Quantifying Mercury Use and Modeling Its Fate and Transport in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in the Lom Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
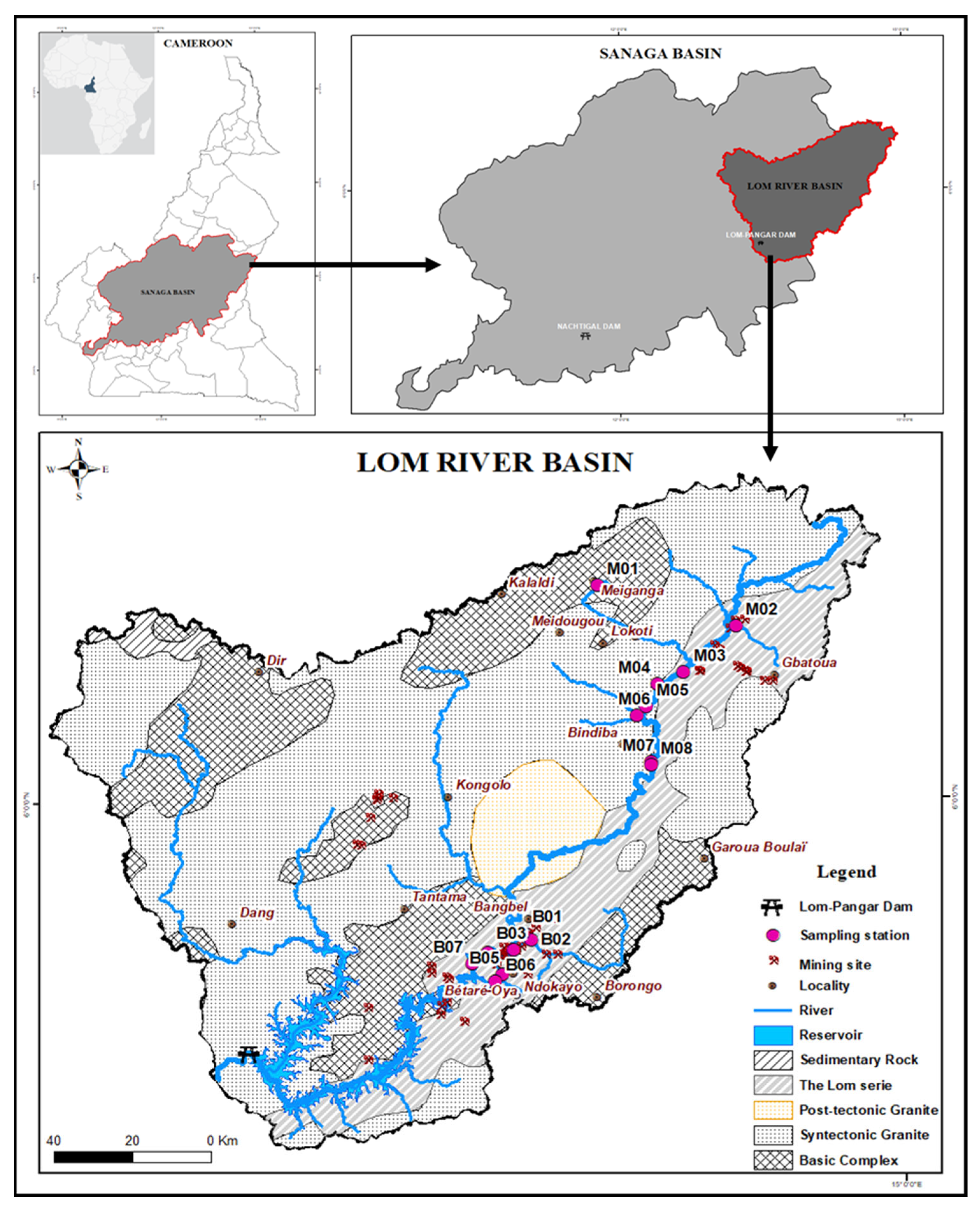
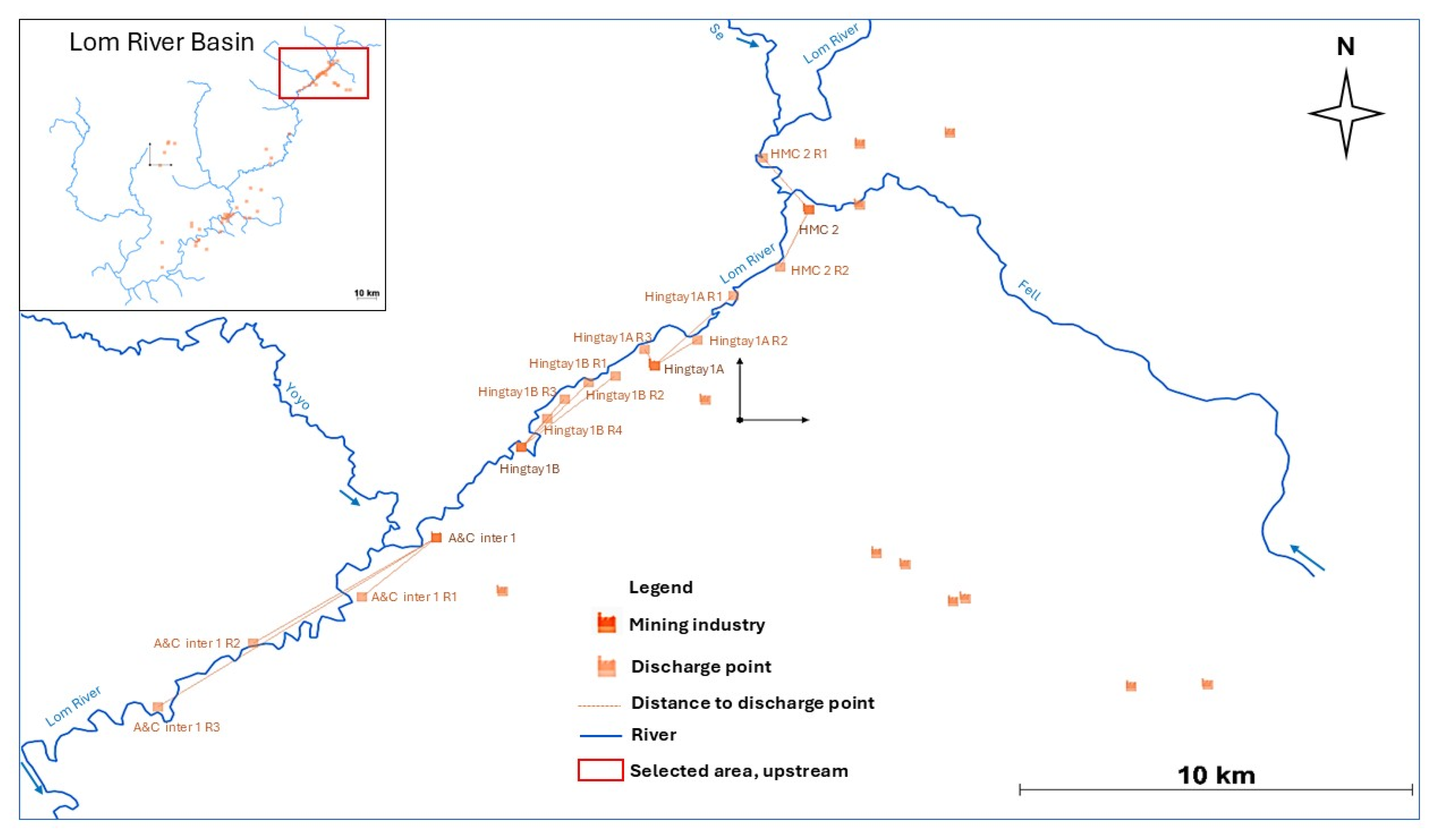
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Water Quality Monitoring
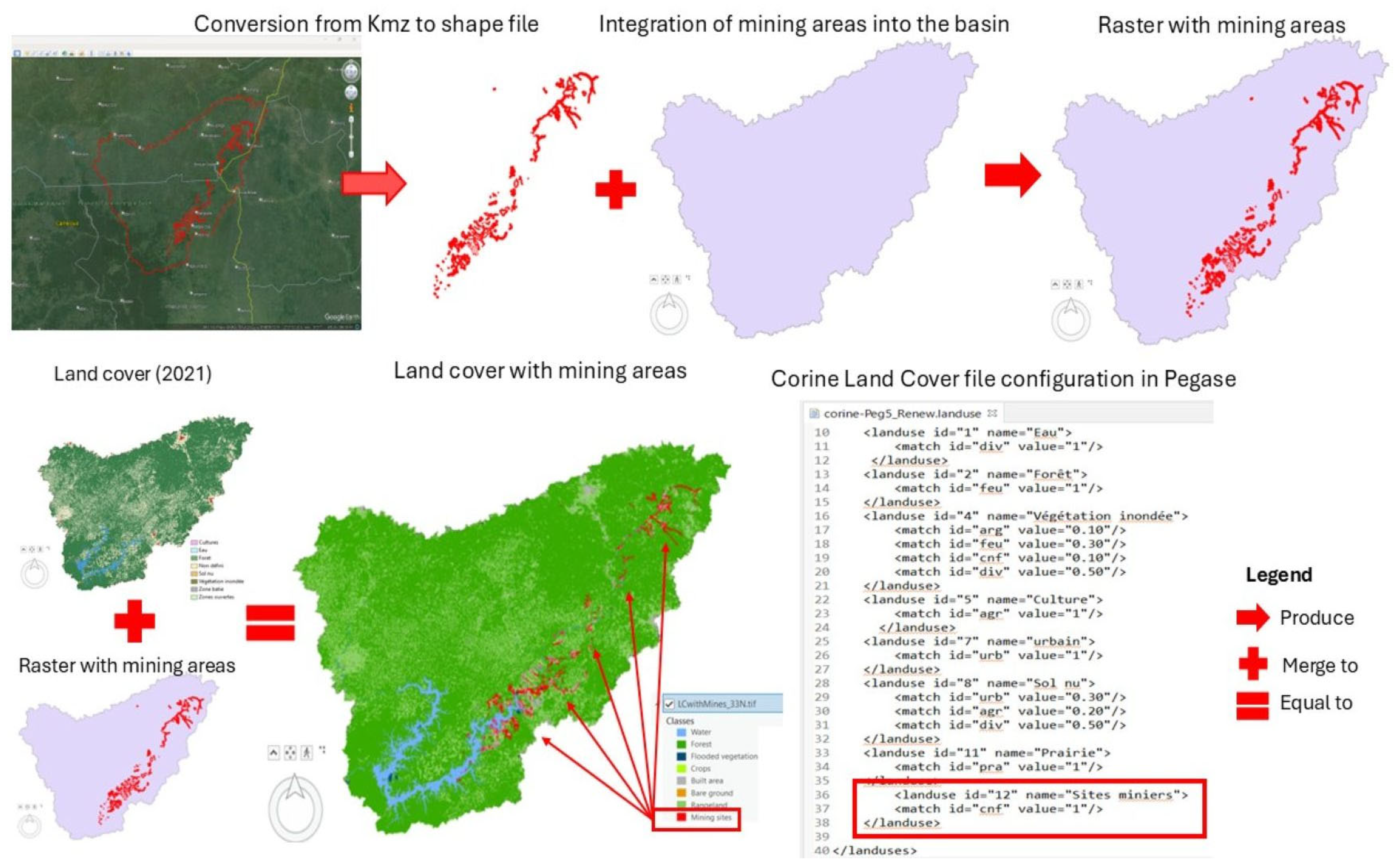
2.3. Description of the PEGASE Model
Model Implementation and Calibration
- -
- Urban discharges, based on the concept of equivalent inhabitants for mercury;
- -
- Industrial discharges, derived from emission inventories;
- -
- Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), accounted for through a removal efficiency rate specific to each facility;
- -
- Direct inputs from livestock, estimated using a direct emission rate per livestock unit;
- -
- Diffuse inputs from soils, incorporated using a soil input function to represent land-based contributions.
- -
- Type of ore: When the ore contains silver (Ag), an average of 3 g of mercury is required to amalgamate 1 g of silver, resulting in a Hg:Ag ratio of 3:1. To this, the Hg:Au ratio is added, depending on the type of amalgamation practiced. The Lom basin gold mineralization effectively contains silver (7.11–20.56% of Ag), as shown in different works [32,33,34].
- -
- Method of amalgamation: On average, 1 g of mercury is typically needed to amalgamate 1 g of gold (Hg:Au = 1:1). However, this ratio can vary depending on whether the mercury is applied to the entire milled ore [Whole Ore Amalgamation (WOA)] or to the concentrated ore [Concentrated Ore Amalgamation (COA)]. For WOA, a minimum of 5 times more mercury is required, resulting in a Hg:Au ratio of 5:1 or more. In the case of COA, the average ratio is Hg:Au = 1:1 [35].
- -
- Number of washing days: The number of washing days corresponds to the actual number of days during which mercury is mixed to the ore for its treatment through amalgamation and subsequently discharged.
- -
- High mercury use: WOA (Hg:Au = 10:1);
- -
- Mixed practice with average mercury use: WOA (3/4) and COA (1/4) (Hg:Au = 6:1);
- -
- Low mercury use: COA (Hg:Au = 3:1).
| Period | Estimated Mean Gold Production per Day (kg Au d−1) | Number of Washing Days (d_wsh) | Total Gold Production per Period (kg Au) | Hg:Au Ratio Used | Hg:Ag Ratio Used | Total Hg:Au Ratio Used | Mercury Used per Washing Day (kg Hg d−1_wsh) | Total Mercury Used per Period (kg Hg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1 | Intense activity | 5 | 10/30 | 750 | 08:01 | 02:01 | 10:01 | 150 | 7500 |
| High water | 3.5 | 10/30 | 525 | 105 | 4200 | ||||
| Scenario 2 | Intense activity | 5 | 10/30 | 750 | 5:1 × 3/4 1:1 × 1/4 | 02:01 | 6:01 | 90 | 4500 |
| High water | 3.5 | 10/30 | 525 | 63 | 2520 | ||||
| Scenario 3 | Intense activity | 5 | 10/30 | 750 | 1:1 | 02:01 | 3:1 | 45 | 2250 |
| High water | 3.5 | 10/30 | 525 | 31.5 | 1260 |
3. Results
3.1. Estimation of Mercury Use During Ore Processing
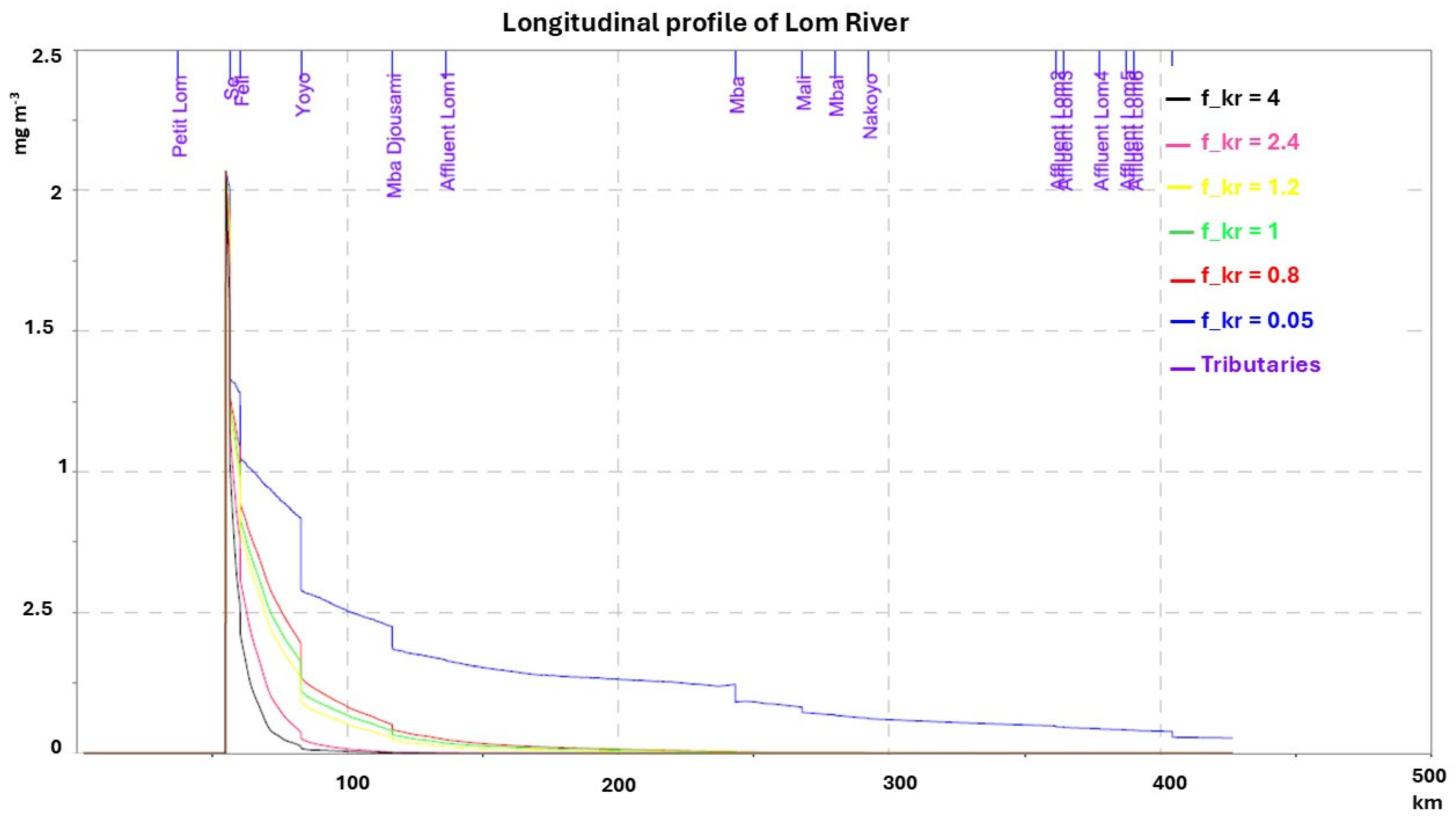
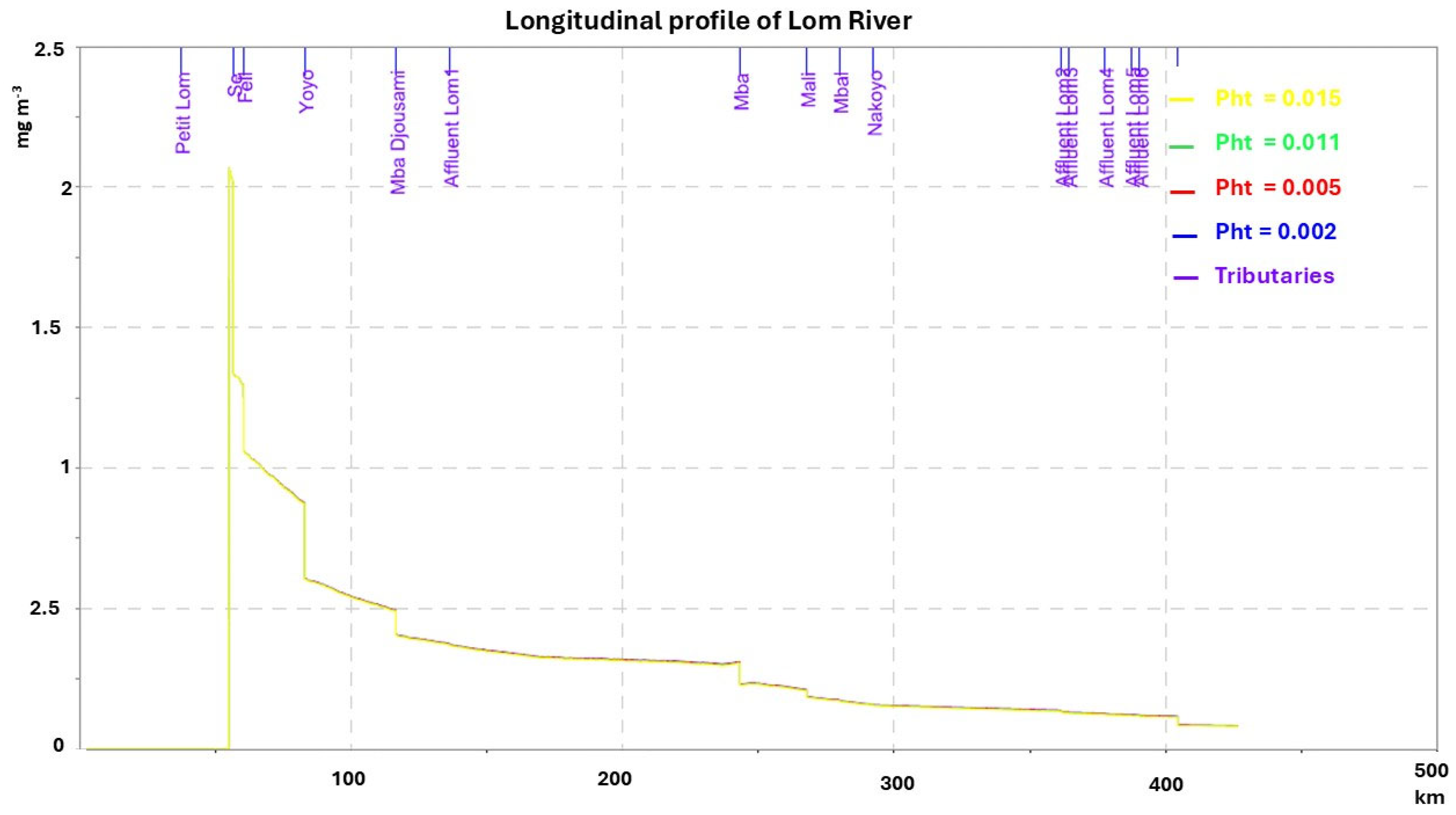
3.2. Sensitivity to Volatilization and Photodissociation Processes
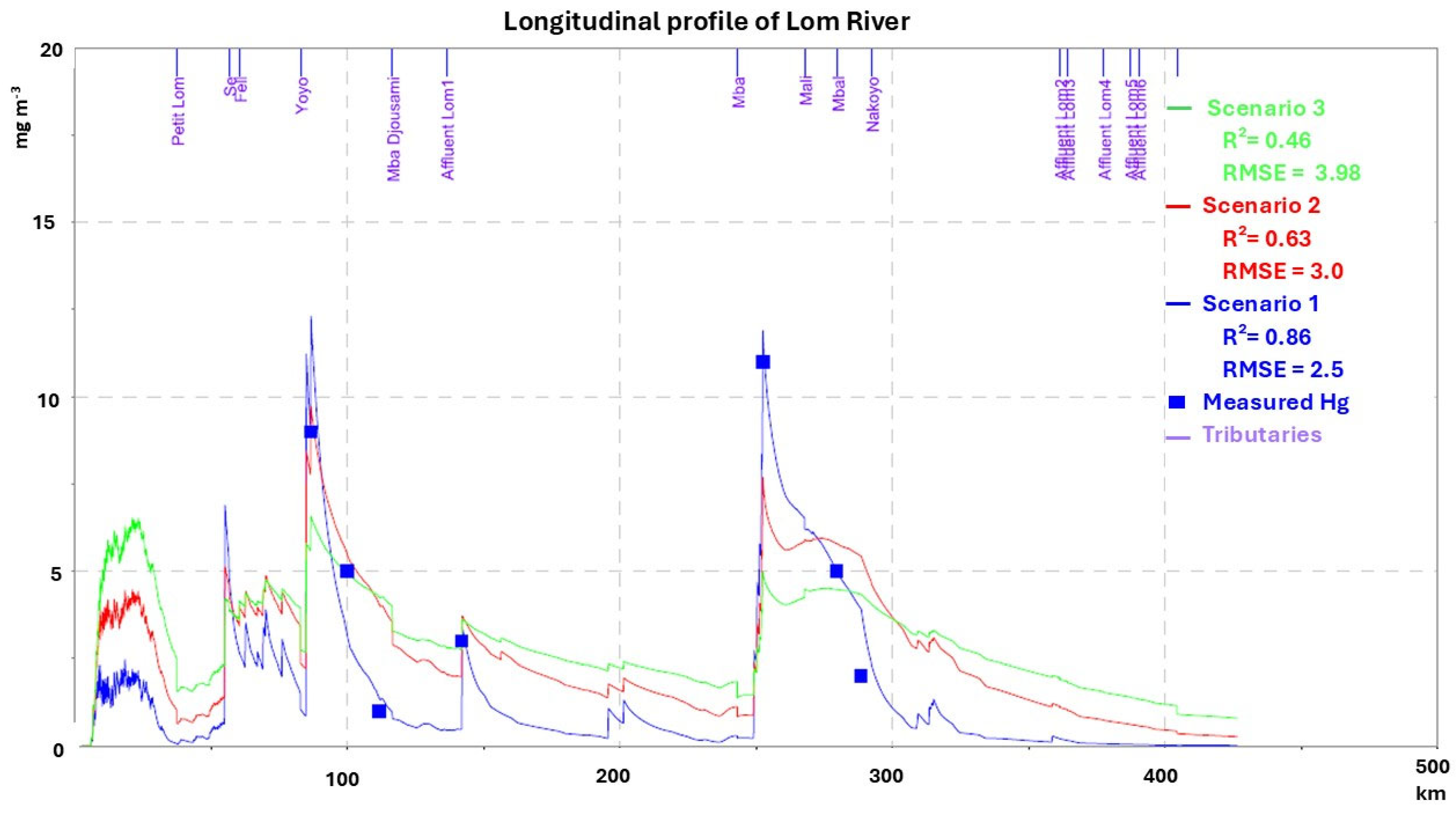
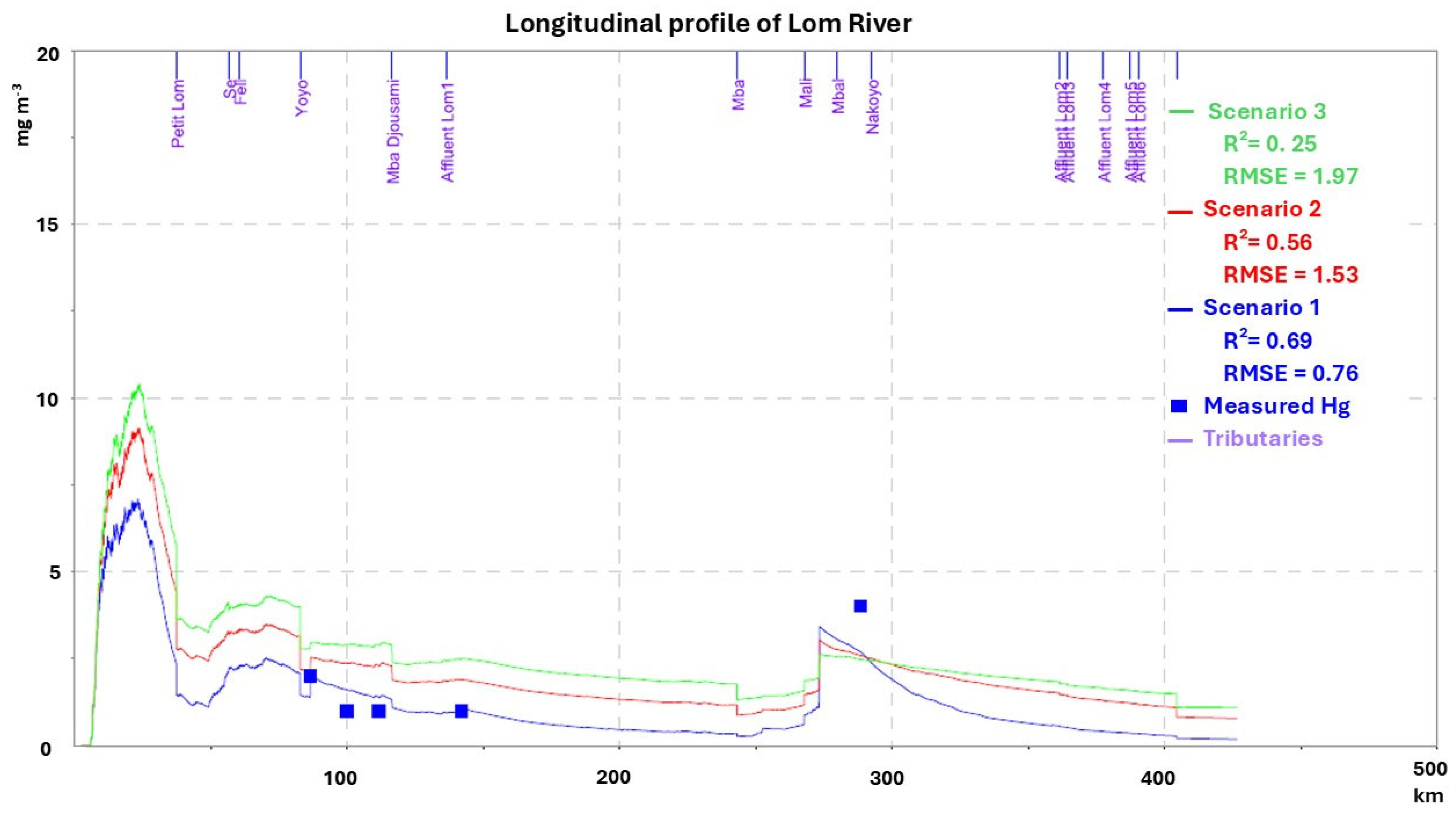
3.3. Assessment of Model Simulation Results
3.3.1. Dry Season
3.3.2. Rainy Season
3.4. Mercury Transport and Pollution
3.4.1. Spatial Distribution and Seasonal Variation
3.4.2. Assessment of Mercury Pollution: Mineral Micropollutant Index
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ndzana, C.E.; Mvondo, V.Y.E.; Tchouta, K.D.; Ngatcha, B.N. Assessment of the Impact of Small-Scale Mining on Soil Contamination by Mercury and Hydrocarbons in the Kadey Catchment (East Cameroon). Heliyon 2023, 9, e18786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNEP. UNEP Global Mercury Assessment 2018; UNEP–UN Environment Programme Chemicals and Health Branch: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; p. 62. [Google Scholar]
- Bella Atangana, M.; Ndam Ngoupayou, J.; Deliege, J.-F. Hydrogeochemistry and Mercury Contamination of Surface Water in the Lom Gold Basin (East Cameroon): Water Quality Index, Multivariate Statistical Analysis and Spatial Interpolation. Water 2023, 15, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotondrabe, F.; Ngoupayou, J.R.N.; Mfonka, Z.; Rasolomanana, E.H.; Nyangono Abolo, A.J.; Asone, B.L.; Ako Ako, A.; Rakotondrabe, M.H. Assessment of Surface Water Quality of Bétaré-Oya Gold Mining Area (East-Cameroon). JWARP 2017, 9, 960–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotondrabe, F.; Ndam Ngoupayou, J.R.; Mfonka, Z.; Rasolomanana, E.H.; Nyangono Abolo, A.J.; Ako Ako, A. Water Quality Assessment in the Bétaré-Oya Gold Mining Area (East-Cameroon): Multivariate Statistical Analysis Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngounouno Ayiwouo, M.; Mambou Ngueyep, L.L.; Mache, J.R.; Takougang Kingni, S.; Ngounouno, I. Waters of the Djouzami Gold Mining Site (Adamawa, Cameroon): Physicochemical Characterization and Treatment Test by Bana Smectite (West, Cameroon). Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2020, 2, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayiwouo, N.M.; Yamgouot, F.N.; Ngueyep Mambou, L.L.; Kingni, S.T.; Ngounouno, I. Impact of Gold Mining on the Water Quality of the Lom River, Gankombol, Cameroon. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abende Sayom, Y.R.; Mefomdjo, B.F.; Tarkwa, J.-B.; Sop, B.T.; Ngueyep, L.L.M.; Tchuikoua, B.L.; Meying, A. Comprehensive Water Quality and Heavy Metal Pollution Assessment of the Lom River in Bekao Gold Mining Sites (Adamawa-Cameroon) Using the Pollution Indices and Multivariate Statistical Approach. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2023, 234, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayiwouo, M.N.; Kingni, S.T.; Mambou, L.L.N.; Ngounouno, I.; Iqtadar, H. Modelling of Heavy Metals Transport along the Lom River in the Mining Site of Gankombol (Adamawa Cameroon). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 10793–10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmouze, J.-P.; Lucotte, M.; Boudou, A. Le Mercure en Amazonie: Rôle de L’homme et de L’environnement, Risques Sanitaires; Expertise collégiale; IRD Éditions: Paris, France, 2001; ISBN 978-2-7099-1467-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich, S.M.; Tanton, T.W.; Abdrashitova, S.A. Mercury in the Aquatic Environment: A Review of Factors Affecting Methylation. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 31, 241–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.G.; Klapstein, S.J.; Keenan, R.; O’Driscoll, N.J. Mercury Photoreduction and Photooxidation Kinetics in Estuarine Water: Effects of Salinity and Dissolved Organic Matter. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Liang, S.; Li, Y. Adsorption and Environmental Behavior of Mercury on Suspended Particulate Matter from the Yellow River and Xiaoqing River Estuaries. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malm, O.; Castro, M.B.; Bastos, W.R.; Branches, F.J.P.; Guimarães, J.R.D.; Zuffo, C.E.; Pfeiffer, W.C. An Assessment of Hg Pollution in Different Goldmining Areas, Amazon Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 1995, 175, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diringer, S.E.; Feingold, B.J.; Ortiz, E.J.; Gallis, J.A.; Araújo-Flores, J.M.; Berky, A.; Pan, W.K.Y.; Hsu-Kim, H. River Transport of Mercury from Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining and Risks for Dietary Mercury Exposure in Madre de Dios, Peru. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Brush, M.; Vega, C.; Fernandez Luis, E. Monitoring of Mercury and Mercury Compounds in and Around Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining Sites Technical Background Document | Minamata Convention on Mercury; UNEP/MC/COP.5/INF/9; Centro de Innovación Científica Amazónica (CINCIA): Madre de Dios, Peru, 2023; p. 67. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, J.D.; Telmer, K. Estimating Mercury Use and Documenting Practices in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining (ASGM); UN Environment: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-0-9939459-8-4. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, M.; Smits, K.; Phelan, T. Quantifying Mercury Use in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining for the Minamata Convention on Mercury’s National Action Plans: Approaches and Policy Implications. Environ. Sci. Policy 2023, 141, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WFD. WFD Directive—2000/60–EN–Water Framework Directive–EUR-Lex; WFD: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tsakiris, G.; Alexakis, D. Water Quality Models: An Overview. Eur. Water 2012, 37, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Žagar, D. Mercury Transport and Fate Models in Aquatic Systems: A Review and Synthesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliège, J.-F.; Everbecq, E.; Magermans, P.; Grard, A.; Bourouag, M.; Blockx, C. PEGASE, A Software Dedicated to Surface Water Quality Assessment and to European Database Reporting. In Towarde eEnvironment; Masaryk University: Brno, Czech Republic, 2009; pp. 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Olivry, J.-C. Fleuves et Rivières du Cameroun; Collection “Monographies Hydrologiques ORSTOM”; Ministère de l’enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche Scientifique au Cameroun; ORSTOM: Paris, France, 1986; ISBN 978-2-7099-0804-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mimba, M.E.; Ohba, T.; Nguemhe Fils, S.C.; Wirmvem, M.J.; Tibang, E.E.B.; Nforba, M.T.; Togwa Aka, F. Regional Hydrogeochemical Mapping for Environmental Studies in the Mineralized Lom Basin, East Cameroon: A Pre-Industrial Mining Survey. Hydrology 2017, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngako, V.; Affaton, P.; Nnange, J.M.; Njanko, T. Pan-African Tectonic Evolution in Central and Southern Cameroon: Transpression and Transtension during Sinistral Shear Movements. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2003, 36, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchindjang, M.; Philippes, M.; Unusa, H.; Eric, V.; Igor, N.; Saha, F. Mines Contre Forêts et Conservation Au Cameroun: Enjeux de l’évaluation Environnementale Du Secteur Minier Pour Le Développement Durable Au Cameroun. In Proceedings of the 20 ème Colloque International en Evaluation Environnementale, Antananarivo, Madagascar, 9 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jean, R.; Bernard, L.; Nicole, M.; Bernard, L. L’analyse de L’eau, 9th ed.; Dunod: Paris, France, 2009; ISBN 978-2-10-007246-0. [Google Scholar]
- Deliege, J.-F.; Everbecq, E.; Magermans, P.; Grard, A.; Bourouag, T.; Blockx, C.; Smitz, J. Pegase, An Integrated River/Basin Model Dedicated To Surface Water Quality Assessment: Application To Cocaine. Acta Clin. Belg. 2010, 65, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grard, A.; Everbecq, E.; Magermans, P.; Bourouag, M.; Deliège, J.-F. Transnational Modelling of the Meuse District with PegOpera Simulation Software. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2014, 12, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukari, A.; Benabdallah, S.; Everbecq, E.; Magermans, P.; Grard, A.; Habaieb, H.; Deliège, J.-F. Assessment of Agriculture Pressures Impact on the Joumine River Water Quality Using the PEGASE Model. Environ. Manag. 2019, 64, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everbecq, E.; Gosselain, V.; Viroux, L.; Descy, J.-P. Potamon: A Dynamic Model for Predicting Phytoplankton Composition and Biomass in Lowland Rivers. Water Res. 2001, 35, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, C.E.; Lehmann, B.; Mafany, G.T. Geology and Geochemical Aspects of Lode Gold Mineralization at Dimako–Mboscorro, SE Cameroon. GEEA 2006, 6, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishiti, A.; Etame, J.; Suh, C.E. Features of Gold-Bearing Quartz Veins in an Artisanal Mining-Dominated Terrain, Batouri Gold District, Eastern Region of Cameroon. Episodes 2019, 42, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeuda Ndonfack, K.I.; Xie, Y.; Goldfarb, R.; Zhong, R.; Qu, Y. Genesis and Mineralization Style of Gold Occurrences of the Lower Lom Belt, Bétaré Oya District, Eastern Cameroon. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMAP/UN Environment Technical Background Report for the Global Mercury Assessment 2018|AMAP. Available online: https://www.amap.no/documents/doc/technical-background-report-for-the-global-mercury-assessment-2018/1815 (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Everbecq, E.; Deliège, J.-F.; Bourouag, M.; Markatos, M. PIRENE: Programme Intégré de Recherche Environnement-Eau: Partims ‘ Elaboration du Module Qualité des Eaux de Surface ‘et ‘Elaboration du Modèle Intégré MOIRA (Modèle Intégré Pour Les Ressources Aquatiques)’—Rapport Final 2001–2005; University of Liège: Liège, Belgium, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, R.W.H.; Warwick, J.J.; Heim, K.J.; Bonzongo, J.C.; Miller, J.R.; Lyons, W.B. Simulation of Mercury Transport and Fate in the Carson River, Nevada. Ecol. Model. 2000, 125, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, R.W.H.; Warwick, J.J. Uncertainty Analysis of the Carson River Mercury Transport Model. Ecol. Model. 2001, 137, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, R.B., Jr.; Tsiros, I.X.; Wool, T.A. Modeling Mercury Fluxes and Concentrations in a Georgia Watershed Receiving Atmospheric Deposition Load from Direct and Indirect Sources. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2005, 55, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knightes, C. Development and Test Application of a Screening-Level Mercury Fate Model and Tool for Evaluating Wildlife Exposure Risk for Surface Waters with Mercury-Contaminated Sediments (SERAFM). Environ. Model. Softw. 2008, 23, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knightes, C.D.; Ambrose, R.B.; Avant, B.; Han, Y.; Acrey, B.; Bouchard, D.C.; Zepp, R.; Wool, T. Modeling Framework for Simulating Concentrations of Solute Chemicals, Nanoparticles, and Solids in Surface Waters and Sediments: WASP8 Advanced Toxicant Module. Env. Model. Softw. 2019, 111, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muresan, B.; Cossa, D.; Richard, S.; Burban, B. Mercury Speciation and Exchanges at the Air–Water Interface of a Tropical Artificial Reservoir, French Guiana. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 385, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niane, B.; Moritz, R.; Guédron, S.; Ngom, P.M.; Pfeifer, H.R.; Mall, I.; Poté, J. Effect of Recent Artisanal Small-Scale Gold Mining on the Contamination of Surface River Sediment: Case of Gambia River, Kedougou Region, Southeastern Senegal. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 144, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niane, B.; Guédron, S.; Feder, F.; Legros, S.; Ngom, P.M.; Moritz, R. Impact of Recent Artisanal Small-Scale Gold Mining in Senegal: Mercury and Methylmercury Contamination of Terrestrial and Aquatic Ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngounouno Ayiwouo, M.; Ngueyep, L.L.M.; Kingni, S.T.; Nforsoh, S.N.; Ngounouno, I. Evaluation of the Impact of Gold Mining Activities on the Waters and Sediments of Lom River, Wakaso, Cameroon and the Restorative Effect of Moringa Oleifera Seeds. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Brush, M.; McLagan, D.S.; Biester, H. Fate of Mercury from Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in Tropical Rivers: Hydrological and Biogeochemical Controls. A Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 437–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudin, L.C.; Maupas, D.; L’eau, A.D. Système d’évaluation de La Qualité de l’eau Des Cours d’eau (Seq-Eau); MEDD Agences de l’eau: Lyon, France, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mandizha, N.T.; Kugara, J.; Mombeshora, E.T.; Zaranyika, M.F. Elemental Composition and Speciation Trends in Upper Mazowe River, a Typical Sub-Tropical River Ecosystem Impacted by Gold Mining and Agriculture in Zimbabwe. Environ. Adv. 2023, 14, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data Type | Responsible Authorities/References | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geographic | Administrative boundaries | Earth Explorer IRD map library | 2015–2016 2021 |
| Digital Elevation Model | |||
| Land use | |||
| Population | Population | National Institute of Statistics (INS) | 2010 |
| Industrial discharges | Mining site locations | Artisan Mining Support and Promotion Framework (CAPAM)/Ministry of Mines, Industry and Technological Development | 2019 |
| Mercury amalgamation practice | |||
| Livestock | Cattle and pigs by district | Cameroon Ministry of Livestock, Fisheries and Animal Industries | 2021 |
| Hydro- meteorological | Flow rates | Hydrological Research Center | 1951–2023 |
| Water depths | |||
| Daily rainfall | National Meteorological Office/global weather website | 1979–2023 | |
| Daily insolation | |||
| Water temperature | |||
| Parameter | Value | Unit of Measure |
|---|---|---|
| Soil leaching functions for mercury concentration in mining surface | 25 | mg m−3 |
| Number of people equivalent | 0.1 | mg PE−1 d−1 |
| Porcine livestock unit in pasture | 1.0 | mg lsu−1 d−1 |
| Bovine livestock unit in stable | 1.0 | mg lsu−1 d−1 |
| Discharge adsorbed on sediment | 0.2 | |
| Q10 degradation rate variation | 1 | |
| Volatilization factor | 0.05–4 | |
| Photodissociation rate at 100 W | 0.002–0.015 | d−1 |
| Sedimentation rate of suspended matter | 0.8 | m d−1 |
| Dissolved–bound transfer rate | 0.5 | d−1 |
| Bound–dissolved transfer rate | 0.3 | d−1 |
| Bottom adsorption rate | 0.25 | m d−1 |
| High saturation constant for bottom adsorption | 0.2 | mg m−3 |
| Low saturation constant for bottom adsorption | 5.0 | mg m−3 |
| Minimum concentration for dissolved calculation | 1 × 10−6 | mg m−3 |
| Minimum concentration for particulate calculation | 1 × 10−6 | mg m−3 |
| Molar mass | 200.59 | g mol−1 |
| Electric charge | 2.0 | |
| Molar ionic conductivity | 0.01272 | S·m2 mol−1 |
| Turbidity | 0.22–4758 | NTU |
| Total dissolved solids (TSS) | 2.62–452 | mg L−1 |
| Insolation | 2838 | W m−2 |
| Water height | 0.3–57.5 | m |
| Velocity | 0.16–1.65 | m s−1 |
| Temperature | 21.26–26.91 | °C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atangana, M.S.B.; Magermans, P.; Ngoupayou, J.R.N.; Deliege, J.-F. Quantifying Mercury Use and Modeling Its Fate and Transport in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in the Lom Basin. Hydrology 2025, 12, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040077
Atangana MSB, Magermans P, Ngoupayou JRN, Deliege J-F. Quantifying Mercury Use and Modeling Its Fate and Transport in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in the Lom Basin. Hydrology. 2025; 12(4):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040077
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtangana, Marie Sorella Bella, Pol Magermans, Jules Rémy Ndam Ngoupayou, and Jean-François Deliege. 2025. "Quantifying Mercury Use and Modeling Its Fate and Transport in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in the Lom Basin" Hydrology 12, no. 4: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040077
APA StyleAtangana, M. S. B., Magermans, P., Ngoupayou, J. R. N., & Deliege, J.-F. (2025). Quantifying Mercury Use and Modeling Its Fate and Transport in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in the Lom Basin. Hydrology, 12(4), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040077






