Swift Removal of the Heavy Metals Cadmium and Lead from an Aqueous Solution by a CAN-Zeolite Synthesized from Natural Clay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
- -
- Crushing of the sample rocks into pieces using a mortar;
- -
- Drying in the oven for 24 h (T = 308 K);
- -
- Grinding pieces of the clay sample in a grinder;
- -
- Sieving the sample powder (50 μm sieve).
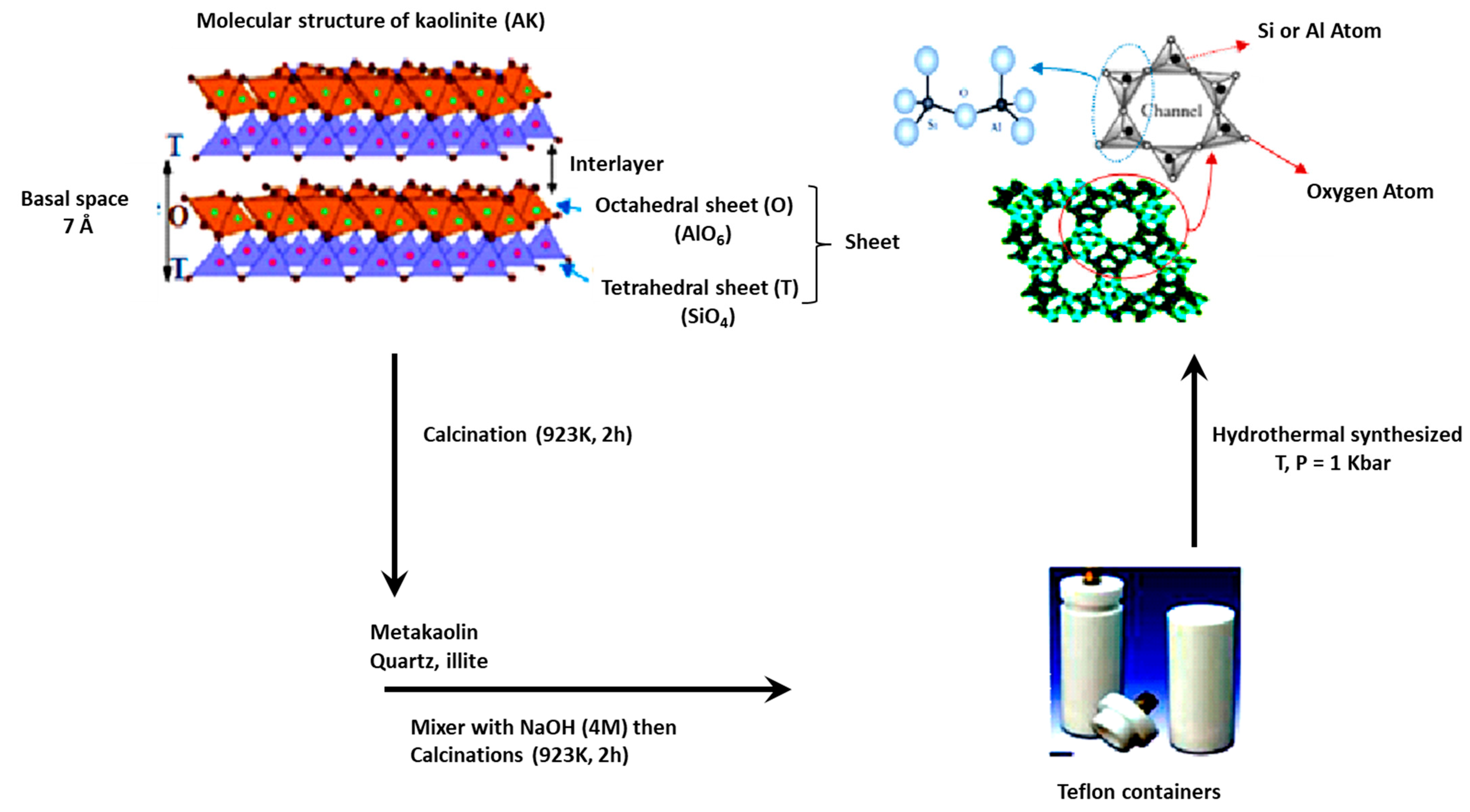
2.2. Preparation of Cancrinite Zeolite
2.3. Characterization of Clay and Zeolite
2.4. Kinetics Study
2.5. Adsorption Isotherms of Cd and Pb by Clay and CAN-Zeolite
3. Results and discussion
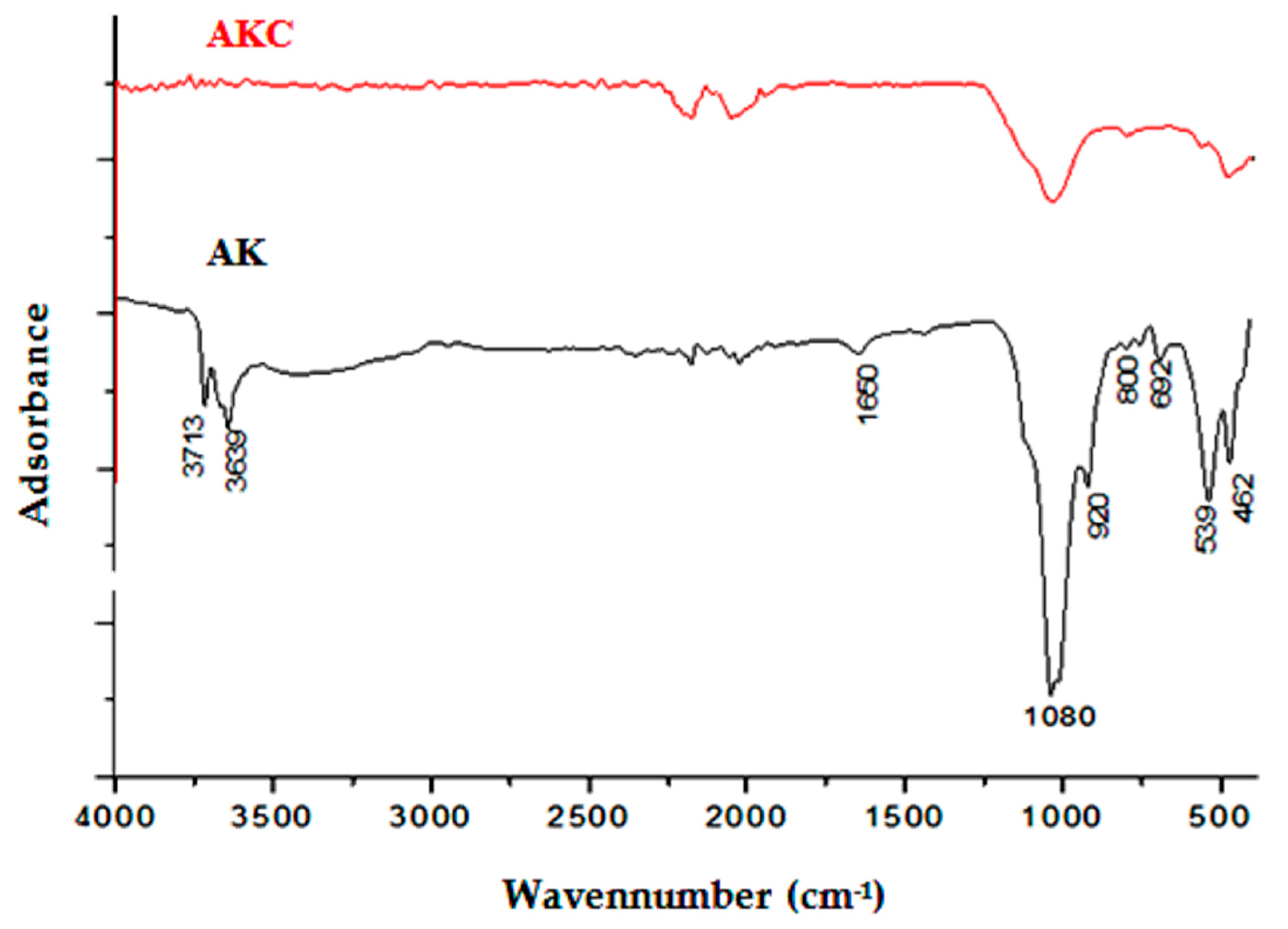
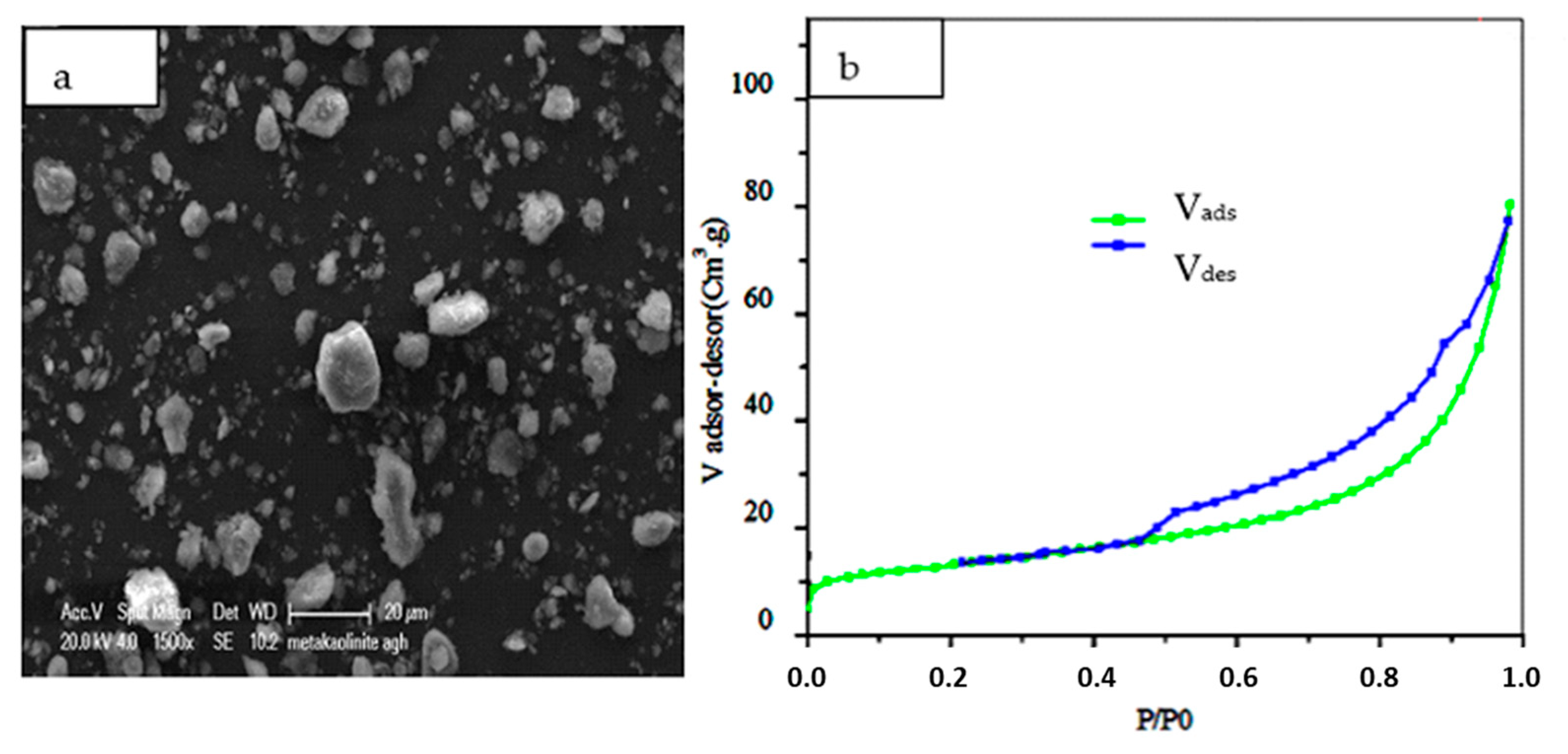
3.1. Characterization of Purified Kaolinite Clay before and after Heating and NaOH Treatment
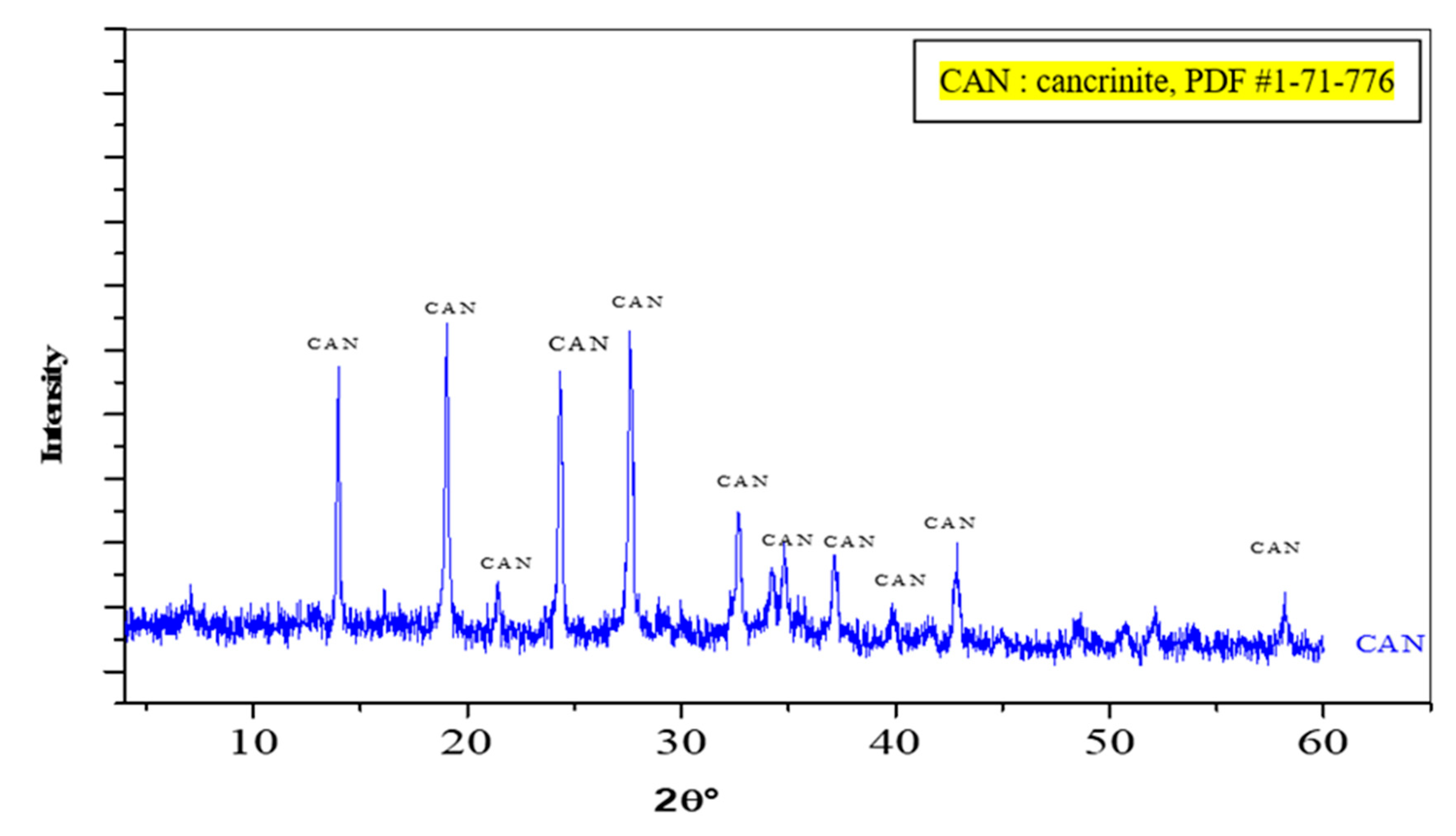
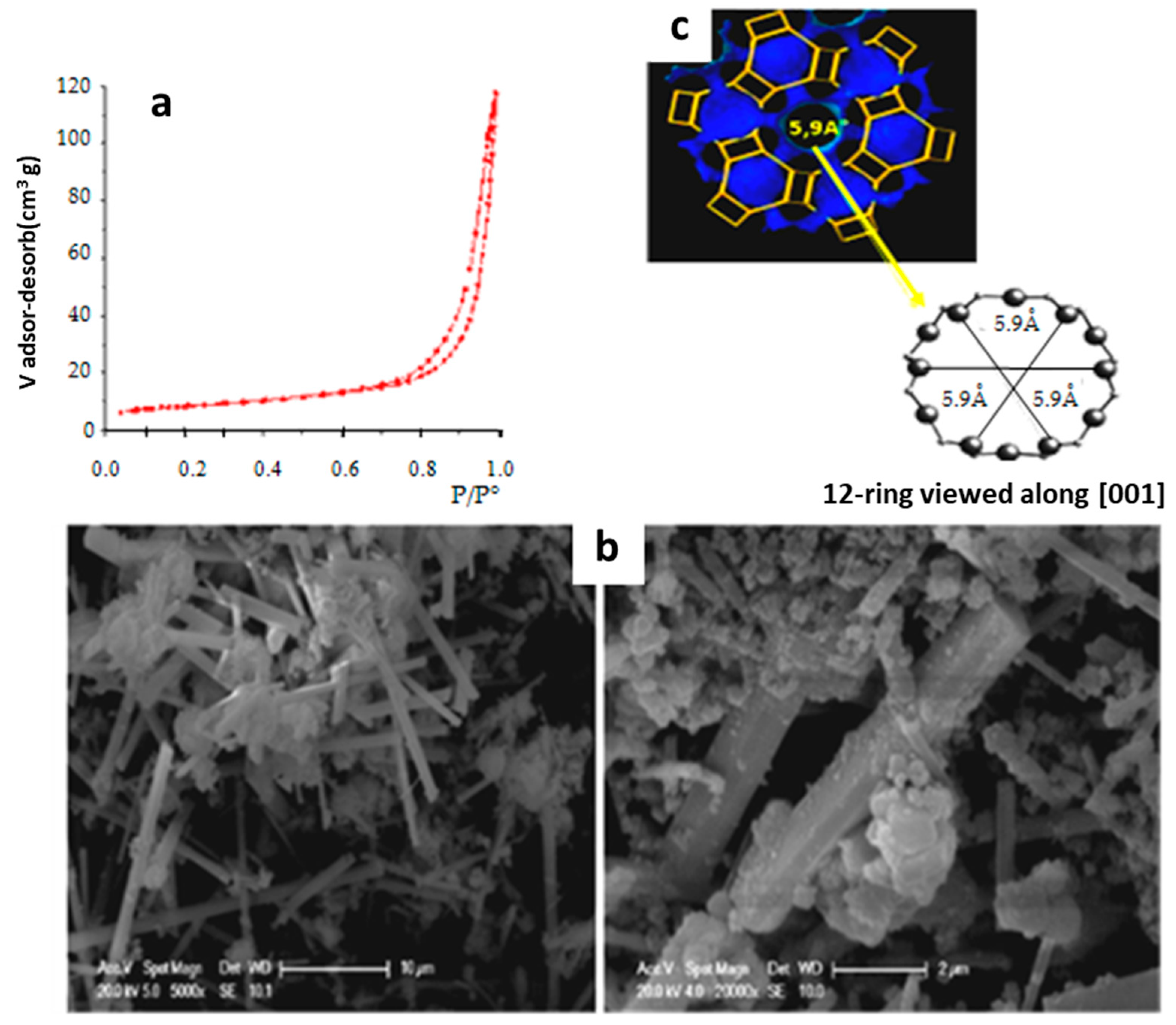
3.2. Characterization of Synthetic CAN-Zeolite
3.3. Cadmium and Lead Immobilization by AK and Synthesized CAN-Zeolite
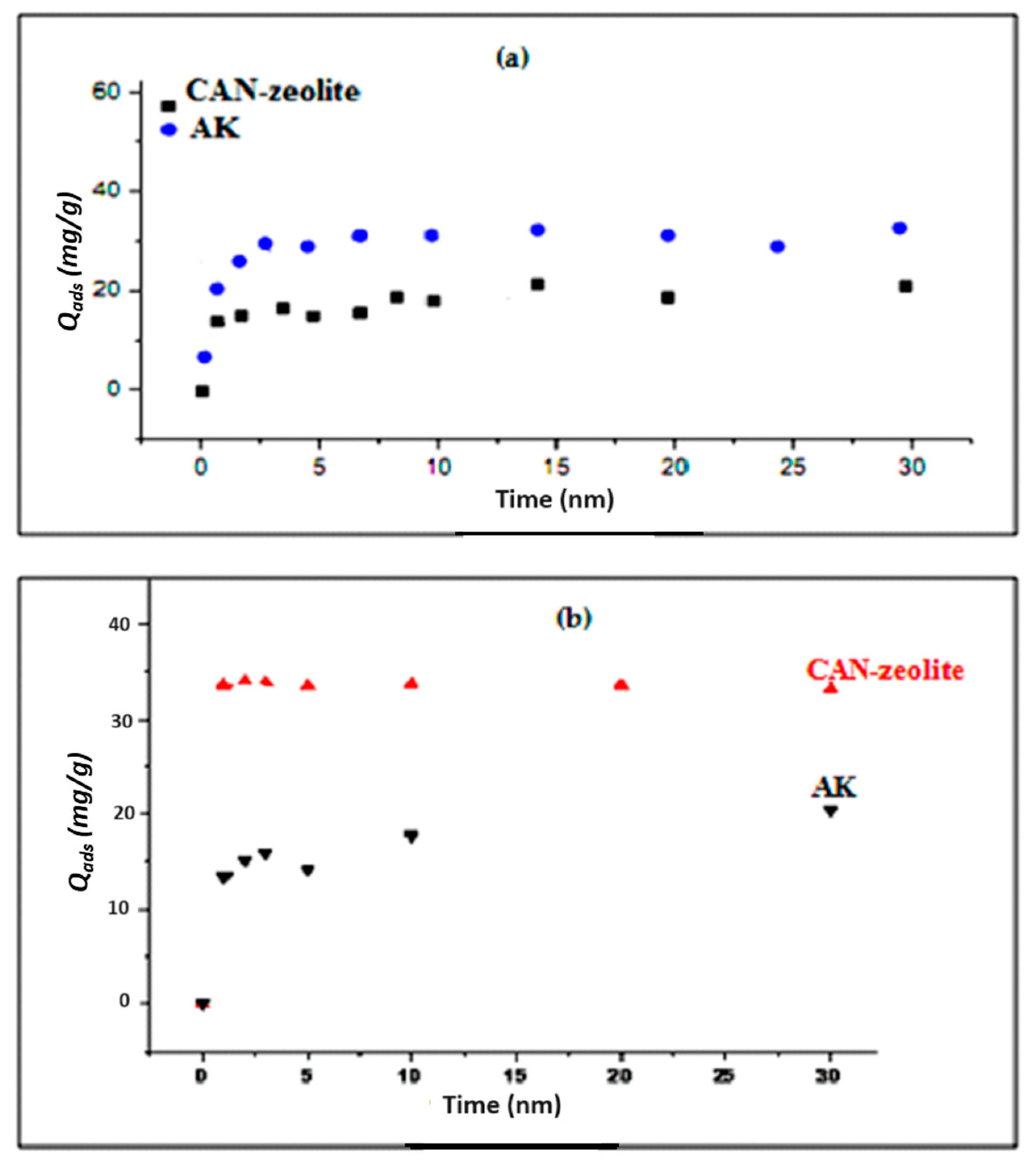
3.3.1. Effect of Contact Time
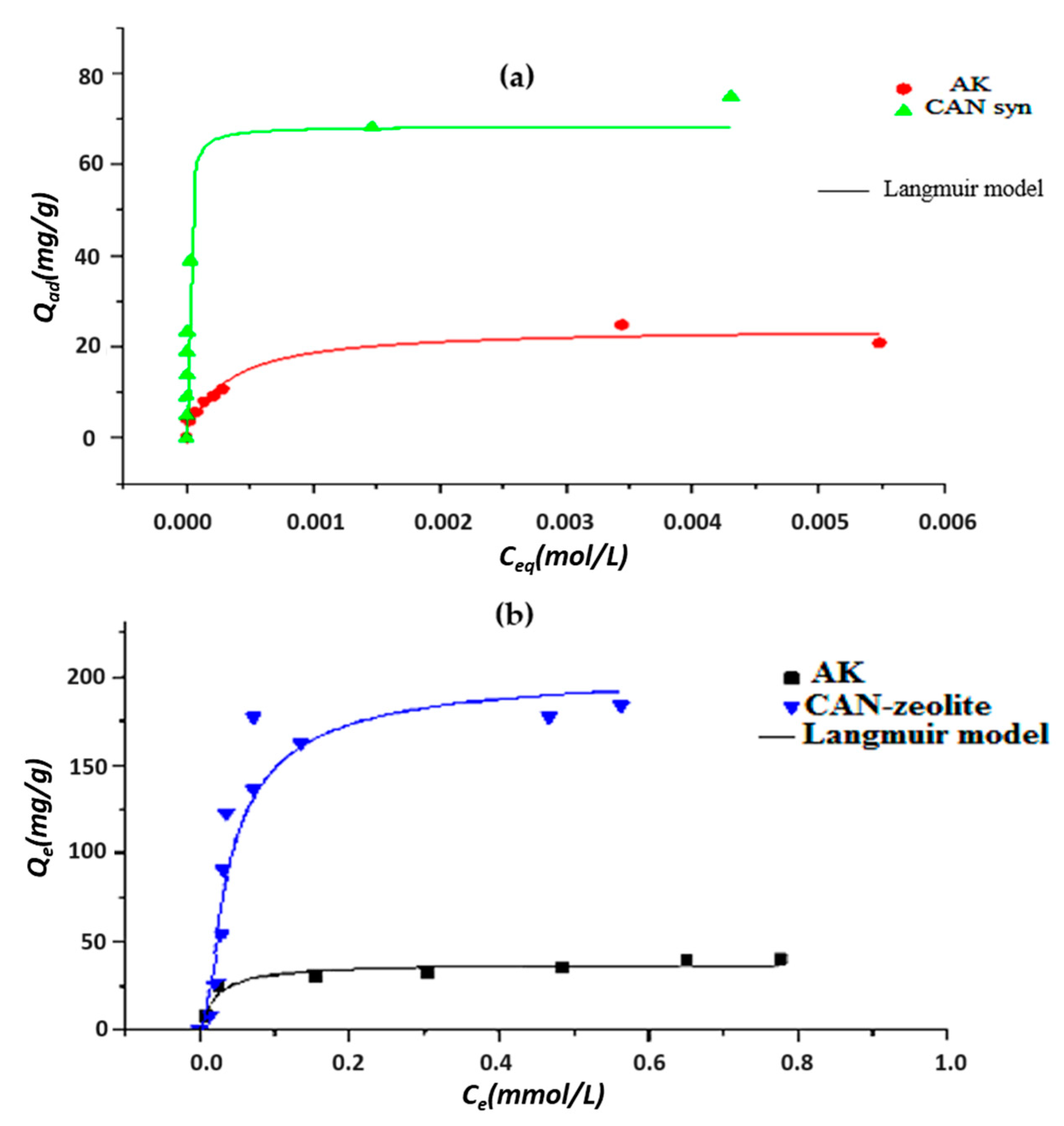
3.3.2. Cadmium and Lead Adsorption Isotherms
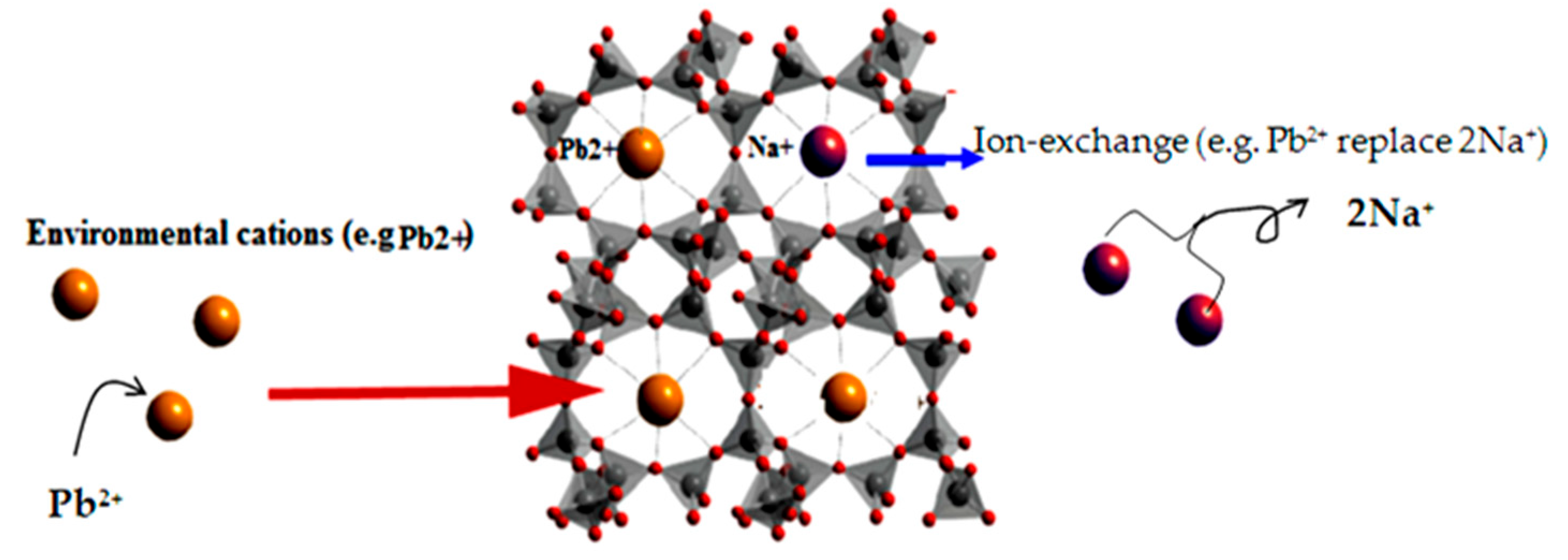
3.4. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loué, A. Oligo-Eléments En Agriculture, 2nd ed; SCPA (Société Commerciale des Potasses et de l’Azote): Nathan, Australia, 1993; pp. 45–177. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants; CRC Press: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Adriano, D.C. Trace Elements in Terrestrial Environments: Biochemistry, Bioavailability and Risks of Metals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, A.J.M.; Walker, P.L. Ecophysiology of metal uptake by tolerant plants. In Heavy Metal Tolerance in Plants—Evolutionary Aspects; Shaw, A.J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989; pp. 155–177. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, N.; Rengasamy, G. Comparison of cadmium ion adsorption on various activated carbons. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 163, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Tripathi, B.P.; Shahi, V.K. Crosslinked chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol blend beads for removal and recovery of Cd(II) from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granados-Correa, F.; Corral-Capulin, N.G.; Olguín, M.T.; Acosta-León, C.E. Comparisonof the Cd (II) adsorption processes between boehmite (γ-AlOOH) and goethite (α-FeOOH). Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality: Recommendations, 3rd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kadirvelu, K.; Namasivayam, C. Activated carbon from coconut coirpith as metal adsorbent: Adsorption of Cd (II) from aqueous solution. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 7, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourrut, B. Implication du Stress Oxydatif Dans la Toxicité du Plomb Sur Une Plante Modèle, Vicia Faba. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, R.R.; Wada, S.; Tatsumi, K. Heavy metal precipitation by polycation-polyanion complex of PEI and its phosphonomethylated derivative. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 123, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grader, C.; Buhl, J. The intermidiate phase between sodalite and cancrinite: Synthesis of nano-crystals in the presence the Na2CO3/TEA and its themal and hydrothermal stability. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 171, 110117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.C.; Loganothan, P.; Nguyen, T.V.; Vigneswaram, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Nadu, R. Simultaneous adsorption of Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn by an iron-coated Australian zeolite in batch and fixed-bed column studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; Yan, C.; Al-Ani, Y.; Dawood, A.S.; Ibrahim, A.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H.Q. An investigation into the adsorption removal of ammonium by salt activated Chinese (Hulaodu) natural Zeolite: Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.H.; Liu, J.D.; Chen, R.F. Preparation ofhighly ordered cubic NaA zeolite from halloysite mineral for adsorption of ammonium ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddine, H.; Ezzeddine, S. Removal of phosphate ions from aqueous solution using Tunisian clays minerals and synthetic zeolite. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 617–623. [Google Scholar]
- Wernert, V.; Schaf, O.; Ghobarkar, H.; Denoyel, R. Adsorption properties of zeolites for artificial kidney applications. J. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 83, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, R.; Li, Z. Sulfhydryl functionalized hydrogel with magnetism, synthesis, characterization and adsorption behavior study for heavy metal removal. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 249, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.R.; Salleh, N.M.; Othman, M.H.D.; Matsuura, T.; Ali, M.H.; Puteh, M.H.; Jaafar, J. The adsorptive removal of chromium (VI) in aqueous solution by novel natural zeolite based hollow fibre ceramic membrane. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, E.; Rokhmat, M.; Abdullah, M. Reduction of seawater salinity by natural zeolite (Clinoptilolite): Adsorption isotherms, thermodynamics and kinetics. Desalination 2017, 409, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuna, Z. Review of the natural, modified, and synthetic zeolites for heavy metals removal from wastewater. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.M.; Selim, A.Q.; Mohamed, E.A.; Wahed, M.S.A.; Seliem, M.K.; Sillanpää, M. Adsorption characteristics of Na-A zeolites synthesized from Egyptian kaolinite for manganese in aqueous solutions: Response surface modeling and optimization. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 140, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauanov, Z.; Tsakiridis, P.E.; Mikhalovsky, S.V.; Inglezakis, V.J. Synthetic coal fly ash-derived zeolites doped with silver nanoparticles for mercury (II) removal from water. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghrib, Y.; Frini-Srasra, N.; Srasra, E.; Martínez-Triguero, J.; Corma, A. Synthesis of cocrystallized USY/ZSM-5 zeolites from kaolin and its use as fluid catalytic cracking catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelić, S.K.; Medica, J.S.; Gumbarević, D.; Filošević, A.; Pržulj, N.; Pavelić, K. Critical Review on Zeolite Clinoptilolite Safety and Medical Applications in vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, M.; Akachi, T.; Matsuda, M. Preparation, structure and photocatalytic properties of cancrinite encapsulating lead and sulfide ions. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Incorporating First Addendum. 2017. Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/gdwq0506.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2018).
- Denoyel, R.; Giordano, F.; Rouquerol, J. Thermodynamic study of non-ionic-anionic surfactant mixtures: Micellization and adsorption on silica. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1993, 76, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denoyel, R.; Rouquerol, F.; Rouquerol, J. Thermodynamics of adsorption from solution: Experimental and formal assessment of the enthalpies of displacement. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1990, 136, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayari, F.; Srasra, E.; Trabelsi-Ayadi, M. Characterization of bentonitic clays and their use as adsorbent. Desalination 2005, 185, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liao, L.; Hursthouse, A.; Song, N.; Ren, B. Sepiolite-based adsorbents for the removal of potentially toxic elements from water: A strategic review for the case of environmental contamination in Hunan, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esaifan, M.; Warr, L.N.; Grathoff, G.; Meyer, T.; Schafmeister, M.T.; Kruth, A.; Testrich, H. Synthesis of Hydroxy-Sodalite/Cancrinite Zeolites from Calcite-Bearing Kaolin for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions in Aqueous Media. J. Miner. 2019, 9, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicka, E.H.; Calmano, W.; Breeger, A. Heavy metals sorption/desorption on competing clay minerals; an experimental study. Appl. Clay Sci. 1995, 9, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Bhattacharyya, K. Removal of Cd(II) from aqueous solution by kaolinite, montmorillonite and their poly(oxo zirconium) and tetrabutylammonium derivatives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 128, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriaa, A.; Ben Saad, K.; Hamzaoui, A.H. Synthesis and Characterization of Cancrinite Type Zeolite, and Its Ionic Conductivity Study by AC Impedance Analysis. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 2012, 86, 2024–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.C.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Gerson, A.R. The mechanism of the sodalite-to-cancrinite phase transformation in synthetic spent bayer liquor. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 31, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalak, S.; Jankowska, A.; Zeidler, S. Ultramarine analogs synthesized from cancrinite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 93, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.-C.; Xu, X.-W.; Zuo, F.; Long, Y.-C. Crystallization of JBW, CAN, SOD and ABW type zeolite from transformation of meta-kaolin. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 70, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, A.; Tuzen, M.; Citak, D.; Soylak, M. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution onto Turkish kaolinite clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, A. Kinetic and isothermal studies of lead ion adsorption onto palygorskite clay. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 307, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borhade, A.V.; Kshirsagar, T.A.; Dholi, A.G.; Agashe, J.A. Removal of Heavy Metals Cd2+, Pb2+, and Ni2+ From Aqueous Solutions Using Synthesized Azide Cancrinite, Na8[AlSiO4]6(N3)2.4(H2O)4.6. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwakeel, K.Z.; El-Bindary, A.A.; Kouta, E.Y. Retention of copper, cadmium and lead from water by Na-Y-Zeolite confined in methyl methacrylate shell. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3698–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihajlović, M.T.; Lazarević, S.S.; Janković-Častvan, I.M.; Kovač, J.; Jokić, B.M.; Janaćković, D.T.; Petrović, R.D. Kinetics, thermodynamics, and structural investigations on the removal of Pb2+, Cd2+, and Zn2+ from multicomponent solutions onto natural and Fe(III)-modified zeolites. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2015, 17, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unuabonah, E.I.; Adebowale, K.O.; Olu-Owolabi, B.I. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the adsorption of lead (II) ions onto phosphate-modified kaolinite clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, K.S.; Chao, C.Y.H.; Kot, S.C. Removal of mixed heavy metal ions in wastewater by zeolite 4A and residual products from recycled coal fly ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 127, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianăşi, C.; Picioruş, M.; Nicola, R.; Ciopec, M.; Negrea, A.; Nižňanský, D.; Len, A.; László Almásy, L.; Putz, A.M. Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions using inorganic porous nanocomposites. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saida, B.; Sandouqa, A.; Shawabkeh, R.A.; Ibnelwaleed, H. Synthesis of Nanosilica for the Removal of Multicomponent Cd2+ and Cu2+ from Synthetic Water: An Experimental and Theoretical Study. J. Mol. 2022, 27, 7536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M. Industrial wastes as low-cost potential adsorbents for the treatment of wastewater laden with heavy metals. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 166, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Element | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | K | Ti | Fe | Si/Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % atomic | 45.74 | 21.54 | 0.57 | 13.70 | 16.99 | 0.70 | 0.16 | 0.60 | 1.24 |
| Metal | Adsorbent | Qmax (mg g−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cd(II) | Fe2O4-P(Cys/HEA) hydrogel | 27.37 | [13] |
| Iron-modified zeolite | 6.72 | [13] | |
| Cancrinite | 45.46 | [33] | |
| Fly ash zéolithe X | 97.78 | [23] | |
| Kaolinite | 9.9 | [21] | |
| Nanocomposites | 1.94 | [46] | |
| Azide cancrinite | 37 | [41] | |
| Cancrinite | 20.6 | [41] | |
| Nanosillica | 72.13 | [47] | |
| Natural kaolin | 24.17 | This study | |
| Cancrinite zeolite | 68.42 | This study | |
| Pb(II) | Cancrinite | 52.3 | [33] |
| Cancrinite zeolite | 90 | [32] | |
| Fe2O4-P(Cys/HEA) hydrogel | 39.06 | [13] | |
| Fly ash zeolite | 70.6 | [48] | |
| Azid cancrinite | 38.46 | [41] | |
| Azide cancrinite | 52.63 | [33] | |
| Kaolinite | 11.2 | [22] | |
| Na-Bentonite | 38 | [48] | |
| Natural kaolin | 37.97 | This study | |
| Cancrinite zeolite | 192.7 | This study |
| Metal | Sample | Qm (mg/g) | KL | R2 | (KJ·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd(II) | AK | 24.17 | 3357 | 0.952 | −3.87 |
| Synthesized CAN | 68.42 | 100,617.7 | 1 | −28.53 | |
| Pb(II) | AK | 37.973 | 47.633 | 0.884 | −9.572 |
| Synthesized CAN | 192.708 | 28.224 | 0.774 | −8.275 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aloui, L.; Mezghich, S.; Mansour, L.; Hraiech, S.; Ayari, F. Swift Removal of the Heavy Metals Cadmium and Lead from an Aqueous Solution by a CAN-Zeolite Synthesized from Natural Clay. ChemEngineering 2023, 7, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering7060113
Aloui L, Mezghich S, Mansour L, Hraiech S, Ayari F. Swift Removal of the Heavy Metals Cadmium and Lead from an Aqueous Solution by a CAN-Zeolite Synthesized from Natural Clay. ChemEngineering. 2023; 7(6):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering7060113
Chicago/Turabian StyleAloui, Lobna, Soumaya Mezghich, Lamjed Mansour, Sana Hraiech, and Fadhila Ayari. 2023. "Swift Removal of the Heavy Metals Cadmium and Lead from an Aqueous Solution by a CAN-Zeolite Synthesized from Natural Clay" ChemEngineering 7, no. 6: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering7060113
APA StyleAloui, L., Mezghich, S., Mansour, L., Hraiech, S., & Ayari, F. (2023). Swift Removal of the Heavy Metals Cadmium and Lead from an Aqueous Solution by a CAN-Zeolite Synthesized from Natural Clay. ChemEngineering, 7(6), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering7060113