Study on Retardation Factors of Cr(VI) Transport in Typical Soils of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Soils
2.2. Chemicals and Instruments
2.3. Experimental Procedure
3. Results
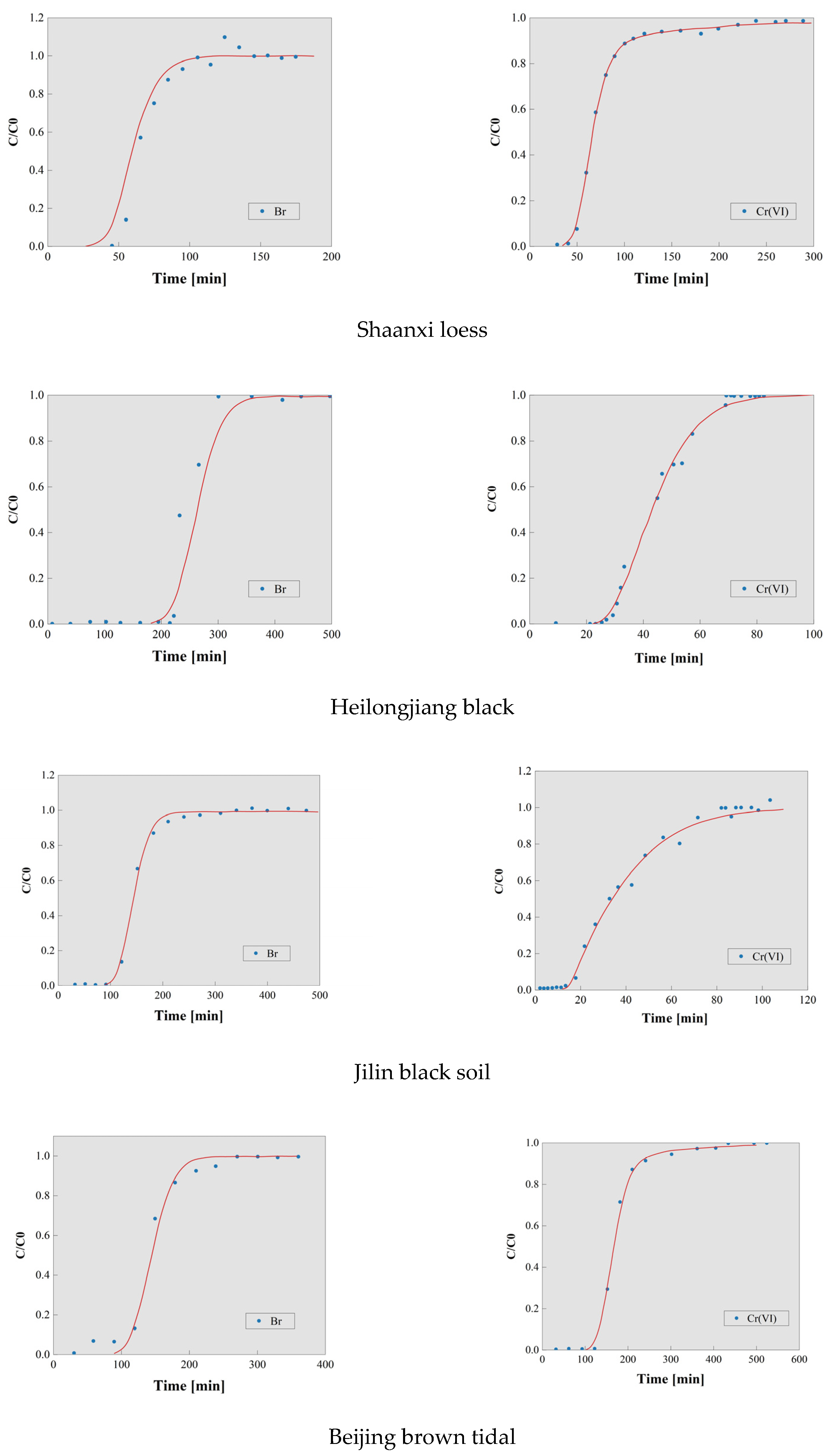
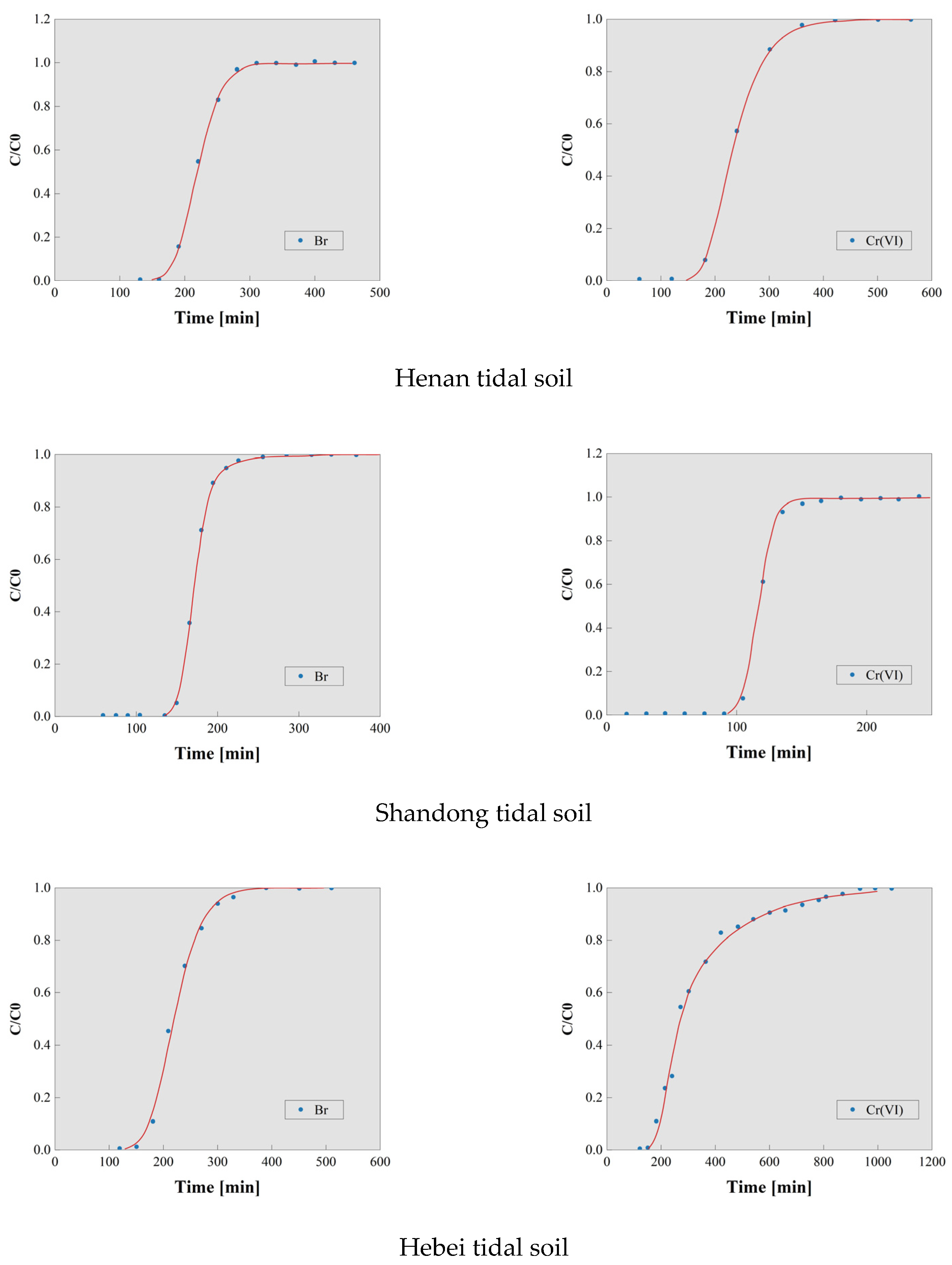
3.1. Results of the Soil Column Leaching Experiment
3.2. Calculation of Dispersion Coefficient (D) for Cr(VI) in Typical Soils
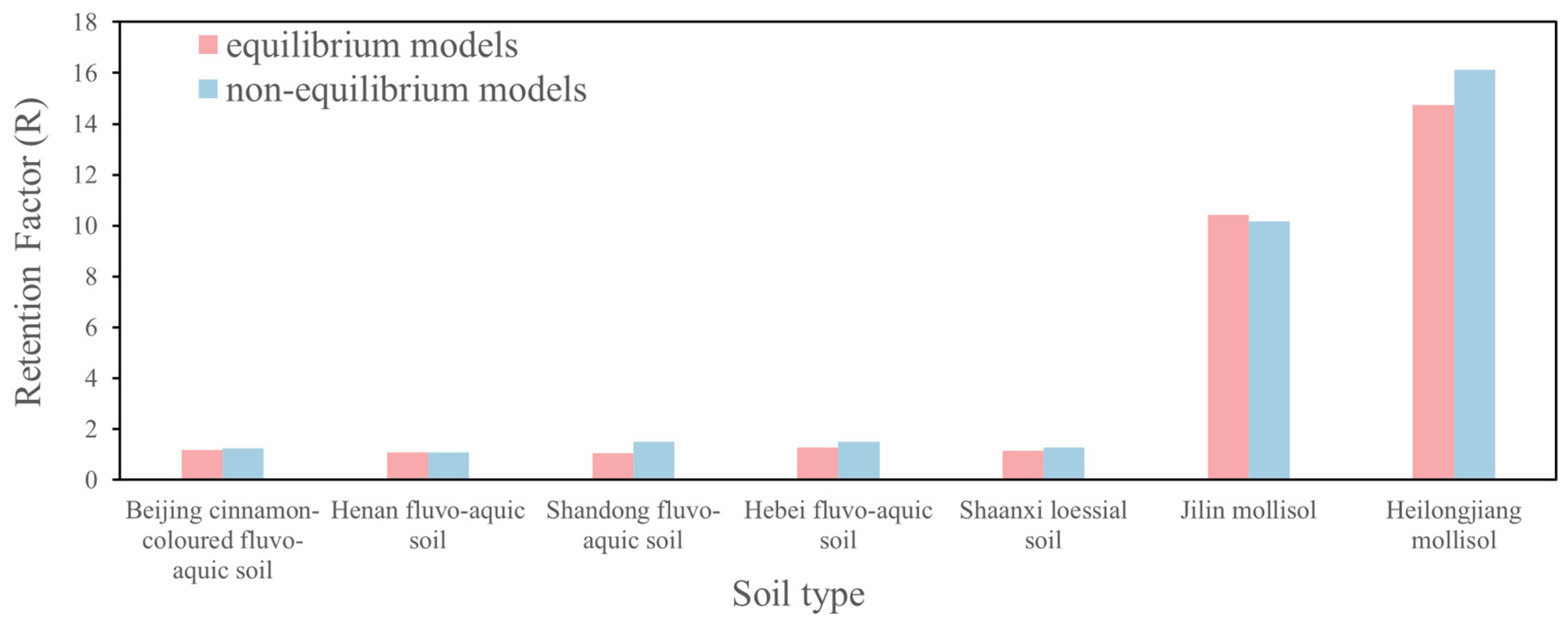
3.3. Retention Factor of Cr(VI) in Typical Soils
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kimbrough, D.E.; Cohen, Y.; Winer, A.M.; Creelman, L.; Mabuni, C. A critical assessment of chromium in the environment. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 29, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhal, B.; Thatoi, H.N.; Das, N.N.; Pandey, B.D. Chemical and microbial remediation of hexavalent chromium from contaminated soil and mining/metallurgical solid waste: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250, 272–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobby, R.; Jha, P.; Yadav, A.K.; Desai, N. Biosorption and biotransformation of hexavalent chromium [Cr (VI)]: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgaki, M.N.; Charalambous, M.; Kazakis, N.; Talias, M.A.; Georgakis, C.; Papamitsou, T.; Mytiglaki, C. Chromium in water and carcinogenic human health risk. Environments 2023, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, L.; Yan, X.; Tian, Y. Advances in Remediation Technologies for Chromium-Contaminated Sites. Environ. Eng. 2020, 38, 1–8+23. [Google Scholar]
- Sabur, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Safiullah, S. Treatment of tannery effluent by locally available commercial grade lime. J. Sci. Res. 2013, 5, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, T.B.; Lei, M.; Yang, J.; Guo, Q.J.; Song, B.; Zhou, X.Y. Spatial distribution of soil heavy metal pollution estimated by different interpolation methods: Accuracy and uncertainty analysis. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, Q.; Shi, T.; Gong, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, Y. Status of chromium accumulation in agricultural soils across China (1989–2016). Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Cai, M.L. Study on pollution situation at typical chrome residue contaminated sites and corresponding integrated remediation plan. Res. Environ. Sci. 2009, 22, 248–253. [Google Scholar]
- Sarangi, A.; Krishnan, C. Comparison of in vitro Cr (VI) reduction by CFEs of chromate resistant bacteria isolated from chromate contaminated soil. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4130–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederkvist, K.; Ingvertsen, S.T.; Jensen, M.B.; Holm, P.E. Behaviour of chromium (VI) in stormwater soil infiltration systems. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 35, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, C.D.; Rowe, R.K. Contaminant transport modeling. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress on Environmental Geotechnics, Lisboa, Portugal, 7–11 September 1998; Seco e Pinto, P., Ed.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 3, pp. 939–956. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.A.; Muthukrishnan, M.; Guha, B.K. Sorption and transport modeling of hexavalent chromium on soil media. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Study on Adsorption and Migration Characteristics of Cr(VI) in Typical Soils. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Wu, X.; Tan, X.; Wang, X. Sorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions: A review. Open Colloid Sci. J. 2011, 4, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwatuyi, O.E.; Ojuri, O.O. Environmental performance of lime–rice husk ash stabilized lateritic soil contaminated with lead or naphthalene. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2017, 35, 2947–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Q.; Zheng, J.; He, H.; Han, F.; Zhang, X. Effects of Pisha sandstone content on solute transport in a sandy soil. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2214–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Gschwend, P.M.; Imboden, D.M. Environmental Organic Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, K.; Trakal, L.; Sillerova, H.; Avelar-González, F.J.; Guerrero-Barrera, A.L.; Hough, R.; Beesley, L. Mobility of As, Cr and Cu in a contaminated grassland soil in response to diverse organic amendments; a sequential column leaching experiment. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 88, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tong, J.; Hu, B.X.; Wei, W. Adsorption and desorption for dynamics transport of hexavalent chromium (Cr (VI)) in soil column. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Sejna, M. Development and applications of the HYDRUS and STANMOD software packages and related codes. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toride, N.; Leij, F.J.; van Genuchten, M.T. The CXTFIT Code for Estimating Transport Parameters from Laboratory or Field Tracer Experiments; Research Report No. 137; U.S. Salinity Laboratory Agricultural Research Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture: Riverside, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Mao, M. Simulation of Nonequilibrium Transport of Atrazine in Saturated Sandy Loam Soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2003, 40, 829–837. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C. Experimental Study on Vertical Transport of Cr(VI) in the Vadose Zone. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Raoof, A.; Hassanizadeh, S.M. Saturation-dependent solute dispersivity in porous media: Pore-scale processes. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Rolle, M.; Kitanidis, P.K. Longitudinal dispersion coefficients for numerical modeling of groundwater solute transport in heterogeneous formations. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 212, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Research Progress on Hydrodynamic Dispersion Coefficient in Soil. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 4, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, Z.; Li, F. Research on the Evaluation Method of Cr (VI) Migration Parameters in Topsoil and Its Application. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2016, 25, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, T.; Wang, B. Groundwater Pollution and Groundwater Quality Simulation Methods; Beijing Normal University Press: Beijing, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Woo, H.; Park, H.; Park, J. Application of a newly developed column test device to analyze seawater transport in sandy soils. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, A.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Ghanbarian, B.; Ebrahimian, H. Analytical solute transport modeling of furrow fertigation using the STANMOD software package. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2025, 73, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, D.R.; Van Genuchten, M.T.; Biggar, J.W. Water flow and solute transport processes in the unsaturated zone. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 89S–108S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharoni, C.; Sparks, D.L. Kinetics of soil chemical reactions—A theoretical treatment. Rates Soil Chem. Process. 1991, 27, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Gaber, H.M.; Inskeep, W.P.; Comfort, S.D.; Wraith, J.M. Nonequilibrium transport of atrazine through large intact soil cores. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995, 59, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamerdinger, A.P.; Wagenet, R.J.; Genuchten, M.T.V. Application of two-site/two-region models for studying simultaneous nonequilibrium transport and degradation of pesticides. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuchten, M.T.V.; Wagenet, R.J. Two-Site/Two-Region Models for Pesticide Transport and Degradation: Theoretical Development and Analytical Solutions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1989, 53, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.Z.; Sun, A. Mathematical Modeling of Groundwater Pollution; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Jiang, X.; He, J.; Bian, Y.; Gao, H. Adsorption and Transport Characteristics of Cd2+ in Acidic Soils. Environ. Chem. 2007, 26, 307–313. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza Braz, A.M.; Fernandes, A.R.; Ferreira, J.R.; Alleoni, L.R.F. Prediction of the distribution coefficients of metals in Amazonian soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 95, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
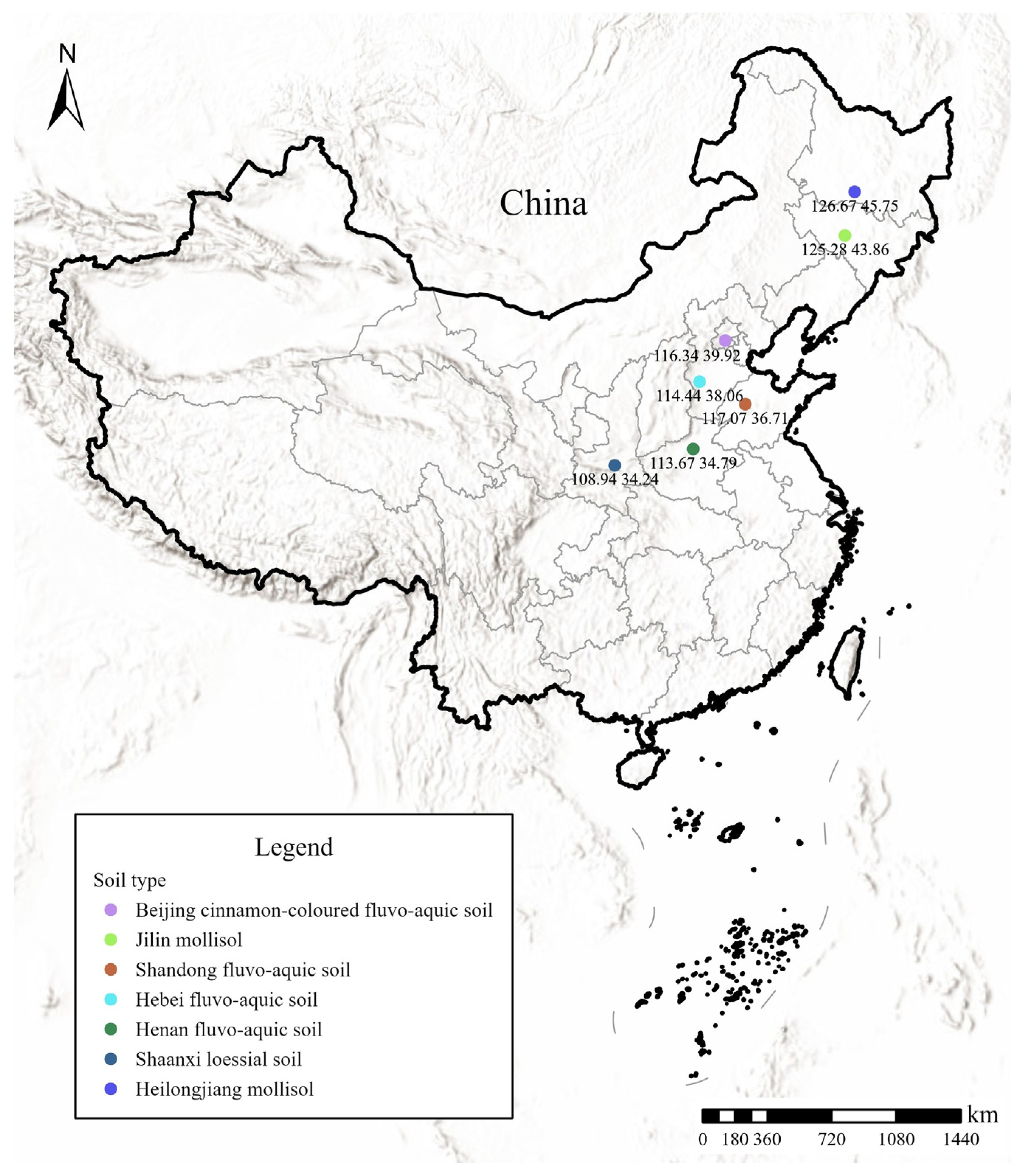
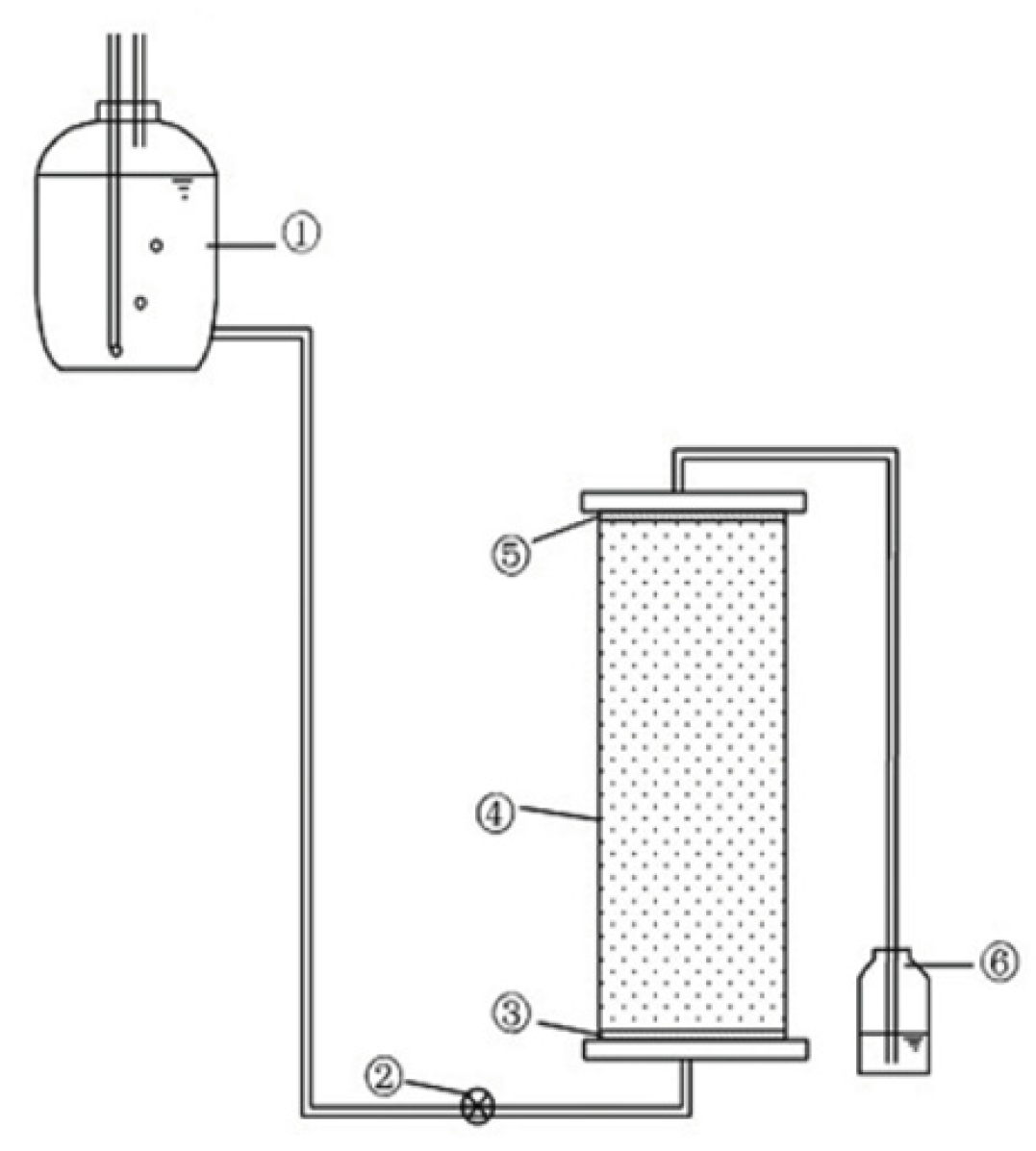
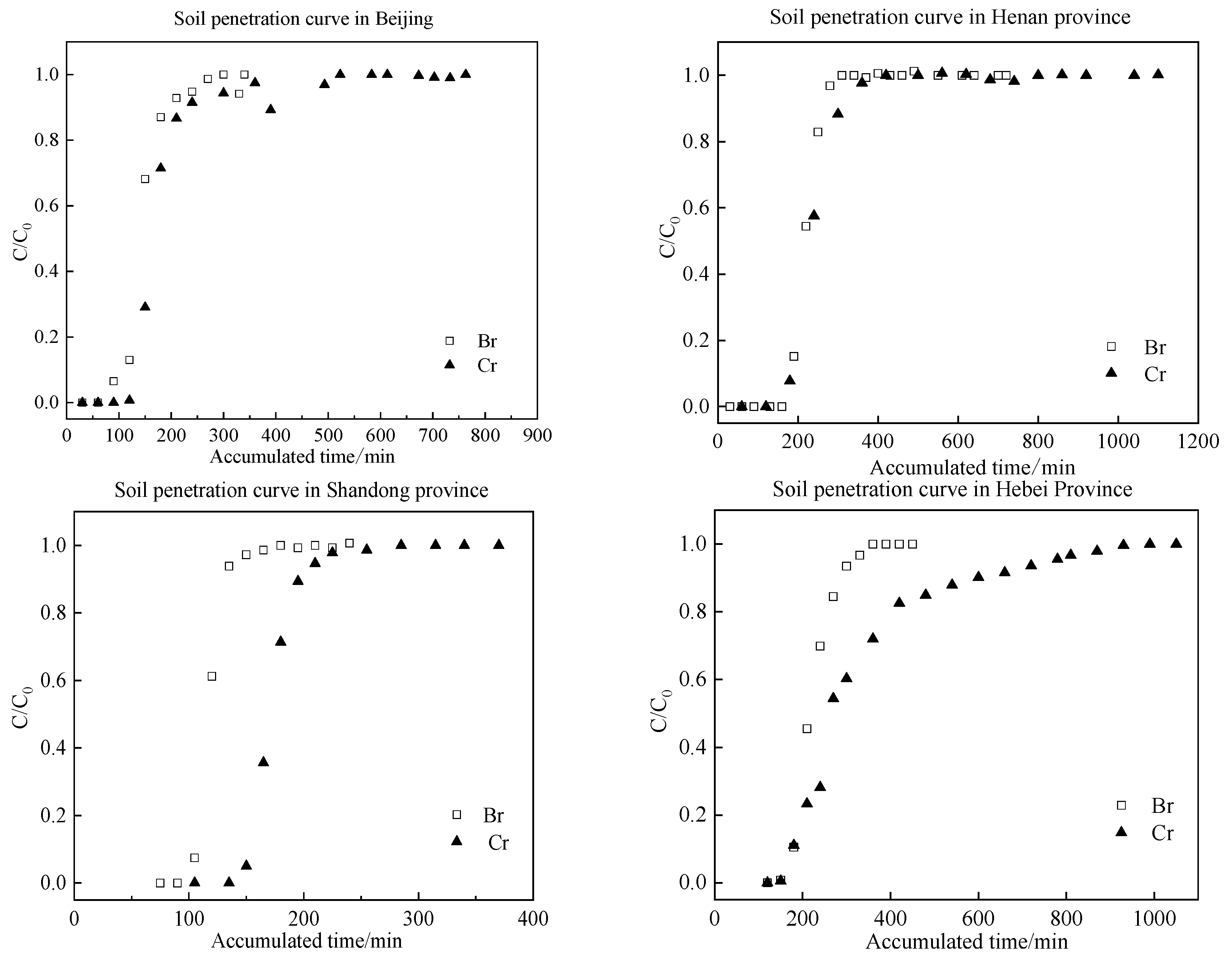
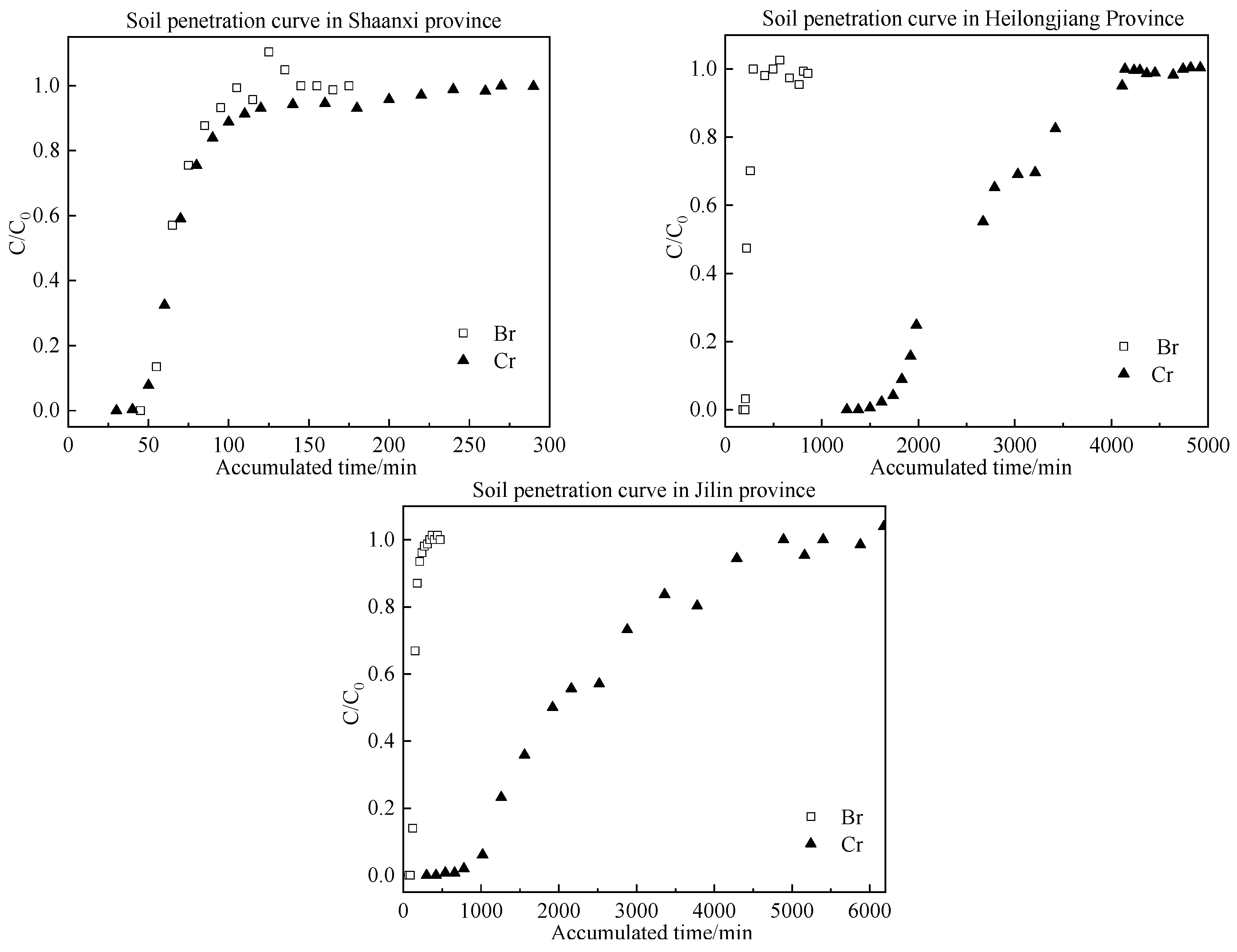
| Soil Indices | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | pH | SOM (g/kg) | CEC (cmol/kg) | Particle Density (kg/dm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing cinnamon-colored fluvo-aquic soil | 12.0 | 79.6 | 8.4 | 8.47 | Not detected | 7.56 | 2.597 |
| Henan fluvo-aquic soil | 11.0 | 81.5 | 7.5 | 8.01 | 4.78 | 5.37 | 2.682 |
| Shandong fluvo-aquic soil | 35.5 | 56.1 | 8.4 | 8.56 | 2.70 | 8.01 | 2.706 |
| Hebei fluvo-aquic soil | 5.0 | 74.7 | 20.3 | 8.25 | 13.40 | 15.2 | 2.595 |
| Shaanxi loessial soil | 2.7 | 85.0 | 12.3 | 6.38 | 43.4 | 30.20 | 2.690 |
| Heilongjiang mollisol | 8.9 | 78.6 | 12.5 | 8.09 | 12.6 | 12.30 | 2.633 |
| Jilin mollisol | 8.6 | 71.8 | 19.6 | 7.01 | 16.5 | 26.70 | 2.628 |
| Soil Type | (min) | (min) | (min) | v (cm/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing cinnamon-colored fluvo-aquic soil | 121.89 | 139.34 | 175.57 | 0.17 |
| Henan fluvo-aquic soil | 186.31 | 217.77 | 255.44 | 0.12 |
| Shandong fluvo-aquic soil | 105.29 | 117.44 | 131.65 | 0.22 |
| Hebei fluvo-aquic soil | 181.65 | 216.54 | 270.05 | 0.12 |
| Shaanxi loessial soil | 56.22 | 59.26 | 79.12 | 0.44 |
| Jilin mollisol | 215.01 | 240.74 | 282.20 | 0.10 |
| Heilongjiang mollisol | 56.22 | 59.26 | 79.12 | 0.18 |
| Soil Type | Average Pore ·Water Flowrate v (cm/min) | Calculated Dispersion Coefficient D (cm2/min) |
|---|---|---|
| Beijing cinnamon-colored fluvo-aquic soil | 0.17 | 0.077 |
| Henan fluvo-aquic soil | 0.12 | 0.039 |
| Shandong fluvo-aquic soil | 0.22 | 0.034 |
| Hebei fluvo-aquic soil | 0.12 | 0.065 |
| Shaanxi loessial soil | 0.44 | 0.21 |
| Jilin mollisol | 0.18 | 0.12 |
| Heilongjiang mollisol | 0.10 | 0.027 |
| Soil Type | Average Pore Water Velocity v (cm min−1) | Dispersion Coefficient D (cm2 min−1) | Retarding Factor R | Correlation Coefficient | Mean Square Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing brown tidal soil | 0.17 | 0.063 | 1 | 0.9901 | 2.06 × 10−3 |
| Henan tidal soil | 0.12 | 0.029 | 1 | 0.9998 | 5.55 × 10−5 |
| Shandong tidal soil | 0.22 | 0.019 | 1 | 0.9990 | 1.63 × 10−4 |
| Hebei tidal soil | 0.12 | 0.056 | 1 | 0.9971 | 5.75 × 10−4 |
| Shaanxi loess | 0.40 | 0.198 | 1 | 0.9816 | 2.35 × 10−3 |
| Jilin black soil | 0.18 | 0.116 | 1 | 0.9953 | 9.42 × 10−4 |
| Heilongjiang black soil | 0.11 | 0.015 | 1 | 0.9786 | 5.14 × 10−3 |
| Soil Type | Average Pore Water Velocity v (cm min−1) | Dispersion Coefficient D (cm2 min−1) | Retarding Factor R | Correlation Coefficient | Mean Square Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing brown tidal soil | 0.17 | 0.063 | 1 | 0.9923 | 1.66 × 10−3 |
| Henan tidal soil | 0.12 | 0.029 | 1 | 0.9998 | 5.55 × 10−5 |
| Shandong tidal soil | 0.22 | 0.019 | 1 | 0.9990 | 1.63 × 10−4 |
| Hebei tidal soil | 0.12 | 0.056 | 1 | 0.9971 | 5.75 × 10−4 |
| Shaanxi loess | 0.44 | 0.217 | 1.1 | 0.9816 | 2.35 × 10−3 |
| Jilin black soil | 0.18 | 0.076 | 1 | 0.9968 | 6.97 × 10−4 |
| Heilongjiang black soil | 0.10 | 0.015 | 0.94 | 0.9786 | 5.14 × 10−3 |
| Soil Type | Average Pore Water Velocity v (cm min−1) | Dispersion Coefficient D (cm2 min−1) | Retarding Factor R | Correlation Coefficient | Mean Square Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing brown tidal soil | 0.17 | 0.064 | 1 | 0.9915 | 2.02 × 10−3 |
| Henan tidal soil | 0.12 | 0.029 | 1 | 0.9996 | 6.57 × 10−5 |
| Shandong tidal soil | 0.22 | 0.021 | 1 | 0.9984 | 3.80 × 10−4 |
| Hebei tidal soil | 0.12 | 0.057 | 1 | 0.9965 | 6.13 × 10−4 |
| Shaanxi loess | 0.44 | 0.299 | 1 | 0.9603 | 7.10 × 10−3 |
| Jilin black soil | 0.18 | 0.076 | 1 | 0.9968 | 6.51 × 10−4 |
| Heilongjiang black soil | 0.10 | 0.022 | 1 | 0.9555 | 9.95 × 10−3 |
| Soil Type | Average Pore Water Velocity v (cm min−1) | Dispersion Coefficient D (cm2 min−1) | Retarding Factor R | Correlation Coefficient | Mean Square Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing brown tidal soil | 0.17 | 0.064 | 1.17 | 0.994847 | 1.02 × 10−3 |
| Henan tidal soil | 0.12 | 0.029 | 1.08 | 0.994199 | 1.23 × 10−3 |
| Shandong tidal soil | 0.22 | 0.021 | 1.06 | 0.943362 | 8.37 × 10−3 |
| Hebei tidal soil | 0.12 | 0.057 | 1.26 | 0.927071 | 9.36 × 10−3 |
| Shaanxi loess | 0.44 | 0.299 | 1.15 | 0.98533953 | 1.87 × 10−3 |
| Jilin black soil | 0.18 | 0.076 | 14.74 | 0.91042588 | 1.64 × 10−2 |
| Heilongjiang black soil | 0.10 | 0.022 | 10.41 | 0.957929 | 7.85 × 10−3 |
| Soil Type | Average Pore Water Velocity v (cm min−1) | Dispersion Coefficient D (cm2 min−1) | Retarding Factor R | Partition Coefficient (β) | Mass Transfer Coefficient (ω) | Correlation Coefficient | Mean Square Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing brown tidal soil | 0.169745505 | 0.06358 | 1.24 | 0.9204 | 4.05 × 10−3 | 0.9984 | 3.75 × 10−4 |
| Henan tidal soil | 0.119389841 | 0.02939 | 1.09 | 0.8712 | 5.07 × 10−2 | 0.9999 | 5.74 × 10−6 |
| Shandong tidal soil | 0.22421213 | 0.0209 | 1.49 | 0.9765 | 4.82× 10−3 | 0.9998 | 4.64 × 10−5 |
| Hebei tidal soil | 0.120070107 | 0.05657 | 1.51 | 0.7045 | 2.48 × 10−2 | 0.9940 | 8.65 × 10−4 |
| Shaanxi loess | 0.438743273 | 0.2987 | 1.29 | 0.8502 | 4.50 × 10−3 | 0.9990 | 1.87 × 10−4 |
| Jilin black soil | 0.183589888 | 0.07611 | 16.13 | 0.4763 | 7.77 × 10−2 | 0.9990 | 1.87 × 10−4 |
| Heilongjiang black soil | 0.099692937 | 0.02228 | 10.17 | 0.6269 | 1.69 × 10−1 | 0.9944 | 1.13 × 10−3 |
| Soil Type | Dispersion Coefficient D Fitting Value | Soil Type |
|---|---|---|
| Beijing brown tidal soil | 0.064 | 1.24 |
| Henan tidal soil | 0.029 | 1.09 |
| Shandong tidal soil | 0.021 | 1.49 |
| Hebei tidal soil | 0.057 | 1.51 |
| Shaanxi loess | 0.299 | 1.29 |
| Heilongjiang black soil | 0.022 | 10.17 |
| Jilin black soil | 0.076 | 16.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, D.; Sun, N.; Ding, Z.; Bai, L.; Zhang, Z. Study on Retardation Factors of Cr(VI) Transport in Typical Soils of China. Toxics 2025, 13, 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090774
Qiao X, Zhang X, Zhou D, Sun N, Ding Z, Bai L, Zhang Z. Study on Retardation Factors of Cr(VI) Transport in Typical Soils of China. Toxics. 2025; 13(9):774. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090774
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Xiongbiao, Xiangyang Zhang, Dejin Zhou, Ning Sun, Zhenyu Ding, Liping Bai, and Zongwen Zhang. 2025. "Study on Retardation Factors of Cr(VI) Transport in Typical Soils of China" Toxics 13, no. 9: 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090774
APA StyleQiao, X., Zhang, X., Zhou, D., Sun, N., Ding, Z., Bai, L., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Study on Retardation Factors of Cr(VI) Transport in Typical Soils of China. Toxics, 13(9), 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090774







