Assessment of Satellite-Based Rainfall Products for Flood Modeling in the Ouémé River Basin in Benin (West Africa)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
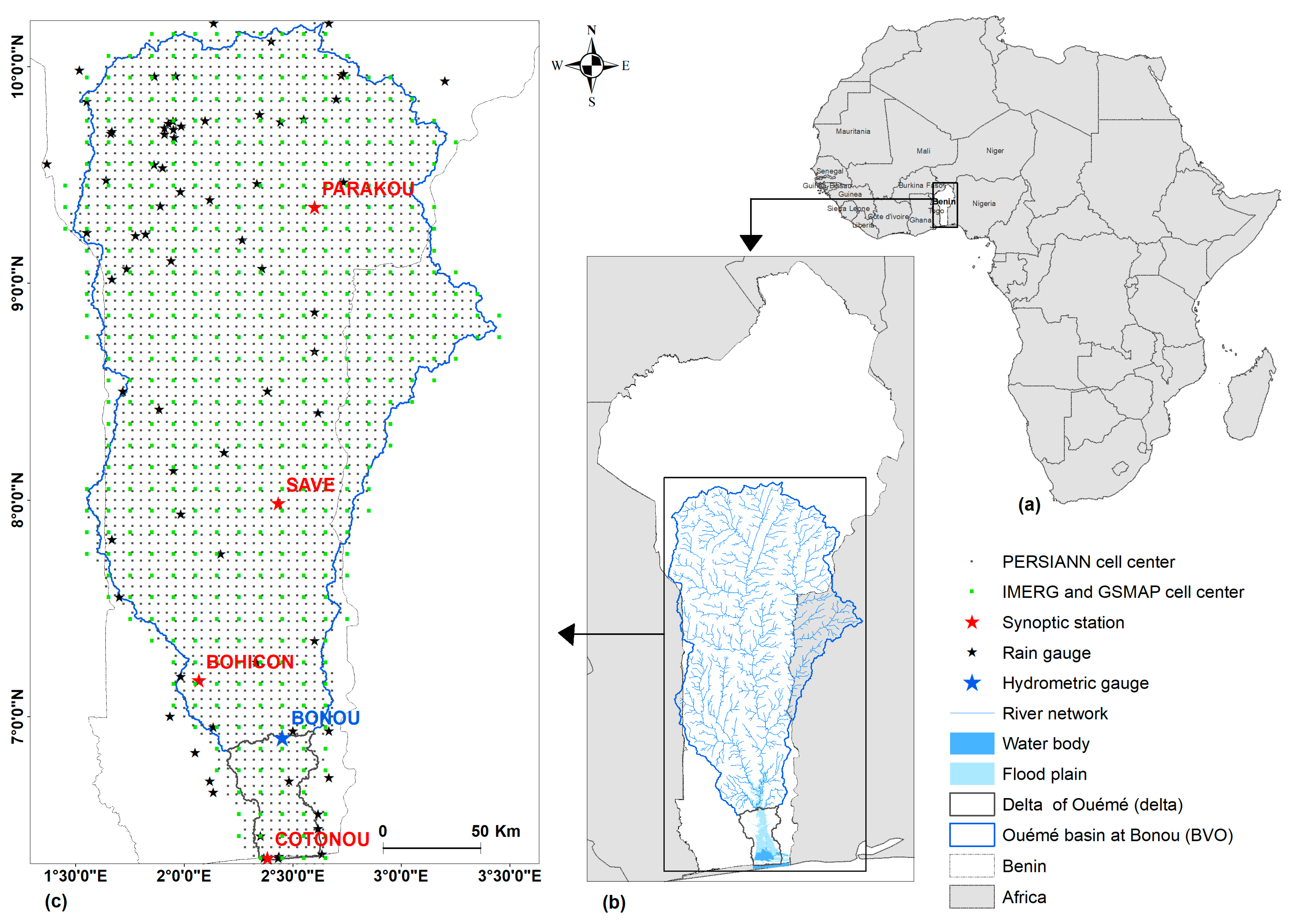
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Methodology
2.2.1. Data Used
2.2.2. Satellite-Based Rainfall Assessment
- The coefficient of correlation (R) is the expression of how well the estimation qualitatively fits the variation in the reference data. It is scale- and unit-independent, and thus allows for cross-comparison among data at different spatial or temporal resolutions and/or different units. The worst value is 0 when predictions are uncorrelated with observations and the best value is 1.
- The percentage of bias (PBIAS) is another scale- and unit-independent metric to quantify the bias in estimates. The estimation is considered as good as its value is close to zero, which is the optimum score; very good, good, satisfactory and unsatisfactory scores are values smaller than 10, from 10 to 15, from 15 to 25 and above or equal to 25, respectively [44,45].
- The Kling–Gupta efficiency (KGE) combines the effects of correlation, bias and variability. A good score is a value greater than 0.5 and its optimum value is 1 [46].
2.2.3. Bias-Correction Methods
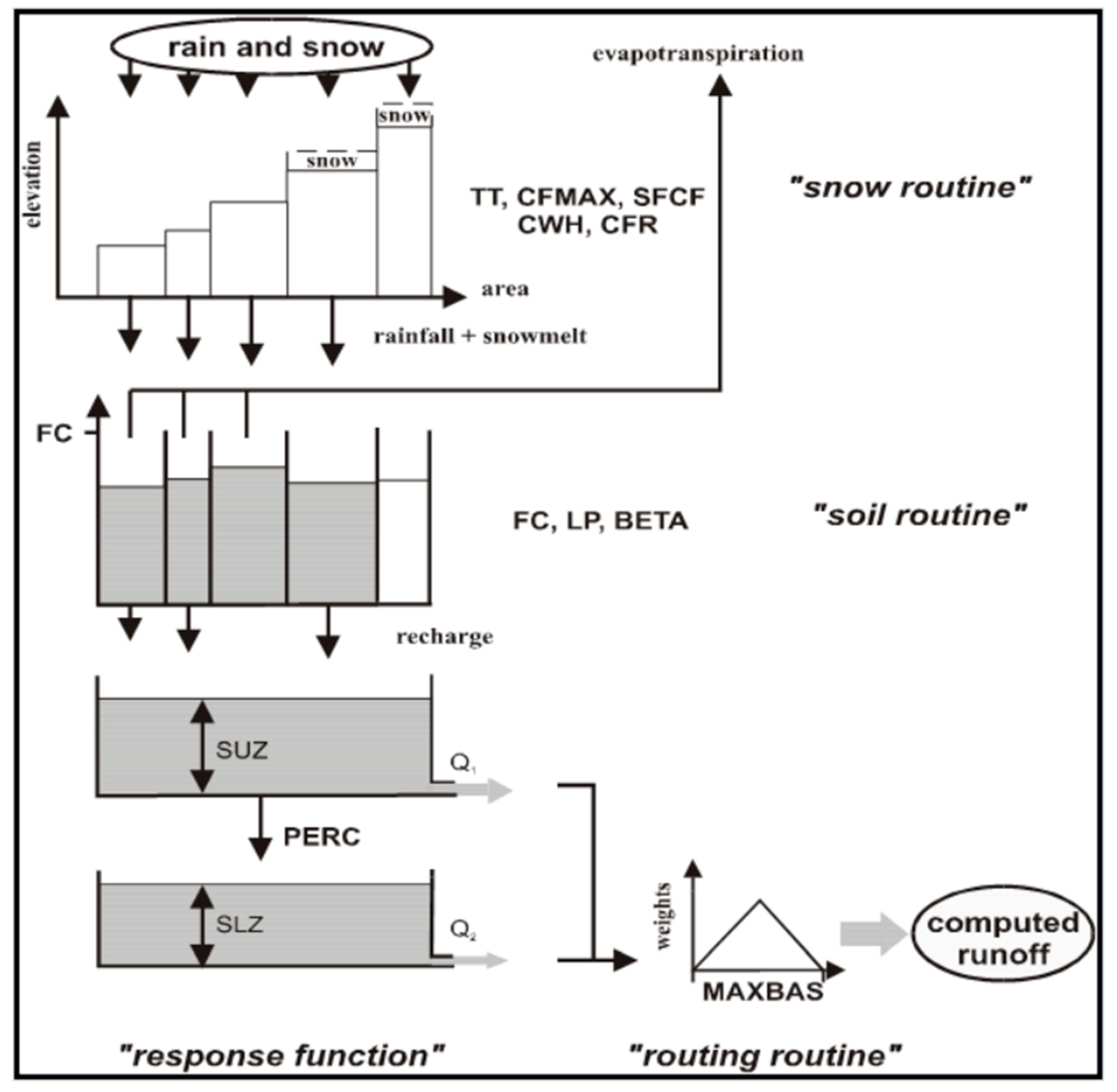
2.2.4. Hydrological Modeling Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Satellite-Based Rainfall Data
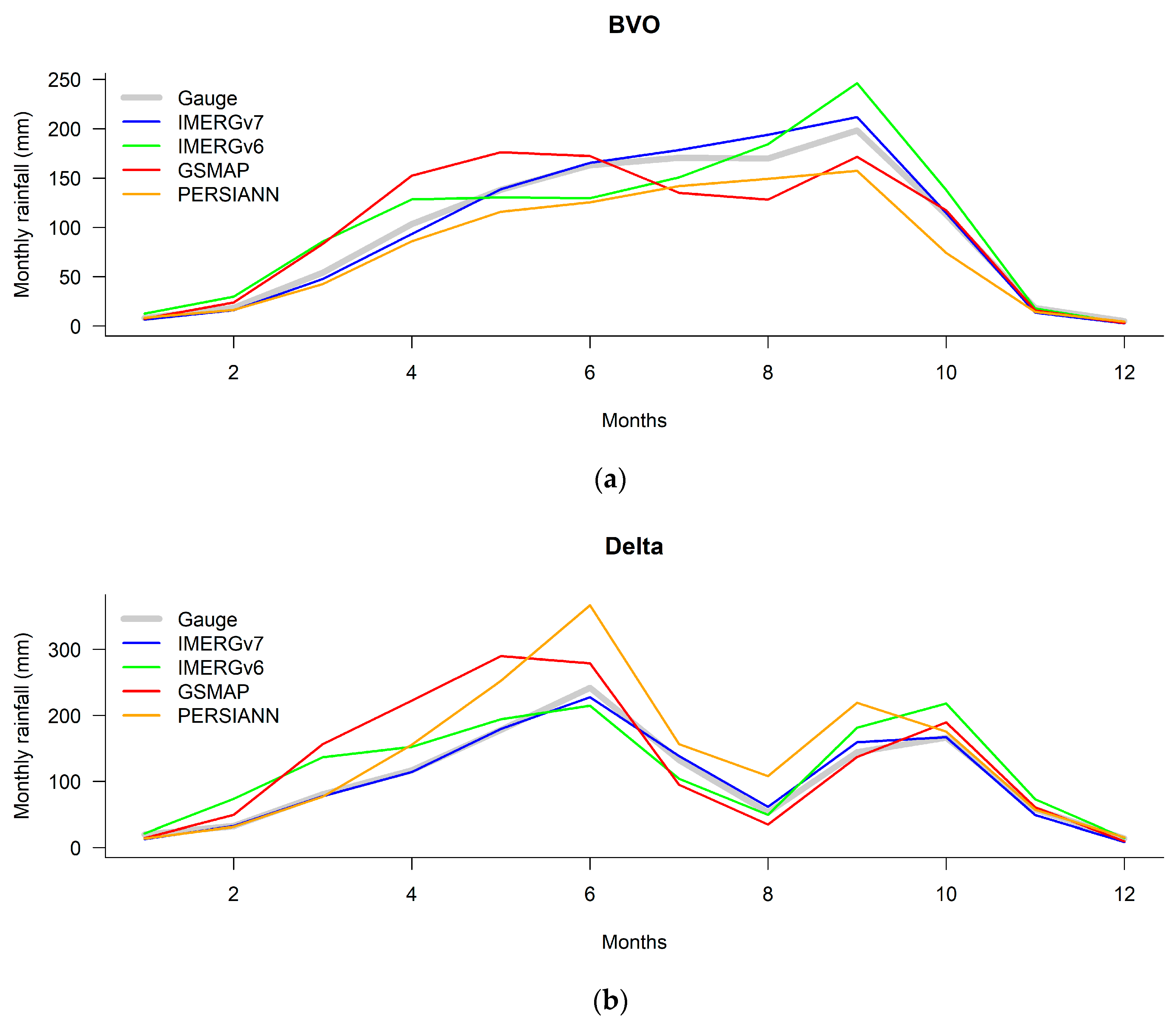
3.1.1. Qualitative Analysis
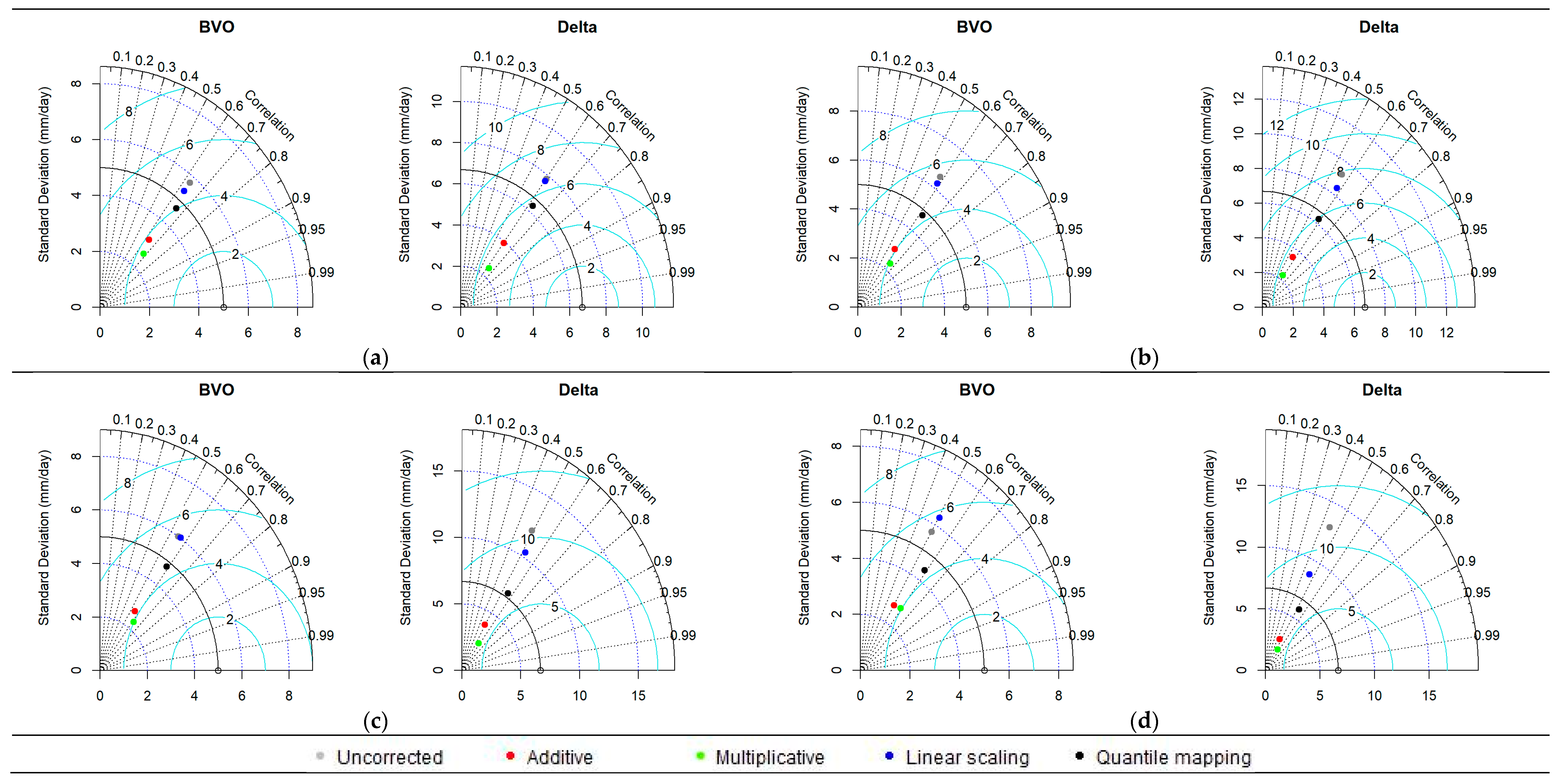
3.1.2. Quantitative Analysis
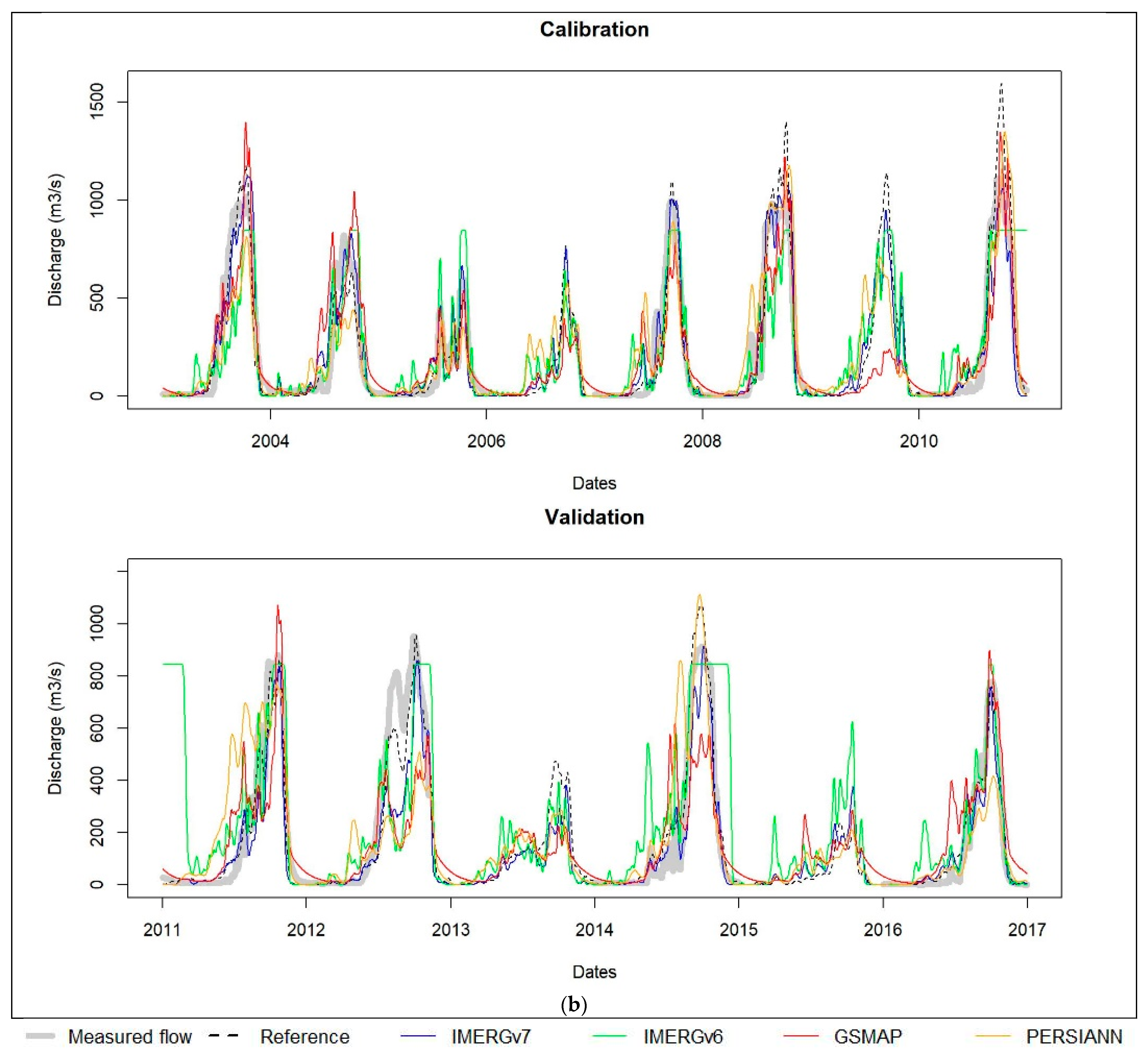
3.2. Bias Correction of Satellite-Based Rainfall Data
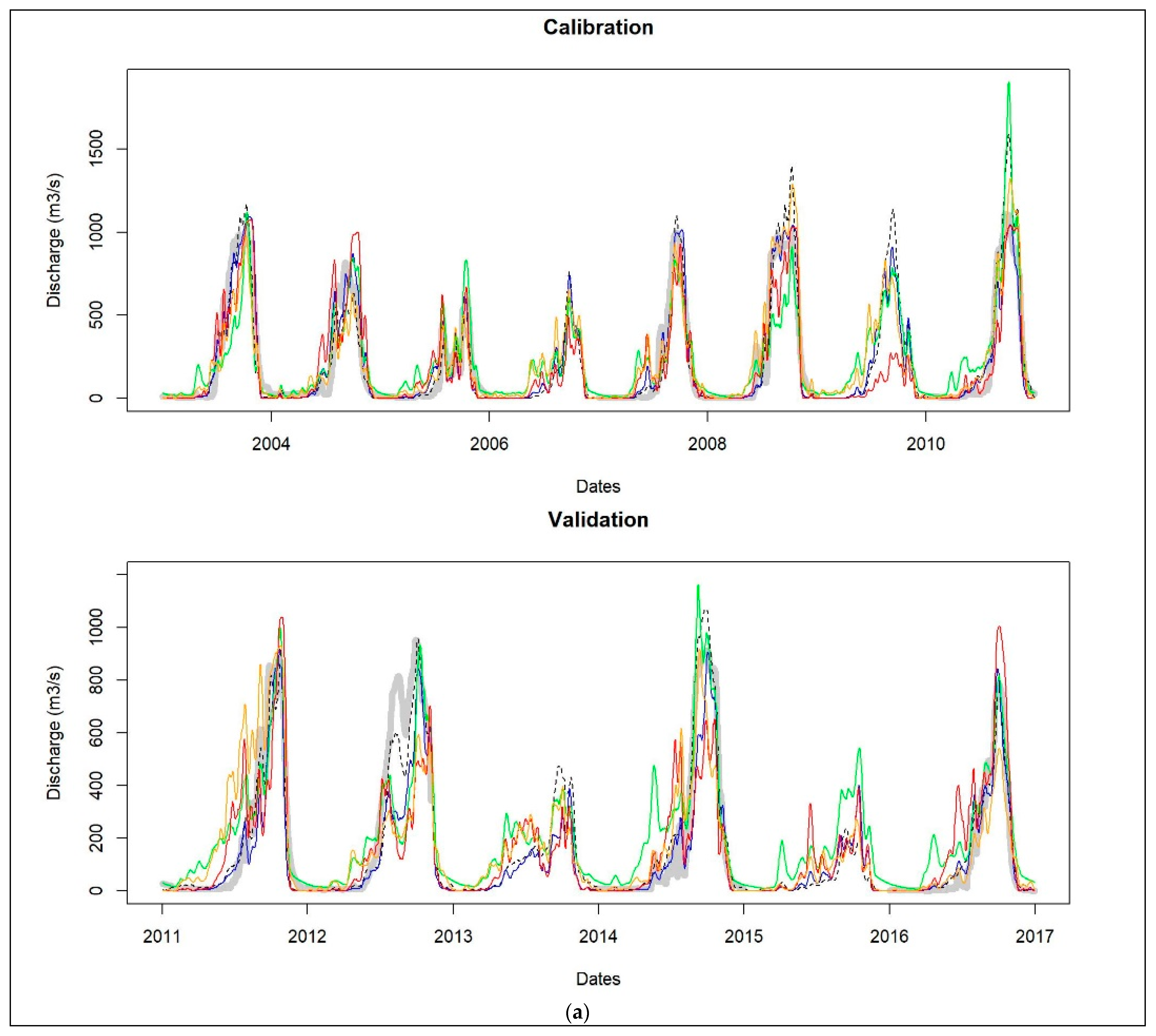
3.3. Hydrological Modeling Assessment of Satellite-Based Rainfall Data
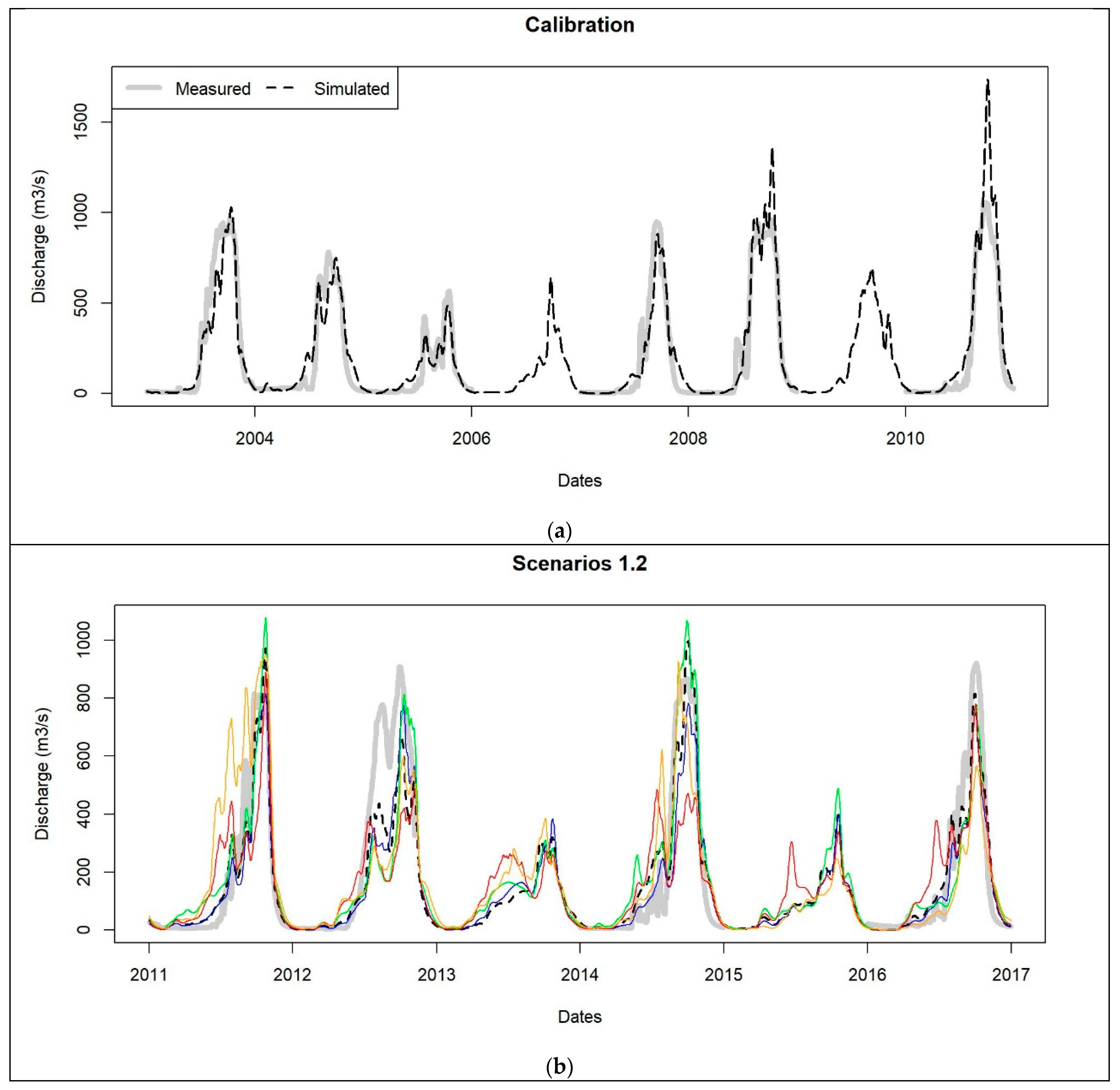
3.3.1. Reference Scenario
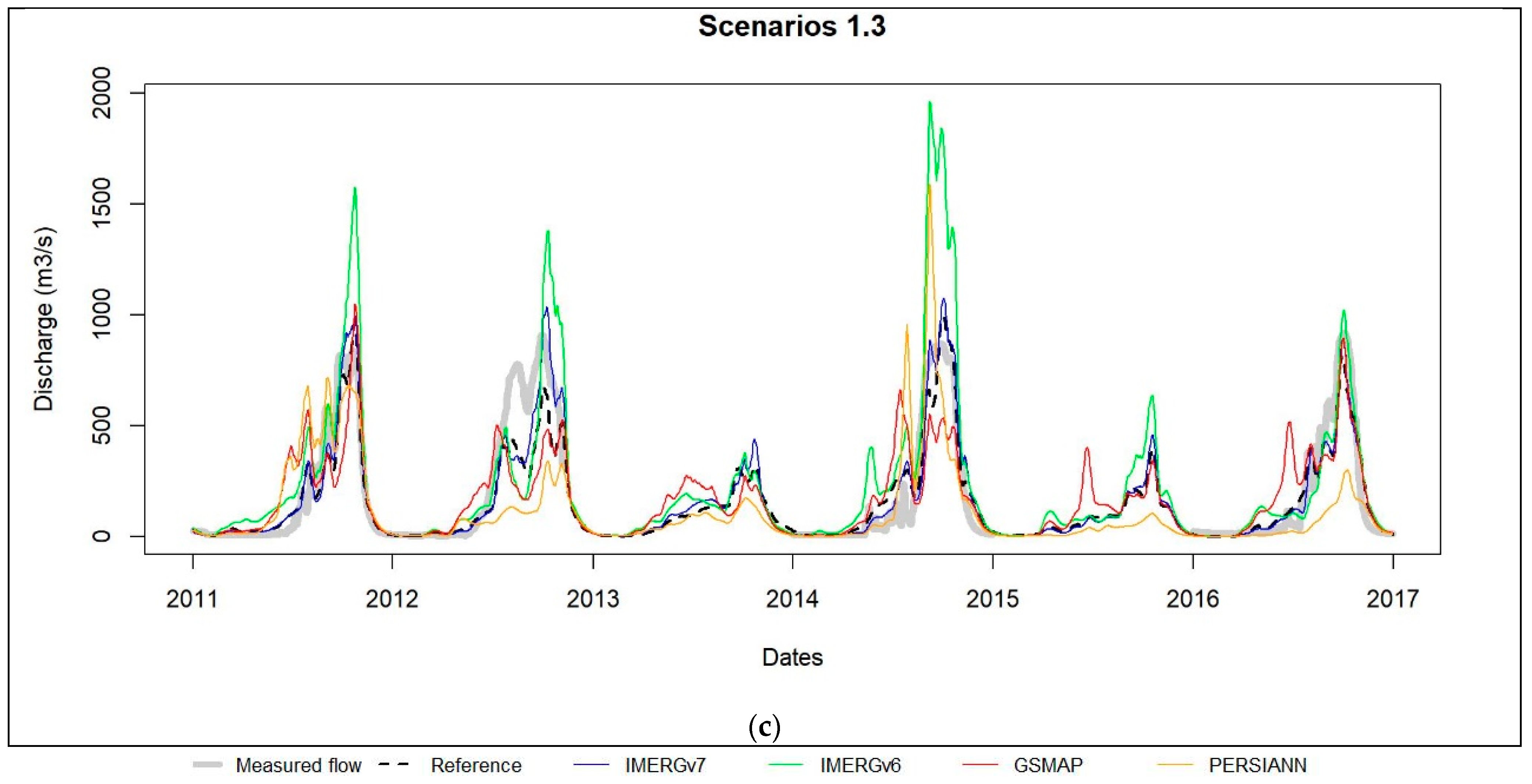
3.3.2. Satellite-Only Scenarios
4. Discussion
4.1. Satellite-Based Rainfall Data Accuracy
4.2. Bias Correction of Satellite-Based Rainfall Data
4.3. Hydrological Modeling Accuracy
4.4. Interests and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC; Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change. Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-1-009-15789-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sylla, M.B.; Nikiema, P.M.; Gibba, P.; Kebe, I.; Klutse, N.A.B. Climate Change over West Africa: Recent Trends and Future Projections. In Adaptation to Climate Change and Variability in Rural West Africa; Yaro, J.A., Hesselberg, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 25–40. ISBN 978-3-319-31497-6. [Google Scholar]
- Tabari, H.; Hosseinzadehtalaei, P.; Thiery, W.; Willems, P. Amplified Drought and Flood Risk Under Future Socioeconomic and Climatic Change. Earth’s Future 2021, 9, e2021EF002295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekolu, J.; Dieppois, B.; Tramblay, Y.; Villarini, G.; Slater, L.J.; Mahé, G.; Paturel, J.-E.; Eden, J.M.; Moulds, S.; Sidibe, M.; et al. Variability in flood frequency in sub-Saharan Africa: The role of large-scale climate modes of variability and their future impacts. J. Hydrol. 2024, 640, 131679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthou, G.; Lebel, T.; Vischel, T.; Quantin, G.; Sane, Y.; Ba, A.; Ndiaye, O.; Diongue-Niang, A.; Diopkane, M. Rainfall intensification in tropical semi-arid regions: The Sahelian case. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 064013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramblay, Y.; Villarini, G.; Zhang, W. Observed changes in flood hazard in Africa. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1040b5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quenum, G.M.L.D.; Nkrumah, F.; Klutse, N.A.B.; Sylla, M.B. Spatiotemporal Changes in Temperature and Precipitation in West Africa. Part I: Analysis with the CMIP6 Historical Dataset. Water 2021, 13, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibi-Anoh, P.A.; Koné, M.; Gerdener, H.; Kusche, J.; N’Da, C.K. Hydrometeorological Extreme Events in West Africa: Droughts. Surv. Geophys. 2023, 44, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, P.; Lavabre, J.; Fouchier, C.; Diss, S.; Javelle, P. Sensitivity of hydrological models to uncertainty in rainfall input. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, G.; Reinoso, R.; Van De Giesen, N.C.; Clemens, F.H.L.R.; Ten Veldhuis, J.A.E. On the sensitivity of urban hydrodynamic modelling to rainfall spatial and temporal resolution. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 691–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Bárdossy, A.; Zhang, K. Sensitivity of hydrological models to temporal and spatial resolutions of rainfall data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 2647–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliefernicht, J.; Salack, S.; Waongo, M.; Annor, T.; Laux, P.; Kunstmann, H. Towards a historical precipitation database for West Africa: Overview, quality control and harmonization. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 4001–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounkpè, J.; Diekkrüger, B.; Badou, D.; Afouda, A. Change in Heavy Rainfall Characteristics over the Ouémé River Basin, Benin Republic, West Africa. Climate 2016, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belabid, N.; Zhao, F.; Brocca, L.; Huang, Y.; Tan, Y. Near-Real-Time Flood Forecasting Based on Satellite Precipitation Products. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Massari, C.; Pellarin, T.; Filippucci, P.; Ciabatta, L.; Camici, S.; Kerr, Y.H.; Fernández-Prieto, D. River flow prediction in data scarce regions: Soil moisture integrated satellite rainfall products outperform rain gauge observations in West Africa. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggioni, V.; Massari, C. On the performance of satellite precipitation products in riverine flood modeling: A review. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, K.; Velpuri, N.M.; Leh, M.; Akpoti, K.; Owusu, A.; Tinonetsana, P.; Hamouda, T.; Ghansah, B.; Paranamana, T.P.; Munzimi, Y. Accuracy of satellite and reanalysis rainfall estimates over Africa: A multi-scale assessment of eight products for continental applications. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 49, 101514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo-Duc, T.; Matsumoto, J.; Kamimera, H.; Bui, H.-H. Monthly adjustment of Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) data over the VuGia–ThuBon River Basin in Central Vietnam using an artificial neural network. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2013, 7, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casse, C.; Gosset, M.; Peugeot, C.; Pedinotti, V.; Boone, A.; Tanimoun, B.A.; Decharme, B. Potential of satellite rainfall products to predict Niger River flood events in Niamey. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonaba, R.; Belemtougri, A.; Fowé, T.; Mounirou, L.A.; Nkiaka, E.; Dembélé, M.; Komlavi, A.; Coly, S.M.; Koïta, M.; Karambiri, H. Rainfall estimation in the West African Sahel: Comparison and cross-validation of top-down vs. bottom-up precipitation products in Burkina Faso. Geocarto Int. 2024, 39, 2391956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satgé, F.; Defrance, D.; Sultan, B.; Bonnet, M.-P.; Seyler, F.; Rouché, N.; Pierron, F.; Paturel, J.-E. Evaluation of 23 gridded precipitation datasets across West Africa. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houngnibo, M.C.M.; Minoungou, B.; Traore, S.B.; Maidment, R.I.; Alhassane, A.; Ali, A. Validation of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over West Africa for rainfall monitoring and early warning. Front. Clim. 2023, 5, 1185754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badou, D.F.; Diekkrüger, B.; Kapangaziwiri, E.; Mbaye, M.L.; Yira, Y.; Lawin, E.A.; Oyerinde, G.T.; Afouda, A. Modelling blue and green water availability under climate change in the Beninese Basin of the Niger River Basin, West Africa. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2526–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyerinde, G.T.; Fademi, I.O.; Denton, O.A. Modeling runoff with satellite-based rainfall estimates in the Niger basin. Cogent Food Agric. 2017, 3, 1363340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounguè, N.R.; Ogbu, K.N.; Almoradie, A.D.S.; Evers, M. Evaluation of the performance of remotely sensed rainfall datasets for flood simulation in the transboundary Mono River catchment, Togo and Benin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 36, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembélé, M.; Zwart, S.J. Evaluation and comparison of satellite-based rainfall products in Burkina Faso, West Africa. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 3995–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, M.X.; Molkenthin, F. Flood hazard mapping for data-scarce and ungauged coastal river basins using advanced hydrodynamic models, high temporal-spatial resolution remote sensing precipitation data, and satellite imageries. Nat. Hazards 2021, 109, 441–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodjrenou, R.; Cohard, J.-M.; Hector, B.; Lawin, E.A.; Chagnaud, G.; Danso, D.K.; N’tcha M’po, Y.; Badou, F.; Ahamide, B. Evaluation of Reanalysis Estimates of Precipitation, Radiation, and Temperature over Benin (West Africa). J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2023, 62, 1005–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodjrènou, R.; Sintondji, L.O.; Comandan, F. Hydrological modeling with physics-based models in the oueme basin: Issues and perspectives for simulation optimization. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 48, 101448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Barbé, L.; Alé, G.; Millet, B.; Texier, H.; Borel, Y.; Gualde, R. Les Ressources en Eaux Superficielles de la RÉPUBLIQUE du Bénin; ORSTOM Edition: Paris, France, 1993; ISBN 2-7099-1168-X. [Google Scholar]
- Ague, A.; Afouda, A. Analyse fréquentielle et nouvelle cartographie des maxima annuels de pluies journalières au Bénin. Int. J. Bio. Chem. Sci. 2015, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpo, A.B.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; Laouali, D.; Delon, C.; Liousse, C.; Adon, M.; Gardrat, E.; Mariscal, A.; Darakpa, C. Precipitation chemistry and wet deposition in a remote wet savanna site in West Africa: Djougou (Benin). Atmos. Environ. 2015, 115, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djossou, J.; Akpo, A.; Afféwé, J.; Donnou, V.; Liousse, C.; Léon, J.-F.; Nonfodji, F.; Awanou, C. Dynamics of the Inter Tropical Front and Rainy Season Onset in Benin. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossa, Y.A.; Djangni, O.; Yira, Y.; Hounkpè, J.; Avossè, A.D.; Sintondji, L.O. Flood Risk Assessment in the Lower Valley of Ouémé, Benin. Open J. Mod. Hydrol. 2024, 14, 130–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawin, A.E.; Hounguè, R.; N’Tcha M’Po, Y.; Hounguè, N.R.; Attogouinon, A.; Afouda, A.A. Mid-Century Climate Change Impacts on Ouémé River Discharge at Bonou Outlet (Benin). Hydrology 2019, 6, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaigneau, A.; Okpeitcha, O.V.; Morel, Y.; Stieglitz, T.; Assogba, A.; Benoist, M.; Allamel, P.; Honfo, J.; Awoulmbang Sakpak, T.D.; Rétif, F.; et al. From seasonal flood pulse to seiche: Multi-frequency water-level fluctuations in a large shallow tropical lagoon (Nokoué Lagoon, Benin). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 267, 107767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobard, I.; Chopin, F.; Berges, J.C.; Roca, R. An intercomparison of 10-day satellite precipitation products during West African monsoon. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 2353–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poméon, T.; Jackisch, D.; Diekkrüger, B. Evaluating the performance of remotely sensed and reanalysed precipitation data over West Africa using HBV light. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwachukwu, P.N.; Satge, F.; Yacoubi, S.E.; Pinel, S.; Bonnet, M.-P. From TRMM to GPM: How Reliable Are Satellite-Based Precipitation Data across Nigeria? Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Gebremichael, M.; Nourani, V. Performance of the Global Forecast System’s medium-range precipitation forecasts in the Niger river basin using multiple satellite-based products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntoro, A.A.; Hapsari, R.K.; Adityawan, M.B.; Farid, M. Estimation of Extreme Rainfall over Kalimantan Island based on GPM IMERG Daily Data. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1065, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Hong, Y.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Evaluation of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) and Its Utility in Hydrologic Prediction in the La Plata Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Fu, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Shi, K.; Sivakumar, B. Evaluation of Quantitative Precipitation Predictions by ECMWF, CMA, and UKMO for Flood Forecasting: Application to Two Basins in China. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2018, 19, 05018003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences, 2nd ed.; International geophysics series; Elsevier: Amsterdam,The Netherlands; Paris, France, 2006; ISBN 978-0-12-751966-1. [Google Scholar]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Pan, M.; Roy, T.; Weedon, G.P.; Pappenberger, F.; Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Wood, E.F. Daily evaluation of 26 precipitation datasets using Stage-IV gauge-radar data for the CONUS. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, U.; Shekhar, M.S.; Singh, G.P. Correction of mesoscale model daily precipitation data over Northwestern Himalaya. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 143, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO. Guide D’utilisation de L’indice de Précipitations Normalize; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Tang, L.; Sapiano, M.; Maggioni, V.; Wu, H. Modeling errors in daily precipitation measurements: Additive or multiplicative? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2060–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, L.; Bremnes, J.B.; Haugen, J.E.; Engen-Skaugen, T. Technical Note: Downscaling RCM precipitation to the station scale using statistical transformations—A comparison of methods. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3383–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stisen, S.; Sandholt, I. Evaluation of remote-sensing-based rainfall products through predictive capability in hydrological runoff modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Tang, G.; Zhao, P.; Hong, Y.; Gou, Y.; Yang, K. Statistical assessment and hydrological utility of the latest multi-satellite precipitation analysis IMERG in Ganjiang River basin. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Vergopolan, N.; Pan, M.; Levizzani, V.; Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Weedon, G.P.; Brocca, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Huffman, G.J.; Wood, E.F. Global-scale evaluation of 22 precipitation datasets using gauge observations and hydrological modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 6201–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, J.; Vis, M.J. Teaching hydrological modeling with a user-friendly catchment-runoff-model software package. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3315–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Haile, A.; Sazib, N.; Zhang, Y.; Rientjes, T. Effect of Bias Correction of Satellite-Rainfall Estimates on Runoff Simulations at the Source of the Upper Blue Nile. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6688–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshime, D.W.; Absi, R.; Ledésert, B. Evaluation and Bias Correction of CHIRP Rainfall Estimate for Rainfall-Runoff Simulation over Lake Ziway Watershed, Ethiopia. Hydrology 2019, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, T.A.; Peel, M.C.; Lowe, L.; Srikanthan, R.; McVicar, T.R. Estimating actual, potential, reference crop and pan evaporation using standard meteorological data: A pragmatic synthesis. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1331–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, M.; Naveed, M.; Iqbal, M.; Nabi, G.; Kashif, H.M.; Jawad, M.; Mujtaba, A. Evaluation of Satellite Precipitation Products for Estimation of Floods in Data-Scarce Environment. Adv. Meteorol. 2023, 2023, 1685720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbu, K.N.; Hounguè, N.R.; Gbode, I.E.; Tischbein, B. Performance Evaluation of Satellite-Based Rainfall Products over Nigeria. Climate 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinó, E.; Bech, J.; Udina, M.; Polls, F. Disentangling Satellite Precipitation Estimate Errors of Heavy Rainfall at the Daily and Sub-Daily Scales in the Western Mediterranean. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranan, M.; Fink, A.H.; Knippertz, P.; Francis, S.D.; Akpo, A.B.; Jegede, G.; Yorke, C. Interactions between Convection and a Moist Vortex Associated with an Extreme Rainfall Event over Southern West Africa. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2019, 147, 2309–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranan, M.; Fink, A.H.; Knippertz, P.; Amekudzi, L.K.; Atiah, W.A.; Stengel, M. A Process-Based Validation of GPM IMERG and Its Sources Using a Mesoscale Rain Gauge Network in the West African Forest Zone. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 729–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Gao, L.; Zhong, Y.; Peng, X. Comparison of GPM IMERG Version 06 Final Run Products and Its Latest Version 07 Precipitation Products across Scales: Similarities, Differences and Improvements. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Themeßl, M.J.; Gobiet, A.; Heinrich, G. Empirical-statistical downscaling and error correction of regional climate models and its impact on the climate change signal. Climatic Change 2012, 112, 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Po, Y.N.; Lawin, A.E.; Oyerinde, G.T.; Yao, B.K.; Afouda, A.A. Comparison of Daily Precipitation Bias Correction Methods Based on Four Regional Climate Model Outputs in Ouémé Basin, Benin. Hydrology 2016, 4, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biao, E. Assessing the Impacts of Climate Change on River Discharge Dynamics in Oueme River Basin (Benin, West Africa). Hydrology 2017, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodja, D.J.; Akognongbé, A.J.S.; Amoussou, E.; Mahé, G.; Vissin, E.W.; Paturel, J.-E.; Houndénou, C. Calibration of the hydrological model GR4J from potential evapotranspiration estimates by the Penman-Monteith and Oudin methods in the Ouémé watershed (West Africa). Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2020, 383, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essou, G.; Brissette, F. Climate Change Impacts on the Ouémé River, Benin, West Africa. J. Earth Sci. Clim. Change 2013, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Ren, L.L.; Hong, Y.; Wang, J.H.; Gourley, J.J.; Jiang, S.H.; Chen, X.; Wang, W. Hydrologic evaluation of Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis standard precipitation products in basins beyond its inclined latitude band: A case study in Laohahe basin, China. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 2009WR008965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
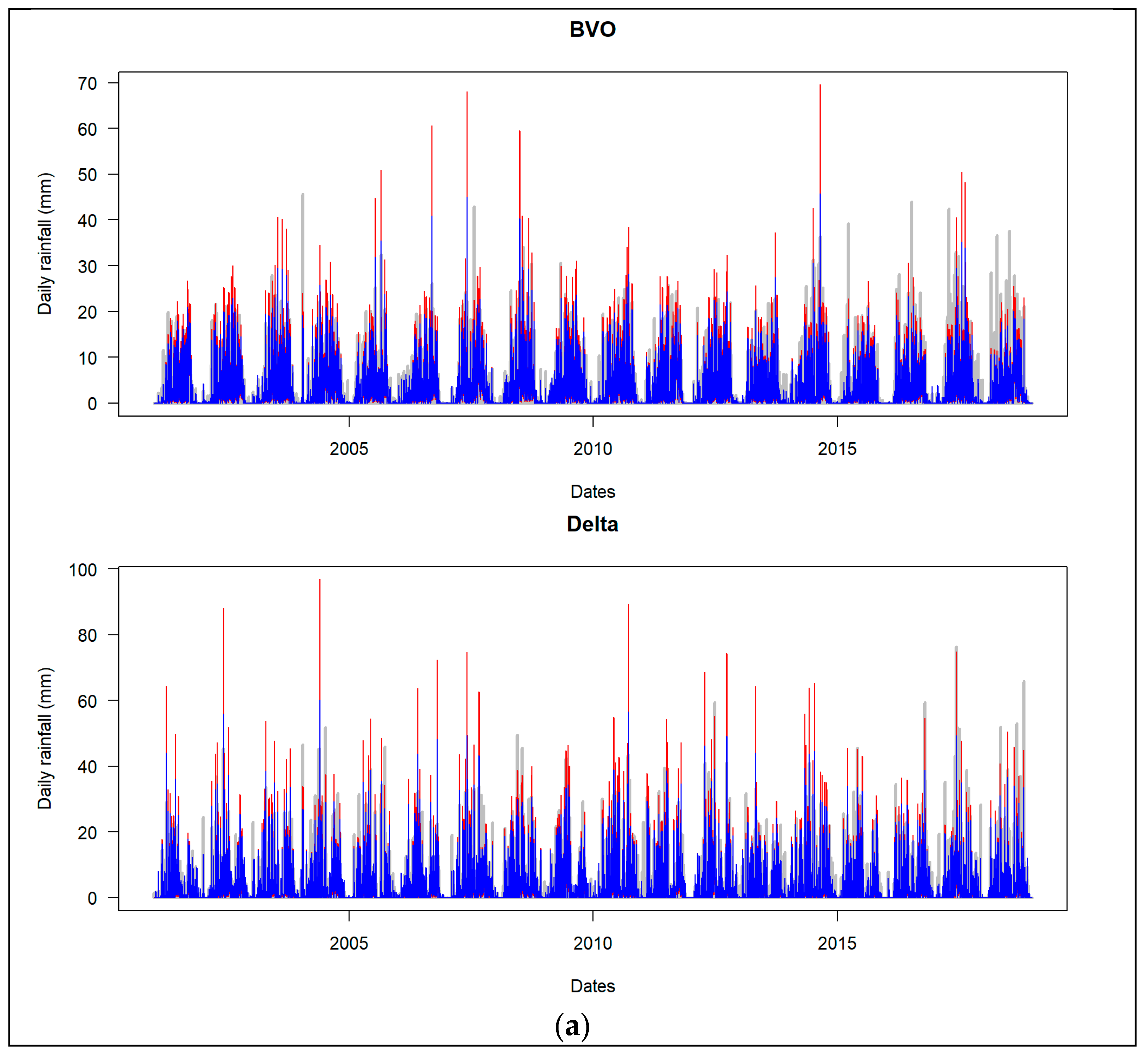
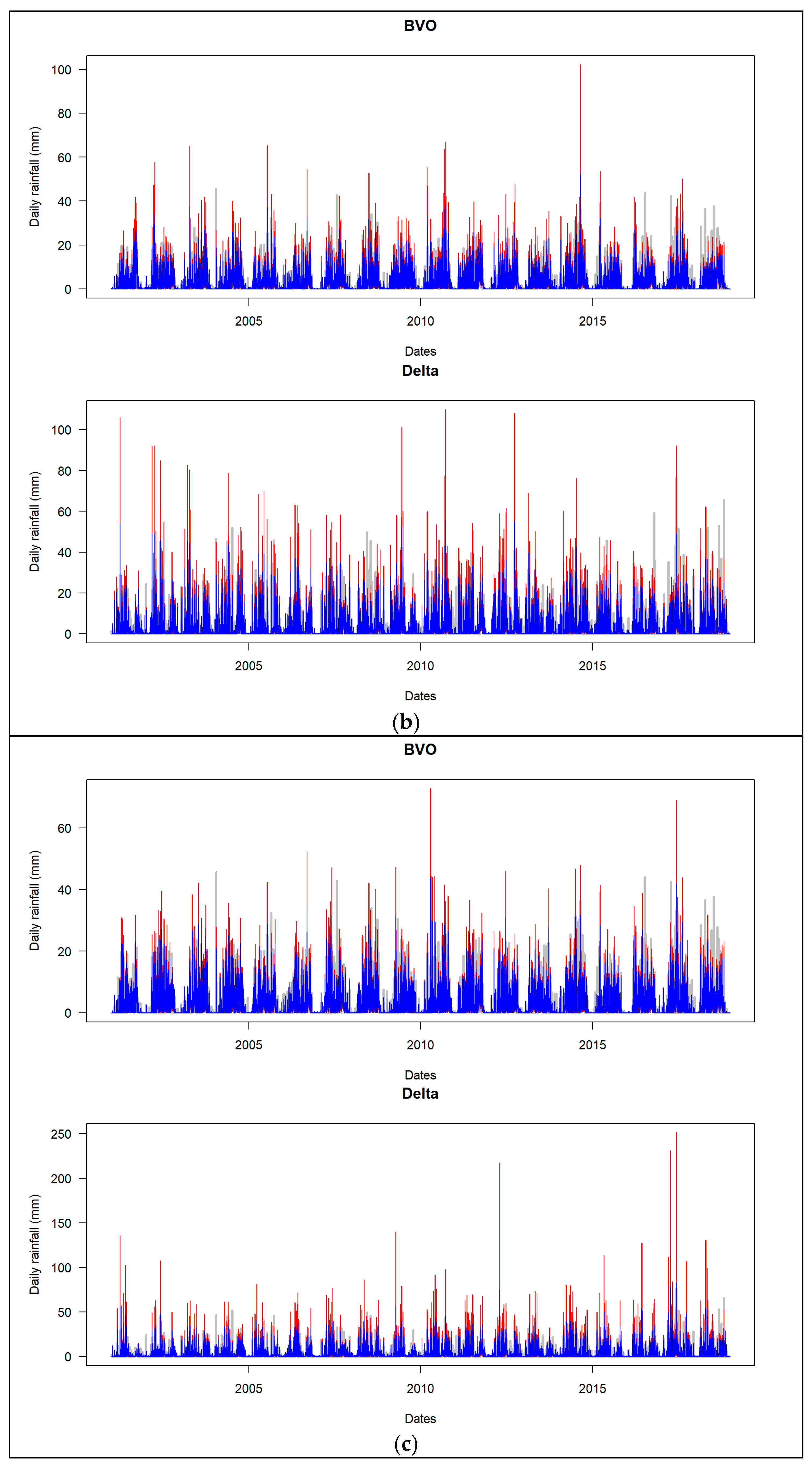

| Product | Latency | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Sensors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integrated Multi-satellite Retrieval for Global Precipitation Measurement—GPM IMERG—version 7 Late (IMERGv7) | 12 h | 0.1° × 0.1° (approximately 10 km × 10 km) | Half hour | Passive microwave, Infrared |
| Integrated Multi-satellite Retrieval for Global Precipitation Measurement—GPM IMERG—version 6 Early (IMERGv6) | 4 h | 0.1° × 0.1° (approximately 10 km × 10 km) | Half hour | Passive microwave, Infrared |
| Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMAP) near real-time | 4 h | 0.1° × 0.1° (approximately 10 km × 10 km) | Hourly | Passive microwave, Infrared |
| Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information using Artificial Neural Networks—PERSIANN—Dynamic Infrared Rain Rate in near real-time (PERSIANN) | 30–60 min | 0.04° × 0.04° (approximately 4 km × 4 km) | Daily | Infrared |
| Parameter | Explanation | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Snow routine: | ||
| TT | Threshold temperature | °C |
| CFMAX | Degree — Δt factor | mm °C−1Δt−1 |
| SFCF | Snowfall correction factor | - |
| CWH | Water-holding capacity of snow | - |
| CFR | Refreezing coefficient | - |
| SP | Seasonal variability in degree — Δt factor | - |
| Soil moisture routine: | ||
| FC | Field capacity: maximum soil moisture storage | mm |
| LP | Soil moisture value above which AET reaches PET | - |
| BETA | Shape coefficient | - |
| Response routine: | ||
| K0 | Additional recession coefficient of upper groundwater store | Δt−1 |
| K1 | Recession coefficient of upper groundwater store | Δt−1 |
| K2 | Recession coefficient of lower groundwater store | Δt−1 |
| UZL | Threshold parameter for K0 outflow | mm |
| PERC | Threshold parameter | mm Δt−1 |
| Routing routine: | ||
| MAXBAS | Length of equilateral triangular weighting function | mm Δt−1 |
| Calibration Driven Data | Ground-Based (1) | Corrected Satellite-Based (2) | Uncorrected Satellite-Based (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Validation Driven Data | ||||
| Ground-based (1) | 1.1 | - | - | |
| Corrected satellite-based (2) | 1.2 | 2.2 | - | |
| Uncorrected satellite-based (3) | 1.3 | - | 3.3 | |
| IMERGv7 | IMERGv6 | GSMAP | PERSIANN | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistics | BVO | Delta | BVO | Delta | BVO | Delta | BVO | Delta |
| POD | 0.77 | 0.67 | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.58 | 0.73 | 0.70 |
| FAR | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.35 |
| R | 0.63 | 0.6 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.55 | 0.49 | 0.5 | 0.45 |
| PBIAS (%) | 1.9 | −0.7 | 8.3 | 15.8 | 2.3 | 24.4 | −19.3 | 31.7 |
| KGE | 0.6 | 0.57 | 0.47 | 0.39 | 0.51 | 0.01 | 0.44 | −0.14 |
| IMERGv7 | IMERGv6 | GSMAP | PERSIANN | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale | Statistics | BVO | Delta | BVO | Delta | BVO | Delta | BVO | Delta |
| 10-day | R | 0.93 | 0.9 | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0.72 | 0.73 | 0.72 |
| PBIAS (%) | 1.9 | −0.7 | 8.3 | 15.8 | 2.3 | 24.4 | −19.3 | 31.7 | |
| KGE | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 0.4 | 0.67 | 0.2 | |
| Month | R | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.9 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.79 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| PBIAS (%) | 1.9 | −0.7 | 8.3 | 15.8 | 2.3 | 24.4 | −19.3 | 31.7 | |
| KGE | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.88 | 0.47 | 0.72 | 0.27 | |
| IMERGv7 Corrected | IMERGv6 Corrected | GSMAP Corrected | PERSIANN Corrected | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistics | BVO | Delta | BVO | Delta | BVO | Delta | BVO | Delta |
| R | 0.66 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.53 |
| PBIAS (%) | −2.9 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 1.9 | −0.5 | 8.5 | −3.1 | 1.9 |
| KGE | 0.65 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.55 | 0.57 | 0.51 |
| IMERGv7 Corrected | IMERGv6 Corrected | GSMAP Corrected | PERSIANN Corrected | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BVO | Delta | BVO | Delta | BVO | Delta | BVO | Delta | |
| Change in score of KGE (%) | +8.33 | +8.77 | +31.91 | +48.72 | +13.73 | +5400.00 | +29.55 | +464.29 |
| Change in score of PBIAS (%) | +252.63 | +271.43 | −95.18 | −87.97 | −121.74 | −65.16 | −83.94 | −94.01 |
| Change in score of RMSE (%) | −15.63 | −15.75 | −27.87 | −32.04 | −18.61 | −64.03 | −25.69 | −90.55 |
| (a) | ||||||||||
| Scenario | 1.1 | 1.2 (corrected data) | 1.3 (uncorrected data) | |||||||
| Data source | Ground-based | IMERGv7 | IMERGv6 | GSMAP | PERSIANN | IMERGv7 | IMERGv6 | GSMAP | PERSIANN | |
| Metrics | Calibration | Validation | ||||||||
| R | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.75 | 0.79 | 0.94 | 0.86 | 0.72 | 0.64 |
| NSE | 0.9 | 0.95 | 0.81 | 0.77 | 0.54 | 0.62 | 0.88 | 0.39 | 0.51 | 0.36 |
| NSE rainy season | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.73 | 0.68 | 0.31 | 0.44 | 0.83 | 0.11 | 0.27 | 0.03 |
| KGE | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.67 | 0.81 | 0.52 | 0.73 | 0.9 | 0.42 | 0.59 | 0.51 |
| PBIAS (%) | −0.7 | −0.6 | −17.4 | −0.1 | −12.3 | 0.6 | 0 | 41.1 | −1.6 | −25.4 |
| (b) | ||||||||||
| Scenario | 1.1 | 2.2 Corrected | ||||||||
| Data source | Ground-based | IMERGv7 | IMERGv6 | GSMAP | PERSIANN | |||||
| Metrics | Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation |
| R | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.9 | 0.77 | 0.92 | 0.79 |
| NSE | 0.9 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.81 | 0.59 | 0.85 | 0.62 |
| NSE rainy season | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.74 | 0.4 | 0.79 | 0.42 |
| KGE | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.72 | 0.82 | 0.72 | 0.89 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.71 |
| PBIAS (%) | −0.7 | −0.6 | −0.6 | −19.1 | 4.9 | 20 | 0.6 | −5.4 | 3.3 | −1.4 |
| (c) | ||||||||||
| Scenario | 1.1 | 3.3 Uncorrected | ||||||||
| Data source | Ground-based | IMERGv7 | IMERGv6 | GSMAP | PERSIANN | |||||
| Metrics | Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation | Calibration | Validation |
| R | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.83 | 0.67 | 0.89 | 0.77 | 0.87 | 0.7 |
| NSE | 0.9 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.83 | 0.68 | 0.24 | 0.79 | 0.58 | 0.75 | 0.46 |
| NSE rainy season | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.76 | 0.7 | 0.64 | 0.7 | 0.38 | 0.67 | 0.19 |
| KGE | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.47 | 0.85 | 0.62 | 0.84 | 0.67 |
| PBIAS (%) | −0.7 | −0.6 | 0.6 | −18.7 | 3.7 | 41.4 | 4.4 | −5.7 | −0.7 | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bodjrènou, M.; Peng, K.; Afféwé, D.J.; Hounkpè, J.; Donnou, H.E.V.; Adounkpè, J.; Akpo, A.B. Assessment of Satellite-Based Rainfall Products for Flood Modeling in the Ouémé River Basin in Benin (West Africa). Hydrology 2025, 12, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040071
Bodjrènou M, Peng K, Afféwé DJ, Hounkpè J, Donnou HEV, Adounkpè J, Akpo AB. Assessment of Satellite-Based Rainfall Products for Flood Modeling in the Ouémé River Basin in Benin (West Africa). Hydrology. 2025; 12(4):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040071
Chicago/Turabian StyleBodjrènou, Marleine, Kaidi Peng, Dognon Jules Afféwé, Jean Hounkpè, Hagninou E. V. Donnou, Julien Adounkpè, and Aristide B. Akpo. 2025. "Assessment of Satellite-Based Rainfall Products for Flood Modeling in the Ouémé River Basin in Benin (West Africa)" Hydrology 12, no. 4: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040071
APA StyleBodjrènou, M., Peng, K., Afféwé, D. J., Hounkpè, J., Donnou, H. E. V., Adounkpè, J., & Akpo, A. B. (2025). Assessment of Satellite-Based Rainfall Products for Flood Modeling in the Ouémé River Basin in Benin (West Africa). Hydrology, 12(4), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12040071






