Assessment of Time Series Models for Mean Discharge Modeling and Forecasting in a Sub-Basin of the Paranaíba River, Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Gauging Stations
2.2. SARIMA and SARIMAX Forecasting Models
2.3. Identification, Evaluation, and Prediction Criteria
3. Results
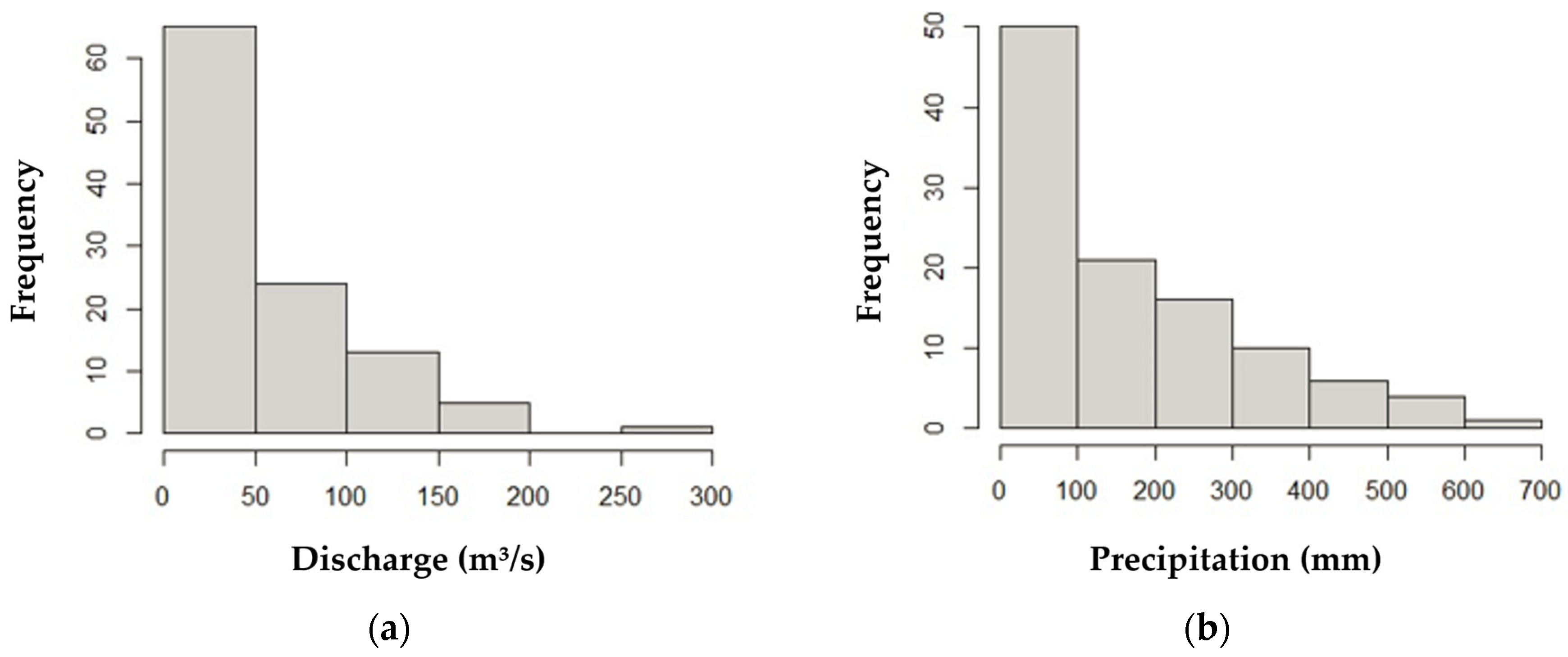
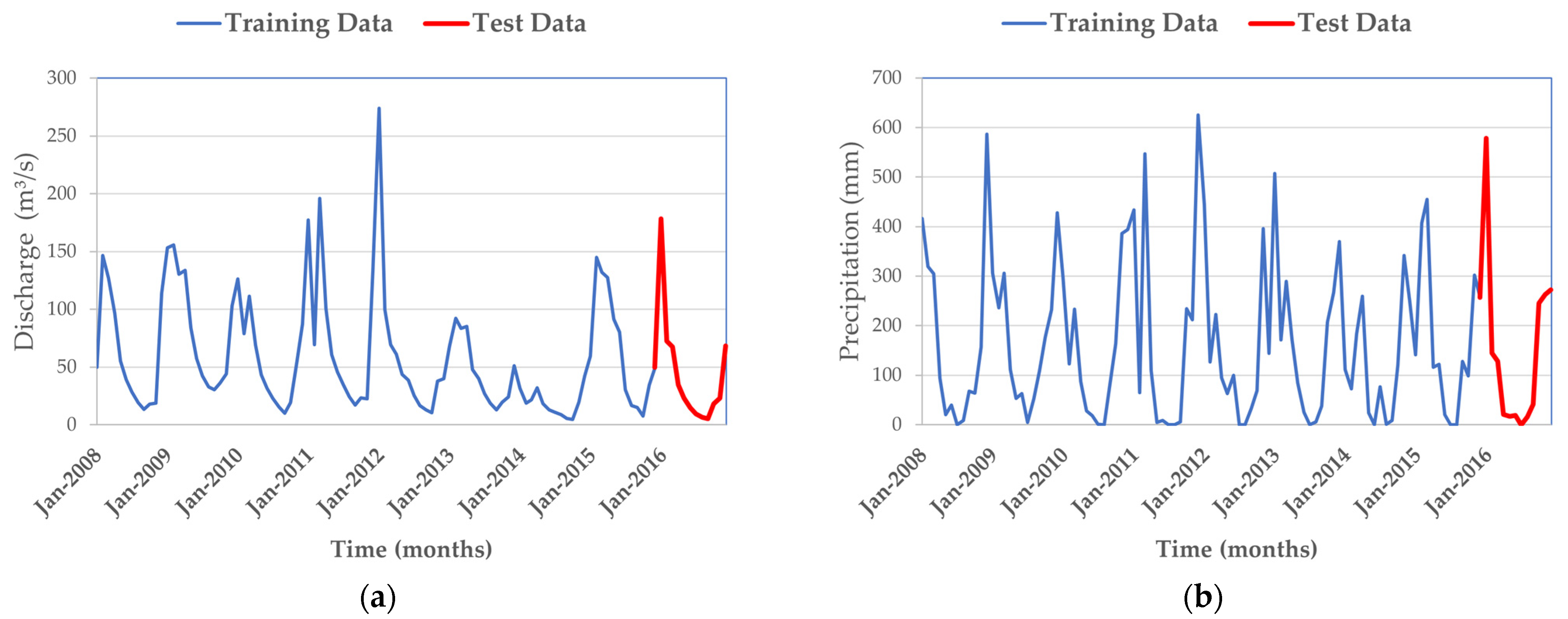
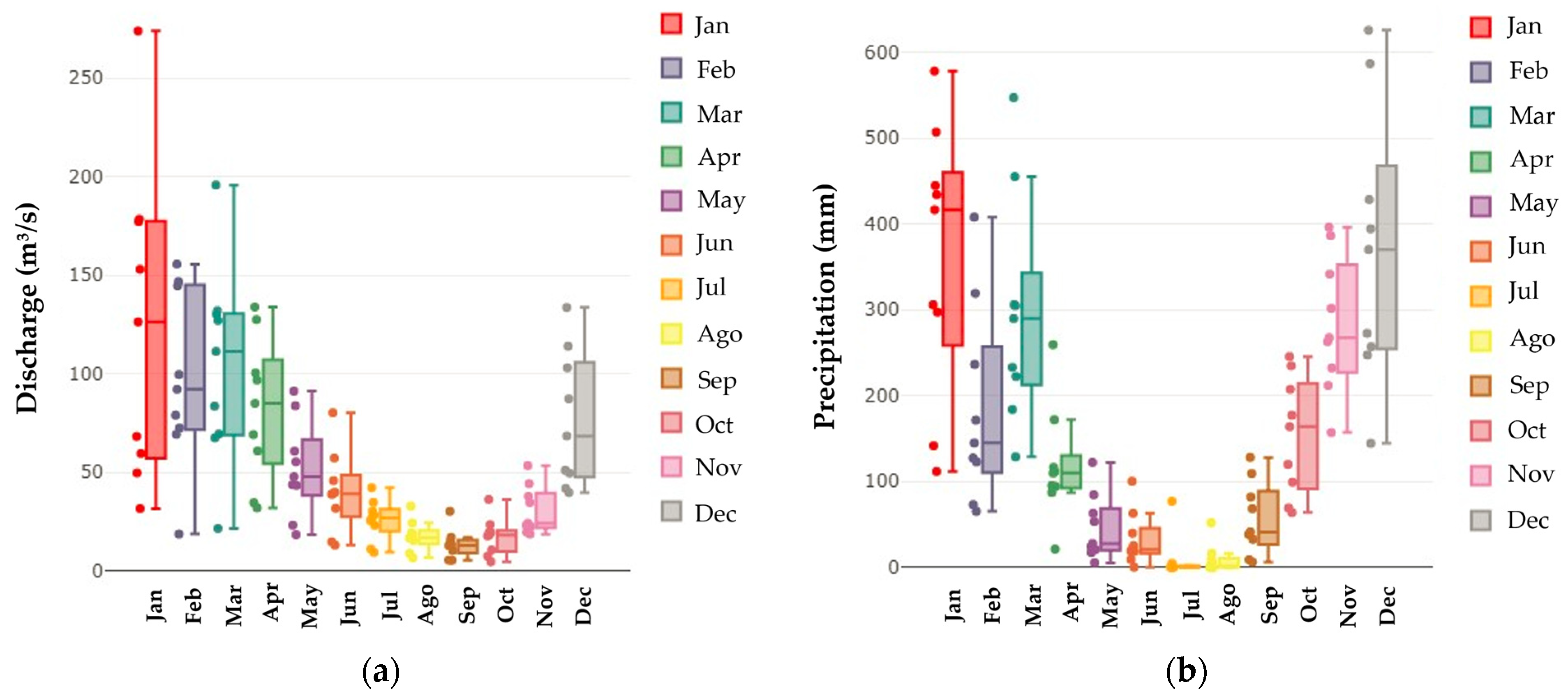
3.1. Statistical Analysis of Flow and Precipitation Data
3.2. Model Identification
3.3. Diagnostic Analysis of the Models
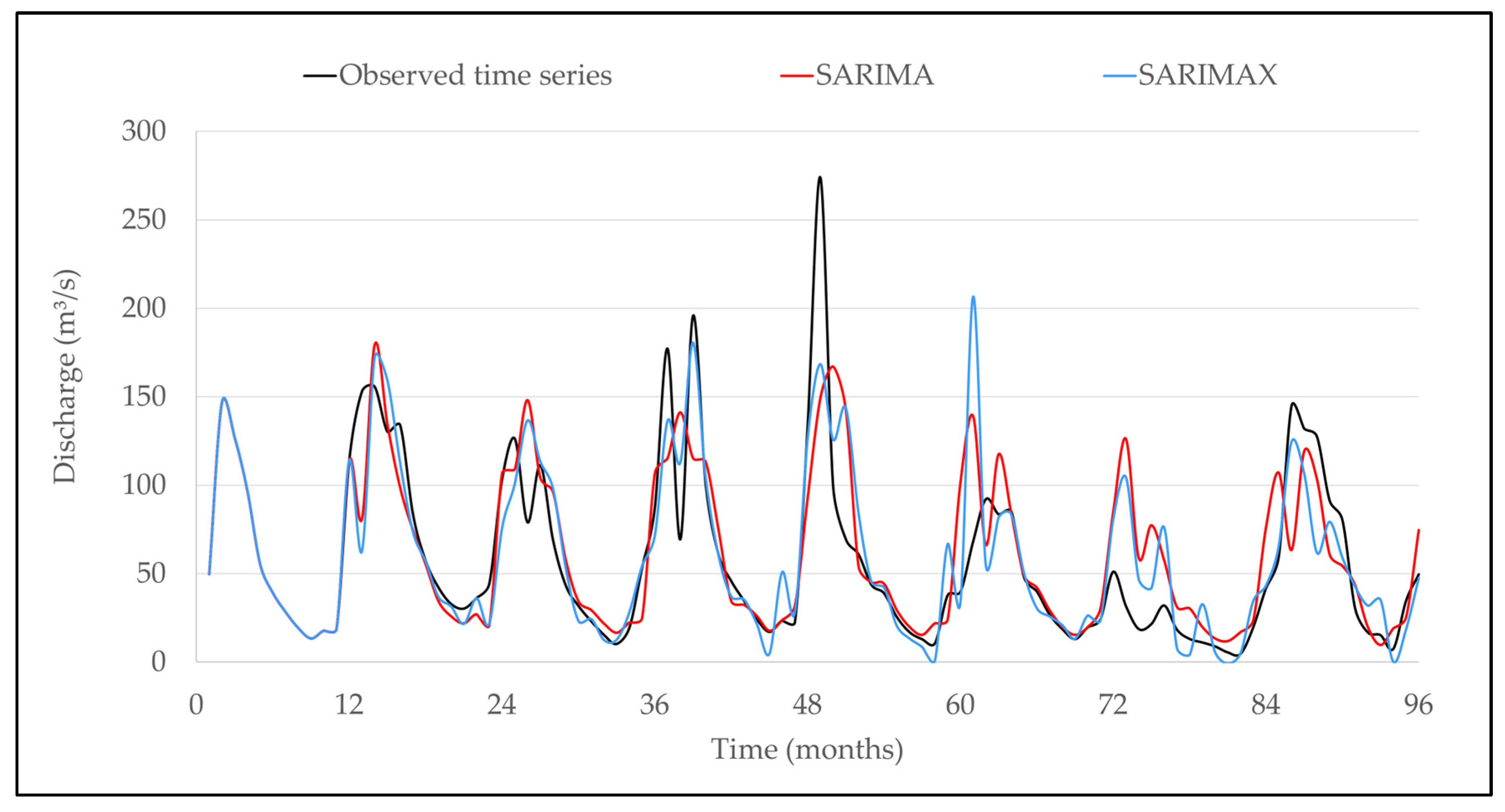
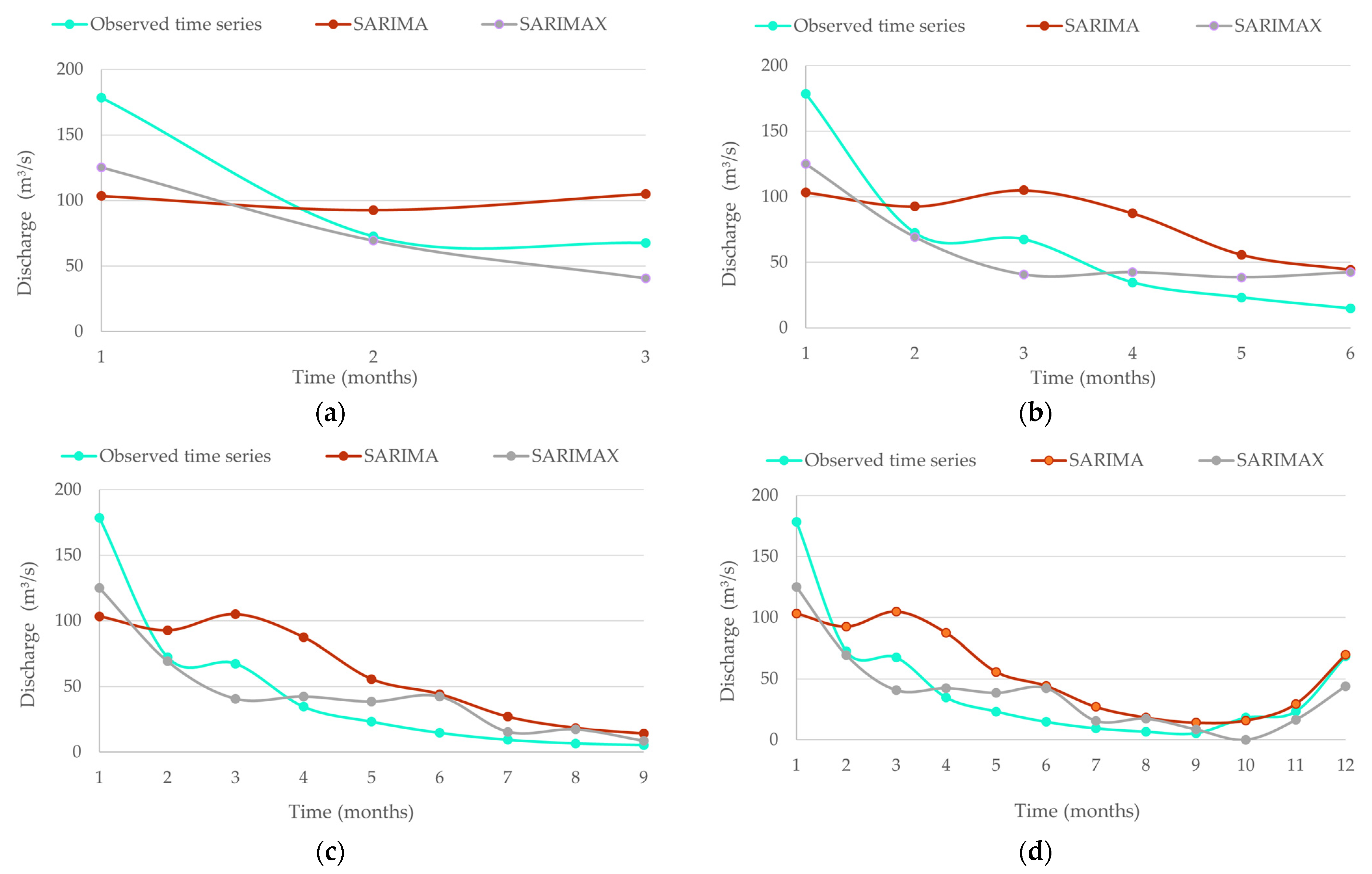
3.4. Forecasting Average Monthly Discharge
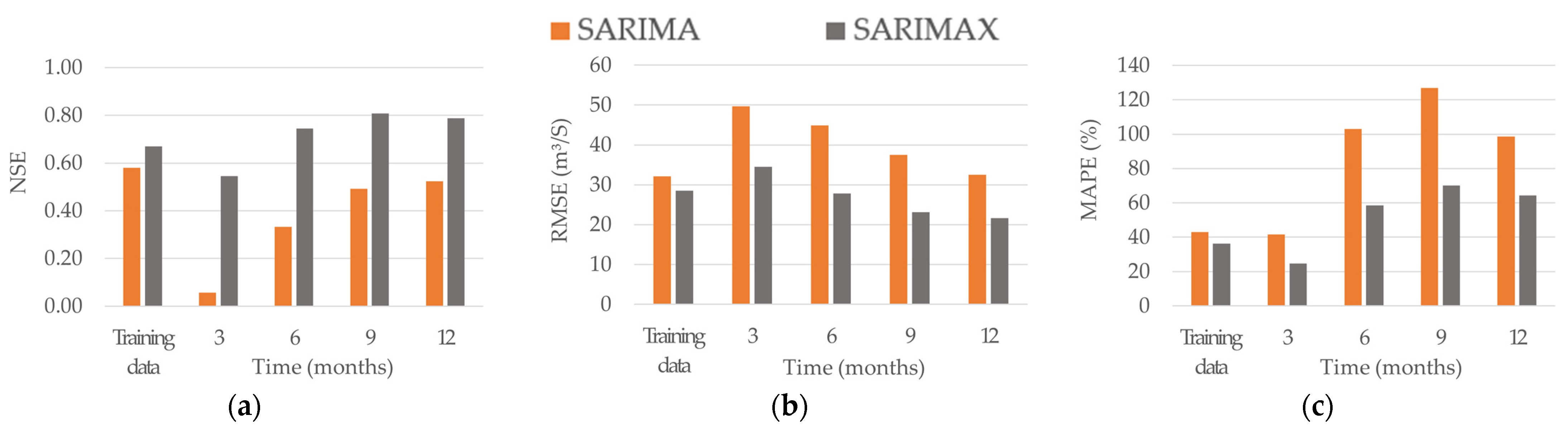
3.5. Performance Assessment of the Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, S.S.; Ramachandran, P. A Comparison of Machine Learning Techniques for Modeling River Flow Time Series: The Case of Upper Cauvery River Basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehteram, M.; Afan, H.A.; Dianatikhah, M.; Ahmed, A.N.; Ming Fai, C.; Hossain, M.S.; Allawi, M.F.; Elshafie, A. Assessing the Predictability of an Improved ANFIS Model for Monthly Streamflow Using Lagged Climate Indices as Predictors. Water 2019, 11, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höge, M.; Scheidegger, A.; Baity-Jesi, M.; Albert, C.; Fenicia, F. Improving Hydrologic Models for Predictions and Process Understanding Using Neural ODEs. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 5085–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolentino, A.H.A.; Vieira, E.D.O.; Rezende, B.N.; Amaral, P.A.A.; Frazão, L.A. Soil loss in the São Lamberto river basin with use of temporary series of Landsat. Agrarian 2020, 13, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairuddin, N.; Aris, A.Z.; Elshafie, A.; Sheikhy Narany, T.; Ishak, M.Y.; Isa, N.M. Efficient Forecasting Model Technique for River Stream Flow in Tropical Environment. Urban Water J. 2019, 16, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, G.K.; Ganasri, B.P.; Dwarakish, G.S. A Review on Hydrological Models. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandi, D.; Kothandaraman, S.; Kuppusamy, M. Hydrological Models: A Review. Int. J. Hydrol. Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagena, M.B.; Goering, D.; Collick, A.S.; Bock, E.; Fuka, D.R.; Buda, A.; Easton, Z.M. Comparison of Short-Term Streamflow Forecasting Using Stochastic Time Series, Neural Networks, Process-Based, and Bayesian Models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 126, 104669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.W.; Huang, Y.F.; Koo, C.H.; Chong, K.L.; El-Shafie, A.; Najah Ahmed, A. A Review of Hybrid Deep Learning Applications for Streamflow Forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehanzaib, M.; Ajmal, M.; Achite, M.; Kim, T.-W. Comprehensive Review: Advancements in Rainfall-Runoff Modelling for Flood Mitigation. Climate 2022, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Machiwal, D. Streamflow Forecasting. In Advances in Streamflow Forecasting. From Traditional to Modern Approaches; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1–50. ISBN 978-0-12-820673-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kilinc, H.C.; Yurtsever, A. Short-Term Streamflow Forecasting Using Hybrid Deep Learning Model Based on Grey Wolf Algorithm for Hydrological Time Series. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghettini, M. (Ed.) Fundamentals of Statistical Hydrology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-43560-2. [Google Scholar]
- Cibin, R.; Athira, P.; Sudheer, K.P.; Chaubey, I. Application of Distributed Hydrological Models for Predictions in Ungauged Basins: A Method to Quantify Predictive Uncertainty. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 2033–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, R.M. Stochastic Watershed Models for Hydrologic Risk Management. Water Secur. 2017, 1, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, S.; Karaus, U.; Claret, C.; Sporka, F.; Hamerlík, L.; Tockner, K. Flooding and Hydrologic Connectivity Modulate Community Assembly in a Dynamic River-Floodplain Ecosystem. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machiwal, D.; Jha, M.K. Hydrologic Time Series Analysis: Theory and Practice; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 978-94-007-1860-9. [Google Scholar]
- Maçaira, P.M.; Tavares Thomé, A.M.; Cyrino Oliveira, F.L.; Carvalho Ferrer, A.L. Time Series Analysis with Explanatory Variables: A Systematic Literature Review. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 107, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M. Time Series Analysis, Forecasting and Control; Holden-Day: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Bayer, F.M.; Souza, A.M. Forecasting with Wavelets and Traditional Models: A Comparative. Rev. Bras. Biom. 2010, 28, 40–61. [Google Scholar]
- Vagropoulos, S.I.; Chouliaras, G.I.; Kardakos, E.G.; Simoglou, C.K.; Bakirtzis, A.G. Comparison of SARIMAX, SARIMA, Modified SARIMA and ANN-Based Models for Short-Term PV Generation Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Energy Conference and Exhibition, Leuven, Belgium, 4–8 April 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, R.M.; Yuan, X.; Kisi, O.; Yuan, Y.; Tayyab, M.; Lei, X. Application of Soft Computing Models in Streamflow Forecasting. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2019, 172, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleidorn, M.T.; Pinto, W.D.P.; Braum, E.S.; Lima, G.B.; Montebeller, C.A. Modelling and Prevision of Monthly Mean Flow of Jucu River, ES, Using SARIMA Model. IRRIGA 2019, 24, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjalla, V.F.; Pires, A.P.F.; Agostinho, A.A.; Amado, A.M.; Bozelli, R.L.; Dias, B.F.S.; Dib, V.; Faria, B.M.; Figueiredo, A.; Gomes, E.A.T.; et al. Turning Water Abundance into Sustainability in Brazil. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANA—Agência Nacional de Águas e Saneamento Básico Conjuntura Dos Recursos Hídricos No Brasil. 2021. Available online: https://relatorio-conjuntura-ana-2021.webflow.io/ (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- Gordy, M. Disaster Risk Reduction and the Global System; SpringerBriefs in Climate Studies; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-41666-3. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2023; ISBN 9781009157896. [Google Scholar]
- Lyra, A.; Tavares, P.; Chou, S.C.; Sueiro, G.; Dereczynski, C.; Sondermann, M.; Silva, A.; Marengo, J.; Giarolla, A. Climate Change Projections over Three Metropolitan Regions in Southeast Brazil Using the Non-Hydrostatic Eta Regional Climate Model at 5-Km Resolution. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 132, 663–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.C.; Lyra, A.; Mourão, C.; Dereczynski, C.; Pilotto, I.; Gomes, J.; Bustamante, J.; Tavares, P.; Silva, A.; Rodrigues, D.; et al. Assessment of Climate Change over South America under RCP 4.5 and 8.5 Downscaling Scenarios. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2014, 3, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towner, J.; Cloke, H.L.; Lavado, W.; Santini, W.; Bazo, J.; Coughlan de Perez, E.; Stephens, E.M. Attribution of Amazon Floods to Modes of Climate Variability: A Review. Meteorol. Appl. 2020, 27, e1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, F.A.A.D.; Mendiondo, E.M.; Taffarello, D.; Guzmán-Arias, D.; Fava, M.C.; Abreu, F.; Freitas, C.C.; de Macedo, M.B.; Estrada, C.R.; do Lago, C.A. Socio-Hydrological Observatory for Water Security (SHOWS): Examples of Adaptation Strategies with Next Challenges from Brazilian Risk Areas. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, New Orleans, LA, USA, 11–15 December 2017; Volume 2017, p. H13S-08. [Google Scholar]
- Centro Nacional de Monitoramento e Alertas de Desastres Naturais. Anuário Da Sala de Situação Do CEMADEN, 2017; CEMADEN: São José dos Campos, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kassem, A.A.; Raheem, A.M.; Khidir, K.M. Daily Streamflow Prediction for Khazir River Basin Using ARIMA and ANN Models. Zanco J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2020, 32, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Niu, J.; Sivakumar, B. A Comparative Study of Models for Short-Term Streamflow Forecasting with Emphasis on Wavelet-Based Approach. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2019, 33, 1875–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danandeh Mehr, A.; Ghadimi, S.; Marttila, H.; Torabi Haghighi, A. A New Evolutionary Time Series Model for Streamflow Forecasting in Boreal Lake-River Systems. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 148, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, D.; Castro, N.; Bayer, F. Modeling and forecasting mean monthly streamflows using time series. Rev. Bras. Recur. Hídricos 2012, 17, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chechi, L.; Sanches, F. de O. Analysis of a Series of Precipitation for Erechim (RS) and a Method of Possible Climate Prediction. Rev. Ambiência 2013, 9, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, W.D.P.; Lima, G.B.; Zanetti, J.B. Comparative Analysis of Models for Times to Series Modeling and Forecasting of Scheme of Average Monthly Streamflow of the Doce River, Colatina Espirito Santo, Brazil. Ciência Nat. 2015, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caixeta, L.T.; de Menezes Filho, F.C.M.; Fonseca, V.L.A. Modeling and forecasting mean monthly streamflows of Paranaiba River using SARIMA model. Rev. Ibero-Am. Ciências Ambient. 2021, 12, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.L.; Goulart, A.T.; de Melo, C.; de Oliveira, R.d.C.W. Microbiological, Chemical and Physical-Chemical Assessment of the Contamination in the Paranaíba River. Soc. Nat. 2006, 18, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANA—Agência Nacional de Águas e Saneamento Básico HIDROWEB. Available online: https://www.snirh.gov.br/hidroweb/apresentacao (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- IBGE—Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística Portal Cidades. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/cidades-e-estados/mg/patos-de-minas.html (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Mendonça, F.; Danni-Oliveira, I.M. Climatologia: Noções Básicas e Climas Do Brasil; Oficina de Textos: São Paulo, Brazil, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, F.B.; Gonzaga, G.; Dos Santos, D.F.; Reboita, M.S. Climate classification of Köppen and Thornthwaite for Minas Gerais: Crrent climate and climate changes. Rev. Bras. Climatol. 2018, 14, 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, N.M.; Ribeiro, K.L.N.; Pereira, S.G.; Vieira, S.M. Milk Quality Assessment of Properties in the City of Patos de Minas, MG. Rev. Multidiscip. 2020, 23, 279–301. [Google Scholar]
- Caixeta, C.L.B.; Piccinato Junior, D. Territory, Urbanity and Sustainability: A Study about the Recovery of Springs in a Rural Community in Patos de Minas/MG. Rev. Arquitetura IMED 2021, 10, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federação das Indústrias do Estado do Rio de Janeiro IFDM. Índice FIRJAN de Desenvolvimento Municipal: Consulta. Available online: https://www.firjan.com.br/ifdm/ (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Hyndman, R.J.; Athanasopoulos, G. Forecasting: Principles and Practice, 3rd ed.; OTexts: Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2021; ISBN 978-0987507136. [Google Scholar]
- Alharbi, F.R.; Csala, D. A Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average with Exogenous Factors (SARIMAX) Forecasting Model-Based Time Series Approach. Inventions 2022, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazla, A.; Aydin, M.E.; Kozat, S.S. Joint Optimization of Linear and Nonlinear Models for Sequential Regression. Digit. Signal Process. 2023, 132, 103802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, P.D.; Alzraiee, A.H.; Karavitis, C.A.; Waskom, R.M. A Novel Framework for Filling Data Gaps in Groundwater Level Observations. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 119, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.J. Discussion of “High-Dimensional Autocovariance Matrices and Optimal Linear Prediction”. Electron. J. Stat. 2015, 9, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morettin, P.A. The Levinson Algorithm and Its Applications in Time Series Analysis. Int. Stat. Rev. 1984, 52, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.; Athanasopoulos, G.; Bergmeir, C.; Caceres, G.; Chhay, L.; Kuroptev, K.; O’Hara-Wild, M.; Petropoulos, F.; Razbash, S.; Wang, E.; et al. CRAN—Package Forecast. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/forecast/ (accessed on 18 September 2022).
- Chakrabarti, A.; Ghosh, J.K. AIC, BIC and Recent Advances in Model Selection. In Philosophy of Statistics; Bandyopadhyay, P.S., Forster, M.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 583–605. [Google Scholar]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H. A New Metric of Absolute Percentage Error for Intermittent Demand Forecasts. Int. J. Forecast. 2016, 32, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dazzi, S.; Vacondio, R.; Mignosa, P. Flood Stage Forecasting Using Machine-Learning Methods: A Case Study on the Parma River (Italy). Water 2021, 13, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpalatha, R.; Perrin, C.; Le Moine, N.; Andréassian, V. A Review of Efficiency Criteria Suitable for Evaluating Low-Flow Simulations. J. Hydrol. 2012, 420–421, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and Water Quality Models: Performance Measures and Evaluation Criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legates, D.R.; McCabe, G.J. Evaluating the Use of “Goodness-of-fit” Measures in Hydrologic and Hydroclimatic Model Validation. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmel, R.D.; Smith, P.K. Consideration of Measurement Uncertainty in the Evaluation of Goodness-of-Fit in Hydrologic and Water Quality Modeling. J. Hydrol. 2007, 337, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmel, R.D.; Smith, P.K.; Migliaccio, K.W. Modifying Goodness-of-Fit Indicators to Incorporate Both Measurement and Model Uncertainty in Model Calibration and Validation. Trans. ASABE 2010, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, J.; Sharma, R.K.; Juyal, A.; Singh, D.; Pant, H.; Pant, P. A Machine-Learning Approach to Time Series Forecasting of Temperature. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology, Coimbatore, India, 1–3 December 2022; pp. 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Khandakar, Y. Automatic Time Series Forecasting: The Forecast Package for R. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 27, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cho, Y. National-Scale Electricity Peak Load Forecasting: Traditional, Machine Learning, or Hybrid Model? Energy 2022, 239, 122366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Mani, P.; Jain, S.K.; Prakash, P.; Singh, V.P.; Tullos, D.; Kumar, S.; Agarwal, S.P.; Dimri, A.P. A Brief Review of Flood Forecasting Techniques and Their Applications. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2018, 16, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, S.; Kitagawa, G. Information Criteria and Statistical Modeling; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 27, ISBN 978-0-387-71886-6. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Acosta, L.; Medrano-Barboza, J.P.; López-Ramos, Á.; Remolina López, J.F.; López-Lambraño, Á.A. SARIMA Approach to Generating Synthetic Monthly Rainfall in the Sinú River Watershed in Colombia. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F.; Kalinowski, T.; Allaire, J.J. Deep Learning with R, 2nd ed.; Manning Publications: Shelter Island, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 3, ISBN 9781633439849. [Google Scholar]
- Mosavi, A.; Ozturk, P.; Chau, K.W. Flood Prediction Using Machine Learning Models: Literature Review. Water 2018, 10, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso Brito, G.R.; Rivero Villaverde, A.; Lau Quan, A.; Ruíz Pérez, M.E. Comparison between SARIMA and Holt–Winters Models for Forecasting Monthly Streamflow in the Western Region of Cuba. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Huang, G.H.; Cheng, G.H.; Li, Y.P. Impacts of Climate Variations on Non-Stationarity of Streamflow over Canada. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, G.V.; Verkhoturov, A.L.; Korolev, S.P. Impact of Deforestation on Streamflow in the Amur River Basin. Geosciences 2019, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingray, B.; Picouet, C.; Musy, A. Hydrology—A Science for Engineers; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-4665-9060-1. [Google Scholar]
- Danandeh Mehr, A.; Gandomi, A.H. MSGP-LASSO: An Improved Multi-Stage Genetic Programming Model for Streamflow Prediction. Inf. Sci. 2021, 561, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meis, M.; Benjamín, M.; Rodriguez, D. Forecasting the Daily Variability Discharge in the Fluvial System of the Paraná River: An ODPC Hydrology Application. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2022, 67, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harat, Z.A.; Asadi Zarch, M.A. Comparison of SARIMA and SARIMAX for Long-Term Drought Prediction. Desert Manag. 2022, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Narasimha Murthy, K.V.; Saravana, R.; Vijaya Kumar, K. Modeling and Forecasting Rainfall Patterns of Southwest Monsoons in North–East India as a SARIMA Process. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2018, 130, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes Filho, F.C.M. de Modeling and forecasting of monthly mean temperatures in Rio Paranaíba/MG using time series model. Rev. Ibero-Am. Ciências Ambient. 2020, 11, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengo, J.A.; Nobre, C.A.; Seluchi, M.E.; Cuartas, A.; Alves, L.M.; Mendiondo, E.M.; Obregón, G.; Sampaio, G. A Seca e a Crise Hídrica de 2014–2015 Em São Paulo. Rev. USP 2015, 106, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Shin, J.-Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Heo, J.-H. The Use of Large-Scale Climate Indices in Monthly Reservoir Inflow Forecasting and Its Application on Time Series and Artificial Intelligence Models. Water 2019, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meis, M.; Llano, M.P.; Rodriguez, D. A Statistical Tool for a Hydrometeorological Forecast in the Lower La Plata Basin. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2022, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cheng, X.; Li, N.; Du, X.; Yu, Q.; Kan, G. A Framework for Flood Risk Analysis and Benefit Assessment of Flood Control Measures in Urban Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houspanossian, J.; Giménez, R.; Whitworth-Hulse, J.I.; Nosetto, M.D.; Tych, W.; Atkinson, P.M.; Rufino, M.C.; Jobbágy, E.G. Agricultural Expansion Raises Groundwater and Increases Flooding in the South American Plains. Science 2023, 380, 1344–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Yin, J.; Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Huo, X.; Liu, Y.; Yeh, T.C.J. The Role of Anthropogenic Activities in Karst Spring Discharge Volatility. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 2855–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Durán, J.; Escalante-Castro, B.; Canales, F.A.; Acuña, G.J.; Kaźmierczak, B. Evaluation of Areal Monthly Average Precipitation Estimates from MERRA2 and ERA5 Reanalysis in a Colombian Caribbean Basin. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brêda, J.P.L.F.; Cauduro Dias de Paiva, R.; Siqueira, V.A.; Collischonn, W. Assessing Climate Change Impact on Flood Discharge in South America and the Influence of Its Main Drivers. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Prasad, A.D.; Verma, M.K. Time Series Modelling and Forecasting of Mean Annual Rainfall Over MRP Complex Region Chhattisgarh Associated with Climate Variability. In Recent Advances in Sustainable Environment—Select Proceedings of RAiSE 2022; Reddy, K.R., Kalia, S., Tangellapalli, S., Prakash, D., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 51–67. ISBN 9789811655463. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, F.A.L.; do Valle Junior, R.F.; de Melo Silva, M.M.A.P.; Pissarra, T.C.T.; Carvalho de Melo, M.; Valera, C.A.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F. Prognosis of Metal Concentrations in Sediments and Water of Paraopeba River Following the Collapse of B1 Tailings Dam in Brumadinho (Minas Gerais, Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
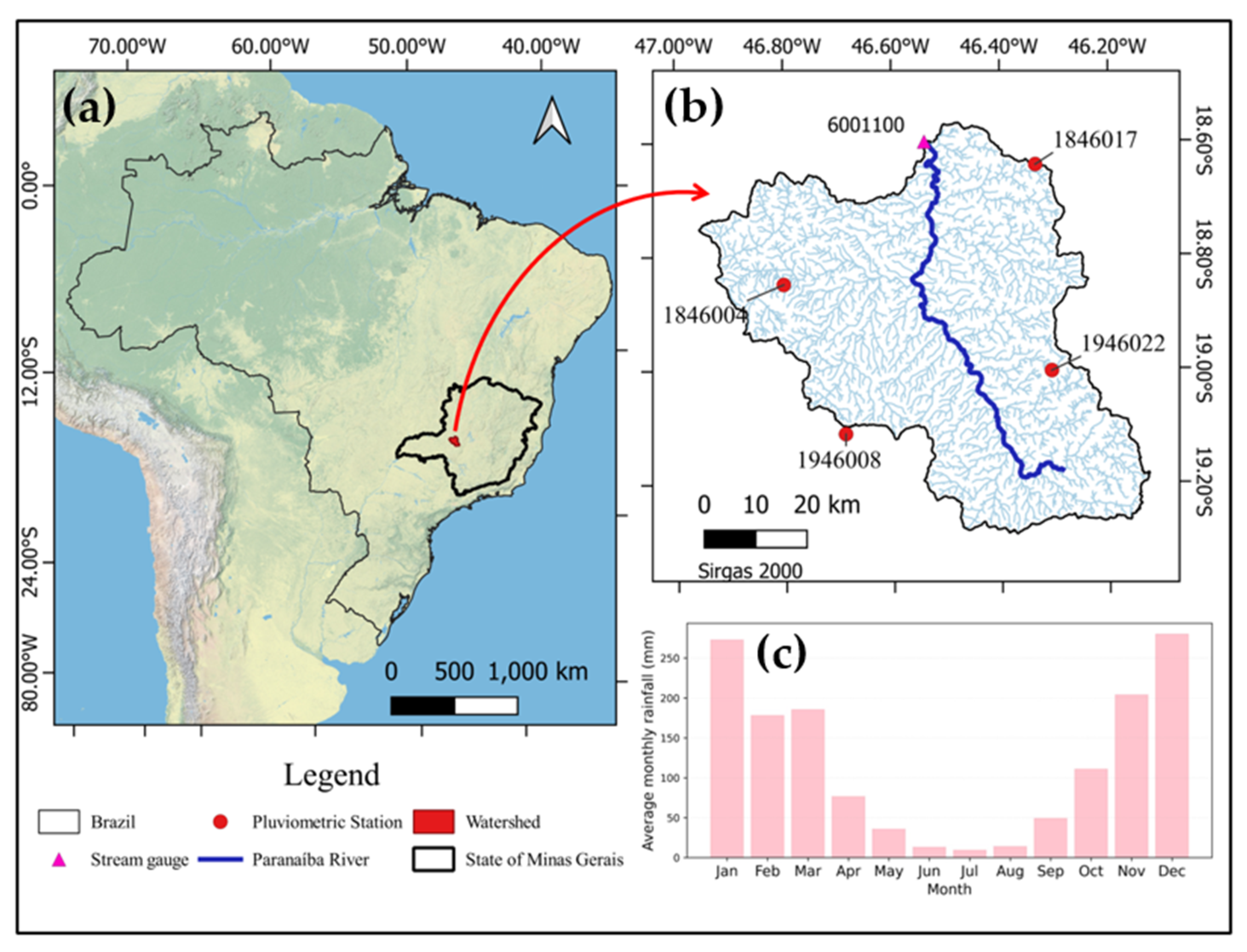



| Hydrometeorological Stations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANA Code | Type of Variable | Name of the Station | Latitude (Degrees) | Longitude (Degrees) | ||
| 6001100 | Discharge | Patos de Minas | −18.6017 | −46.5394 | ||
| 1846004 | Precipitation | Guimarânia | −18.8497 | −46.8008 | ||
| 1946008 | Precipitation | Serra do Salitre | −19.1128 | −46.6883 | ||
| 1846017 | Precipitation | Leal de Patos | −18.6411 | −46.3344 | ||
| 1946022 | Precipitation | Carmo do Paranaíba | −19.0033 | −46.3061 | ||
| Descriptive Statistics | ||||||
| Discharge | Precipitation | |||||
| Maximum value (m3/s): | 273.98 | Maximum value (mm): | 625.73 | |||
| Minimum value (m3/s): | 4.68 | Minimum value (mm): | 0.00 | |||
| Average (m3/s): | 56.89 | Average (mm): | 160.10 | |||
| Median (m3/s): | 39.45 | Median (mm): | 111.52 | |||
| Standard deviation (m3/s): | 49.87 | Standard deviation (mm): | 157.82 | |||
| Asymmetry: | 1.52 | Asymmetry | 1.01 | |||
| Coefficient of variation (%): | 87.65 | Coefficient of variation (%): | 98.58 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, G.E.d.M.e.; Menezes Filho, F.C.M.d.; Canales, F.A.; Fava, M.C.; Brandão, A.R.A.; de Paes, R.P. Assessment of Time Series Models for Mean Discharge Modeling and Forecasting in a Sub-Basin of the Paranaíba River, Brazil. Hydrology 2023, 10, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology10110208
Costa GEdMe, Menezes Filho FCMd, Canales FA, Fava MC, Brandão ARA, de Paes RP. Assessment of Time Series Models for Mean Discharge Modeling and Forecasting in a Sub-Basin of the Paranaíba River, Brazil. Hydrology. 2023; 10(11):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology10110208
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Gabriela Emiliana de Melo e, Frederico Carlos M. de Menezes Filho, Fausto A. Canales, Maria Clara Fava, Abderraman R. Amorim Brandão, and Rafael Pedrollo de Paes. 2023. "Assessment of Time Series Models for Mean Discharge Modeling and Forecasting in a Sub-Basin of the Paranaíba River, Brazil" Hydrology 10, no. 11: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology10110208
APA StyleCosta, G. E. d. M. e., Menezes Filho, F. C. M. d., Canales, F. A., Fava, M. C., Brandão, A. R. A., & de Paes, R. P. (2023). Assessment of Time Series Models for Mean Discharge Modeling and Forecasting in a Sub-Basin of the Paranaíba River, Brazil. Hydrology, 10(11), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology10110208










