Insecticide Exposure and Risk of Asthmatic Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Searching Strategy
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Search Study
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Insecticide Exposure and Possible Risk of Asthmatic Symptoms
3.4. Meta-Analysis of Exposure to Insecticides and Asthma Disease
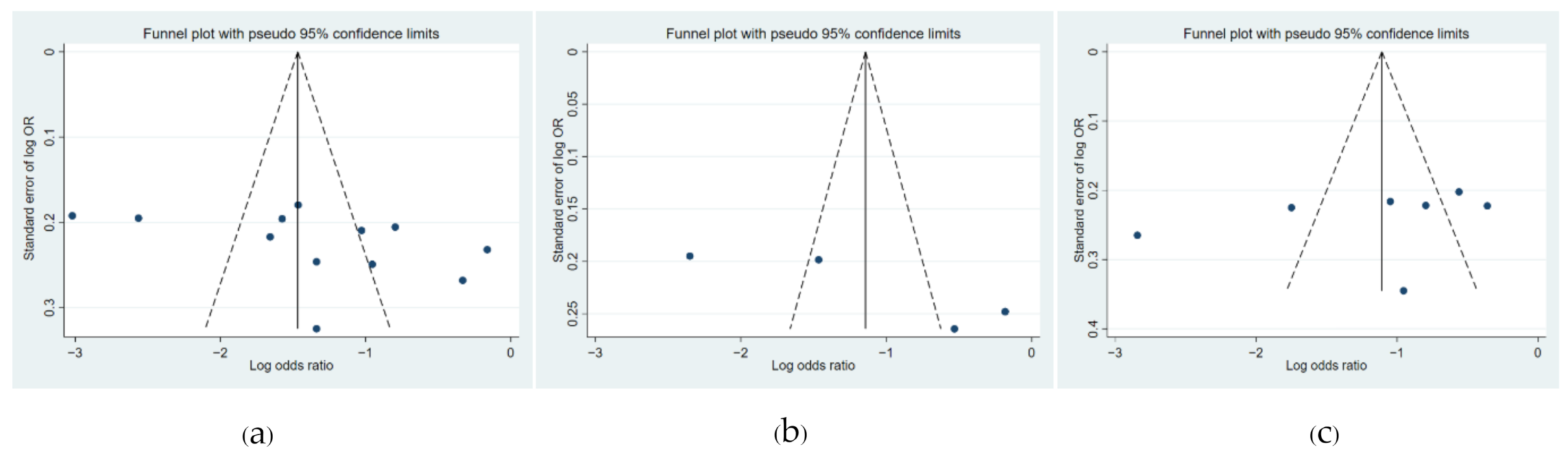
3.5. Funnel Plot
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ratiu, I.A.; Ligor, T.; Bocos-Bintintan, V.; Mayhew, C.A.; Buszewski, B. Volatile Organic Compounds in Exhaled Breath as Fingerprints of Lung Cancer, Asthma and COPD. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Chronic Respiratory Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/chronic-respiratory-diseases#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Kuruvilla, M.E.; Vanijcharoenkarn, K.; Shih, J.A.; Lee, F.E. Epidemiology and risk factors for asthma. Respir. Med. 2019, 149, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolote, J.M.; Fleischmann, A.; Butchart, A.; Besbelli, N. Suicide, suicide attempts and spesticides: A major hidden public health problem. Bull. World Health Organ. 2006, 84, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, I.C.; Devi, N.L. Pesticides Classification and Its Impact on Human and Environment; Studium Press LLC: Houston, TX, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ligor, M.; Bukowska, M.; Ratiu, I.A.; Gadzala-Kopciuch, R.; Buszewski, B. Determination of Neonicotinoids in Honey Samples Originated from Poland and Other World Countries. Molecules 2020, 25, 5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akashe, M.M.; Pawade, U.C.; Nikam, A.V. Classification of pesticides: A review. Int. J. Res. Ayurveda Pharm. 2018, 9, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Mavi, G.K.; Raghav, S. Pesticides Classification and its Impact on Environment. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 1889–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolopoulou-Stamati, P.; Maipas, S.; Kotampasi, C.; Stamatis, P.; Hens, L. Chemical Pesticides and Human Health: The Urgent Need for a New Concept in Agriculture. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ratiu, I.A.; Beldean-Galea, M.S.; Bocos-Bintintan, V.; Costea, D. Priority Pollutants Present in the Tisza River Hydrographic Basin and their Effectcts on Living Organisms. Jordan J. Chem. 2018, 13, 85–99. [Google Scholar]
- Gangemi, S.; Miozzi, E.; Teodoro, M.; Briguglio, G.; De Luca, A.; Alibrando, C.; Polito, I.; Libra, M. Occupational exposure to pesticides as a possible risk factor for the development of chronic diseases in humans (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 4475–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eskenazi, B.; Bradman, A.; Castorina, R. Exposures of children to organophosphate pesticides and their potential adverse health effects. Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, M.; Beach, J.; Martin, J.W.; Senthilselvan, A. Occupational Pesticide Exposures and Respiratory Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 6442–6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damalas, C.A.; Koutroubas, S.D. Farmers’ Exposure to Pesticides: Toxicity Types and Ways of Prevention. Toxics 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez, A.F.; Parron, T.; Alarcon, R. Pesticides, and asthma. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 11, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Criollo, S.; Palma, M.; Monroy-Garcia, A.A.; Idrovo, A.J.; Combariza, D.; Varona-Uribe, M.E. Chronic pesticide mixture exposure including paraquat and respiratory outcomes among Colombian farmers. Ind. Health 2020, 58, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faria, N.M.X.; Facchinib, L.A.; Fassab, A.G.; Tomasic, E. Pesticides and respiratory symptoms among farmers. Rev. Saude Publica 2005, 39, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senthilselvan, A.; Mcduffie, H.H.; Dosman, J.A. Association of asthma with use of pesticides. Results of a cross-sectional survey of farmers. Am. Rev. Respir Dis. 1992, 146, 884–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppin, J.A.; Umbach, D.M.; London, S.J.; Henneberger, P.K.; Kullman, G.J.; Coble, J.; Alavanja, M.C.; Freeman, L.E.B.; Sandler, D.P. Pesticide use and adult-onset asthma among male farmers in the Agricultural Health Study. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, N.; Beach, J.; Senthilselvan, A.; Burstyn, I. Pesticide Use and Asthma in Alberta Grain Farmers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, O.; Syamlal, G.; Henneberger, P.K.; Alarcon, W.A.; Mazurek, J.M. Pesticide use, allergic rhinitis, and asthma among US farm operators. J. Agromed. 2018, 23, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, J.; Sladden, T.; Morgan, G.; Berry, G.; Brooks, L.; McMichael, A. Health impacts of pesticide exposure in a cohort of outdoor workers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoecklin-Marois, M.T.; Bigham, C.W.; Bennett, D.; Tancredi, D.J.; Schenker, M.B. Occupational exposures and migration factors associated with respiratory health in California Latino farm workers: The MICASA study. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2015, 57, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, A.J.C.; Robinson, L.B.; Downing, N.L.; Camargo, C.A., Jr. Occupational exposures and asthma prevalence among US farmworkers: National Agricultural Workers Survey, 2003–2014. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 2135–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, E.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Moon, E.K.; Kim, Y.B.; Lee, Y.J.; Jeong, W.C.; Cho, E.Y.; Lee, I.J.; Hur, J.; Ha, M.; et al. Paraquat application and respiratory health effects among South Korean farmers. Occup. Environ. Med. 2012, 69, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarmure, S.; Alexescu, T.G.; Orasan, O.; Negrean, V.; Sitar-Taut, A.V.; Coste, S.C.; Todea, D.A. Influence of pesticides on respiratory pathology-a literature review. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2020, 27, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Huang, Q.; Lu, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Zong, M.; Tao, L. The organophosphate insecticide chlorpyrifos confers its genotoxic effects by inducing DNA damage and cell apoptosis. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapbamrer, R. Pesticide and Health Effects, 1st ed.; O.S. Printing House: Boangkok, Thailand, 2013; pp. 37–136. [Google Scholar]
- Shaffo, F.C.; Grodzki, A.C.; Fryer, A.D.; Lein, P.J. Mechanisms of organophosphorus pesticide toxicity in the context of airway hyperreactivity and asthma. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2018, 315, L485–L501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami-Mohajeri, S.; Abdollahi, M. Toxic influence of organophosphate, carbamate, and organochlorine pesticides on cellular metabolism of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates: A systematic review. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 1119–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lein, P.J.; Fryer, A.D. Organophosphorus insecticides induce airway hyperreactivity by decreasing neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor function independent of acetylcholinesterase inhibition. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 83, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gosens, R.; Zaagsma, J.; Meurs, H.; Halayko, A.J. Muscarinic receptor signaling in the pathophysiology of asthma and COPD. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veronesi, B.; Oortgiesen, M. Neurogenic inflammation, and particulate matter (PM) air pollutants. Neurotoxicology 2001, 22, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.S.; Moon, H. The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2010, 2, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdollahi, M.; Ranjbar, A.; Shadnia, S.; Nikfar, S.; Rezaie, A. Pesticides and oxidative stress: A review. Med. Sci. Monit. 2004, 10, RA141–RA147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kehrer, J.P.; Klotz, L.O. Free radicals and related reactive species as mediators of tissue injury and disease: Implications for Health. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2015, 45, 765–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spickett, D.M.; Pitt, A.R. Protein oxidation: Role in signalling and detection by mass spectrometry. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
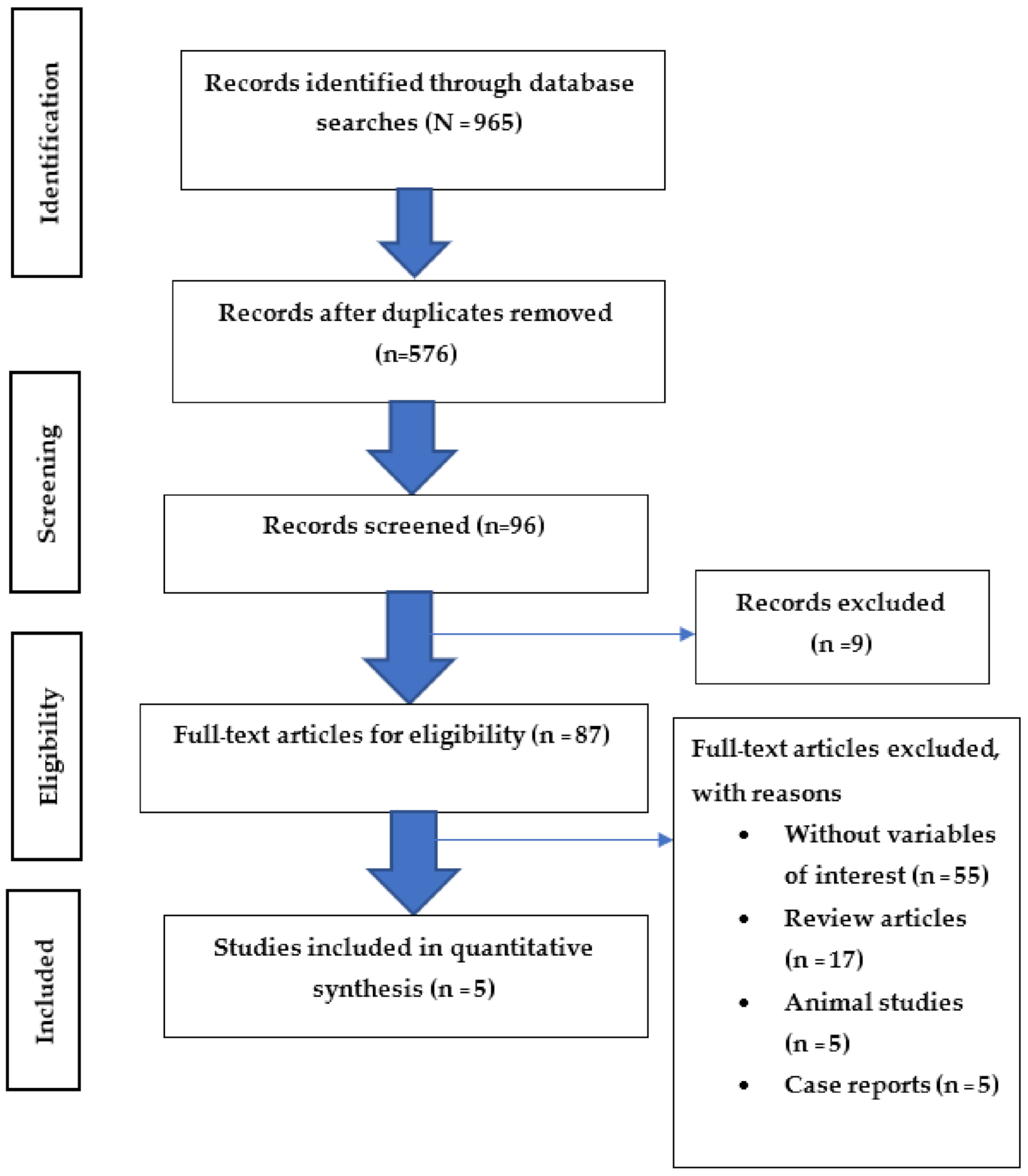
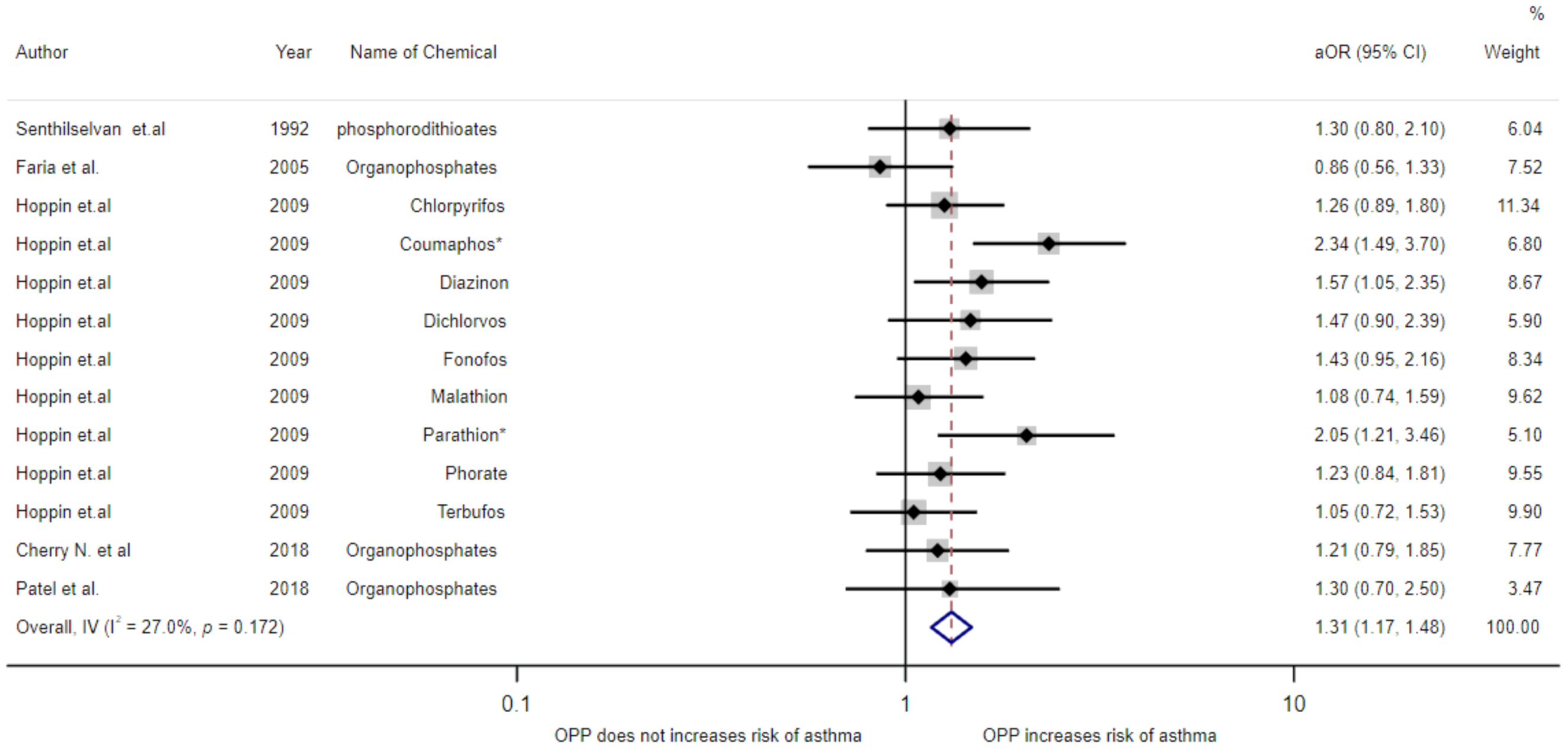
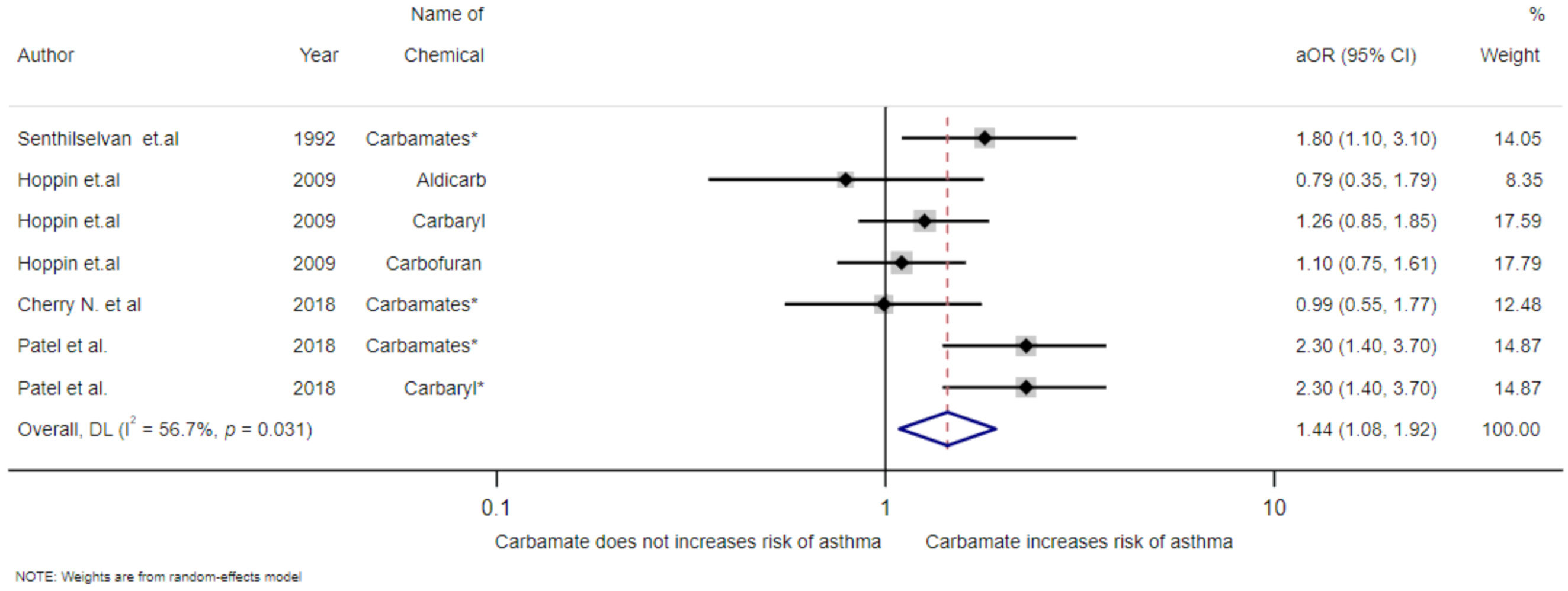
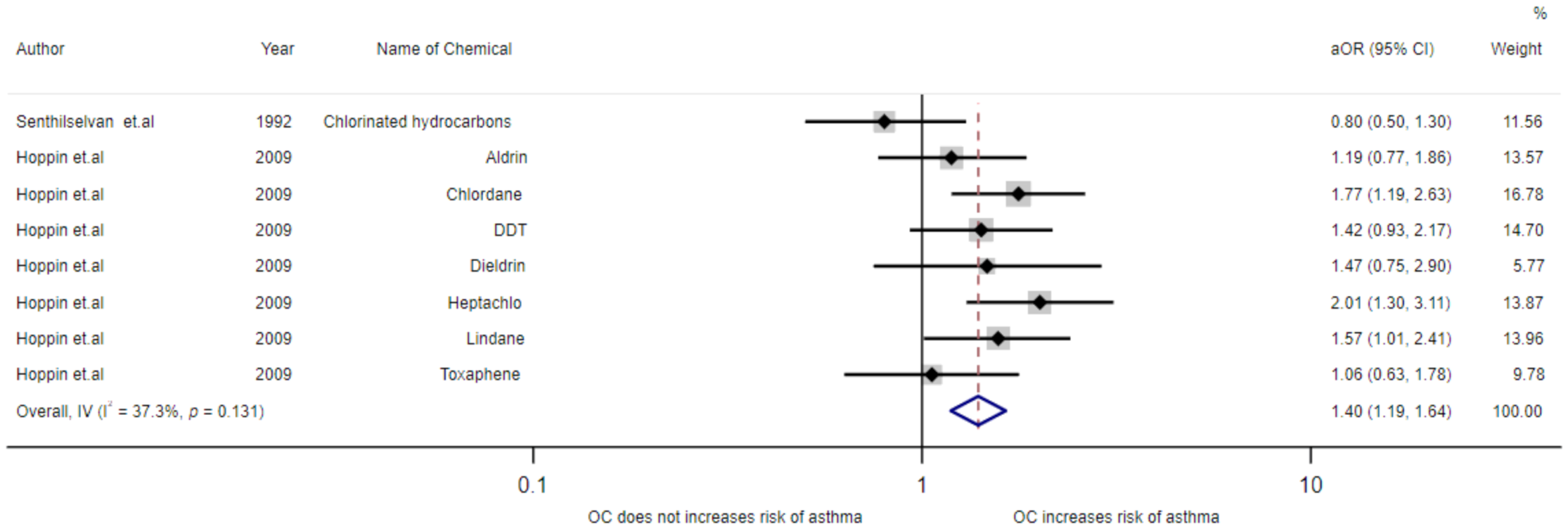
| Authors (Years)/ Country | Study Design | Age Mean ± SD (Years) | Gender | Sample Size | Length of Work | Diagnosis of Asthma | Name of Chemical | Adjusted OR (95%CI) | Confounding Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senthilselvan et al. (1992)/Canada [18] | Cross-sectional | 45.2 ± 15.6 | Both genders | 2375 | - | Self-report | Phosphorodithioates | 1.3(0.8–2.1) | Age, height, weight, smoking pack-years |
| Faria et al. (2005)/Brazil [17] | Cross-sectional | 42 ± 15.6 | Both genders | 1379 | - | Self-report | Organophosphates | 0.86(0.56–1.33) | Sex, age, schooling, marital status, smoking, socioeconomic indicators, agricultural production, exposure to dust, industrial rations, years of chemical exposure |
| Hoppin et al. (2009)/USA [19] | Cohort | - | Male | 19,704 | ≥31 years | Use genitive in doctor’s diagnosis | Chlorpyrifos Coumaphos Diazinon Dichlorvos Fonofos Malathion Parathion Phorate Terbufos | 1.26(0.89–1.80) 2.34(1.49–3.70) 1.57(1.05–2.35) 1.47(0.90–2.39) 1.43(0.95–2.16) 1.08(0.74–1.59) 2.05(1.21–3.46) 1.23(0.84–1.81) 1.05(0.72–1.53) | Age, smoking, state, high pesticide exposure events, and BMI |
| Cherry et al. (2018)/ Canada [20] | Cohort | - | Male | 10,767 | 0–≥35 years | Self-report | Organophosphates | 1.21(0.79–1.85) | Sex, age, smoking, work state now, exposure to pesticide in last month, ever had symptoms of pesticide poisoning, doctor has said you have allergies, doctor has said you have asthma |
| Patel et al. (2018)/USA [21] | Cross-sectional | - | Both gender | 11,210 | - | Self-report | Organophosphates | 1.3(0.7–2.5) | Sex and region |
| Authors (Years)/ Country | Study Design | Age (Mean ± SD) (Years) | Gender | Sample Size | Length of Work | Diagnosis of Asthma | Name of Chemical | Adjusted OR (95%CI) | Confounding Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senthilselvan et al. (1992)/Canada [18] | Cross-sectional | 45.2 ± 15.6 | Both genders | 2375 | - | Self-report | Carbamates | 1.8(1.1–3.1) | Age, height, weight, pack-years |
| Hoppin et al. (2009)/USA [19] | Cohort | - | Male | 19,704 | ≥31 years | Use genitive in doctor’s diagnosis | Aldicarb Carbaryl Carbofuran | 0.79(0.35–1.79) 1.26(0.85–1.85) 1.10(0.75–1.61) | Age, smoking, state, high pesticide exposure events, and BMI |
| Cherry et al. (2018)/ Canada [20] | Cohort | - | Male | 10,767 | 0- ≥35 years | Self-report | Carbamates | 0.99(0.55–1.77) | Sex, age, smoking, work state now, exposure to pesticide in last month, ever had symptoms of pesticide poisoning, doctor has said you have allergies, doctor has said you have asthma |
| Patel et al. (2018)/USA [21] | Cross-sectional | - | Both gender | 11,210 | - | Self-report | Carbamates Carbaryl | 2.3(1.4–3.7) 2.3(1.4–3.7) | Sex and region |
| Authors (Years)/ Country | Study Design | Age (Mean ± SD) (Years) | Gender | Sample Size | Length of Work | Diagnosis of Asthma | Name of Chemical | Adjusted OR (95%CI) | Confounding Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senthilselvan et al. (1992)/Canada [18] | Cross-sectional | 45.2 ± 15.6 | Both genders | 2375 | - | Self-report | Chlorinated hydrocarbons | 0.8(0.5–1.3) | Age, height, weight, pack-years |
| Hoppin et al. (2009)/USA [19] | Cohort | - | Male | 19,704 | ≥31 years | Use genitive in doctor’s diagnosis | Aldrin Chlordane DDT Dieldrin Heptachlor Lindane Toxaphene | 1.19(0.77–1.86) 1.77(1.19–2.63) 1.42(0.93–2.17) 1.47(0.75–2.90) 2.01(1.30–3.11) 1.57(1.01–2.41) 1.06(0.63–1.78) | Age, smoking, state, high pesticide exposure events, and BMI |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chittrakul, J.; Sapbamrer, R.; Sirikul, W. Insecticide Exposure and Risk of Asthmatic Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Toxics 2021, 9, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9090228
Chittrakul J, Sapbamrer R, Sirikul W. Insecticide Exposure and Risk of Asthmatic Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Toxics. 2021; 9(9):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9090228
Chicago/Turabian StyleChittrakul, Jiraporn, Ratana Sapbamrer, and Wachiranun Sirikul. 2021. "Insecticide Exposure and Risk of Asthmatic Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Toxics 9, no. 9: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9090228
APA StyleChittrakul, J., Sapbamrer, R., & Sirikul, W. (2021). Insecticide Exposure and Risk of Asthmatic Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Toxics, 9(9), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics9090228







