Abstract
Stabilization/solidification (S/S) is an effective method used to reduce the leaching of heavy metals from soils, which is a serious environmental problem when soil is contaminated with heavy metals. In this study, a new stabilizing agent consisting of acetate-ethylene copolymer emulsion (VAE)-hydrated calcium silicate-polycarboxylate (V-CSH-PCE), water-soluble thiourea-formaldehyde (WTF) resins, cement, and fly ash was prepared for the solidification of heavy metal-contaminated soil under low-temperature conditions. The results showed that the agents significantly enhanced the compressive properties of the soil. When 10% cement, 8% fly ash, 1.5% V-CSH-PCE, and 0.5% WTF were added, the compressive strength of the subsoil after 1 day of curing was 0.3755 MPa, which was nearly 12 times higher compared with a blank sample. Meanwhile, the leaching concentrations of Cu2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, and Cr3+ in the substrate were 2.52, 1.12, 1.32, and 0.51 mg/L, respectively, which were lower than the leaching standard of “Hazardous Waste Identification Standard Leaching Toxicity Identification (GB 5085.3-2007)”. In addition, the compressive strength of the soil after 1 day of curing at a low temperature (4 °C) was 0.2915 MPa, which was 30.9% higher compared with the soil without the V-CSH-PCE. The results showed that the cement-fly ash-(V-CSH-PCE)-WTF mixture has good application prospects in improving the compressive strength of soil and stabilizing heavy metal ions.
1. Introduction
Pollution of soil by metals and quasi-metals has been a long-standing concern due to rapid urbanization, mining, metal processing, and intensive use of industrial fertilizers [1,2,3,4,5]. The metals and quasi-metals contributing to this problem include cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), chromium (Cr), mercury (Hg), cobalt (Co), selenium (Se), nickel (Ni), and arsenic (As) [6]. Due to their high mobility and non-biodegradability, heavy metals continue to accumulate rapidly in soils, leading to a decrease in soil productivity and food security, with serious implications for animal and human health [7,8,9]. To cope with the increase in metal-contaminated soils, extensive research has been conducted over the past few decades to develop effective soil remediation strategies, which can be categorized according to the principles of soil replacement, physical remediation (electrokinetic remediation and soil drenching), phytoremediation, and chemical remediation [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Of these, the stabilization/solidification (S/S) method is effective and practical. Stabilization/solidification is a well-established method used to treat a wide range of metal-containing hazardous wastes prior to land disposal, including the treatment of solutions, slurries, sludges, contaminated soils, dust, and other particulate matter [18,19,20]. During the stabilization/solidification process, the ionic form of heavy metals is altered by mixing them with binders. The solubility, mobility, leaching toxicity, and bioavailability of the contaminant metals are reduced through mechanisms such as metal hydroxide precipitation, ionic adsorption/hydration product substitution, and physical encapsulation [21,22,23,24]. Ordinary Portland cement (OPC) is a well-established stabilizing curing agent due to its low cost, wide applicability, and workability, which can effectively immobilize potentially toxic elements in OPC-based matrices through a combination of physical encapsulation and chemical immobilization mechanisms [25,26,27,28]. However, OPC produces significant amounts of carbon dioxide when applied and has limited compatibility between cement and soil or clay, as well as durability issues such as decalcification, degradation, and potential leaching. Despite the excellent fixation efficiency of cement for metallic elements, the use of cement alone is not sufficient to fix quasi-metallic elements, especially in the presence of both metallic and quasi-metallic elements. A total of 50–70% of cement hydration products are nano-sized hydrated calcium silicate (C-S-H), which plays a role in promoting nucleation during cement hydration and thus contributes to the development of strength at different ages, especially in the early stages. C-S-H nanoparticles are prone to agglomeration due to their high specific surface area and high surface energy. This instability greatly limits their use as cement admixtures. To improve the stability of C-S-H nanoparticles, stabilizers are often used. Organic polymers such as polycarboxylic acid high-efficiency water reducing agent (PCE) and vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymer emulsion (VAE) can be adsorbed on the surface of nano C-S-H, which hinders collision between particles, reduces the tendency of agglomeration, and serves to stabilize the nanoparticles.
Geopolymers are synthetic alkaline aluminosilicates produced by activating aluminosilicate particles through concentrated alkaline solutions (e.g., sodium hydroxide or sodium silicate) and have also received widespread attention. Commonly used aluminosilicate solids include fly ash, blast furnace slag, and metakaolin [29,30]. Geopolymers have been reported to exhibit better chemical and physical properties than cement in certain stabilization curing applications, including reduced leachability of treated scrap metal, reduced permeability, improved resistance to chloride attack, and improved compressive strength [31,32,33,34]. In addition, organic (thiourea-based polymers) and inorganic-organic composite curing stabilizers have been applied to achieve environmentally safe disposal of heavy metals in soil [35,36,37], but at the same time, it is difficult for a single product to satisfy the demand in terms of cost, stabilizing effect, and long-lasting stability.
In this study, VAE emulsion-hydrated calcium silicate-polycarboxylate (V-CSH-PCE) early strength agent was synthesized by stabilizing nanoscale hydrated calcium silicate (C-S-H) with polycarboxylic acid ether (PCE) and vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymer emulsion (VEA). Using formaldehyde and thiourea as raw materials, water-soluble thiourea-formaldehyde resin (WTF) heavy metal chelating agent was synthesized with a hydroxymethylation reaction and condensation reaction. Using cement as the curing agent and fly ash as the reinforcing agent, a long-lasting and stable heavy metal-contaminated soil treatment environmental protection agent was developed, which was used for the long-lasting stabilization of heavy metal ions and, at the same time, improve the mechanical strength of the subsoil when it was used as road base material. The chemical compositions of the early strengthening agent and the heavy metal chelating agent were analyzed by means of characterization methods, such as Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and particle size analysis, and the chemical compositions of the agent and the heavy metal chelating agent were evaluated. The effects of environmentally friendly agents for heavy metal-contaminated substrate treatment on the compressive strength and heavy metal stabilization of the cured substrate were evaluated, as well as the early strength of the substrate in the presence of an early strengthening agent under low-temperature curing conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Methyl allyl alcohol polyoxyethylene ether (HPEG-4000) was purchased from Longxin Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China). Ammonium persulfate and acrylic acid were purchased from Kmart Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China), and 2-Acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid (AR, 98%), methacryloyloxyethyltrimethylammonium chloride, 3-mercaptopropionic acid (AR, 98%), and ascorbic acid were purchased from Hynes Optech Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China). Na2SiO3-5H2O, Ca(NO3)2-4H2O, melamine (AR, 99%), vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymer emulsion, thiourea, and formaldehyde (37% aqueous solution) were purchased from Aladdin Biochemical Science and Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Hydrochloric acid (AR, 37%) and sodium hydroxide (AR, >97 wt.%) were purchased from Windship Chemical Reagent Technology Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China). P-I 42.5 silicate cement and fly ash were purchased from Fushun Cement Company Limited (Fushun, China).
2.2. Pretreatment of Soil
The soil was naturally air-dried to evaporate most of its water and then placed in an oven at 60 °C for more than 12 h to dry the remaining water until reaching a constant weight. Then, the soil was crushed with a shredder and passed through a 20 mesh sieve (<0.85 mm) to remove the larger clods. Finally, the sieved soil was sealed and stored for later use.
2.3. Synthesis of V-CSH-PCE
The synthesis of polycarboxylate ether (PCE) was borrowed from the optimized procedure reported by Kanchanason and Zhu et al. [38,39]. The approach employed methyl allyl alcohol polyoxyethylene ether (HPEG-4000) with 90 ethylene oxide (EO) units and acrylic acid as monomeric components, undergoing free radical polymerization at a ratio of 1:6. The reaction was initiated using ammonium persulfate, with mercaptopropionic acid serving as a chain transfer agent. The polymerization reaction was carried out at 70 °C for 2 h, followed by 2 h of incubation and subsequent cooling to room temperature. Then, a 30% sodium hydroxide solution was introduced to adjust the pH level to 5, followed by a subsequent water addition to achieve a PCE solid content of 50%. The obtained PCE exhibited an average molecular weight (Mw) of approximately 36 K and a polydispersity index (PDI) of 1.75.
As shown in Figure 1, 20 g of vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymer emulsion was mixed well with 4.25 g of 50 wt.% PCE solution, and the pH level was adjusted to 8.0–9.0 by adding 30 wt.% NaOH solution. Then, 9.45 g Ca(NO3)2·4H2O (0.04 mol) was dissolved in 15.55 g water to form solution A, while 8.49 g Na2SiO3·5H2O (0.04 mol) was dissolved in 16.51 g water to form solution B. Then, solutions A and B were dropped simultaneously into the PCE solution over a 12 min period using a dual-channel peristaltic pump in a nitrogen atmosphere at 25 °C with rapid agitation (400 rpm). In addition, the pH level of the mixed solution was maintained at 11.7 ± 0.1 with the addition of 1 mol/L HNO3 or 30 wt.% NaOH solution. Finally, the reaction was completed by stirring (200 rpm) under nitrogen for 24 h to obtain a milky white suspension. The solid content of calcium silicate in the suspension was 4.7%, and the total solid content obtained by elevated temperature drying was 44.46%.
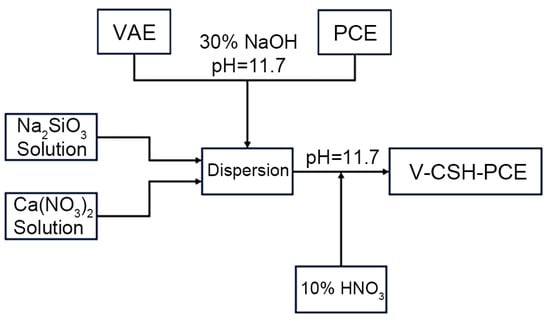
Figure 1.
Schematic of the synthesis of V-CSH-PCE.
2.4. Synthesis of WTF Resins
The WTF resins were prepared according to previous reports [40]. Specifically, WTF resins were synthesized with an amine-formaldehyde reaction (Cannizzaro reaction) involving hydroxymethylation and condensation [41,42]. Firstly, thiourea (15.2 g, 0.2 mmol) and formaldehyde were mixed by heating and stirring. After adjusting the pH level to 7.8–9 using 20 wt.% NaOH solution, the mixture was heated for about 30 min at 60 °C. Then, the heating temperature was increased to 80 °C, and the pH level was further adjusted to 4.5–5.5 by adding 20% HCl solution. The reaction finished when the solution was turbid and not dissolved, which was identified with a turbidity point method [40]. The pH level of the mixture was adjusted to 7 after the reaction finished. Finally, the mixture was freeze-fried for 24 h to obtain WTF resins after cooling them down to room temperature.
2.5. Structural Analysis
A Zetasizer Nano ZS (Nano ZS, Malvern, UK) was used to measure the particle size of the V-CSH-PCE nanocomposites by dynamic light scattering (DLS). The bonding in the WTF resins was evaluated by testing with a FTIR spectrometer (Tensor II, BRUKER AXS GMBH, Saarbrücken, Germany). The sizes of the V-CSH-PCE nanocomposites were investigated using JEOL transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM-1400Flash, Akishima-shi, Japan) at an accelerating voltage of 120 kV. The V-CSH-PCE nanocomposites were observed using a JEM-2100F TEM microscope (JEOL, Akishima-shi, Japan) at an acceleration voltage of 200 kV.
2.6. Measurement of Unconfined Compressive Strength
The unconfined compressive strength was tested according to “JTG E51-2009 Test Procedure for Inorganic Binder Stabilising Materials for Highway Engineering” [43]. A certain amount of soil and different contents of deionized water, cement, fly ash, VAE emulsion-hydrated calcium silicate-polycarboxylate (V-CSH-PCE), and water-soluble thiourea-formaldehyde (WTF) resin were thoroughly mixed and stirred and put into airtight containers or plastic pockets to be moistened for 12 h and set aside. They were then compacted and molded in a cylindrical mold 50 × 50 mm in size three times. After being demolded, the products were maintained at a constant temperature in a humidity chamber for 1 day at a temperature of 25 ± 5 °C and humidity of >95%. The unconfined compressive strength test was carried out with a test loading rate of 1 mm/min, and the unconfined compressive strength was calculated according to Equations (1) and (2):
Here, Rc is the unconfined compressive strength of the subsoil specimen in megapascals; P is the maximum pressure of the subsoil specimen at the time of destruction in Newtons; and A is the cross-sectional area of the subsoil specimen in square millimeters:
Here, D is the diameter of the specimen in millimeters. Repeated experiments with 6 specimens were required for the same set of ratios.
2.7. Heavy Metal Leaching Test
First, 0.15 g of soil was placed in a digestion container and moistened with a small amount of deionized water. Then, 10 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid was added, boiled at 150 °C, and then cooled to 120 °C. Next, 5 mL of concentrated nitric acid, 3 mL of perchloric acid, and 3 mL of hydrofluoric acid were added in turn, and digestion was carried out at 220 °C for 1 h. A large amount of white smoke was found when the lid was opened, and digestion was carried out until the last drop of gray or light yellow droplets was left. The solution was diluted to 1 L with 1 % nitric acid and filtered through a 0.45 μm filter membrane, and the heavy metal ions in the filtrate were detected by ICP-OES.
The stabilization ability of the stabilization/solidification agent on heavy metal ions was tested, with reference to the “Solid Waste Leaching Toxicity Leaching Method Sulphuric Acid Nitric Acid Method (HJ 299-2007)” [44] for the acid leaching test. Firstly, a leaching solution with a pH level of 3.2 ± 0.05 was prepared; that is, a mixture of concentrated sulphuric acid and concentrated nitric acid with a mass ratio of 2:1 (about two drops) was added dropwise to 1 L of deionized water. Then, the soil and leachate were mixed at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:20, placed in a shaker at 25 °C, and shaken at 150 r/min for 12 h before being passed through a 0.45 μm filter membrane, and the concentrations of Pb2+, Ni2+, Cd2+, and Cr3+ in the filtrate were detected by ICP-OES after dilution. All of the above experiments were repeated three times.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characteristics of V-CSH-PCE
As shown in Table 1, the effect of the addition of VAE emulsion and HPEG-4000 during the synthesis of V-CSH-PCE on the particle size of the early strength agent was tested. The results show that VAE emulsion increased the particle size of the nano-hydrated calcium silicate (C-S-H), and the final V-CSH-PCE obtained had the smallest particle size.

Table 1.
Particle size analysis of synthetically prepared V-CSH-PCE.
The synthesized VAE emulsion-hydrated calcium silicate-polycarboxylate (V-CSH-PCE) was analyzed through transmission electron microscopy, as shown in Figure 2. In the presence of PCE, the CSH-PCE composites showed a spherical core-shell structure. The core of the nanocomposite was C-S-H, and the PCE layer was wrapped around the outer layer.
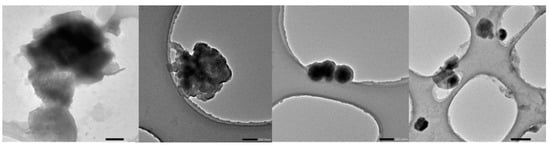
Figure 2.
TCM of V-CSH-PCE.
3.2. Structural Characterization of WTF Resins
The structure of the WTF resins was confirmed using FTIR spectra (Bruker Alpha FTIR spectrometer, German). As shown in Figure 3, FTIR analysis of the WTF resins showed two absorption peaks positioned at 3315 and 1018 cm−1, which corresponded to the stretching vibration of the N-H, H-O, and C-O-C groups. Furthermore, the WTF resins displayed prominent adsorption bands at 1534 and 1590 cm−1, which were attributed to the N-C=S and N=C stretching vibration, respectively. The peaks at 1355 and 1459 cm−1 were assigned to the stretching vibration of the N-C group. The peak at 1293 cm−1 was due to the C-H stretching of =N-C-N=. The above results indicate that the N atoms in the resins were cross-linked.
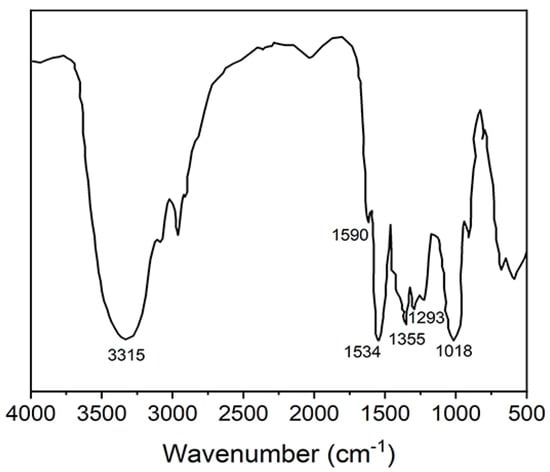
Figure 3.
ATR−FTIR spectra of WTF.
3.3. Strength Characteristics of the Cured Substrate
To investigate the effect of the moisture content of the subsoil on its compressive strength, comparative experiments were set up with water contents of 13%, 16%, 19%, and 21%, and the curing time was 1 day. As shown in Figure 4, the compressive strength of the soil was low at 13% and 21% water content, being 0.0127 MPa for both. When the water content was 19%, the compressive strength of the soil was 0.0145 MPa. The compressive strength of the substrate with 16% water content could reach 0.0293 MPa, which was 131% and 102% higher than those with 13% and 21% water content and 19% water content, respectively. Therefore, the optimum water content of the substrate was 16%, and the subsequent experiments were carried out under this condition.
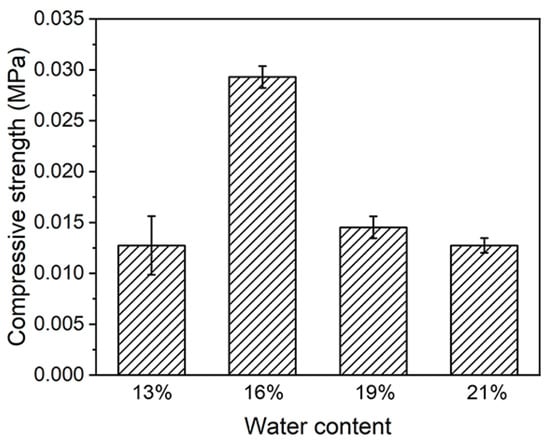
Figure 4.
Compressive strengths of substrates at different water contents.
The minerals on the surface of the cement particles rapidly hydrolyze and hydrate with the water in the subsoil, forming compounds such as calcium hydroxide, aqueous calcium silicate, and aqueous calcium ferrate [45,46]. Therefore, comparative experiments with cement contents of 0%, 6%, 8%, 10%, and 12% were designed to determine the optimal ratio. The experimental results are shown in Figure 5. When the cement addition was 6% or 8%, the compressive strength was 0.147 MPa or 0.188 MPa, respectively. When the cement content was increased to 12%, the compressive strength of the subsoil reached 0.262 MPa. Excessive cement content caused the cured soil to be alkaline. When the cement content was increased to 10%, the maximum compressive strength of the subsoil was 0.284 MPa, which was about 900%, 93.5%, 12.3%, and 8.6% higher than the compressive strength of the subsoil with no cement added and with a cement content of 6%, 8%, and 12%, respectively. Therefore, the cement content of 10% was selected as the optimum ratio, and the subsequent experiments were carried out under this condition.
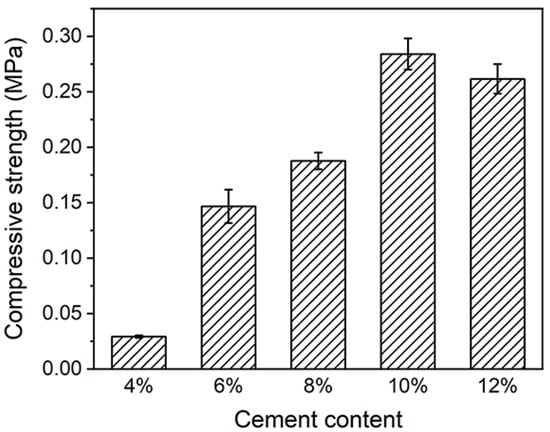
Figure 5.
Compressive strengths of substrates at different cement contents.
Industrial wastes such as fly ash have attracted much attention due to their abundant production and relatively low price. The hydration reaction and volcanic ash reaction occurring in fly ash-based reinforcing agents can generate a large number of calcareous alumina (C-S-H, C-A-S-H, and N-A-S-H) gels which can gel the soil particles to form a more stable structure, thus increasing the strength of the modified soil [47]. Further addition of fly ash to improve the compressive strength of the subsoil was carried out to determine the optimum ratio by designing controlled experiments with fly ash additions of 0%, 4%, 6%, 8%, and 10% under a conditioning time of 1 day. As shown in Figure 6, when the fly ash content was 4% or 6%, the compressive strength of the subsoil was 0.314 MPa or 0.276 MPa, increasing by 10.7% and decreasing by 2.7% compared with that of the subsoil with 0% fly ash content, respectively. The compressive strength of the subsoil reached a maximum of 0.339 MPa at 8% fly ash addition, which was 19.3% higher than that of the subsoil without added fly ash. The compressive strength of the subsoil started to decrease by increasing the fly ash content; the compressive strength of the subsoil was 0.296 MPa when the fly ash content was 10%, which was 12.8% lower than that of the subsoil with 8% fly ash content. Therefore, 8% fly ash content was selected as the optimal ratio for the subsequent experiments, and the subsequent experiments were carried out under this condition.
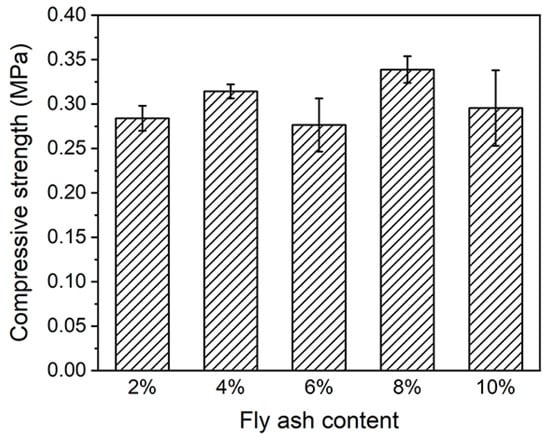
Figure 6.
Compressive strengths of substrates at different reinforcing agent contents.
The nano-C-S-H crystal species are able to promote the early strength of soil with filling and nucleation effects [48]. In this experiment, VAE emulsion-hydrated calcium silicate-polycarboxylate (V-CSH-PCE) and water-soluble thiourea-formaldehyde (WTF) resins were synthesized as an early strengthening agent and heavy metal trapping agent, respectively, and were added to the subsoil at different ratios to test their compressive strength. The additive amounts of the early strengthening agent and heavy metal trapping agent are shown in Table 2. As shown in Figure 7, when keeping the total addition amount of 2% constant, the compressive strength of the subsoil increased and then decreased as the content of V-CSH-PCE decreased and the content of WTF increased. When the content of V-CSH-PCE was 1.5% and the content of WTF was 0.5%, the compressive strength of the substrate was the largest (0.373 MPa), increasing by 10.2% compared with that of the substrate without the addition of VAE emulsion-calcium silicate hydrated polycarboxylate (V-CSH-PCE) and water-soluble thiourea-formaldehyde resin (WTF). This indicates that a small amount of WTF could improve the compressive strength of the substrate. Therefore, 1.5% V-CSH-PCE and 0.5% WTF were selected as the optimal ratios for subsequent experiments.

Table 2.
Content of V-CSH-PCE and WTF.
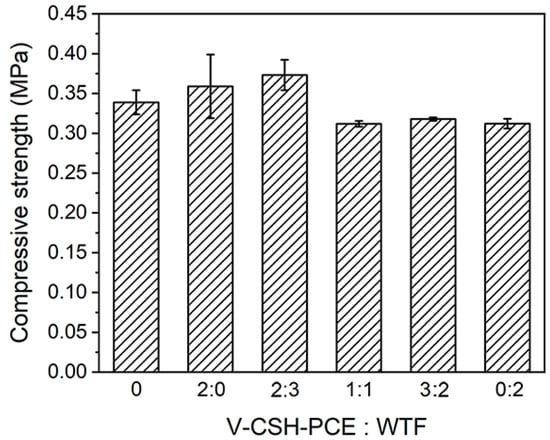
Figure 7.
Compressive strengths of substrates at different V-CSH-PCE and WTF contents.
When used in cold climates, cement hydration is delayed, resulting in a significant decrease in early strength. CSH-PCE acted as a secondary nucleation or growth site for cement hydration, reducing the degree of supersaturation required for the precipitation of hydration products, lowering the nucleation barrier, and accelerating the hydration reaction [48]. The enhancement effect of the VAE emulsion-hydrated calcium silicate-polycarboxylate (V-CSH-PCE) early strengthening agent on the early strength of the substrate at low temperatures was verified. As shown in Figure 8, the compressive strength of the subsoil with the addition of the early strengthening agent increased by 30.9% compared with that of the soil without the addition of the early strengthening agent at 4 °C after 1 day of curing. In addition, at 10 °C, 15 °C, and 25 °C, the addition of the early strengthening agent also effectively increased the compressive strength of the subsoil by 19.4%, 13.8%, and 13.9%, respectively, indicating that the VAE emulsion-calcium silicate hydrate-polycarboxylate (V-CSH-PCE) early strengthening agent was still able to enhance the early strength of the subsoil under extreme low-temperature environments.
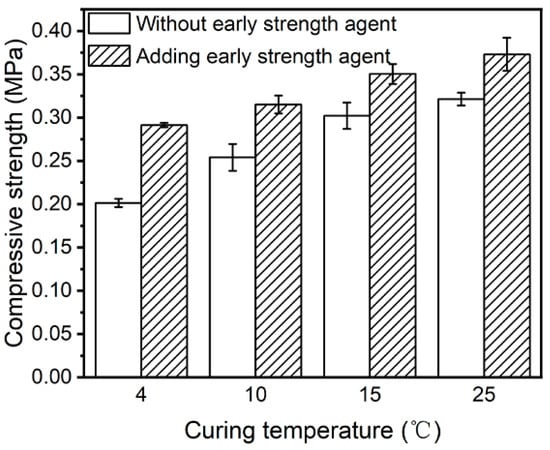
Figure 8.
Compressive strengths of substrates with different curing temperatures.
In order to investigate the effect of the curing time on the compressive strength of the soil, comparative experiments were set up with curing times of 1, 3, 7, and 14 days under the conditions of 10% cement content, 8% fly ash content, 1.5% VAE emulsion-hydrated calcium silicate-polycarboxylate (V-CSH-PCE) content, and 0.5% water-soluble sulfuric aldehyde resin (WTF), respectively. As shown in Figure 9, the compressive strength of the substrate gradually increased with an increase in curing time. The strength was 0.373 MPa for 1 day, 0.512 MPa for 3 days, 0.543 MPa for 7 days, and 0.550 MPa for 14 days, which was an increase of 47.4% compared with that of 1 day, indicating that the longer the curing time, the better the curing effect, and the greater the compressive strength of the substrate.
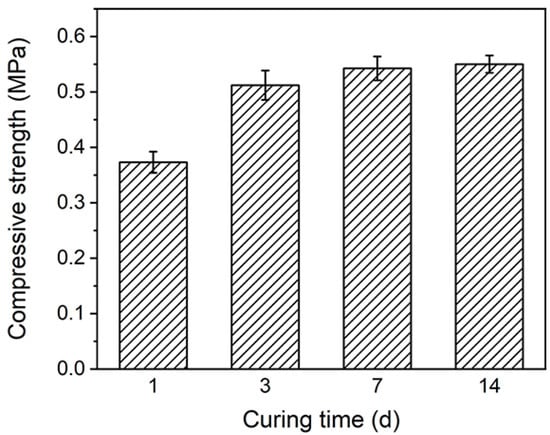
Figure 9.
Compressive strengths of substrates with different curing times.
3.4. Subsoil Solidification Mechanism
The curing and stabilizing agents added in this experiment included cement, fly ash, VAE emulsion-hydrated calcium silicate-polycarboxylate (V-CSH-PCE), and water-soluble thiourea-formaldehyde (WTF) resin. In this case, needle-like crystalline substances and various hydrates were formed as a result of hydrolysis and hydration reactions between the cement fly ash and water in the soil. A secondary volcanic ash reaction then occurred between the hydration products and the soil, promoting the bond strength between soil particles and achieving soil curing [49]. During the hydration process, VAE will be hydrolyzed in the cement environment, and the generated CH3COO− will react with Ca2+ to generate organic salts, leading to morphological changes in the phase microstructure, which will form a hydrated phase and improve the compressive strength of the soil [50]. Due to nucleation, nano-hydrated calcium silicate (C-S-H) shows significant promotion of cement hydration, resulting in the formation of a denser microstructure, which can effectively improve the early strength [51].
3.5. Leaching of Heavy Metal Ions from Soil
The above experiments proved that the mixture of cement, fly ash, polycarboxylate (V-CSH-PCE), and water-soluble thiourea-formaldehyde (WTF) resin was effective in improving the early strength of the substrate. However, the content of heavy metals in the substrate exceeded the standard limit of the “Hazardous Waste Identification Criteria Leaching Toxicity Identification (GB 5085.3-2007)” [52]. We evaluated the stabilization effect of curing and stabilization chemicals on heavy metals. The effect of curing and stabilizing chemicals on the stabilization of heavy metals was evaluated. As shown in Figure 10, the leaching concentrations of Cu2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, and Cr3+ in the blank group were 9.21, 8.22, 7.23, and 8.32 mg/L, respectively, which exceeded the standard limits. After the addition of cement, the leaching concentration decreased to 7.02, 7.15, 6.32, and 6.87 mg/L. The hydration product of cement, C-S-H, had a strong adsorption capacity due to its high internal surface, while the presence of a large number of defects in the structure of C-S-H promoted the replacement and integration of exogenous ions. In addition, the pore structure of the cement provided a large surface area, which enhanced the adsorption of heavy metals. The leaching concentration decreased to 6.15, 6.55, 5.62, and 5.54 mg/L with the continued addition of fly ash. After adding AVE emulsion-hydrated calcium silicate-polycarboxylate (V-CSH-PCE) and water-soluble thiourea-formaldehyde (WTF) resin, the leaching concentrations of the heavy metals were 2.52, 1.12, 1.32 and 0.51 mg/L, being reduced to below the leaching standard of “Hazardous Waste Identification Criteria for Leaching Toxicity Identification (GB 5085.3-2007)”. Heavy metals can replace different types of sites in the CSH of V-CSH-PCE, such as through tetrahedral substitution of heavy metals for silicon chains [53,54,55,56], Ca substitution at the interlayer position, adsorption on the surface of hydrated calcium silicate particles [57,58,59], and octahedral substitution of calcium-oxygen layers [55]. Moreover, the thiourea functional group of WTF resin has been demonstrated to possess the capacity to adsorb precious ions (e.g., Au, Ag, and Pt) and heavy metal ions (e.g., Cd, Pb, and Cu) [41].
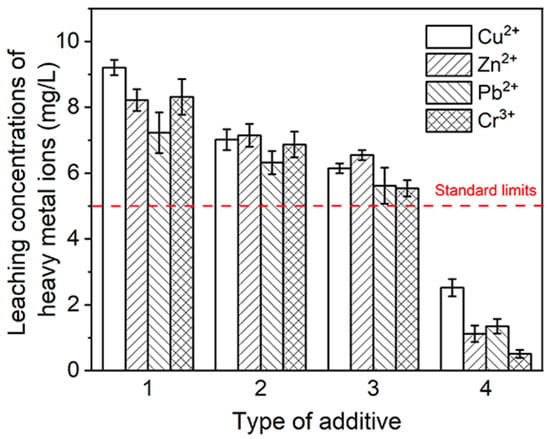
Figure 10.
Leaching of heavy metal ions from soil (1 = blank control; 2 = 10% cement added; 3 = 10% cement and 8% fly ash added; 4 = 10% cement, 8% fly ash, 1.5% VAE emulsion-calcium silicate hydrate-polycarboxylate (V-CSH-PCE), and 0.5% water-soluble thiourea-formaldehyde (WTF) resin added).
4. Conclusions
In summary, a new early strength agent (V-CSH-PCE) consisting of VAE, C-S-H, and PCE was synthesized with the one-pot co-precipitation method by using PCE as a colloidal stabilizer with an average particle size of 126.9 nm, and the V-CSH-PCE early strength agent was stable under the aqueous system. Meanwhile, the water-soluble thiourea formaldehyde (WTF) resin heavy metal trap was synthesized from formaldehyde and thiourea with carboxymethylation and condensation reactions. Furthermore, the curing and stabilizing agents were prepared using cement, fly ash, V-CSH-PCE, and WTF. When 10% cement was added, the compressive strength of the substrate was 0.284 MPa, which was nearly nine times higher compared with the compressive strength of the substrate without cement. After adding 8% fly ash, the compressive strength of the subsoil was 0.296 MPa, increasing by 4.01% compared with the subsoil without fly ash. After continuing to add 1.5% V-CSH-PCE and 0.5% WTF, the compressive strength of the substrate was 0.3755 MPa, increasing by 10.2% compared with that without the added substances. In addition, the compressive strength of the subsoil increased with the increase in curing time, and the compressive strengths at 1, 3, 7, and 14 days were 0.373 MPa, 0.512 MPa, 0.543 MPa, and 0.550 MPa, respectively. Specifically, the compressive strength of the subsoil with the addition of 10% cement, 8% fly ash, 1.5% V-CSH-PCE, and 0.5% WTF was 0.2915 MPa at a low temperature (4 °C), an increase of 30.9% in comparison with that of the subsoil without the addition of early strengthening agents. Due to adsorption, electrostatic attraction, and integration, the leaching concentrations of Cu2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, and Cr3+ were below the leaching toxicity identification of hazardous wastes in the “Hazardous Waste Identification Standards for Leaching Toxicity Identification (GB 5085.3-2007)”, being 2.52, 1.12, 1.32, and 0.51 mg/L, respectively.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation and conceptualization, Y.C. and J.W.; validation and funding acquisition, Y.C.; methodology, J.W. and Z.G.; investigation, methodology, formal analysis, and visualization, Z.G.; writing—review and editing, M.C.; project administration, supervision, writing—review and editing, and funding acquisition, R.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by CCCC First Harbor Engineering Co., Ltd. under grant number 2022-7-3.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Chen Yuntao and Wang Jiannan were employed by the company CCCC Tianjin Port Engineering Institute Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Bi, X.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Fu, Z.; Sun, G.; Shang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, P. Distribution patterns and sources of heavy metals in soils from an industry undeveloped city in Southern China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, S. Identification of the sources and influencing factors of potentially toxic elements accumulation in the soil from a typical karst region in Guangxi, Southwest China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; Ma, J.; Wu, H.; Qu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Yang, S.; An, Y.; Zhou, Y. Heavy metal(loid)s in the topsoil of urban parks in Beijing, China: Concentrations, potential sources, and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Z. Source-specific ecological risk analysis and critical source identification of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorello, D.; Barreca, S.; Gulli, E.; Orecchio, S. Platinum and rhodium in wine samples by using voltammetric techniques. Microchem. J. 2017, 130, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I.; Dumat, C. A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 182, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Jiang, R.; Xiao, W.; Yu, J. Use of surfactants for the remediation of contaminated soils: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 285, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, A.; Azam, M.; Siddiqui, K.; Ali, A.; Choi, I.; Haq, Q. Heavy Metals and Human Health: Mechanistic Insight into Toxicity and Counter Defense System of Antioxidants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29592–29630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hao, L.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, T.; Meng, Y.; Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Qiao, N.; Wang, T. Eco-health risks and main sources of persistent pollutants bound by bus stops dust in Qingyang city, an important energy base on the west side of the Ziwuling primitive Forest. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 204, 116536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Sajad, M. Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Q. An overview of field-scale studies on remediation of soil contaminated with heavy metals and metalloids: Technical progress over the last decade. Water Res. 2018, 147, 440–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Gao, J.; Pierce, E.; Strong, P.; Wang, H.; Liang, L. In situ remediation technologies for mercury-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8124–8147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, D.; Hou, D.; Li, F.; Gu, Q. Mercury removal from contaminated soil by thermal treatment with FeCl3 at reduced temperature. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, V.; Daverey, A. Phytoremediation: A multidisciplinary approach to clean up heavy metal contaminated soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Dong, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y. Thermal desorption for remediation of contaminated soil: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 841–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Lin, Q.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H.; Huang, Z.; Fu, H.; Chen, H.; Xiao, R. The removal of Cu, Ni, and Zn in industrial soil by washing with EDTA-organic acids. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 5160–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balint, R.; Boajă, P. Assisted phytoextraction as a nature-based solution for the sustainable remediation of metal(loid)-contaminated soils. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2024. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Liang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, L.; Cao, X. An integrated approach for simultaneous immobilization of lead in both contaminated soil and groundwater: Laboratory test and numerical modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Feng, Y.; Jin, F.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y. Stabilization and solidification of a heavy metal contaminated site soil using a hydroxyapatite based binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Fu, R.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Guo, X. Chemical stabilization remediation for heavy metals in contaminated soils on the latest decade: Available stabilizing materials and associated evaluation methods—A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ke, Y.; Hills, C.; Kang, Y. Influence of carbonation on the acid neutralization capacity of cements and cement-solidified/stabilized electroplating sludge. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, J.; Hoeffner, S. A Critical Review of Stabilization/Solidification Technology. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 28, 397–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, R.; Chaudhary, R. Leaching behavior and immobilization of heavy metals in solidified/stabilized products. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gougar ML, D.; Scheetz, B.E.; Roy, D.M. Ettringite and CSH Portland cement phases for waste ion immobilization: A review. Waste Manag. 1996, 16, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Mahmud, H.; Shaaban, M. Stabilization/solidification of lead-contaminated soil using cement and rice husk ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1758–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Shi, P.; Yuan, Z.; Shi, S.; Xu, X.; Katsumi, T. Potential of zero-valent iron in remediation of Cd(II) contaminated soil: From laboratory experiment, mechanism study to field application. Soils Found. 2019, 59, 2099–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Du, Y.; Jin, F. Unconfined compressive strength properties of cement solidified/stabilized lead-contaminated soils. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2010, 32, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Du, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, M.; Xu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; et al. Experimental Study of Stress–Strain Properties of Cement Treated Lead-Contaminated Soils. Rock Soil Mech. 2011, 3, 013. [Google Scholar]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers and geopolymeric materials. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 1989, 35, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 1991, 37, 1633–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugteren, H.; Izquierdo, M.; Almera, J. High strength geopolymers produced from coal combustion fly ash. Glob. NEST J. 2009, 11, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández Pereira, C.; Luna, Y.; Querol, X.; Antenucci, D.; Vale, J. Waste stabilization/solidification of an electric arc furnace dust using fly ash-based geopolymers. Fuel 2009, 88, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Fernandez-Jimenez, A. Stabilization/solidification of hazardous and radioactive wastes with alkali-activated cements. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yao, X.; Zhu, H. Potential application of geopolymers as protection coatings for marine concrete: I. Basic properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 49, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Rolle, E.; Ceremigna, D.; Propris, L.; Gabellini, M.; Tornato, A. A kinetic study of chelant-assisted remediation of contaminated dredged sediment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chang, Q.; Han, X.; Zhang, M. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by flocculant with the capacity of reduction and chelation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 248–249, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanchi, S.; Singh, P.; Bisetty, K. Dithiocarbamates as hazardous remediation agent: A critical review on progress in environmental chemistry for inorganic species studies of 20th century. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchanason, V.; Plank, J. Effect of calcium silicate hydrate—polycarboxylate ether (C-S-H–PCE) nanocomposite as accelerating admixture on early strength enhancement of slag and calcined clay blended cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 119, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, M.; Zou, F.; Zhou, F.; Wang, F.; Hu, C. Calcium-silicate-hydrates/polycarboxylate ether nanocomposites doped by magnesium: Enhanced stability and accelerating effect on cement hydration. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 105, 4930–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Ding, H.; Qi, Y. Synthesis of a water-soluble thiourea-formaldehyde (WTF) resin and its application to immobilize the heavy metal in MSWI fly ash. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, Z.; Gülfen, M.; Aydın, A.O. Synthesis of a novel dithiooxamide–formaldehyde resin and its application to the adsorption and separation of silver ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertan, E.; Gülfen, M. Separation of gold (III) ions from copper (II) and zinc (II) ions using thiourea–formaldehyde or urea–formaldehyde chelating resins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 2798–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E51-2009; Test Methods of Materials Stabilized with Inorganic Binders for Highway Engineering. Ministry of Transportation: Beijing, China, 2009.
- HJ/T 299-2007; Solid Waste-Extraction Procedure for Leaching Toxicity-Sulphuric Acid & Nitric Acid Method. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Yin, C.; Ghazaly, S.; Bin, M. Chemical stabilization of scrap metal yard contaminated soil using ordinary portland cement: Strength and leachability aspects. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Yang, W.; Kang, Z.; Kang, S.; Cheng, B. Study on the mechanical properties of phosphogypsum composite cementing materials based on alkali excitation. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 669, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Bui, Q.; Jung, S.; Yang, I. Selected Strength Properties of Coal Bottom Ash (CBA) Concrete Containing Fly Ash under Different Curing and Drying Conditions. Materials 2021, 14, 5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z. Effect of nano-CaCO3 slurry on the mechanical properties and micro-structure of concrete with and without fly ash. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 117, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Xie, X.; Gen, J.; Wang, W. Effect of stabilization/solidification on mechanical and phase characteristics of organic river silt by a stabilizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 236, 117538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.; Roman, H.; Gleize, P. Evidences of chemical interaction between EVA and hydrating Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shi, H.; Qian, B.; Xu, Z.; Li, W.; Shen, X. Effects of synthetic C-S-H/PCE nanocomposites on early cement hydration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 140, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5085.3—2007; Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes-Identification for Extraction Toxicity. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Ivey, D.; Heimann, R.; Neuwirth, M.; Shumborski, S.; Conrad DMikula, R.; Lam, W. Electron microscopy of heavy metal waste in cement matrices. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 5055–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldermann, A.; Preissegger, V.; Šimić, S.; Letofsky-Papst, I.; Mittermayr, F.; Dietzel, M. Uptake of aqueous heavy metal ions (Co2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+) by calcium-aluminium-silicate-hydrate gels. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 147, 106521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Chen, J.; Lin, C. An NMR, XRD and EDS study of solidification/stabilization of chromium with Portland cement and C3S. J. Hazard. Mater. 1997, 56, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommaseo, C.; Kersten, M. Aqueous solubility diagrams for cementitious waste stabilization systems. 3. Mechanism of zinc immobilizaton by calcium silicate hydrate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2919–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, F.; Gieré, R.; Johnson, C. Sorption mechanisms of zinc to calcium silicate hydrate: Sorption and microscopic investigations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4556–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, A.; Wieland, E.; Geng, G.; Lothenbach, B.; Wehrli, B.; Dähn, R. Fe (II) interaction with cement phases: Method development, wet chemical studies and X-ray absorption spectroscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 588, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, N. Binding mechanisms of radionuclides to cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).