Role of Hungry Water on Sediment Dynamics: Assessment of Valley Degradation, Bed Material Changes and Flood Inundation in Pamba River During Kerala Flood, 2018
Abstract
1. Introduction
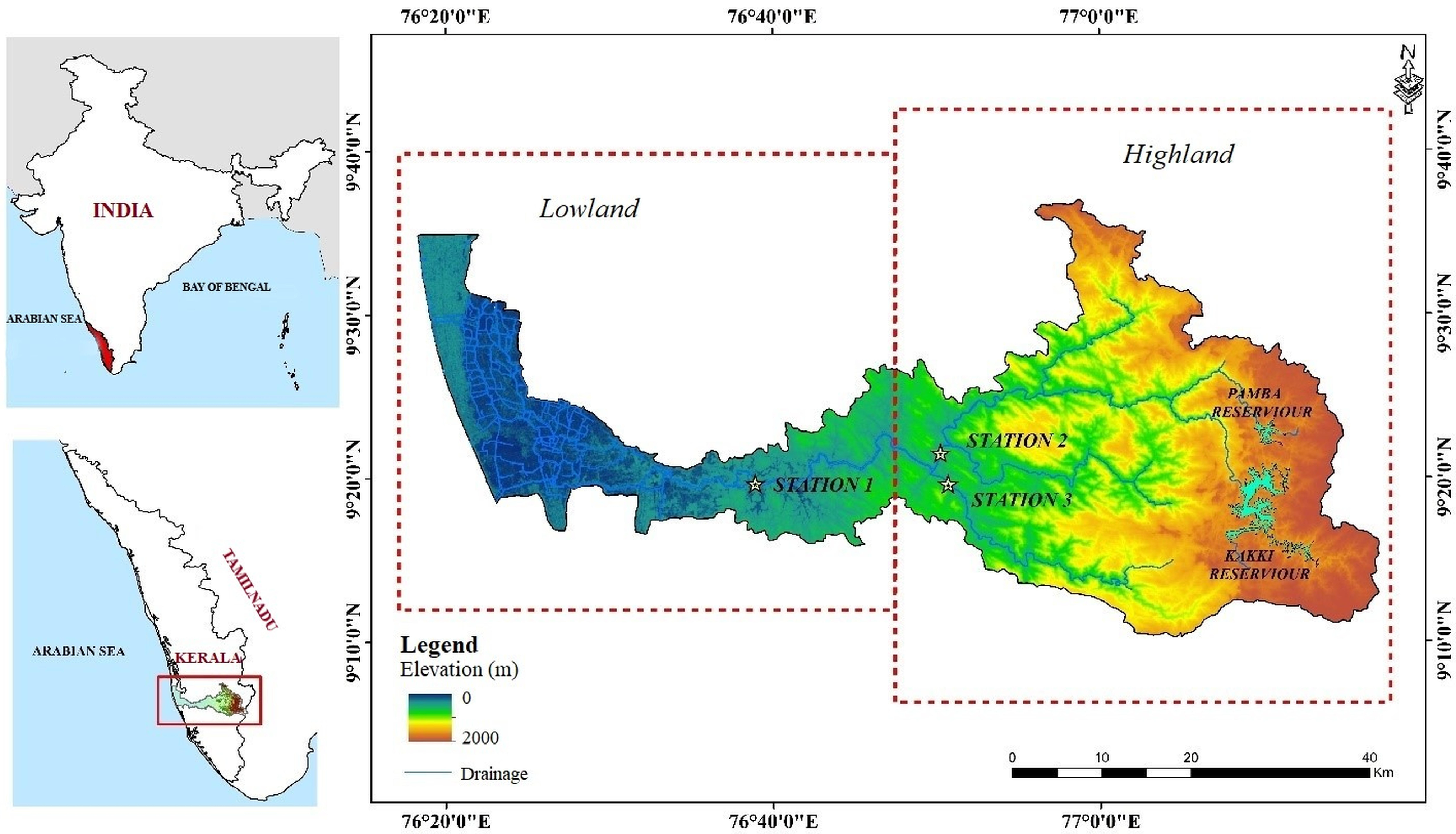
2. Pamba River Basin—Geo-Environmental Settings
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Hydrological Data
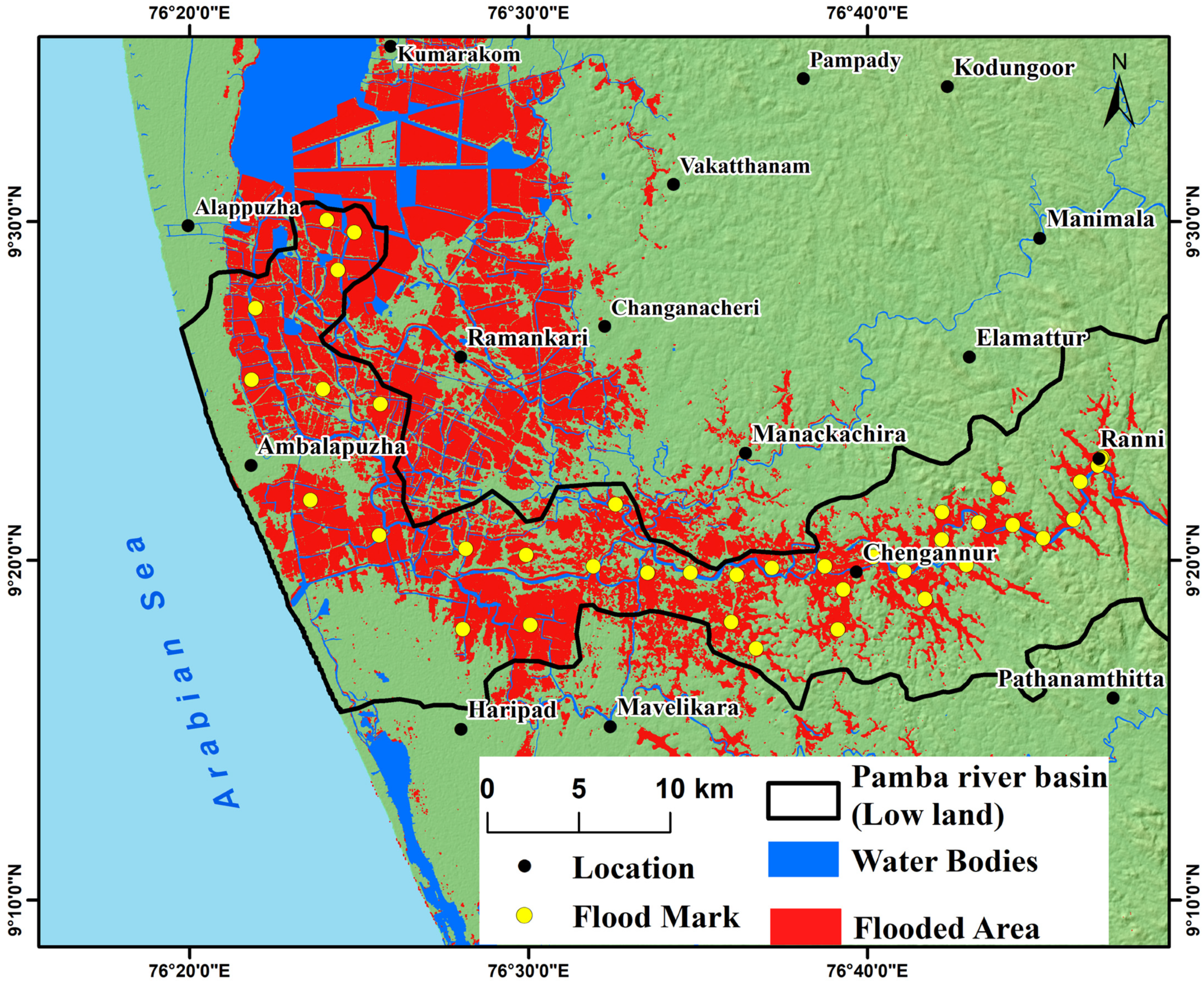
3.2. Flood Area Mapping
3.3. Flood Deposit Sediment—Rapid Reserve Estimation (RRE)
3.4. Flood Deposit Characterization
4. Results
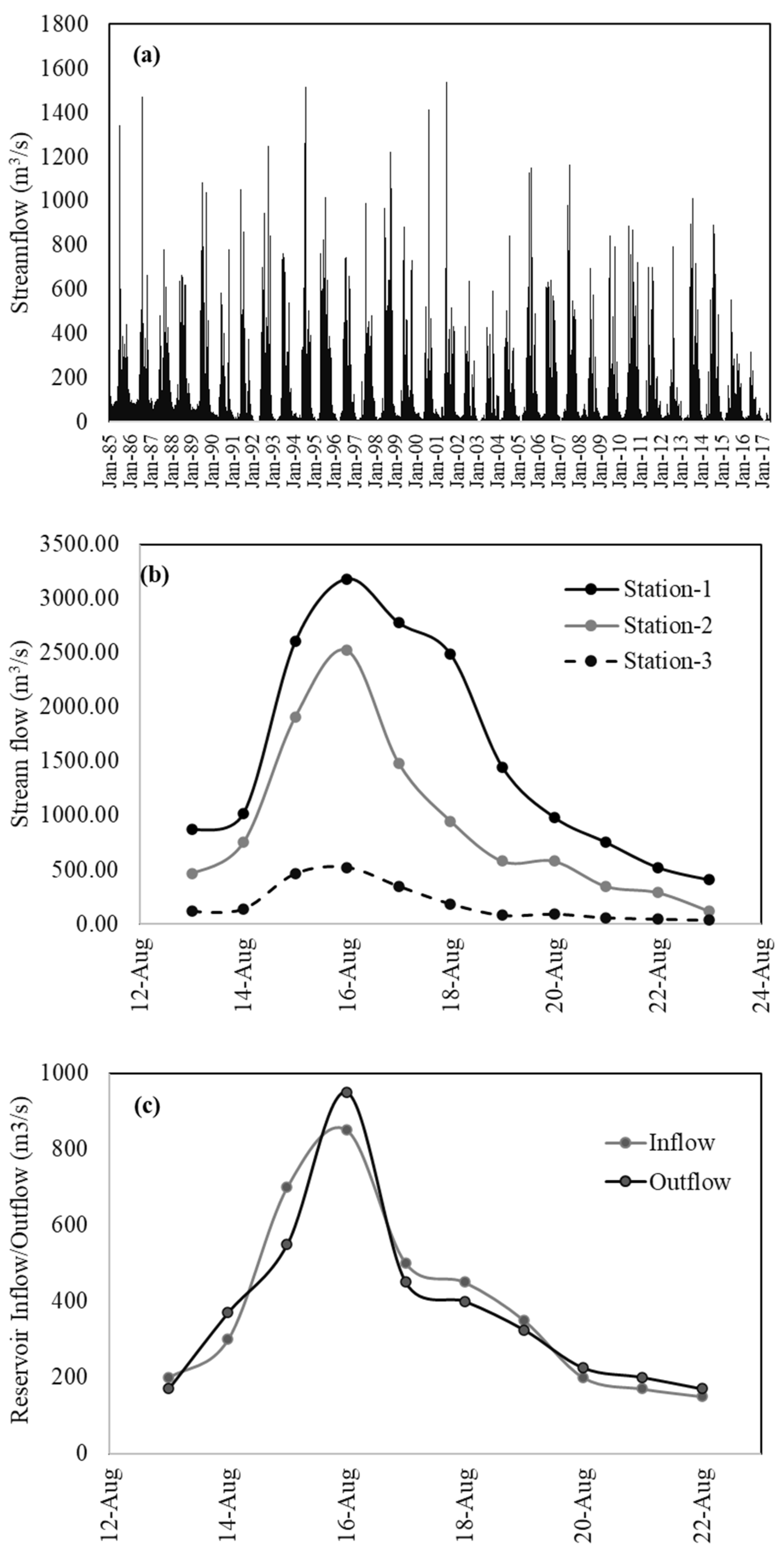
4.1. Streamflow and Flooding
4.2. Nature and Characteristics of the Flood Deposits
4.3. Quantification of Flood Deposits
4.4. Surface Textural Characteristics of Sand Grains (SEM-EDS Analysis)
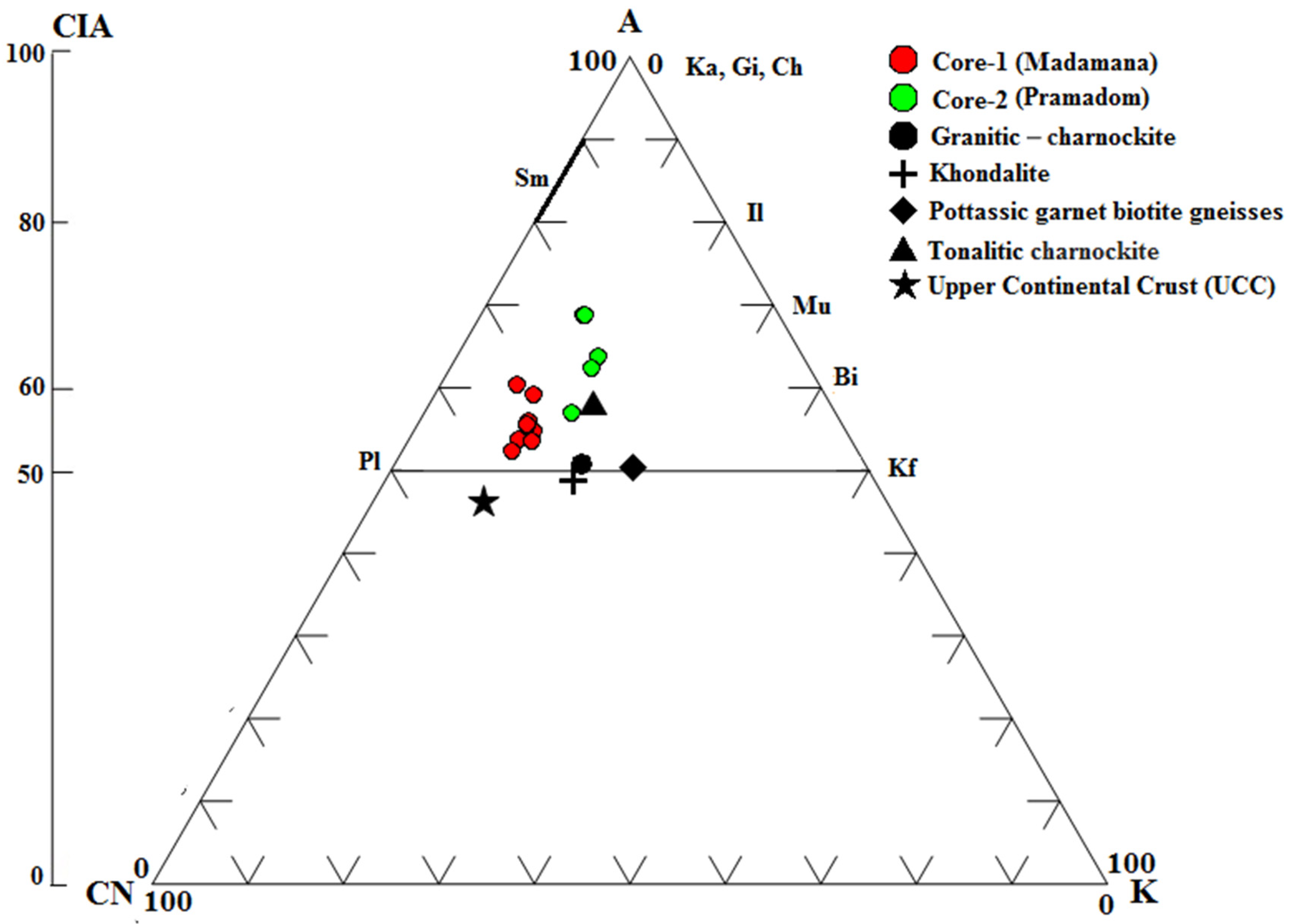
4.5. Chemical Index of Alteration
5. Discussion
5.1. Effects of Hungry Water and Post-Flood Sediment Characteristics
5.2. Streamflow and Flooding Dynamics
5.3. Socio-Economic Implications
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blöschl, G.; Hall, J.; Viglione, A.; Perdigão, R.A.P.; Parajka, J.; Merz, B.; Lun, D.; Arheimer, B.; Aronica, G.T.; Bilibashi, A.; et al. Changing Climate Both Increases and Decreases European River Floods. Nature 2019, 573, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudet, H.; Giordono, L.; Zanocco, C.; Satein, H.; Whitley, H. Event Attribution and Partisanship Shape Local Discussion of Climate Change after Extreme Weather. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongman, B.; Ward, P.J.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. Global Exposure to River and Coastal Flooding: Long Term Trends and Changes. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 22, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegatte, S.; Green, C.; Nicholls, R.J.; Corfee-Morlot, J. Future Flood Losses in Major Coastal Cities. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, Y.; Mahendran, R.; Koirala, S.; Konoshima, L.; Yamazaki, D.; Watanabe, S.; Kim, H.; Kanae, S. Global Flood Risk Under Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnell, N.W.; Lloyd-Hughes, B. The Global-scale Impacts of Climate Change on Water Resources and Flooding Under New Climate and Socio-economic Scenarios. Clim. Chang. 2014, 122, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, S.; Fowler, H.J.; Evans, J.P.; Alexander, L.V.; Berg, P.; Johnson, F.; Kendon, E.J.; Lenderink, G.; Roberts, N.M. Future Changes to the Intensity and Frequency of Short-duration Extreme Rainfalls. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 522–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, I.; Villarini, G. The Changing Nature of Flooding Across the Central United States. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winsemius, H.C.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Bouwman, A.; Jongman, B.; Kwadijk, J.C.J.; Ligtvoet, W.; Lucas, P.L.; Van Vuuren, D.P.; et al. Global Drivers of Future River Flood Risk. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milly, P.C.D.; Wetherald, R.T.; Dunne, K.A.; Delworth, T.L. Increasing Risk of Great Floods in a Changing Climate. Nature 2002, 415, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwer, L.M.; Crompton, R.P.; Faust, E.; Hoppe, P.; Pielke, R.A. Confronting Disaster Losses. Science 2007, 318, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, H.; Petersen, A.C.; Ligtvoet, W. On the Relation Between Weather-related Disaster Impacts, Vulnerability and Climate Change. Clim. Chang. 2014, 125, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vuuren, D.P.; Edmonds, J.; Kainuma, M.; Riahi, K.; Thomson, A.; Hibbard, K.; Hurtt, G.C.; Kram, T.; Krey, V.; Lamarque, J.-F.; et al. The Representative Concentration Pathways: An Overview. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dottori, F.; Szewczyk, W.; Ciscar, J.-C.; Zhao, F.; Alfieri, L.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Bianchi, A.; Mongelli, I.; Frieler, K.; Betts, R.A.; et al. Increased Human and Economic Losses From River Flooding with Anthropogenic Warming. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WRI. Aqueduct Global Flood Analyzer; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; Available online: https://www.wri.org/data/aqueduct-global-flood-analyzer (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- Mishra, V.; Shah, H.L. Hydroclimatological Perspective of the Kerala Flood of 2018. J. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 92, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheer, K.P.; Bhallamudi, B.S.; Narasimhan, B.; Thomas, J.; Bindhu, V.M.; Vema, V.; Kurian, C. Role of Dams on the Floods of August 2018 in Periyar River Basin, Kerala. Curr. Sci. 2019, 166, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, G. Monsoon Fury in Kerala—A Geo-environmental Appraisal. J. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 92, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.M.R.; Menon, A. The 2018 Kerala floods: A Climate Change Perspective. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 2433–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M. Hungry Water: Effects of Dams and Gravel Mining on River Channels. Environ. Manag. 1997, 21, 533–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Smeltzer, M.; Kimball, L. Freshwater Gravel Mining and Dredging Issues; Report Prepared for Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife; Washington Department of Ecology, Washington Department of Transportation, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2001; 122p. [Google Scholar]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Gao, Y.; Annandale, G.W.; Morris, G.L.; Jiang, E.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Carling, P.; Fu, K.; Guo, Q.; et al. Earth’s Future Sustainable Sediment Management in Reservoirs and Regulated Rivers: Experiences from Five Continents. Earth’s Future 2014, 2, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmalal, D.; Maya, K. Sand Mining: Environmental Impacts and Selected Case Studies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; 162p. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Tarrío, D.; Ruiz-Villanueva, V.; Garrote, J.; Benito, G.; Calle, M.; Lucía, A.; Díez-Herrero, A. Effects of sediment transport on flood hazards: Lessons learned and remaining challenges. Geomorphology 2024, 446, 108976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, S.A.; Gardin, B.; Belleudy, P. Impacts of dams on river flows, sediment dynamics and geomorphic processes: A systematic review in tropical rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.T.P.; Kantoush, S.; Kawamura, A.; Du, T.L.T.; Bui, N.T.; Capell, R.; Nguyen, N.T.; Bui, D.D.; Saber, M.; Sumi, T.; et al. Reservoir operation impacts on streamflow and sediment dynamics in the transboundary river basin, Vietnam. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e14994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Han, S. Dam impacts on seasonality of water and sediment transport in intensively managed river basins: A case study of the Yangtze River. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2021, 126, e2021JF006573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study Report: Kerala Floods of August; Hydrological Studies Organization, Hydrology Directorate, Central Water Commission, Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2018; 46p.
- Water Atlas of Kerala; Centre for Water Resources Development and Management: Kozhikode, India, 1995; 65p.
- Mathew, M.M.; Sreelash, K.; Mathew, M.; Arulbalaji, P.; Padmalal, D. Spatiotemporal Variability of Rainfall and its Effect on Hydrological Regime in a Tropical Monsoon-Dominated Domain of Western Ghats, India. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 36, 100861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmalal, D.; Maya, K.; Babu, N.K.; Baijulal, B. Environmental Appraisal and Sand Auditing of Manimala River, Kerala, India; CESS-PR-05-2010; Centre for Earth Science Studies: Trivandrum, India, 2010; 195p. [Google Scholar]
- Goldich, S.S. A Study in Rock Weathering. J. Geol. 1938, 46, 17–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Early Proterozoic Climates and Plate Motions Inferred from Major Element Chemistry of Lutites. Nature 1982, 299, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Prediction of some Weathering Trends of Plutonic and Volcanic Rocks based on Thermodynamic and Kinetic Considerations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Formation and Diagenesis of Weathering Profiles. J. Geol. 1989, 97, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Petrogenesis of Sediments in the Absence of Chemical Weathering: Effects of Abrasion and Sorting on Bulk Composition and Mineralogy. Sedimentology 1996, 43, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M.; McLennan, S.M.; Keays, R.R. Effects of Chemical Weathering and Sorting on the Petrogenesis of Siliciclastic Sediments, with Implications for Provenance Studies. J. Geol. 1996, 104, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, T.; Ravindra Kumar, G.R.; Meen, J.K.; Rogers, J.J.W. Geochemistry of High-grade Supracrustal Rocks from the Kerala Khondalite Belt and Adjacent Massif Charnockites. Precambrian Res. 1992, 55, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra Kumar, G.R.; Sreejith, C. Petrology and Geochemistry of charnockites (felsic ortho-granulites) from the Kerala Khondalite Belt, Southern India: Evidence for Intra-crustal Melting, Magmatic Differentiation and Episodic Crustal Growth. Lithos 1996, 262, 334–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
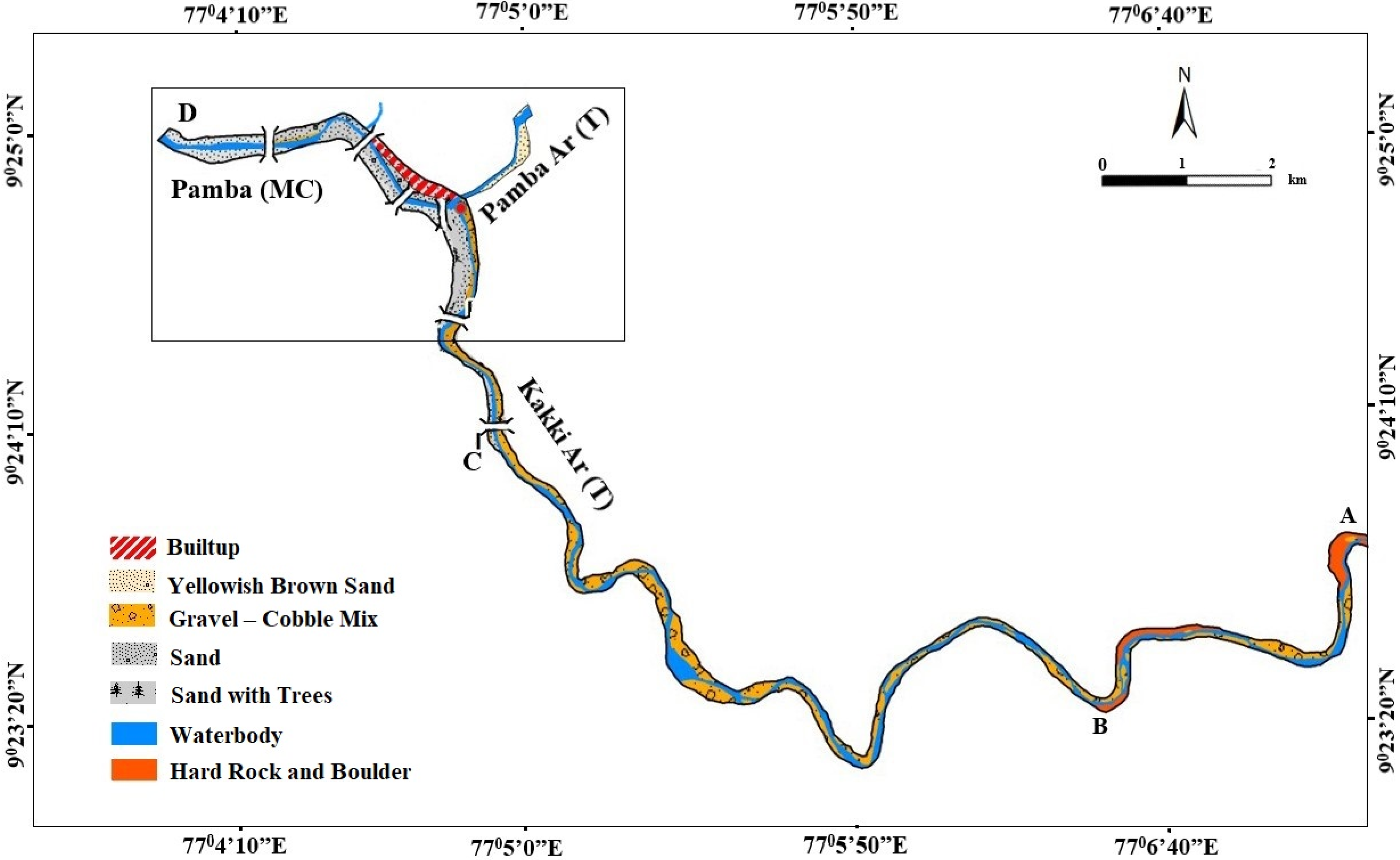
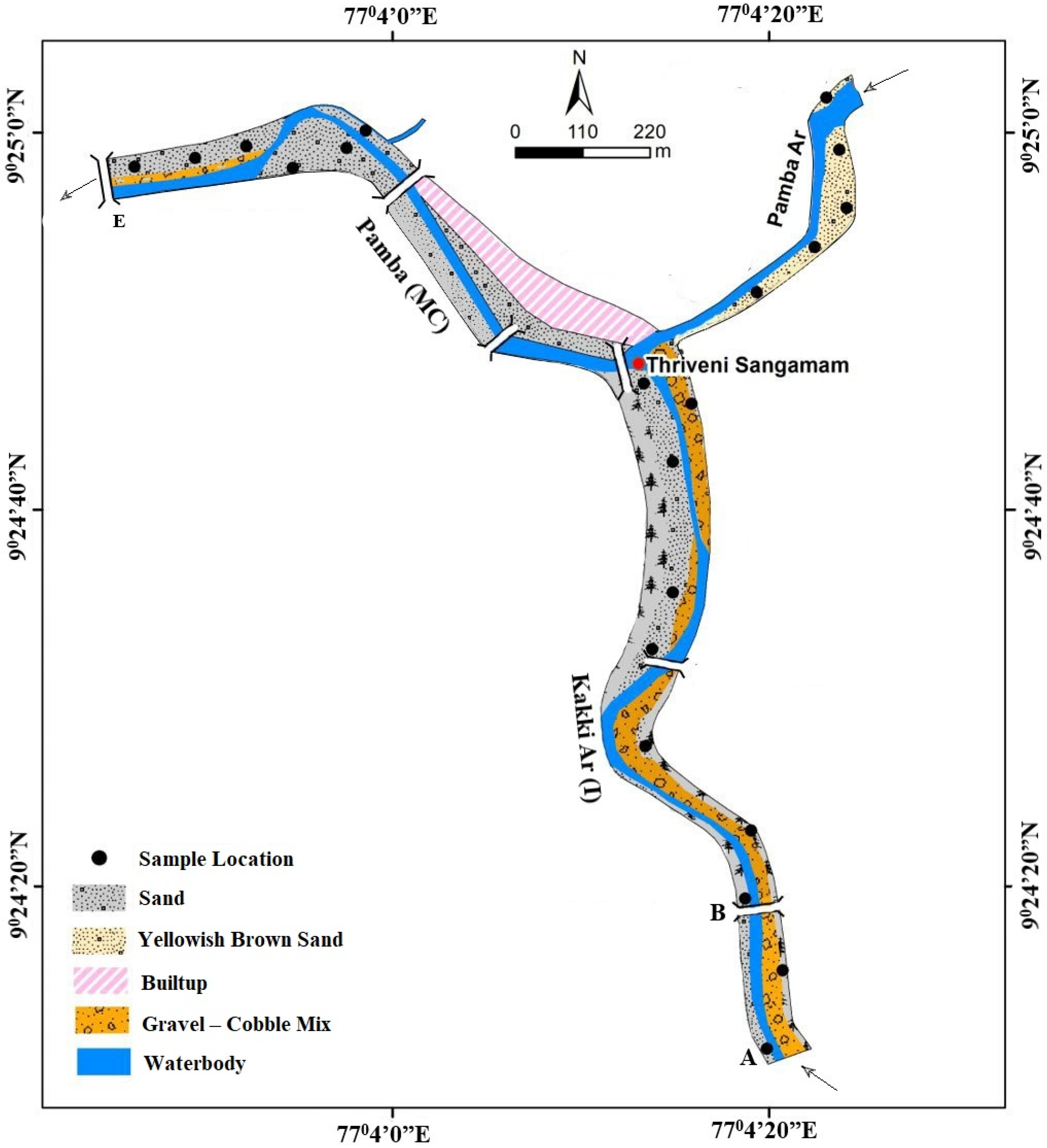



| River/Tributary | Segment | Sediment Type | Volume (m3) | Observations/Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kakki Ar (T) | B–C | Sand | 71,700 | Sands are generally first-generation, formed as a result of abrasion and attrition in extremely high-energy hydrodynamic conditions. |
| In-Channel Sand and Gravel | 5765 | |||
| Gravel–Cobble Mix | 42,775 | |||
| A–B | Sand | 28,426 | Sands are generally first-generation, formed under extremely high hydrodynamic/energy conditions. The segment represents the transitional zone between cobble–boulder-dominated reach and sand and gravel-dominated reach. | |
| In-Channel Sand | 600 | |||
| Gravel–Cobble Mix | 37,260 | |||
| Pamba Ar (T) | C–D | Sand | 8188 | Sand and gravel are generally yellowish-brown in color, (i.e., coated grains). This indicates the long residence of the grains in the river channel under oxidizing exposed conditions, and these are not subjected to an extremely high rate of wear and tear under the flood event of August 2018. |
| Gravelly Sand | 225 | |||
| In-Channel Sand | 2429 | |||
| Pamba River (MC) | C–E | Sand | 65,224 | Two varieties of sands are noticed. Coarse sands are the dominant variety, which are generally yellowish-brown in nature. Fine sands are deposited on the overbank areas of the river channel. They are white, silty and of a first-generation type. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krishnan Kutty, S.; Damodaran, P.; Mathai, J.; Mathew, M.; Rani, A.; Kumar Sharma, R.; Kesavan, M. Role of Hungry Water on Sediment Dynamics: Assessment of Valley Degradation, Bed Material Changes and Flood Inundation in Pamba River During Kerala Flood, 2018. Hydrology 2025, 12, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040079
Krishnan Kutty S, Damodaran P, Mathai J, Mathew M, Rani A, Kumar Sharma R, Kesavan M. Role of Hungry Water on Sediment Dynamics: Assessment of Valley Degradation, Bed Material Changes and Flood Inundation in Pamba River During Kerala Flood, 2018. Hydrology. 2025; 12(4):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040079
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrishnan Kutty, Sreelash, Padmalal Damodaran, Jeenu Mathai, Micky Mathew, Asha Rani, Rajat Kumar Sharma, and Maya Kesavan. 2025. "Role of Hungry Water on Sediment Dynamics: Assessment of Valley Degradation, Bed Material Changes and Flood Inundation in Pamba River During Kerala Flood, 2018" Hydrology 12, no. 4: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040079
APA StyleKrishnan Kutty, S., Damodaran, P., Mathai, J., Mathew, M., Rani, A., Kumar Sharma, R., & Kesavan, M. (2025). Role of Hungry Water on Sediment Dynamics: Assessment of Valley Degradation, Bed Material Changes and Flood Inundation in Pamba River During Kerala Flood, 2018. Hydrology, 12(4), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040079






