2019, 47, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasă, F.; Nechifor, M.; Ignat, M.-E.; Teacă, C.-A. Geotextiles—A Versatile Tool for Environmental Sensitive Applications in Geotechnical Engineering. Textiles 2022, 2, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. III. Specific Treatment Measures. 2024. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/ad082e/ad082e03.htm (accessed on 30 November 2024).
- Pierce, S.; Kröger, R.; Pezeshki, R. Managing Artificially Drained Low-Gradient Agricultural Headwaters for Enhanced Ecosystem Functions. Biology 2012, 1, 794–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimas, N.; Mekonnen, M.; Tsegaye, D.; Senamaw, A. Gully Erosion and Effectiveness of Its Treatment Measures, Upper Abay Basin, in the Northwest Highlands of Ethiopia. In Nile and Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 397–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huzita, T.; Noda, R.; Kayo, C. Regional Economic Impacts from Timber Check Dam Construction—A Comparison with Concrete Check Dam Construction. Forests 2020, 11, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayo, C.; Noda, R. Climate Change Mitigation Potential of Wood Use in Civil Engineering in Japan Based on Life-Cycle Assessment. Sustainability 2018, 10, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withanachchi, C.R. Technology and techniques applied in ancient Sri Lanka in constructing dams. ResearchGate 2012, 23, 43–58. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281937136_Technology_and_techniques_applied_in_ancient_Sri_Lanka_in_constructing_dams (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Huzita, T.; Kayo, C. Regional Economic Impacts from Timber Check Dam Construction—A Comparison with Concrete Check Dam Construction, Part II: The Question of Premium Vouchers. Forests 2021, 12, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Berhe, T.G.; Ashour, T. Embankments and dams. In Modern Earth Buildings; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 538–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmocker, L. The failure of embankment dams due to overtopping. J. Hydraul. Res. 2009, 47, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewickreme, D.; Atukorala, U.D. Chapter 16 Ground improvement for mitigating liquefaction-induced geotechnical hazards. In Elsevier Geo-Engineering Book Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 3, pp. 447–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhou, G.G.D.; Song, D.; Cui, K.F.E.; Huang, Y.; Choi, C.E.; Chen, H. Effect of slit size on the impact load against debris-flow mitigation dams. Eng. Geol. 2020, 274, 105764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golpira, A.; Pierce, R.; Baki, M. Influences of Boulder Placement on Stream Habitat Quality Metrics. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2021, Virtual, 7–11 June 2021; pp. 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Rong, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, C.; Cao, L.; Yang, H. Short-term effects of substrate surface structure on macroinvertebrates community structure and functional characteristics. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 201, 107215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.B. Dams, Dikes, and Levees. Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Sun, J.; Zhong, D.; Song, L. Compaction Quality Control of Earth-Rock Dam Construction Using Real-Time Field Operation Data. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2012, 138, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Cao, X.; Cao, R.; Huang, J.; Yan, A.; Xu, D. The critical role of c and φ in ensuring stability: A study on rockfill dams. Open Geosci. 2024, 16, 20220712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Shen, Z.; Xu, L.; Gan, L.; Tan, J. A New Method for Inversion of Dam Foundation Hydraulic Conductivity Using an Improved Genetic Algorithm Coupled with an Unsaturated Equivalent Continuum Model and Its Application. Materials 2023, 16, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalko, I.; Wohl, E.; Nepf, H.M. Flow and wake characteristics associated with large wood to inform river restoration. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscombe, D.; Warrick, J.A.; Ritchie, A.; East, A.E.; McHenry, M.; McCoy, R.; Foxgrover, A.; Wohl, E. Remote Sensing Large-Wood Storage Downstream of Reservoirs During and After Dam Removal: Elwha River, Washington, USA. Earth Space Sci. 2024, 11, e2024EA003544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daus, M.; Koberger, K.; Koca, K.; Beckers, F.; Encinas Fernández, J.; Weisbrod, B.; Dietrich, D.; Gerbersdorf, S.U.; Glaser, R.; Haun, S.; et al. Interdisciplinary Reservoir Management—A Tool for Sustainable Water Resources Management. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yao, C.; Li, C.; Miao, M.; Zhong, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, T. Review of Application and Innovation of Geotextiles in Geotechnical Engineering. Materials 2020, 13, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, A.; Koda, E.; Kawalec, J. Geosynthetics for Filtration and Stabilisation: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, A.; Dey, A. Combined Functioning of Geotextile as Barrier and Drainage Material in Unsaturated Earth Retaining Structures. Indian Geotech. J. 2017, 48, 342–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, G.; Li, P.; Su, Z. Dynamic characteristics of tailings dam with geotextile tubes under seismic load. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2021, 60, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, B.; Wolff, E.; Valderrama, J.; Valbuena, J.; Colombia, G.; Segovia, G.; Branch, C. Experience with Geotextile Tubes in Mining Tailings Storage: Gran Colombia Gold Segovia. 2020. Available online: https://papers.acg.uwa.edu.au/d/2052_20_Garcia/20_Garcia.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Berhane, G.; Walraevens, K. Quantifying water loss in leaky micro-dam reservoir through water balance analysis and high-resolution water level data modeling. Water Pract. Technol. 2024, 19, 852–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egedusevic, M.; Bennett, G.; Roskilly, K.; Sgarabotto, A.; Manzella, I.; Raby, A.; Boulton, S.J.; Clark, M.; Curtis, R.; Panici, D.; et al. Monitoring the stability of leaky dams and their influence on debris transport with innovative sensor technology on the SENSUM project. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2022, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A. Saturated-Unsaturated Flow through Leaky Dams. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental. Eng. 2008, 134, 1564–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompor, W.; Yoshikawa, S.; Kanae, S. Use of Seasonal Streamflow Forecasts for Flood Mitigation with Adaptive Reservoir Operation: A Case Study of the Chao Phraya River Basin, Thailand, in 2011. Water 2020, 12, 3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterwerp, J.C.; Albers, T.; Anthony, E.J.; Friess, D.A.; Mancheño, A.G.; Moseley, K.; Muhari, A.; Naipal, S.; Noordermeer, J.; Oost, A.; et al. Managing erosion of mangrove-mud coasts with permeable dams—Lessons learned. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 158, 106078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IHA. Harnessing the Power of Dams for Flood Protection. 2023. Available online: https://www.hydropower.org/blog/harnessing-the-power-of-dams-for-flood-protection (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Pope, C.I. What Is Natural Flood Management (NFM)?—Ribble Rivers Trust. 2023. Available online: https://ribbletrust.org.uk/what-is-natural-flood-management-nfm/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Lankenau, L.; Koppe, B. Sandbagging versus Sandbag Replacement Systems: Costs, Time, Helpers, Logistics. In Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Discussions; EGU: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, E.; Van Der Keur, P.; Cauwenbergh, V.N.; Le Coent, P.; Giordano, R. Water Security in a New World Greening Water Risks Natural Assurance Schemes. 2023. Available online: https://library.oapen.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.12657/62981/978-3-031-25308-9.pdf?sequence=1#page=224 (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Landezine. Renaturation of the River Aire, Geneva. 2016. Available online: https://landezine.com/renaturation-of-the-river-aire-geneva/ (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Kingsford, R.T.; Bino, G.; Porter, J.L. Continental impacts of water development on waterbirds, contrasting two Australian river basins: Global implications for sustainable water use. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 4958–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niadmin. DAMS DEMYSTIFIED—National Irrigation Authority. 2015. Available online: https://www.irrigationauthority.go.ke/2022/05/04/dams-demystified/ (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Bestuzheva, A.; Gotsiridze, G. Hydrodynamic pressure of water on the head face of an earth dam during an earthquake. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 457, 02008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athani, S.S.; Shivamanth; Solanki, C.H.; Dodagoudar, G.R. Seepage and Stability Analyses of Earth Dam Using Finite Element Method. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leakey, S.; Hewett, C.J.M.; Glenis, V.; Quinn, P.F. Modelling the Impact of Leaky Barriers with a 1D Godunov-Type Scheme for the Shallow Water Equations. Water 2020, 12, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, Q.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xia, J.; Ni, J.; Cooke, S.J.; Best, J.; He, S.; Feng, T.; et al. River Damming Impacts on Fish Habitat and Associated Conservation Measures. Rev. Geophys. 2023, 61, e2023RG000819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twardek, W.M.; Cowx, I.G.; Lapointe, N.W.R.; Paukert, C.; Beard, T.D.; Bennett, E.M.; Browne, D.; Carlson, A.K.; Clarke, K.D.; Hogan, Z.; et al. Bright spots for inland fish and fisheries to guide future hydropower development. Water Biol. Secur. 2022, 1, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Wilson, C.A.M.E.; Ouro, P.; Cable, J. Leaky barriers: Leaky enough for fish to pass? R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 201843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazier, R.E.; Puttock, A.; Graham, H.A.; Auster, R.E.; Davies, K.H.; Brown, C.M.L. Beaver: Nature’s Ecosystem Engineers. WIREs Water 2020, 8, e1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, M.P.; Sullivan, C.A.; Acreman, M.C. Ecosystem Impacts of Large Dams. 2001. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/45165880_Ecosystem_Impacts_of_Large_Dams (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Bradlow, D.D.; Palmieri, A.; Salman, M.A. Regulatory Frameworks for Dam Safety: A Comparative Study. In Law, Justice and Development Series; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Villavicencio, G.; Espinace, R.; Palma, J.; Fourie, A.; Valenzuela, P. Failures of sand tailings dams in a highly seismic country. Can. Geotech. J. 2014, 51, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylward, B.; Berkhoff, J.; Green, C.; Gutman, P.; Unsworth, R. Thematic Review Economic and Financial Issues [In Large Dams]. 2001. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/365926255_Thematic_Review_Economic_and_Financial_Issues_in_large_dams (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Pompeu, C.R.; Peñas, F.J.; Goldenberg-Vilar, A.; Álvarez-Cabria, M.; Barquín, J. Assessing the effects of irrigation and hydropower dams on river communities using taxonomic and multiple trait-based approaches. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhawenimana, V.; Follett, E.; Maddock, I.; Wilson, C.A.M.E. Field-based monitoring of instream leaky barrier backwater and storage during storm events. J. Hydrol. 2023, 622, 129744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, R. Damming the river: A changing perspective on altering nature. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2006, 10, 165–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingfield, T.; Macdonald, N.; Peters, K.; Spees, J.; Potter, K. Natural Flood Management: Beyond the evidence debate. Area 2019, 51, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type of Dam | Materials/Substances Used | Main Features | Contribution to Water Control/Flood Mitigation | Other Ecosystem Services | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Woody Debris Dams | Fallen trees, branches, Douglas fir logs | Semi-permanent; reduces flow velocity (~40%); promotes channel complexity | Slows surface flow, reduces flashiness in streams | Habitat creation, stream shading, sediment retention | Kraft and Warren [111]; Lo et al. [112] |
| Brushwood Dams | Twigs, live willow, coppiced hazel | Dense vegetative matrix; traps sediment; fosters riparian growth | Attenuates peak runoff by up to 30% in small catchments | Soil stabilization, vegetation regeneration, carbon capture | Fakhari et al. [113]; Frankl et al. [114]; Rotherham and Harrison [115]; Tahy et al. [116] |
| Wooden Board Dams | Oak, elm, cedar planks; treated lumber | Interlocking panels; adjustable flow; forms upstream pools | Flow regulation; delays runoff; improves channel storage | Fish passage, instream habitat, water quality buffering | Adamo et al. [117]; Piton et al. [118]; Timber [119] |
| Rock and Boulder Dams | Boulders, natural stone, compacted rockfill | Durable under high flow; geotechnical stability; permeable | High capacity for flood buffering; withstands strong hydraulic forces | Channel stability, aquatic habitat structure, erosion protection | Crane [120]; Degerman [121]; Lenzi [122] |
| Wood–Rock Hybrid Dams | Treated timber, large stones, aggregates | Interlocked structure; high sediment retention (60–85%) | Effective for 1:100-year events; smooths hydrographs in variable flow systems | Salmonid habitat, sediment balance, aesthetic integration | Piton et al. [118]; Al-Ruzouq et al. [123] |
| Geotextile-Assisted Dams | Geosynthetic permeable fabrics | Soil stabilization; improves filtration; limits particle migration | Enhances embankment resistance; supports drainage and overflow control | Reduces turbidity; supports embankment vegetation; improves infiltration | Allaire [1]; Basu et al. [124]; Tanasă et al. [125] |
| Seasonal/Movable Dams | Inflatable rubber membranes, metal frameworks | Temporary deployment; collapsible or inflatable; repositionable | Provides short-term flood defense or storage during seasonal peaks | Minimal ecological disruption; fast recovery; wetland habitat preservation | Adamo et al. [95] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hansamali, U.; Makumbura, R.K.; Rathnayake, U.; Azamathulla, H.M.; Muttil, N. Leaky Dams as Nature-Based Solutions in Flood Management Part I: Introduction and Comparative Efficacy with Conventional Flood Control Infrastructure. Hydrology 2025, 12, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040095
Hansamali U, Makumbura RK, Rathnayake U, Azamathulla HM, Muttil N. Leaky Dams as Nature-Based Solutions in Flood Management Part I: Introduction and Comparative Efficacy with Conventional Flood Control Infrastructure. Hydrology. 2025; 12(4):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040095
Chicago/Turabian StyleHansamali, Umanda, Randika K. Makumbura, Upaka Rathnayake, Hazi Md. Azamathulla, and Nitin Muttil. 2025. "Leaky Dams as Nature-Based Solutions in Flood Management Part I: Introduction and Comparative Efficacy with Conventional Flood Control Infrastructure" Hydrology 12, no. 4: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040095
APA StyleHansamali, U., Makumbura, R. K., Rathnayake, U., Azamathulla, H. M., & Muttil, N. (2025). Leaky Dams as Nature-Based Solutions in Flood Management Part I: Introduction and Comparative Efficacy with Conventional Flood Control Infrastructure. Hydrology, 12(4), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040095











