Single Super Phosphate Improves Lolium perenne Quality and Rhizosphere Microorganism Structure Under Combined Cadmium and Arsenic Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Experimental Design
2.1.1. Materials
2.1.2. Experimental Design
2.2. Research Methods
2.3. Laboratory Methods
2.4. Calculation and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Phosphorus Fertilizer Applications on Plant Growth, Hay Yield, and Root Morphology of Lolium perenne
3.1.1. Plant Height of L. perenne
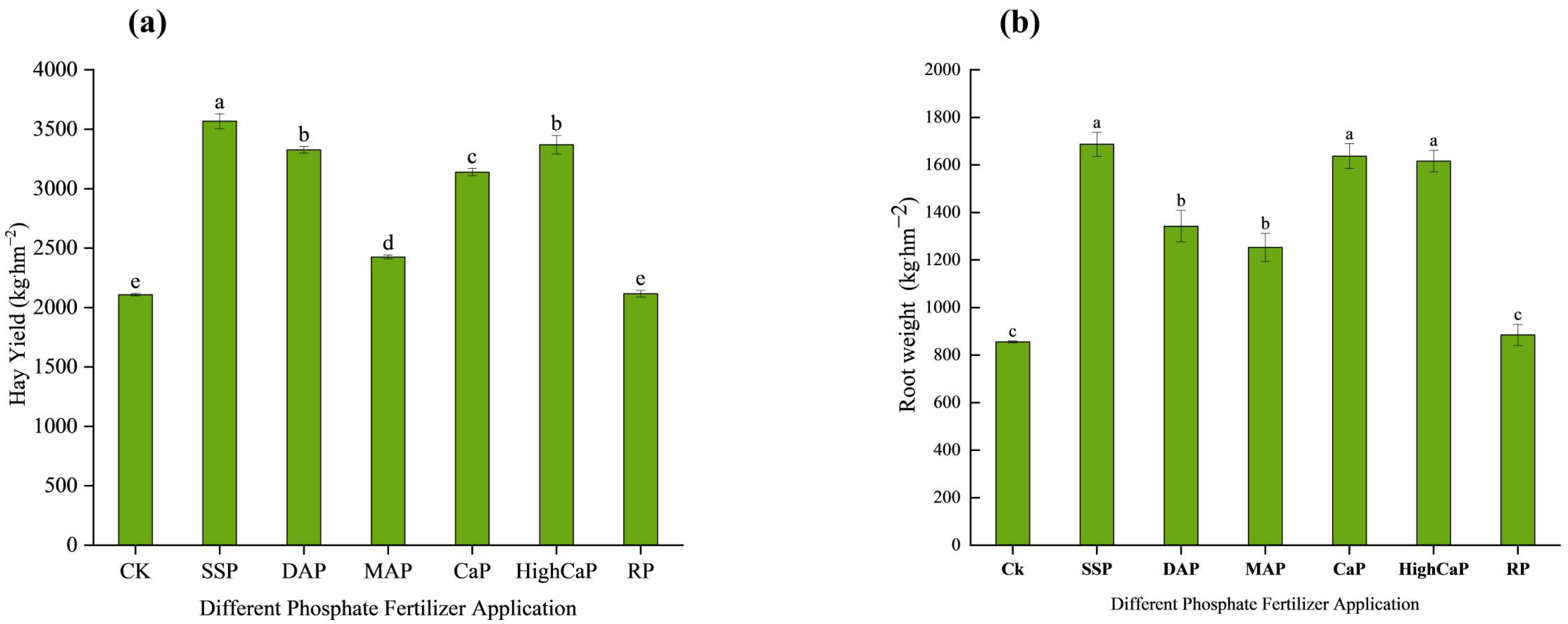
3.1.2. Biomass Production of L. perenne
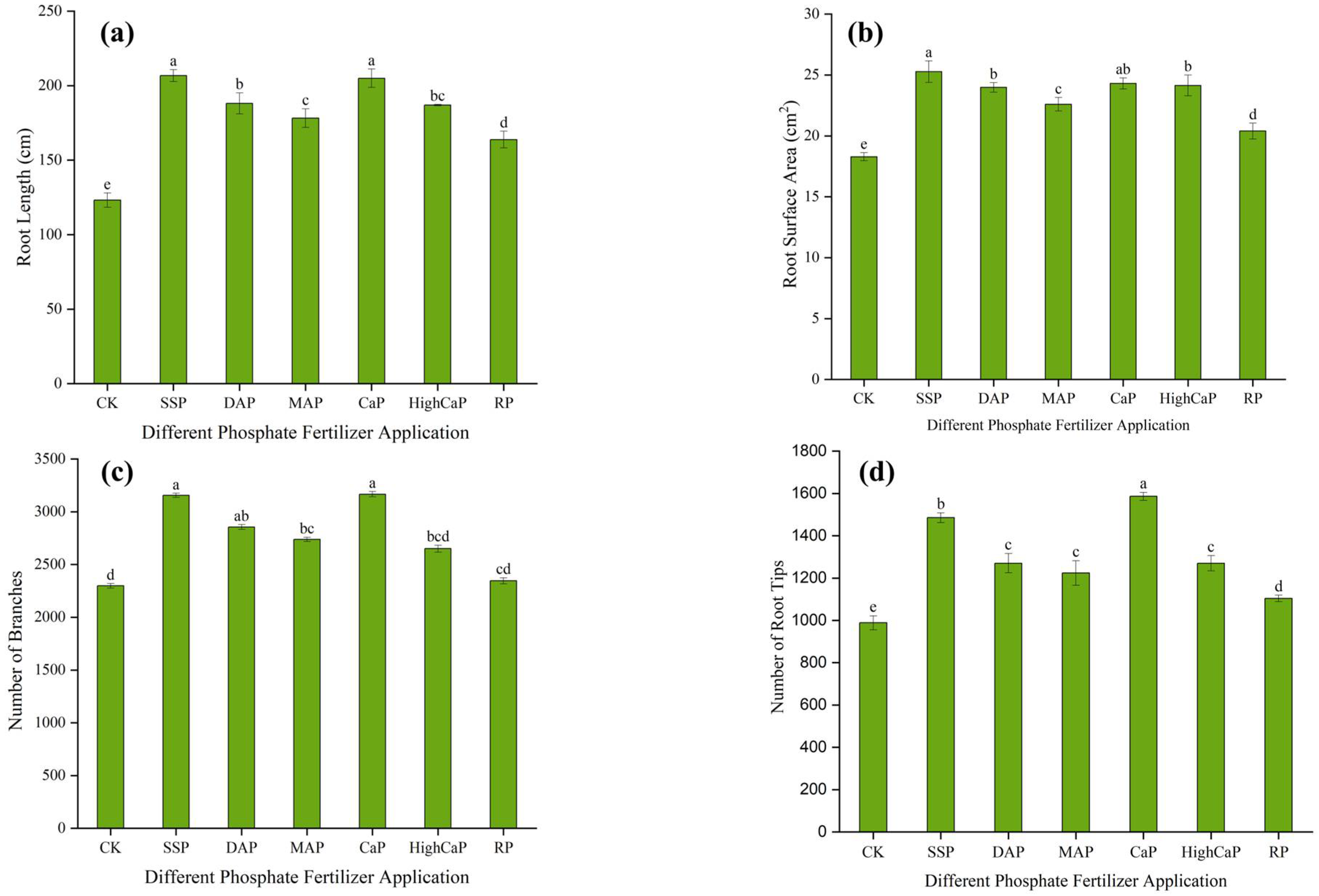
3.1.3. Root Morphology of L. perenne
3.2. Effects of Different Phosphorus Fertilizer Applications on P, Cd, and As Contents of Lolium perenne
3.2.1. Total P Concentration in L. perenne
3.2.2. Cadmium Accumulation in L. perenne
3.2.3. As Accumulation in L. perenne
3.3. Effects of Different Phosphorus Fertilizer Applications on Antioxidant Enzyme and Non-Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Plants
3.3.1. Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in L. perenne
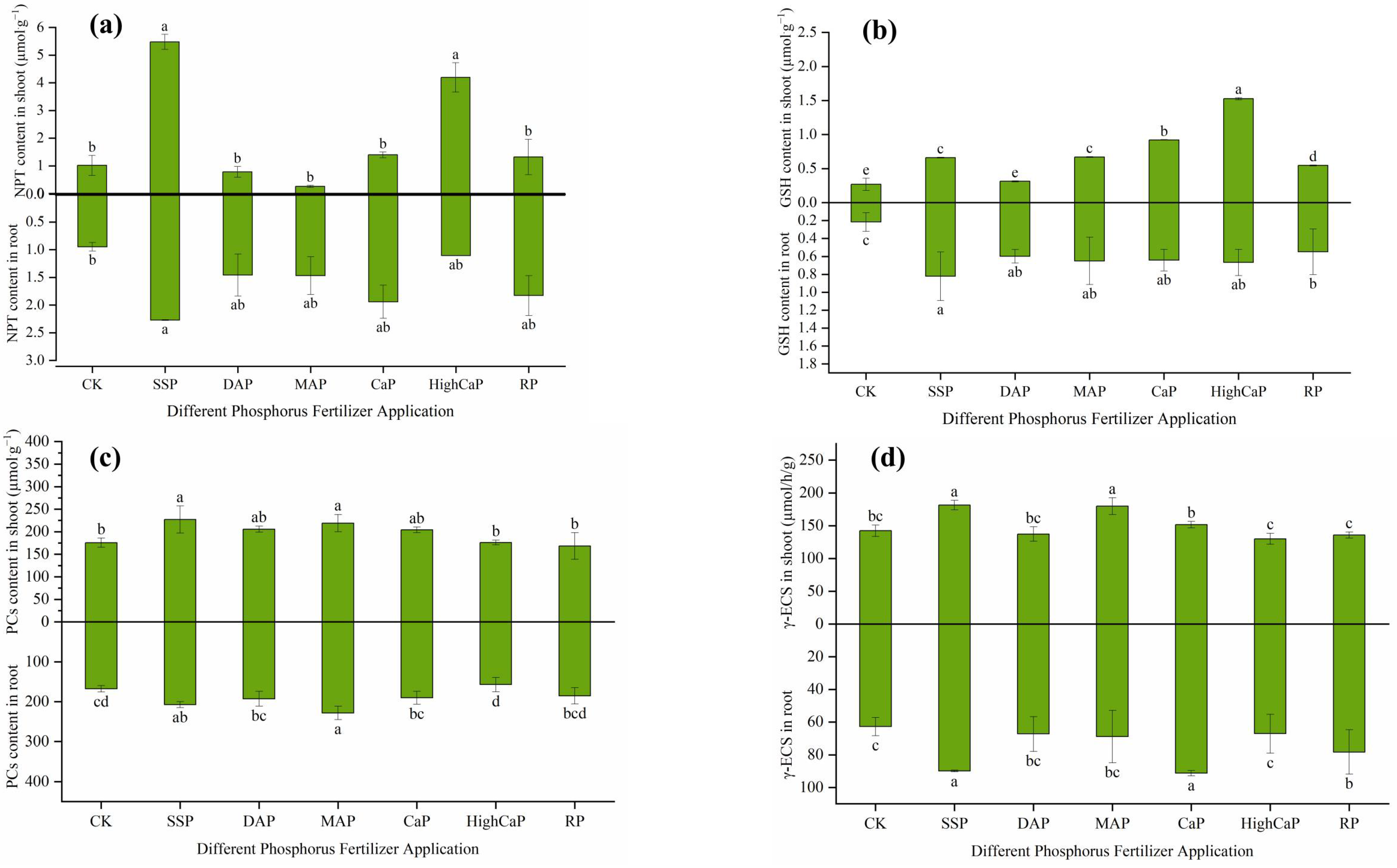
3.3.2. Non-Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in L. perenne
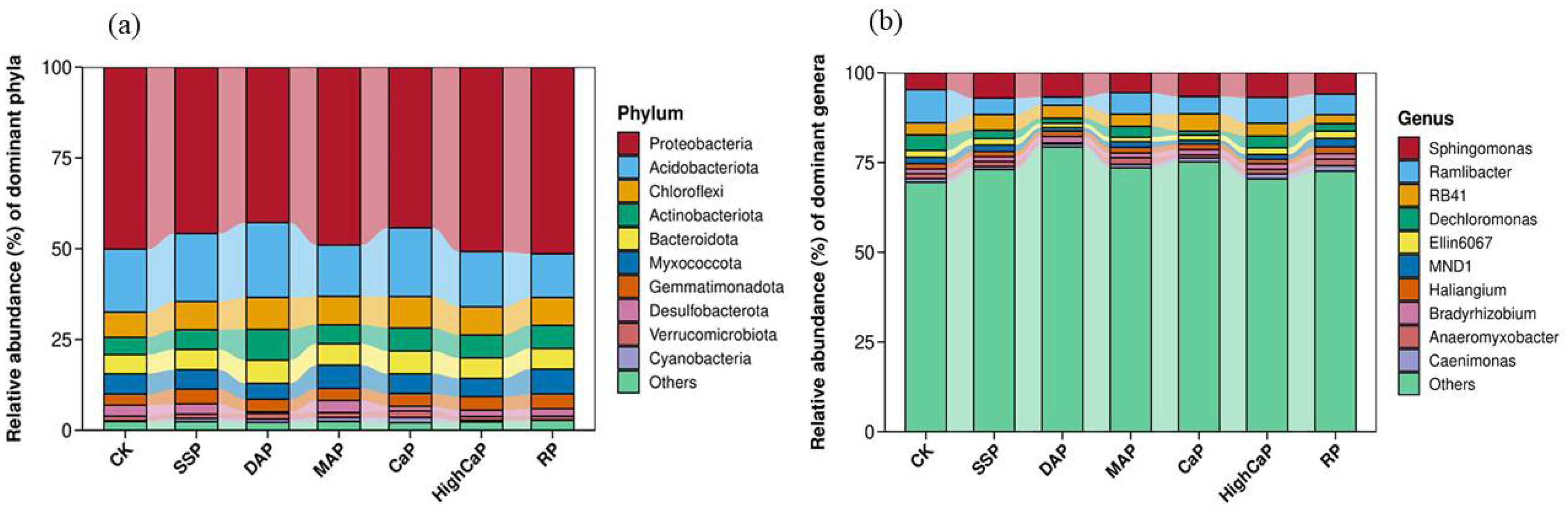
3.4. Soil Rhizosphere Microbial Community
3.5. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Phosphorus Fertilizer Applications on Growth, Accumulation, and Rhizosphere Microbial Community of Lolium perenne Under Cd- and As-Contaminated Soil
4.2. Physiological Mechanisms of the Effects of Different Phosphorus Fertilizer Applications on Lolium perenne Under Cd- and As-Contaminated Soil
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SSP | Single Super Phosphate |
| DAP | Diammonium Phosphate |
| MAP | Monoammonium Phosphate |
| CaP | Calcium Phosphate |
| HighCaP | High Calcium Phosphate |
| RP | Rock Phosphate |
| Cd | Cadmium |
| As | Arsenic |
| POD | Peroxidase |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| NPT | Non-Protein Sulfhydryl |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| PCs | Phytochelatin Synthetase |
| γ-ECS | γ-Glutamylcysteine Synthetase |
References
- Yao, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Shen, Z.; Li, J.; Mei, N.; Luo, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D. Heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils from surrounding industries with low emissions: Assessing contamination levels and sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Geng, X.; Zhao, M.; Sun, T.; Fan, Z. Health risk assessment of heavy metal (loid) s in park soils of the largest megacity in China by using Monte Carlo simulation coupled with Positive matrix factorization model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrett, M.; Sivarajah, B.; Cheney, C.L.; Korosi, J.B.; Kimpe, L.; Blais, J.M.; Smol, J.P. Impacts on aquatic biota from salinization and metalloid contamination by gold mine tailings in sub-Arctic lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibanda, T.; Selvarajan, R.; Msagati, T.; Venkatachalam, S.; Meddows-Taylor, S. Defunct gold mine tailings are natural reservoir for unique bacterial communities revealed by high-throughput sequencing analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2199–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, W.; Song, W.; Guo, M. Remediation techniques for heavy metal-contaminated soils: Principles and applicability. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palansooriya, K.N.; Shaheen, S.M.; Chen, S.S.; Tsang, D.C.; Hashimoto, Y.; Hou, D.; Bolan, N.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Soil amendments for immobilization of potentially toxic elements in contaminated soils: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, Z.; Yu, T.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, X.; Li, B.; Lin, K. Cadmium accumulation in paddy soils affected by geological weathering and mining: Spatial distribution patterns, bioaccumulation prediction, and safe land usage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Dou, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Shi, J.; Yu, M.; Xu, J. Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in Phytolacca americana L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, P.-A.; Mougel, C.; Ranjard, L. Soil microbial diversity: Methodological strategy, spatial overview and functional interest. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2011, 334, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Dai, Y. Quantifying source-specific intake risks of wheat cadmium by associating source contributions of soil cadmium with human health risk. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 228, 112982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolan, N.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Thangarajan, R.; Kumpiene, J.; Park, J.; Makino, T.; Kirkham, M.B.; Scheckel, K. Remediation of heavy metal (loid) s contaminated soils–to mobilize or to immobilize? J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 266, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esshaimi, M.; Ouazzani, N.; Avila, M.; Perez, G.; Valiente, M.; Mandi, L. Heavy metal contamination of soils and water resources Kettara abandoned mine. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 8, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.-P.; Shan, C.-J.; Jia, G.-L.; Yang, T.-X.; Wei, A.-Z.; Zhao, H.; Wu, S.-Q.; Huo, K.-K.; Chen, W.-Q.; Cao, X.-Y. Responses to cadmium tolerance, accumulation and translocation in Populus× canescens. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.E.; Pan, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, T. Plant growth, antioxidative enzyme, and cadmium tolerance responses to cadmium stress in Canna orchioides. Hortic. Plant J. 2021, 7, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, M.; Chi, G. Effects of cadmium on growth and photosynthetic activities in pakchoi and mustard. Bot. Stud. 2011, 52, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Mansoor, S.; Ali Wani, O.; Lone, J.K.; Manhas, S.; Kour, N.; Alam, P.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, P. Reactive oxygen species in plants: From source to sink. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, M. Reactive oxygen species (ROS): Plant perspectives on oxidative signalling and biotic stress response. Discov. Plants 2025, 2, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaličová Malčovská, S.; Dučaiová, Z.; Maslaňáková, I.; Bačkor, M. Effect of silicon on growth, photosynthesis, oxidative status and phenolic compounds of maize (Zea mays L.) grown in cadmium excess. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Roychoudhury, A.; Saha, P.P.; Sengupta, D.N. Differential antioxidative responses of indica rice cultivars to drought stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2010, 60, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, N.; Li, Y.W.; Cai, Q.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Mo, C.H.; Wong, M.H. Cadmium in rice: Transport mechanisms, influencing factors, and minimizing measures. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xiao, E.; Häggblom, M.; Krumins, V.; Dong, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Yan, B. Bacterial survival strategies in an alkaline tailing site and the physiological mechanisms of dominant phylotypes as revealed by metagenomic analyses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13370–13380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Sun, X.; Li, B.; Xu, R.; Young, L.Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Kong, T.; Xiao, E.; Wang, Q. Bacterial response to sharp geochemical gradients caused by acid mine drainage intrusion in a terrace: Relevance of C, N, and S cycling and metal resistance. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Lin, H.; Li, B.; Dong, Y.; Yin, T. Responses of microbial communities and metabolic activities in the rhizosphere during phytoremediation of Cd-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 202, 110958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, D. Responses of soil microbial communities and their network interactions to saline-alkaline stress in Cd-contaminated soils. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1609–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ling, A.; Li, H.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y. Effects of biocontrol agents application on soil bacterial community and the quality of tobacco. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Pan, X. Simultaneous removal of As (III) and Cu (II) from real bottom ash leachates by manganese-oxidizing aerobic granular sludge: Performance and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Liang, J.L.; Yang, S.X.; Zhang, S.C.; Liu, J.; Liang, Z.W.; Li, F.M.; Zeng, Q.W.; Fang, Z.; Liao, B. Plant diversity enhances the reclamation of degraded lands by stimulating plant–soil feedbacks. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-T.; Gurajala, H.K.; Wu, L.-H.; Van Der Ent, A.; Qiu, R.-L.; Baker, A.J.; Tang, Y.-T.; Yang, X.-E.; Shu, W.-S. Hyperaccumulator plants from China: A synthesis of the current state of knowledge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11980–11994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Chen, Y.; Weng, L.; Ma, J.; Khan, Z.H.; Liao, Z.; Magid, A.S.I.A.; Li, Y. Watering techniques and zero-valent iron biochar pH effects on As and Cd concentrations in rice rhizosphere soils, tissues and yield. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 100, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, S.; Ali, Q.; Zahir, Z.A.; Ashraf, S.; Asghar, H.N. Phytoremediation: Environmentally sustainable way for reclamation of heavy metal polluted soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Cui, X.; Luo, X.; Mao, P.; Zhuang, P.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Effects of plant growth regulator and chelating agent on the phytoextraction of heavy metals by Pfaffia glomerata and on the soil microbial community. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, M.; Gul, I.; Manzoor, A.; Kallerhoff, J.; Arshad, M. Optimization of integrated phytoremediation system (IPS) for enhanced lead removal and restoration of soil microbial activities. Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Zhou, J.; Xu, X.; Na, M.; Xu, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zheng, X. Inoculation of cadmium-tolerant bacteria to regulate microbial activity and key bacterial population in cadmium-contaminated soils during bioremediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 271, 115957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Feng, S.; Zhang, J.; Gong, S.; Qiao, K.; Zhou, A. Comparison of cadmium uptake and transcriptional responses in roots reveal key transcripts from high and low-cadmium tolerance ryegrass cultivars. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 203, 110961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Chen, F.; Jia, S.; Wang, Z.; Zuo, Q.; He, H. Effect of biochar on Cd and pyrene removal and bacteria communities variations in soils with culturing ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, K.; Zhan, W.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Chen, R.; Zhang, C. Highly effective stabilization of Cd and Cu in two different soils and improvement of soil properties by multiple-modified biochar. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Ma, S.; Liu, J.; Jiang, X.; Dai, D. Remediation of arsenic and cadmium co-contaminated soil: A Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, M.; Vaněk, A.; Ettler, V. Chemical stabilization of metals and arsenic in contaminated soils using oxides—A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 172, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hou, J.; Wu, L.; Christie, P.; Liu, W. Microbial community assembly of the hyperaccumulator plant Sedum plumbizincicola in two contrasting soil types with three levels of cadmium contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor Roch, G.; Maharajan, T.; Ceasar, S.A.; Ignacimuthu, S. The role of PHT1 family transporters in the acquisition and redistribution of phosphorus in plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2019, 38, 171–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielgusz, K.; Praczyk, M.; Irzykowska, L.; Świerk, D. Fertilization and soil pH affect seed and biomass yield, plant morphology, and cadmium uptake in hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 175, 114245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, K.; Khan, A.; Naz, F.; Ilyas, M.; Azeem, I.; Anwar, F.; Ahmad, W. The impact of different P fertilizer sources on growth, yield and yield component of maize varieties. Agric. Res. Technol. 2018, 13, 555881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Hussain, S.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X. Characteristics and mechanisms of soil Co-contamination affecting the transfer of cadmium and arsenic in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Agronomy 2023, 13, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Chen, W.-W.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Huang, Z.-R.; Ye, X.; Chen, L.-S.; Yang, L.-T. Effects of phosphorus deficiency on the absorption of mineral nutrients, photosynthetic system performance and antioxidant metabolism in Citrus grandis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.A.; Moussa, H.R.; Dessoky, E.S. The influence of Spirulina platensis on physiological characterization and mitigation of DNA damage in salt-stressed Phaseolus vulgaris L. plants. Egypt. J. Bot. 2023, 63, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dutt, S.; Bagler, G.; Ahuja, P.S.; Kumar, S. Engineering a thermo-stable superoxide dismutase functional at sub-zero to> 50 C, which also tolerates autoclaving. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmeyer, H.-U. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, P.; Wang, F.; Luo, B.; Li, A.; Wang, C.; Shabala, L.; Ahmed, H.A.I.; Deng, S.; Zhang, H.; Song, P. Antioxidant enzymatic activity and osmotic adjustment as components of the drought tolerance mechanism in Carex duriuscula. Plants 2021, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Zu, Y. Responses of antioxidant enzymes and key resistant substances in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) to cadmium and arsenic stresses. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humayra Bashir, H.B.; Ibrahim, M.; Rita Bagheri, R.B.; Javed Ahmad, J.A.; Arif, I.; Baig, M.; Qureshi, M. Influence of sulfur and cadmium on antioxidants, phytochelatins and growth in Indian mustard. AoB Plants 2015, 7, plv001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, B. Insights into the effects of cadmium stress on endophytic bacterial community in the hyperaccumulating plant ryegrass. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2021, 33, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C. Enrichment and Management of Heavy Metals in Sewage Irrigated Soil; Lap LAMBERT Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Maw, T.T.; Tang, S.; Liang, X.; Yan, W.; Li, B.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Dual-strategy regulation of soil water dynamics: Integrating planting patterns and amendments to mitigate cadmium and arsenic migration in agricultural soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 302, 118713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, D.; Yadav, A.; Prasad, M.; Singh, T.B.; Shrivastav, P.; Ali, A.; Dantu, P.K.; Mishra, S. Effect of heavy metals on plant growth: An overview. In Contaminants in Agriculture: Sources, Impacts and Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 79–101. [Google Scholar]
- Khatun, J.; Intekhab, A.; Dhak, D. Effect of uncontrolled fertilization and heavy metal toxicity associated with arsenic (As), lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd), and possible remediation. Toxicology 2022, 477, 153274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Shah, S.S.; Khan, A.; Sarwar, M.; Shoaib, A. Efficacy of manually prepared single super phosphate fertilizer on rain-fed wheat crop under sub-humid climate. Pak. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 32, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndagi, H.; Agera, S.; Chenge, I.; Tunku, P. Effect of organic and inorganic fertilizer treatments on Moringa oleifera seedlings Lafia, Nasarawa State, Nigeria. J. Res. For. Wildl. Environ. 2023, 15, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mani, D.; Patel, N.K.; Kumar, S. Impact of single super phosphate on the uptake of cadmium by Carrot (Daucus carota L.). Int. J. Appl. Pure Sci. Agric. 2015, 1, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi, J. Effect of phosphorus accumulation on nitrogen accumulation and dry matter production in soybeans differing with nodulation type. J. Jpn. Soc. Agric. Technol. Manag. 2018, 25, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Suleman, M.; Ashraf, M.; Raza, Q.-U.-A.; Bashir, M.A.; Rahman, S.U.; Aon, M.; Ali, S.; Shahzad, S.M.; Khalid, M.U.; Raza, H.M.A. Determining the cadmium accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) and soil influenced by phosphoric fertilizers in two different textured soils. Land 2022, 11, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Inostroza, N.G.; Gianfreda, L.; Greiner, R.; Mora, M.L.; Jorquera, M.A. Phytase-producing Bacillus sp. inoculation increases phosphorus availability in cattle manure. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2016, 16, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Su, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, L. Effect of different types of phosphate fertilizer on phosphorus absorption and desorption in acidic red soil of Southwest China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, J.; You, J.; Li, J.; Qian, C.; Leng, S.; Yang, G.; Zuo, Q. Effects of phosphorus supply on the leaf photosynthesis, and biomass and phosphorus accumulation and partitioning of canola (Brassica napus L.) in saline environment. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Meng, F.; Wang, G.; Hartmann, T.E.; Feng, G.; Wu, J.; Jiao, X.; Zhang, F. Toward the sustainable use of mineral phosphorus fertilizers for crop production in China: From primary resource demand to final agricultural use. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharajan, T.; Ceasar, S.A.; Krishna, T.P.A.; Ignacimuthu, S. Management of phosphorus nutrient amid climate change for sustainable agriculture. J. Environ. Qual. 2021, 50, 1303–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Liu, W.; Hong, H.; Lu, H.; Liu, J.; Jia, H.; Yan, C. Exogenous phosphorus enhances cadmium tolerance by affecting cell wall polysaccharides in two mangrove seedlings Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh and Kandelia obovata (S., L.) Yong differing in cadmium accumulation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Pan, K.; Olatunji, O.A.; Graciano, C.; Li, Z.; Sun, F.; Sun, X.; Song, D.; Chen, W.; Zhang, A. Phosphorous application improves drought tolerance of Phoebe zhennan. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbarasan, S.; Ramesh, S. The Role of Plant Roots in Nutrient Uptake and Soil Health. Plant Sci. Arch. 2021, 5, 1837–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanying, H.; Xiaoe, Y.; Zhenli, H.; Virupax, C.B. Morphological and physiological responses of plants to cadmium toxicity: A review. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shoaib, N.; Lin, K.; Mughal, N.; Wu, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, L.; Pan, K. Boosting cadmium tolerance in Phoebe zhennan: The synergistic effects of exogenous nitrogen and phosphorus treatments promoting antioxidant defense and root development. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1340287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liang, J.; Björn, L.O.; Li, J.; Shu, W.; Wang, Y. Phosphorus-arsenic interaction in the ‘soil-plant-microbe’system and its influence on arsenic pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-M.; Tang, D.-D.; Zhang, X.-H.; Uchimiya, M.; Yuan, X.-Y.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.-Z. Effects of soil amendments on cadmium transfer along the lettuce-snail food chain: Influence of chemical speciation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Szteke, B. Trace Elements in Abiotic and Biotic Environments; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mubeen, S.; Ni, W.; He, C.; Yang, Z. Agricultural strategies to reduce cadmium accumulation in crops for food safety. Agriculture 2023, 13, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Guo, G.; Du, P.; Li, F. Phosphate-induced differences in stabilization efficiency for soils contaminated with lead, zinc, and cadmium. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Hussain, S.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Rana, M.S.; Saleem, M.H.; Riaz, M.; Ashraf, U.; Potcho, M.P.; Duan, M.; Rajput, I.A. Molybdenum supply alleviates the cadmium toxicity in fragrant rice by modulating oxidative stress and antioxidant gene expression. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, J.; Wang, X.; Saleem, M.H.; Sun, X.; Hussain, S.; Khan, I.; Rana, M.S.; Ahmed, S.; Awan, S.A.; Fiaz, S. Application of ferrous sulfate alleviates negative impact of cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Biocell 2021, 45, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, C.; Okant, M.; Ugurlar, F.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ashraf, M.; Ahmad, P. Melatonin-mediated nitric oxide improves tolerance to cadmium toxicity by reducing oxidative stress in wheat plants. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Saha, J.; Sarkar, M.; Mandal, P. Bacterial survival strategies and responses under heavy metal stress: A comprehensive overview. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 48, 327–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Lyu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Kong, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Riddles of lost city: Chemotrophic prokaryotes drives carbon, sulfur, and nitrogen cycling at an extinct cold seep, South China Sea. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e03322–e03338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogati, K.; Walczak, M. The impact of drought stress on soil microbial community, enzyme activities and plants. Agronomy 2022, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X. Shifts in bacterial diversity, interactions and microbial elemental cycling genes under cadmium contamination in paddy soil: Implications for altered ecological function. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Tu, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Hu, L.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, K. Inoculation of Sinorhizobium saheli YH1 leads to reduced metal uptake for Leucaena leucocephala grown in mine tailings and metal-polluted soils. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Lata, C. Heavy metal stress, signaling, and tolerance due to plant-associated microbes: An overview. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Oliveira, R.S.; Nai, F.; Rajkumar, M.; Luo, Y.; Rocha, I.; Freitas, H. The hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola harbors metal-resistant endophytic bacteria that improve its phytoextraction capacity in multi-metal contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 156, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Rafiq, M.T.; Khan, K.Y.; Pan, F.; Yang, X.; Feng, Y. Improvement of cadmium uptake and accumulation in Sedum alfredii by endophytic bacteria Sphingomonas SaMR12: Effects on plant growth and root exudates. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, S.; Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, C.; You, R.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Xiao, X. Determination of H2O2 and its antioxidant activity by BCM@ Au NPs ratiometric SERS sensor. Talanta 2024, 268, 125323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-Y. Effect of cadmium stress on the growth, antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in two kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) plant seedlings. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Tripathi, D.K.; Deshmukh, R.; Pratap Singh, V.; Corpas, F.J. Revisiting the role of ROS and RNS in plants under changing environment. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 161, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, O.; Akinloye, O. First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Ali, S.; Noman, A.; Ali, Q.; Rizwan, M.; Farid, M.; Irshad, M.K. Phosphorus amendment decreased cadmium (Cd) uptake and ameliorates chlorophyll contents, gas exchange attributes, antioxidants, and mineral nutrients in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under Cd stress. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 62, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, A.; Rizwan, M.; Yasmeen, T.; Arif, M.S.; Hussain, A.; Mansha, A.; Ali, S.; Alshaya, H.; Okla, M.K. Phosphorus fertilizers enhance the phytoextraction of cadmium through Solanum nigrum L. Plants 2022, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuc, P.; Wasinkiewicz, K.; Janczur, K.L.; Tomaszewska, B. Phytoremediative potential of Brassica napus L.-heavy metal tolerance and accumulation, phytochelatin system response and γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase genetic background. Environ. Sci. Biol. 2012, 319–323. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:203627605 (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Mendoza-Cózatl, D.G.; Jobe, T.O.; Hauser, F.; Schroeder, J.I. Long-distance transport, vacuolar sequestration, tolerance, and transcriptional responses induced by cadmium and arsenic. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, J.D.; Sabovljević, A.D.; Sabovljević, M.S. Bryophytes and heavy metals: A review. Acta Bot. Croat. 2018, 77, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manara, A. Plant responses to heavy metal toxicity. In Plants and Heavy Metals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 27–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, D.; Huang, H.; Yang, X.; Razafindrabe, B.; Inouhe, M. The detoxification of lead in Sedum alfredii H. is not related to phytochelatins but the glutathione. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Vivancos, P.; de Simone, A.; Kiddle, G.; Foyer, C.H. Glutathione–linking cell proliferation to oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 89, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; He, Z.; Yang, X.; Stoffella, P.J.; Baligar, V.C. Soil biogeochemistry, plant physiology, and phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soils. Adv. Agron. 2015, 134, 135–225. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, N.; Mei, X.; Zu, Y.; Li, Z.; Qin, L.; Li, B. Effects of lime and oxalic acid on antioxidant enzymes and active components of Panax notoginseng under cadmium stress. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Liang, L.; Chen, C.; Wei, S.; Zhou, Q. Phytochelatin and oxidative stress under heavy metal stress tolerance in plants. In Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Damage in Plants Under Stress; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 191–217. [Google Scholar]






| Phosphorus Fertilizer Sources | Available Cd Content (mg·kg−1) | Available As Content (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Single super phosphate | 0.742 | 0.366 |
| Diammonium phosphate | 4.439 | 8.732 |
| Monoammonium phosphate | 2.833 | 0 |
| Calcium phosphate | 6.226 | 8.606 |
| High Calcium phosphate | 6.348 | 9.208 |
| Rock phosphate | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maw, T.T.; Deng, J.; Li, B.; Zu, Y.; Li, Z. Single Super Phosphate Improves Lolium perenne Quality and Rhizosphere Microorganism Structure Under Combined Cadmium and Arsenic Stress. Toxics 2025, 13, 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090805
Maw TT, Deng J, Li B, Zu Y, Li Z. Single Super Phosphate Improves Lolium perenne Quality and Rhizosphere Microorganism Structure Under Combined Cadmium and Arsenic Stress. Toxics. 2025; 13(9):805. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090805
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaw, Toe Toe, Jiangdi Deng, Bo Li, Yanqun Zu, and Zuran Li. 2025. "Single Super Phosphate Improves Lolium perenne Quality and Rhizosphere Microorganism Structure Under Combined Cadmium and Arsenic Stress" Toxics 13, no. 9: 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090805
APA StyleMaw, T. T., Deng, J., Li, B., Zu, Y., & Li, Z. (2025). Single Super Phosphate Improves Lolium perenne Quality and Rhizosphere Microorganism Structure Under Combined Cadmium and Arsenic Stress. Toxics, 13(9), 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090805






