Physicochemical Study of Water Contamination for Health Risks and Environmental Implications: A Case Study of Barite Mining Sites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
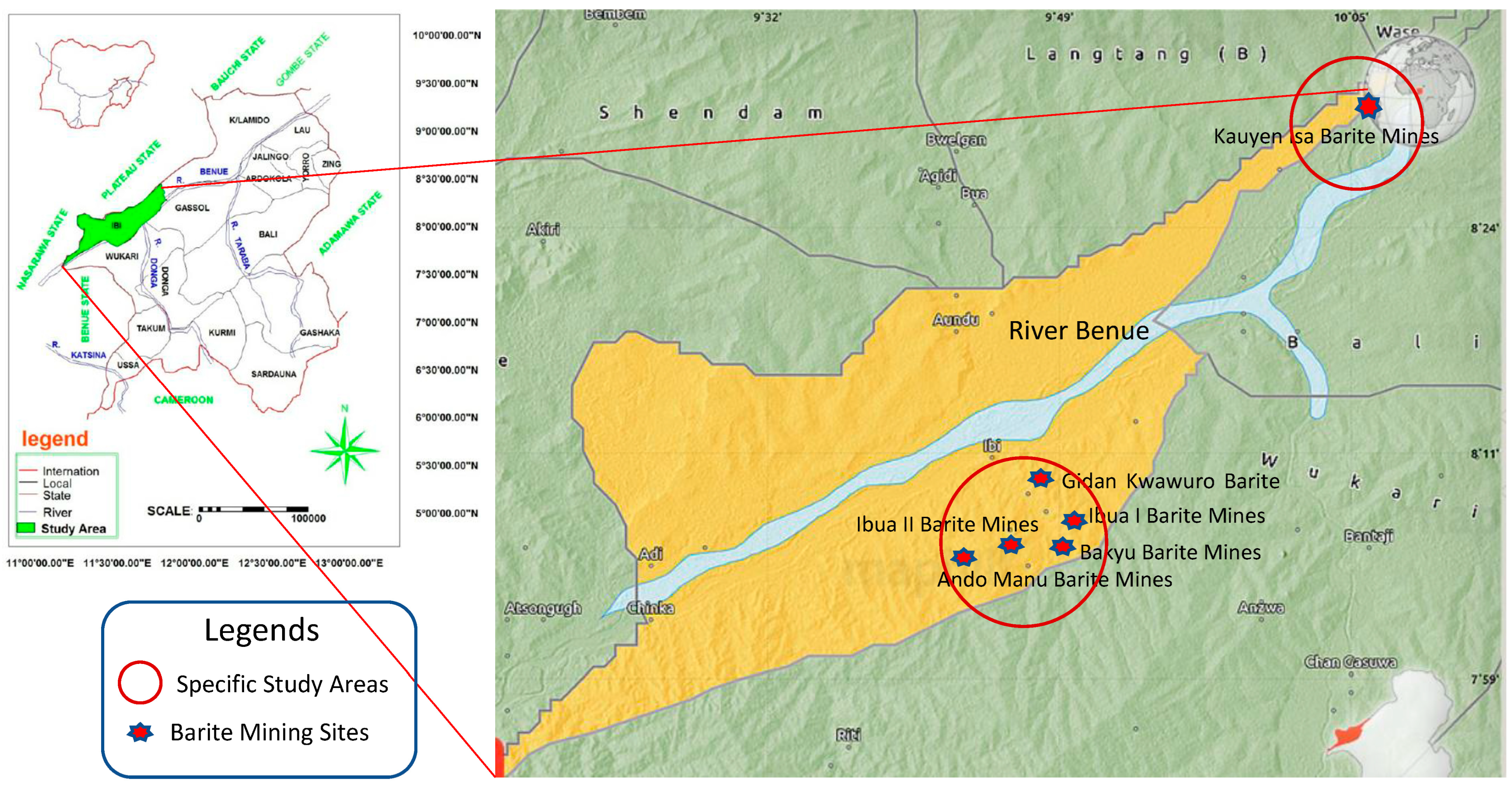
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Cleaning/Digestion
2.3. Analysis of Water Samples for Heavy Metals Concentration
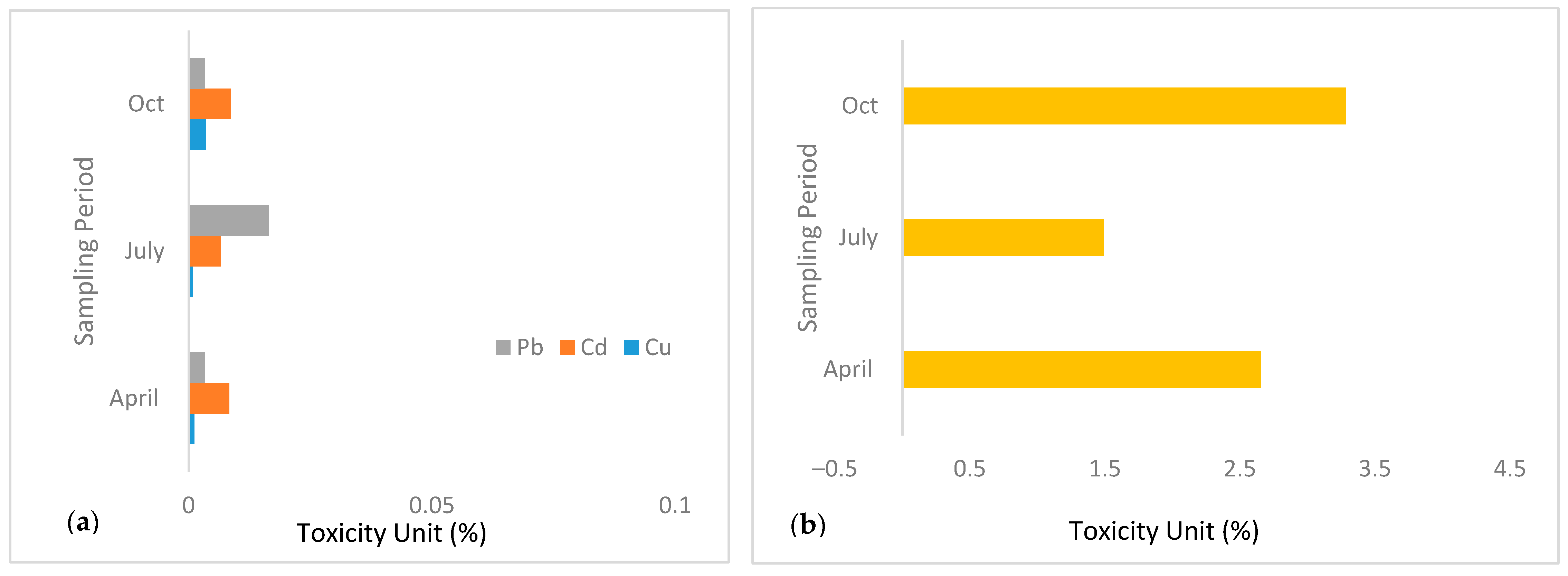
Toxicity Index for Heavy Metals in Mine Water (TU)
2.4. Quantitative Risk Analysis and Calculation
2.4.1. Contamination Assessment
2.4.2. Geo Accumulation Index ()
2.4.3. Contamination Factors (CF)
2.5. Health Risk Assessment and Chronic Daily Intake (CDI)
2.6. Exposure Assessment
2.7. Non-Carcinogenic Risk
Hazard Quotient (HQ)
3. Results and Discussion
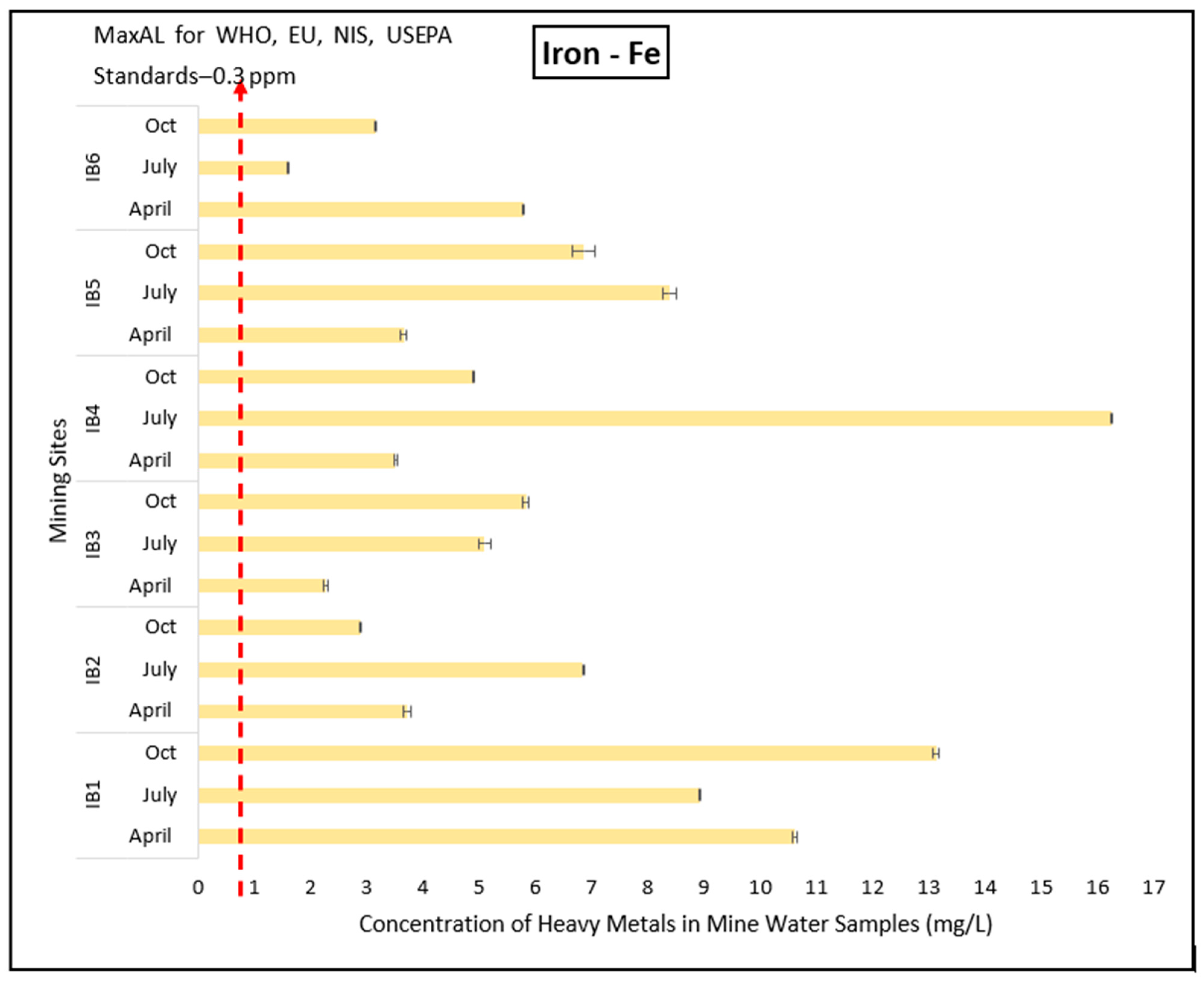
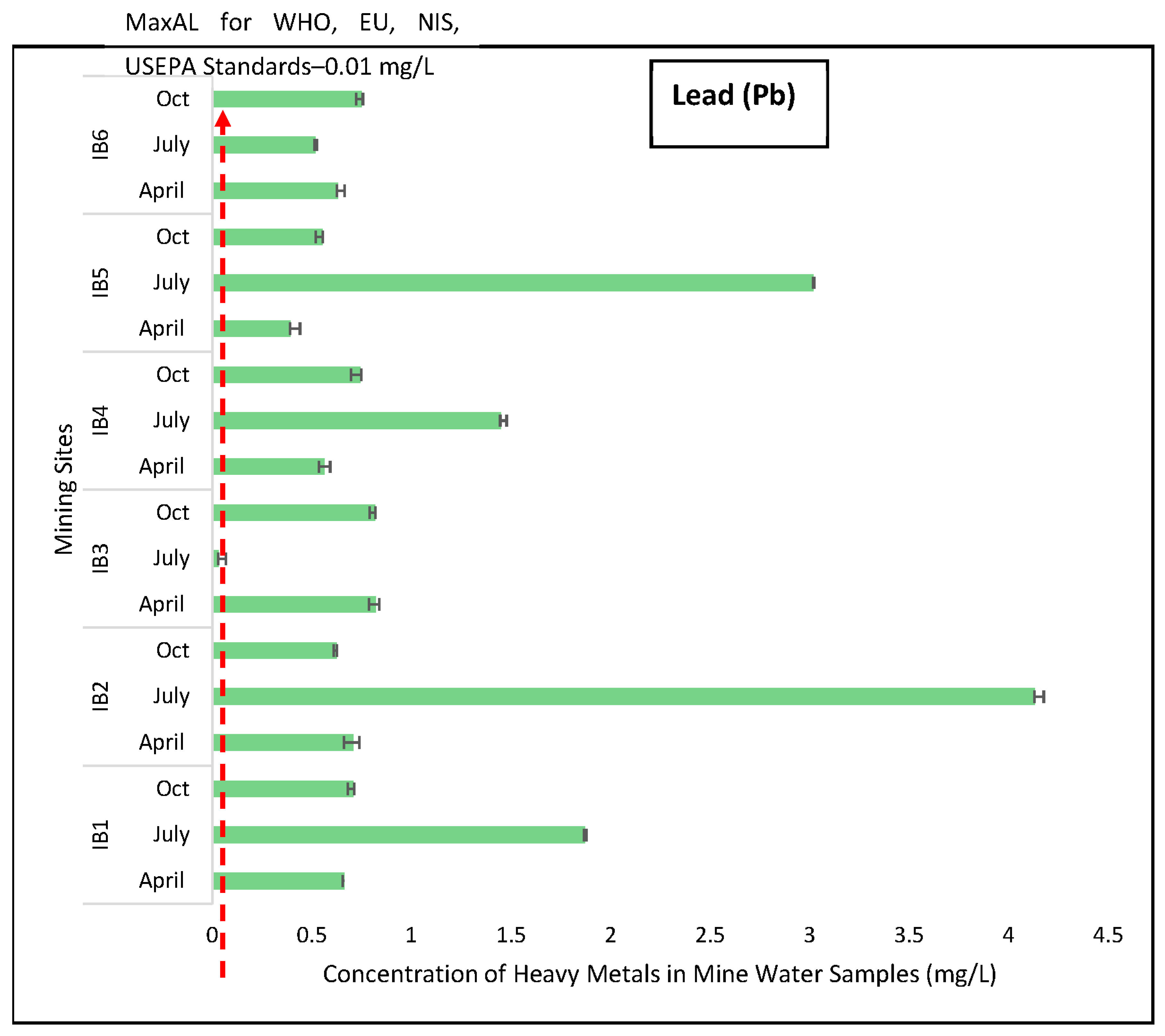
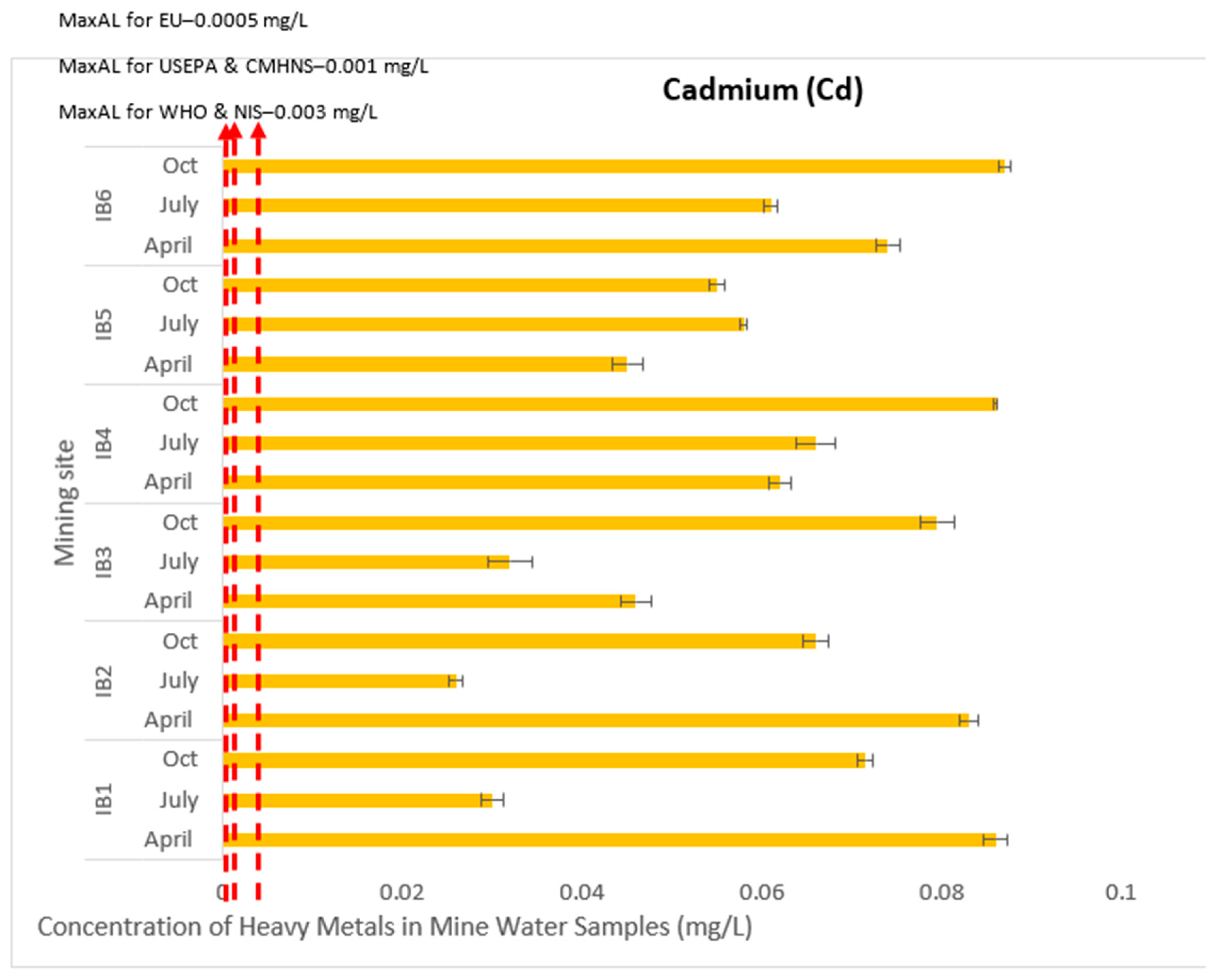
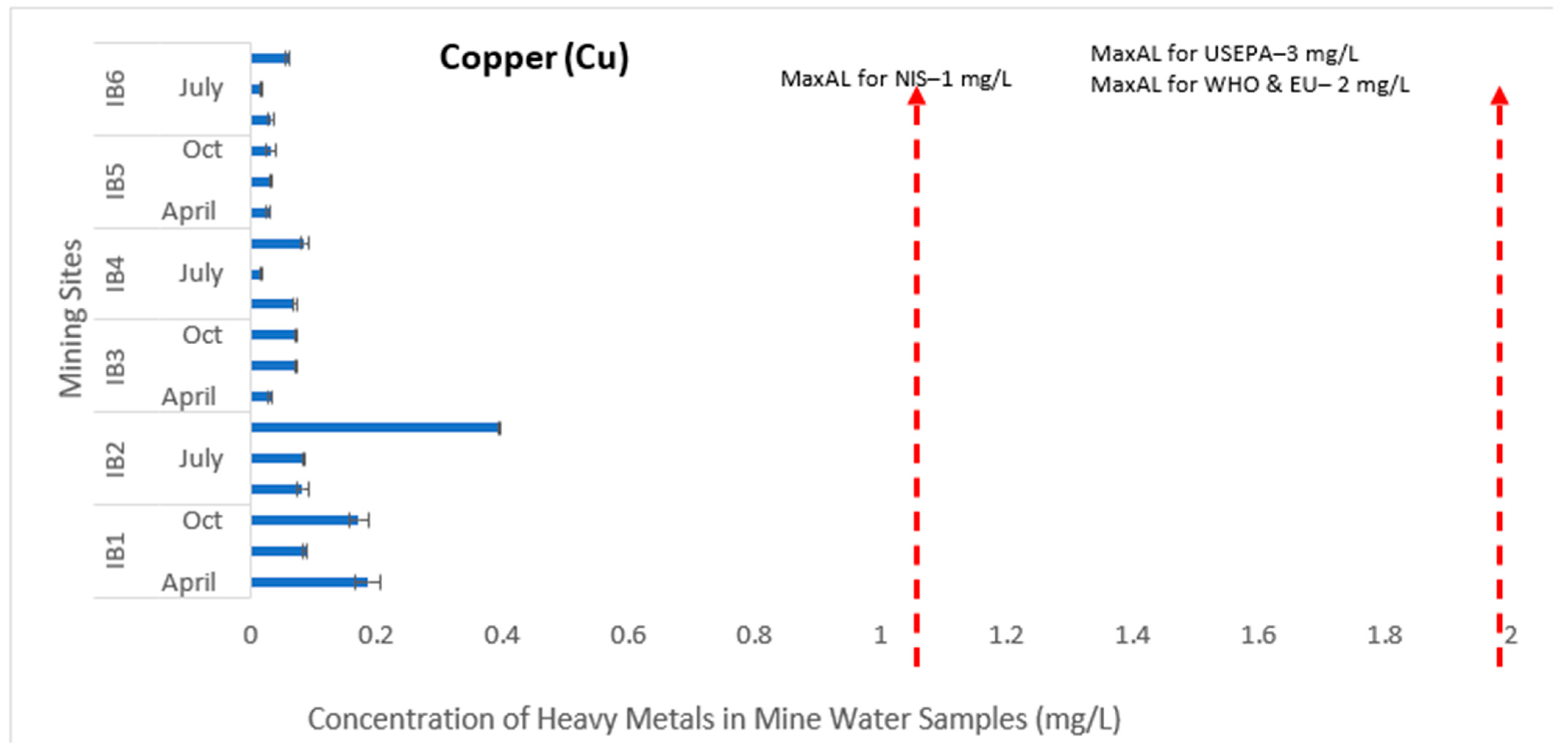
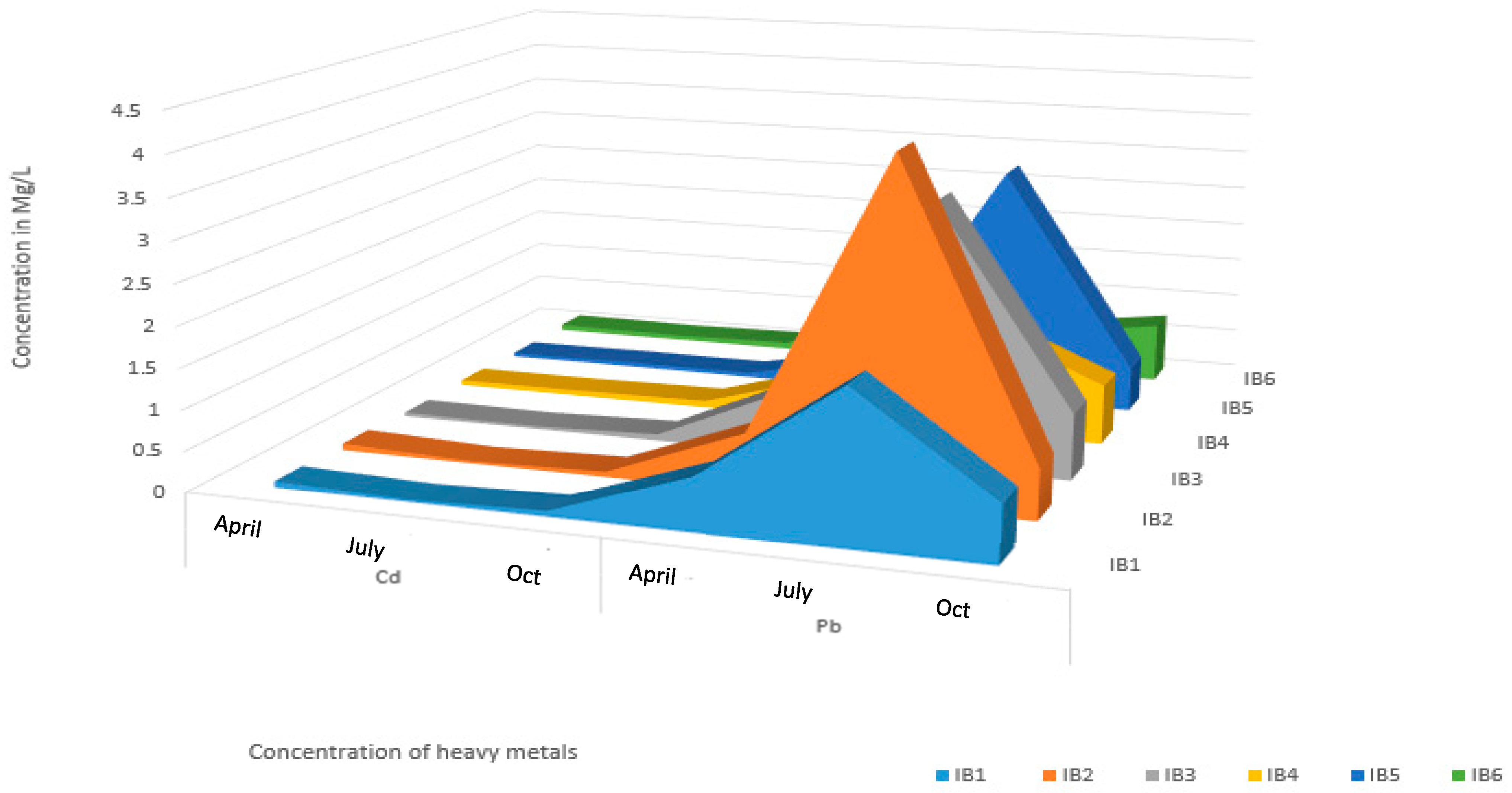
3.1. Evaluation of Toxic Effects of Heavy Metals in Mining Pond Water
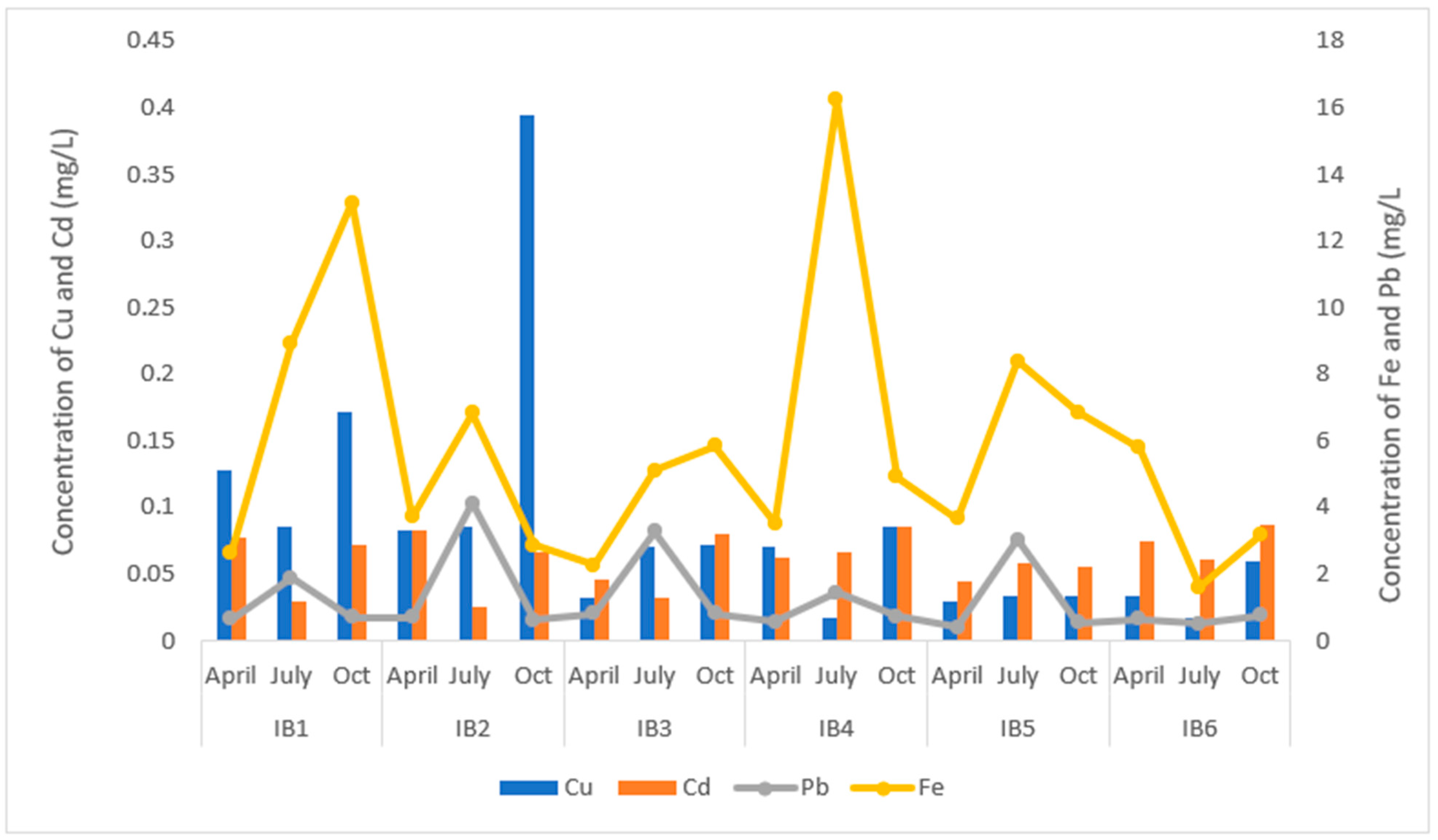
3.2. Contamination Levels of the Heavy Metals in the Mining Ponds
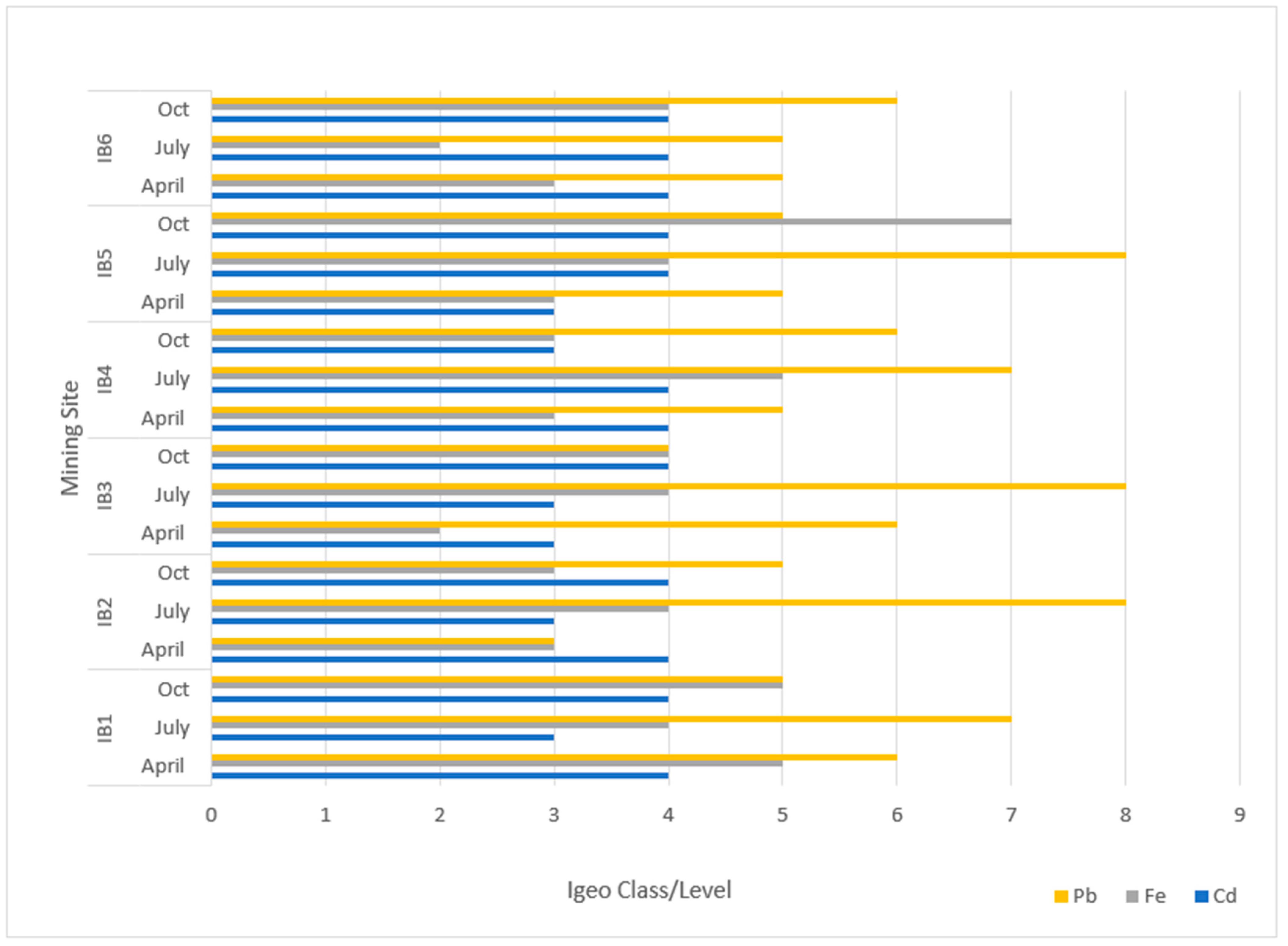
3.3. Geoaccumulation Index () of Heavy Metals in the Ponds and Rivers Within the Mining Sites
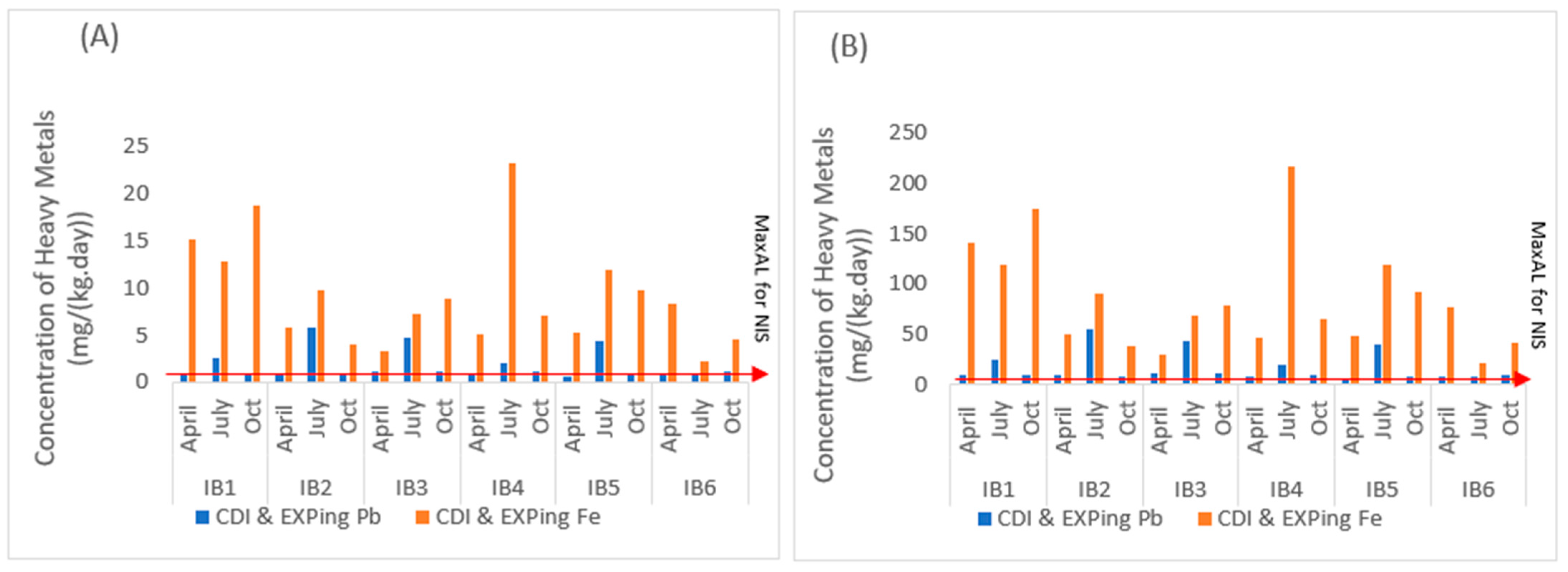
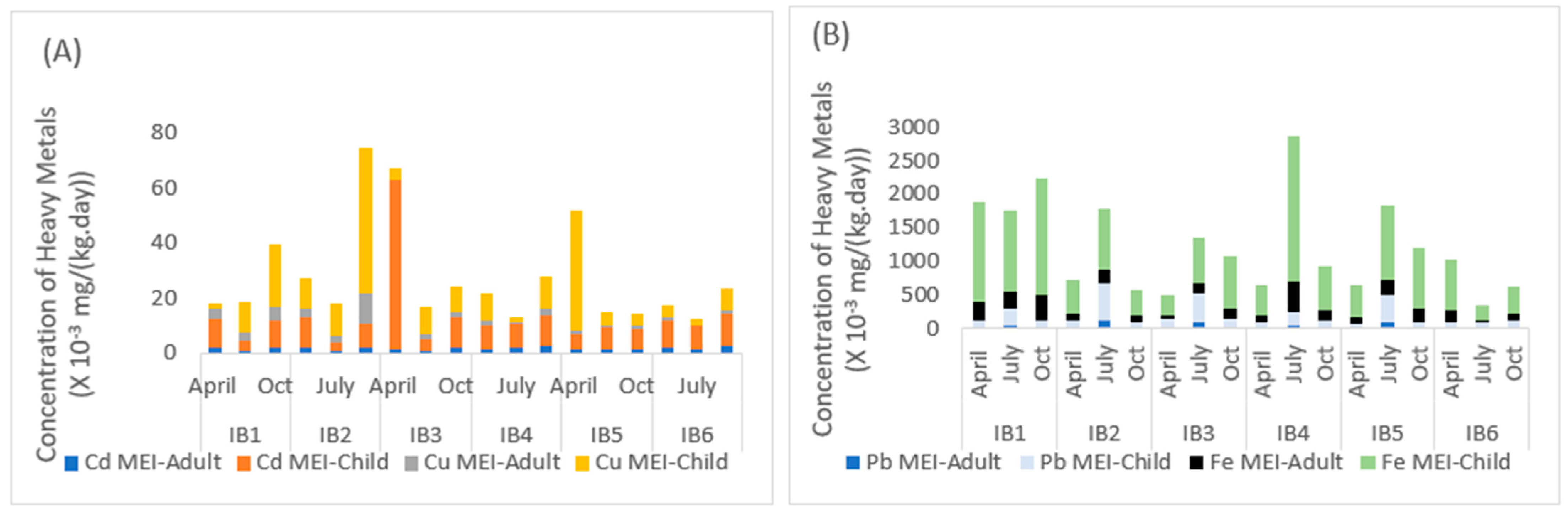
3.4. Chronic Daily Intake (CDI) and Maximally Exposed Individual (MEI) to HMs in Ponds and Rivers with the Barite Mining Sites
3.5. Vulnerability of the Mining Operation Caused by Heavy Metal Contamination of Mining Ponds and Host Rivers
3.6. Characterization of Associated Mining Risks—Non-Carcinogenic Risk Level
4. Conclusions
- The cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), iron (Fe), and copper (Cu) contamination of the River Benue tributaries and sub-tributaries, as well as the mining ponds, exceeds the recommended reference doses and tolerable daily intake limits. This is attributed to multiple contamination sources, which are exacerbated by the seasons throughout the year.
- Seasonal variations, climate change, soil water levels, and anthropogenic activities such as farming and mineral extraction replenish HMs in water, posing the highest potential risk to children throughout the year.
- The findings underscore the urgent need for sustainable and well-integrated policies and government investments to address mining-aided HM contamination of the River Benue tributaries and ponds that connect major rivers in Nigeria. Considering the vastness of the River Benue, a low-level HM contamination at any of the mining sites can cause widespread water contamination that is difficult to clean in the near future.
5. Recommendation
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Elements | Kp or Pc () | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 0.0004 | 0.0014 | 0.00042 | [53] |
| Ba | 0.003 | 0.07 | 0.000062 | [53,64] |
| Fe | 0.001 | 0.7 | 0.14 | [53] |
| Cd | 0.001 | 0.0005 | 0.000025 | [52,53] |
| Cu | 0.001 | 0.04 | 0.008 | [53] |
| Zn | 0.0006 | 0.03 | 0.06 | [53,54] |
| Elements | Inhalation RfD | Oral CSF | Dermal CSF | Inhalation CSF | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | NA | 0.0085 | NA | 420 | [54,65] |
| Ba | 0.0076 | ID | ID | ID | [52,53] |
| Fe | NA | NA | NA | NA | [53,54] |
| Cd | 0.000057 | NA | NA | 6.3 | [52,65] |
| Cu | NA | NA | NA | NA | [52] |
| Zn | NA | NA | NA | NA | [65] |
| Parameters | Unit | Child | Adult/Resident | Worker | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (BW) | kg | 15 | 70 | 70 | [52,65] |
| Contact rate (CR) | L/day | 1.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | [56] |
| Exposure factor (EF) | days/year | 350 | 350 | 250 | [65] |
| Exposure duration (ED) | years | 6 | 30 | 25 | [65,66] |
| Exposure time (ET) | days | 2190 | 10,950 | - | [67,68] |
| Exposure frequency (ER) | Days/year | 365 | 365 | 365 | [52,65] |
| Ingestion rate (IR or IR) | mg/day | 200 | 100 | - | [65] |
| Inhalation rate (IRih) | 10 | 20 | - | [65] | |
| Skin surface area (SA/EA) | cm2 | 2100 | 5800 | - | [65] |
| Soil adherence factor (AF) | 0.2 | 0.07 | - | [65] | |
| Dermal adsorption factor (ABS) | none | 0.1 | 0.1 | - | [52,65] |
| Dermal exposure (FE) | none | 0.61 | 0.61 | - | [65] |
| Particulate emission factor | 1.3 × 109 | 1.3 × 109 | - | [65] | |
| (PEF) | |||||
| Conversion factor (CF) | - | [52,65] | |||
| Average time (AT) | |||||
| For carcinogens | days | 365 × 70 | 365 × 70 | - | [56,65] |
| For non-carcinogens | - | 365 × ED | 365 × ED | - | [56,65] |
References
- Omokaro, G.; Idama, V.; Aireughian, E.; Michael, I. Water Resources, Pollution, Integrated Management and Practices in Nigeria-An Overview. Am. J. Environ. Econ. 2024, 3, 10–54536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longe, E.O.; Omole, D.O.; Adewumi, I.K.; Ogbiye, A.S. Water resources use, abuse and regulations in Nigeria. J. Sustain. Dev. Afr. 2010, 12, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ngene, B.U.; Nwafor, C.O.; Bamigboye, G.O.; Ogbiye, A.S.; Ogundare, J.O.; Akpan, V.E. Assessment of water resources development and exploitation in Nigeria: A review of integrated water resources management approach. Heliyon 2021, 7, e05955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akujieze, C.N.; Coker, S.J.L.; Oteze, G.E. Groundwater in Nigeria–A millennium experience–Distribution, practice, problems and solutions. Hydrogeol. J. 2003, 11, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, D.M.; Boger, D.V.; Côte, C.M.; Mulligan, D.R. Sustainable development principles for the disposal of mining and mineral processing wastes. Resour. Policy 2011, 36, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolayan, D.O.; Eggleston, C.M.; Onwualu, A.P.; Adetunji, A.R.; Tao, M.; Amankwah, R.K. Physicochemical Studies for Risk Identification, Assessment, and Characterization of Artisanal Barite Mining in Nigeria. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolayan, D.O.; Onwualu, A.P.; Eggleston, C.M.; Adetunji, A.R.; Tao, M.; Amankwah, R.K. Safe Mining Assessment of Artisanal Barite Mining Activities in Nigeria. Mining 2021, 1, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JohnPaul, A.A.; Ayodeji, L.T.; Tangfu, X.; Ning, Z.; Liu, Y. Toxicity, uptake, potential ecological and health risks of Thallium (Tl) in environmental media around selected artisanal mining sites in Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 102, 5391–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laniyan, T.A.; Adewumi, A.J. Potential ecological and health risks of toxic metals associated with artisanal mining contamination in Ijero, southwest Nigeria. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2020, 55, 858–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izah, S.C.; Chakrabarty, N.; Srivastav, A.L. A review on heavy metal concentration in potable water sources in Nigeria: Human health effects and mitigating measures. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Luqueno, F.; Lopez-Valdez, F.; Gamero-Melo, P.; Luna-Suarez, S.; Aguilera-Gonzalez, E.N.; Martínez, A.I.; García-Guillermo, M.D.S.; Hernandez-Martinez, G.; Herrera-Mendoza, R.; Álvarez-Garza, M.A. Heavy metal pollution in drinking water-a global risk for human health: A review. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 567–584. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, K.; Fatima, F.; Waheed, I.; Akash, M.S.H. Prevalence of exposure of heavy metals and their impact on health consequences. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Sillanpää, M.; Gjessing, E.T.; Peräniemi, S.; Vogt, R.D. Environmental impact of mining activities on the surface water quality in Tibet: Gyama valley. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4177–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolkersdorfer, C.; Mugova, E. Effects of mining on surface water. Encycl. Inland Waters 2022, 4, 170–188. [Google Scholar]
- Jhariya, D.C.; Khan, R.; Thakur, G.S. Impact of mining activity on water resource: An overview study. Proc. Recent Pract. Innov. Min. Ind. Raipur India 2016, 201, 19–20. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Bryan, B.A.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, R.; Barrett, D. Managing too little and too much water: Robust mine-water management strategies under variable climate and mine conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhlongo, S.; Mativenga, P.T.; Marnewick, A. Water quality in a mining and water-stressed region. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwary, R.K. Environmental impact of coal mining on water regime and its management. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 132, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Osman, M.; Yang, F.; Massey, I.Y. Exposure routes and health effects of heavy metals on children. Biometals 2019, 32, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dytłow, S.; Górka-Kostrubiec, B. Concentration of heavy metals in street dust: An implication of using different geochemical background data in estimating the level of heavy metal pollution. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, A.J.P.; Laniyan, T.A. Ecological and human health risks associated with metals in water from Anka Artisanal Gold Mining Area, Nigeria. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 27, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, A.J.P.; Laniyan, T.A.; Xiao, T.; Liu, Y.; Ning, Z. Exposure of children to heavy metals from artisanal gold mining in Nigeria: Evidences from bio-monitoring of hairs and nails. Acta Geochim. 2020, 39, 451–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolayan, D.O. Characterisation and Processing of Baryte Ores for Oil Drilling Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, African University of Science and Technology, Abuja, Nigeria, 2021; pp. 1–184. [Google Scholar]
- Ackah, M. Soil elemental concentrations, geoaccumulation index, non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks in functional areas of an informal e-waste recycling area in Accra, Ghana. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, A.; Naghizadeh, A.; Biglari, H.; Peirovi, R.; Ghasemi, A.; Zarei, A. Assessment of human health risks and pollution index for heavy metals in farmlands irrigated by effluents of stabilization ponds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10317–10327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embirsh, M. Lead Toxicity in Children: A Public Health Issue. Libyan J. Med. Res. 2022, 16, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, J.; Krishan, K.; Kanchan, T. Lead Poisoning: An updated Review of Literature. J. Indian Acad. Forensic Med. 2022, 44, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khreis, H.; Bredell, C.; Wai Fung, K.; Hong, L.; Szybka, M.; Phillips, V.; Abbas, A.; Lim, Y.H.; Jovanovic Andersen, Z.; Woodcock, J.; et al. Impact of long-term air pollu-tion exposure on incidence of neurodegenerative diseases: A protocol for a systematic review and expo-sure-response meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2022, 170, 107596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, A.M.; Awomeso, J.A. Assessment of trace metal concentration and health risk of artisanal gold mining activities in Ijeshaland, Osun State Nigeria—Part 1. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 177, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Lin, K.; Cao, M.; Miao, X.; Guo, H.; Rui, D.; Hu, Y.; Yan, Y. Patterns of global burden of 13 diseases attributable to lead exposure, 1990–2019. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyemi, A.W.; Owonikoko, W.M.; Okoro, T.D.; Adagbonyi, O.; Ajeigbe, K.O. Water contamination: A culprit of serum heavy metals concentration, oxidative stress and health risk among residents of a Nigerian crude oil-producing community. Toxicol. Rep. 2024, 12, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimah, N.; Salami, I.R.S.; Oginawati, K.; Mubiarto, H. Appraisal of pollution levels and non-carcinogenic health risks associated with the emergence of heavy metals in Indonesian community water for sanitation, hygiene, and consumption. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulatlet, G.M.; Yacelga, N.; Rico, A.; Mora, A.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Cabrera, M.; Capparelli, M.V. A systematic review on metal contamination due to mining activities in the Amazon basin and associated environmental hazards. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borda, D.R.; Cociuba, I.; Cruceru, N.; Papp, D.C.; Meleg, I.N. A Cost-Effective and Straightforward Approach for Conducting Short-and Long-Term Biomonitoring of Gold Mine Waters. Water 2023, 15, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gololobova, A.; Legostaeva, Y. An assessment of the impact of the mining industry on soil and plant contamination by potentially toxic elements in boreal forests. Forests 2023, 14, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laoye, B.; Olagbemide, P.; Ogunnusi, T.; Akpor, O. Heavy metal contamination: Sources, health impacts, and sustainable mitigation strategies with insights from nigerian case studies. F1000Research 2025, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwatuyi, O.E.; Ajibade, F.O.; Ajibade, T.F.; Adelodun, B.; Olowoselu, A.S.; Adewumi, J.R.; Akinbile, C.O. Total concentration, contamination status and distribution of elements in a Nigerian State dumpsites soil. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2020, 5, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udom, G.J.; Turyahabwe, B.; Aturamu, A.; Aziakpono, O.M.; Agbana, R.D.; Joseph, O.G.; Udom, N.G.; Mugide, N.; Odey, O.P.; Olot, H. Heavy metal and metalloid pollution: A systematic review of health implications for pregnant women, children, and geriatrics in the East African region. Environ. Adv. 2025, 19, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Gorain, B.; Choudhury, H.; Roychoudhury, S.; Sengupta, P. Environmental and occupational exposure of metals and female reproductive health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 62067–62092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, A.N.; Raphael, P.B.; Olumide, O.J.; Amarachukwu, O.F. The synopsis of environmental heavy metal pollution. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 18, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Saha, P.; Palit, D. Heavy Metal Pollution and Environmental Sustainability: Issues, Challenges, and Bioremediation Strategies. In Ecosystem Management: Climate Change and Sustainability; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 249–289. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Song, J.; Liu, D.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J. Mapping mining-affected water pollution in China: Status, patterns, risks, and implications. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2024, 2024, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macklin, M.G.; Thomas, C.J.; Mudbhatkal, A.; Brewer, P.A.; Hudson-Edwards, K.A.; Lewin, J.; Scussolini, P.; Eilander, D.; Lechner, A.; Owen, J. Impacts of metal mining on river systems: A global assessment. Science 2023, 381, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolayan, D.O.; Charles, G.; Azikiwe, K.; Onwualu, P. Physico-chemical studies and mineralogical characterisation of clays for ceramic raw materials. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaibu, L.; Abdullahi, U.; Yaradua, A.I.; Bungudu, J.I. Phytoremediation Potentials of Cynodon dactylon on Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils from Challawa Industrial Estate, Kano-Nigeria. Asian J. Appl. Chem. Res. 2021, 9, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omeka, M.E.; Igwe, O.; Onwuka, O.S.; Obajaja, H.A.; Omang, B.O.; Unigwe, C.O.; Aluma, V.C. Modeling the vulnerability of water resources to pollution in a typical mining area, SE Nigeria using speciation, geospatial, and multi-path human health risk modeling approaches. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 10, 5923–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Definition and Procedure for the Determination of the Method Detection Limit, Revision 2. 2016; pp. 1–6. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/cwa-methods/procedures-detection-and-quantitation-documents (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Adewumi, A.J.; Laniyan, T.A. Contamination, sources and risk assessments of metals in media from Anka artisanal gold mining area, Northwest Nigeria. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persaud, D.; Jaagumagi, R.; Hayton, A. Guidelines for the Protection and Management of Aquatic Sediment Quality in Ontario; Queen’s Printer for Ontario: Ontario, ON, Canada, 1993; pp. 20–23. ISBN 0-7778-9248-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, A.; Tajik, R.; Atif, K.; Zarei, A.A.; Abbaspour, S.; Teimori-Boghsani, G.; Attar, M. Respiratory symptoms and diminished lung functions associated with occupational dust exposure among iron ore mine workers in iran. Open Respir. Med. J. 2020, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIS-554-2015; Nigerian Standard for Drinking Water Quality Technical Committee for Standard for Drinking Water Quality. Standards Organisation of Nigeria: Lagos, Nigeria, 2015.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Guidelines for Water Reuse, US Environmental Protection Agency. EPA/625/R-04/108; 2004. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2019-08/documents/2004-guidelines-water-reuse.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Fact Sheet PFOA & PFOS Drinking Water Health Advisories. EPA 800-F-16-003; 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2016-06/documents/drinkingwaterhealthadvisories_pfoa_pfos_updated_5.31.16.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Shah, I.; Khan, T.; Hanif, M.; Shah, A.; Siddiqui, S.; Khattak, S.A. Environmental aspects of selected heavy and trace elements of Cherat Coal deposits. J. Himal. Earth Sci. 2016, 49, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Laniyan, T.A.; Adewumi, A.J. Evaluation of contamination and ecological risk of heavy metals associated with cement production in Ewekoro, Southwest Nigeria. J. Health Pollut. 2020, 10, 200306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapant, S.; Fajcikova, K.; Khun, M.; Cveckova, V. Application of health risk assessment method for geological environment at national and regional scales. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Alternative Disinfectants and Oxidants Guidance Manual. 1999. Available online: https://eec.ky.gov/Environmental-Protection/Water/Drinking/DWProfessionals/ComplianceDocuments/Alternative%20Disinfection%20and%20Oxidants%20Guidance%20Manual.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Nazaroff, W.W.; Alvarez-Cohen, L. Environmental Engineering Science; John Willey & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Emodi, A.I.; Albert, C.O. Family farming practices in Taraba State. J. Agric. Ext. 2016, 20, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiora, S.C.; Chukwu, A.; Toteu, S.F.; Davies, T.C. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soils Around Lead (Pb)-Zinc (Zn) Mining Areas in Enyigba, Southeastern Nigeria. Jour. Geol. Soc. 2016, 87, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, C.I.; Nganje, T.N.; Edet, A. Major and trace elements pollution of sediments associated with Abandoned Barite Mines in parts of Oban Massif and Mamfe Embayment, SE Nigeria. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 151, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Quick Guide to Drinking Water Sample Collection 2ND EDITION. 2016; pp. 6–20. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2017-04/documents/quick-guide-drinking-water-sample-collection-2ed-update-508.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Provisional Peer Reviewed Toxicity Values for Iron and Compounds. EPA/690/R-, 11; 2006. Available online: https://assessments.epa.gov/risk/document/&deid%3D338968 (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Brenniman, G.R.; Levy, P.S. Epidemiological study of barium in Illinois drinking water supplies. Adv. Mod. Toxicol. 1984, 9, 231–249. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Barium in Drinking-Water. Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. 2004. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/wash-documents/wash-chemicals/barium-2004-background.pdf?sfvrsn=49da360a_4 (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- WHO. Environmental and Occupational Health Hazards Associated with Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining. 2016. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241510271 (accessed on 13 June 2025).





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afolayan, D.O.; Adamu, H.A.; Olajuyi, S.I.; Ogunmodimu, O.S.O. Physicochemical Study of Water Contamination for Health Risks and Environmental Implications: A Case Study of Barite Mining Sites. ChemEngineering 2025, 9, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9060137
Afolayan DO, Adamu HA, Olajuyi SI, Ogunmodimu OSO. Physicochemical Study of Water Contamination for Health Risks and Environmental Implications: A Case Study of Barite Mining Sites. ChemEngineering. 2025; 9(6):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9060137
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfolayan, David Oluwasegun, Hassan Abubakar Adamu, Seun Isaiah Olajuyi, and Olumide Samuel Oluwaseun Ogunmodimu. 2025. "Physicochemical Study of Water Contamination for Health Risks and Environmental Implications: A Case Study of Barite Mining Sites" ChemEngineering 9, no. 6: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9060137
APA StyleAfolayan, D. O., Adamu, H. A., Olajuyi, S. I., & Ogunmodimu, O. S. O. (2025). Physicochemical Study of Water Contamination for Health Risks and Environmental Implications: A Case Study of Barite Mining Sites. ChemEngineering, 9(6), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9060137






