Water Quality Evaluation and Countermeasures of Pollution in Wan’an Reservoir Using Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
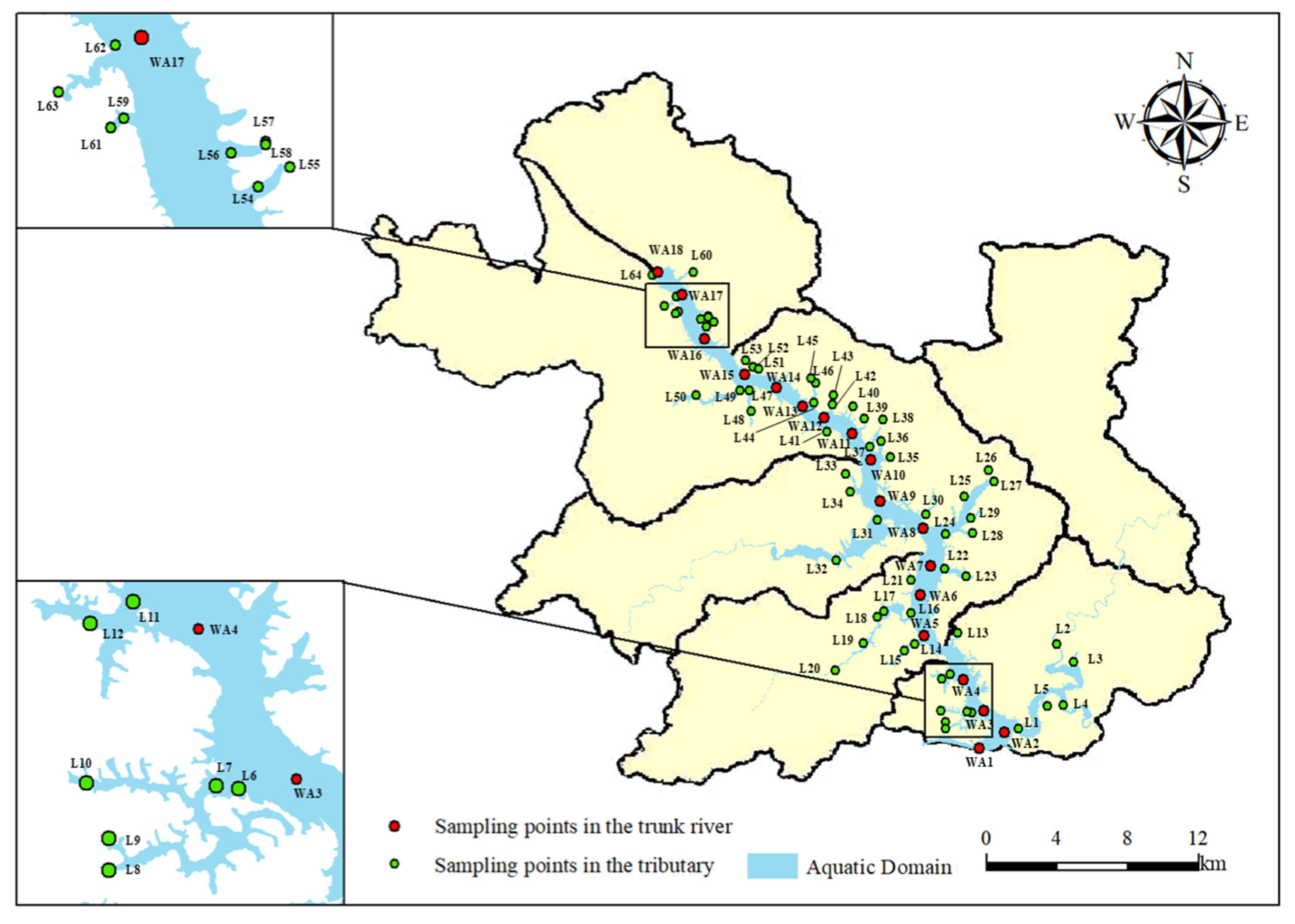
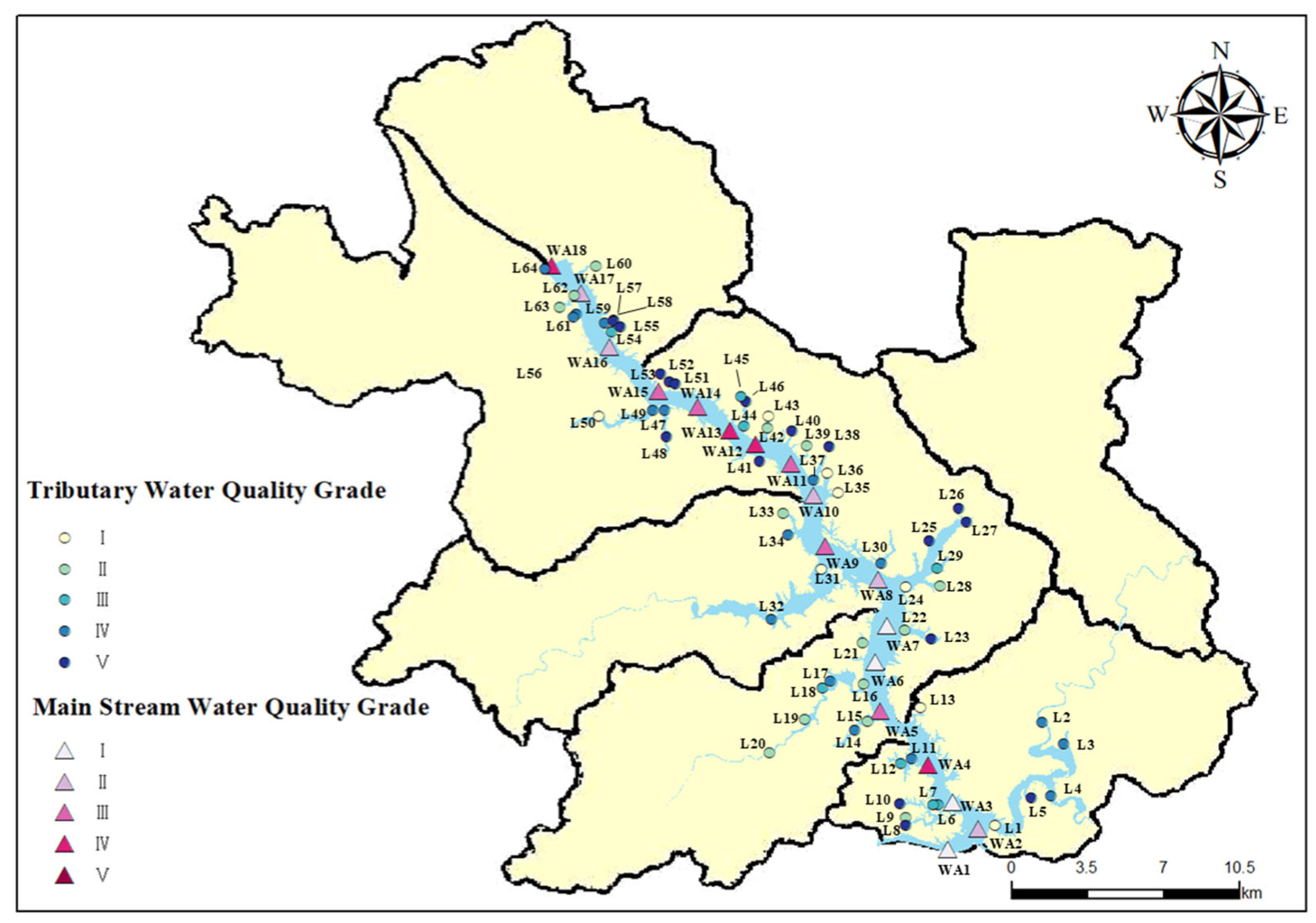
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Model
- (1)
- Determining index weight by using entropy weight method
- (2)
- Construction of fuzzy membership model
- (3)
- Comprehensive evaluation
3. Results
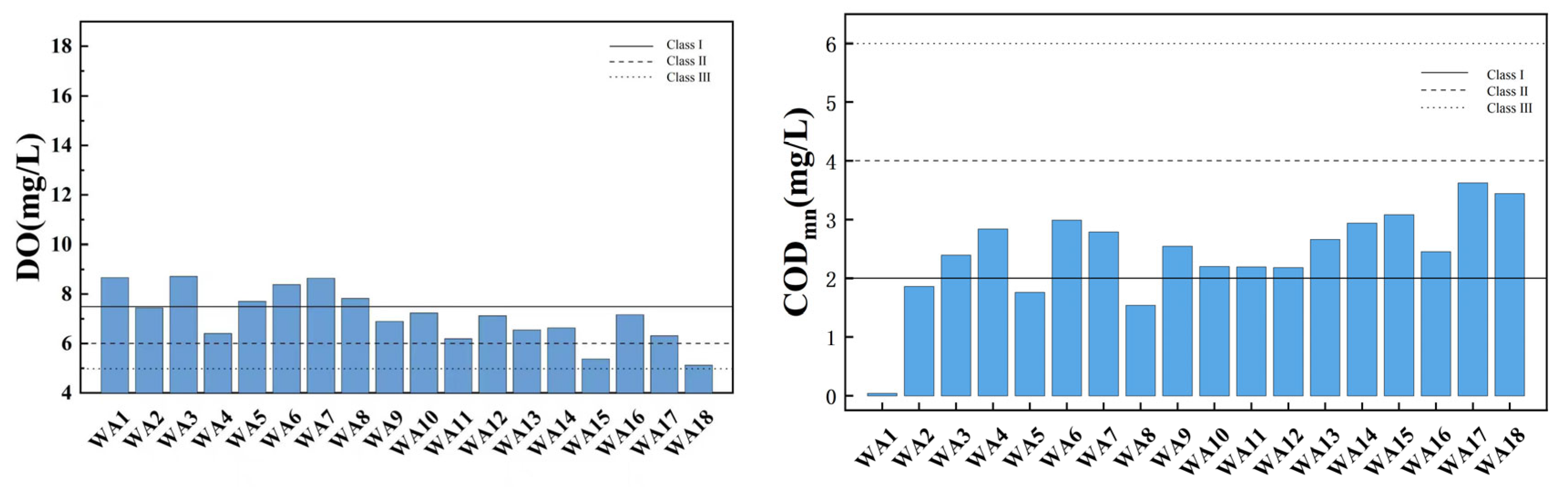
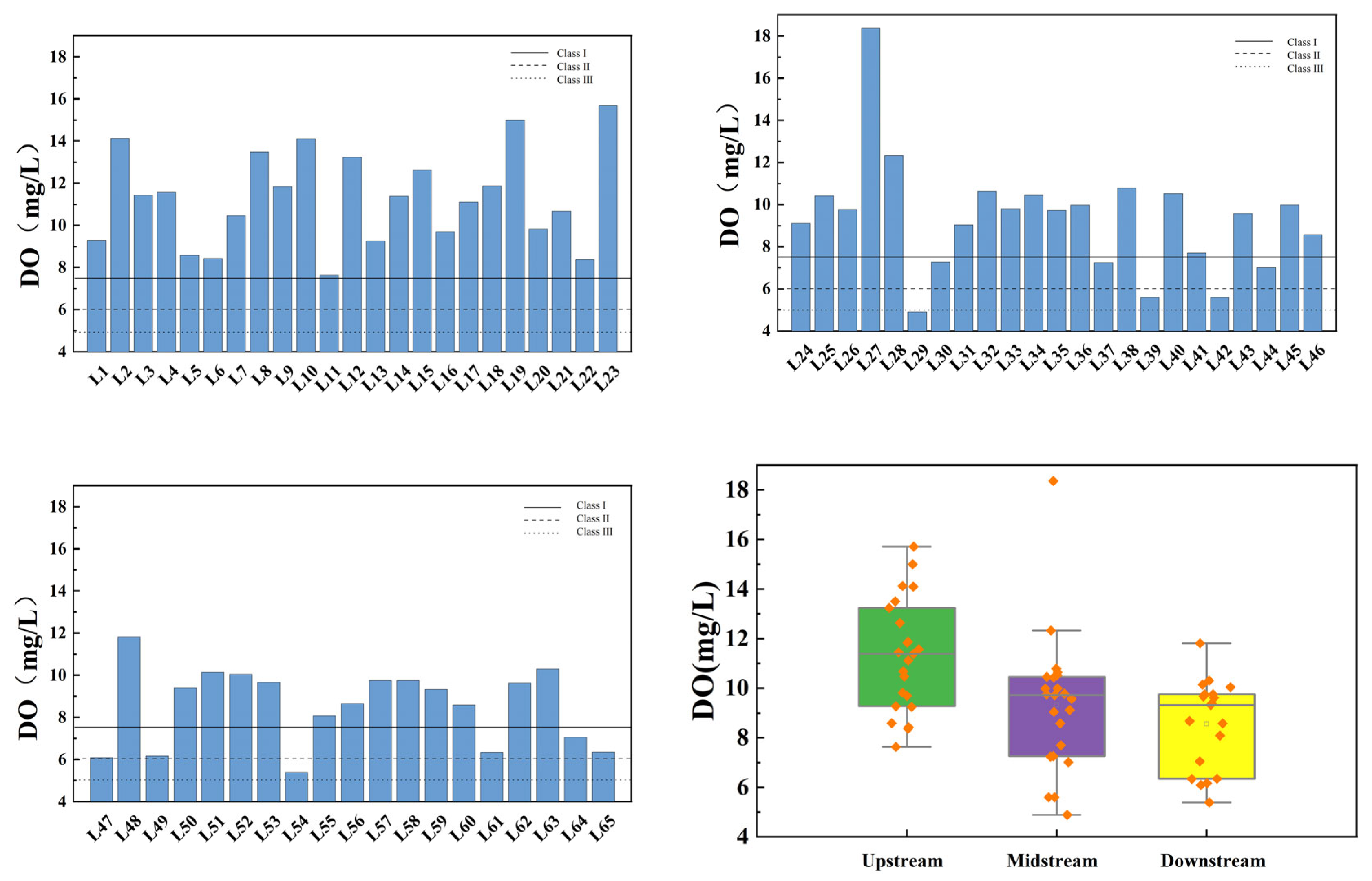
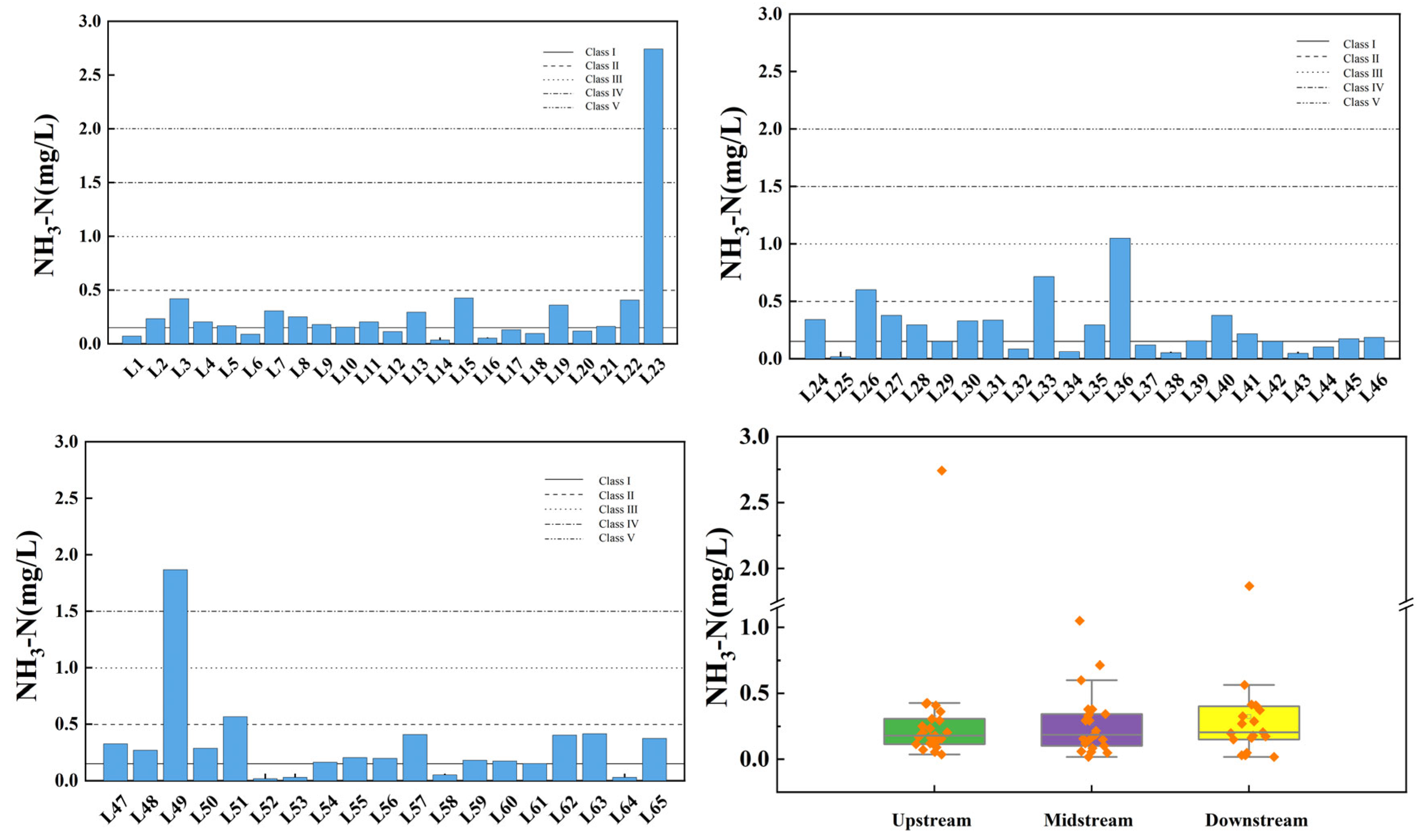
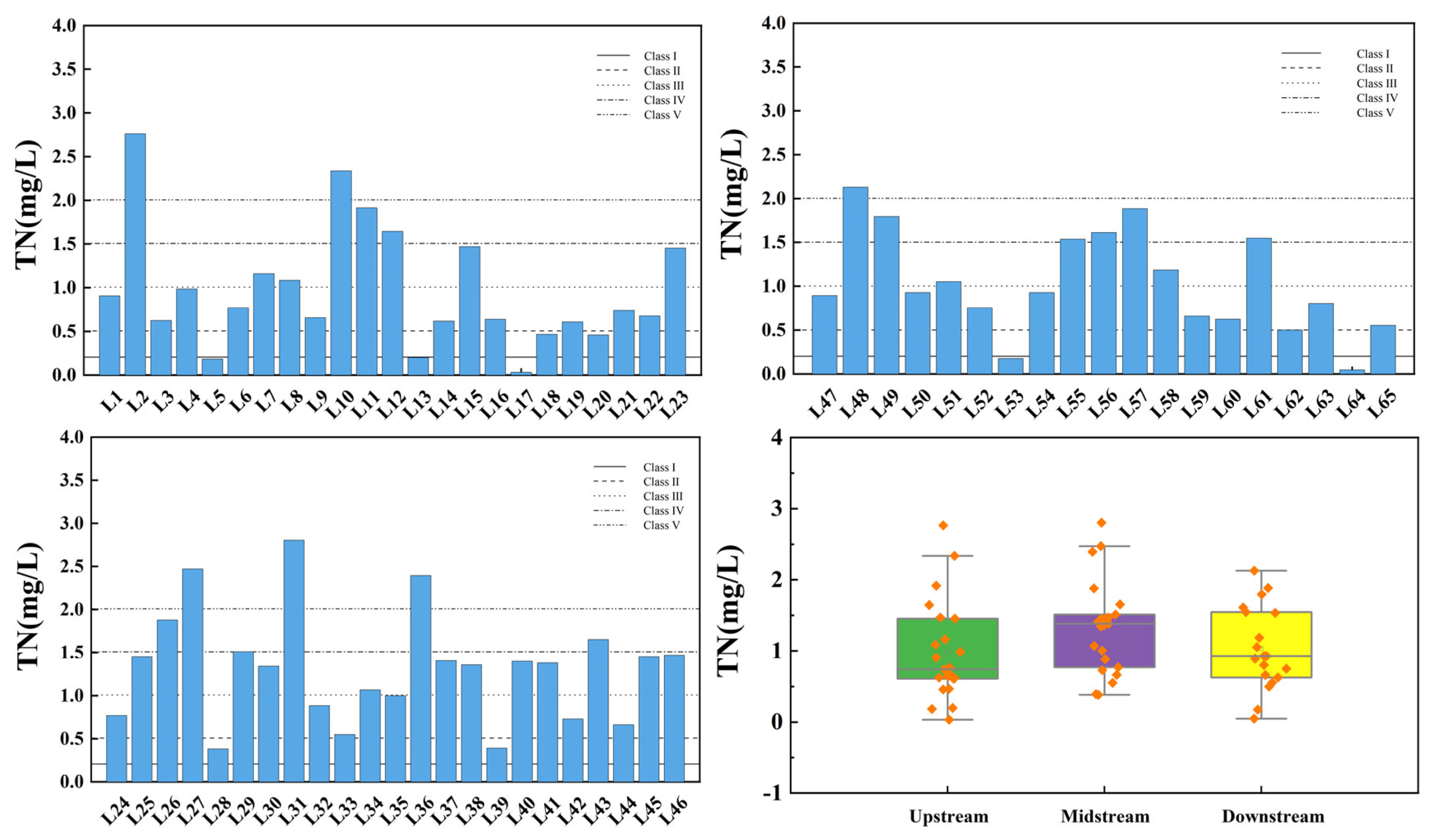
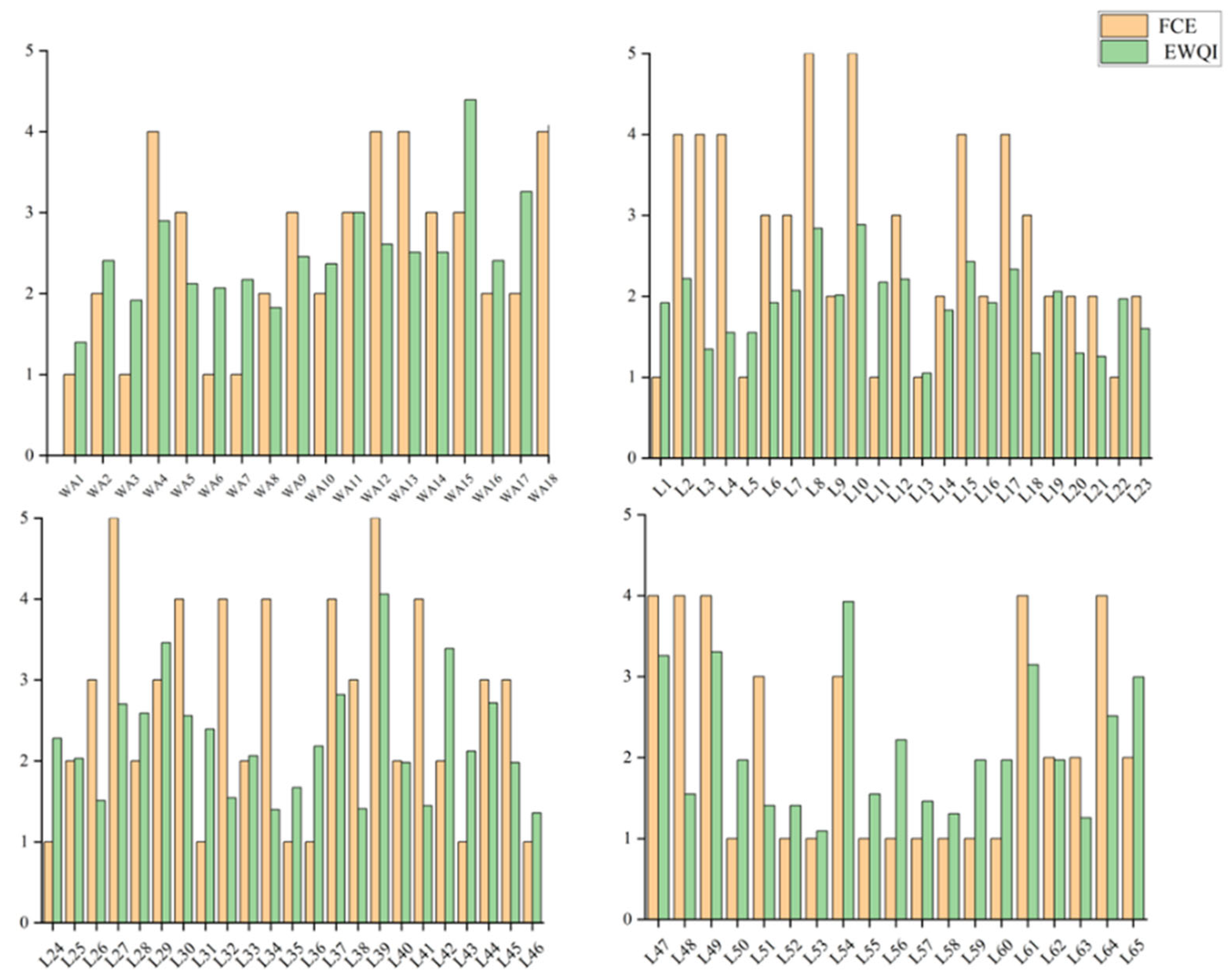
3.1. Spatial Variation Characteristics of Water Quality Index in the Main Stream of Wan’an Reservoir
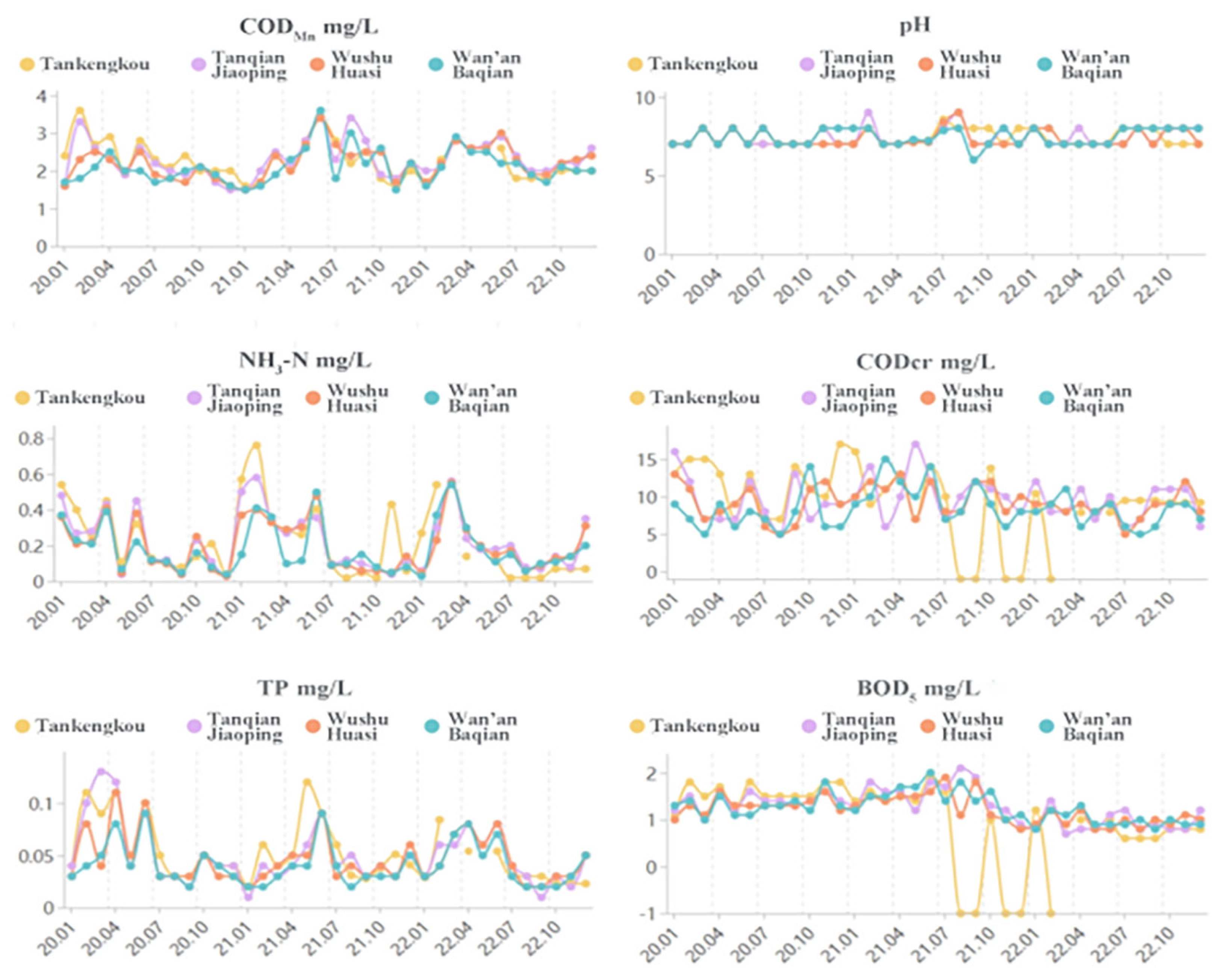
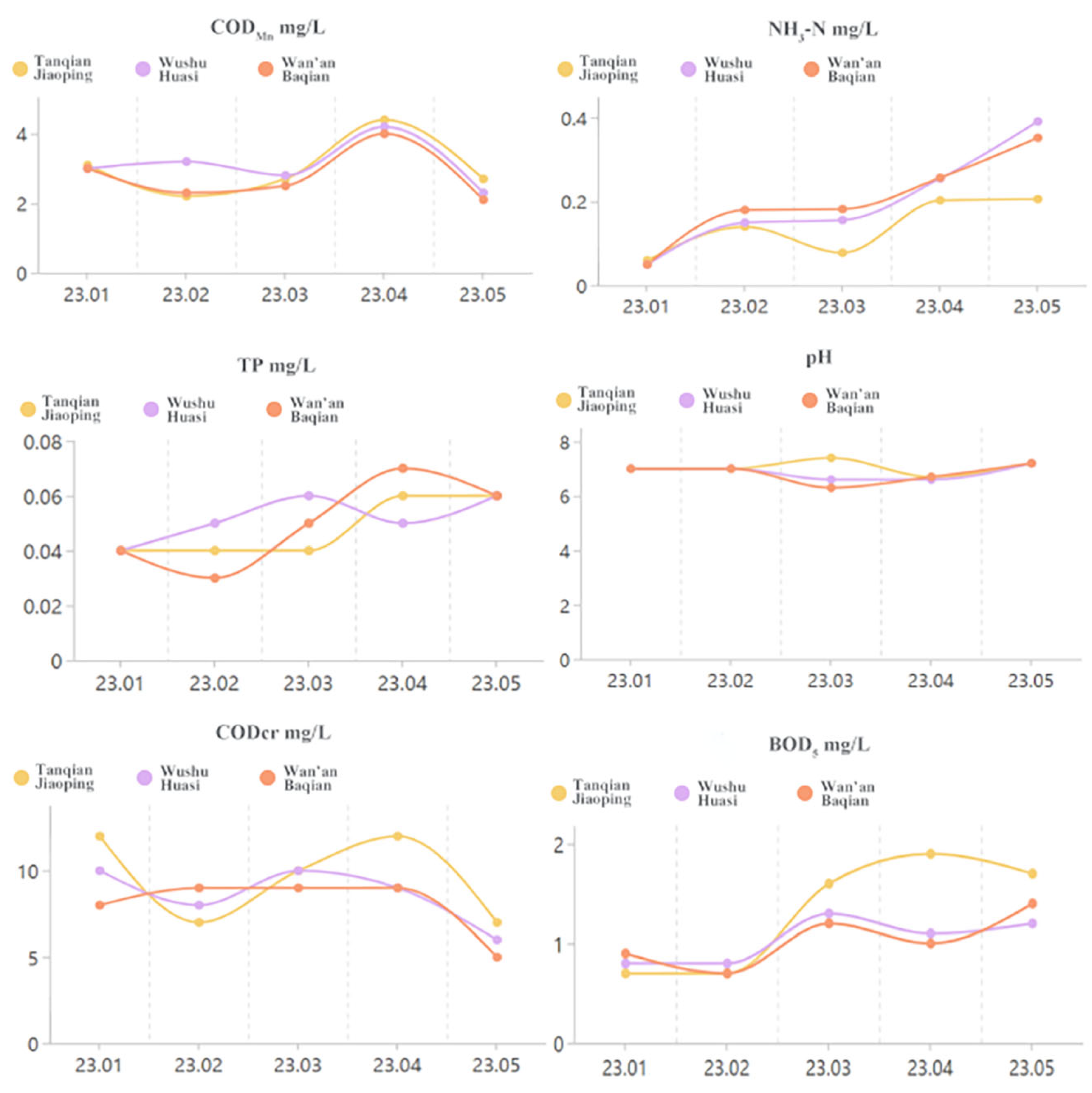
3.2. Spatial Variation Characteristics of the Water Quality Index at the Inlet and Control Point of Tributaries of Wan’an Reservoir
3.3. Spatial Variation Analysis Using Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Index of Water Quality
- (1)
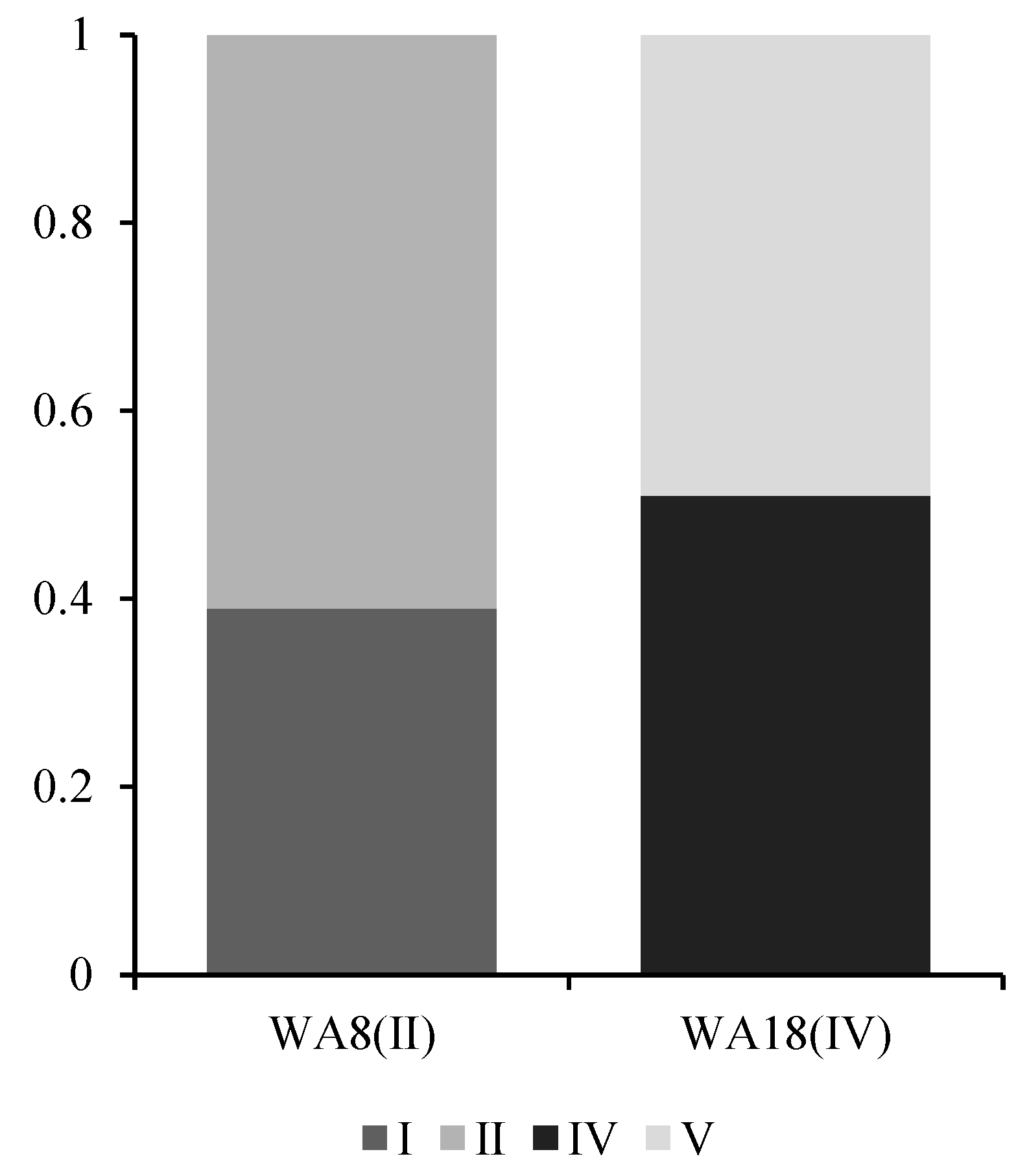
- Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of the main stream of Wan’an Reservoir
- (2)
- Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of tributaries of Wan’an Reservoir
- (3)
- Analysis of Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Results
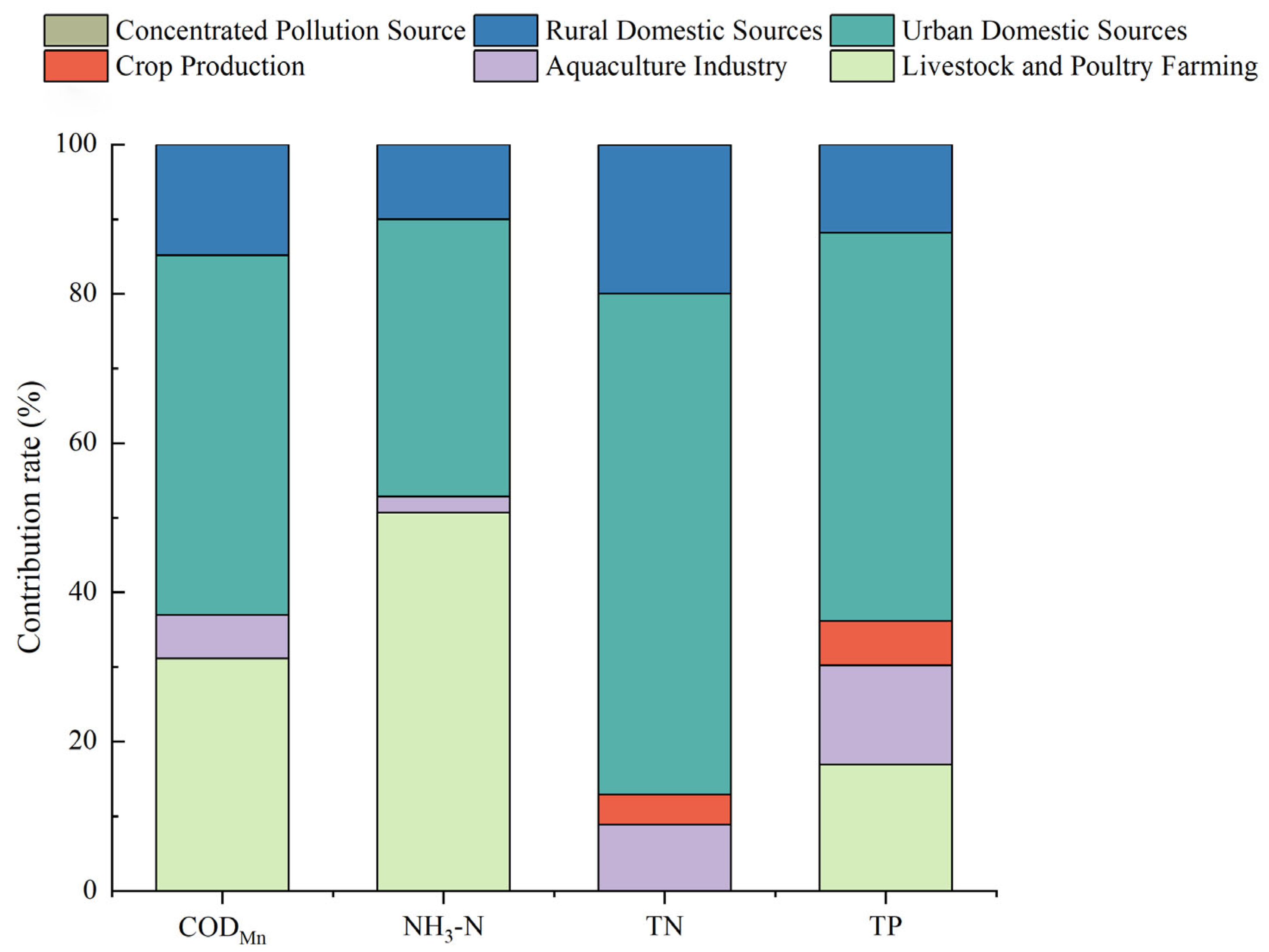
3.4. Analysis of Water Quality Impact Sources of Wan’an Reservoir
3.5. Limitations
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
4.1. Conclusions
4.2. Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, X.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Y. Water quality variation in the highly disturbed Huai River Base, China from 1994 to 2005 by multi- statistical analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.; Asif, Z. Identification of point source emission in river concentration incidents based on Bayesian inference and genetic algorithm: Inverse modeling, sensitivity, and understanding analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, G.; Lin, X.; Qiu, D.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y. Dataset of stable isotopes of precipitation in the Eurasian continent. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 1543–1557. [Google Scholar]
- Panagopoulos, A.; Giannika, V. Decarbonized and circular brine management/valorization for water & valuable resource recovery via minimal/zero liquid discharge (MLD/ZLD) strategies. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116239. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, G.; Lin, X.; Li, R.; Lu, S.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Q. The Complexity of Moisture Sources Affects the Altitude Effect of Stable Isotopes of Precipitation in Inland Mountainous Regions. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR036084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lu, H.; Wang, G.; Qiu, J. Long-term capturability of atmospheric water on a global scale. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR034757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Li, C.Y.; Liu, P.; Li, T.; Luo, Y.; Yang, L.; Che, L.L.; Li, M.H. Spatiotemporal comprehensive evaluation of water quality based on enhanced variable fuzzy set theory: A case study of a landfill in karst area. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualhaija, M. Applying the Quality and Pollution Indices for Evaluating the Wastewater Effluent Quality of Kufranja Wastewater Treatment Plant, Jordan. Water Conserv. Manag. 2023, 7, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Han, Q.; Shang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, T.T.; Liu, J.L.; Liu, L. Quality assessment and prediction of municipal drinking water using water quality index and artificial neural network: A case study of Wuhan, central China, from 2013 to 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.C.; Yi, Z.Y. Development of modified integrated water quality index to assess the surface water quality: A case study of Tuo River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Y.; Chen, J.; Jin, Q.; Liu, H.Z.; Yang, W.; Li, W.; Jiang, J.; Sha, Y.; Tian, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; et al. Improved principal component-fuzzy comprehensive assessment coupling model for urban river water quality: A case study in Chongqing, China. Water 2020, 12, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Zhao, T.; Cao, J.; Li, P. Water quality prediction model based on interval type-2 fuzzy neural network with adaptive membership function. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Son, S.; Luo, J.; Oh, S.; Wang, Y. A Deep-Learning Ensemble Method to Detect Atmospheric Rivers and Its Application to Projected Changes in Precipitation Regime. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2023, 128, e2022JD037041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.L.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M.H. Comparison of seven water quality assessment methods for the characterization and management of highly impaired river systems. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Berndtsson, R.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Adamowski, J.F.; Abyaneh, M.R. A critical review on the application of the National Sanitation Foundation Water Quality Index. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.S. The research of dynamic variable fuzzy set assessment model in water quality evaluation. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, R.L.; Guo, Z.B. A water quality assessment method based on an improved grey relational analysis and particle swarm optimization multi-classification support vector machine. Front. Plant. Sci. 2023, 14, 1099668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.L.; Zhang, C. Early warning of water quality degradation: A copula-based Bayesian network model for highly efficient water quality risk assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Dong, F.; Peng, W.Q.; Liu, X.B. Bayesian-based calibration for water quality model parameters. Water Environ. Res. 2023, 95, e10936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilipkumar, J.; Shanmugam, P. Fuzzy-based global water quality assessment and water quality cells identification using satellite data. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Su, C.Q.; Li, Z.X.; Hu, X.Y. Waterfront ecotourism quality evaluation under the water ecological challenge in West Strait, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1134905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, Q.; Yun, M.H.; Huang, J.J.; Sun, J.M. Development of a comprehensive pollution evaluation system based on entropy weight-fuzzy evaluation model for urban rivers: A case study in North China. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 67, 106192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.G.; Cui, Y.X.; Yang, C.X.; Wei, S.J.; Dong, W.P.; Huang, L.H.; Liu, C.Q.; Ren, Z.M.; Wang, W.L. The fuzzy comprehensive evaluation (FCE) and the principal component analysis (PCA) model simulation and its applications in water quality assessment of Nansi Lake Basin, China. Environ. Eng. Res. 2021, 26, 200022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.P.; Li, B.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhang, B.B. Application of improved fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method in karst groundwater quality evaluation: A case study of Cengong county. Earth Sci. Inform. 2021, 14, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.F.; Xiong, L.H.; Jiang, C.; Hu, J.M.; Liu, Z.J. Effects of climate variability and human activities on suspended sediment load in the Ganjiang River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2019, 24, 05019029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhu, G.; Lu, S.; Meng, G.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, E.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Q. Effects of cascade hydropower stations on hydrologic cycle in Xiying river basin, a runoff in Qilian mountain. J. Hydrol. 2025, 646, 132342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Xu, W.; Deng, J.; Guo, Y. Self-aeration development and fully cross-sectional air diffusion in high-speed open channel flows. J. Hydraul. Res. 2022, 60, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwathaf, Y.; Kawy, W.A.; Al-Areeq, N.; Al-Areeq, A.M.; Al-qatni, K.Y. Urban water security index assessment for Ibb City, Yemen: Comprehensive vision. Water Conserv. Manag. 2023, 7, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.Q.; Huang, X.; Nie, Y.; Li, S.Q.; Sun, F.H. Evaluating asset-based management of water resources based on the water asset stocks and changes table. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 505, 145473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Environmental Protection of China: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- GB 5749-2022; SAM & SAC. Sanitary Standard for Drinking Water. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2022. (In Chinese)
- Yaghouti, M.; Heidarzadeh, N.; Ulloa, H.N.; Nakhaei, N. The impacts of climate change on thermal stratification and dissolved oxygen in the temperate, dimictic Mississippi Lake, Ontario. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 75, 102087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, W.; Ouyang, W.Y.; Shen, C.P.; Li, L. Temperature outweighs light and flow as the predominant driver of dissolved oxygen in US rivers. Nat. Water 2023, 1, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.J.; Wu, X.D.; Chao, J.Y.; Ge, X.G.; Liu, H.T.; Liu, D.D. Temporal-spatial pattern of dissolved organic carbon and its Influencing factors in a typical subtropical lake, Lake Gehu, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 3221–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Liang, Z.J.; Xin, P.L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.C. Identification of Identification of key water environmental factor contributions and spatiotemporal differential characteristics for eutrophication in Dianchi Lake. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.L.; Cheng, X.L.; Tian, S.M. Evaluation of spatiotemporal variation of water quality in China: A study on the effectiveness of the River Chief System. Water Policy 2024, 26, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Wang, L.J.; Li, H.; Tian, Z.B.; Zheng, B.H. Temporal and spatial variation in water quality in the Three Gorges Reservoir from 1998 to 2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Z.H.; Ye, L.; Zhang, C. Application of export coefficient model and QUAL2K for water environmental management in a rural watershed. Sustainability 2020, 11, 6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memet, V. Spatio-temporal changes in surface water quality and sediment phosphorus content of a large reservoir in Turkey. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.X.; Jin, H.H.; Zhao, H.P.; Sun, J. Distribution characteristics of sediments phosphorus species of Xiangjiaba Reservoir and release risk. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2022, 42, 182–190. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Ou, J.; Qian, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, H. Prediction of non-equilibrium transport of nitrate nitrogen from unsaturated soil to saturated aquifer in a watershed: Insights for groundwater quality and pollution risk assessment. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2025, 274, 104649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.L.; Cheng, K.Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, W.R.; Guo, J. Simulation of Water Quality in a River Network with Time-Varying Lateral Inflows and Pollutants. Water 2023, 15, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.D.; Jun, Z. Water resource risk assessment based on non-point source pollution. Water 2021, 13, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.X.; Zhou, Y.C.; Liu, J.G.; Qiu, P.; Shao, Y.W. Non- point source pollution loads estimation in Three Gorges Reservoir Area based on improved observation experiment and export coefficient model. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.S.; Fu, R.; Liu, Y.; Suo, C.Y. Spatiotemporal variations of water quality and their driving forces in the Yangtze River Basin, China, from 2008 to 2020 based on multi-statistical analyses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 69388–69401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.L.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Niu, C.; Wang, H.W. Spatiotemporal Patterns in River Water Quality and Pollution Source Apportionment in the Arid Beichuan River Basin of Northwestern China Using Positive Matrix Factorization Receptor Modeling Techniques. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Feng, M.Q.; Chen, K.L.; Cai, Y.M. Spatiotemporal distributions and mixing dynamics of characteristic contaminants at a large asymmetric confluence in northern China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Water Quality Indicators | Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB 3838-2002) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | |
| DO (mg/L) | ≥7.5 | [6.5, 7.5] | [6.0, 6.5] | [3.0, 6.0] | [2.0, 3.0] |
| TN (mg/L) | ≤0.2 | (0.2, 0.5] | (0.5, 1.0] | (1.0, 1.5] | (1.5, 2.0] |
| NH3-N (mg/L) | ≤0.15 | (0.15, 0.5] | (0.5, 1.0] | (1.0, 1.5] | (1.5, 2.0] |
| TP (mg/L) | ≤0.01 | (0.01, 0.025] | (0.025, 0.05] | (0.05, 0.1] | (0.1, 0.2] |
| CODMn (mg/L) | ≤2.0 | (2.0, 4.0] | (4.0, 6.0] | (6.0, 10.0] | (10.0, 15.0] |
| Water quality indicators | Water Quality Grade | ||||
| I | II | III | IV | V | |
| DO (mg/L) | ≥7.5 | (6.5,7.5] | (6.0, 6.5] | (5.5, 6.0] | (4.5, 5.5] |
| TN (mg/L) | ≤0.2 | (0.2, 0.5] | (0.5, 1.0] | (1.0, 1.5] | (1.5, 2.0] |
| NH3-N (mg/L) | ≤0.15 | (0.15, 0.5] | (0.5, 1.0] | (1.0, 1.5] | (1.5, 2.0] |
| TP (mg/L) | ≤0.01 | (0.01, 0.025] | (0.025, 0.05] | (0.05, 0.1] | (0.1, 0.2] |
| CODMn (mg/L) | ≤1.0 | (1.0, 2.0] | (2.0, 3.0] | (3.0, 4.0] | (4.0, 5.0] |
| Water Quality Indicators | Min | Max | Mean | Std. Dev | Median |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO (mg/L) | 4.890 | 18.360 | 9.219 | 2.567 | 9.250 |
| TN (mg/L) | 0.000 | 18.940 | 2.277 | 3.714 | 1.050 |
| NH3-N (mg/L) | 0.020 | 2.740 | 0.271 | 0.374 | 0.180 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.000 | 0.300 | 0.031 | 0.039 | 0.022 |
| CODMn (mg/L) | 0.000 | 4.840 | 1.942 | 1.236 | 1.972 |
| Type | Source | Emissions (T) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CODMn | NH3-N | TN | TP | ||
| Industrial source | / | / | / | / | |
| Agricultural source | Livestock and poultry breeding | 1146.37 | 231.85 | / | 7.25 |
| Aquaculture | 212.65 | 9.82 | 30.90 | 5.69 | |
| Planting industry | / | / | 14.01 | 2.54 | |
| Domestic source | Urban life source | 1775.75 | 170.26 | 233.98 | 22.30 |
| Rural life source | 546.04 | 45.73 | 69.33 | 5.06 | |
| Centralized pollution | 1.00 | 0.10 | 0.28 | 0.02 | |
| Total | 3681.81 | 457.76 | 348.51 | 42.86 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, G.; Peng, L.; Wang, C.; Lu, Q. Water Quality Evaluation and Countermeasures of Pollution in Wan’an Reservoir Using Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Model. Toxics 2025, 13, 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090712
Duan G, Peng L, Wang C, Lu Q. Water Quality Evaluation and Countermeasures of Pollution in Wan’an Reservoir Using Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Model. Toxics. 2025; 13(9):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090712
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Gaoqi, Li Peng, Chunrong Wang, and Qiongqiong Lu. 2025. "Water Quality Evaluation and Countermeasures of Pollution in Wan’an Reservoir Using Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Model" Toxics 13, no. 9: 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090712
APA StyleDuan, G., Peng, L., Wang, C., & Lu, Q. (2025). Water Quality Evaluation and Countermeasures of Pollution in Wan’an Reservoir Using Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Model. Toxics, 13(9), 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090712







