The Effect of Radon Concentration on MS Prevalence: A Door-to-Door Survey in the Fault Zone in Afyonkarahisar, Turkey
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Relationship Between Radon, Tectonic Structure, and Lithology
1.2. Tectonic Structure of Afyonkarahisar
2. Materials and Methods
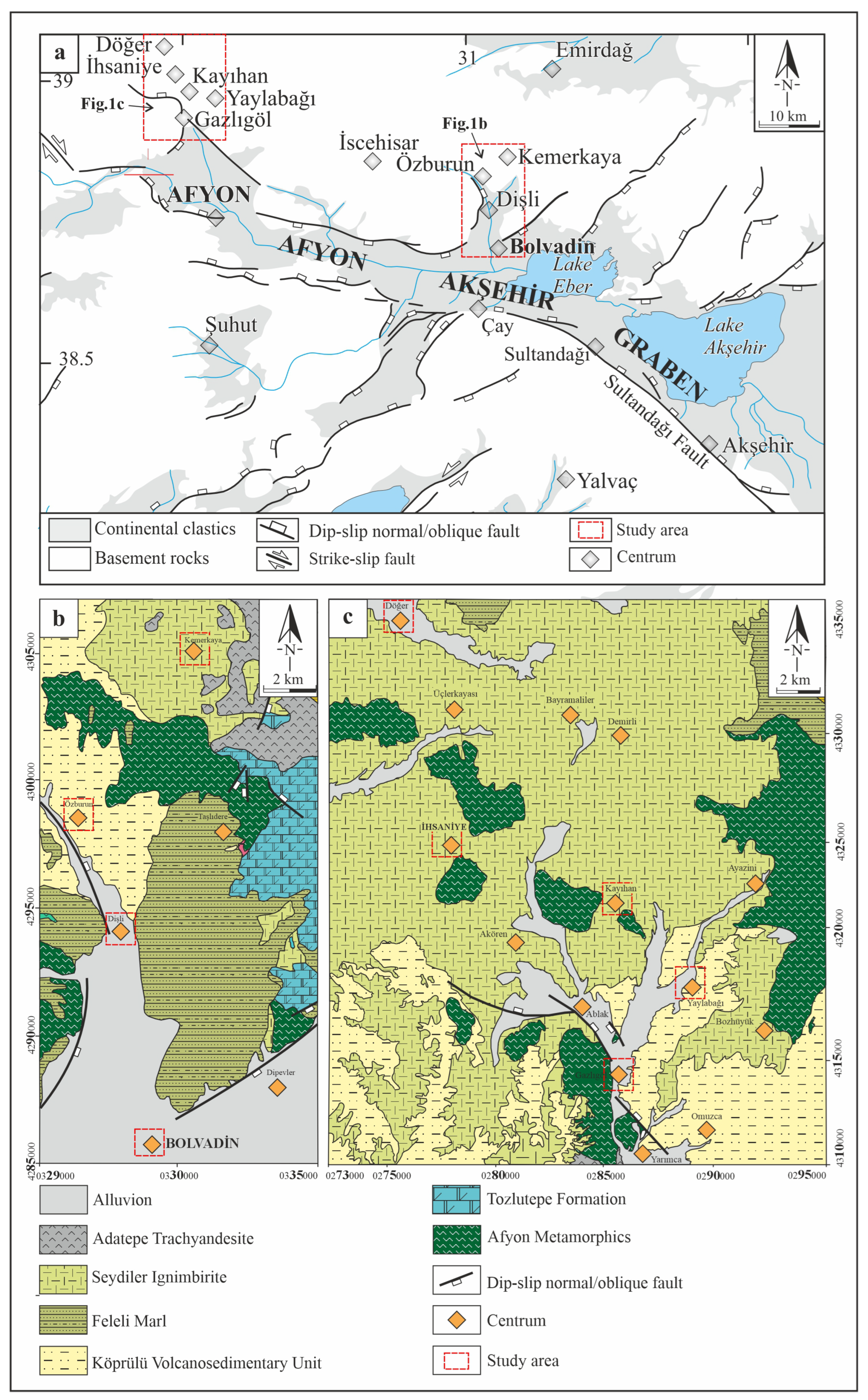
2.1. Determination of the Study Area
2.2. Determination of Sample Size
2.3. Geology of the Study Area
2.4. Radon Measurement and Data Analysis
2.4.1. CR-39 Detector
2.4.2. Distribution and Collection of CR-39 Detectors
2.4.3. Analysis of Detectors
- E: Irradiation Value;
- D: Trace Intensity (value found from the reader in the laboratory);
- CF: Calibration Factor.
2.5. Informed Consent
2.6. Patient Screening in the Field
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Radon Concentrations
3.2. Prevalence of MS
3.3. Patient Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Possible Mechanism for Radon
4.2. Limitations and Advantages of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sriwastava, S.; Khan, E.; Peterson, S.; Srivastava, S.; Lisak, R.P. Introduction to multiple sclerosis: Subtypes, pathogenesis, and diagnostic criteria. In Clinical Aspects of Multiple Sclerosis Essentials and Current Updates; Sriwastava, S.K., Triantafylou-Bernitsas, E., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bölük, C.; Börü, Ü.T.; Taşdemir, M.; Gezer, T. Epidemiology of multiple sclerosis in Turkey; a ten-year trend in rural cities. Turk. J. Neurol. 2021, 27, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börü, Ü.T.; Bölük, C.; Taşdemir, M.; Gezer, T.; Serim, V.A. Air pollution, a possible risk factor for multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2020, 141, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, J.E.; Root, P.J. The behavior of naturally fractured reservoirs. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1963, 3, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volfson, I.F.; Paul, W.; Pechenkin, I.G. Geochemical anomalies: Sickness and health. In Man and the Geosphere (Earth Sciences in the 21st Century); Florinsky, I.V., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 69–113. [Google Scholar]
- Bølviken, B.; Celius, E.G.; Nilsen, R.; Strand, T. Radon: A possible risk factor in multiple sclerosis. Neuroepidemiology 2003, 22, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves-Kirkby, C.J.; Denman, A.R.; Campbell, J.; Crockett, R.G.M.; Phillips, P.S.; Rogers, S. Is environmental radon gas associated with the incidence of neurodegenerative conditions? A retrospective study of multiple sclerosis in radon affected areas in England and Wales. J. Environ. Radioact. 2016, 154, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussbaum, E.; Harsh, J.B. Radon solubility in fatty acids and triglycerides. J. Phys. Chem. 1958, 62, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Anca, S.; Barros-Dios, J.M. Radon exposure and neurodegenerative disease. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Berriault, C.; Arrandale, V.H.; DeBono, N.L.; Harris, M.A.; Demers, P.A. Radon exposure and risk of neurodegenerative diseases among male miners in Ontario, Canada: A cohort study. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2023, 66, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson, S.; Robinson, I.; Rose, F.C. Ecological correlates of motor neuron disease mortality: A hypothesis concerning an epidemiological association with radon gas and gamma exposure. J. Neurol. 1996, 243, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Klug, M.G. Motor neuron disease mortality rates in U.S. states are associated with well water use. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener 2016, 17, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kunovska, B.; Ivanova, K.; Stojanovska, Z.; Vuchkov, D.; Zaneva, N. Measurements of radon concentration in soil gas of urban areas, Bulgaria. Rom. J. Phys. 2013, 58, S172–S179. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- UNSCEAR. UNSCEAR 2020/2021 Report Volume I: Sources, Effects and Risks of Ionizing Radiation; Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR): New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Darby, S.; Hill, D.; Doll, R. Radon: A likely carcinogen at all exposures. Ann. Oncol. 2001, 12, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.J.R.; Curado, A.; Lopes, S.I. The relationship between radon and geology: Sources, transport and indoor accumulation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, T.K.; Cameron, D.G.; Colman, T.B.; Roberts, P.D. Behaviour of radon in the geological environment: A review. Q. J. Eng. Geol. 1991, 24, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykara, O.; Dogru, M. Measurements of radon and uranium concentration in water and soil samples from East Anatolian active fault systems (Turkey). Radiat. Meas. 2006, 41, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, M. Radon: A Tracer for Geological, Geophysical and Geochemical Studies; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Choubey, V.M.; Bartarya, S.K.; Ramola, R.C. Radon in groundwater of eastern Doon valley, Outer Himalaya. Radiat. Meas. 2003, 36, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, K.; Swakoń, J.; Paszkowski, M.; Gradziński, R.; Łoskiewicz, J.; Janik, M.; Mazur, J.; Bogacz, J.; Horwacik, T.; Olko, P. Correlation between radon concentration and geological structure of the Kraków area. Radioact. Environ. 2005, 7, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaupotič, J. Review of radon research in Slovenia. In Sources and Measurements of Radon and Radon Progeny Applied to Climate and Air Quality Studies; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2012; pp. 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen, L.C.S.; Schumann, R.R.; Otton, J.K.; Dubiel, R.F.; Owen, D.E.; Dickinson, K.A. Geology of radon in the United States. In Geologic Controls on Radon; Gates, A.E., Gundersen, L.C., Eds.; G.S.A. Special Paper 271; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1992; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, L.M.O.; Gomes, M.E.P.; Neves, L.J.P.F.; Pereira, A.J.S.C. The influence of geological factors on radon risk in groundwater and dwellings in the region of Amarante (Northern Portugal). Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, A. Radon in caves. Int. J. Speleol. 2005, 34, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, K.; Yoshinaga, T.; Ueyama, T.; Asaue, H. Increased radon-222 in soil gas because of cumulative seismicity at active faults. Earth Planets Space 2014, 66, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćujić, M.; Mandić, L.J.; Petrović, J.; Dragović, R.; Đorđević, M.; Đokić, M.; Dragović, S. Radon-222: Environmental behavior and impact to (human and non-human) biota. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2021, 65, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, A.; Dumlupunar, İ.; Bağcı, M.; Ulutürk, Y.; Başaran, C.; Erdoğan, E. Afyonkarahisar ve çevresinin depremselliği. Afyon Kocatepe Üniv Fen. Bilim. Derg. 2012, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yıldız, A.; Başaran, C.; Bağcı, M.; Gümüş, A.; Çonkar, F.E.; Ulutürk, Y.; Yalım, H.A. The measurement of soil gases and shallow temperature for determination of active faults in a geothermal area: A case study from Ömer–Gecek, Afyonkarahisar (West Anatolia). Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkaymak, Ç.; Sözbilir, H.; Geçievi, M.O.; Tiryakioğlu, İ. Late Holocene coseismic rupture and aseismic creep on the Bolvadin Fault, Afyon Akşehir Graben, Western Anatolia. Turk. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 28, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MTA. Maden Tetkik Arama (MTA) Genel Müdürlüğü Jeoloji Etütleri Dairesi. 1:100.000 Ölçekli Afyon K26 Jeoloji Haritası; General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration: Ankara, Türkiye, 2011. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- MTA. Maden Tetkik Arama (MTA) Genel Müdürlüğü Jeoloji Etütleri Dairesi. 1:100.000 Ölçekli Afyon K25 Jeoloji Haritası; General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration: Ankara, Türkiye, 2011. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- MTA. Maden Tetkik Arama (MTA) Genel Müdürlüğü Jeoloji Etütleri Dairesi. 1:100.000 Ölçekli EskişehirJ24 Jeoloji Haritası; General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration: Ankara, Türkiye, 2018. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- NEA (National Education). Sampling and Statistics Handbook for Survey in Education; Asociation Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Sekaran, U. Research Methods for Business; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Emre, Ö.; Duman, T.Y.; Özalp, S.; Elmacı, H. Active Fault Map of Turkey (Scale 1:250,000), General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration Special Publication Series, Isparta (NJ 36-9) Quadrangle, Serial Number: 17; MTA: Ankara, Turkey, 2011. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Emre, Ö.; Duman, T.Y.; Özalp, S.; Şaroğlu, F.; Olgun, Ş.; Elmacı, H.; Can, T. Active fault database of Turkey. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 16, 3229–3275. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metin, S.; Genç, S.; ve Bulut, V. Afyon ve yakın dolayının jeolojisi. In General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration’s Report; No: 2113; General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration: Ankara, Türkiye, 1987; 93p. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Yalım, H.A.; Gümüş, A.; Açil, D.; Ünal, R.; Yıldız, A. Indoor radon activity concentrations and effective dose rates at houses in the Afyonkarahisar province of Turkey. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RADOSYS. RS_Man81: User’s Manual; Radosys Kft: Budapest, Hungary, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Börü, Ü.T.; Alp, R.; Sur, H.; Gül, L. Prevalence of multiple sclerosis door-to-door survey in Maltepe, Istanbul, Turkey. Neuroepidemiology 2006, 27, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; Edan, G.; Filippi, M.; Hartung, H.P.; Kappos, L.; Lublin, F.D.; Metz, L.M.; McFarland, H.F.; O’Connor, P.W.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 revisions to the “McDonald Criteria”. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 58, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICRP. Summary of ICRP Recommendations on Radon; ICRP Publications ref 4836-9756-8598; International Commission on Radiological Protection: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 26 January 2018; 6p. [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger, J.S.; Nazir, N.; Keighley, J.; Lynch, S. Residential radon exposure and multiple sclerosis: A pilot study. In Proceedings of the 21st International Radon Symposium, American Association of Radon Scientists and Technologists, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–19 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Eidbo, W.B.; Prater, M.P. Ionizating radiation: The long sought environmental “trigger” for multiple sclerosis. In Proceedings of the National Multiple Sclerosis Society Annual Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, November 1994; pp. 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Axelson, O.; Landtblom, A.-M.; Flodin, U. Multiple sclerosis and ionizing radiation. Neuroepidemiology 2001, 20, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidbo, W.B.; Prater, M.P. Linkage: Multiple sclerosis and ionizing radiation. Med. Veritas 2004, 1, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gilmore, M.; Grennan, E. A pilot study of the relationship between multiple sclerosis and the physical environment in northwest Ireland. Environ. Geochem. Health 2003, 25, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhdani, M.F.; Jalili, M.; Salehi-Abargouei, A.; Mirzaei, M.; Rahimdel, A.; Ebrahimi, A.A. Interaction of MS prevalence, radon gas concentration, and patient nutrition: A case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entezari, M.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Rahimdel, A.; Shahi, M.A.; Keyghobady, N.; Jalili, M.; Fathabadi, Z.A.; Fallah Yakhdani, M.; Ebrahimi, A.A. Is there a relationship between homes’ radon gas of MS and non-MS individuals, and the patients’ paraclinical magnetic resonance imaging and visually evoked potentials in Yazd-Iran? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 8907–8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathabadi, Z.A.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Mirzaei, M.; Mokhtari, M.; Sakhvidi, M.N.; Rahimdel, A.; Tafti, A.D.; Yakhdani, M.F.; Atefi, A.; Eslami, H.; et al. The relationship of indoor radon gas concentration with multiple sclerosis: A case-control study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 16350–16361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lykken, G.I.; Magness, A.T.; Momcilovic, B. Whole body Bi-214 and bedroom radon concentration in multiple sclerosis. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 708.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joswig, J. Direct Effects of Radon Exposure on the Neural System—A Possible Target for Pain Relief. Master’s Thesis, Technische University Darmstadt, Darmstadt, Germany, 2023; 86p. [Google Scholar]
- Lykken, G.I.; Momcilovic, B. Myelin fat storage of envirnomental radon daughters in the etiology of multiple sclerosis—A new appoach. Proc. North Dak. Acad. Sci. 2003, 57, 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Neilson, S.; Robinson, I.; Rose, F.C. The correlation of motor neuron disease with radiation: An objection to the hypothesis of Neilson et al. J. Neurol. 1997, 244, 57–58. [Google Scholar]
- Raaschou-Nielsen, O. Indoor radon and childhood leukaemia. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2008, 132, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, G.M.; Smith, T.J. Doses from radon and its decay products to children. J. Radiol. Prot. 2005, 25, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzywa-Celińska, A.; Krusiński, A.; Mazur, J.; Szewczyk, K.; Kozak, K. Radon-the element of risk. Impact Radon Expo. Hum. health. Toxics 2020, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henyoh, A.M.S.; Laurent, O.; Mandin, C.; Clero, E. Radon exposure and potential health effects other than lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1439355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S. Measurements of lung doses from radon and thoron in the dwellings of Al-Zulfi, Saudi Arabia, for the assessment of health risk due to ionizing radiation. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, F.; Panahi, M.; Bateni, S.M.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Yoo, J.; Kim, H.; Won Kim, S.; Lee, S. Spatial modeling of geogenic indoor radon distribution in Chungcheongnam-do, South Korea using enhanced machine learning algorithms. Environ. Int. 2023, 171, 107724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langlois, P.H.; Lee, M.; Lupo, P.J.; Rahbar, M.H.; Cortez, R.K. Residential radon and birth defects: A population-based assessment. Birth Defects Res. Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2016, 106, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräuner, E.V.; Andersen, Z.J.; Andersen, C.E.; Pedersen, C.; Gravesen, P.; Ulbak, K.; Hertel, O.; Loft, S.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O. Residential radon and brain tumour incidence in a Danish cohort. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, F.K.T.; Irvine, J.L.; Jacques, W.R.; Salgia, S.R.; Innes, D.G.; Winquist, B.D.; Torr, D.; Brenner, D.R.; Goodarzi, A.A. Radon exposure is rising steadily within the modern North American residential environment, and is increasingly uniform across seasons. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.C.; Krewski, D.; Chen, Y.; Pope, C.A.; Gapstur, S.; Thun, M.J. Radon and lung cancer in the American Cancer Society Cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2011, 20, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneaux, S. The Link Between Radon Exposure and Neurodegenerative Disease Risk Factors. In Honors Theses; Eastern Kentucky University: Richmond, KY, USA, 2024; Available online: https://encompass.eku.edu/honors_theses/1047 (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, W.; He, Z.; Fu, C.; Du, F. Radon and lung cancer: Current status and future prospects. Crit. Rev. Oncol/Hematol. 2024, 198, 104363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hursh, J.B.; Morken, D.A.; Davis, T.P.; Lovaas, A. The fate of radon ingested by man. Health Phys. 1965, 11, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Region | Radon Sources | Radon Distribution (Bq/m3) | MS Prevalence per 100,000 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geology | Type of Fault | Minimum | Maximum | Average ± S.D. | ||
| City Center of Bolvadin | Alluvium Bolvadin fault | Active fault | 21 | 1325 | 307 ± 5.48 | 70.3 |
| Kemerkaya | Seydiler ignimbirite Adatepe andesite | - | 66 | 1603 | 350 ± 4.9 | 0 |
| Kayıhan | Seydiler ignimbirite | - | 65 | 1688 | 407 ± 4.45 | 0 |
| City Center of İhsaniye | Seydiler ignimbirite | - | 45 | 1878 | 399 ± 5 | 29.7 |
| Döğer | Seydiler ignimbirite | - | 69 | 941 | 314 ± 7.44 | 0 |
| Dişli | Alluvium Dişli fault | Nonactive fault | 27 | 489 | 192 ± 4.5 | 0 |
| Yaylabağı | Köprülü volcano-sedimentary unit Gazlıgöl fault | Nonactive fault | 61 | 447 | 182 ± 4.21 | 0 |
| Gazlıgöl | Afyon metamorphics Gazlıgöl fault | Nonactive fault | 12 | 607 | 162 ± 3.73 | 56.3 |
| Özburun | Köprülü volcano-sedimentary unit Dişli fault | Nonactive fault | 68 | 220 | 159 ± 11.49 | 34.1 |
| Baseline Characteristics | Mean Values |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 42.5 ± 15.7 |
| Female/male (n) | 10/4 |
| RRMS/SPMS/PPMS (n) | 10/3/1 |
| Disease duration (years) | 10.0 ± 10.9 |
| Disease onset (years) | 30.7 ± 8.3 |
| EDSS (mean) | 3.4 ± 1.8 |
| Symptoms | Number of Patients |
|---|---|
| Pyramidal | 4 |
| Cerebellar | 3 |
| Brainstem | 2 |
| Sensory | 5 |
| Visual | 2 |
| Autonomic | 1 |
| Mental | 4 |
| Rock Types | Uranium | Thorium | Potassium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alluvium | 62.49 | 5.33 | 7.83 |
| Limestone | 3.54 | 4.98 | 5.85 |
| Trahcyte | 351.77 | 44.52 | 304 |
| Tuff | 264.51 | 53.63 | 1275.97 |
| Schist | 6.16 | 2.2 | 52.37 |
| Marble | 143.51 | 14.94 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Türk Börü, Ü.; Yıldız, A.; Bağcı, M.; Sandıkçıoğlu Gümüş, A.; Issı, E.S.; İncebacak, F.; Acar, H.; Bölük, C. The Effect of Radon Concentration on MS Prevalence: A Door-to-Door Survey in the Fault Zone in Afyonkarahisar, Turkey. Toxics 2025, 13, 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090797
Türk Börü Ü, Yıldız A, Bağcı M, Sandıkçıoğlu Gümüş A, Issı ES, İncebacak F, Acar H, Bölük C. The Effect of Radon Concentration on MS Prevalence: A Door-to-Door Survey in the Fault Zone in Afyonkarahisar, Turkey. Toxics. 2025; 13(9):797. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090797
Chicago/Turabian StyleTürk Börü, Ülkü, Ahmet Yıldız, Metin Bağcı, Ayla Sandıkçıoğlu Gümüş, Elif Simin Issı, Furkan İncebacak, Hakan Acar, and Cem Bölük. 2025. "The Effect of Radon Concentration on MS Prevalence: A Door-to-Door Survey in the Fault Zone in Afyonkarahisar, Turkey" Toxics 13, no. 9: 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090797
APA StyleTürk Börü, Ü., Yıldız, A., Bağcı, M., Sandıkçıoğlu Gümüş, A., Issı, E. S., İncebacak, F., Acar, H., & Bölük, C. (2025). The Effect of Radon Concentration on MS Prevalence: A Door-to-Door Survey in the Fault Zone in Afyonkarahisar, Turkey. Toxics, 13(9), 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090797






