Effects of Systemic Enzyme Supplements on Symptoms and Quality of Life in Patients with Pulmonary Fibrosis—A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Study Design
2.5. Screening and Enrolment
2.6. Dose
2.7. Statistical Analysis
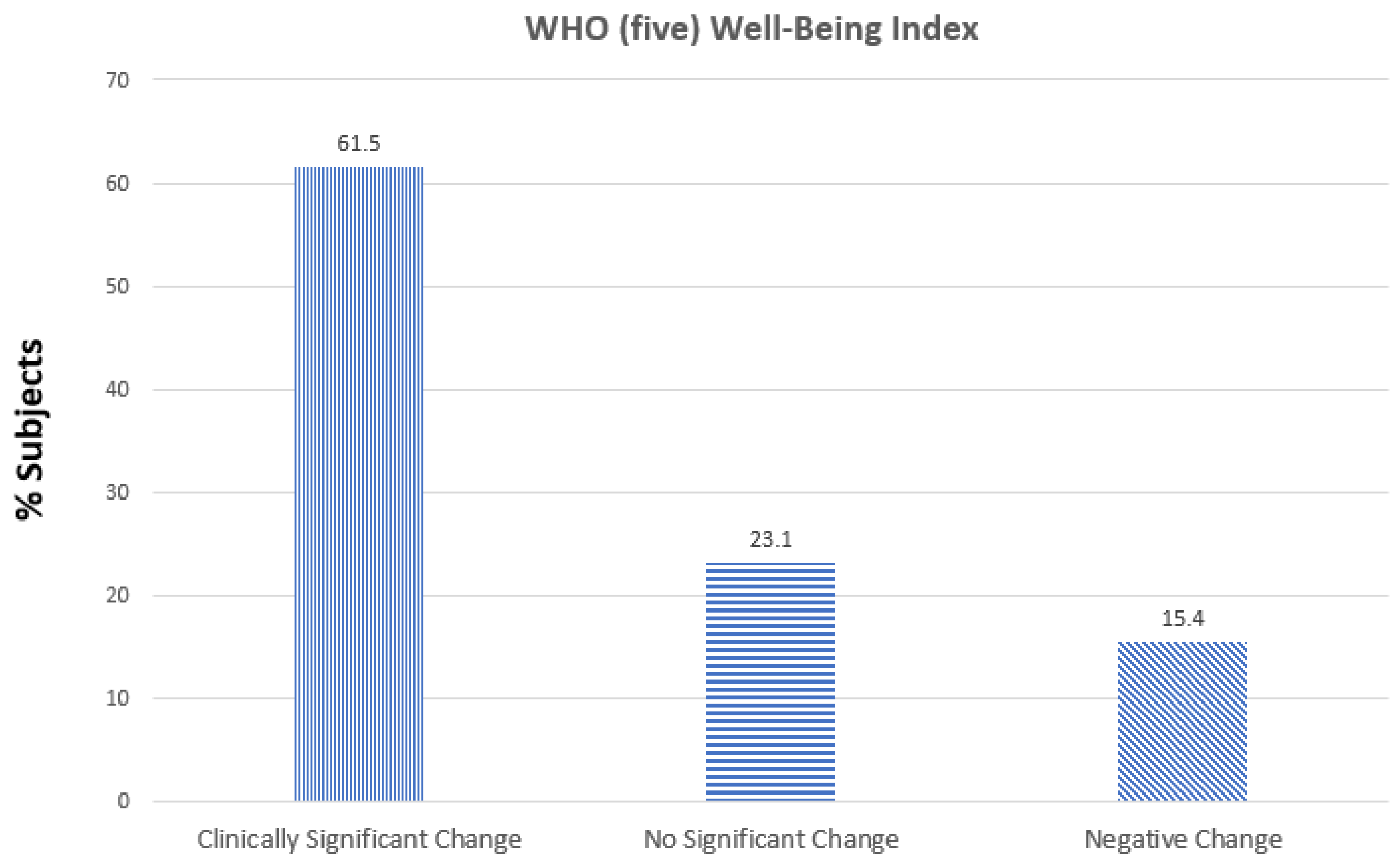
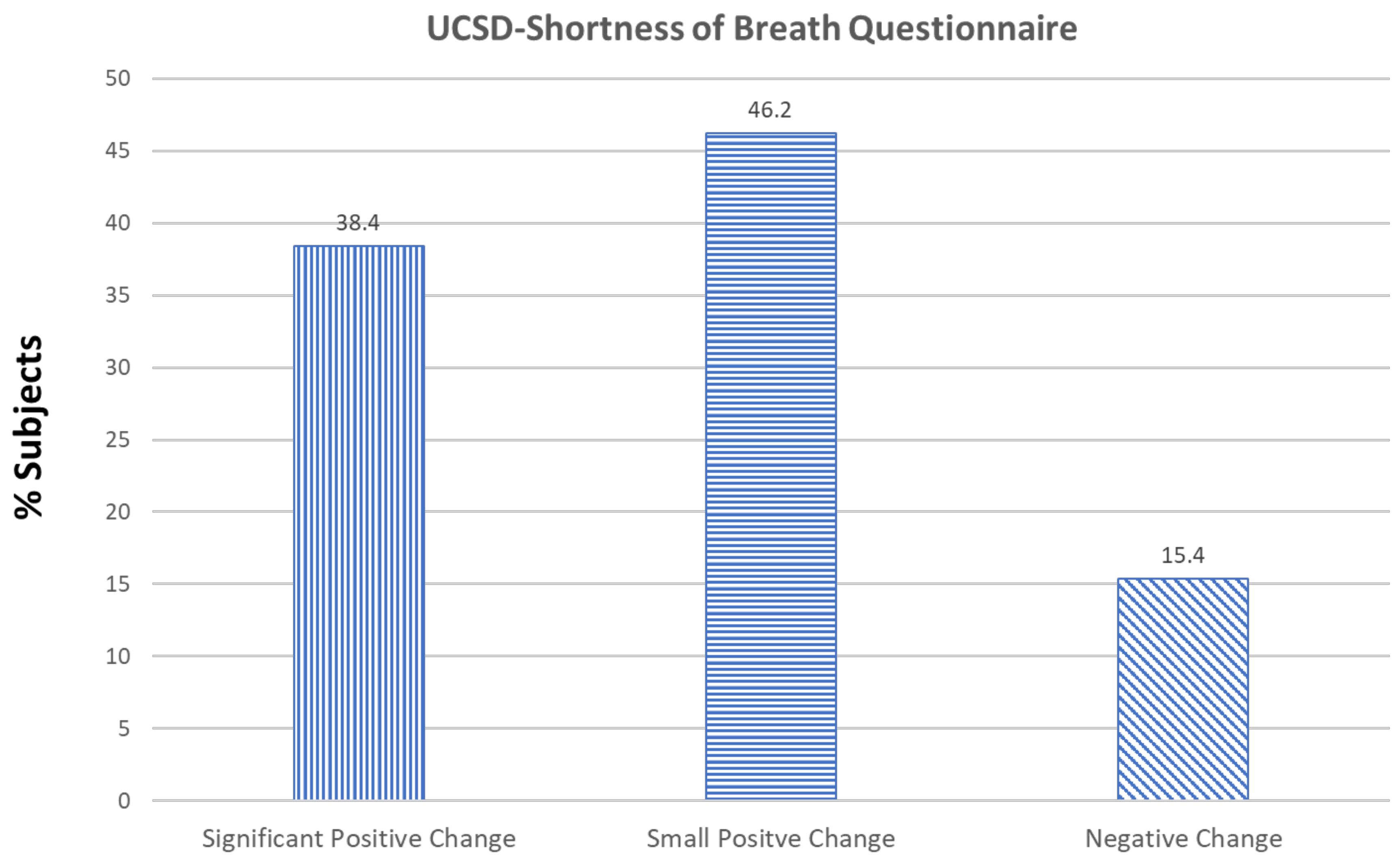
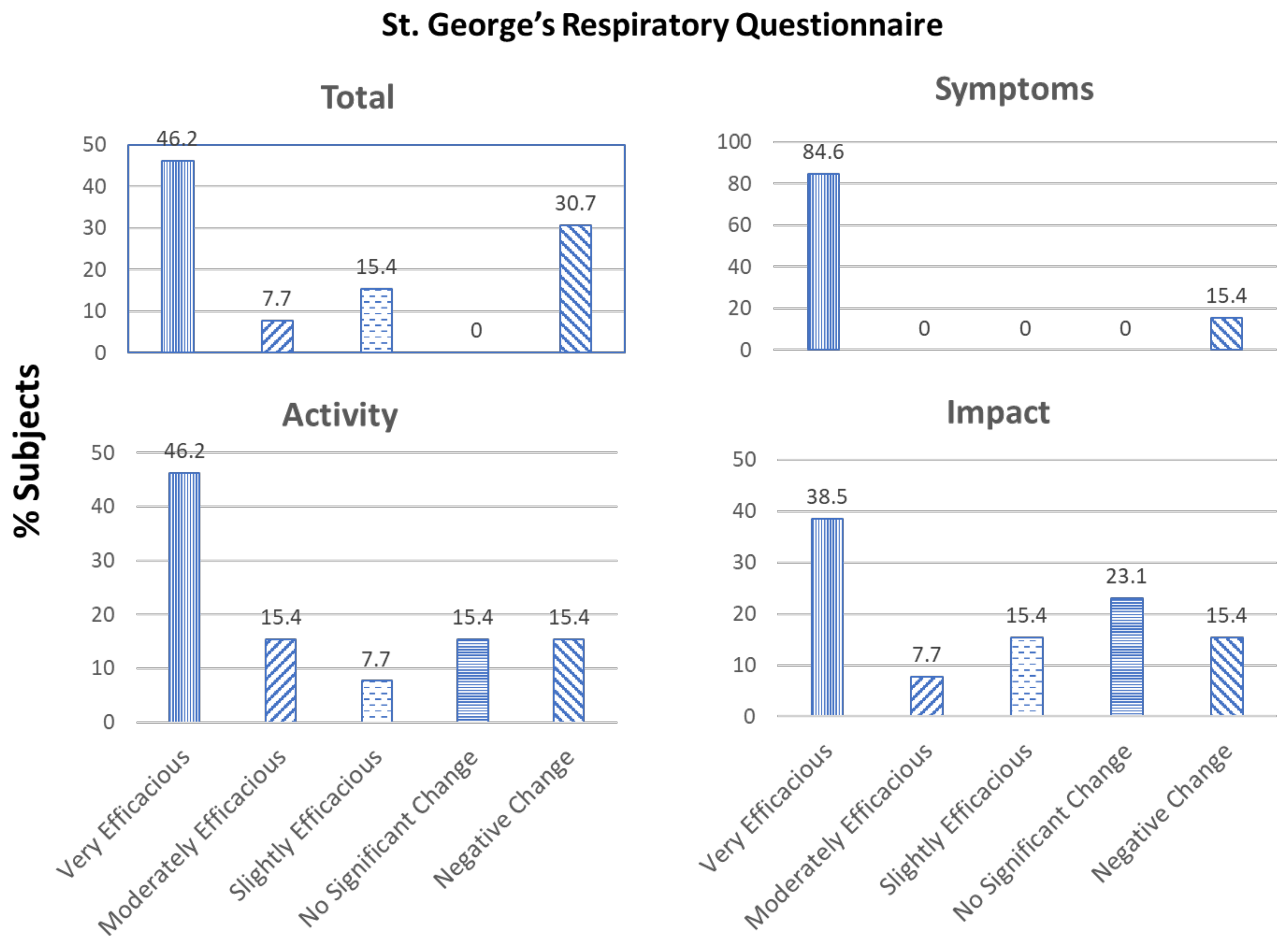
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar]
- Raghu, G.; Rochwerg, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cuello-Garcia, C.; Azuma, A.; Behr, J.; Brozek, J.L.; Collard, H.R.; Cunningham, W.; Homma, S.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline: Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Update of the 2011 Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, e3–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, M.; Luppi, F.; Ferrara, G. What patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and caregivers want: Filling the current gaps with patient reported outcomes and experience measures. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russell, A.-M.; Ripamonti, E.; Vancheri, C. Qualitative European survey of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Patients’ perspectives of the disease and treatment. BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yount, S.E.; Beaumont, J.L.; Chen, S.-Y.; Kaiser, K.; Wortman, K.; Van Brunt, D.L.; Swigris, J.; Cella, D. Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Lung 2016, 194, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomioka, H.; Imanaka, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Iwasaki, H. Health-related Quality of Life in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis -Cross-sectional and Longitudinal Study-. Intern. Med. 2007, 46, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sherry, S.; Fletcher, A.P. Proteolytic enzymes: A therapeutic evaluation. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1960, 19, 202–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, H.; Tsuji, H.; Saeki, K. Anti-inflammatory action of a protease, TSP, produced by Serratia. Folia Pharmacol. Jpn. 1967, 63, 302–314. [Google Scholar]
- Bhagat, S.; Agarwal, M.; Roy, V. Serratiopeptidase: A systematic review of the existing evidence. Int. J. Surg. 2013, 11, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohanasrinivasan, V.; Mohanapriya, A.; Potdar, W.; Chatterji, S.; Konne, S.; Kumari, S.; Devi, C.S. In vitro and in silico studies on fibrinolytic activity of nattokinase: A clot buster from Bacillus sp. Front. Biol. 2017, 12, 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, A.-M.; Sprangers, M.A.G.; Wibberley, S.; Snell, N.; Rose, D.M.; Swigris, J.J. The need for patient-centred clinical research in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonella, F.; Wijsenbeek, M.; Molina-Molina, M.; Duck, A.; Mele, R.; Geissler, K.; Wuyts, W. European IPF patient charter: Unmet needs and a call to action for healthcare policymakers. Eur. Resp. J. 2016, 47, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thickett, D.; Kendall, C.; Spencer, L.; Screaton, N.; A Wallace, W.; Pinnock, H.; Bott, J.; Pigram, L.; Watson, S.; Millar, A.B. Improving care for patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) in the UK: A round table discussion. Thorax 2014, 69, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FDA. Guidance for Industry Patient-Reported Outcome Measures: Use in Medical Product Development to Support Labeling Claims. 2009. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/77832/download (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Devlin, N.J.; Parkin, D.; Browne, J. Patient-reported outcome measures in the NHS: New methods for analysing and reporting EQ-5D data. Health Econ. 2010, 19, 886–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, E.; Orwelius, L.; Kristenson, M. Patient-reported outcomes in the Swedish National Quality Registers. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 279, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, G.; Luppi, F.; Birring, S.S.; Cerri, S.; Caminati, A.; Sköld, M.; Kreuter, M. Best supportive care for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Current gaps and future directions. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 170076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO (Five) Well-Being Index (WHO-5)|SNAP-Ed. Available online: usda.gov (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.thoracic.org/members/assemblies/assemblies/srn/questionaires/sobq.php (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Available online: https://www.thoracic.org/members/assemblies/assemblies/srn/questionaires/sgrq.php (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Jones, P.W.; Quirk, F.H.; Baveystock, C.M. The St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire. Respir Med. 1991, 85 (Suppl. B), 25–31, discussion 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, C.W.; Østergaard, S.D.; Søndergaard, S.; Bech, P. The WHO-5 Well-Being Index: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Psychother. Psychosom. 2015, 84, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Choi, S.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Choon-Taek, L.; Yoon, H.I.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, C.-T.; Park, J.S. Clinical impact of depression and anxiety in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gries, K.S.; Esser, D.; Wiklund, I. Content Validity of CASA-Q Cough Domains and UCSD-SOBQ for Use in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2013, 5, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swigris, J.J.; Han, M.; Vij, R.; Noth, I.; Eisenstein, E.L.; Anstrom, K.J.; Brown, K.K.; Fairclough, D. The UCSD shortness of breath questionnaire has longitudinal construct validity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jadhav, S.B.; Shah, N.; Rathi, A.; Rathi, V.; Rathi, A. Serratiopeptidase: Insights into the therapeutic applications. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 28, e00544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Hashimoto, Y.; Mikami, M.; Yamanaka, E.; Soma, T.; Hino, M.; Azuma, A.; Kudoh, S. Effect of the proteolytic enzyme serrapeptase in patients with chronic airway disease. Respirology 2003, 8, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Y.; Yao, J.; Sparks, S.; Wang, K.Y. Nattokinase: An Oral Antithrombotic Agent for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Required Study Procedure | Screening (Day-14 to Day-1) | Day 0 (Baseline/Registration) | Days from Registration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 36 | Day 64 | Day 92 | Day 100 | |||
| Informed Consent Form | √ | |||||
| HIPAA Authorization | √ | |||||
| Intake Form (demographics, disease severity, comorbidities) | √ | |||||
| UCSD-SOB (approx. 7 minutes to complete) | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| SGRQ (approx. 9 minutes to complete) | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| WHO-5 (approx. 2 minutes to complete) | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Supplement Intake * | Daily, Starting day1 | |||||
| Medication Log | Daily, Starting day1 | |||||
| Follow-up | √ | |||||
| Directions: Take on an Empty Stomach (45 min before a Meal or 2 h after a Meal, with a Glass of Water) | |
|---|---|
| Step 1 (Days 1–4) | Take 1 capsule Settacor-NK, 3 times a day Due to the body not being accustomed to systemic enzyme therapy, it is important to start at a minimal dosage and increase as needed. Minor symptoms of intestinal cleansing may occur. |
| Step 2 (Days 5–8) | Take 2 capsule Settacor-NK, 3 times a day At this point, your body should be completed with the cleaning stage and becoming more accustomed to systemic enzyme therapy. |
| Step 3 (Days 9–92) | Take 2 capsule Settacor-NK + 1 capsule Serra Rx, 3 times a day This is what we believe to be the therapeutic dosage. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shah, N. Effects of Systemic Enzyme Supplements on Symptoms and Quality of Life in Patients with Pulmonary Fibrosis—A Pilot Study. Medicines 2021, 8, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines8110068
Shah N. Effects of Systemic Enzyme Supplements on Symptoms and Quality of Life in Patients with Pulmonary Fibrosis—A Pilot Study. Medicines. 2021; 8(11):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines8110068
Chicago/Turabian StyleShah, Neha. 2021. "Effects of Systemic Enzyme Supplements on Symptoms and Quality of Life in Patients with Pulmonary Fibrosis—A Pilot Study" Medicines 8, no. 11: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines8110068
APA StyleShah, N. (2021). Effects of Systemic Enzyme Supplements on Symptoms and Quality of Life in Patients with Pulmonary Fibrosis—A Pilot Study. Medicines, 8(11), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines8110068






