Effect of Geothermal Heating on Deep-Water Temperature in Lake Baikal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Numerical Model
- (a)
- At the surface of the lake
- (b)
- At the solid boundaries
- (c)
- At the river inflow boundary
- (d)
- At the open boundary, where the following conditions for the radiation type [31] were set:
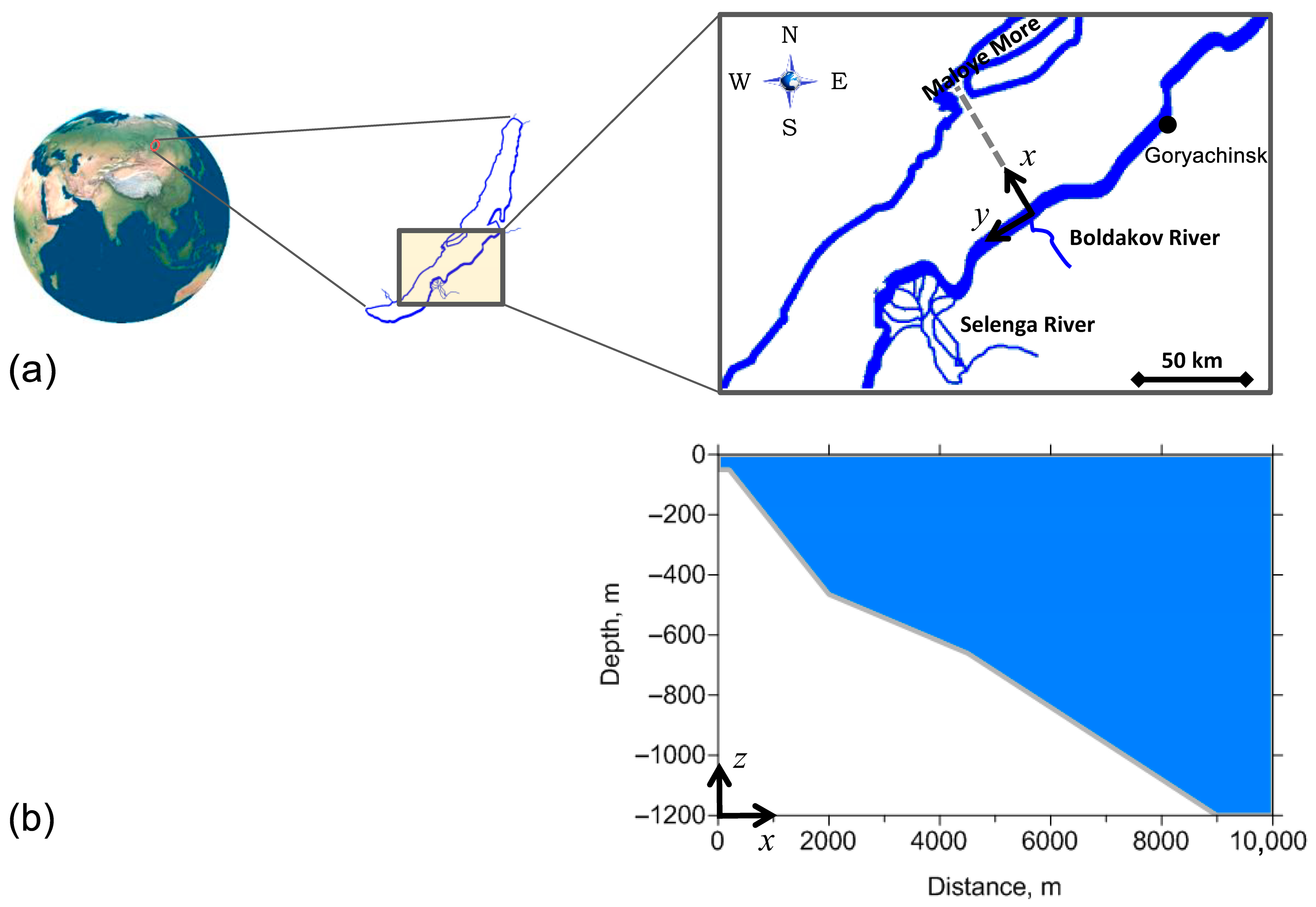
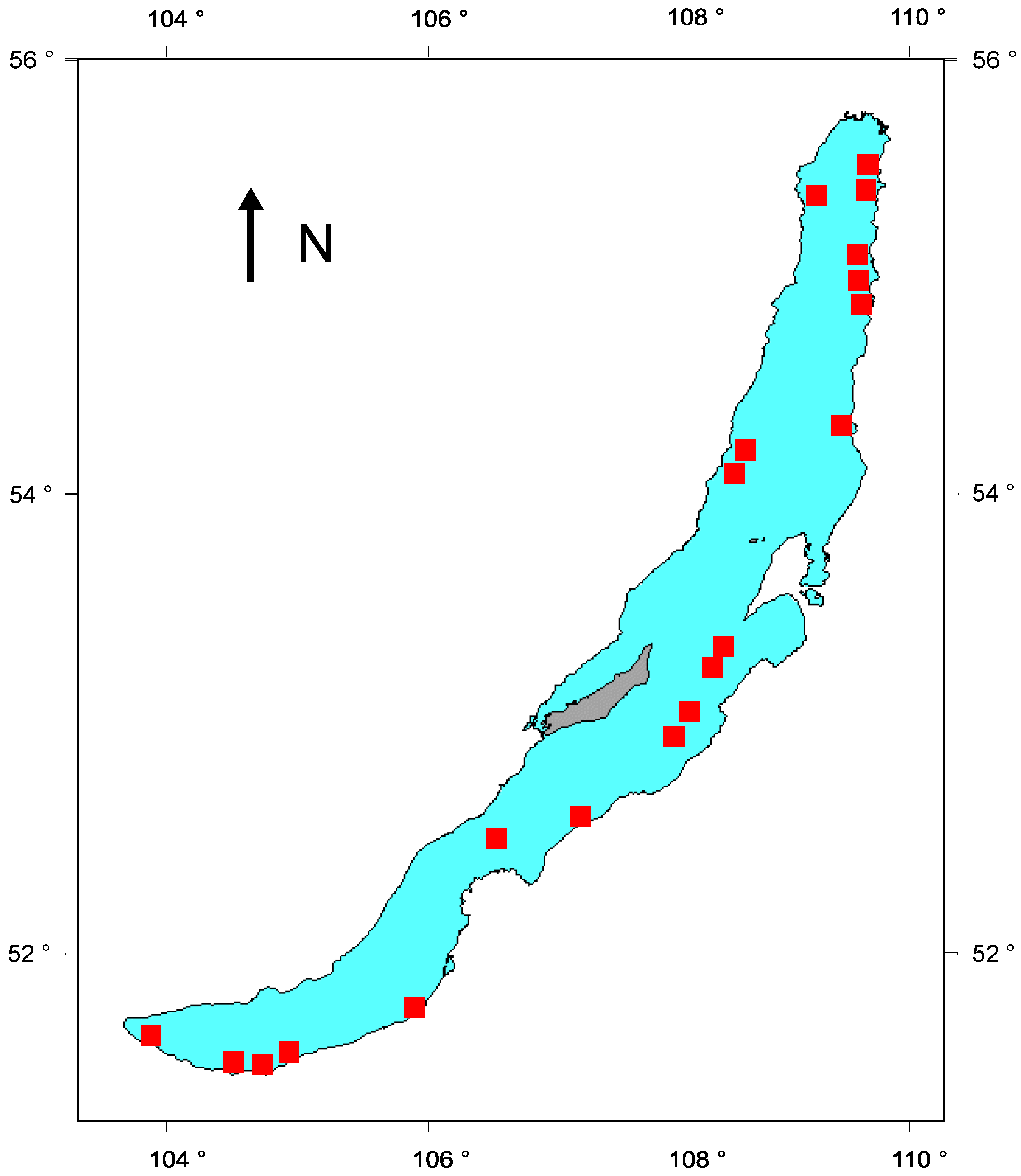
2.2. Study Area and Problem Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
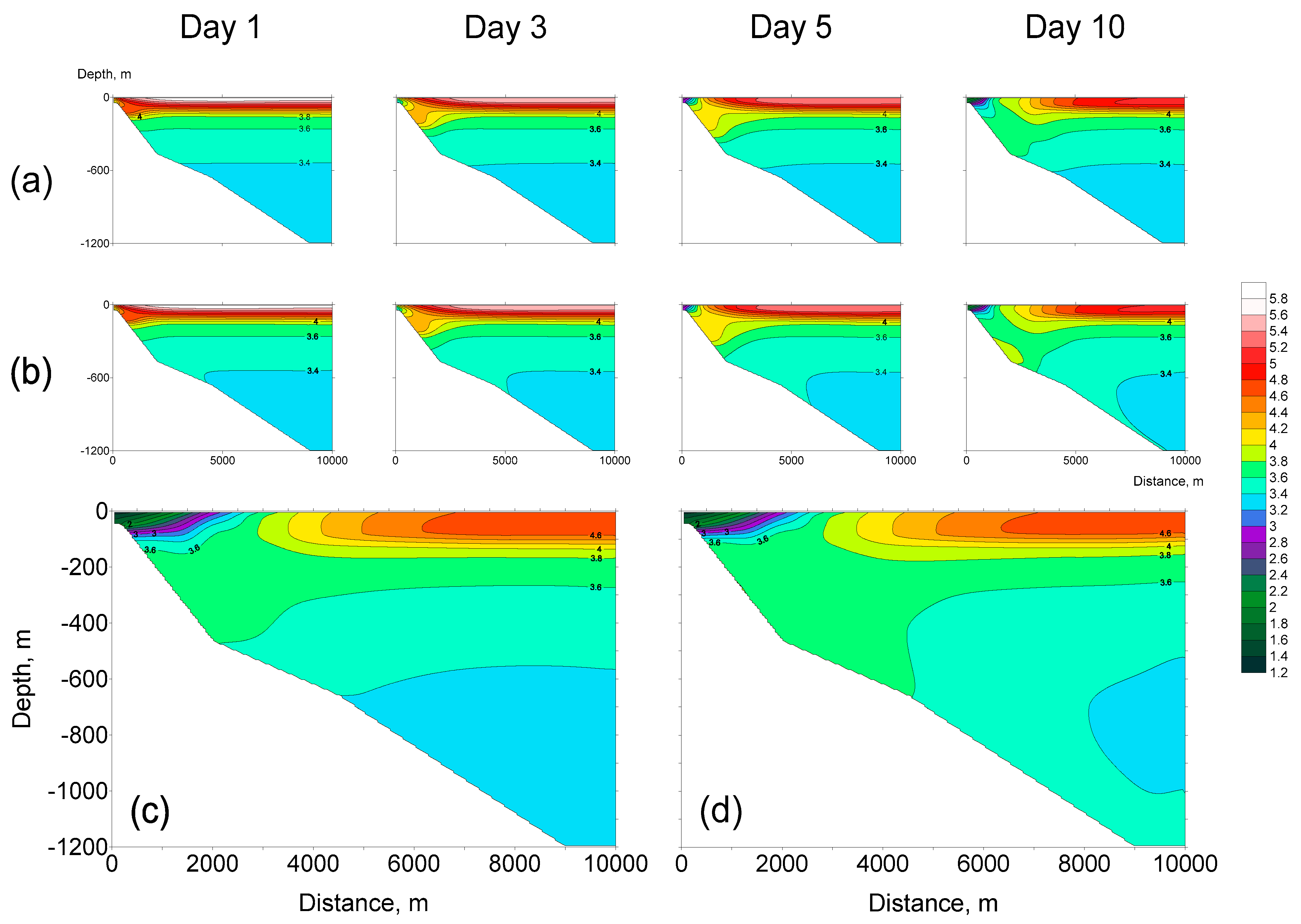
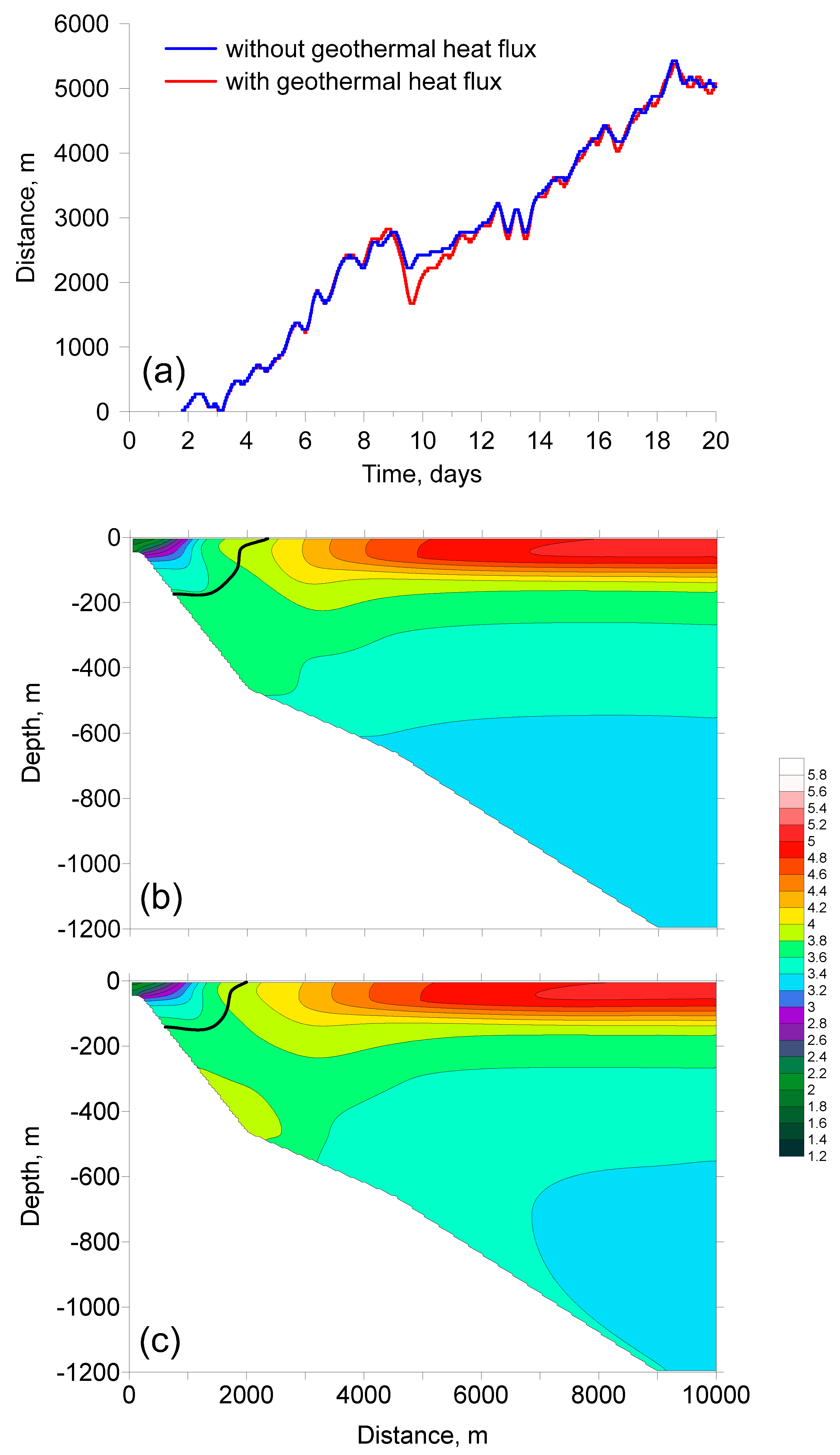
3.1. Geothermal Heating and Deep Convection
3.2. Impact of the Thermal Bar
3.3. Mechanism of Water Renewal
3.4. Potential Zones with High Ventilation
4. Conclusions
- (i)
- Wind forcing (up to ~200 m);
- (ii)
- Cabbeling at the thermal bar (up to ~600 m);
- (iii)
- Tributary mineralization and/or geothermal heating (up to maximum depths).
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beeton, A.M. Large freshwater lakes: Present state, trends, and future. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimaraev, M.N.; Verbolov, V.I.; Granin, N.G.; Sherstyankin, P.P. Physical Limnology of Lake Baikal: A Review; BYCER: Irkutsk, Russia; Okayama, Japan, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, H. Helium, tritium, methane, and temperature in deep rift-valley lakes: Tanganyika, Kivu, and Baikal. EOS Trans. AGU 1989, 70, 1137. [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann, R.; Hofer, M.; Kipfer, R.; Peeters, F.; Imboden, D.M.; Baur, H.; Shimaraev, M.N. Distribution of helium and tritium in Lake Baikal. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 12823–12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.; Carmack, E.; Koropalov, V. Deep-water renewal and biological production in Lake Baikal. Nature 1991, 349, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimaraev, M.N.; Grachev, M.A.; Imboden, D.M.; Okuda, S.; Granin, N.G.; Kipfer, R.; Levin, L.A.; Endo, S. International hydrophysical experiment in Lake Baikal: Spring deep water renewal. Dokl. Acad. Nauk 1995, 343, 824–827. [Google Scholar]
- Carmack, E.C.; Farmer, D.M. Cooling processes in deep, temperate lakes: A review with examples from two lakes in British Columbia. J. Mar. Res. 1982, 40, 85–111. [Google Scholar]
- Eklund, H. Stability of lakes near the temperature of maximum density. Science 1965, 149, 632–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Budnev, N.M.; Granin, N.G.; Sturm, M.; Schurter, M.; Wüest, A. Lake Baikal deepwater renewal mystery solved. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L09605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botte, V.; Kay, A. A model of the wind-driven circulation in Lake Baikal. Dynam. Atmos. Oceans 2002, 35, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killworth, P.D.; Carmack, E.C.; Weiss, R.F.; Matear, R. Modeling deep-water renewal in Lake Baikal. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 1521–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, R.; Kipfer, R.; Peeters, F.; Piepke, G.; Shimaraev, M.N.; Imboden, D.M. Processes of deep-water renewal in Lake Baikal. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 841–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimaraev, M.N.; Granin, N.G.; Zhdanov, A.A. Deep ventilation of Lake Baikal waters due to spring thermal bars. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, T.J. The relative roles of diapycnal and isopycnal mixing on subsurface water mass conversion. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1984, 14, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüest, A.; Ravens, T.M.; Granin, N.G.; Kosis, O.; Schurter, M.; Sturm, M. Cold intrusions in Lake Baikal: Direct observational evidence for deep-water renewal. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokhina, N.S.; Ordanovich, A.E.; Savel’eva, O.S. Model of formation and development of spring thermal bar. Water Resour. 2001, 28, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubarenko, I.P.; Demchenko, N.Y. Laboratory modeling of the structure of a thermal bar and related circulation in a basin with a sloping bottom. Oceanology 2008, 48, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, D.E. A numerical model of the hydrodynamics of the thermal bar. J. Fluid Mech. 1995, 303, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.R.; Kay, A. A review of the physics and ecological implications of the thermal bar circulation. Limnologica 2003, 33, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbolov, V.I.; Sokolnikov, V.M.; Shimaraev, M.N. Hydrometeorological Regime and Heat Balance of Lake Baikal; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Sherstyankin, P.P. Spatial distribution of transparency in Maloe More and its connection with water dynamics. In Baikal Productivity and Anthropogenic Changes of Its Nature; ISU: Irkutsk, Russia, 1974; pp. 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Shimaraev, M.N. Elements of Heat Regime of Lake Baikal; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Likhoshway, Y.V.; Kuzmina, A.Y.; Potyemkina, T.G.; Potyemkin, V.L.; Shimaraev, M.N. The distribution of diatoms near a thermal bar in Lake Baikal. J. Great Lakes Res. 1996, 22, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenova, V.V.; Shimaraev, M.N.; Kostornova, T.Y.; Domysheva, V.M.; Levin, L.A.; Dryukker, V.V.; Zhdanov, A.A.; Gnatovskii, R.Y.; Tsekhanovskii, V.V.; Logacheva, N.F. On the vertical distribution of microorganisms in Lake Baikal during spring deep-water renewal. Mikrobiologiya 2000, 69, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotova, V.A.; Mankovskij, B.I. Report on the Study of Currents in Lake Baikal in 1962; LIN Library Funds: Irkutsk, Russia, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolnikov, V.M. Currents and water exchange in Lake Baikal. In Elements of Hydrometeorological Regime of Lake Baikal; Nauka: Moscow–Leningrad, Russia, 1964; pp. 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Tsydenov, B.O. A numerical study of the thermal bar in shallow water during the autumn cooling. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsydenov, B.O. Effects of heat fluxes on the phytoplankton distribution in a freshwater lake. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2021, 34, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsydenov, B.O. Numerical modeling of the effect of inflow water mineralization in the dynamics of the autumnal thermal bar in Kamloops Lake. Mosc. Univ. Phys. Bull. 2018, 73, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsydenov, B.O. The effect of the Coriolis force and wind on the dynamics of the autumn thermal bar. Moscow Univ. Phys. Bull. 2019, 74, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlanski, I. A simple boundary condition for unbounded hyperbolic flows. J. Comput. Phys. 1976, 21, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D. Reassessment of the scale-determining equation for advanced turbulence models. AIAA J. 1988, 26, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, J. Spring circulation associated with the thermal bar in large temperate lakes. Nord. Hydrol. 1995, 26, 331–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetova, E.A. Mathematical modelling of Lake Baikal hydrodynamics. Hydrobiologia 1999, 407, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.R.; Kay, A.; Botte, V. A numerical study of the dynamics of the riverine thermal bar in a deep lake. J. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2001, 1, 311–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.; Millero, F.G. Precise thermodynamic properties for natural waters covering only limnologies range. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1986, 31, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, S. Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow; Hemisphere Publishing Corporation: Washington, DC, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, B. A stable and accurate convective modelling procedure based on quadratic upstream interpolation. Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Engineer. 1979, 19, 59–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsydenov, B.O.; Kay, A.; Starchenko, A.V. Numerical modeling of the spring thermal bar and pollutant transport in a large lake. Ocean Model. 2016, 104, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsydenov, B.O. The impact of easterly wind force on Lake Baikal water temperature in autumn. In Proceedings of the All-Russian Scientific Conference “Water and Ecological Problems of Siberia and Central Asia”, Barnaul, Russia, 29 August–3 September 2022; Volume 1, pp. 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Tsydenov, B.O. The fall thermal bar dynamics under a differential wind load. Mosc. Univ. Phys. 2022, 77, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsydenov, B.O.; Trunov, N.S.; Churuksaeva, V.V.; Degi, D.V. Wind effects on deep convection in Lake Baikal during the autumnal thermal bar. Mosc. Univ. Phys. Bull. 2024, 79, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsydenov, B.; Churuksaeva, V.; Trunov, N.; Bart, A.; Degi, D. The impact of tributary mineralization on deep-water renewal in Lake Baikal during the thermal bar. Water 2025, 17, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votintsev, K.K. Hydrochemistry. In Problems of Lake Baikal; Galazii, G.I., Votintsev, K.K., Eds.; Siberian Branch of the USSR Academy of Sciences: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1978; pp. 124–146. [Google Scholar]
- Reliable Prognosis. Available online: https://rp5.ru (accessed on 21 August 2023).
- Imboden, D.M.; Wüest, A. Mixing mechanisms in lakes. In Physics and Chemistry of Lakes; Lerman, A., Imboden, D., Gat, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 83–138. [Google Scholar]
- Golubev, V.A. Geothermics of Lake Baikal; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Adcroft, A.; Scott, J.R.; Marotzke, J. Impact of geothermal heating on the global ocean circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 1735–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, T.M.; Speer, K.G. Modeling the large-scale influence of geothermal source on abyssal flow. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 2843–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.; Johnson, G. Abyssal currents generated by diffusion and geothermal heating over rises. Deep Sea Res. 1996, 43, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.; Morales Maqueda, M.A. Geothermal heat flux and its influence on the oceanic abyssal circulation and radiocarbon distribution. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L03603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorofeeva, R.P.; Lysak, S.V. Heat flow of Central Asia. In Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress, Bali, Indonesia, 25–29 April 2010; Available online: https://www.geothermal-energy.org/pdf/IGAstandard/WGC/2010/1308.pdf (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Duchkov, A.D.; Lysak, S.V.; Golubev, V.A.; Dorofeeva, R.P.; Sokolova, L.S. Heat flow and geothermal field of the Baikal region. Geol. Geofiz. 1999, 40, 287–303. [Google Scholar]
- Golubev, V.A.; Klerkx, I.; Kipfer, R. Heat flow, hydrothermal vents and static stability of discharging thermal water in Lake Baikal (South-Eastern Siberia). BCREDP Elf Aquitaine 1993, 17, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Golubev, V.A. Geothermal field and distribution for earthquake source depths in the Baikal Rift zone. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2010, 433, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.E. Gravity currents in the laboratory, atmosphere, and ocean. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1982, 14, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsydenov, B.O. Effect of underwater relief on the dynamics of the autumnal thermal bar. Mosc. Univ. Phys. Bull. 2023, 78, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsydenov, B.O.; Starchenko, A.V. Numerical model of river-lake interaction in the case of a spring thermal bar in Kamloops Lake. Vestn. Tomsk. Gos. Univ. Mat. Mekh. 2013, 5, 102–115. [Google Scholar]
- Kolokoltseva, E.M. Morphometric characteristics of Baikal. In Mesozoic and Cenozoic Lakes of Siberia; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1968; pp. 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Piccolroaz, S.; Toffolon, M. Deep water renewal in Lake Baikal: A model for long-term analyses. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 6717–6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.X. Mixing and energetics of the oceanic thermohaline circulation. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1999, 29, 727–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, C.; Ferrari, R. Vertical mixing, energy and the general circulation of the oceans. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2004, 36, 281–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.R.; Marotzke, J.; Adcroft, A.A. Geothermal heating and its influence on the meridional overturning circulation. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 31141–31154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
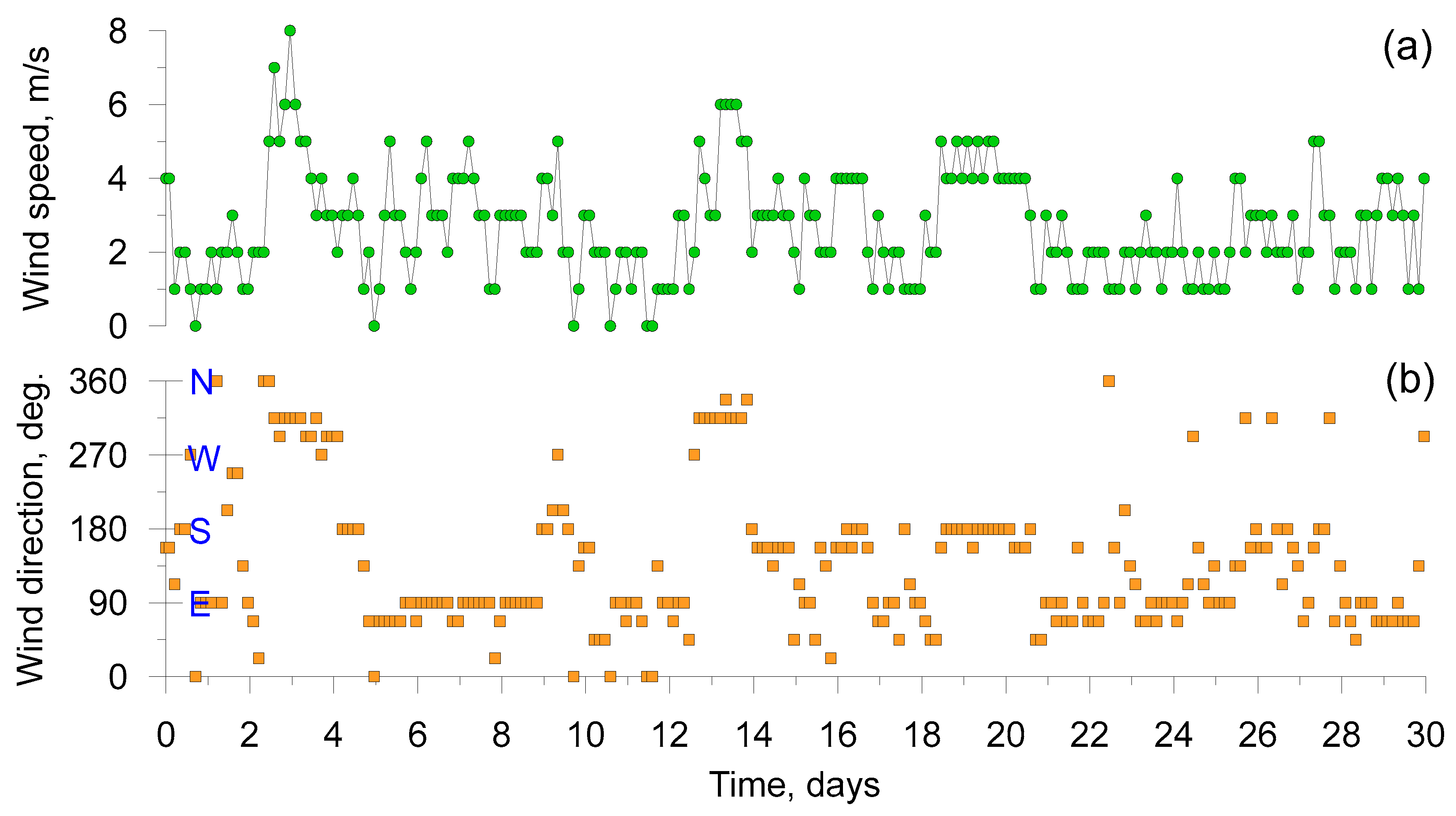

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsydenov, B.O. Effect of Geothermal Heating on Deep-Water Temperature in Lake Baikal. Hydrology 2025, 12, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12100256
Tsydenov BO. Effect of Geothermal Heating on Deep-Water Temperature in Lake Baikal. Hydrology. 2025; 12(10):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12100256
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsydenov, Bair O. 2025. "Effect of Geothermal Heating on Deep-Water Temperature in Lake Baikal" Hydrology 12, no. 10: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12100256
APA StyleTsydenov, B. O. (2025). Effect of Geothermal Heating on Deep-Water Temperature in Lake Baikal. Hydrology, 12(10), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12100256




