Solvent-Dependent Coordination Geometry Shift in Copper(II)-D2EHPA Complexes: How Diluent Polarity Dictates Extraction Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals Used
2.2. Extraction and Analytical Procedures
2.3. General Expressions for the Extraction Equilibrium of Cu(II) with D2EHPA
2.4. Spectroscopic Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Effect of pH
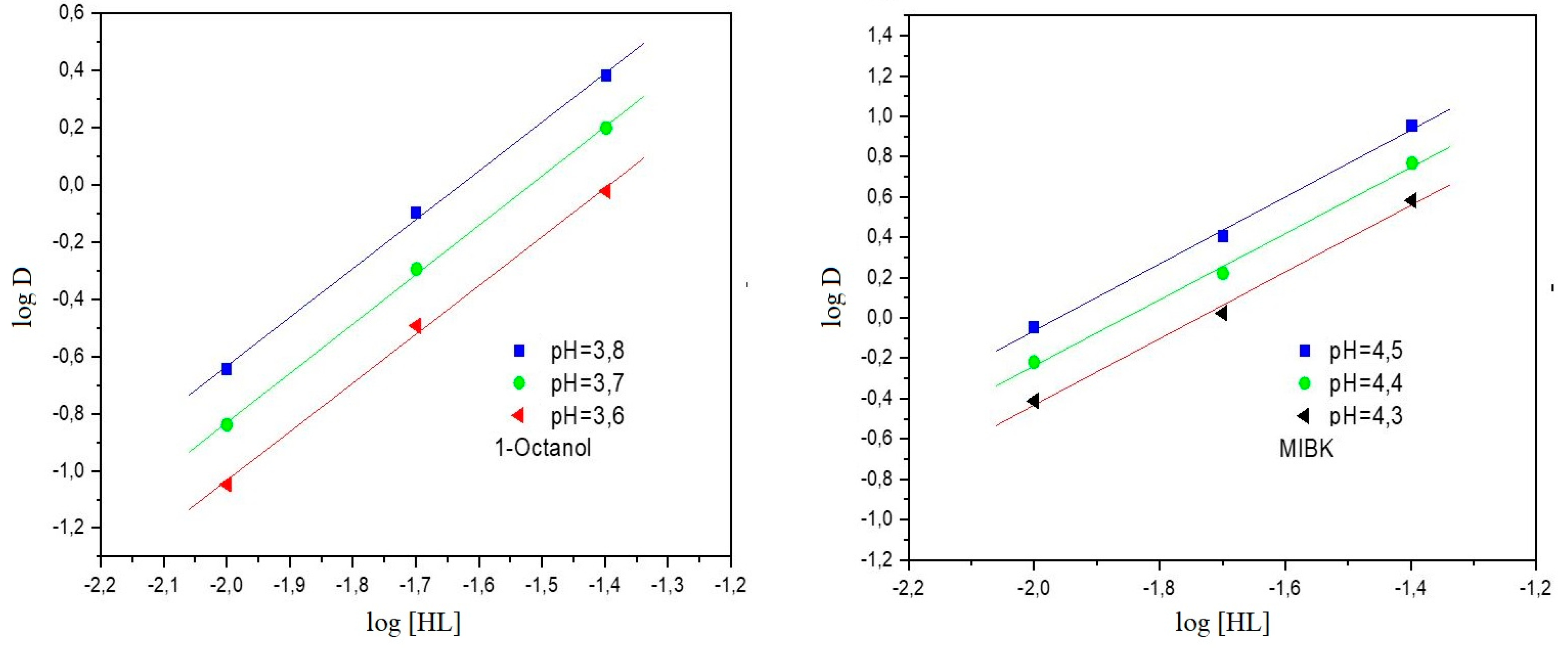
3.2. Influence of Extractant Concentration
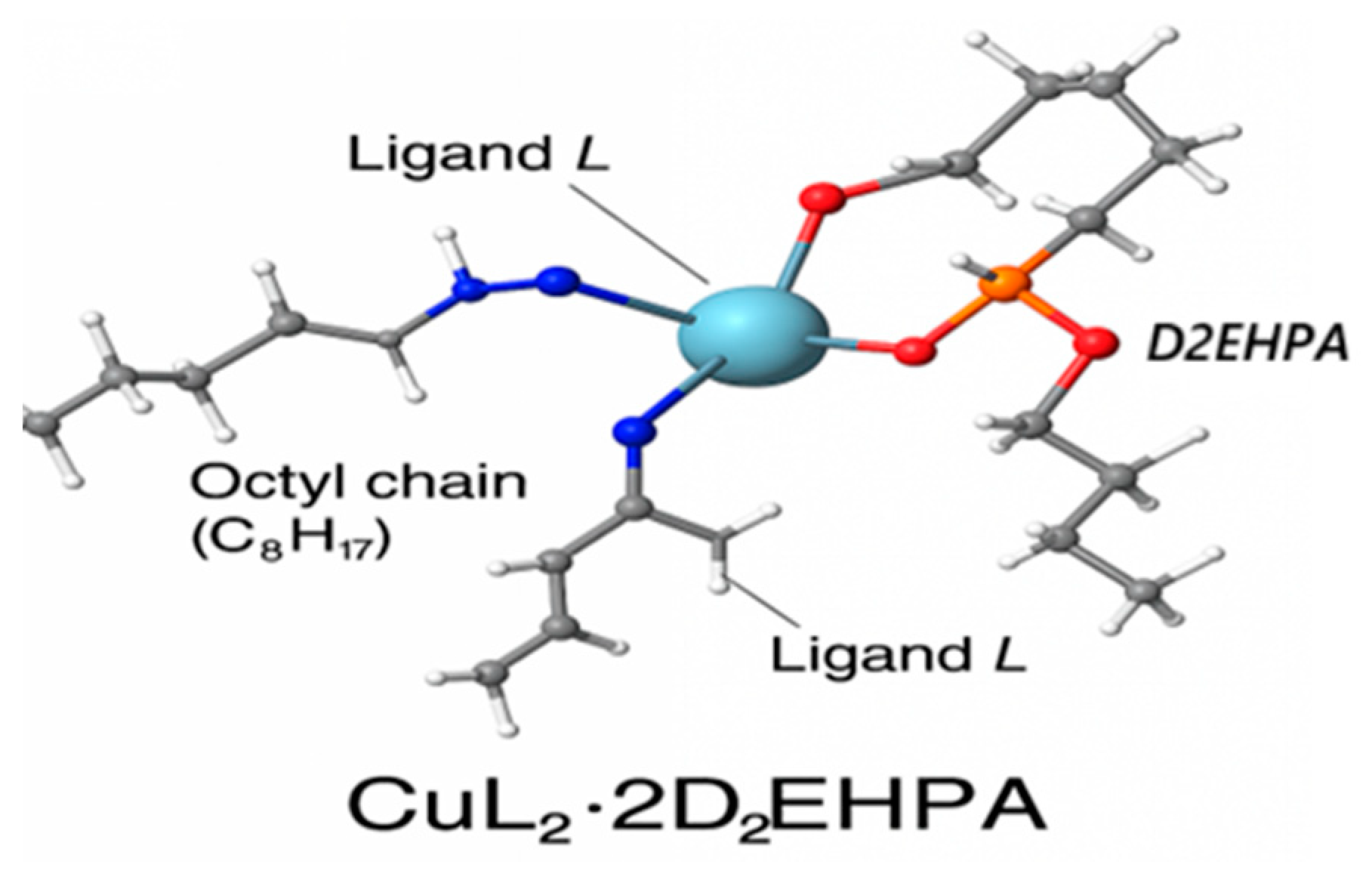
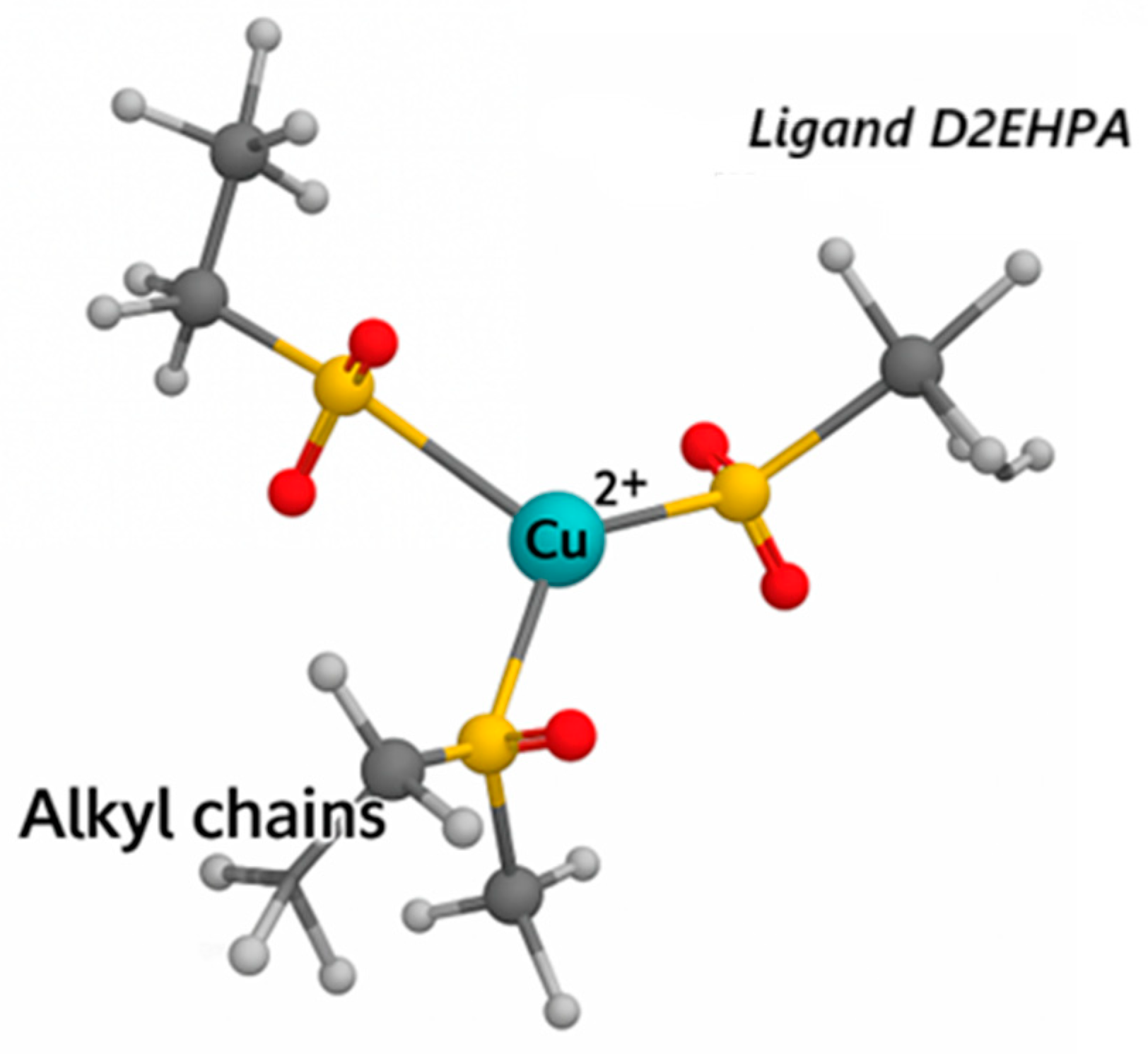
3.3. Effect of Diluent on Copper(II) Extraction by D2EHPA
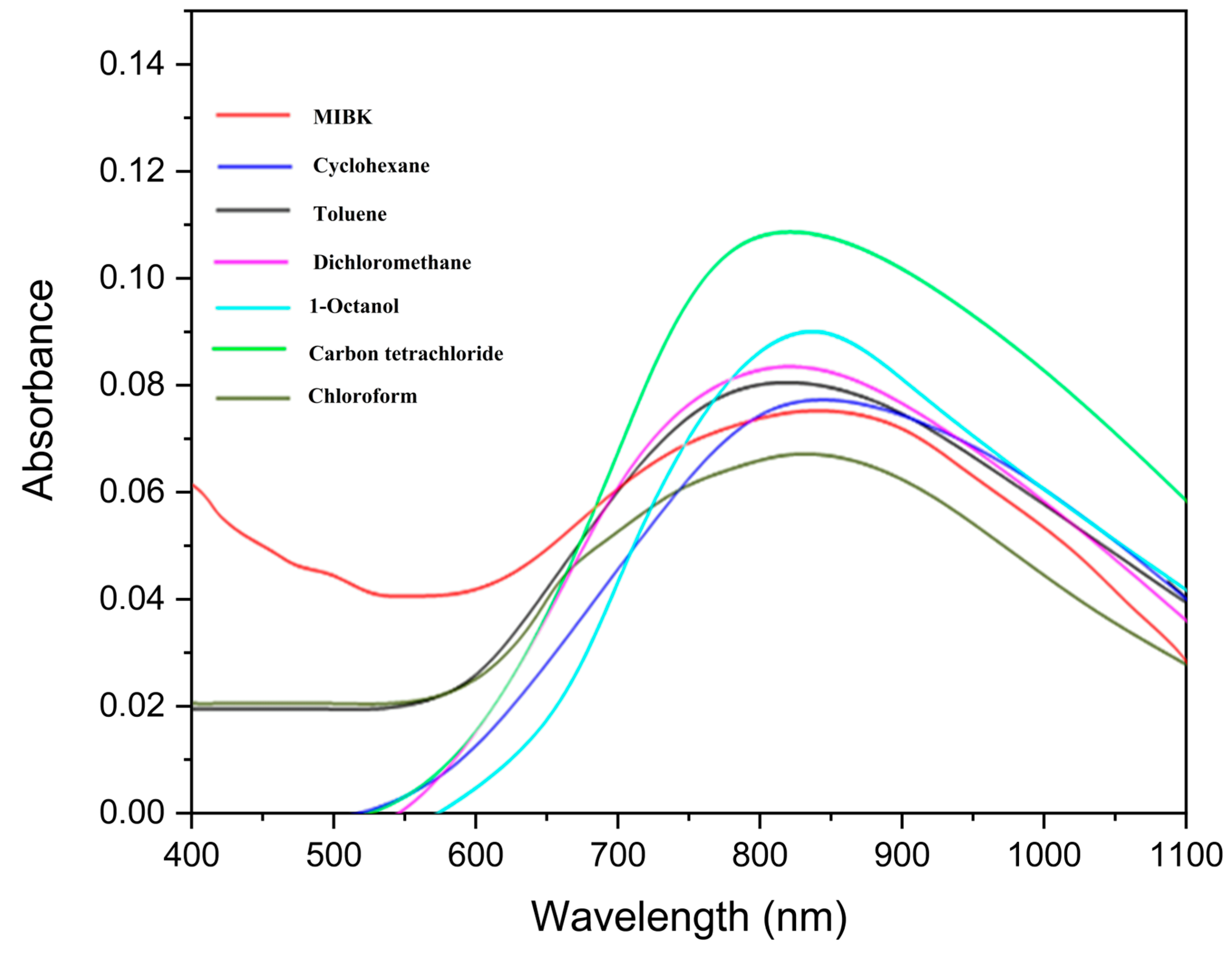
3.4. Visible Spectra of the Organic Phase During Copper (II) Extraction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, C.A.; Kanehashi, S.; Stevens, G.W.; Kentish, S.E. Water permeability and competitive permeation with CO2 and CH4 in perfluorinated polymeric membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 195–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, N.; Liu, T.; Feng, C.; Ma, L.; Chen, S.; Li, M. The mechanism of nitrate-Cr(VI) reduction mediated by microbial under different initial pHs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, Q.; Liang, J.; Weng, Z.; Xu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Gu, A. Urinary biomarkers of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their associations with liver function in adolescents. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Chen, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, L. Bacterial-mediated recovery of copper from low-grade copper sulphide using acid-processed rice straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Liu, J.S.; Wang, J. Solvent extraction of copper and zinc from bioleaching solutions with LIX984 and D2EHPA. J. Cent. South. Univ. Technol. 2005, 12, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, T.; Fujiwara, I.; Baba, Y. Extraction behavior of metal ions using D2EHPA in cyclopentyl methyl ether. Solvent Extr. Res. Dev. Japan 2015, 22, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, M.M.J.; Silvas, F.P.C.; Aliprandini, P.; de Moraes, V.T.; Dreisinger, D.; Espinosa, D.C.R. Separation of copper from a leaching solution of printed circuit boards by using solvent extraction with D2EHPA. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongkapetchawan, P. Emulsion liquid membrane separation of copper from aqueous solution. Master's Thesis, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zinov’eva, I.V.; Kozhevnikova, A.V.; Milevskii, N.A.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. Extraction of Cu(II), Ni(II), and Al(III) with the Deep Eutectic Solvent D2EHPA/Menthol. Theor. Found Chem. Eng. 2022, 56, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchu, N.K.; Binnemans, K. Effect of the diluent on the solvent extraction of neodymium(III) by bis(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (D2EHPA). Hydrometallurgy 2018, 177, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas Fatmehsari, D.; Darvishi, D.; Etemadi, S.; Eivazi Hollagh, A.R.; Keshavarz Alamdari, E.; Salardini, A.A. Interaction between TBP and D2EHPA during Zn, Cd, Mn, Cu, Co and Ni solvent extraction: A thermodynamic and empirical approach. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 98, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zeng, L.; Cao, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Guan, W.; Zhang, G. A green and efficient process for the stepwise extraction of Cu, Ni, Co, Mn, and Li from Hazardous waste with a novel solvent extraction system of D2EHPA-NNPA. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 10020–10032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sözen, S.; Dulkadiroglu, H.; Begum Yucel, A.; Insel, G.; Orhon, D. Pollutant footprint analysis for wastewater management in textile dye houses processing different fabrics. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Teng, T.T.; Ismail, N. Optimization of Cu(II) extraction from aqueous solutions by soybean-oil-based organic solvent using response surface methodology. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2011, 217, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelouaou, S. Synergistic extraction of copper Cu(II) using di (2-ethyl hexyl) phosphoric acid (D2EHPA) and tri-n-octyl phosphine oxide (TOPO). In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Xiamen, China, 21–23 November 2024; pp. 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Dreisinger, D. Solvent extraction of copper from chloride solution I: Extraction isotherms. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 137, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.C.; González, I.; Rodriguez, V.; Padilla, R. Solvent Extraction of Copper from Sulfate–Chloride Solutions Using LIX 84-IC and LIX 860-IC. Miner Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2021, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, A.M.; Swoboda, B.; Arora, Z.; Lansot, J.Y.; Chagnes, A. Low-carbon footprint diluents in solvent extraction for lithium-ion battery recycling. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 23334–23345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.; Toro, N.; Hernández, P.; Navarro, P.; Vargas, C.; Gálvez, E.; Sepúlveda, R. Extraction of Cu(II), Fe(III), Zn(II), and Mn(II) from aqueous solutions with ionic liquid R4NCy. Metals 2021, 11, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipa, P.K.; Hughes, M.A. Diluent effect on the solvent extraction rate of copper. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 1135–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, I.; Lundberg, D.; Bajnóczi, É.G.; Klementiev, K.; Just, J.; Sigfridsson Clauss, K.G.V. EXAFS Study on the Coordination Chemistry of the Solvated Copper(II) Ion in a Series of Oxygen Donor Solvents. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 9538–9550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špadina, M.; Bohinc, K.; Zemb, T.; Dufrêche, J.F. Synergistic Solvent Extraction Is Driven by Entropy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13745–13758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, M.; Dai, Y. Extraction Equilibria of Copper(II) with D2EHPA in Kerosene from Aqueous Solutions in Acetate Buffer Media. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2007, 52, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, R.; Kolařík, Z. Acidic organophosphorus extractants—XXV: Properties of complexes formed by Cu(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Zn(II) and Cd(II) with di(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid in organic solvents. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1976, 38, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, R.S.; Chang, Y.T. Kinetics and Mechanism for Copper(II) Extraction from Sulfate Solutions with Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric Acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1993, 32, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almi, S.; Bouzgou, M.; Adjal, F.; Barkat, D. Methyl-isobutyl ketone and 1-octanol as synergistic agents and phase modifiers in solvent extraction of cobalt(II) by the N-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)aniline from sulfate medium. Inorg. Nano-Metal. Chem. 2020, 50, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerdouh, A.; Barkat, D. Influence of the solvent on the extraction of copper(II) from nitrate medium using salicylideneaniline. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebghoub, F.; Labed, N.; Barkat, D. Improved copper (II) extraction from aqueous solutions using di-2-ethylhexyl phosphoric acid and MIBK. Stud. Eng. EXACT Sci. 2024, 5, e12318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Nagaosa, Y. Solvent Extraction of Copper (II) with Di-2-Methylnonylphosphoric Acid in Some Organic Diluents. Solvent Extr. Ion. Exch. 2003, 21, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlevčar, B.; Gamez, P.; de Gelder, R.; Jagličić, Z.; Strauch, P.; Kitanovski, N.; Reedijk, J. Counterion and Solvent Effects on the Primary Coordination Sphere of Copper(II) Bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)acetic Acid Coordination Compounds. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 2011, 3650–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Voorde, I.; Pinoy, L.; Courtijn, E.; Verpoort, F. Influence of acetate ions and the role of the diluents on the extraction of copper (II), nickel (II), cobalt (II), magnesium (II) and iron (II, III) with different types of extractants. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 78, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, F.A.; Wilkinson, G.; Murillo, C.A.; Bochmann, M. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, G.; Wei, Q.; Ren, X. The effect of diluent on the extraction: Amide extracting chromium (VI) as an example. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 384, 122205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Aqueous Phase | Diluent | log Kex | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.33 M Na2SO4 | 1-octanol | −3.69 | This work |
| Dichloromethane | −4.80 | ||
| Chloroform | −5.01 | ||
| 0.1 M (Na, H)ClO4 | Toluene | −3.82 | [29] |
| 1-octanol | −3.78 |
| Solvents | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|
| Chloroform | 820 |
| Toluene | 819 |
| Dichloromethane | 820 |
| Carbon Tetrachloride | 818 |
| Cyclohexane | 821 |
| Solvents | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|
| MIBK | 844 |
| 1-octanol | 843 |
| Solvents | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|
| Chloroform | 12.67 |
| Dichloromethane | 16.94 |
| 1-Octanol | 66.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghebghoub, F.; Barkat, D.; Ben-Ameur, M.-C.; Kethiri, M.-A. Solvent-Dependent Coordination Geometry Shift in Copper(II)-D2EHPA Complexes: How Diluent Polarity Dictates Extraction Efficiency. ChemEngineering 2025, 9, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9050107
Ghebghoub F, Barkat D, Ben-Ameur M-C, Kethiri M-A. Solvent-Dependent Coordination Geometry Shift in Copper(II)-D2EHPA Complexes: How Diluent Polarity Dictates Extraction Efficiency. ChemEngineering. 2025; 9(5):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9050107
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhebghoub, Fatima, Djamel Barkat, Mohamed-Cherif Ben-Ameur, and Mohamed-Aymen Kethiri. 2025. "Solvent-Dependent Coordination Geometry Shift in Copper(II)-D2EHPA Complexes: How Diluent Polarity Dictates Extraction Efficiency" ChemEngineering 9, no. 5: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9050107
APA StyleGhebghoub, F., Barkat, D., Ben-Ameur, M.-C., & Kethiri, M.-A. (2025). Solvent-Dependent Coordination Geometry Shift in Copper(II)-D2EHPA Complexes: How Diluent Polarity Dictates Extraction Efficiency. ChemEngineering, 9(5), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering9050107







