Assessing Multiple Risks in Regulating Reservoirs: Perspectives on Heavy Metal Contamination
Highlights
- Multi-Media Assessment: We conducted an integrated analysis of 12 heavy metals (HMs) in both water and sediments of Dongping Lake, which is used as a reservoir as part of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project.
- Cd Dominates Ecological Risk: The sediments were significantly enriched with Cd, posing a moderate ecological risk (RI = 175.82).
- Source Apportionment: Agricultural runoff (phosphate fertilizers) and industrial discharge are primary sources of bioavailable Cd, confirmed by spatial correlation with farmland/sewage inputs.
- The implications of these findings are significant for both environmental management and public health protection.
- The clear identification of Cd as the major pollutant can help prioritize monitoring and remediation efforts in Dongping Lake, ensuring water quality and safety in this strategically important reservoir.
- The attribution of Cd pollution to agricultural and industrial sources provides a scientific basis for source control policies, such as regulating fertilizer use and improving wastewater treatment discharges.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Lack of chemical speciation data concerning HM mobility and toxicity.
- Insufficient research on the release risk and transport of heavy metals from sediments.
- Outdated health risk models ignoring exposure pathway interactions.
- Characterize the spatial heterogeneity of 12 heavy metals (Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd, Pb) in water–sediment systems and conduct a pollution assessment.
- Determine the chemical speciation (BCR sequential extraction) to evaluate the remobilization risks.
- Model the multi-pathway health risks (ingestion/dermal/inhalation) for residents during high-exposure periods.
- Predict the pollution sources through correlation analysis and existing studies.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Measurements
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Ecological and Health Risk Assessment
Assessment of Surface Water Pollution Levels
2.3.2. Sediment Ecological Risk Assessment
Potential Ecological Risk Index
Geo-Accumulation Index
Risk Assessment Code
2.3.3. Monte Carlo Health Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Distribution and Contamination of HMs
3.2. Chemical Speciation of HMs in Surface Sediments
3.2.1. Human Health Risk Assessment of HMs in Sediments
3.2.2. Sensitivity Analysis
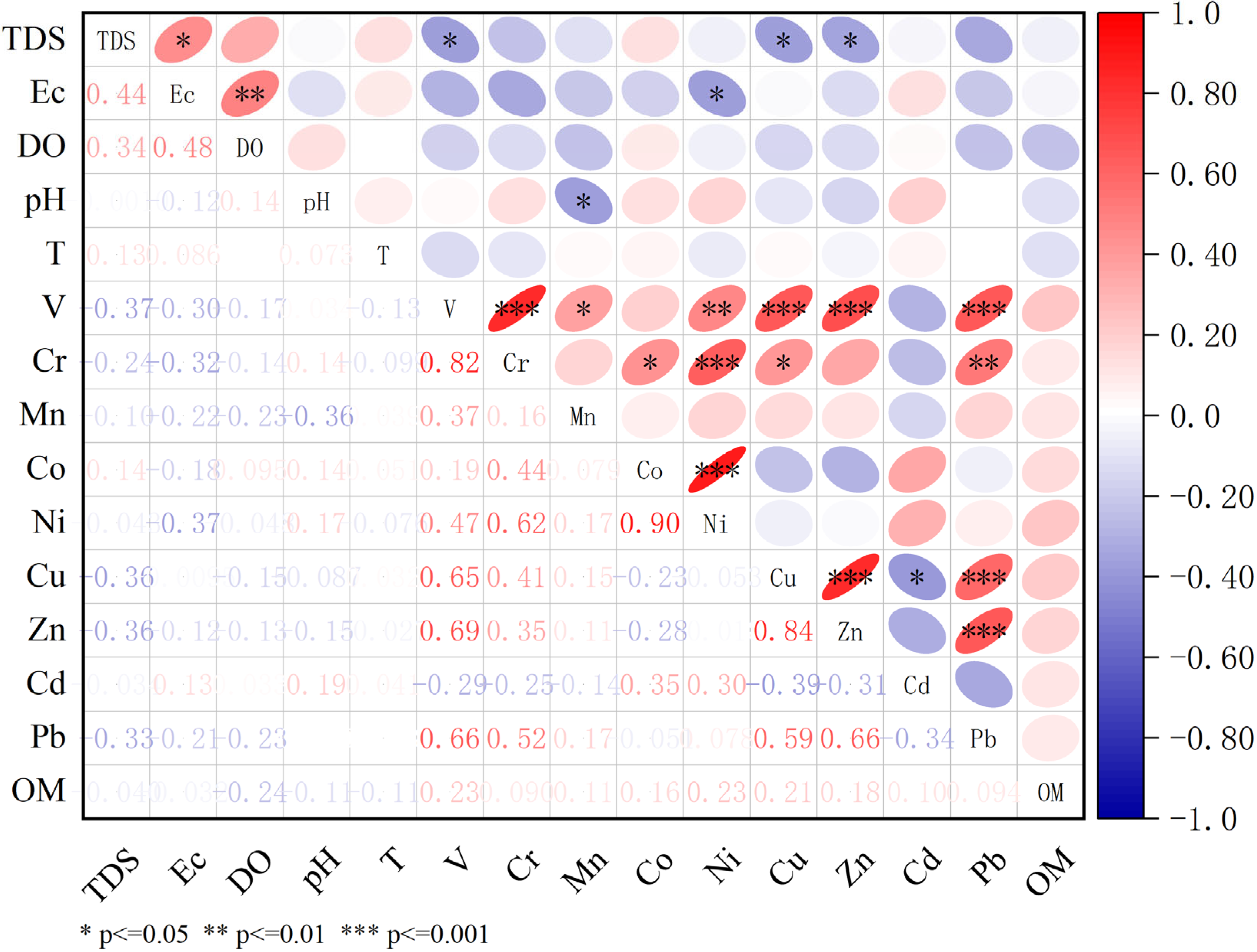
3.3. Correlation Analysis and Pollution Source Identification
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, G.L.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Yang, Z.F. Inputting history of heavy metals into the inland lake recorded in sediment profiles: Poyang Lake in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.J.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, L.F.; Liang, T.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ma, C.X.; Xing, B.S. Multivariate geostatistical analysis and source identification of heavy metals in the sediment of Poyang Lake in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, L.L.; Zhang, X.X.; Jiang, S.H.; Gao, J.F.; Zhang, S.J. Distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments along the Weihai coast, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 190, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adimalla, N.; Wang, H. Distribution, contamination, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface soils from northern Telangana, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Tang, Z.; McGrath, S.P. Soil contamination in China: Current status and mitigation strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.Q.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, Z.H.; Lv, X.N.; Fei, X.F. Risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in agricultural soil: A case study in the coastal city of Zhejiang Province, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2019, 33, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakyayita, G.K.; Norrström, A.C.; Kulabako, R.N. Assessment of Levels, Speciation, and Toxicity of Trace Metal Contaminants in Selected Shallow Groundwater Sources, Surface Runoff, Wastewater, and Surface Water from Designated Streams in Lake Victoria Basin, Uganda. J. Environ. Public Health 2019, 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobaradaran, S.; Naddafi, K.; Nazmara, S.; Ghaedi, H. Heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Ni and Pb) content in two fish species of Persian Gulf in Bushehr Port, Iran. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 6191–6193. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y. Water quality assessment and pollution source analysis of the Dawen River. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2023, 28, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Yu, N.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, D.Y.; Deng, H.G.; Yao, X. Characteristics and source analysis of water pollution in dry season (November to March) of Dongping Lake (China). Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 273, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Meng, F.P.; Du, Y.X.; Tan, Y.H. Distribution, speciation, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Jiaozhou Bay, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2016, 22, 1253–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Yu, N.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhang, Y.H. Assessment and source analysis of heavy metal contamination in water and surface sediment in Dongping Lake, China. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, L.H.; Ma, B.; Shao, S.W.; Tian, X.; Zhang, L. Heavy metal distribution and risk assessment of Dongping Lake water bodies and sediments. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2023, 46, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.; Bose, J. Evaluation of the heavy metal pollution index for surface and spring water near a limestone mining area of the lower Himalayas. Environ. Geol. 2001, 41, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Yongsheng, G. On Historical Change of Lakes Inshandong Province. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 1990, 3, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, X.H.; Hou, Q.Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Ye, J.; Yu, T.; Xia, X.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, G.; Yao, L. Big data based studies of the variation features of Chinese soil’s background value versus reference value: A paper written on the occasion of Soil Geochemical Parameters of China’s publication. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 45, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Ni, S.J.; Tuo, X.G.; Zhang, C.J. Calculat ion of Heavy Metals’ Toxicity Coefficient in the Evaluation of Potential Ecological Risk Index. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 31, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G.J.J. Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geol. J. 1969, 2, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Xiao, J.Y.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Ling, J.H.; Chang, B.J.; Zhao, G.L. Assessment of heavy metal content, distribution, and sources in Nansi Lake sediments, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 30929–30942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.-Z.; Shen, J.; Liu, E.-F.; Wang, J.-J.; Meng, X.-H. Assessment of nutrients and heavy metals enrichment in surface sediments from Taihu Lake, a eutrophic shallow lake in China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2010, 33, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Lai, J. Metals Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Sediments in the Poyang Lake, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Hu, K.; Xu, J.; Liu, R.; Gong, Z.; Cai, Y. Determining heavy metal pollution in sediments from the largest impounded lake in the eastern route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project: Ecological risks, sources, and implications for lake management. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lin, J.; Wu, X.; Xue, Y.; Han, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, J.; Shen, Q. Spatial distributions and risk assessments of nutrients and heavy metals in sediments from an impounded lake of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 63305–63318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.X.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhu, L.Y. Pollution and Risk Assessment of Typical Heavy Metals in River Sediments of Seven Major Watersheds in China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 423–432. [Google Scholar]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.H.; Gao, G.L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D.E.; Zhang, S.B.; Gao, P. Heavy Metal Speciation Distribution and Bioavailability Assessment in Soils Surrounding a Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Plant in the Typical Plain Area in China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.F.; Zhang, L.X.; Dong, Y.L.; Zhu, L.Y.; Wang, Z.; Lü, J.S. Source Apportionment and Spatial Distribution Simulation of Heavy Metals in a Typical Petrochemical Industrial City. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Jiang, H.B.; Zhang, X.F.; Hu, X.X. Fraction Distribution and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soils Around the Gold Mine of DetiangouQifengcha, Beijing City, China. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2014, 34, 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.L.; Zhang, H.Z.; Zhao, X.X.; Du, Z.B.; Xiang, L.X.; Wang, W. Assessment of heavy metal contamination and wetland management in a newly created coastal natural reserve, China. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 32, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y. Health Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ground Water of a Chemical Industry Park and Its Surrounding Area in Liaoning Province Based on Monte Carlo Simulation. J. Shenyang Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2022, 32, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outa, J.O.; Kowenje, C.O.; Plessl, C.; Jirsa, F. Distribution of arsenic, silver, cadmium, lead and other trace elements in water, sediment and macrophytes in the Kenyan part of Lake Victoria: Spatial, temporal and bioindicative aspects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapra, S.C.; Hecky, R.E.; Orihel, D.M. Reducing Phosphorus to Curb Lake Eutrophication is a Success. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8923–8929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christophoridis, C.; Dedepsidis, D.; Fytianos, K. Occurrence and distribution of selected heavy metals in the surface sediments of Thermaikos Gulf, N. Greece. Assessment using pollution indicators. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Ding, S.; Li, C.; Tang, Y.; Fan, X.; Xu, H.; Tsang, D.C.; Zhang, C. High cadmium pollution from sediments in a eutrophic lake caused by dissolved organic matter complexation and reduction of manganese oxide. Water Res. 2021, 190, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Li, Z.W.; Huang, B.; Luo, N.L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, X.Q.; Zeng, G.M. Investigating binding characteristics of cadmium and copper to DOM derived from compost and rice straw using EEM-PARAFAC combined with two-dimensional FTIR correlation analyses. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.S.; Li, Z.W.; Huang, M.; Wen, J.J.; Ding, X.; Zhou, M.; Cai, C.Q. Laboratory and simulation study on the Cd(II) adsorption by lake sediment: Mechanism and influencing factors. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangwei, Z.; Yingxu, C. A Review of Geochemical Behaviors and Environmental Effects of Organic Matter in Sediments. J. Lake Sci. 2001, 3, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dean, W.E. Determination of carbonate and organic matter in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition; comparison with other methods. J. Sediment. Res. 1974, 44, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Bai, L.; Li, C.; He, Z.; Liu, X. Assessment of heavy metal contamination levels and health risks in environmental media in the northeast region. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Tian, W.; Zhang, X.Y. Distribution Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Metal Elements for Groundwater in the Ningxia Region of China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 43, 329–338. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Cao, W.J.; Liu, W.; Lan, S.T. Seasonal Distribution Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Surface Water of Qingjiang River. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Carrizales, L.; Razo, I.; Téllez-Hernández, J.I.; Torres-Nerio, R.; Torres, A.; Batres, L.E.; Cubillas, A.C.; Díaz-Barriga, F. Exposure to arsenic and lead of children living near a copper-smelter in San Luis Potosi, Mexico: Importance of soil contamination for exposure of children. Environ. Res. 2006, 101, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Cai, Y.; Wang, T.; Xiao, R.; Chen, W. Regional probabilistic risk assessment of heavy metals in different environmental media and land uses: An urbanization-affected drinking water supply area. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Health Effects Assessment for Barium; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1984. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/2000FDFS.PDF?Dockey=2000FDFS.PDF (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Barium: Health Advisory. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1987. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/94006C0D.PDF?Dockey=94006C0D.PDF (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1989. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-09/documents/rags_a.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Volume III–Part A, Process for Conducting Probabilistic Risk Assessment; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2001. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-09/documents/rags3adt_complete.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Method 6200: Field Portable X–Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry for the Determination of Elemental Concentrations in Soils and Sediment; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2007. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-12/documents/6200.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2018).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Method 1340: In Vitro Bioaccessibility Assay for Lead in Soil; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2017. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/hw-sw846/sw-846-test-method-1340-vitro-bioaccessibility-assay-lead-soil (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Smith, R.L. Use of Monte Carlo simulation for human exposure assessment at a superfund site. Risk Anal. 1994, 14, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Risk Assessment Information System (RAIS). RAIS Chemical PRG Calculator. 2020. Available online: https://rais.ornl.gov/cgi-bin/prg/PRG_search?select=chem (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of trace metals in surface soils of Beijing metropolitan, China. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

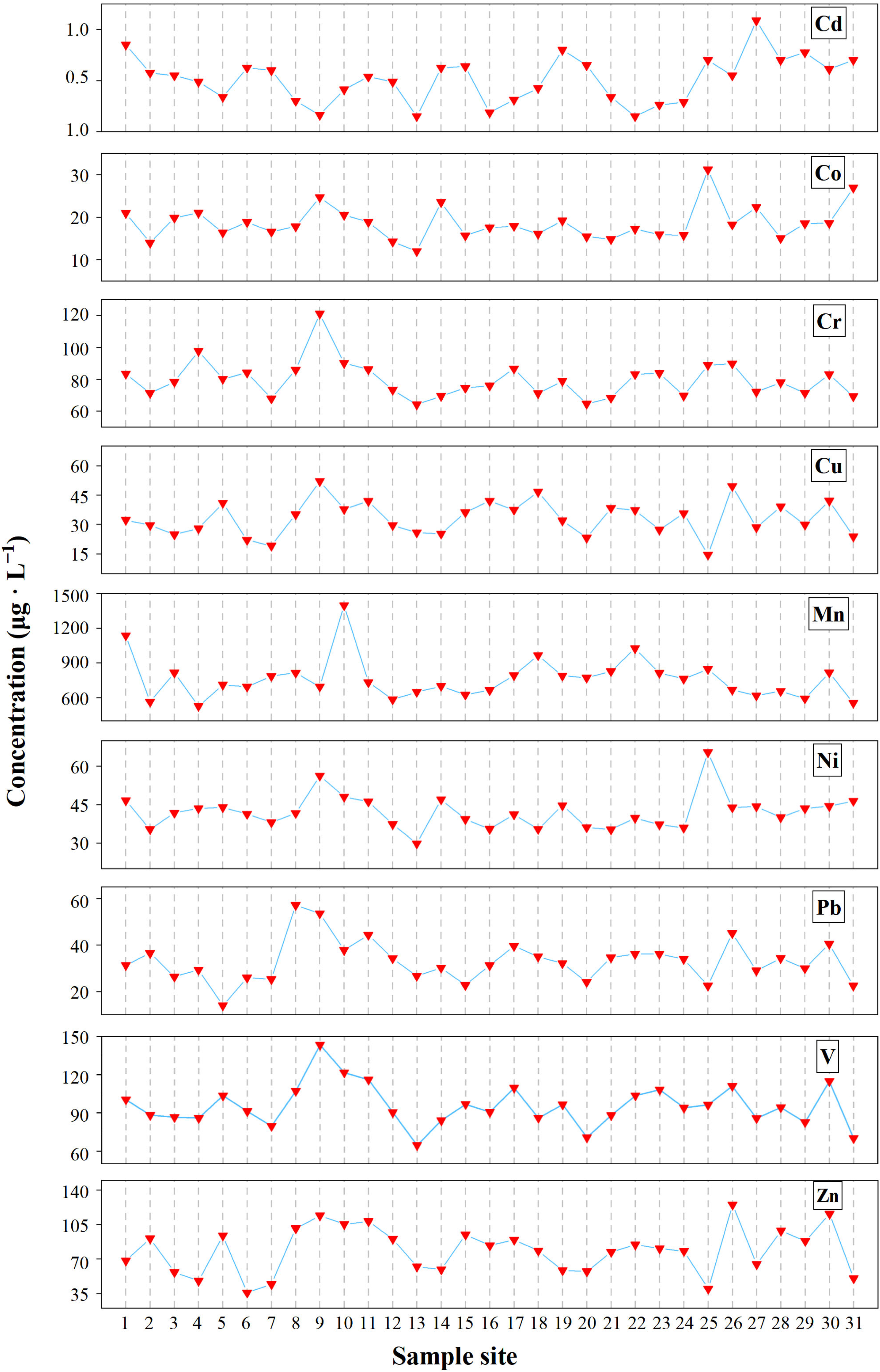
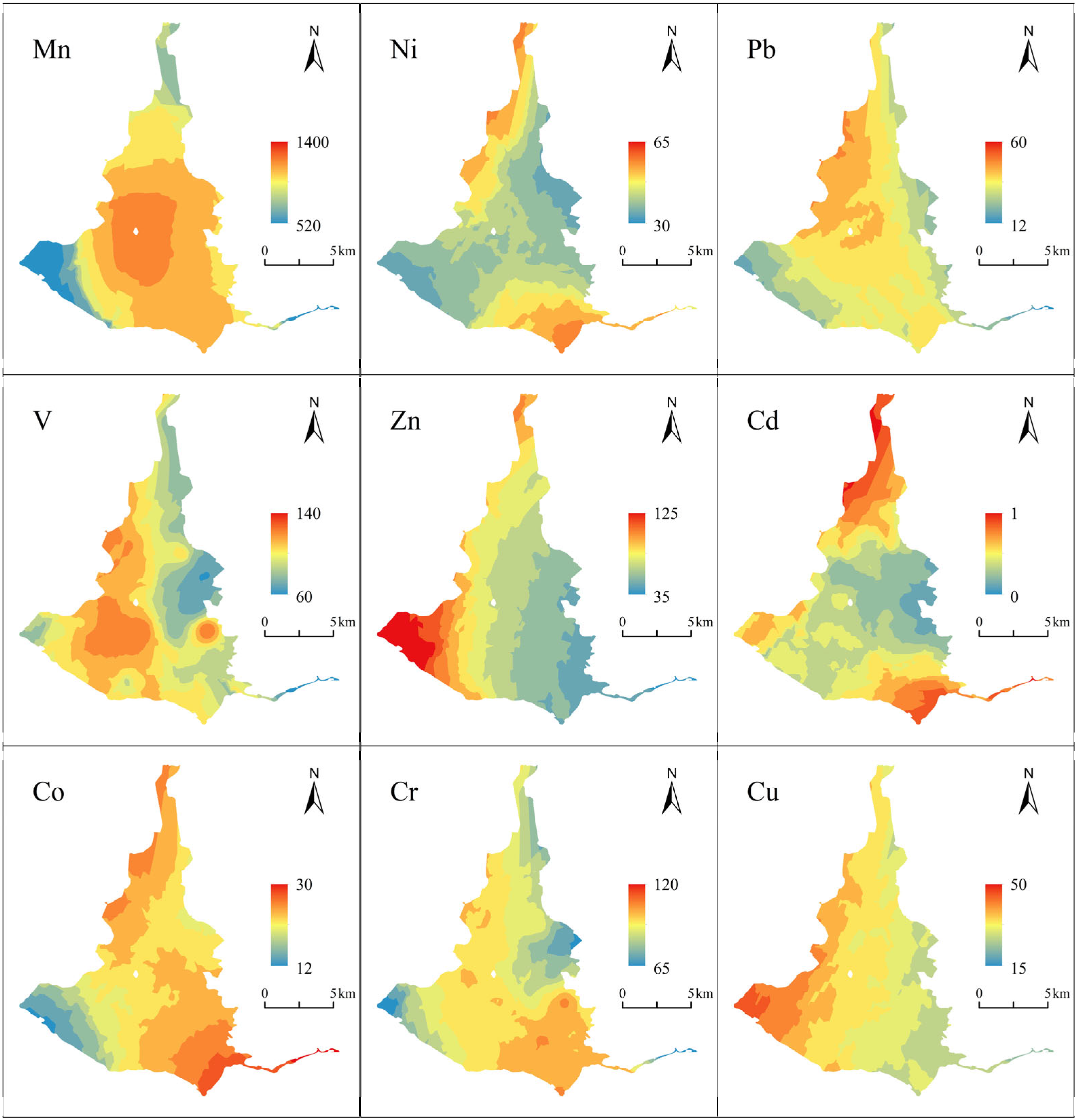
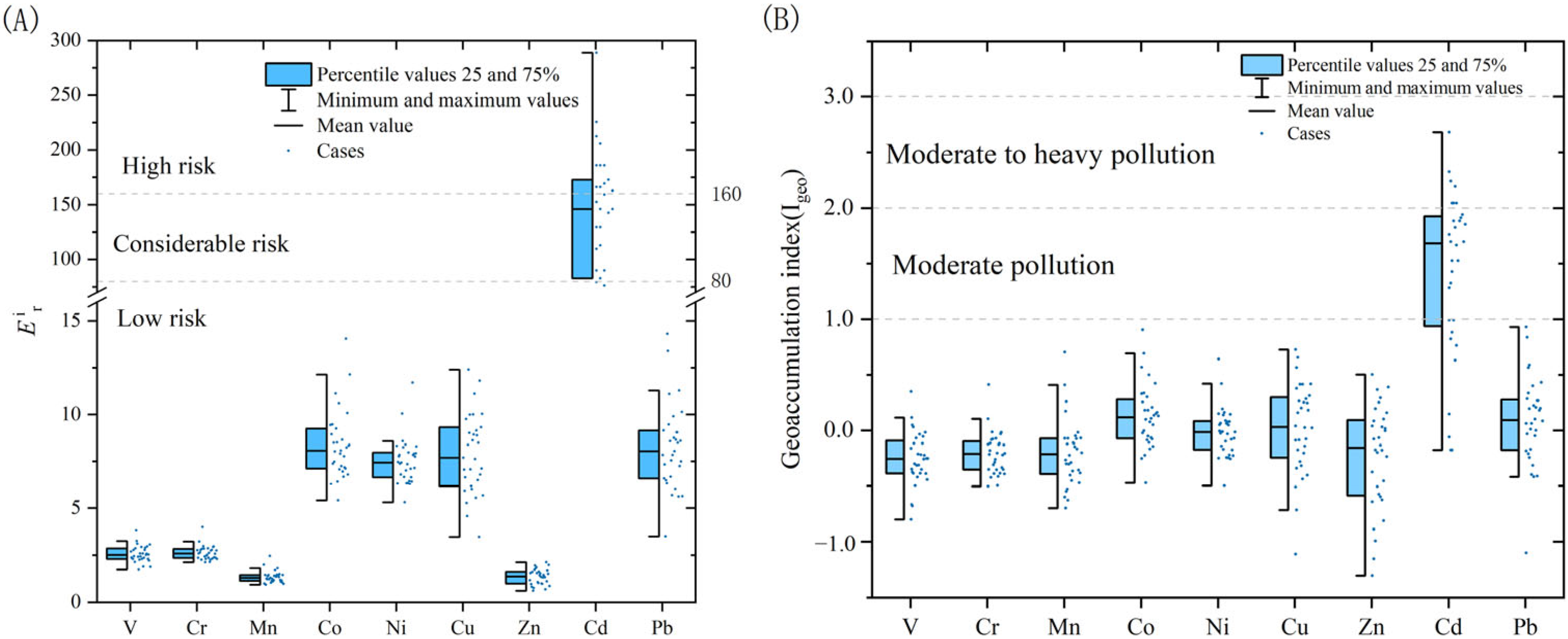

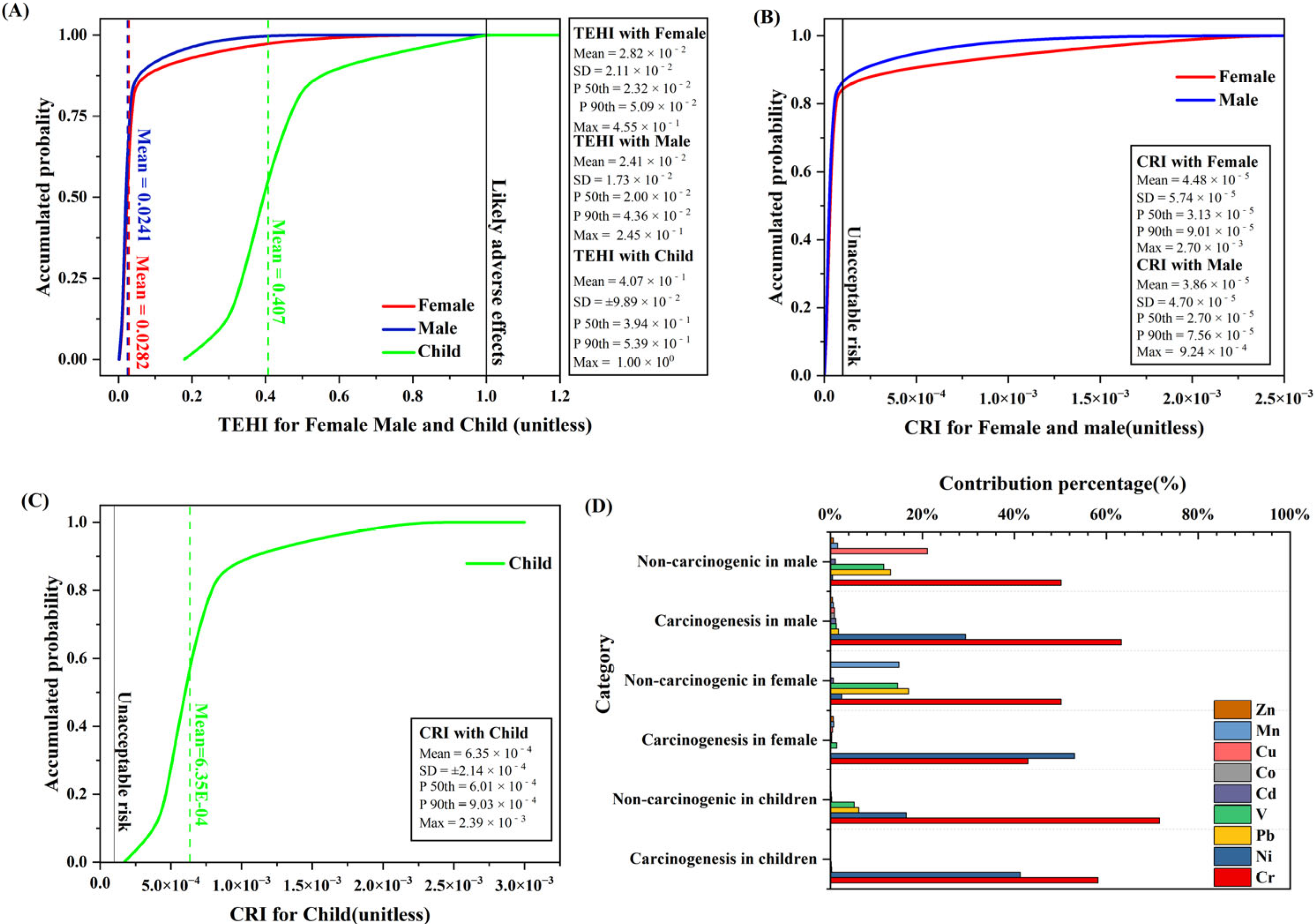
| Water | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Ti | V | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ia (μg/L) | 0.464 | 1.332 | 15.002 | 0.097 | 1.145 | 1.335 | 1.505 | 0.900 | 3.620 | 3.483 | 0.022 | 0.050 |
| xmax (μg/L) | 1.390 | 5.860 | 36.810 | 0.180 | 1.540 | 4.300 | 1.890 | 1.510 | 10.260 | 5.530 | 0.040 | 0.120 |
| xmin (μg/L) | 0.170 | 0.350 | 7.510 | 0.070 | 0.930 | 0.070 | 0.950 | 0.630 | 0.560 | 2.050 | 0 | 0 |
| SD b | 0.369 | 1.088 | 7.354 | 0.020 | 0.106 | 1.185 | 0.195 | 0.150 | 2.432 | 0.939 | 0.110 | 0.038 |
| CV (%) | 0.795 | 0.817 | 0.490 | 0.206 | 0.093 | 0.888 | 0.130 | 0.167 | 0.672 | 0.270 | 0.150 | 0.760 |
| GB c (μg/L) | 5 | 100 | 300 | 1000 | 20 | 100 | 50 | 1000 | 1000 | 50 | 5 | 50 |
| i_mean_12 d (2020) (μg/L) | 31.880 | 58.060 | 16.030 | 1.230 | 1.200 | 15.270 | 1.230 | 0.040 | 0.240 | |||
| i_mean_3 d (2021) (μg/L) | 38.330 | 4.280 | 111.900 | 14.690 | 3.950 | 35.560 | 1.760 | 0.030 | 0.740 | |||
| i_mean_9 d (2021) (μg/L) | 0.710 | 1.390 | 57.250 | 1.550 | 1.300 | 27.980 | 2.160 | 0.030 | 0.390 | |||
| Sediment | Cr | Mn | Ni | Cu | Zn | V | Cd | Pb | Co | |||
| i (mg/kg) | 79.44 | 761.46 | 42.07 | 33.19 | 78.84 | 95.65 | 0.512 | 32.99 | 18.57 | |||
| xmax (mg/kg) | 121.06 | 1396.08 | 29.78 | 52.09 | 125.28 | 143.45 | 1.09 | 57.20 | 31.19 | |||
| xmin (mg/kg) | 64.15 | 527.41 | 65.50 | 14.58 | 35.83 | 64.58 | 0.15 | 13.98 | 12.01 | |||
| SD | 11.46 | 180.07 | 6.79 | 8.94 | 23.76 | 16.30 | 0.23 | 9.06 | 4.01 | |||
| CV (%) | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.22 | |||
| Bi e (mg/kg) | 60.65 | 571 | 28 | 21 | 59 | 75 | 0.113 | 20 | 11.1 | |||
| i_mean_12 f (2020) (mg/kg) | 82.10 | 741.07 | 41.08 | 38.5 | 91.17 | 79.69 | 0.25 | 27.32 | 16.47 | |||
| i_mean_3 f (2021) (mg/kg) | 80.67 | 699.97 | 40 | 37.28 | 68.52 | 79.72 | 0.23 | 26.14 | 16.29 | |||
| i_mean_9 f (2021) (mg/kg) | 79.94 | 692.04 | 37.32 | 34.89 | 68.51 | 73.25 | 0.25 | 25.80 | 14.89 | |||
| Nansi Lake [22] | 136.54 | 838.53 | 46.21 | 41.85 | 149.96 | 0.27 | 50.18 | 21.84 | ||||
| Taihu Lake [23] | 82.10 | 841.60 | 40.60 | 26.10 | 99.50 | 97.30 | 36.60 | 15.40 | ||||
| Poyang Lake [24] | 42.95 | 71.37 | 123.98 | 0.82 | 47.37 | |||||||
| Hongze Lake [25] | 82.00 | 40.64 | 24.11 | 79.07 | 0.22 | 27.87 | ||||||
| Luoma Lake [26] | 101.70 | 56.21 | 22.59 | 7.39 | 89.21 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, A.; Zhu, J.; Han, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D. Assessing Multiple Risks in Regulating Reservoirs: Perspectives on Heavy Metal Contamination. Toxics 2025, 13, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090762
Zhou H, Li Z, Wang A, Zhu J, Han Z, Zhang Y, Chen D. Assessing Multiple Risks in Regulating Reservoirs: Perspectives on Heavy Metal Contamination. Toxics. 2025; 13(9):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090762
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Hui, Zhiping Li, Anming Wang, Jiawei Zhu, Zongyuan Han, Yalin Zhang, and Dongdong Chen. 2025. "Assessing Multiple Risks in Regulating Reservoirs: Perspectives on Heavy Metal Contamination" Toxics 13, no. 9: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090762
APA StyleZhou, H., Li, Z., Wang, A., Zhu, J., Han, Z., Zhang, Y., & Chen, D. (2025). Assessing Multiple Risks in Regulating Reservoirs: Perspectives on Heavy Metal Contamination. Toxics, 13(9), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090762






