β-Thujaplicin Enhances TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis via the Dual Effects of XIAP Inhibition and Degradation in NCI-H460 Human Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Trypan Blue Staining
2.4. Measurements of Cell Viability
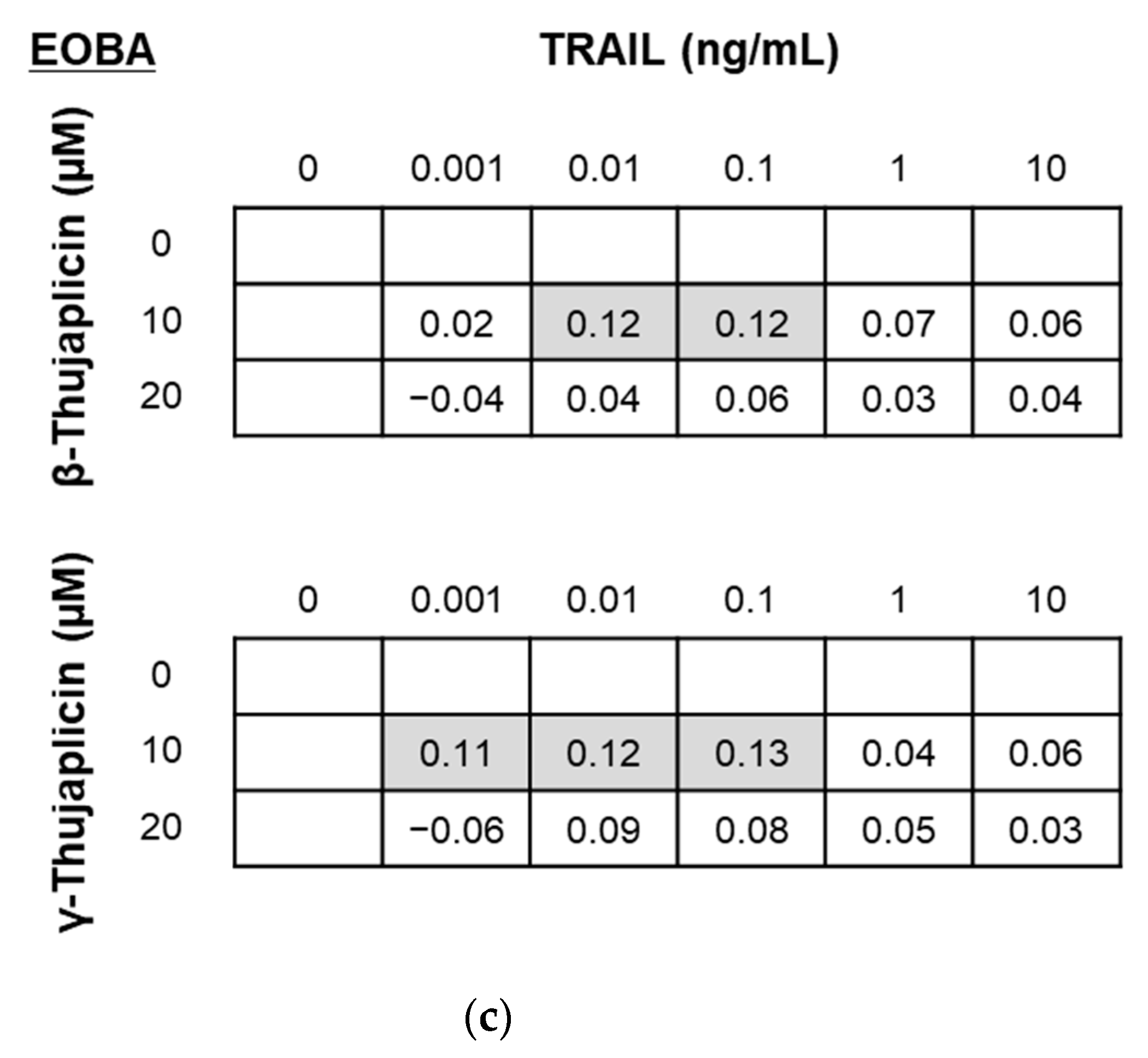
2.5. Evaluation of the Combinatorial Effects of Drugs
2.6. Caspase-3/7 Activity Assay
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Expression and Purification of Recombinant GST-Tagged XIAP-BIR3 Domain in an Escherichia coli Expression System
2.9. Fluorescence Polarization Binding Assay
3. Results
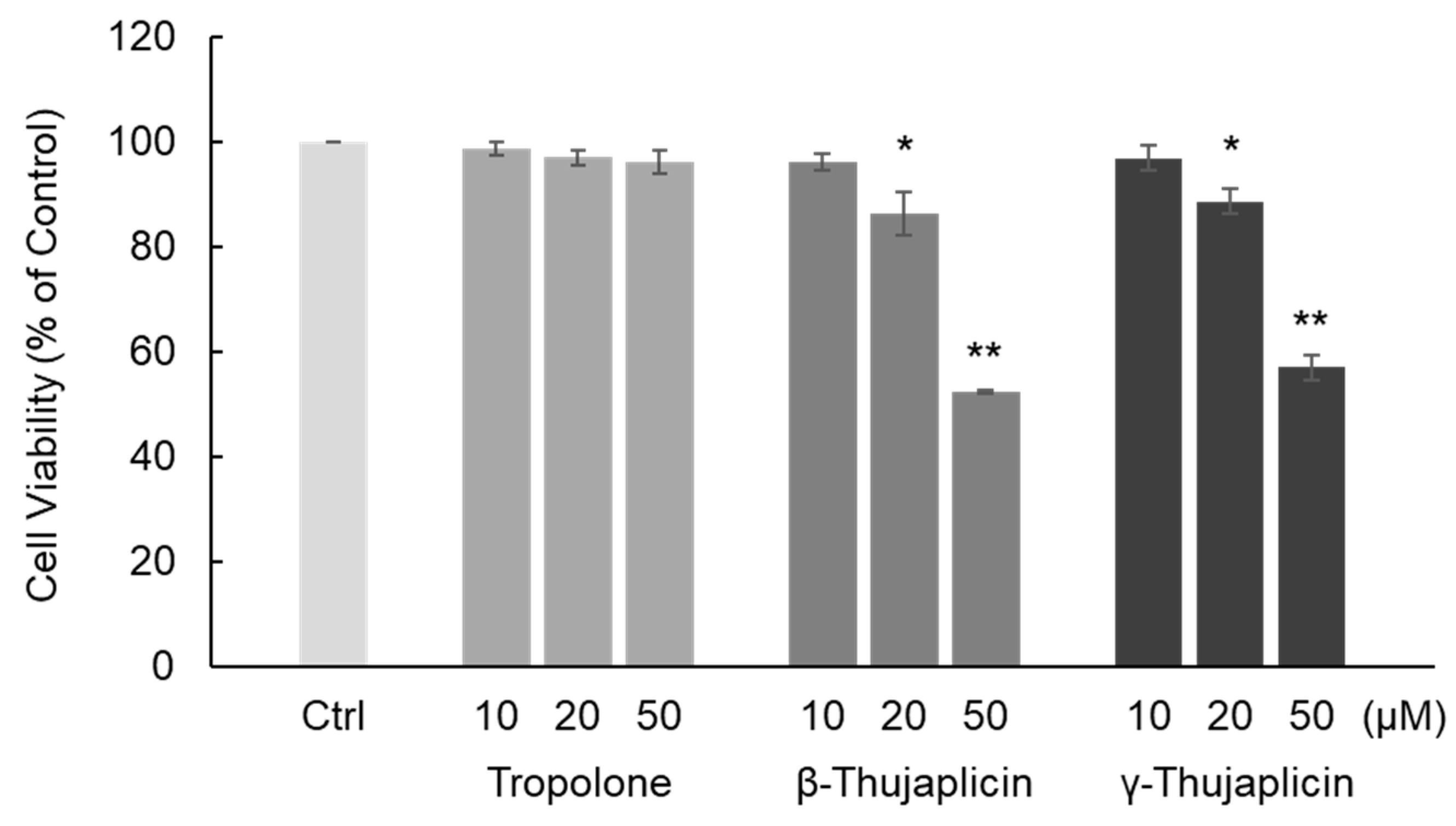
3.1. β-. and γ-Thujaplicins Decrease the Viability of NCI-H460 Cells
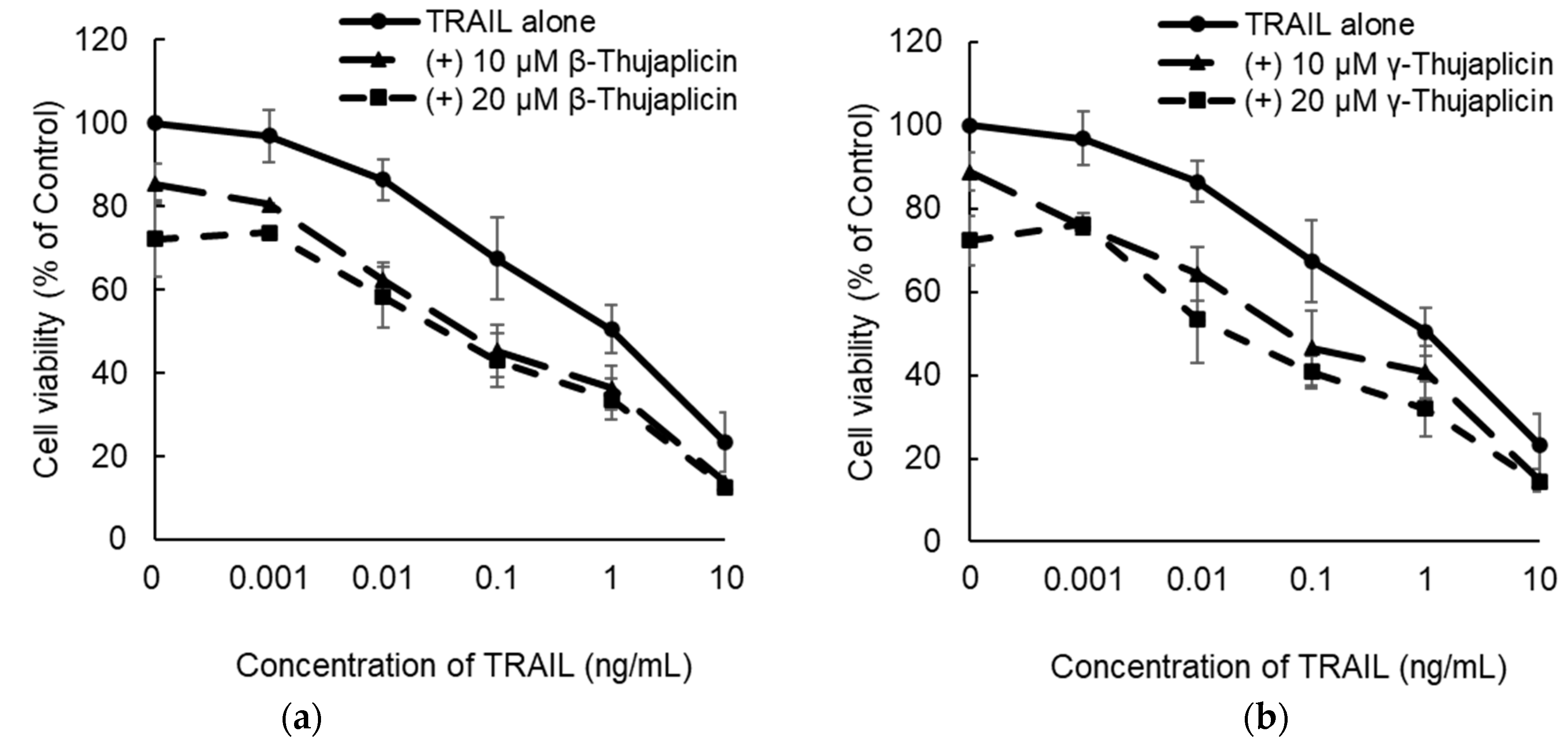
3.2. β-. and γ-Thujaplicins Enhance the Antiproliferative Effect of TRAIL on NCI-H460 Cells
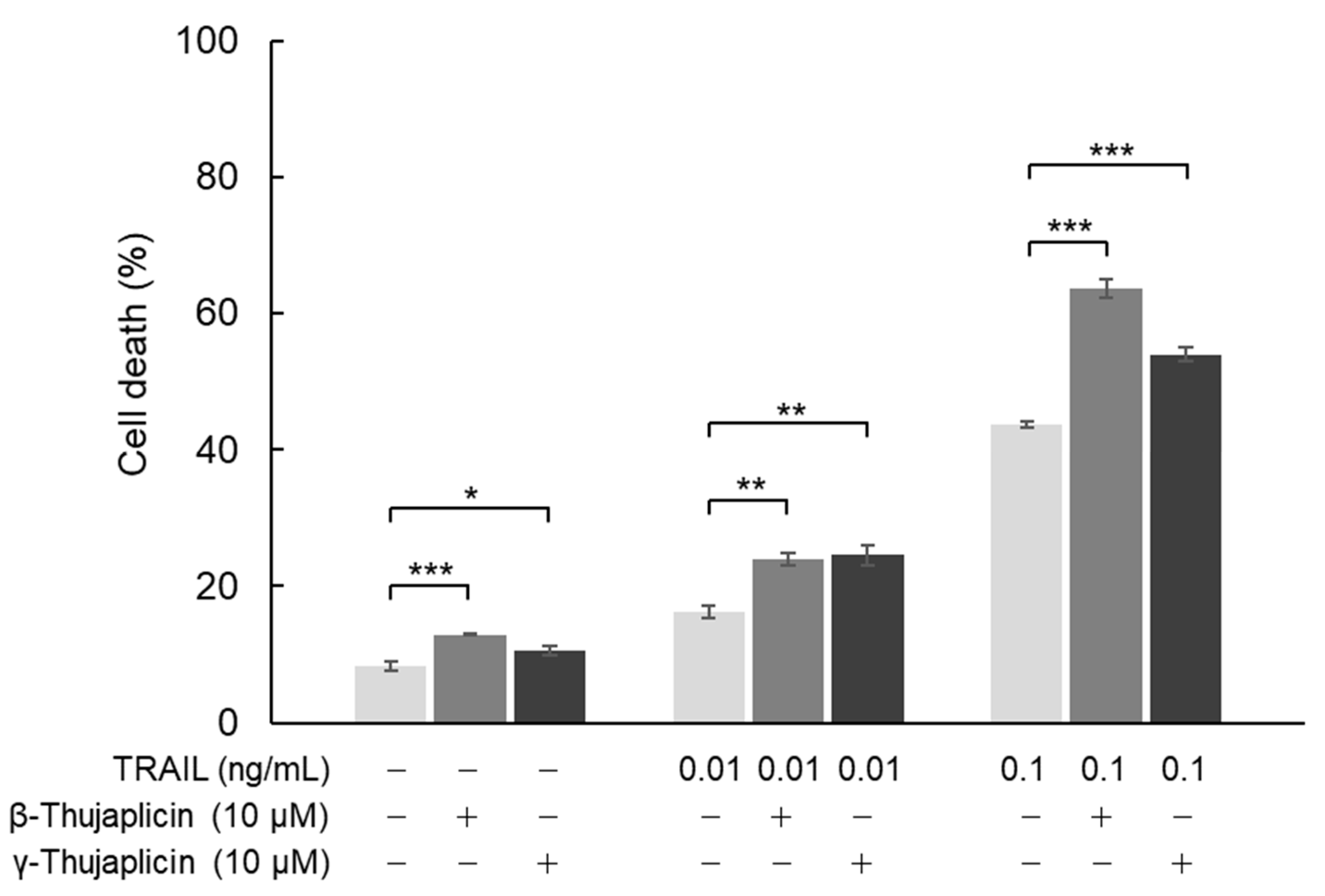
3.3. β-. Thujaplicin Enhances the Cell Death Induction Effect of TRAIL on NCI-H460 Cells
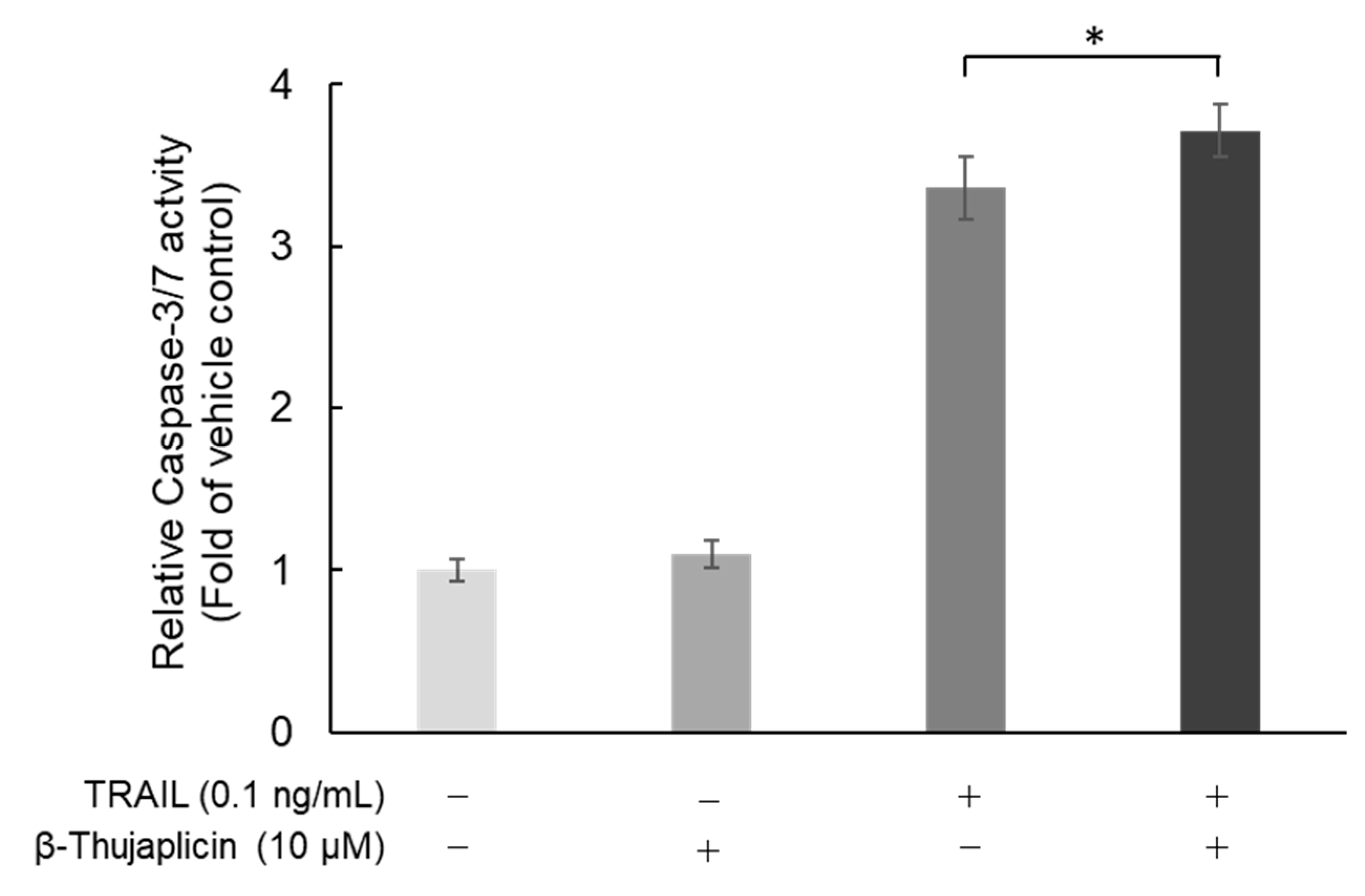
3.4. Potentiating Effect of β-Thujaplicin on TRAIL-Induced Cell Death in NCI-H460 Cells Is Accompanied by Enhanced Caspase-3/7 Activity
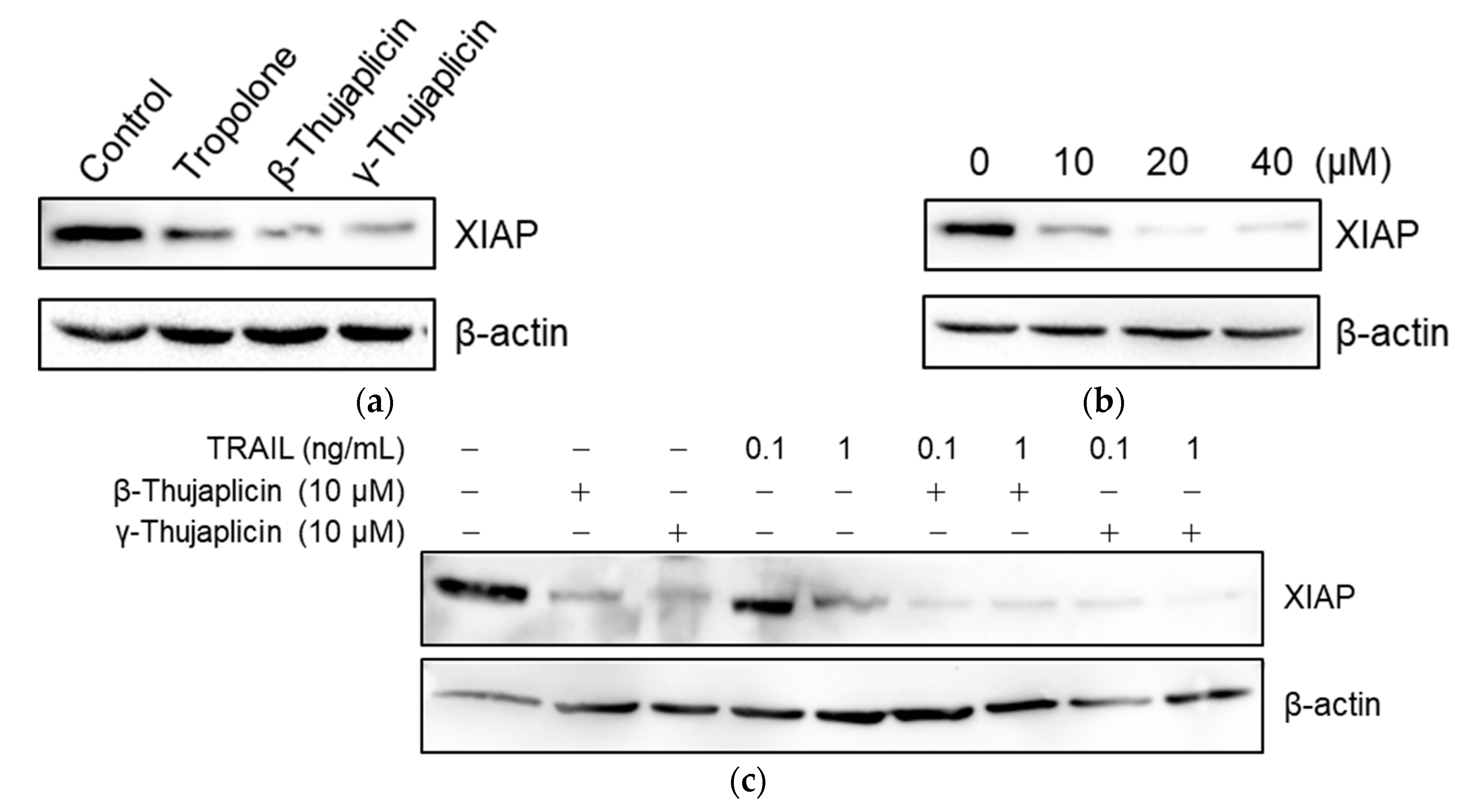
3.5. Tropolone, β-Thujaplicin, and γ-Thujaplicin Treatments Decrease the Amount of XIAP Protein in NCI-H460 Cells
3.6. Tropolone, β-Thujaplicin, and γ-Thujaplicin Inhibit the Binding of the Smac N-Terminal Peptide to the XIAP-BIR3 Domain
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miyamoto, D.; Endo, N.; Oku, N.; Arima, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Suzuki, Y. β-thujaplicin zinc chelate induces apoptosis in mouse high metastatic melanoma B16BL6 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 21, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamori, Y.; Shinohara, S.; Tsujibo, H.; Okabe, T.; Morita, Y.; Sakagami, Y.; Kumeda, Y.; Ishida, N. Antimicrobial activity and metalloprotease inhibition of hinokitiol-related compounds, the constituents of Thujopsis dolabrata S. and Z. hondai MAK. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 22, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotopoulou, T.; Ćirić, A.; Kritsi, E.; Calhelha, R.C.; Ferreira, I.C.; Soković, M.; Zoumpoulakis, P.; Koufaki, M. Antimicrobial/antibiofilm activity and cytotoxic studies of β-Thujaplicin derivatives. Arch. Pharm. 2016, 349, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baya, M.; Soulounganga, P.; Gelhaye, E.; Gérardin, P. Fungicidal activity of β-thujaplicin analogues. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2001, 57, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, D.; Kusagaya, Y.; Endo, N.; Sometani, A.; Takeo, S.; Suzuki, T.; Arima, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Suzuki, Y. Thujaplicin-copper chelates inhibit replication of human influenza viruses. Antivir. Res. 1998, 39, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamori, Y.; Tsujibo, H.; Ohishi, H.; Ishii, F.; Mizugaki, M.; Aso, H.; Ishida, N. Cytotoxic effect of hinokitiol and tropolone on the growth of mammalian cells and on blastogenesis of mouse splenic T cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 16, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yamauchi, H. p27-associated G1 arrest induced by hinokitiol in human malignant melanoma cells is mediated via down-regulation of pRb, Skp2 ubiquitin ligase, and impairment of Cdk2 function. Cancer Lett. 2009, 286, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.H.; Chang, K.W.; Hsia, S.M.; Yu, C.C.; Fuh, L.J.; Chi, T.Y.; Shieh, T.M. In vitro antimicrobial and anticancer potential of hinokitiol against oral pathogens and oral cancer cell lines. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Choi, K.M.; Kim, W.; Jeon, Y.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Hong, J.T.; Yun, Y.P.; Yoo, H.S. Hinokitiol inhibits cell growth through induction of S-phase arrest and apoptosis in human colon cancer cells and suppresses tumor growth in a mouse xenograft experiment. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.H.; Wu, P.; Lee, J.Y.; Li, P.R.; Hsieh, W.Y.; Ho, C.C.; Ho, C.L.; Chen, W.J.; Wang, C.C.; Yen, M.Y.; et al. Hinokitiol induces DNA damage and autophagy followed by cell cycle arrest and senescence in gefitinib-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Wang, B.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, H.T.; Li, J.J.; Hong, G.C.; Hung, Y.C.; Chien, P.J.; Chang, C.Y.; Hsu, L.S.; et al. Hinokitiol up-regulates miR-494-3p to suppress BMI1 expression and inhibits self-renewal of breast cancer stem/progenitor cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 76057–76068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, T.; Liu, C.H.; Wu, G.Y.; Lee, T.Y.; Manubolu, M.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Yang, C.H.; Sheu, J.R. Hinokitiol inhibits migration of A549 lung cancer cells via suppression of MMPs and induction of antioxidant enzymes and apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, J.; Ye, X.; Zhu, J.; Hu, X.; Shen, M.; Ma, Y.; Mao, Z.; Song, H.; Chen, F. β-Thujaplicin induces autophagic cell death, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest through ROS-mediated Akt and p38/ERK MAPK signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckelman, B.P.; Salvesen, G.S.; Scott, F.L. Human inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: Why XIAP is the black sheep of the family. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimmer, A.D.; Dalili, S.; Batey, R.A.; Riedl, S.J. Targeting XIAP for the treatment of malignancy. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluger, H.M.; McCarthy, M.M.; Alvero, A.B.; Sznol, M.; Ariyan, S.; Camp, R.L.; Rimm, D.L.; Mor, G. The X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) is up-regulated in metastatic melanoma, and XIAP cleavage by phenoxodiol is associated with carboplatin sensitization. J. Transl. Med. 2007, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, F.; Luo, Q.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Huang, Y. Inhibition of XIAP increases carboplatin sensitivity in ovarian cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 8751–8759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhov, P.; Golovine, K.; Uzzo, R.G.; Rothman, J.; Crispen, P.L.; Shaw, T.; Scoll, B.J.; Kolenko, V.M. Zinc chelation induces rapid depletion of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis and sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolovska-Coleska, Z.; Xu, L.; Hu, Z.; Tomita, Y.; Li, P.; Roller, P.P.; Wang, R.; Fang, X.; Guo, R.; Zhang, M.; et al. Discovery of embelin as a cell-permeable, small-molecular weight inhibitor of XIAP through structure-based computational screening of a traditional herbal medicine three-dimensional structure database. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Y.; Yue, P.; Zhou, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Choi Kim, H.R.; Lotan, R.; Wu, G.S. Overexpression of BCL2 blocks TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Mashima, T.; Sato, S.; Mochizuki, M.; Sakamoto, H.; Yamori, T.; Oh-hara, T.; Tsuruo, T. Predominant suppression of apoptosome by inhibitor of apoptosis protein in non-small cell lung cancer H460 cells: Therapeutic effect of a novel polyarginine-conjugated Smac peptide. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borisy, A.A.; Elliott, P.J.; Hurst, N.W.; Lee, M.S.; Lehar, J.; Price, E.R.; Serbedzija, G.; Zimmermann, G.R.; Foley, M.A.; Stockwell, B.R.; et al. Systematic discovery of multicomponent therapeutics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7977–7982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotin, L.E.; Gronda, M.; MacLean, N.; Hurren, R.; Wang, X.; Lin, F.H.; Wrana, J.; Datti, A.; Barber, D.L.; Minden, M.D.; et al. Ibrutinib synergizes with poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase inhibitors to induce cell death in AML cells via a BTK-independent mechanism. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 2765–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Manzoni, L.; Gornati, D.; Manzotti, M.; Cairati, S.; Bossi, A.; Arosio, D.; Lecis, D.; Seneci, P. Dual action Smac mimetics–zinc chelators as pro-apoptotic antitumoral agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 4613–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Structure | IC50 (μM) a |
|---|---|---|
| Tropolone | 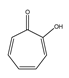 | 83.1 ± 6.9 |
| β-thujaplicin | 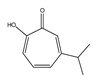 | 58.5 ± 2.8 |
| γ-thujaplicin | 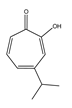 | 56.2 ± 2.9 |
| Embelin |  | 3.1 ± 0.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seno, S.; Kimura, M.; Yashiro, Y.; Kimura, R.; Adachi, K.; Terabayashi, A.; Takahashi, M.; Oyama, T.; Abe, H.; Abe, T.; et al. β-Thujaplicin Enhances TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis via the Dual Effects of XIAP Inhibition and Degradation in NCI-H460 Human Lung Cancer Cells. Medicines 2021, 8, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines8060026
Seno S, Kimura M, Yashiro Y, Kimura R, Adachi K, Terabayashi A, Takahashi M, Oyama T, Abe H, Abe T, et al. β-Thujaplicin Enhances TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis via the Dual Effects of XIAP Inhibition and Degradation in NCI-H460 Human Lung Cancer Cells. Medicines. 2021; 8(6):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines8060026
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeno, Saki, Minori Kimura, Yuki Yashiro, Ryutaro Kimura, Kanae Adachi, Aoi Terabayashi, Mio Takahashi, Takahiro Oyama, Hideaki Abe, Takehiko Abe, and et al. 2021. "β-Thujaplicin Enhances TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis via the Dual Effects of XIAP Inhibition and Degradation in NCI-H460 Human Lung Cancer Cells" Medicines 8, no. 6: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines8060026
APA StyleSeno, S., Kimura, M., Yashiro, Y., Kimura, R., Adachi, K., Terabayashi, A., Takahashi, M., Oyama, T., Abe, H., Abe, T., Tanuma, S.-i., & Takasawa, R. (2021). β-Thujaplicin Enhances TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis via the Dual Effects of XIAP Inhibition and Degradation in NCI-H460 Human Lung Cancer Cells. Medicines, 8(6), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines8060026






