Differential Toxicity of Ionic Silver and Silver Nanoparticles: A Meta-Analysis of Ecotoxicological Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria for Meta-Analysis
- The primary screening criterion was based on study type and language. Studies not written in English were excluded, as were encyclopedias, reviews, conference abstracts, book chapters, and abstracts of articles that were not available in full. All years for which the database was searchable (1945–2024) were included. So, this criterion ensured the inclusion of studies that were methodologically reliable and accessible for full-text evaluation, improving the transparency and reproducibility of the screening process.
- The secondary exclusion criterion is based on the methodology of research studies. Studies showing the toxicity of nano and ionic silver on the same species in the same study were included. This allowed for a comparative assessment of toxicity differences within the same biological context. Including studies that assessed both forms within the same biological context allowed for a more controlled and meaningful comparison of ionic versus nanoparticulate silver toxicity, addressing potential confounding factors.
- The third criterion of exclusion is related to the units of the results. The study included toxicity value and effective concentration dose–response curves. Additionally, studies lacking standard deviation values in toxicity results were excluded. This criterion is essential for the reliability of effect size calculations to be used in statistical analysis. Requiring compatible units on data and the presence of standard deviation ensured that effect sizes could be calculated accurately, which is essential for maintaining the statistical validity of the meta-analysis.
2.2. Data Extraction and Coding
2.3. Meta-Analysis
2.3.1. Heterogeneity Testing and Model Selection
2.3.2. Subgroup Analysis
2.3.3. Publication Bias
3. Results
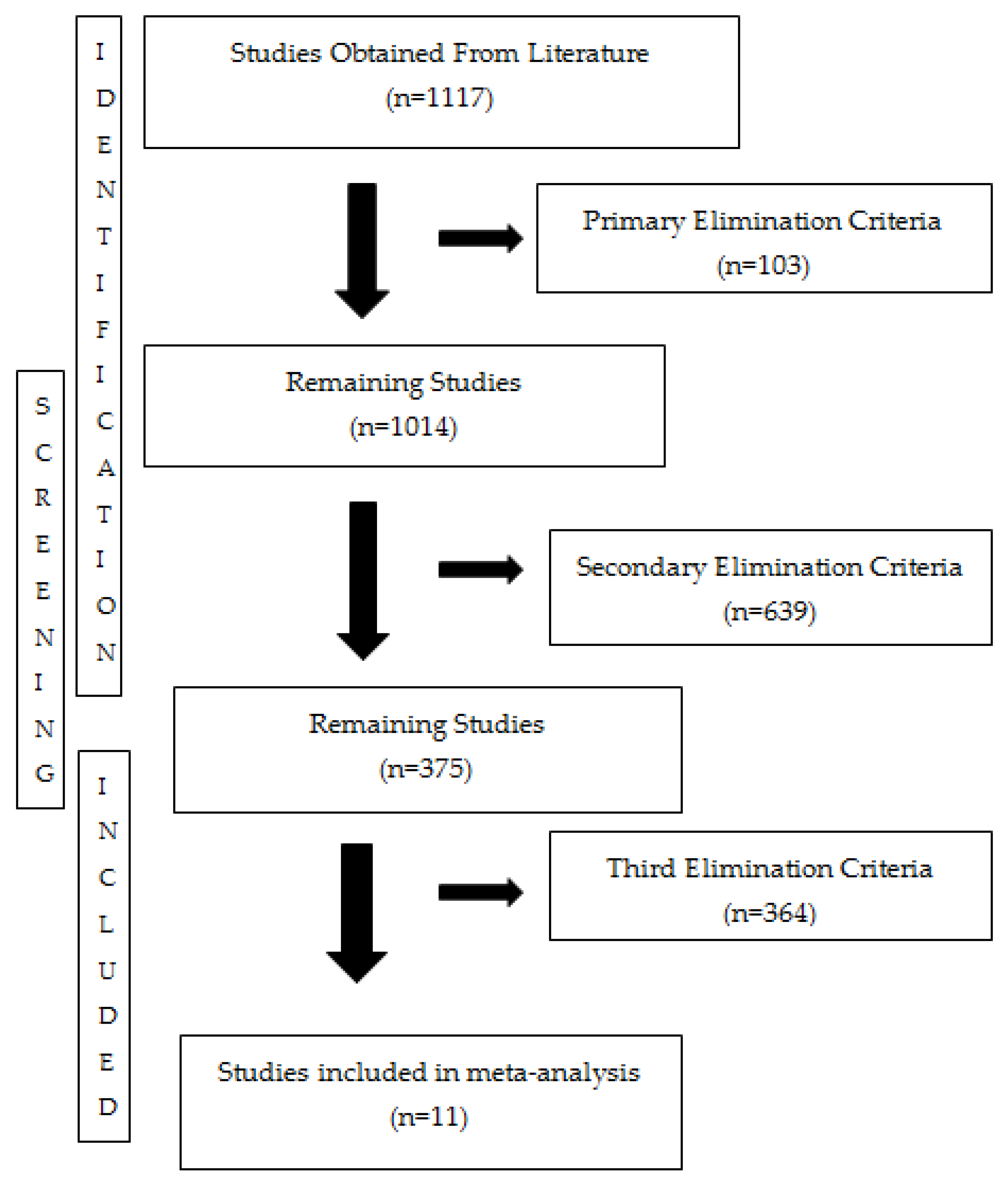
3.1. Literature Search and Inclusion Criteria Results
3.2. Data Extraction Results and Coding
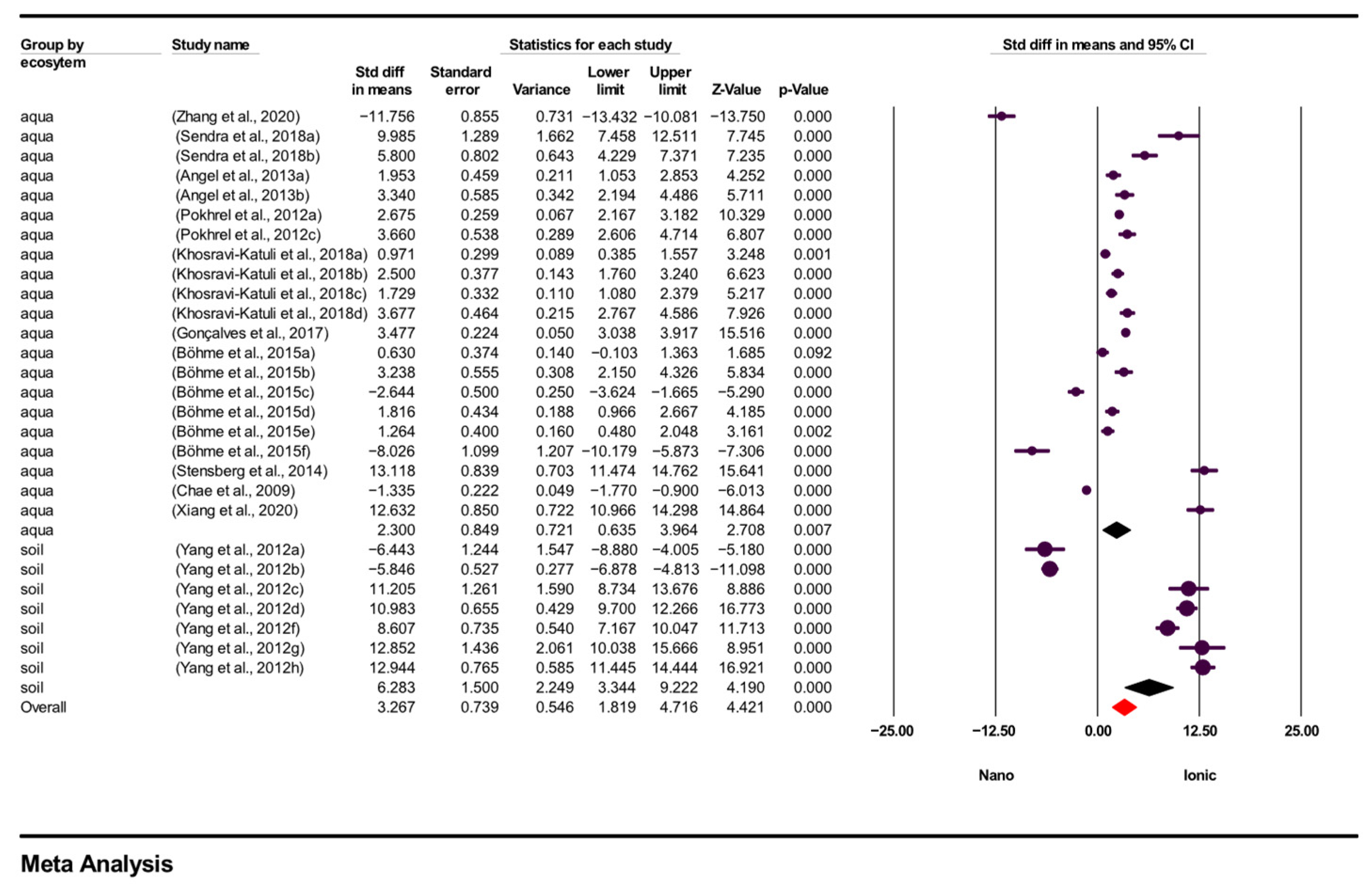
3.3. Meta-Analysis
3.3.1. Heterogeneity Testing and Model Selection
3.3.2. Subgroup Analysis Results
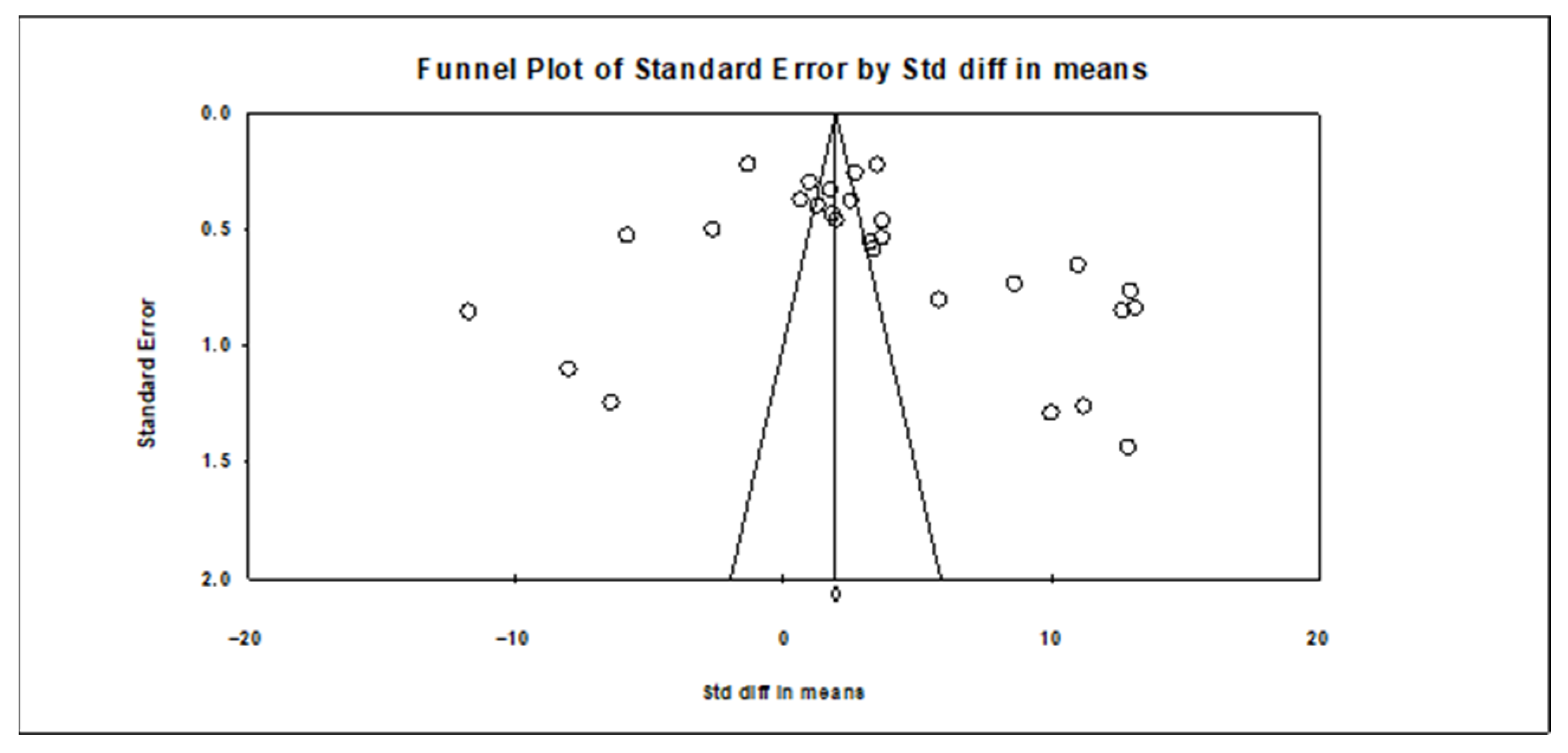
3.3.3. Publication Bias Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AgNPs | Silver nanoparticles |
| AgNO3 | Silver nitrate |
| Ag+ | Ionic silver |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CMA | Comprehensive Meta-Analysis |
| EC50 | Half maximal effective concentration |
| h | Hour |
| LC50 | Lethal Concentration 50 |
| LD50 | Lethal Dose 50 |
| n | Sample size |
| p | Probability value |
| pH | Potential of Hydrogen |
| SMD | Standardized mean difference |
| t | temperature |
| TV | Toxicity values |
References
- Marambio-Jones, C.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2010, 12, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gondikas, A.P.; Marinakos, S.M.; Auffan, M.; Liu, J.; Hsu-Kim, H.; Meyer, J.N. Mechanism of silver nanoparticle toxicity is dependent on dissolved silver and surface coating in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.D.; Hugo, W.B. Antimicrobial Activity and Action of Silver. Prog. Med. Chem. 1994, 31, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, I.; Mijnendonckx, K.; Leys, N.; Mahillon, J.; Silver, S.; Van Houdt, R.; Drake, P.L.; Hazelwood, K.J.; Guidelines, W.H.O.; Bragg, P.D.; et al. Antimicrobial silver: Uses, toxicity and potential for resistance. BioMetals 2013, 26, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.J.; Jinwon, P.C.H.L. Evaluation of the toxic impact of silver nanoparticles on Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 94, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asharani, P.V.; Wu, Y.L.; Gong, Z.; Valiyaveettil, S. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in zebrafish models. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 255102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, C.E.; Hofstetter, W.; Siebenrock, K.A.; Sebald, H.J.; Landmann, R.; Klenke, F.M. Cytotoxic effects of ionic silver and silver nano-particles on osteoblasts and osteoclasts in vitro. Bone 2011, 48, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.M.; Kwak, J.I.; An, Y.J. Effect of silver nanoparticles in crop plants Phaseolus radiatus and Sorghum bicolor: Media effect on phytotoxicity. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.; Pradhan, A.; Pascoal, C.; Cássio, F. Effects of metal nanoparticles on freshwater rotifers may persist across generations. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 229, 105652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinova, I.; Niskanen, J.; Kajankari, P.; Kanarbik, L.; Käkinen, A.; Tenhu, H.; Penttinen, O.P.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of two types of silver nanoparticles to aquatic crustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 3456–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, J.; Christian, P.; Urrea, J.A.G.; Roos, N.; Hassellöv, M.; Tollefsen, K.E.; Thomas, K.V. Effects of silver and gold nanoparticles on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatocytes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 96, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo, A.C.; Lynch, I.; Valsami-Jones, E. Silver nanoparticle induced toxicity and cell death mechanisms in embryonic zebrafish cells. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 6142–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toxicological Profile for Silver; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry U.S. Public Health Service: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1990.
- Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y. Silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Schluesener, H.J. Nanosilver: A nanoproduct in medical application. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 176, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabrega, J.; Zhang, R.; Renshaw, J.C.; Liu, W.-T.; Lead, J.R. Impact of silver nanoparticles on natural marine biofilm bacteria. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völker, C.; Kämpken, I.; Boedicker, C.; Oehlmann, J.; Oetken, M. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles and ionic silver: Comparison of adverse effects and potential toxicity mechanisms in the freshwater clam Sphaerium corneum. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levard, C.; Hotze, E.M.; Lowry, G.V.; Brown, G.E. Environmental transformations of silver nanoparticles: Impact on stability and toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6900–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, G.; Pang, L.; Doolette, C.; Kirby, J.K.; McLaughlin, M.J. Transport of silver nanoparticles in saturated columns of natural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, G.; Donner, E.; Laera, G.; Sekine, R.; Scheckel, K.G.; Khaksar, M.; Vasilev, K.; De Mastro, G.; Lombi, E. Fate of zinc and silver engineered nanoparticles in sewerage networks. Water Res. 2015, 77, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, O.; Juganson, K.; Ivask, A.; Kasemets, K.; Mortimer, M.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of Ag, CuO and ZnO nanoparticles to selected environmentally relevant test organisms and mammalian cells in vitro: A critical review. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1181–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, Applications, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.; Hussain, S.M.; Schrand, A.M.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Hess, K.L.; Jones, R.L.; Schlager, J.J. Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: Size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J. Phys. Chem. 2008, 112, 13608–13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.V.; Fau, N.A.; Vermeulen, J.P.; Fonteyne, L.J.J.; Verharen, H.W.; Briedé, J.J.; Loveren, H.; Jong, W.H. The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9810–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, B.J.; Handy, R.D. Physiological effects of nanoparticles on fish: A comparison of nanometals versus metal ions. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 1083–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J. Conducting polymer-silver composites. Chem. Pap. 2013, 67, 814–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhong, C.; Zhao, N.; Deng, Y.; Han, X.; Hu, W. Spontaneous Synthesis of Silver-Nanoparticle-Decorated Transition-Metal Hydroxides for Enhanced Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7245–7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Ortiz, M.; Lahive, E.; George, S.; Ter Schure, A.; Van Gestel, C.A.M.; Jurkschat, K.; Svendsen, C.; Spurgeon, D.J. Short-term soil bioassays may not reveal the full toxicity potential for nanomaterials; bioavailability and toxicity of silver ions (AgNO3) and silver nanoparticles to earthworm Eisenia fetida in long-term aged soils. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 203, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffan, M.; Rose, J.; Bottero, J.-Y.; Lowry, G.V.; Jolivet, J.-P.; Wiesner, M.R. Towards a definition of inorganic nanoparticles from an environmental, health and safety perspective. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGillicuddy, E.; Murray, I.; Kavanagh, S.; Morrison, L.; Fogarty, A.; Cormican, M.; Dockery, P.; Prendergast, M.; Rowan, N.; Morris, D. Silver nanoparticles in the environment: Sources, detection and ecotoxicology. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruoja, V.; Dubourguier, H.C.; Kasemets, K.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of nanoparticles of CuO, ZnO and TiO2 to microalgae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missaoui, W.N.; Arnold, R.D.; Cummings, B.S. Toxicological status of nanoparticles: What we know and what we don’t know. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2018, 295, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Toxic Effects of Nano-CuO, Micro-CuO and Cu2+ on Chlorella sp. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 04, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melvin, S.D.; Wilson, S.P. The utility of behavioral studies for aquatic toxicology testing: A meta-analysis. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducharme, N.A.; Peterson, L.E.; Benfenati, E.; Reif, D.; McCollum, C.W.; Gustafsson, J.Å.; Bondesson, M. Meta-analysis of toxicity and teratogenicity of 133 chemicals from zebrafish developmental toxicity studies. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 41, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notter, D.A.; Mitrano, D.M.; Nowack, B. Are nanosized or dissolved metals more toxic in the environment? A meta-analysis. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 2733–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevitch, J.; Koricheva, J.; Nakagawa, S.; Stewart, G. Meta-analysis and the science of research synthesis. Nature 2018, 555, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, H.A.-O.; Martins, C.A.-O.; Prior, J.A.-O.X. Silver Nanoparticles as Carriers of Anticancer Drugs for Efficient Target Treatment of Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials 2021, 4, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, M.S.; Nick, K.E.; Hall, M.; Milligan, J.R.; Chen, Q.; Perry, C.C. Synthesis and Catalytic Activity of Pluronic Stabilized Silver-Gold Bimetallic Nanoparticles. R. Soc. Chem. 2014, 4, 52279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsioni, A.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. Meta-analysis. Int. Encycl. Public Health 2017, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockwell, S.E.; Gordon, I.R. A comparison of statistical methods for meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2001, 20, 825–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshkumar, P.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis: Understanding the Best Evidence in Primary Healthcare. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2013, 2, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, L.T.M.; Su, J.; Wang, Q.; Stringer, L.C.; Switzer, A.D.; Gasparatos, A. Meta-analysis indicates better climate adaptation and mitigation performance of hybrid engineering-natural coastal defence measures. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, I.S. Recent Research Trends in Meta-analysis. Asian Nurs. Res. 2017, 11, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.R.; French, K.E. The use of meta-analysis in exercise and sport: A tutorial. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1986, 57, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H.R. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V. Distribution Theory for Glass’s Estimator of Effect Size and Related Estimators. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 1981, 6, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating Characteristics of a Rank Correlation Test for Publication Bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.E.; Schmidt, F.L. Methods of Meta-Analysis: Correcting Error and Bias in Research Findings, 2nd ed.; Sage Publications, Ltd.: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Ning, B.; Sun, C.; Song, K.; Xu, X.; Fang, T.; Yao, L. Dynamic nano-Ag colloids cytotoxicity to and accumulation by Escherichia coli: Effects of Fe3+, ionic strength and humic acid. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 89, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendra, M.; Blasco, J.; Araújo, C.V.M. Is the cell wall of marine phytoplankton a protective barrier or a nanoparticle interaction site? Toxicological responses of Chlorella autotrophica and Dunaliella salina to Ag and CeO2 nanoparticles. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, B.M.; Batley, G.E.; Jarolimek, C.V.; Rogers, N.J. The impact of size on the fate and toxicity of nanoparticulate silver in aquatic systems. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, L.R.; Silva, T.; Dubey, B.; El Badawy, A.M.; Tolaymat, T.M.; Scheuerman, P.R. Rapid screening of aquatic toxicity of several metal-based nanoparticles using the MetPLATE™ bioassay. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi-Katuli, K.; Shabani, A.; Paknejad, H.; Imanpoor, M.R. Comparative toxicity of silver nanoparticle and ionic silver in juvenile common carp (Cyprinus carpio): Accumulation, physiology and histopathology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, S.F.; Pavlaki, M.D.; Lopes, R.; Hammes, J.; Gallego-Urrea, J.A.; Hassellöv, M.; Jurkschat, K.; Crossley, A.; Loureiro, S. Effects of silver nanoparticles on the freshwater snail Physa acuta: The role of test media and snails’ life cycle stage. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffi, B.; Hans-Joachim, S.; Thorsten, R.; Dana, K. Effect propagation after silver nanoparticle exposure in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos: A correlation to internal concentration and distribution patterns. Environ. Sci. Nano 2015, 2, 603–614. Available online: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2015/en/c5en00118h (accessed on 9 December 2025). [CrossRef]
- Stensberg, M.C.; Madangopal, R.; Yale, G.; Wei, Q.; Ochoa-Acuña, H.; Wei, A.; McLamore, E.S.; Rickus, J.; Porterfield, D.M.; Sepúlveda, M.S. Silver nanoparticle-specific mitotoxicity in Daphnia magna. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.Q.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q.Q.; Ling, J.; Chen, L.Q. Proteomic profiling reveals the differential toxic responses of gills of common carp exposed to nanosilver and silver nitrate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Mädler, L.; Li, N. Toxic Potential of Materials at the Nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, A.D.; Aitken, R.J.; Butz, T.; Colvin, V.; Donaldson, K.; Oberdörster, G.; Philbert, M.A.; Ryan, J.; Seaton, A.; Stone, V.; et al. Safe handling of nanotechnology. Nature 2006, 444, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Sheng, X.; Wang, J.; Wen, Y. Silver nanoparticles or free silver ions work? An enantioselective phytotoxicity study with a chiral tool. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, O.; Hu, Z. Size dependent and reactive oxygen species related nanosilver toxicity to nitrifying bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4583–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivask, A.; Juganson, K.; Bondarenko, O.; Mortimer, M.; Aruoja, V.; Kasemets, K.; Blinova, I.; Heinlaan, M.; Slaveykova, V.; Kahru, A. Mechanisms of toxic action of Ag, ZnO and CuO nanoparticles to selected ecotoxicological test organisms and mammalian cells in vitro: A comparative review. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Bae, S.; Lee, S.; Hong, I.S.; Kim, S.H. Ion-release kinetics and ecotoxicity effects of silver nanoparticles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.S.; Li, M.; Chang, F.Y.; Li, W.; Yin, L.Y. Physiological analysis of silver nanoparticles and AgNO3 toxicity to Spirodela polyrhiza. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1880–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, E.; Baun, A.; Behra, R.; Hartmann, N.B.; Filser, J.; Antonietta, A.-J.M.; Peter, Q. Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.M.; Wang, W.X. Comparison of acute and chronic toxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate to Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lead, J.R.; Batley, G.E.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Croteau, M.N.; Handy, R.D.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Judy, J.D.; Schirmer, K. Nanomaterials in the environment: Behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects—An updated review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2029–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilberg, K.; Malte, H.; Wang, T.; Baatrup, E. Silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate cause respiratory stress in Eurasian perch (Perca fluviatilis). Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 96, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Study Name | Sample Size | Organism | Exposure Time | Ecosystem | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang et al., 2020 [52] | 1 | Escherichia coli | 3 h | aquatic | T = 25 °C pH = 6.8 |
| Sendra et al., 2018 [53] | 2 | Chlorella autotrophica, Dunaliella salina | 48 h | aquatic | T = 20 °C pH = 7 |
| Angel et al., 2013 [54] | 2 | Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata, Ceriodaphnia dubia | 72 h | aquatic | T = 24 °C |
| Pokhrel et al., 2012 [55] | 2 | Escherichia coli | 5 h | aquatic | T = 35 °C pH = 7.2 |
| Yang et al., 2012 [2] | 7 | Caenorhabditis elegans | 24 h | terrestrial | T = 22 °C pH = 8.3 |
| Khosravi-Katuli et al., 2018 [56] | 4 | Cyprinus carpio | 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, 96 h | aquatic | T = 21.1 °C pH = 7.3 |
| Gonçalves et al., 2017 [57] | 1 | Physa acuta | 96 h | aquatic | T = 22 °C pH = 7.9 |
| Steffi et al., 2015 [58]. | 6 | Danio rerio | 2 h, 26 h, 71 h | aquatic | T = 26 °C pH = 7.6 |
| Stensberg et al., 2014 [59] | 1 | Daphnia magna | 72 h | aquatic | T = 22 °C pH = 8.2 |
| Chae et al., 2009 [6] | 1 | Oryzias latipes | 96 h | aquatic | T = 25 °C pH = 7.5 |
| Xiang et al., 2020 [60] | 1 | Cyprinus carpio | 96 h | aquatic | T = 18 °C pH = 7.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Karaman, E.; Eravci, D.B.; Sanin, S.L.; Turksoy, V.A. Differential Toxicity of Ionic Silver and Silver Nanoparticles: A Meta-Analysis of Ecotoxicological Studies. Toxics 2026, 14, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics14010028
Karaman E, Eravci DB, Sanin SL, Turksoy VA. Differential Toxicity of Ionic Silver and Silver Nanoparticles: A Meta-Analysis of Ecotoxicological Studies. Toxics. 2026; 14(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics14010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaraman, Esra, Deniz Boz Eravci, Selim Latif Sanin, and Vugar Ali Turksoy. 2026. "Differential Toxicity of Ionic Silver and Silver Nanoparticles: A Meta-Analysis of Ecotoxicological Studies" Toxics 14, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics14010028
APA StyleKaraman, E., Eravci, D. B., Sanin, S. L., & Turksoy, V. A. (2026). Differential Toxicity of Ionic Silver and Silver Nanoparticles: A Meta-Analysis of Ecotoxicological Studies. Toxics, 14(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics14010028







