Abstract
Various methods, such as electrochemical purification, chemical precipitation, solvent extraction, and ion-exchange resins, have been extensively employed for the removal of copper from nickel anolytes. However, these methods exhibit several significant drawbacks when applied in industrial settings. For instance, electrochemical purification fails to efficiently manage nickel anolyte solutions with low copper content. Chemical precipitation presents challenges in residue management and incurs high production costs for precipitants. Solvent extraction raises concerns related to toxicity, while the use of ion-exchange resins demands meticulous selection of suitable materials. In this review, we present a comprehensive review of the nickel removal methods used for nickel anolyte purification, electrochemical purification, chemical precipitation, solvent extraction, and ion-exchange resins. We also examine the suitability and benefits of each technique in industrial settings. The ion-exchange method has drawn significant attention due to its strong selectivity and small adsorption quantity. The ion-exchange separation process does not generate any slag, and the ion-exchange resin can be recycled and reused; this method has great potential in a wide range of applications.
1. Introduction
Nickel is a metal that has always played an important role in human history, and has been widely used in daily life. Nickel production has been used in the field of metal materials, such as manufacturing of stainless steel, heat-resistant alloy steel, and other alloys. Nickel has also been used in many important fields, such as battery energy, chemical dyes, catalysts, and petrochemicals. In its production and metallurgical technology, many researchers have conducted long-term exploration work on electrochemical methods, chemical precipitation methods, solvent extraction methods, and ion-exchange methods [1,2]. Electrochemical methods involve a metal separation technique utilizing differences in metal electrochemical properties. By adjusting its potential, copper is precipitated from a highly concentrated nickel solution [3,4]. Electrochemical methods mainly include displacement and electrolysis methods [5,6]. The displacement method requires high activity and large-particle nickel powder for copper removal, with complex processes and a high activity of nickel powder [7]. The electrolysis method involves electrolysis of a mixed solution containing nickel and copper [8,9]. The chemical precipitation method utilizes different solubilities of metals to separate metals. By increasing OH− and S2− in the solution, copper is precipitated from a highly concentrated nickel solution. The chemical precipitation method mainly includes a hydrolysis precipitation and sulfide precipitation method for OH− and S2− [10,11,12], respectively. The solvent extraction method is a separation technique that separates metals based on differences in binding properties with organic functional groups [13]. The commonly used extractants for copper removal mainly include amine extractants and aldehyde oxime extractants [14,15,16]. The ion-exchange method is a reaction between resin ion-exchange and metal ions [17]. There are three main types of resins: anion-exchange resin, cation-exchange resin, and chelating resin. Anion-exchange resins utilize Cu2+ to form complex anions when Cl− is greater than 1.5 mol/L, while Ni2+ does not form anionic complexes when Cl- is in the range of 0.1–12 mol/L. By adjusting Cl− concentration, copper is separated from nickel anode solution using an anion-exchange resin. Cation-exchange resin [18,19] utilizes metal ions to be adsorbed by functional groups of cation-exchange resin. The selectivity coefficient of cation-exchange resins for heavy metal ions decreases with the increase in hydration radius and charge number [20]. Chelating resins are widely used in wastewater treatment due to their ability to form stable complexes with heavy metal ions [21].
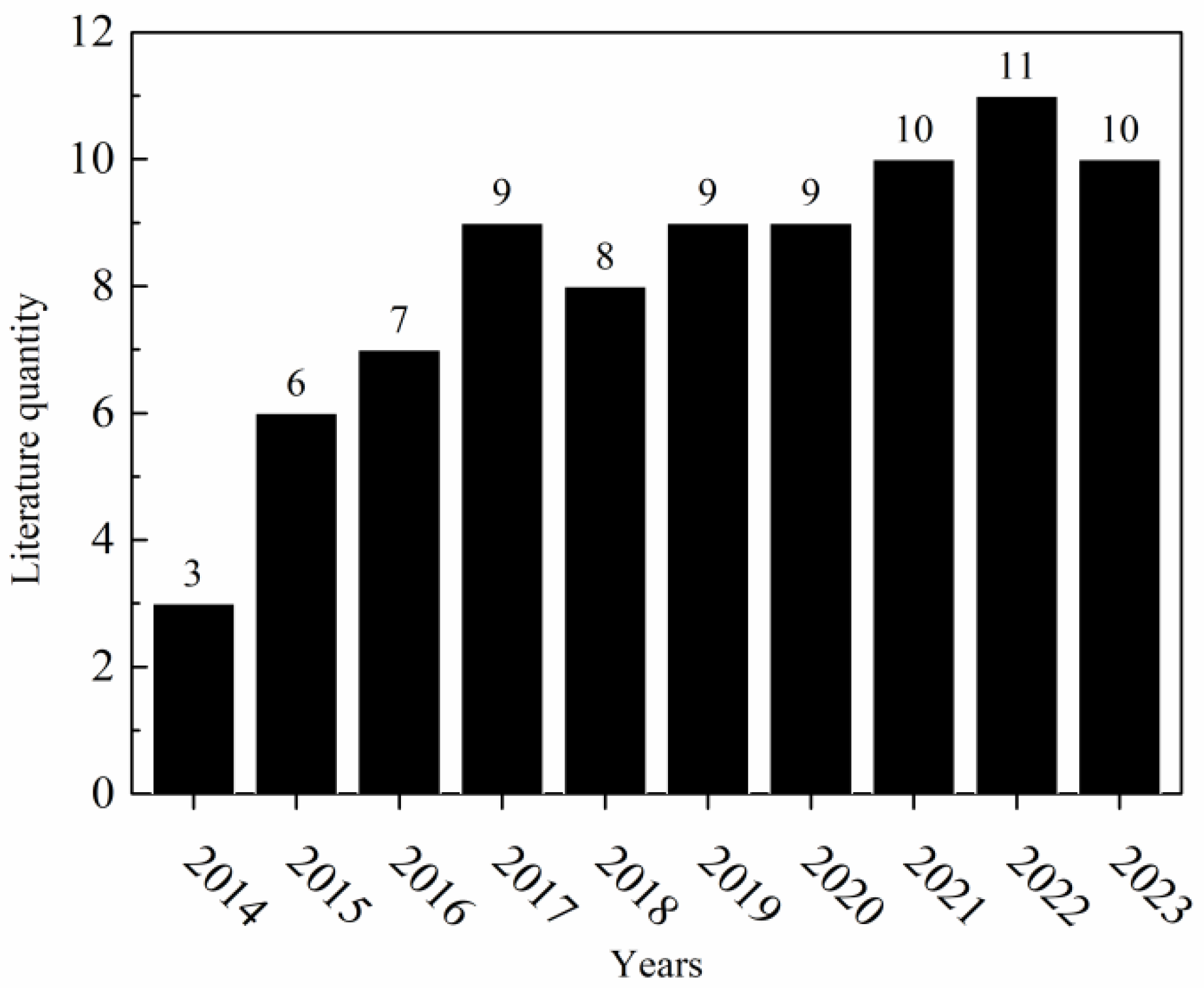
Recently, the production and metallurgical technology of nickel has reached a bottleneck. On the one hand, the scale of production in the nickel industry is constantly being compressed due to the accumulation of excessive products caused by overcapacity and the increasing public awareness of environmental protection [22,23]. On the other hand, along with increasing demand for quality nickel in the international market and the protection of high-purity nickel production technology in developed countries, it has become increasingly difficult for developing countries to create new technologies in the nickel industry [24,25]. Currently, low-quality nickel is barely used in the nickel industry, while it is expensive to produce high-purity nickel, and difficult to innovate in the production process. This is the major dilemma faced by the nickel industry in the industrial transformation period [26,27]. This paper provides a systematic review of the current nickel production process; an analysis on the literature in nickel production and metallurgical technology over the recent decade was conducted and is depicted in Figure 1. In this analysis, “Copper removal from nickel anode solution” acted as a key phrase, and it revealed a year-on-year increase in research papers retrieved through searches conducted in Web of Science and CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure).
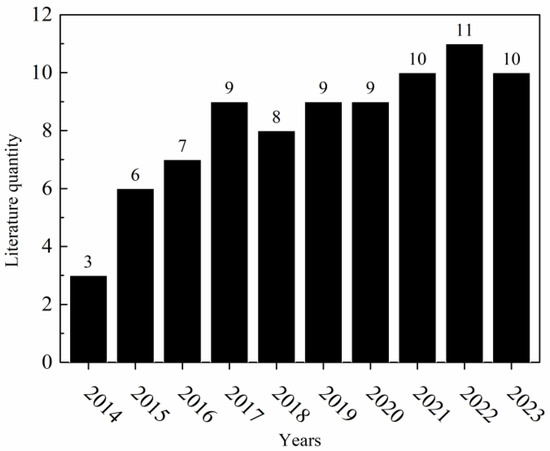
Figure 1.
Analysis of the literature in nickel production and metallurgical technology over the recent decade.
This article summarizes the existing methods for removing copper from nickel electrolyte solutions, and provides an assessment of the advantages and disadvantages of these methods. In the concluding remarks, it is suggested that the ion-exchange method may be a significant metallurgical research tool for nickel, and it is worthy of widespread promotion and adoption within the nickel smelting industry.
2. Nickel Production Process
2.1. Distribution of Nickel Ore
The total nickel reserves in the world comprise approximately 64 million tons. Most of them are located in Cuba, Canada, Russia, South Africa, Australia, China, and Brazil [28]. The total nickel reserves in these countries constitute 91% of the global nickel reserves [29]. In China, nickel ores are primarily distributed in the northwest, southwest, and northeast regions which contribute to 76.8%, 12.1%, and 4.9% of the national nickel reserves in China, respectively [30]. Nickel ores are mainly divided into copper–nickel sulfide ores and nickel oxide ores. The copper–nickel sulfide ores account for 30–40% of the total nickel ores, while the nickel oxide ores account for the remaining 60–70%. Despite the small proportion of copper–nickel sulfide ores, the production of nickel from nickel sulfide ores account for more than 60% of the world’s total nickel production due to its simpler production process [31]. In China, copper–nickel sulfide ores and nickel oxide ores account for 87% and 13% of the total national nickel reserves, respectively; nickel is generally produced from copper–nickel sulfide ores in China [32]. The smelting of copper–nickel sulfide ores is mainly carried out using pyrometallurgy, with the main processes including sulfur smelting, converter blowing, flotation separation, and electrolytic refining [33]. Wet treatment is the second method for copper–nickel sulfide smelting, including pressurized ammonia, oxidation/reduction roasting ammonia, and sulfation roasting and leaching. Nickel oxide ore smelting is also divided into two categories: pyrometallurgical and wet processes. The pyrometallurgical method involves matte smelting and nickel iron smelting. Wet metallurgy includes reduction roasting atmospheric-pressure leaching, high-pressure atmospheric pressure sulfuric acid leaching method, and hydrochloric acid atmospheric pressure leaching method [34,35].
2.2. Primary Production Process of Nickel
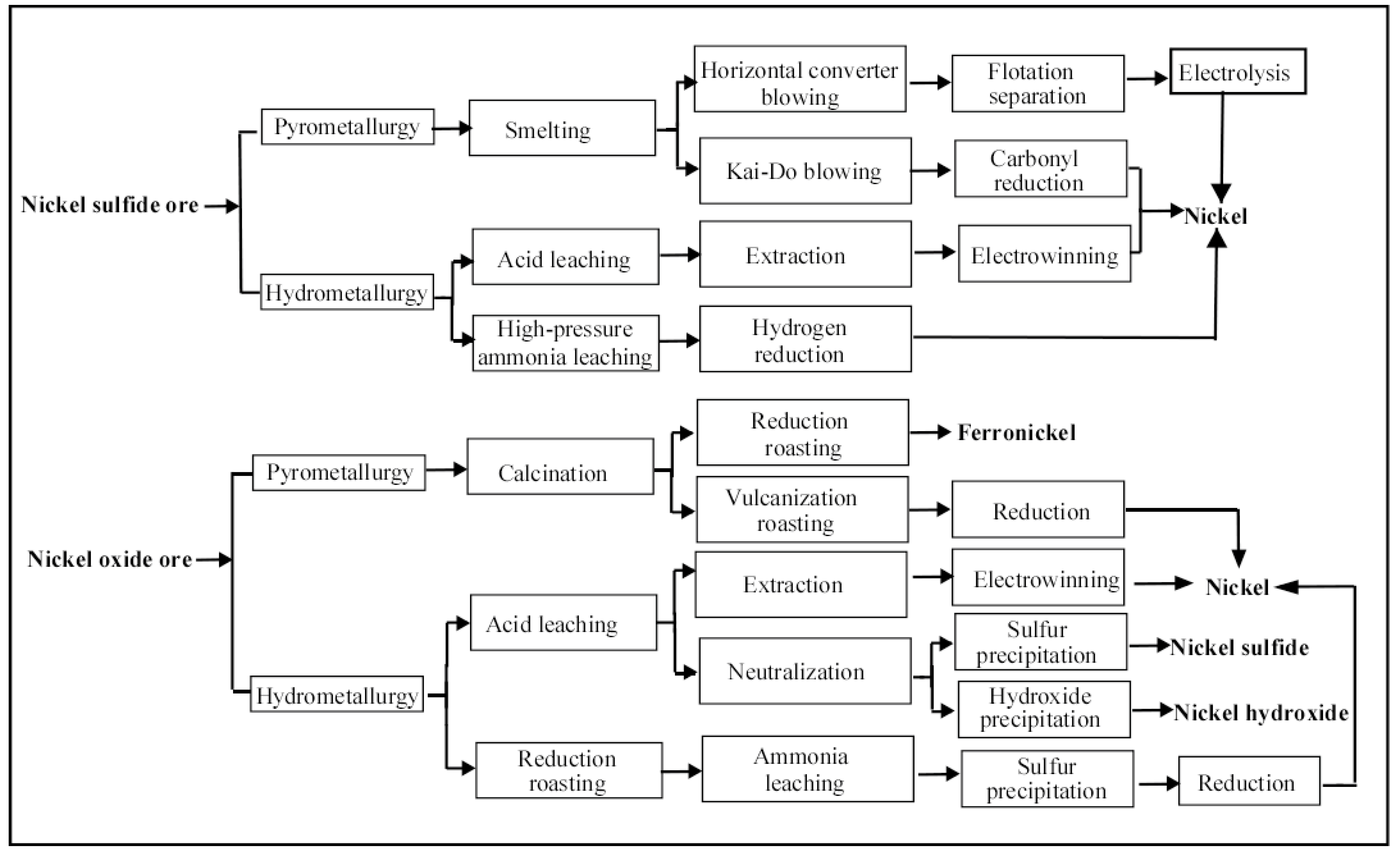
Nickel ore is characterized by low grade, complex composition, large quantity of associated ore, and high smelting difficulty. The products generated from nickel ore can vary substantially. The production process of nickel is generally quite complex. In general, nickel concentrate must first be obtained through ore dressing before it is smelted. Depending on the types of nickel ore (nickel sulfide ore or nickel oxide ore), two basic smelting methods (prometallurgy and hydrometallurgy, respectively) have been used in the production process as shown in Figure 2 [36,37].
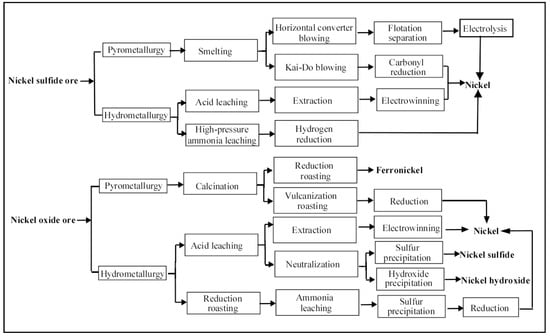
Figure 2.
Experimental apparatus for the production of nickel from nickel sulfide and nickel oxide ore with electrolysis.
2.3. Electrolytic Refining Process of Nickel Sulfide
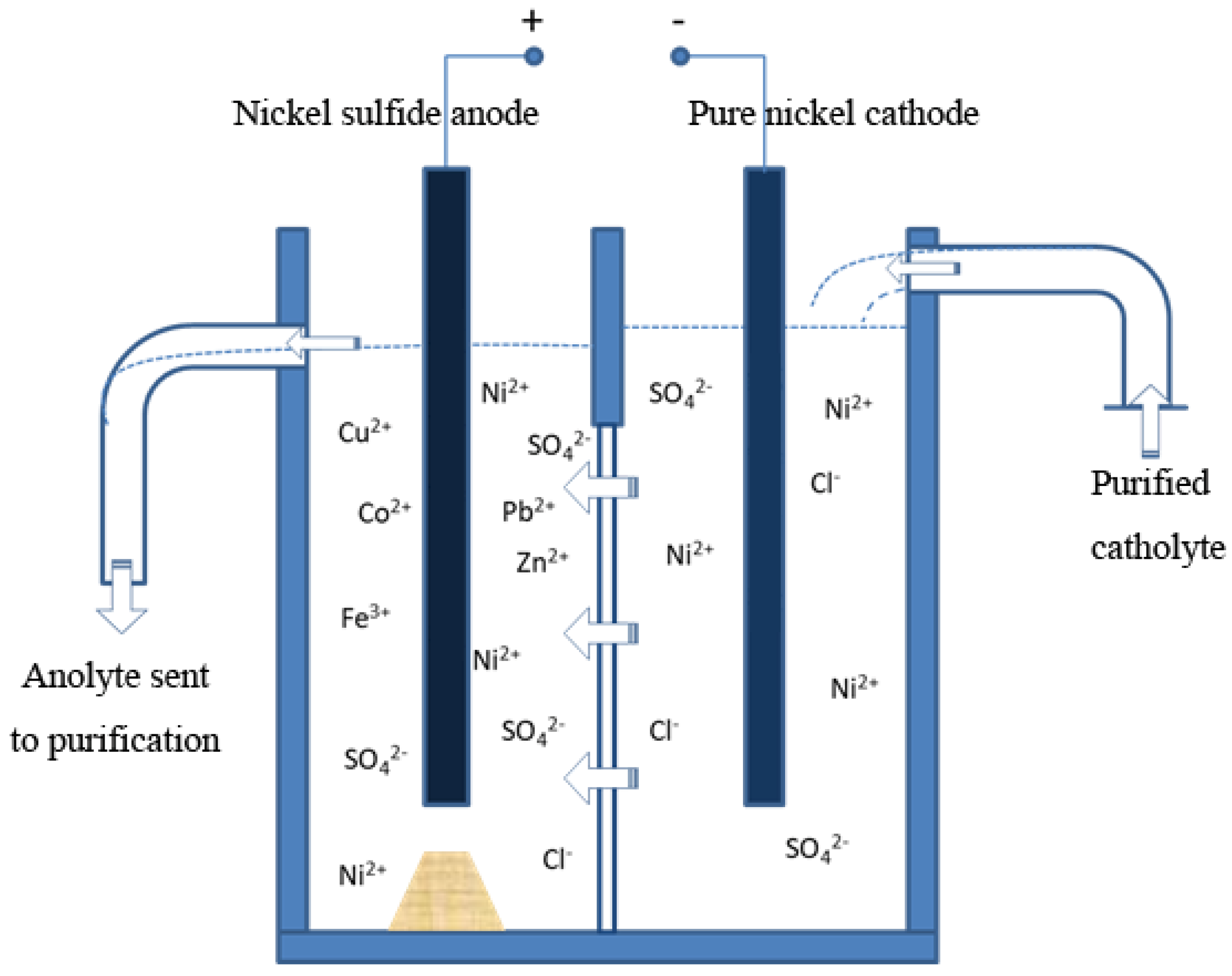
Nickel production generally involves producing a nickel sulfide anode plate from raw copper–nickel sulfide ore and obtaining metal nickel with electrolysis. This process was developed around the 1950s, and adopted for nickel production in a number of plants [38,39]. To date, this method has been used as the primary approach to nickel production in China. There are two procedures involved in this method: electrolysis of nickel and anode purge. A schematic diagram of nickel electrolysis is shown in Figure 3.
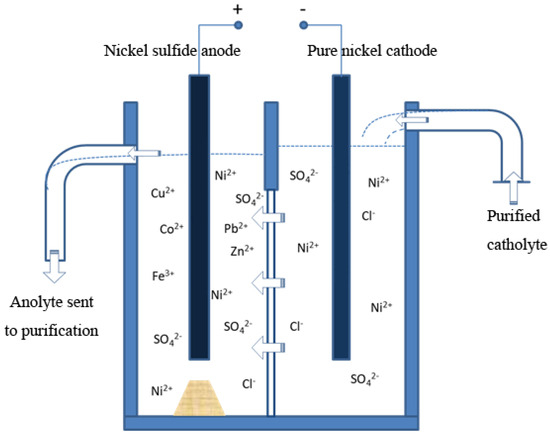
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of producing nickel sulfide anode plate from raw copper–nickel sulfide ore and obtaining metal nickel with electrolysis.
The primary reactions occurring on the anode include the following:
Ni3S2 = Ni2+ + 2NiS + 2e-
NiS = Ni2+ + S + 2e-
Ni3S2 + 8H2O = 3Ni2+ + 2SO42− + 16H+ + 18e−
The primary reactions occurring on the cathode include the following:
Ni2+ + 2e− = Ni
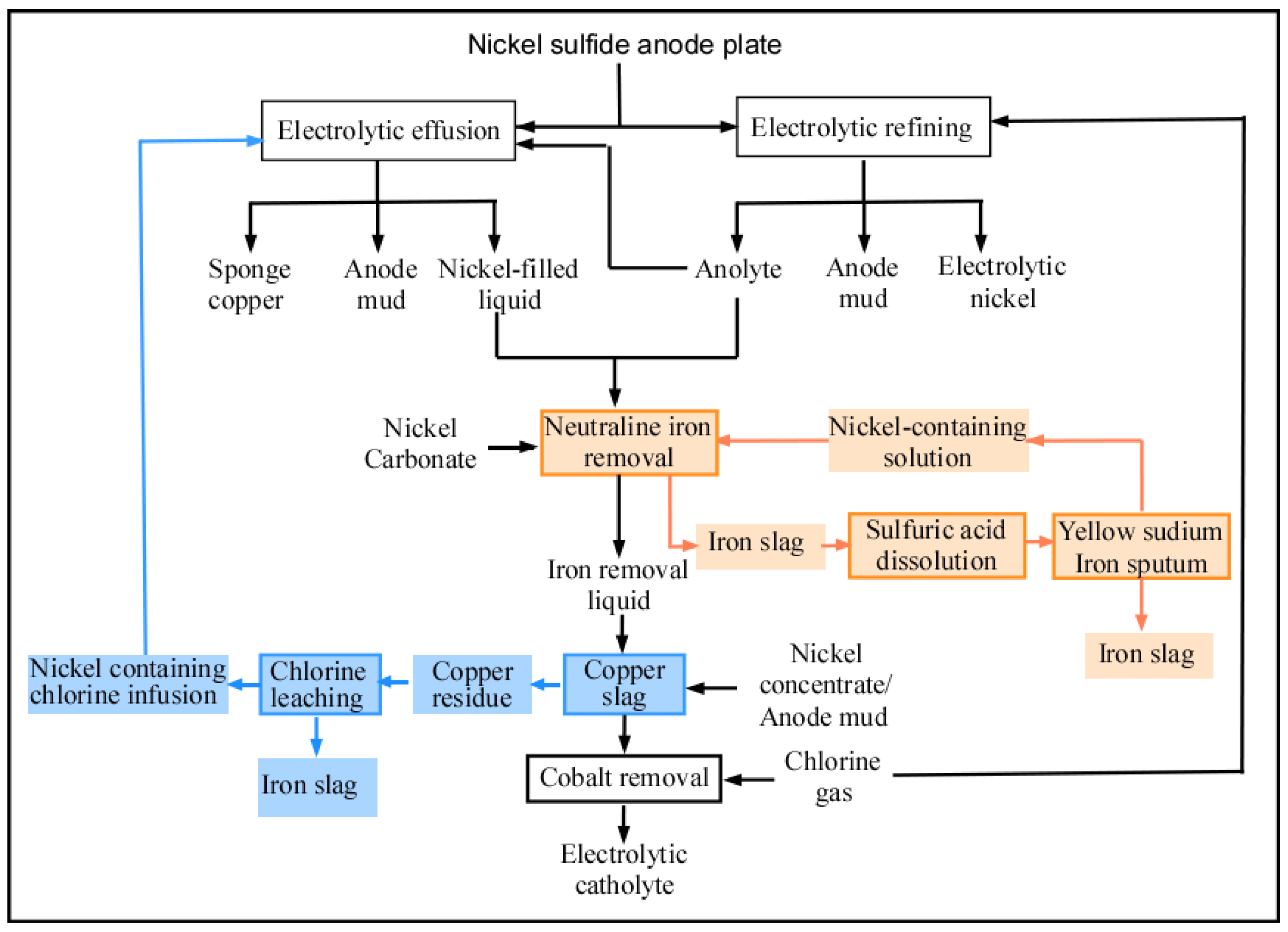
During the deposition of nickel on a cathode, some of the impurities in the solution will also react and deposit on the nickel surface. There is a strict requirement on catholyte composition during the electrolysis process. According to the standards specified in GB-6516-2010 [40], the catholyte composition required to produce 1# electro-nickel and 0# electro-nickel is shown in Table 1. During the electrolysis process, Cu, Zn, Fe, Co, and Pb enter the anolyte through the anode plates. It is necessary to purge the anode for the electrolysis process. The anode purging procedure is shown in Figure 4.

Table 1.
Cathode composition of nickel 1# and 0#.
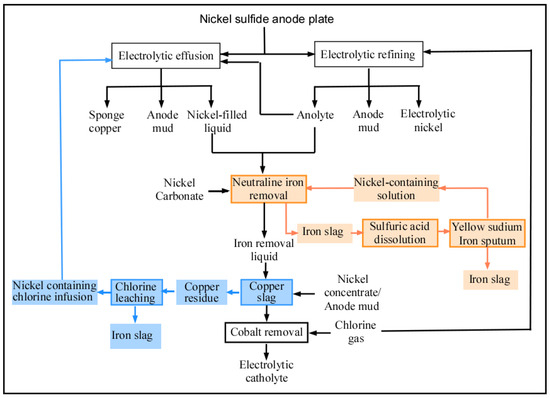
Figure 4.
The anode purging procedure of nickel ore electrolysis.
3. Removal of Copper from Nickel Electrolysis Anolyte
The removal of copper from the nickel electrolysis anolyte is a key issue in the nickel metallurgical industry. The copper concentration in the solution after copper removal has to be less than 4.72 × 10−5 mol/L. Furthermore, the mass ratio of copper to nickel in the copper slag must be greater than or equal to 15 [41,42,43]. To meet these targets, a considerable amount of long-term research work has been performed by many metallurgists. Various methods of removing copper have also been proposed.
3.1. Potential-Based Separation Method
Copper exhibits a relatively high electric potential (φϴ/V = −0.403) (cited from GB3102) [44]. Copper can be precipitated from a solution with high nickel concentration by adjusting the electric potential applied to the solution. Currently, the potential-based separation method has been primarily used as a replacement or electrolysis technique. In replacement separation, since the electric potential of copper is much greater than that of nickel, nickel can completely replace copper in theory. A key issue that needs to be considered here is the reaction time that is determined by reaction kinetics. The displacement method has been used to remove copper in many nickel refineries, including the nickel refinery of Port Colborne in Canada [38] and the Niihama Nickel Refinery in Japan [45]. The replacement method involves the use of nickel powder with nickel purity exceeding 99.8% and a diameter of less than 0.04 mm [46]. Such nickel powder is produced from a hydrogenation reduction reaction; when 1.4 times the theoretical amount of nickel powder is used in copper removal, copper content in a nickel anolyte can be reduced to 6.3 × 10−6 mol/L, which yields a copper removal rate greater than 99% [47]. The advantage of this method is its good copper removal performance and elimination of any impurity. The quality of the nickel powder used to remove copper has a significant impact on the performance and efficiency of copper removal. The replacement method for copper removal has a strict requirement for the quality and particle size of nickel powder. Nickel powder with high activity should not be stored for a long time [48]. In summary, the electrochemical replacement method is costly, and has a complex preparation process. The addition of nickel powder that exceeds the theoretical amount also brings more difficulty to the further treatment of the waste slag.
In the electrolysis technique, copper precipitates on the cathode before nickel when performing electrolysis in a mixed solution containing nickel and copper. Researchers have attempted to remove copper through the electrolysis method, which yields copper powder with a copper content exceeding 95% and nickel content of less than 1%. This method greatly reduces the difficulty of recycling copper. However, this method requires a copper concentration exceeding 0.55 mol/L in the electrolyte [49]. It is only suitable for a nickel electrolyte with a relatively high copper concentration. The concentration of copper in the purging solution of the electrodeposited copper–nickel anode is only 0.08~0.16 mol/L, which does not meet the requirement for the electrolysis method. In addition, electrolysis is performed with difficulty since electric current efficiency is quite low (only 70%). When using porous nickel as a cathode for electrolysis, there is thus no requirement for a copper solution. Along with a cathode potential greater than or equal to −0.50 V, the copper concentration in the anolyte is reduced to less than 3.15 × 10−5 mol/L in ambient temperature conditions [50]. Furthermore, the byproduct of copper removal is copper powder with purity exceeding 99%. This method not only meets the requirement of copper purging in the solution but also eliminates additional steps required to treat the copper slag. Thus, it is not suitable for mass production because the electrolysis process consumes a large amount of powder and a small volume of the treated solution.
3.2. Chemical Precipitation Method
In the chemical precipitation method, metals are separated based on their different solubility products, as shown in Table 2. It can be seen from the table that Cu(OH)2 and CuS exhibit a small solubility product constant. By the increasing concentration of OH- and S2− ions in the solution, copper can be precipitated from the solution with a high nickel concentration. Currently, the chemical precipitation method mainly includes a hydrolysis precipitation method associated with OH− ions and a sulfide precipitation method associated with S2− ions. In the hydrolysis precipitation method, the solubility product of Cu(OH)2 is smaller than that of Ni(OH)2; adjusting the pH value of the solution within a specific range can allow Cu(OH)2 to be preferentially precipitated from the solution, thus realizing the purging effect in nickel anolytes. Some researchers have adopted this method to separate copper from a solution with a nickel concentration of CNi = 20 g/L and a copper concentration of CCu = 2.5 g/L. The copper concentration in the treated solution was reduced to 1.75 × 10−5 mol/L [51]. Moreover, around 9~11% of nickel was also precipitated together with copper during the copper precipitation process. This activity resulted in a huge loss of nickel in the solution and a small copper-to-nickel concentration, 9–10 mol/L in the slag [11]. Hydrolysis precipitation cannot meet nickel production requirements. In sulfide precipitation, the solubility product of CuS is much smaller than that of other metal sulfides (Table 2). The addition of S2− ions to the solution allows the formation of CuS precipitate from Cu2+, even if the concentration of nickel is high in the solution. This characteristic enables copper removal from nickel anolytes. Copper removal with sulfide precipitation is a primary method used in current nickel production and explored in research work. A large number of sulfide additives has been used, including hydrogen sulfide, sulfur and sulfur dioxide, nickel concentrate plus anode mud, nickel xanthate, active sulfur powder, active anode mud, active nickel sulfide, nickel thiosulfate, and NAS. Among them, H2S, S, and SO2 may achieve decent copper removal performance, thus meeting the production requirements without introducing any impurity into the copper slag [52]. These three additives have been widely used in industrial production, and H2S and SO2 are toxic gases generated during the production process. Other additives are also used in precipitation processes to replace these two gases.

Table 2.
Solubility product constant of common insoluble compounds [51,52].
The addition of anode mud and nickel xanthate to the nickel concentrate can reduce the copper concentration to meet the production requirement while avoiding the generation of toxic gases [52]. In addition, these methods can increase the nickel content in the product to a certain extent. The copper slag generated from such methods exhibits a small copper-to-nickel ratio that makes it more difficult to treat the copper slag in the subsequent procedure. Further improvements are also required for these methods. The use of active sulfur powder, active anode mud, active nickel sulfide, and nickel thiosulfate may achieve good copper removal performance, and generate copper slag with a high copper-to-nickel ratio [49,53,54,55]. The copper slag may be directly used in the copper smelting system. Sulfide precipitation using these four additives is one of the major research directions in the field of nickel smelting.
NAS is a novel copper removal agent developed based on active nickel sulfide, and synthesized based on the principle of drug molecules. The synthesis and application of NAS in copper removal have been investigated by many researchers [56]. Experiments have verified that the addition of NAS can reduce the copper concentration to 3 × 10−3 g/L in the solution, while maintaining a copper-to-nickel ratio greater than 20 in the slag [57]. In addition, NAS material can sustain a high activity and a decent copper removal performance for ten days after being synthesized [56]. Further studies are still required to improve the industrial synthesis technique of the NAS copper removal agent, and to reduce the synthesis costs.
3.3. Solvent Extraction
In the solvent extraction method, metal ions are separated based on differences in the binding properties between the metal and the organic functional groups. This method is usually used for the enrichment and separation of heavy metals [58]. Currently, two types of extractants have commonly been used for copper removal in solvent extraction: amine extractants and aldoxime extractants. Amine extractants are based on the different properties of complex anions formed by heavy metals in the aqueous phase, and different metal ions can be extracted and separated from the solution [15]. Metal ions are extracted and separated based on the difference in complex anions formed by heavy metals in the aqueous phase. The extraction reaction is given by the following equation:
Many studies have explored the extraction of transition metals from chloride media using quaternary ammonium salt extractants. Ivanov et al. extracted cobalt, copper, and iron from a nickel electrolyte using alkylbenzylammonium chloride [14]. Bagreev et al. analyzed the effect of coexisting metals in the chloride system on extraction performance [59]. Park et al. used quaternary ammonium salts to extract copper from the solution. They were able to achieve a decent copper removal rate with an initial copper concentration of 2.18 × 10−2 mol/L that was reduced to 7.847 × 10−5 mol/L after extraction. The separation coefficient of their method reached as high as 106 in a copper–nickel system [60]. This process cannot be used to extract copper from a solution with a chloride ion concentration exceeding 1.408 mmol/L. This feature greatly limits the application of this method.
Aldehyde oxime extractant allows the formation of chelate complex by coordinating a copper ion with oxygen atoms in the hydroxy group and nitrogen donor atoms in the oxime group. The copper ion is extracted and separated from the solution. The extraction reaction is given by the following equation:
Cu2+ + 2HR(O) = CuR2(O) + 2H+
Fang Wu et al. separated copper from nickel sulfate using an M5640-kerosene-H2SO4 extraction system [61]. Specifically, they used an M5460 solution with a concentration of 20~30% as the extractant, and sulfuric acid with a concentration of 2 mmol/L as the stripping agent. After three stages of the extraction and stripping process, 99.9% copper was removed from a nickel sulfate solution with 50 g/L nickel concentration and 5.0 g/L copper concentration. The loss rate of nickel was less than 0.5% during the extraction process. The pH value of the solution was maintained at around 2.0 during the extraction process, while the pH of nickel electrolysis anolyte was around 4.5. Excessive acid is required to adjust the pH value of the solution, which reduces the economic value and the applicability of this method.
3.4. Ion-Exchange Method
The ion-exchange resin is a synthetic polymer material containing functional groups. The essence of the ion-exchange method is a reaction between exchangeable ions with metal ions in a solution. There are three types of resins: anion-exchange resin, cation-exchange resin, and chelating resin. The anion-exchange resin is used when the concentration of Cl− is greater than 1.5 mol/L, and the Cu+ ion can form complex anions in the solution. When the concentration of Cl− is lower than 12 mol/L, Ni2+ cannot form an anionic complex [62]. Copper can be separated from a nickel anolyte with an anion-exchange resin by adjusting the concentration of chloride ions in the solution. Ailiang Chen et al. separated copper from nickel sulfate solution using 201 × 7 geltype strong basic anion exchange. Their study demonstrated a good copper removal performance [63]. The adsorbed resin can be regenerated using an acidic NaCl solution containing hydrogen peroxide, and can be reused afterwards. The concentration of copper and nickel is greater than 1.575 mol/L and less than 1.5 × 10−3 mol/L in the regenerant, respectively. The regenerant can be used as a raw material for copper production. A large amount of chloride acid is required in this method, thus leading to a high recovery and separation cost. This method is not suitable for large-scale industrial production. In cation-exchange resin, metal ions can be adsorbed by functional groups in cation-exchange resin through an ionic bond. The adsorption force and distance are determined by the charge number of metal ions and hydrated ions formed by metal ions, respectively. The selective adsorption coefficient of heavy metal ions with cation-exchange resin decreases with the increase in the hydration radius and charge number [64]. Cation-exchange resin exhibits good separation performance on metal ions such as Cr3+ and Pb2+, both of which possess a greater valence difference and small hydration radius, but a weak selectivity for metal ions sharing the same valence. There is no difference in their valence states because Ni2+ and Cu2+ are both divalent. Cation-exchange resin is rarely used for separating nickel and copper. Chelating resins are widely used in wastewater treatment due to their ability to form stable complexes with heavy metal ions [65]. Table 3 shows a selective adsorption of heavy metals by common chelating resins. As shown in Table 3, most chelating resins are more selective for copper than nickel. Considering that chelating resin requires a simple regeneration condition and exhibits a greater number of reuse cycles, they have been used in many separation and purification processes in China [66,67].

Table 3.
Functional groups and adsorption selectivity order of metals comprising chelating resins [60,61,62,63].
4. Extraction of Nickel Using Iminodiacetic Acid Chelating Resin
The chemical formula of iminodiacetic acid (a dicarboxylic acid amine) is HN (CH2COOH)2, and is generally abbreviated as IDA. The nitrogen atom forms a secondary amino group, while the iminodiacetic acid anion may function as a tridentate ligand to form a metal complex with the two coupled five-membered chelate rings. Hydrogen ions in the nitrogen atom can be replaced by carbon atoms in the polymer in order to produce an ion-exchange resin. IDA-based chelating resin has become a major research topic on nickel smelting in recent years due to its superior adsorption and physicochemical properties.
4.1. Chelating Resin Preparation and Character
Chelating resin can be synthesized by two methods. The first method involves the polymerization of functional groups with small molecules, such as imidazole, pyridine, and acrylic acid, into macromolecules. The second method seeks to first obtain a high-molecular polymer and then introduce a functional group [68]. The second synthesis method has drawn more interest from researchers because it is more advantageous in terms of greater structural varieties, high structural stability, and larger adsorption quantity of the product. There are three methods of synthesizing IDA chelating resin: reaction of acetic acid with acrylonitrile styrene-divinylbenzene crosslinked polymer, reaction of ethylenediamine with chloromethyl polystyrene polymer, and bonding of imine acetate group to the surface of macroporous crosslinked polystyrene microspheres. In industrial production, IDA chelating resin is usually synthesized by first performing a Friedel–Craft reaction on a polystyrene-based resin skeleton and then by introducing a highly active chloromethyl group to the aromatic ring [69].
4.2. Adsorption Mechanism
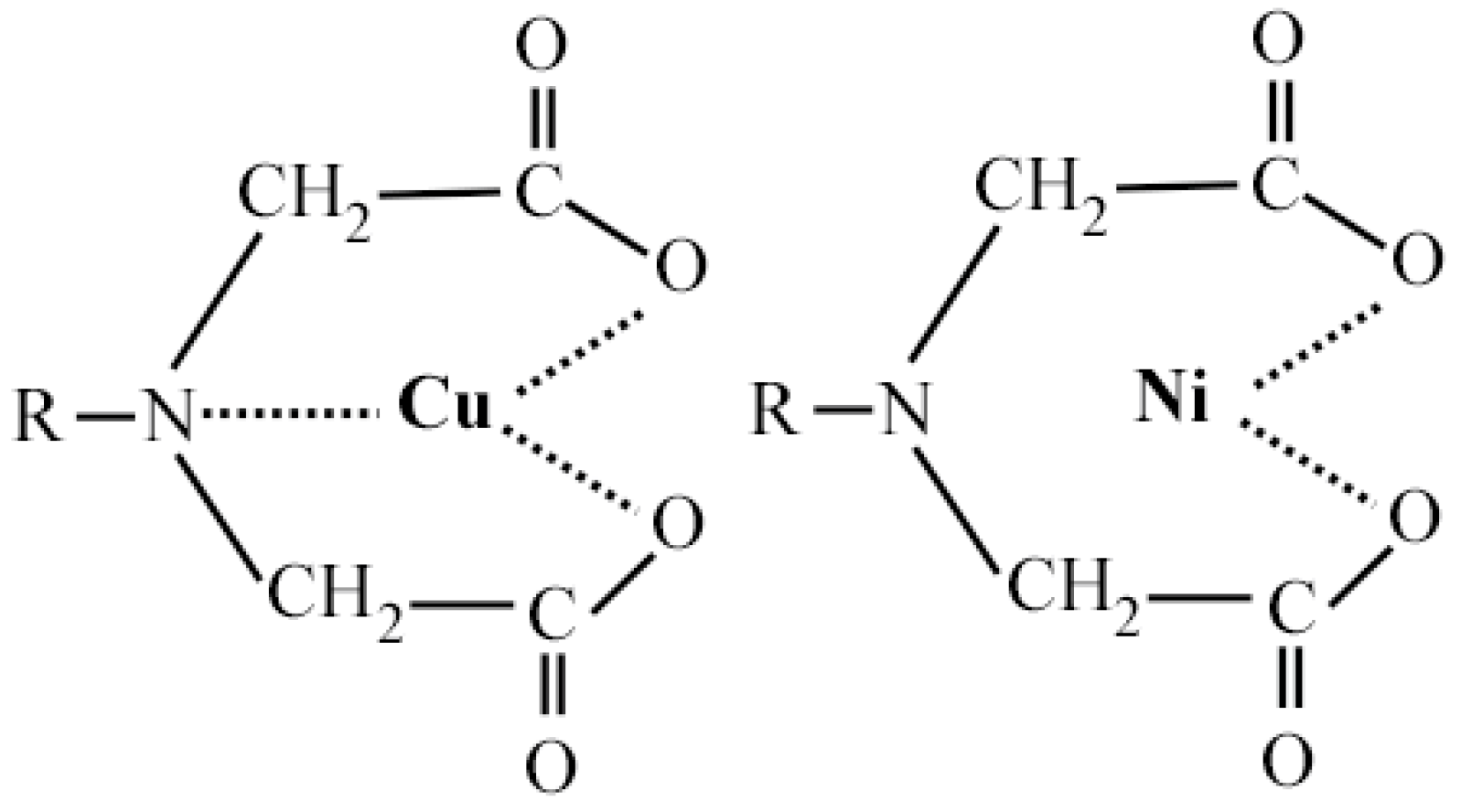
The IDA group, i.e., -N(CH2COOH)2−, is a tridentate ligand where the electrons are provided by an oxygen atom on two carboxyl groups and a nitrogen atom on the amino group. Even if the adsorbed metal ion does not form a coordinate bond with the nitrogen atom, the chemical bond formed by the two oxygen atoms can still form a stable chelating body in IDA. This feature enables a greater adsorption selectivity for IDA resin. As shown in Figure 5, there is a triple bond between copper and IDA, and a double bond between nickel and IDA. The triple bond of IDA with copper results in IDA having a stronger extraction of copper than nickel. Thus, it can be used for the selective adsorption of copper in a nickel anolyte.
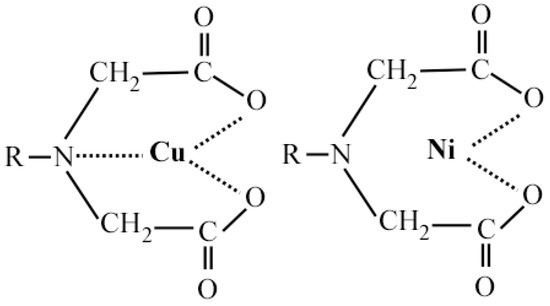
Figure 5.
A triple bond between copper and IDA, and a double bond between nickel and IDA.
4.3. Practical Application of IDA Chelating Resin in Nickel Extraction
Many different models have been developed for IDA chelating resin. These resin models exhibit various levels of selectivity and absorptivity [69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77]. Table 4 shows the adsorption performance of several typical IDA resins currently being used in experimental research and industrial applications. In metal enrichment and recovery, the distinctive feature of IDA chelating resin is its excellent complexing ability of heavy metals, which is far superior than that of alkali metals [78]. The binding ability of IDA functional groups to heavy metals is 5000 times that of alkali metals. IDA-type chelating resin has been widely used in the hydrometallurgical industry. Zaionl et al. used Lewatit TP-207 and Amberlite IRC-748 to recover nickel and cobalt from the acid leachate after leaching laterite nickel ore tailings. A better recovery performance is achieved when a fixed bed is used [79]. Mendes et al. achieved selective adsorption of nickel and cobalt from Brazilian laterite nickel ore oxygen pressure acid leaching solution using the chelating resin Amberlite IRC-748 packed column. The nickel solution is enriched more than 20 times with very few impurities [80]. In water purification, chelating resins with IDA functional groups possess several advantages, including high selectivity, fast adsorption rate, and easy desorption of heavy metals in water. These resins have been widely used for the purification of industrial wastewater and the treatment of domestic water. For example, IRC-718 and Chelex-100 are commonly used for treating the wastewater generated by printed circuit board manufacturers. Korngold et al. used Purolite S930 to remove Cu2+, Ni2+, Co2+, and Cd2+ from tap water containing a small amount of carboxylate, and reduced their content to 10−6. Such content meets the standard for drinking water [81]. In substance analysis, IDA chelating resin exhibits a very high sensitivity to heavy metal, such that even trace amounts of heavy metals can be adsorbed effectively by the resin. Therefore, it can be used to test and analyze the trace metals in solutions. Yebra et al. used flame atomic absorption spectrometry to automatically detect nickel at μg/g content level in food [82]. The metals were enriched in a microcolumn before being tested. Their results showed high accuracy and small deviation in the detection of nickel metal. Nicalai et al. used Metpac CC-1 chelate resin to enrich 17 trace elements in seawater, and subsequently detect them using the ICP-MS technique [83]. They compared the results with the evaluation report, and found a strong agreement between them. This finding demonstrated that using IDA chelating resins can provide strong accurate results in analytical chemistry and radiochemistry applications.

Table 4.
The adsorption proprieties of common typical IDA chelating resins [67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75].
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
In industrial applications, the potential-based separation methods can swiftly remove high concentrations of copper but are unable to minute copper content from nickel anolytes. Sulfide precipitation can effectively extract minute copper amounts from nickel anolytes, yet it generates substantial, challenging-to-handle high-nickel waste residue. Moreover, the precipitating agent cannot be reused, leading to elevated costs. While solvent extraction partially mitigates these limitations in copper removal from nickel anolytes, it still faces issues, such as organic phase entrainment, third-phase formation, and a significant environmental impact.
As an alternative, the ion-exchange method has garnered significant attention due to its robust selectivity and minimal adsorption capacity. These advantages render the ion-exchange method well suited for separating low-concentration substances. As this method does not generate slag during the ion-exchange separation process and allows for the recycling of ion-exchange resin, its potential spans across diverse applications. Specifically, the ion-exchange technique proves especially effective for isolating trace heavy metals. Hence, chelating resin emerges as an ideal contender within the ion-exchange method. The IDA chelating resin, exhibiting high selectivity for both copper and nickel, finds extensive use in enriching the production of these metals. Notably, the IDA resin’s copper selectivity generally surpasses that of nickel. Therefore, future studies should explore harnessing this feature for the effective separation of copper from nickel anolytes.
In conclusion, comparative analysis of electrochemical purification, chemical precipitation, solvent extraction, and ion-exchange resins showed that ion-exchange resin has significant advantages in terms of slag, low cost, and resin recycling, among others. The nickel extraction method based on ion-exchange resin may be a significant metallurgical development in research on nickel, and it is worth promoting its widespread use in the nickel smelting industry.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.T. and K.J.; writing—draft preparation, X.T.; writing—review and editing, K.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Key Research and Development Plan of Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2019YFF0216502) and the Major Science and Technological Innovation Project of Hunan Province (2021SK1020-4).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during thus study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the contributions and helpful discussion of various members in Zhongwei Zhao’s Lab of School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tripathi, C.C.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, D. Atom beam sputtered Mo2C films as a diffusion barrier for copper metallization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 3518–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudelski, A.; Janik-Czachor, M.; Bukowska, J.; Dolata, M.; Szummer, A. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) on copper electrodeposited under nonequilibrium conditions. J. Mol. Struct. 1999, 482–483, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; Gao, L.; Sun, J. A symmetrical bi-electrode electrochemical technique for high-efficiency transfer of CVD-grown graphene. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 145704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhi, X.; Zhai, H.J. A facile approach to improve the electrochemical properties of polyaniline-carbon nanotube composite electrodes for highly flexible solid-state supercapacitors. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 18339–18348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.P.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.D.; Yang, Y.L.; Li, F.S. Preparation of core-shell Cu/Al powders by displacement method. Acta Chim. Sin. 2007, 65, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Gibin, S.R.; Sivagurunathan, P. Synthesis and characterization of nickel cobalt ferrite (Ni1xCoxFe2O4) nano particles by co-precipitation method with citrate as chelating agent. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 28, 1985–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, V.W.D.; Mok, K.W.; Ng, C.Y.; Luong, B.P.; Ma, K.K. Removal and recovery of copper(II), chromium(III), and nickel(II) from solutions using crude shrimp chitin packed in small columns. Environ. Int. 1996, 22, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, W.W.; Choe, S.; Chuang, R.; Lee, C.C. An effective diffusion barrier metallization process on copper. Thin Solid Films 2000, 376, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, J.; Wilcox, G.D. Electrodeposition of zinc–nickel compositionally modulated multilayer coatings and their corrosion behaviours. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 3533–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlock, M.M.; Howerton, B.S.; Atwood, D.A. Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from acid mine drainage. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4757–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlock, M.M.; Howerton, B.S.; Atwood, D.A. Electrochemical deposition of black nickel solar absorber coatings on stainless steel AISI316L for thermal solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2005, 87, 685–694. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, H. Recovery of Sulfur from Anode Slime of Nickel Sulfide Electrolysisby Vacuum Evaporation. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 2002, 24, 410–413. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Steenari, B.M. Solvent extraction separation of copper and zinc from MSWI fly ash leachates. Waste Manag. 2015, 44, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, I.M.; Nikolaev, A.V.; Gindin, L.M.; Kheifez, V.L.; Volkov, L.V.; Maizlish, R.S. Solvent extraction removal of cobalt and other impurity elements from nickel electrolytes. Hydrometallurgy 1979, 4, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Liu, Y.P.; Hu, H.P.; Liu, S.J.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Chen, Q.Y. Removal of Copper from Nickel Anode Electrolyte by AMPY-1. Nonferrous Met. (Extr. Metall.) 2015, 10, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Burkin, A.R.; Preston, J.S. α-Substituted oxime extractants—II: Extraction of Cu(II), Ni(II), Co(II) and Fe(II) by aliphatic α-hydroxyiminoketones and α-dioximes. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1975, 37, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chiang, C.L.; Chen, C.R. Removal of heavy metal ions by a chelating resin containing glycine as chelating groups. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 54, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, G.; Orena, M.; Sandri, S.; Orena, M. Polymer Supported Reagents. Chromic Acid on Anion Exchange Resin. Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones from Allylic and Benzylic Halides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1976, 44, 3985–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.H.; Zhu, X.K.; Cai, J.J.; Li, S.Z.; He, X.X.; Wang, J.H. Chromatographic Separation of Cu, Fe and Zn using AG MP-1 Anion Exchange Resin for Isotope Determination by MC-ICPMS. Rock Miner. Anal. 2006, 1, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Vernon, F. Some aspects of ion exchange in copper hydrometallurgy. Hydrometallurgy 1979, 4, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.A.; Na, B.Y.; Quan, P.H.; Jie, H.E.; Bassig, B.A.; Min, D.; Wei, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.T.; Ning, C. A Retrospective Cohort Mortality Study in Jinchang, the Largest Nickel Production Enterprise in China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. BES 2014, 27, 567–571. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.M.; Bai, Y.N.; Pu, H.Q.; Zheng, T.Z.; Cheng, N. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Chinese Nickel-exposed Workers. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2014, 27, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Yang, W.J.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, H. Mineral Phase Analysis and Treatment Technological Selection of Magnesium-rich Nickel Oxide Ore. Nonferrous Met. (Extr. Metall.) 2016, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.Q.; Gao, Q.; Wu, S. Present Situation and Development Strategy and Key Technologies of China’s Nickel Resources Sustainable Development. Conserv. Util. Miner. Resour. 2016, 2, 58–69. [Google Scholar]
- Murofushi, A.; Otake, T.; Sanematsu, K.; Ya, K.Z.; Ito, A.; Kikuchi, R.; Sato, T. Mineralogical evolution of a weathering profile in the Tagaung Taung Ni laterite deposit: Significance of smectite in the formation of high-grade Ni ore in Myanmar. Miner. Depos. 2022, 57, 1107–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbin, A.; Capilitan, J.; Taboada, E.; Tabañag, I.D. Characteristics of Nickel Laterite Mine Waste in Caraga Region, Philippines and Its Potential Utilization. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2023, 22, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, J.A. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2017; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.S.; Guo, Y.S.; Chen, B.Y.; Cui, Y.L.; Guo, X. The distribution and the exploration, development and utilization situation of the lateritic nickel ore resources in the world. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2013, 34, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.Y.; Lu, X.G.; Zou, X.L.; Cheng, H.W.; Xu, Q. Current situation and utilization technology of nickel ore in China. Chin. J. Nat. 2015, 37, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, N.; Tripathy, S.K.; Patra, S.K.; Jha, G. Recent Progress in Hydrometallurgical Processing of Nickel Lateritic Ore. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2023, 76, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, X.; Xue, M.; Jou, B.J.D.; Lee, W.C. Short-term forecasting through intermittent assimilation of data from Taiwan and Mainland China coastal radars for typhoon Meranti (2010) at landfall. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cheng, S.; Yuan, Z.; Han, Y.; Ma, S. Study on Flotation Technology of Copper-nickel Sulfide Ore in North Korea. Metal Mine 2010, 4, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Tsymbulov, L.B.; Knyazev, M.V.; Tsemekhman, L.S. Oxide nickel ores smelting of ferronickel in two-zone Vaniukov Furnace. Can. Metall. Q. 2011, 50, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirasawa, R.; Matsuoka, J.; Wakabayashi, K. Research for Factorial Effects on Leaching of Nickel Oxide Ore by Nitric Acid Solution. J. Min. Metall. Inst. Jpn. 1980, 96, 337–340. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.P.; Li, Y.Q.; Lei, M.F.; Jing, X.U.; Wang, P.C.; Weng, C.J. New Beneficiation Technique for Certain Refractory Fine Copper-Nickel Sulfide Ore. Min. Metall. Eng. 2015, 35, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Ye, Z.; Hao, F.; Yuan, H. Experimental Study on a Low-grade Copper-nickel Sulfide Ore. Metal Mine 2015, 8, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Dutton, M.D.; Vasiluk, L.; Ford, F.; Bellantino Perco, M.; Taylor, S.R.; Lopez, K.; Bolger, G.T.; Gopalapillai, Y.; Hale, B. Towards an exposure narrative for metals and arsenic in historically contaminated Ni refinery soils: Relationships between speciation, bioavailability, and bioaccessibility. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Y. Development of nickel and progress of technology in China. Ming Metall. 1997, 6, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- GB-6516-2010; Electrolytic nickel. National Nonferrous Metals Standardization Technical Committee: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Ilyas, N.; Ilyas, S.; Sajjad-Ur-Rahman, S.; Yousaf, S.; Zia, A.; Sattar, S. Removal of copper from an electroplating industrial effluent using the native and modified spirogyra. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Chen, A.L. Deep removal of copper from nickel electrolyte using manganese sulfide. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 3802–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, X. Study on removal of copper from nickel-copper mixed solution by membrane electrolysis. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 180, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB3102; Thermodynamics of Standard Solubility Product. National Nonferrous Metals Standardization Technical Committee: Beijing, China, 1996.
- Harumsa, K.; Kazuyuki, T. Nickel and Cobalt Refining at Niihama Nickel Refinery. J. Min. Inst. Jpn. 2010, 123, 678–681. [Google Scholar]
- Ton, S.J.; Neumann, K.T.; Nørby, P.; Skrydstrup, T. Nickel-Mediated Alkoxycarbonylation for Complete Carbon Isotope Replacement. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (ACS) 2021, 143, 17816–17824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusem, G.; Pintauro, P.N.; Cheng, P.C.; An, W. Electrocatalytic hydrogenation of soybean oil in a radial flow-through Raney nickel powder reactor. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1996, 26, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Dandekar, A.; Baker, R.T.K.; Vannice, M.A. Properties of Copper Chromite Catalysts in Hydrogenation Reactions. J. Catal. 1997, 171, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, A.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X.; Shi, Y.; Wang, D. Removal of Cu from the nickel electrolysis anolyte using nickel thiocarbonate. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 113, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.O.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Wu, H.R. Removal copper from an anolyte of nickel electrolysis by electrowinning. J. South China Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 1994, 22, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kravchenko, T.A.; Polyanskiy, L.L.; Krysanov, V.A.; Zelensky, E.S.; Kalinitchev, A.I.; Höll, W.H. Chemical precipitation of copper from copper-zinc solutions onto selective sorbents. Hydrometallury 2009, 95, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.J. Study on the Process of Copper Removal by Nickel Electrolysis Purification; Lanzhou University of Technology: Lanzhou, China, 2012; pp. 6–8. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/thesis/ChJUaGVzaXNOZXdTMjAyMzA5MDESCFkyMTA5ODU4GghzbG84b2JzNw%253D%253D (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Zhai, X.J. Research on sulfur-containing active nickel. Nonferrous Min. Metall. 1998, 14, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Y.D.; Yan, X.X. Preparation of active anode slime for removing copper from nickel electrolyte. Nonferrous Met. (Smelt.) 1996, 5, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, G.B.; Wu, X.M.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, Z.M.; Li, Y.Y. Application of ultrafine particles in chemical separation-research on the characteristics of activated nickel sulfide. J. South China Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 1996, 8, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Yu, H.T.; Ma, X.Q.; Yao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.H.; Cao, K.; Liu, S.L.; Dong, C.; Zhao, B.M.; et al. Copper oxide-modified graphene anode and its application in organic photovoltaic cells. Opt. Express 2018, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Chen, X.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Zhao, Z.W. Removal of Cu from the nickel electrolysis anolyte using amorphous MnS. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 146, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Fan, H.Y.; Gao, J.Z. Solid-liquid solvent extraction of metal ions. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing Miner. Metall. Mater. 2003, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, C.; Wagner, H.; Bagreev, V.V. On the tri-n-octylammonium chloro complexes of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) in benzene solution. Polyhedron 1983, 2, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, K.; Parhi, P.K.; Padhan, E.; Palai, A.K.; Nathsarma, K.C.; Park, K.H. Separation of iron(III), copper(II) and zinc(II) from a mixed sulphate/chloride solution using TBP, LIX 84I and Cyanex 923. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 55, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.U.; Jun, L. Study on Separation of Cu~(2+) from Nickle Sulphate Solution with Extractant M5640. J. Wuyi Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2004, 18, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Avdibegović, D.; Barbier, E.; Jaklič, B.; Škapin, S.D.; Spreitzer, M.; Binnemans, K. Removal of copper and iron from ethanolic solutions by an anion exchange resin and its implication to rare-earth magnet recycling. Chemosphere 2023, 330, 138603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.L.; Qiu, G.Z.; Zhao, Z.W.; Sun, P.M.; Yu, R.L. Removal of copper from nickel anode electrolyte through ion exchange. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2009, 19, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.B.; He, B.L. The application of ion exchange resins in hydrometallurgy. Ion Exch. Adsorpt. 1993, 9, 250–260. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, W.H.; Liu, Z. New Progress of Synthesis and Application Study of Specific Ion Exchanger. Guangxi Chem. Ind. 2003, 32, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, F.; Dong, B.; Bi, Y.B.; Xie, J.C. Adsorption of metalcation by chelating resin. Technol. Water Treat. 2011, 37, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.Y.; He, Y.Y.; Ping, L.H. Study on Chelating Resins Syntheses and Adsorption Properties of Thiourea Type Resins. J. Wuhan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 1999, 45, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, W.; Guo, L. Preparation and adsorption properties of crosslinked polyaminated chitosan chelating resin. Ion Exch. Adsorpt. 2001, 17, 507–514. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.F.; Wang, Z.P.; Zhang, X.C.; Yang, Y.Q. Synthesis and Application of Specific Ion Exchanger. Inn. Mong. Petrochem. Ind. 2006, 32, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kuz’min, V.I.; Kuz’min, D.V. Sorption of nickel and copper from leach pulps of low-grade sulfide ores using Purolite S930 chelating resin. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 141, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddine, C.; Lekhmici, A.; Mubarak, M.S. Sorption properties of the iminodiacetate ion exchange resin, amberlite IRC-718, toward divalent metal ions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 107, 1316–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, F.D.; Martins, A.H. Selective sorption of nickel and cobalt from sulphate solutions using chelating resins. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2004, 74, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, M.V.; Dragan, E.S. Heavy metals adsorption on some iminodiacetate chelating resins as a function of the adsorption parameters. React. Funct. Polym. 2008, 68, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.M.P.; Manso, J.P.H.; Rodrigues, J.R.C.; Lagoa, R.J.L. A comparative study of alginate beads and an ion-exchange resin for the removal of heavy metals from a metal plating effluent. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2008, 43, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Sahu, K. Separation and recovery of lead from a mixture of some heavy metals using Amberlite IRC 718 chelating resin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 133, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, J.L.; Lucas, A.D.; Carmona, M.; González, M.; Rodríguez, J.F. Equilibrium data of the exchange of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Zn2+ ions for H+ on the cationic exchanger Lewatit TP-207. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. 2010, 79, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jachuła, J.; Kołodyńska, D.; Hubicki, Z. Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) complexes with glycolic acid from aqueous solutions on different ion exchangers. Can. J. Chem. 2010, 88, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.E.; Santschi, P.H.; Chuang, C.Y.; Otosaka, S.; Addleman, R.S.; Douglas, M.; Rutledge, R.D.; Chouyyok, W.; Davidson, J.D.; Fryxell, G.E.; et al. Collection of Lanthanides and Actinides from Natural Waters with Conventional and Nanoporous Sorbents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11251–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainol, Z.; Nicol, M.J. Comparative study of chelating ion exchange resins for the recovery of nickel and cobalt from laterite leach tailings. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 96, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, F.D.; Martins, A.H. Selective nickel and cobalt uptake from pressure sulfuric acid leach solutions using column resin sorption. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2005, 77, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korngold, E.; Belayev, N.; Aronov, L.; Titelman, S. Influence of complexing agents on the removal of metals from water by a cation exchanger. Desalination 2001, 133, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yebra-Biurrun, M.C.; Carro-Mariño, N. Flow injection flame atomic absorption determination of Cu, Mn and Zn partitioning in seawater by on-line room temperature sonolysis and minicolumn chelating resin methodology. Talanta 2010, 83, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, M.R.C.; Tousset, N.; Nicolai, Y. Trace metals analysis in estuarine and seawater by ICP-MS using on line preconcentration and matrix elimination with chelating resin. Talanta 1999, 50, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).