Methylxanthines Inhibit Primary Amine Oxidase and Monoamine Oxidase Activities of Human Adipose Tissue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Subjects and Preparation of Adipose Samples
2.3. Benzylamine Oxidation by Human Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue (ScAT)
2.4. Methylamine, Tyramine, and Methylxanthine Oxidation by Human ScAT
2.5. Solubilization of Methylxanthines
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Influence of Methylxanthines, Amine Oxidase Substrates, and Inhibitors on Fluorimetric Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide
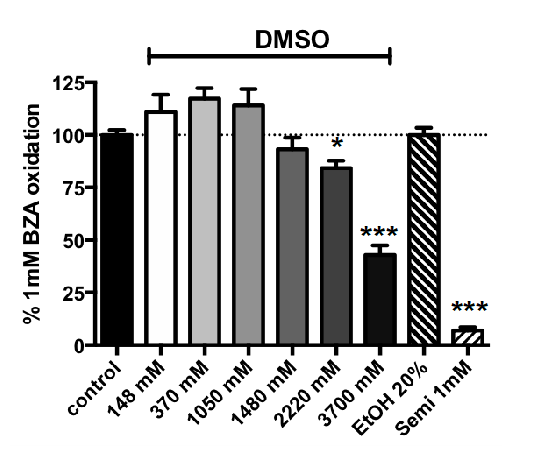
3.2. Influence of Increasing Doses of Vehicles on Primary Amine Oxidase Activity in Human ScAT
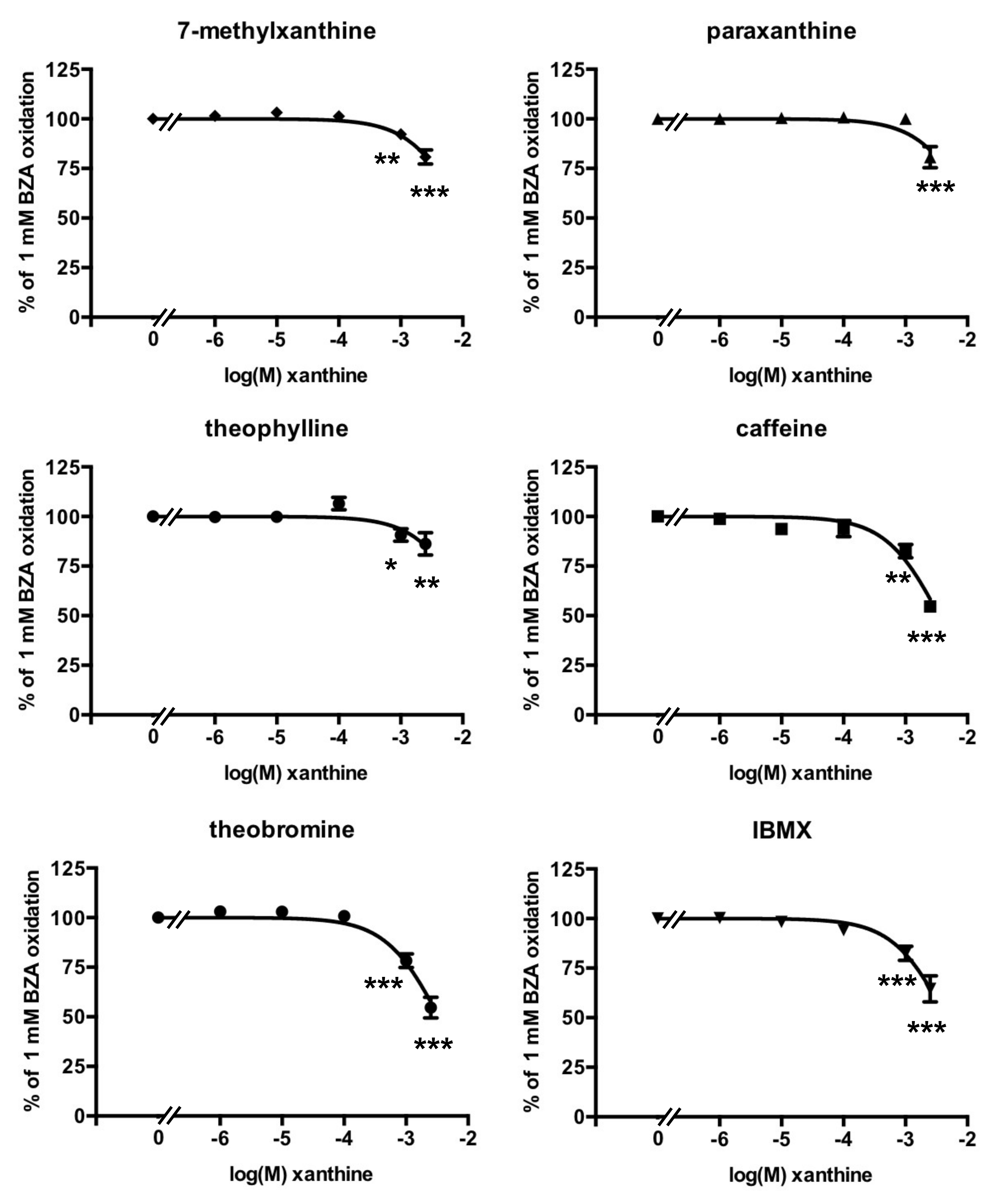
3.3. Methylxanthine-Induced Inhibition of Benzylamine Oxidation in Human Adipose Tissue
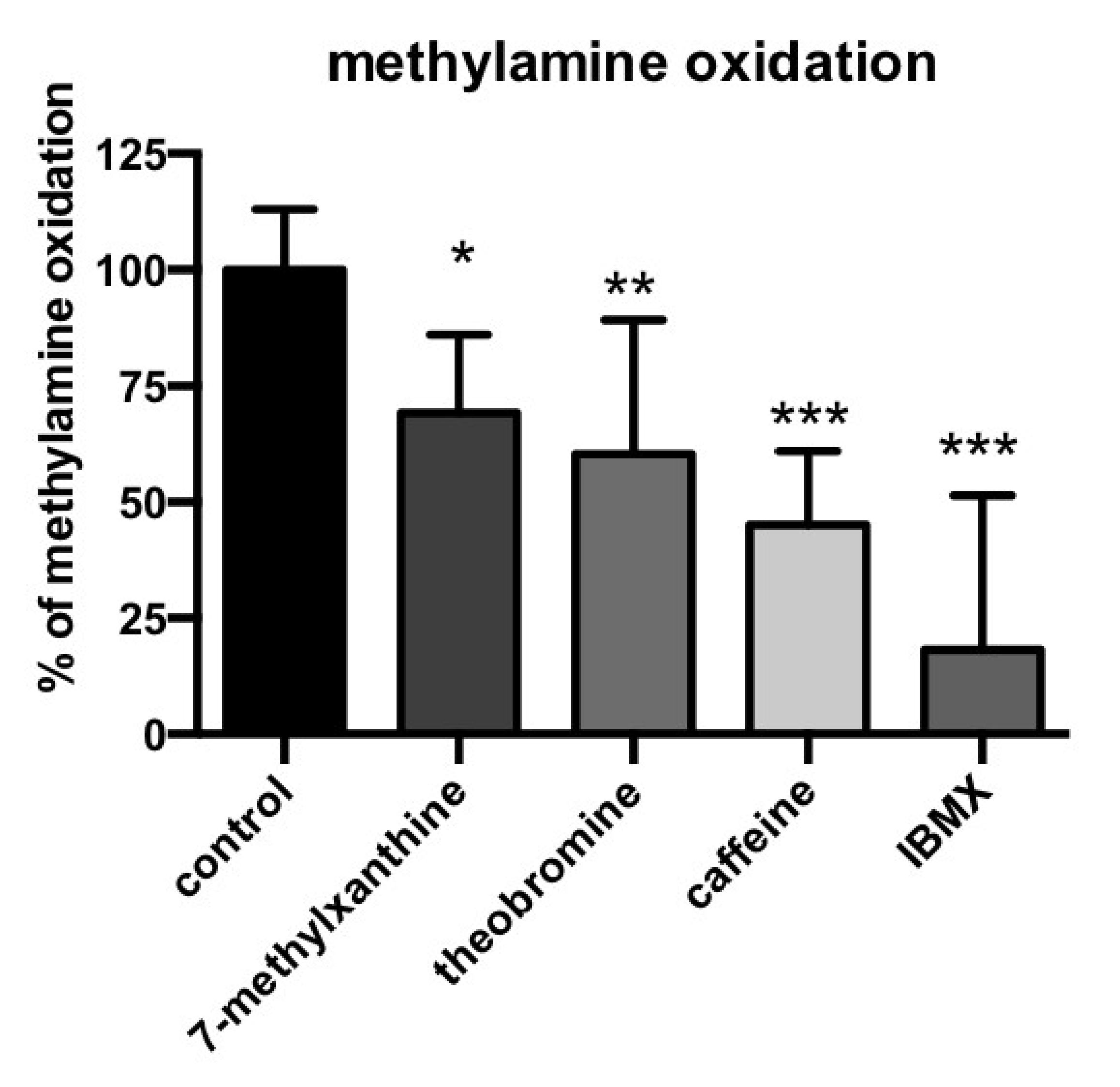
3.4. Methylxanthine-Induced Inhibition of Methylamine Oxidation by Human Adipose Tissue
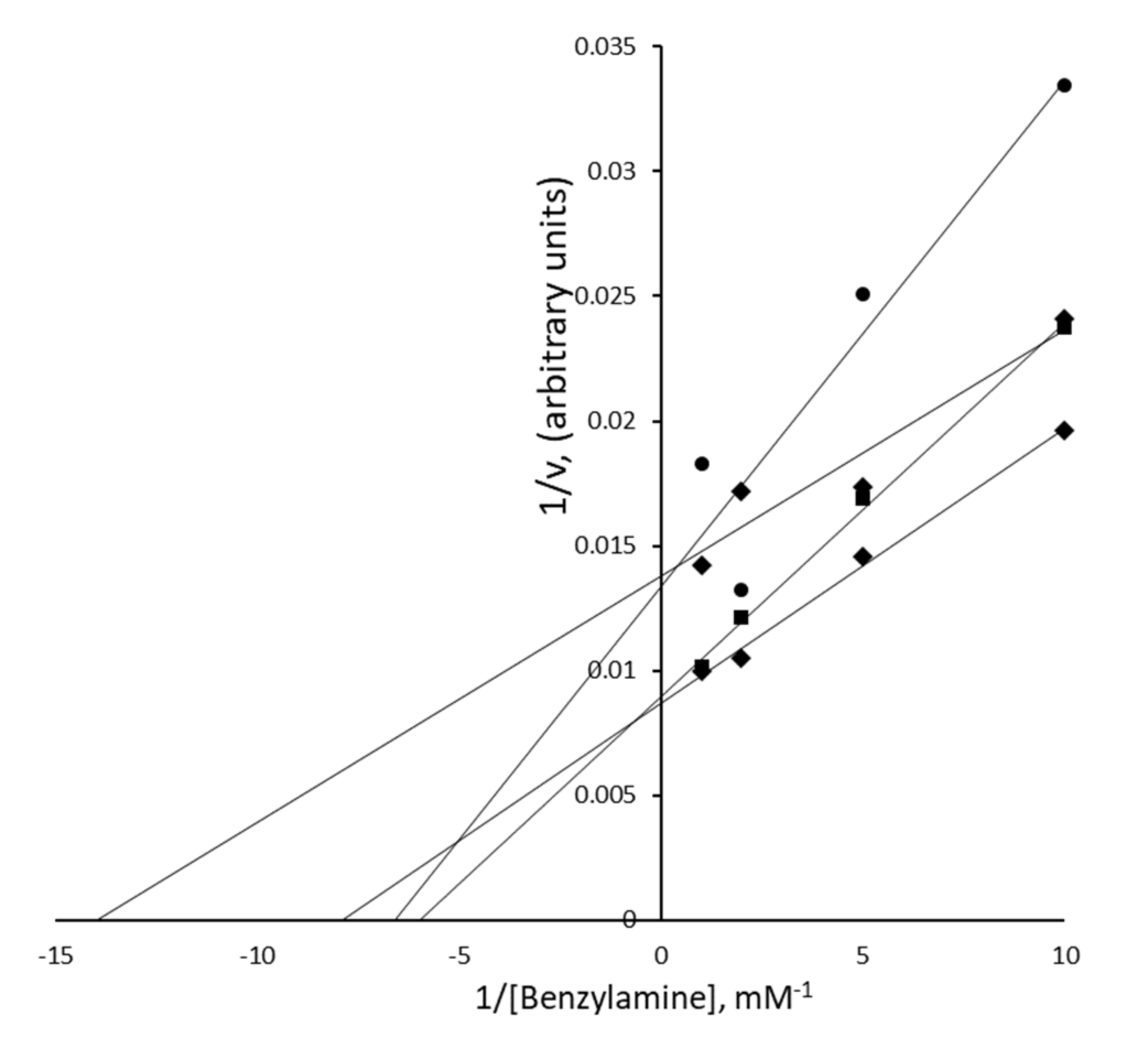
3.5. Nature of the PrAO Inhibition Induced by Methylxanthines in Human Adipose Tissue
3.6. Tyramine Oxidation by Human Adipose Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lorist, M.M.; Tops, M. Caffeine, fatigue, and cognition. Brain Cogn. 2003, 53, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.; Onatibia-Astibia, A.; Martinez-Pinilla, E. Health benefits of methylxanthines in cacao and chocolate. Nutrients 2013, 5, 4159–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, J.; Mitchell, E.S. More than just caffeine: Psychopharmacology of methylxanthine interactions with plant-derived phytochemicals. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 89, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.F.; Chern, Y. Impacts of methylxanthines and adenosine receptors on neurodegeneration: Human and experimental studies. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2011, 200, 267–310. [Google Scholar]
- Nehlig, A. Effects of coffee/caffeine on brain health and disease: What should I tell my patients? Pract. Neurol. 2016, 16, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horrobin, D.F.; Manku, M.S.; Franks, D.J.; Hamet, P. Theophylline and bronchospasm. N. Engl. J. Med. 1977, 297, 1181. [Google Scholar]
- Picano, E.; Lattanzi, F.; Masini, M.; Distante, A.; L’Abbate, A. Aminophylline termination of dipyridamole stress as a trigger of coronary vasospasm in variant angina. Am. J. Cardiol. 1988, 62, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horrigan, L.A.; Kelly, J.P.; Connor, T.J. Immunomodulatory effects of caffeine: Friend or foe? Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 111, 877–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaditis, A.G.; Winnie, G.; Syrogiannopoulos, G.A. Anti-inflammatory pharmacotherapy for wheezing in preschool children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2007, 42, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilley, S.L. Methylxanthines in asthma. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2011, 200, 439–456. [Google Scholar]
- Talmon, M.; Massara, E.; Brunini, C.; Fresu, L.G. Comparison of anti-inflammatory mechanisms between doxofylline and theophylline in human monocytes. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 59, 101851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanahan, P.; O’Sullivan, J.; Tipton, K.F.; Kinsella, G.K.; Ryan, B.J.; Henehan, G.T.M. Theobromine and related methylxanthines as inhibitors of Primary Amine Oxidase. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 43, e12697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwelberger, H.G. Structural organization of mammalian copper-containing amine oxidase genes. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59 (Suppl. 2), S223–S225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes de Carvalho, L.; Bligt-Linden, E.; Ramaiah, A.; Johnson, M.S.; Salminen, T.A. Evolution and functional classification of mammalian copper amine oxidases. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 139, 106571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmi, M.; Jalkanen, S. Vascular Adhesion Protein-1: A Cell Surface Amine Oxidase in Translation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 314–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter-Cid, L.M.; Wang, E.; O’Rourke, A.M.; Miller, A.; Gao, H.; Huang, L.; Garcia, A.; Linnik, M.D. Anti-inflammatory effects of inhibiting the amine oxidase activity of semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkel, P.; Balogh, B.; Meleddu, R.; Maccioni, E.; Gyires, K.; Matyus, P. Semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase/vascular adhesion protein-1: A patent survey. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2011, 21, 1453–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpéné, C.; Boulet, N.; Chaplin, A.; Mercader, J. Past, Present and Future Anti-Obesity Effects of Flavin-Containing and/or Copper-Containing Amine Oxidase Inhibitors. Medicines (Basel) 2019, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercader, J.; Iffiu-Soltesz, Z.; Bour, S.; Carpéné, C. Oral administration of semicarbazide limits weight gain together with inhibition of fat deposition and of primary amine oxidase activity in adipose tissue. J. Obes. 2011, 2011, 475786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulloo, A.G.; Miller, D.S. Thermogenic drugs for the treatment of obesity: Sympathetic stimulants in animal models. Br. J. Nutr. 1984, 52, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabayashi, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Ashida, H.; Nishiumi, S.; Kanazawa, K. Inhibitory effects of caffeine and its metabolites on intracellular lipid accumulation in murine 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biofactors 2008, 34, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulloo, A.G.; Seydoux, J.; Girardier, L. Potentiation of the thermogenic antiobesity effects of ephedrine by dietary methylxanthines: Adenosine antagonism or phosphodiesterase inhibition? Metabolism 1992, 41, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foot, J.S.; Deodhar, M.; Turner, C.I.; Yin, P.; van Dam, E.M.; Silva, D.G.; Olivieri, A.; Holt, A.; McDonald, I.A. The discovery and development of selective 3-fluoro-4-aryloxyallylamine inhibitors of the amine oxidase activity of semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase/vascular adhesion protein-1 (SSAO/VAP-1). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3935–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Tian, H.; Wang, W.; Ru, S. Semicarbazide disturbs the reproductive system of male zebrafish (Danio rerio) through the GABAergic system. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maranghi, F.; Tassinari, R.; Marcoccia, D.; Altieri, I.; Catone, T.; De Angelis, G.; Testai, E.; Mastrangelo, S.; Evandri, M.G.; Bolle, P.; et al. The food contaminant semicarbazide acts as an endocrine disrupter: Evidence from an integrated in vivo/in vitro approach. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 183, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, A.; Rico, D.; Khiari, Z.; Henehan, G.; O’Sullivan, J.; Tipton, K. From caffeine to fish waste: Amine compounds present in food and drugs and their interactions with primary amine oxidase. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2011, 118, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.H.; Wertz, D.L.; Klinman, J.P. Implication for functions of the ectopic adipocyte copper amine oxidase (AOC3) from purified enzyme and cell-based kinetic studies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpéné, C.; Les, F.; Hasnaoui, M.; Biron, S.; Marceau, P.; Richard, D.; Galitzky, J.; Joanisse, D.R.; Mauriège, P. Anatomical distribution of primary amine oxidase activity in four adipose depots and plasma of severely obese women with or without a dysmetabolic profile. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 73, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzinat, N.; Marti, L.; Remaury, A.; Leger, F.; Langin, D.; Lafontan, M.; Carpéné, C.; Parini, A. High expression of monoamine oxidases in human white adipose tissue: Evidence for their involvement in noradrenaline clearance. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzer, A.; Pienaar, A.; Petzer, J.P. The interactions of caffeine with monoamine oxidase. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Panchuk-Voloshina, N. A one-step fluorometric method for the continuous measurement of monoamine oxidase activity. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 253, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Les, F.; Deleruyelle, S.; Cassagnes, L.E.; Boutin, J.A.; Balogh, B.; Arbones-Mainar, J.M.; Biron, S.; Marceau, P.; Richard, D.; Nepveu, F.; et al. Piceatannol and resveratrol share inhibitory effects on hydrogen peroxide release, monoamine oxidase and lipogenic activities in adipose tissue, but differ in their antilipolytic properties. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 258, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentin, V.; Prevot, D.; De Saint Front, V.D.; Morin-Cussac, N.; Thalamas, C.; Galitzky, J.; Valet, P.; Zorzano, A.; Carpéné, C. Alteration of amine oxidase activity in the adipose tissue of obese subjects. Obes. Res. 2004, 12, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizcano, J.M.; Tipton, K.F.; Unzeta, M. Purification and characterization of membrane-bound semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO) from bovine lung. Biochem. J. 1998, 331, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamakumbura, A.H.; Trackman, P.C. A fluorometric assay for detection of lysyl oxidase enzyme activity in biological samples. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 300, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, A.; Palcic, M.M. A peroxidase-coupled continuous absorbance plate-reader assay for flavin monoamine oxidases, copper-containing amine oxidases and related enzymes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2498–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Tang, N.; Asadzadeh, B.; Yan, W. Measurement and correlation of solubility of Theobromine, Theophylline, and Caffeine in water and organic solvents at various temperatures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2017, 62, 2570–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, J.A.; Perkins, E.G. Determination of uric acid in biological fluids by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 88, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, A.; Wieland, B.; Baker, G.B. Allosteric modulation of semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase activities in vitro by imidazoline receptor ligands. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elovaara, H.; Kidron, H.; Parkash, V.; Nymalm, Y.; Bligt, E.; Ollikka, P.; Smith, D.J.; Pihlavisto, M.; Salmi, M.; Jalkanen, S.; et al. Identification of two imidazole binding sites and key residues for substrate specificity in human primary amine oxidase AOC3. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 5507–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, M.; Kumar, R.; Fazili, Z.; Spiegelhalder, B.; Preussmann, R. Increased exposure to dietary amines and nitrate in a population at high risk of oesophageal and gastric cancer in Kashmir (India). Carcinogenesis 1992, 13, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precious, E.; Gunn, C.E.; Lyles, G.A. Deamination of methylamine by semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase in human umbilical artery and rat aorta. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1988, 37, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpéné, C.; Mauriège, P.; Boulet, N.; Biron, S.; Grolleau, J.L.; Garcia-Barrado, M.J.; Iglesias-Osma, M.C. Methylamine Activates Glucose Uptake in Human Adipocytes Without Overpassing Action of Insulin or Stimulating its Secretion in Pancreatic Islets. Medicines (Basel) 2019, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, A.; Tipton, K. Inhibition of bovine plasma semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase by caffeine. J. Biochem. Molec. Toxicol. 2011, 25, 26–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elovaara, H.; Parkash, V.; Fair-Mäkelä, R.; Salo-Ahen, O.M.H.; Guédez, G.; Bligt-Lindén, E.; Grönholm, J.; Jalkanen, S.; Salminen, T.A. Multivalent Interactions of Human Primary Amine Oxidase with the V and C22 Domains of Sialic Acid-Binding Immunoglobulin-Like Lectin-9 Regulate Its Binding and Amine Oxidase Activity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, A.; Smith, D.J.; Cendron, L.; Zanotti, G.; Rigo, A.; Di Paolo, M.L. Multiple binding sites for substrates and modulators of semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidases: Kinetic consequences. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, P.; Kunduzova, O.; Masini, E.; Cambon, C.; Bani, D.; Raimondi, L.; Seguelas, M.H.; Nistri, S.; Colucci, W.; Leducq, N.; et al. Oxidative stress by monoamine oxidase mediates receptor-independent cardiomyocyte apoptosis by serotonin and postischemic myocardial injury. Circulation 2005, 112, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.H.; Wei, J.N.; Yang, C.Y.; Ou, H.Y.; Wu, H.T.; Fan, K.C.; Wang, S.H.; Hua, C.H.; Hsiao, C.H.; Lee, M.K.; et al. Serum vascular adhesion protein-1 is up-regulated in hyperglycemia and is associated with incident diabetes negatively. Int. J. Obes. (Lond) 2018, 43, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Zorita, S.; Treguer, K.; Mercader, J.; Carpéné, C. Resveratrol directly affects in vitro lipolysis and glucose transport in human fat cells. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 69, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Yang, Z.D.; Shi, D.F.; Yao, X.J.; Wang, M.G. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase by Stilbenes from Rheum palmatum. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2016, 15, 885–892. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.Y.; Wang, C.C.; Lu, Y.L.; Wu, W.C.; Hou, W.C. Antioxidant, anti-semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase, and anti-hypertensive activities of geraniin isolated from Phyllanthus urinaria. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, P.; Malik, N.; Khatkar, A. Lead optimization for promising monoamine oxidase inhibitor from eugenol for the treatment of neurological disorder: Synthesis and in silico based study. BMC Chem. 2019, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, J.P.; Alves, M.G.; Oliveira, P.F.; Silva, B.M. Structure-Bioactivity Relationships of Methylxanthines: Trying to Make Sense of All the Promises and the Drawbacks. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2016, 21, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, A.; Tipton, K.F.; O’Sullivan, J. Characterization of the in vitro binding and inhibition kinetics of primary amine oxidase/vascular adhesion protein-1 by glucosamine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Les, F.; Iffiu-Soltesz, Z.; Mercader, J.; Carpéné, C. Tyramine activates lipid accumulation in rat adipocytes: Influences of in vitro and in vivo administration. AIMS Molec. Sci. 2017, 4, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papukashvili, D.; Rcheulishvili, N.; Deng, Y. Attenuation of Weight Gain and Prevention of Associated Pathologies by Inhibiting SSAO. Nutrients 2020, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentin, V.; Prevot, D.; Marti, L.; Carpéné, C. Inhibition of rat fat cell lipolysis by monoamine oxidase and semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase substrates. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 466, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercader, J.; Wanecq, E.; Chen, J.; Carpéné, C. Isopropylnorsynephrine is a stronger lipolytic agent in human adipocytes than synephrine and other amines present in Citrus aurantium. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 67, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga-Gross, A.L.; Esquivel, P. Impact of Cocoa Products Intake on Plasma and Urine Metabolites: A Review of Targeted and Non-Targeted Studies in Humans. Nutrients 2019, 1, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badshah, H.; Ikram, M.; Ali, W.; Ahmad, S.; Hahm, J.R.; Kim, M.O. Caffeine May Abrogate LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation by Regulating Nrf2/TLR4 in Adult Mouse Brains. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janitschke, D.; Nelke, C.; Lauer, A.A.; Regner, L.; Winkler, J.; Thiel, A.; Grimm, H.S.; Hartmann, T.; Grimm, M.O.W. Effect of Caffeine and Other Methylxanthines on Aβ-Homeostasis in SH-SY5Y Cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y. Distribution and accumulation of caffeine in rat tissues and its inhibition on semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
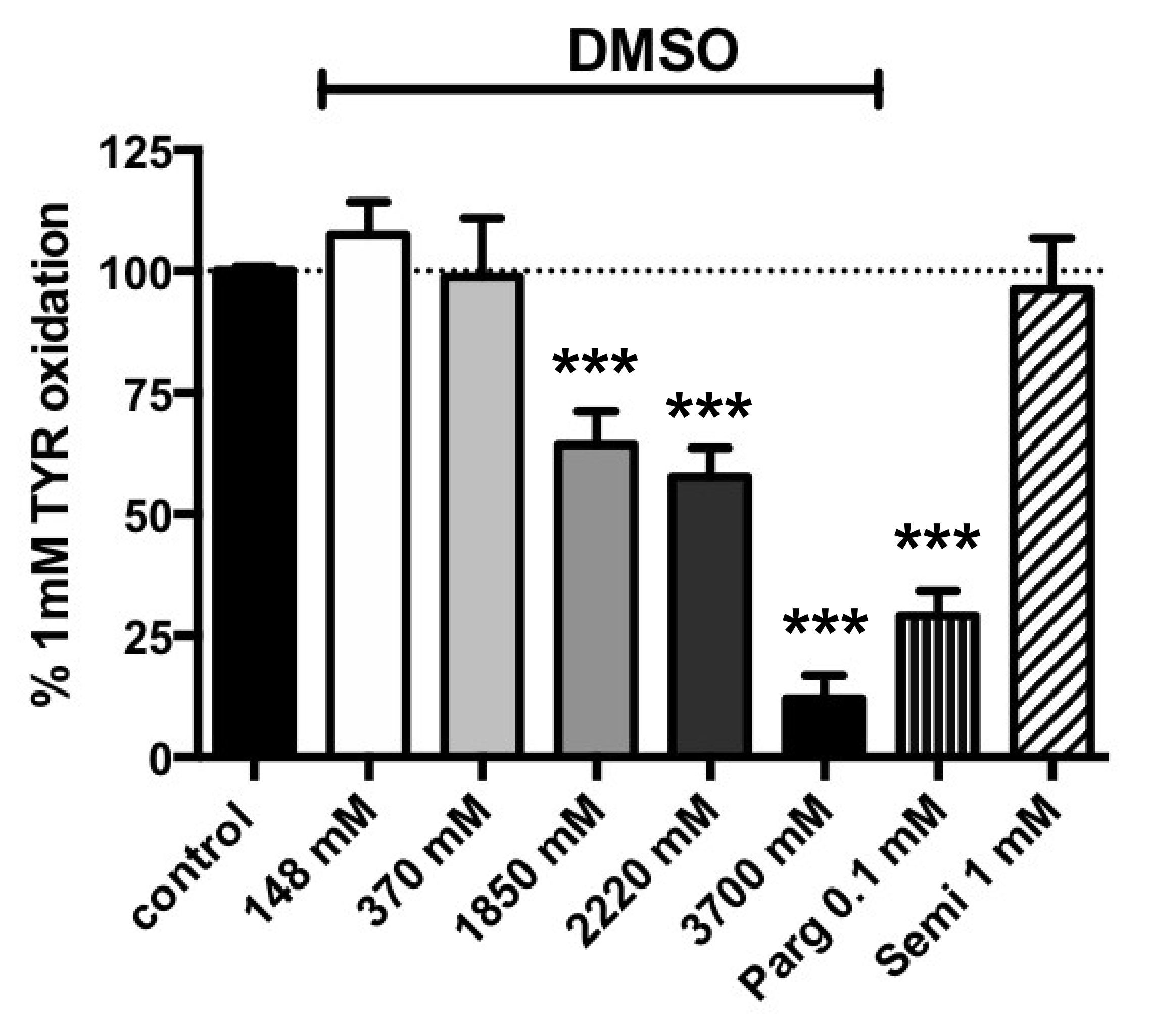
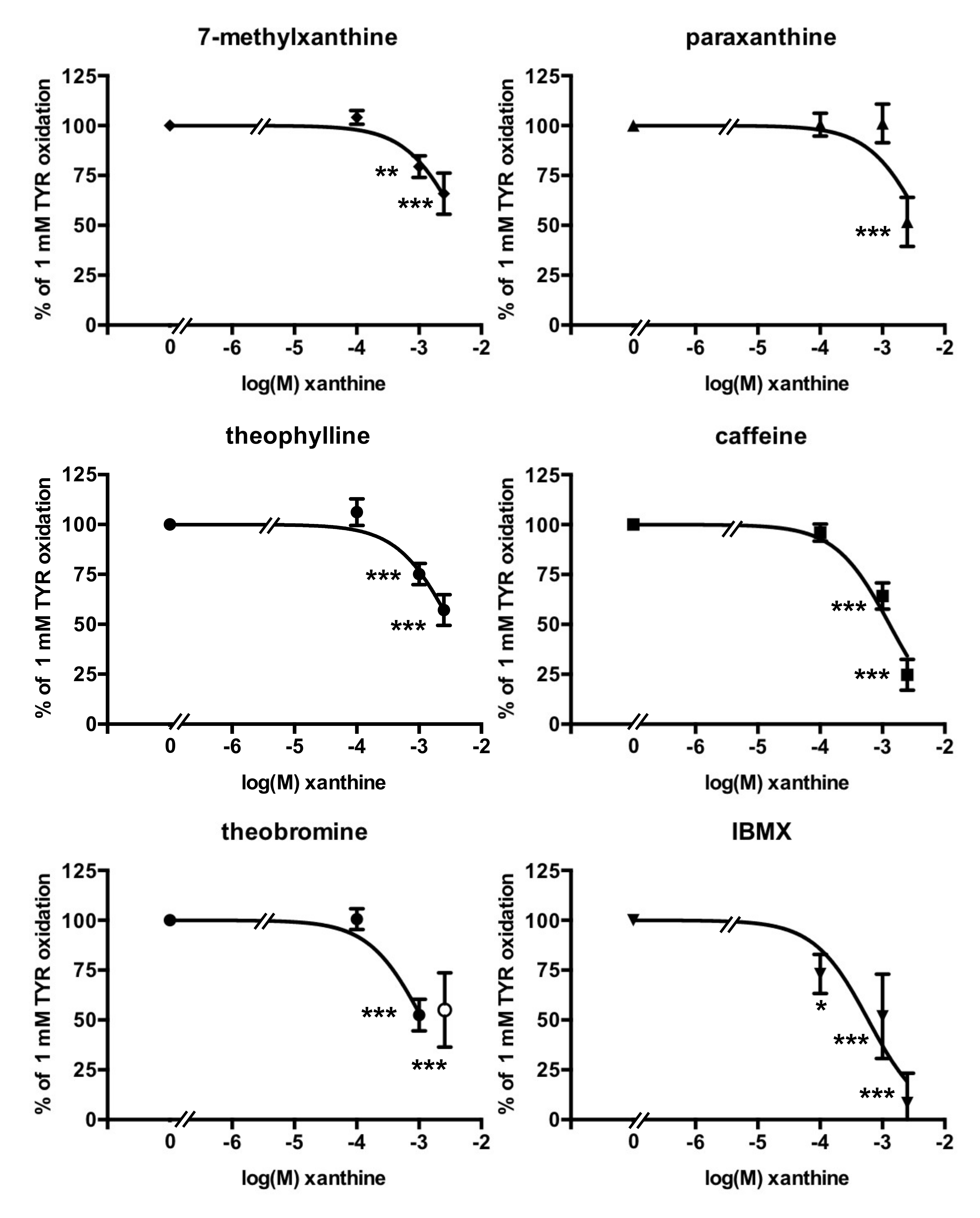
| Condition | Percentage of Tyramine Oxidation |
|---|---|
| Tyramine 1 mM | 100% reference |
| Tyramine 0.2 mM | 76.9 ± 4.6 (9) NS |
| Tyramine 0.1 mM | 63.3 ± 6.1 (17) |
| Tyr 0.1 mM + semicarbazide 1 mM | 65.2 ± 7.8 (4) NS |
| Tyr 0.1 mM + DMSO 148 mM | 52.2 ± 5.8 (10) NS |
| Tyr 0.1 mM + theophylline 1 mM | 28.8 ± 5.0 (15) *** |
| Tyr 0.1 mM + theobromine 1 mM | 27.6 ± 8.2 (11) *** |
| Tyr 0.1 mM + caffeine 1 mM | 26.7 ± 8.3 (9) *** |
| Tyr 0.1 mM + 7-methylxanthine 1 mM | 25.1 ± 2.8 (10) *** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haj Ahmed, W.; Peiro, C.; Fontaine, J.; Ryan, B.J.; Kinsella, G.K.; O’Sullivan, J.; Grolleau, J.-L.; Henehan, G.T.M.; Carpéné, C. Methylxanthines Inhibit Primary Amine Oxidase and Monoamine Oxidase Activities of Human Adipose Tissue. Medicines 2020, 7, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines7040018
Haj Ahmed W, Peiro C, Fontaine J, Ryan BJ, Kinsella GK, O’Sullivan J, Grolleau J-L, Henehan GTM, Carpéné C. Methylxanthines Inhibit Primary Amine Oxidase and Monoamine Oxidase Activities of Human Adipose Tissue. Medicines. 2020; 7(4):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines7040018
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaj Ahmed, Wiem, Cécile Peiro, Jessica Fontaine, Barry J. Ryan, Gemma K. Kinsella, Jeff O’Sullivan, Jean-Louis Grolleau, Gary T.M. Henehan, and Christian Carpéné. 2020. "Methylxanthines Inhibit Primary Amine Oxidase and Monoamine Oxidase Activities of Human Adipose Tissue" Medicines 7, no. 4: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines7040018
APA StyleHaj Ahmed, W., Peiro, C., Fontaine, J., Ryan, B. J., Kinsella, G. K., O’Sullivan, J., Grolleau, J.-L., Henehan, G. T. M., & Carpéné, C. (2020). Methylxanthines Inhibit Primary Amine Oxidase and Monoamine Oxidase Activities of Human Adipose Tissue. Medicines, 7(4), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines7040018






