Abstract
This study mainly explored the characteristics of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants with RDX, CL-20 or TKX-50 by experimental method. Three series of test samples were prepared referring to the formulation of M1 single-base gun propellant (M1 SBP). The thermochemical characteristics, chemical stability, explosion heat, impact and friction sensitivities of prepared samples were determined by simultaneous differential scanning calorimetry–thermogravimetric analysis (STA DSC–TGA), vacuum stability tester (VST), bomb calorimeter (BC), BAM fallhammer and BAM friction tester, respectively, and compared with those of the reference sample M1. The experimental results indicated that the thermochemical characteristics of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants were similar to those of M1 SBP. The NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants had good chemical stability and were superior to M1 SBP. The explosion heat of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants was close to and slightly larger than that of M1 SBP. In addition, the NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants had lower impact and friction sensitivities than the M1 SBP. Therefore, the NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants have the potential to replace the M1 SBP. The combustion performances of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants will be continuously studied and verified in the future.
1. Introduction
Gun propellants are designed to produce very large amounts of gas to propel the projectile at high velocity. The velocity of the projectile depends on the rate at which the gas is produced. This, in turn, depends on the amount of chemical energy released [1]. Traditional gun propellants are broadly classified as a single-base propellant (SBP), double-base propellant (DBP), and triple-base propellant (TBP). SBPs contain nitrocellulose (NC) as the main energetic ingredient, while DBPs contain both NC and nitroglycerine (NG) and TBPs contain nitroguanidine (NQ) in addition to NC and NG [2]. In view of the problem that traditional gun propellants are highly prone to accidental ignition, low vulnerability ammunition (LOVA) gun propellants with low sensitivity have been continuously developed. This has been primarily achieved by removing NG and reducing the amount of NC in the formulation, replacing them with inert and energetic plasticizers and cyclic nitramines [3,4,5,6,7,8].
In recent years, high-energy propellants (HEPs) containing cyclic nitramines (RDX, HMX, etc.) have been developed to increase the muzzle velocity of the projectile. The main source of energy in HEPs is cyclic nitramine along with NC [9]. The cyclic nitramine used in HEPs is primarily RDX, which is chosen because it offers many advantages for advanced gun propulsion, such as improvement in performance (high energy content), better thermal stability and low cost [10]. CL-20 is a high energetic dense caged nitramine that outperforms RDX and HMX in density, enthalpy of formation and oxygen balance [11]. In addition, there are many types of energetic plasticizers that have been recommended for use in HEPs, such as glycidyl azide polymer (GAP) [12,13], acetyl triethyl citrate (ATEC) [14], 1,5-diazido-3-nitrazapentane (DANPE) [15], N-butyl-N-(2-nitroxy-ethyl)nitramine (Bu-NENA) [16], trimethylolethane trinitrate (TMETN) [16], diethyleneglycol dinitrate (DEGDN) [17,18], triethylene glycol dinitrate (TEGDN) [18,19] and bis(2,2-dinitropropyl)acetal/formal (BDNPA/F) [20].
M1 SBP is composed of 85% NC, 10% 2,4-dinitrotoluene (2,4-DNT, flash inhibitor), 5% dibutylphalate (DBP, burn rate modifier and plasticizer) and an additional 1% diphenylamine (DPA, stabilizer), which is used in 105 mm, 155 mm, and 8 inch Howitzers [21]. M1 SBP has a lower flame temperature and therefore less erosion, and its burning rate can be controlled by coating the burning rate modifier. However, irregular burning is a major drawback due to the hygroscopic nature of M1 SBP. In addition, the temperature sensitivity of M1 SBP is relatively high in the range of operating ambient temperatures, which has also attracted the attention of researchers. Several additives can be considered for addition to M1 SBP to improve its combustion behavior, such as stabilizers, plasticizers, and phlegmatizers [22].
In this study, the characteristics of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants with RDX, CL-20 or TKX-50 were preliminarily explored by experimental method. The formulation of M1 SBP was selected as a reference formulation. Three series of test samples were designed and prepared, and their thermochemical characteristics, chemical stability, explosion heat and mechanical sensitivity (impact and friction) were determined by simultaneous differential scanning calorimetry–thermogravimetric analysis (STA DSC–TGA), vacuum stability tester (VST), bomb calorimeter (BC), BAM fallhammer and BAM friction tester, respectively, and compared with those of the reference sample M1. In addition, the feasibility of using NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants to replace the M1 SBP was also analyzed and evaluated.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
Nitrocellulose (NC) with a nitrogen content of 13.15% produced by the 205th Arsenal in Taiwan was used as an energetic ingredient in the preparation of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants. Hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene (HTPB) was an organic polymer used as an inert and energetic binder, which was obtained from the National Chung Shan Institute of Science and Technology (NCSIST) in Taiwan. 1,3,5-Trinitroperhydro-1,3,5-triazine [RDX, (CH2NNO2)3] with a purity of 99.9% was also obtained from the 205th Arsenal, which has been actually used in various military applications. 2,4,6,8,10,12-Hexanitro-2,4,6,8,10,12-hexaazatetracyclo [CL-20, (CHNNO2)6] and dihydroxylammonium 5,5′-bistetrazole-1,1′-diolate [TKX-50, C2H8N10O4] were prepared by the NCSIST. RDX, CL-20 and TKX-50 were used as energetic oxidizers to enhance the performance of gun propellants, and the chemical structural formulas are shown in Figure 1. 2,4-Dinitrotoluene [2,4-DNT, CH3C6H3(NO2)2] with a purity of 97%, dibutylphalate [DBP, C6H4(CO2C4H9)2] with a purity of 99% and diphenylamine [DPA, (C6H5)2NH] with a purity of 99% were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Corporation (St. Louis, MO, USA) and used as additives to improve the combustion performance of gun propellants. Ethanol (C2H5OH, 99.8%) and diethyl ether [(C2H5)2O, 99.7%] were also purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and used as solvents without further purification. In addition, all aqueous solutions were prepared using deionized water.
Figure 1.
Chemical structural formulas of RDX, CL-20, and TKX-50.
2.2. Preparation of Gun Propellant Samples
The M1 single-base gun propellant consisting of 85% NC (13.2% N), 10% 2,4-DNT, 5% DBP and an additional 1% DPA [21] was selected as a reference formulation. Three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples were prepared using HTPB and energetic material (RDX, CL-20 or TKX-50) to partially replace NC in the M1 single-base gun propellant composition in order to reduce sensitivity and increase energy, the formulations are given in Table 1. There were ten steps to prepare the propellant pellets, such as: (1) treating of the ingredients, (2) precise weighing, (3) wet mixing, (4) pressing, (5) cutting, (6) drying, (7) water cooking, (8) final drying, (9) coating, (10) sieving. The diameter, length and hole diameter of the prepared single-perforated cylindrical pellets are 1.14 mm, 5.08 mm and 0.406 mm, respectively.

Table 1.
Compositions of test samples.
2.3. Characterization Measurement of Gun Propellant Samples
The prepared NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples were characterized by means of simultaneous differential scanning calorimetry–thermogravimetric analysis (STA DSC–TGA, Netzsch STA 449 F3 Jupiter®, NETZSCH GmbH, Selb, Germany), a vacuum stability tester (VST, assembled by our laboratory), bomb calorimeter (BC, Parr 6200), BAM fallhammer (Reichel & Partner GmbH, Steinweiler, Germany) and BAM friction tester (Reichel & Partner GmbH, Steinweiler, Germany).
2.3.1. Thermochemical Characteristics Test
The thermochemical characteristics of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples were studied by thermal analysis technique and compared with those of the reference sample M1. The thermal decomposition temperature and mass loss of the test samples during the decomposition reaction were measured by STA DSC–TGA. The test sample was placed in a ceramic crucible using a sample weight of about 3–5 mg. All experiments were carried out at a heating rate of 10 °C/min under a nitrogen flow of 20 mL/min. In addition, STA DSC–TGA was also employed to measure the thermal decomposition temperatures of the test samples at heating rates of 1, 2, 5 and 10 °C/min, and the experimental data were used to calculate the activation energies by the Kissinger [23] and Ozawa [24] methods.
2.3.2. Chemical Stability Test
The chemical stability of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples was determined by VST according to the MIL-STD-1751A method 1061 [25] and compared with that of the reference sample M1. The VST was assembled by our laboratory, which consists of a heating block and glass tubes with temperature and pressure sensors. A 5 g test sample was placed in the glass tube and closed by a head with pressure and temperature transducers. The amount of gas released by thermal decomposition was measured under vacuum at a temperature of 100 °C for 40 h. The gas release required by the MIL-STD-1751A standard must be less than 2 mL/g.
2.3.3. Explosion Heat Test
The explosion heat of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples was measured by BC and compared with that of the reference sample M1. The BC consists of a strong cylindrical stainless container (called bomb) which can withstand high pressure when the material is burnt in it [26]. About 0.5 g of the sample was placed in the bomb, which was then filled with nitrogen. Afterwards, the bomb was placed in the bucket with 2 L of water, and the bucket was placed inside the calorimeter, which was surrounded by an air-jacket to prevent heat loss due to radiation. Finally, the sample was ignited by a fuse wire to measure the heat of explosion.
2.3.4. Mechanical Sensitivity Tests
The impact sensitivity of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples was determined by BAM fallhammer according to the MIL-STD-1751A method 1015 [25] and compared with that of the reference sample M1. The Bruceton method [27] was used to evaluate the impact sensitivity, which was based on a statistical analysis by determining the drop height (H50) at which there was 50% probability of obtaining an ignition. Each sample was tested utilizing a 5 kg drop weight for 30 time to obtain a H50. The impact energy (E50) was calculated using the formula E50(Joule) = mgH50, where m is the drop weight mass [kg], g is the acceleration due to gravity [ms−2], and H50 is the drop height [m].
The friction sensitivity of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples was determined by BAM friction tester according to the MIL-STD-1751A method 1024 [25] and compared with that of the reference sample M1. The 1 of 6 method was used to evaluate the friction sensitivity, which was defined as the smallest load at which an audible or visible decomposition reaction is obtained from at least one out of six trials. The measurement range of friction load was from 0.5 to 360 N.
3. Calculation of Activation Energy
In kinetic analysis, it is generally assumed that the rate of reaction can be described by two separable functions, k(T) and f(α), such that
where dα/dt is the rate of mass loss, α is the fractional decomposition at any time, and k(T) is the temperature-dependent rate constant. The term f(α) is a function of α given by:
where n is an order of reaction. The temperature dependence of the reaction rate is commonly described by the Arrhenius equation:
where Ea is the activation energy, A is the pre-exponential factor, and R is the universal gas constant. By combining Equation (1) with Equation (3), the following expression is obtained:
3.1. Kissinger Method
Because the maximum rate occurs when d2α/dt2 = 0, differentiation of Equation (4) gives:
where TP is the temperature peak of the DSC curve at linear heating rate β = dT/dt. The Kissinger method [23,28] assumed that the product n(1−α)n−1 is independent of β. Therefore, the following expression is derived:
The value of activation energy can be calculated from the slope of the approximately straight line versus .
3.2. Ozawa Method
At linear heating rate β = dT/dt, Equation (4) can be written as:
The Ozawa method [24,28] assumed that A, f(α) and Ea are independent on T, whereas A and Ea are independent on conversion rate α. By separating and integrating Equation (7), the resulting Ozawa equation is:
The straight line obtained by plotting against , and Ea values can be determined from the slope .
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Thermochemical Characteristics Analysis
The thermochemical characteristics of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples were measured by STA DSC–TGA at a heating rate of 10 °C/min under nitrogen atmosphere and compared with those of the reference sample M1. Each experiment was repeated three times, and the reported data were the average value of three measurements. The maximum standard deviations for peak temperature and weight loss measured by STA TG–DSC were 0.5 °C and 0.03%, respectively. The DSC and TG curves of reference sample M1 and three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples are shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, respectively. Curve in Figure 2a and curve in Figure 3a are the DSC and TG curves of reference sample M1, respectively. It can be seen that the DSC curve exhibits a broad exothermic peak in the range of 166–253 °C with a peak temperature at 209.4 °C, and the corresponding TG curve reveals a weight loss of 95.40%, which can reasonably be attributed to the decomposition reaction of reference sample M1. Roduit et al. [29] have also reported similar experimental results. Curves in Figure 2b–g and curves in Figure 3b–g are the DSC and TG curves of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples, respectively, which are similar to those of reference sample M1. However, the decomposition temperature and weight loss of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples are slightly lower than those of reference sample M1. Furthermore, Figure 4 presents the DSC curves of reference sample M1 at heating rates of 1, 2, 5 and 10 °C. The decomposition activation energies calculated by the Kissinger and Ozawa methods are 184.0 and 182.4 kJ/mol, respectively, as shown in Table 2. The DSC curves of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples at heating rates of 1, 2, 5 and 10 °C are shown in Figure 5, and the calculated decomposition activation energies are also listed in Table 2. The activation energies of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples can be compared with that of the reference sample M1. The test samples with RDX (NHR05 and NHR10) or TKX-50 (NHT05 and NHT10) have lower decomposition activation energies than reference sample M1. However, the decomposition activation energies of test samples with CL-20 (NHC05 and NHC10) are higher than that of the reference sample M1. It is also found that the decomposition activation energy of a test sample with lower RDX or TKX-50 content (NHR05 or NHT05) is higher than that of a test sample with higher RDX or TKX-50 content (NHR10 or NHT10). However, the test sample with lower CL-20 content (NHC05) has a lower decomposition activation energy than the test sample with higher CL-20 content (NHC10). Previous literatures [30,31,32] have reported that the activation energies of RDX, CL-20 and TKX-50 are 139.7–148.3 kJ/mol, 186–188 kJ/mol and 168–184 kJ/mol, respectively. Therefore, the decomposition activation energy of test samples with CL-20 is higher than that of test samples with RDX or TKX-50, which can be reasonably attributed to the fact that the decomposition activation energy of CL-20 is higher than that of RDX and TKX-50.
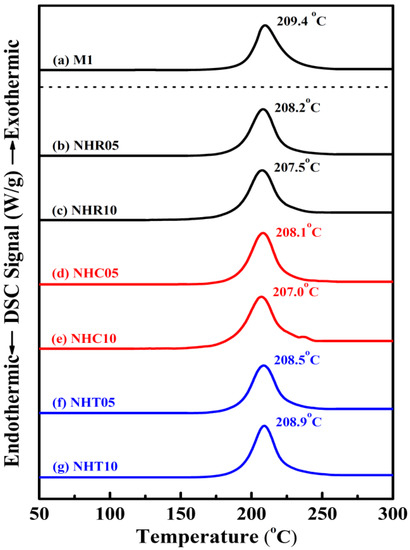
Figure 2.
DSC curves of samples (a) M1, (b) NHR05, (c) NHR10, (d) NHC05, (e) NHC10, (f) NHT05, and (g) NHT10 at a heating rate of 10 °C min−1.
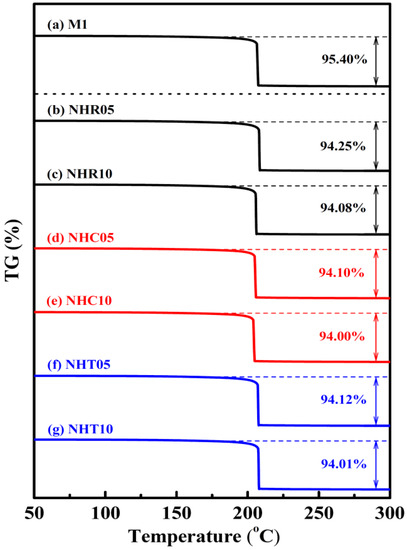
Figure 3.
TGA curves of samples (a) M1, (b) NHR05, (c) NHR10, (d) NHC05, (e) NHC10, (f) NHT05, and (g) NHT10 at a heating rate of 10 °C min−1.
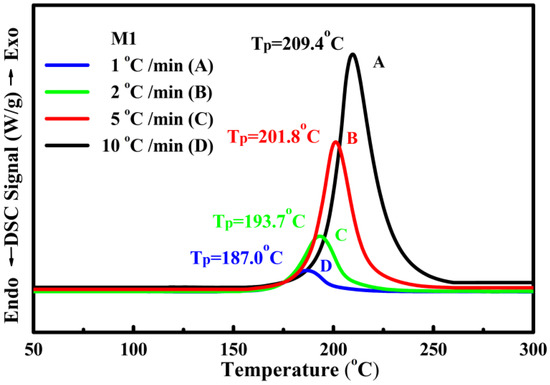
Figure 4.
DSC curves of reference sample M1 at different heating rates of 1, 2, 5 and 10 °C min−1.

Table 2.
Activation energy values of decomposition reactions of test samples calculated by the Kissinger and Ozawa methods.
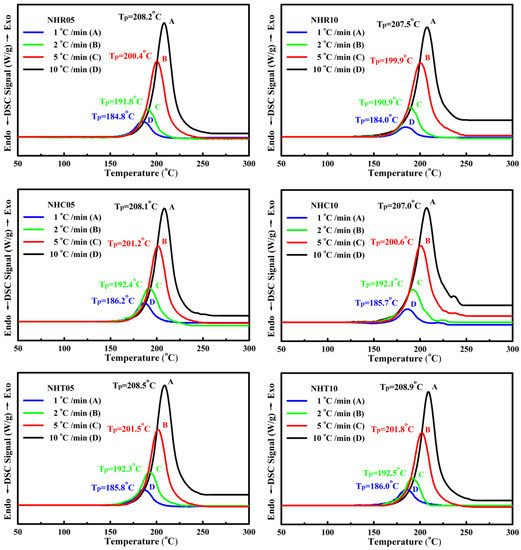
Figure 5.
DSC curves of samples NHR05, NHR10, NHC05, NHC10, NHT05 and NHT10 at different heating rates of 1, 2, 5 and 10 °C min−1.
4.2. Chemical Stability Analysis
The chemical stability analysis of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples was carried out and compared with that of the reference sample M1. The advisory criterion for this test is that the gas evolved per gram of gun propellants does not exceed 2 mL/g. Each experiment was repeated three times and the reported data were the average value of three measurements. The maximum standard deviation for volume of gas evolved per gram measured by VST was 0.02 mL/g. The pressure–time curves of reference sample M1 and three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples are shown in Figure 6, and the volume of gas evolved per gram of these samples is listed in Table 3. The volume of gas evolved per gram of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples is lower than that of the reference sample M1 and does not exceed 2 mL/g, indicating that three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples have good chemical stability. In addition, it is also found that the chemical stability of test samples with higher RDX, CL-20 or TKX-50 content (NHR10, NHC10 or NHT10) is better than that of test samples with lower RDX, CL-20 or TKX-50 content (NHR05, NHC05 or NHT05).
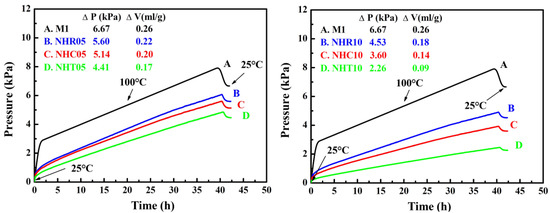
Figure 6.
Pressure–time curves of reference sample M1 and three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples obtained by VST with 100 °C/40 h.

Table 3.
Experimental results of VST, BC and sensitivity tests.
4.3. Explosion Heat Analysis
The explosion heat analysis of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples was carried out and compared with that of the reference sample M1. Each experiment was repeated three times and the reported data were the average value of three measurements. The maximum standard deviation for explosion heat measured by BC was 26 J/g. All experimental results are also listed in Table 3 for comparison. It is found that the explosion heat of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples is close to and slightly larger than that of the reference sample M1. Previous literatures [33,34] have reported that the explosion heats of RDX, CL-20 and TKX-50 are 5294 J/g, 6084 J/g and 5984 J/g, respectively. Therefore, the explosion heat of test samples with CL-20 (NHC05 and NHC10) is higher than that of test samples with RDX (NHR05 and NHR10) or TKX-50 (NHT05 and NHT10), which can be reasonably attributed to the fact that the explosion heat of CL-20 is higher than that of RDX and TKX-50. This also means that the NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants have the potential to replace the M1 single-base gun propellant.
4.4. Mechanical Sensitivity Analysis
The impact and friction sensitivities of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples were determined and compared with those of the reference sample M1. All experimental results are also listed in Table 3. The impact and friction sensitivities of the reference sample M1 are 12.74 J and 240 N, respectively. Three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellant samples have lower impact and friction sensitivities than the reference sample M1. This also means that adding HTPB and energetic material (RDX, CL-20 or TKX-50) to the M1 single-base gun propellant can help reduce the mechanical sensitivity. In addition, the mechanical sensitivity of test samples with CL-20 (NHC05 and NHC10) is higher than that of test samples with RDX (NHR05 and NHR10) or TKX-50 (NHT05 and NHT10).
5. Conclusions
In this study, the characteristics of three series of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants were explored experimentally and compared with those of the M1 single-base gun propellant. Based on the experimental results and analysis, the following conclusions are drawn:
- (1)
- The analysis of thermochemical characteristics indicates that the NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants with RDX or TKX-50 have lower decomposition activation energy than the M1 single-base gun propellant. However, the decomposition activation energy of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants with CL-20 is higher than that of M1 single-base gun propellant.
- (2)
- The analysis of chemical stability shows that the NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants with RDX, CL-20 or TKX-50 have good chemical stability and are superior to M1 single-base gun propellant.
- (3)
- The analysis of explosion heat reveals that the explosion heat of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants with RDX, CL-20 or TKX-50 are close to and slightly larger than that of M1 single-base gun propellant.
- (4)
- The analysis of mechanical sensitivity indicates that the NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants with RDX, CL-20 or TKX-50 have lower impact and friction sensitivities than the M1 single-base gun propellant. Adding HTPB and energetic material (RDX, CL-20 or TKX-50) to the M1 single-base gun propellant can help reduce the mechanical sensitivity.
- (5)
- Based on the above conclusions, the NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants have the potential to replace the M1 single-base gun propellant. The combustion performances of NC/HTPB-based high-energy gun propellants will be continuously studied and verified in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.-H.L. and T.-F.Y.; methodology, T.-M.Y., J.-S.L. and K.-T.L.; formal analysis, Y.-H.L.; investigation, Y.-H.L.; experiment, Y.-H.L.; data curation, Y.-H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, T.-M.Y. and Y.-H.L.; writing—review and editing, J.-S.L., K.-T.L. and T.-F.Y.; supervision, T.-F.Y.; project administration, J.-S.L.; funding acquisition, J.-S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Defense Industrial Development Foundation, R.O.C. under grant number of 107Q0016.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the 205th Arsenal and the National Chung Shan Institute of Science and Technology (NCSIST) in Taiwan for supplying experimental ingredients. The authors would also like to thank Chyi-Ching Hwang for providing helpful suggestions on data processing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Akhavan, J. The Chemistry of Explosives, 2nd ed.; TJ International Ltd.: Padstow, Cornwall, UK, 2004; pp. 149–150. ISBN 978-0-85404-640-9. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, J.P. High Energy Materials: Propellants, Explosives and Pyrotechnics; WILEY-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; pp. 226–227. ISBN 978-3-527-32610-5. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, A.G.S.; Sanghavi, R.R.; Dayanandan, C.R.; Joshi, M.M.; Karir, J.S. Ballistic evaluation of LOVA propellant in high calibre gun. Def. Sci. J. 2001, 51, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.L.B.; da Silva, A.P.; Rosato, R.; Lemos, M.F.; Peixoto, F.C.; França, T.C.C.; Filho, L.G.M. On the replacement of traditional stabilizers by guaiacol in environmentally safe nitrocellulose-based propellants. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2022, 24, 1837–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, D.T.; Ravindra, N.M. A review: Advances and modernization in U.S army gun propellants. JOM 2021, 73, 1144–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.F.; Shi, X.R.; Li, Z.Q.; Duan, X.H.; Wu, B.; Pei, C.H. Effect of 3-methyl-4-nitro-furoxan on morphology, thermal stability, rheological and mechanical properties of nitrocellulose (NC)-based energetic materials. Fire Phys. Chem. 2021, 1, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jin, B.; Chai, Z.H.; Liao, L.; Chu, S.J.; Peng, R.F. Synthesis and stabilization mechanism of novel stabilizers for fullerene-malonamide derivatives in nitrocellulose-based propellants. Polym. Test. 2020, 86, 106493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumlinde, P.; Ek, S.; Tunestal, E.; Hafstrand, A. Synthesis and characterization of novel stabilizers for nitrocellulose-based propellants. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2017, 42, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, A.G.S.; Dayanandan, C.R.; Joshi, M.M.; Patgaonkar, S.S.; Karir, J.S. Studies on the Effects of RDX Particle Size on the Burning Rate of Gun Propellants. Def. Sci. J. 1996, 46, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shoukry, S.A.; Ismail, M.M.; Abd Elgwad, A. Performance and stability of modern gun propellants. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Chemical & Environmental Engineering Conference, Caoro, Egypt, 27–29 May 2008; pp. 679–691. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, A.T.; Chafin, A.P.; Christian, S.L.; Moore, D.W.; Nadler, M.P.; Nissan, R.A.; Vanderah, D.J.; Gilardi, R.D.; George, C.F.; Flippen-Anderson, J.L. Synthesis of polyazapolycyclic caged polynitramines. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 11793–11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damse, R.S.; Singh, A.; Singh, H. High energy propellants for advanced gun ammunition based on RDX, GAP and TAGN compositions. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2007, 32, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Khire, V. Studies on low vulnerability gun propellants based on conventional binders and energetic plasticizers. Int. J. Energetic Mater. Chem. Propuls. 2008, 7, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeih, A.; Wafy, T.Z.; Elshenawy, T.; Hussein, A.K.; Abd-Elghany, M.; Hammad, S.M.; Yehia, M. Performance characteristics of modified HMX-gun propellants. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 610, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damse, R.S.; Singh, A. Studies on the high-energy gun propellant formulations based on 1,5-diazido-3-nitrazapentane. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damse, R.S.; Omprakash, B.; Tope, B.G.; Chakraborthy, T.K.; Singh, A. Study of N-n-butyl-N-(2-nitroxyethyl)nitramine in RDX based gun propellant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Jiang, L.M.; Dong, J.; Li, B.; Shen, J.P.; Chen, L.; Fu, Y.; He, W.D. Three-dimensional network structure nitramine gun propellant with nitrated bacterial cellulose. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 15094–15101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinditskii, V.P.; Egorshev, V.Y.; Berezin, M.V.; Serushkin, V.V.; Filatov, S.A.; Chernyi, A.N. Combustion mechanism of nitro ester binders with nitramines. Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2012, 48, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.P.; Liu, Z.T.; Xu, B.; Liang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liao, X.; Wang, Z.H. Influence of carbon nanofibers on thermal and mechanical properties of NC-TEGDN-RDX triple-base gun propellants. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2019, 44, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, S.S.; Zhang, G.Y.; Yu, Z.Y.; Li, J.X.; Chen, M.L.; Ma, X.; Xiang, K.L.; Jin, S.H.; Chen, Y. Influence of energetic plasticizer bis(2,2-dinitropropyl)acetal/formal on properties of ε-CL-20 based pressed polymer-bonded explosives. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, E.; Brochu, S.; Poulin, I.; Faucher, D.; Marois, A.; Gagnon, A. Environmental Chemistry of Explosives and Propellant Compounds in Soils and Marine Systems: Distributed Source Characterization and Remedial Technologies, Chapter 21 Residual Dinitrotoluenes from Open Burning of Gun Propellant; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 401–414. ISBN 978-0-841-22633-3. [Google Scholar]
- Houck, M.M. Materials Analysis in Forensic Science, 1st ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 425–426. ISBN 978-01-2800-574-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger, H.E. Reaction Kinetics in Differential Thermal Analysis. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T. A New Method of Analyzing Thermogravimetric Data. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1965, 38, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MIL-STD-1751A; Department of Defense Test Method Standard: Safety and Performance Tests for the Qualification of Explosives (High explosives, Propellants, and Pyrotechnics). U.S. Department of Defense: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- 6200 Calorimeter Operating Instruction Manual; Parr Instrument Company: Moline, IL, USA, 2010.
- Dixon, J.W.; Mood, A.M. A method for obtaining and analyzing sensitivity data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1948, 43, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Chen, J.J.; Hwang, C.C.; Lu, K.T.; Yeh, T.F. Study on thermal characteristics of TNT based melt-cast explosives. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2019, 44, 1270–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roduit, B.; Folly, P.; Berger, B.; Mathieu, J.; Sarbach, A.; Andres, H.; Ramin, M.; Vogelsanger, B. Evaluating sadt by advanced kinetics-based simulation approach. J. Therm. Anal. 2008, 93, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hsu, C.K.; Chang, C.L. A study on the thermal decomposition behaviors of PETN, RDX, HNS and HMX. Thermochim. Acta 2002, 392–393, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.M.; Chen, S.S.; Li, X.; Jin, S.H.; Niu, H.; Wang, F.; Chao, H.; Fang, T.; Shu, Q.H. Preparation, thermal investigation and detonation properties of ε-CL-20-based polymer-bonded explosives with high energy and reduced sensitivity. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muravyev, N.V.; Monogarov, K.A.; Asachenko, A.F.; Nechaev, M.S.; Ananyev, I.V.; Fomenkov, I.V.; Kiselev, V.G.; Pivkina, A.N. Pursuing reliable thermal analysis techniques for energetic materials: Decomposition kinetics and thermal stability of dihydroxylammonium 5,5’-Bistetrazole-1,1’-Diolate (TKX-50). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.; Köhler, J.; Homburg, A. Explosives, 7th ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; pp. 32, 176, 179. ISBN 978-3-527-33776-7. [Google Scholar]
- Klapötke, T.M. Energetic materials research at Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (LMU). Eng. Sci. Mil. Technol. 2018, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).