Soil Quality and Trace Element Risk in Urban and Rural Kitchen Gardens: A Comparative Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Study Area and Sampling Sites
2.2. Soil Sampling and Physico-Chemical Analysis
2.3. Evaluation of Environmental Risk and Contamination Level
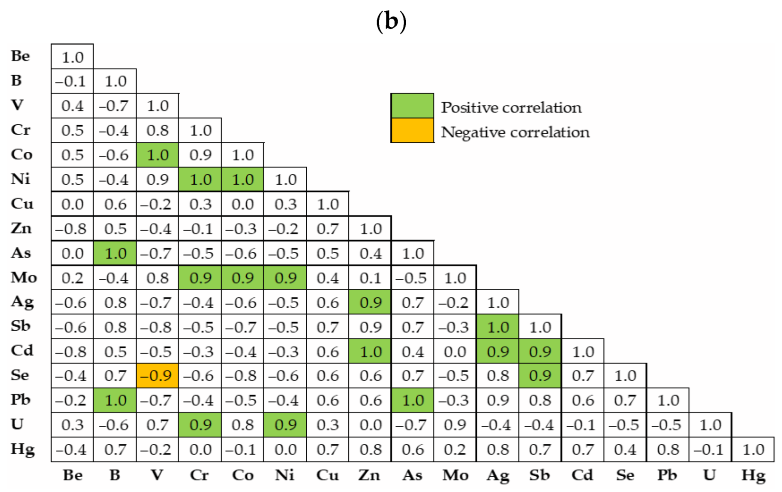
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Fertility and Multi-Elemental Content
3.2. Pollution and Ecological Indexes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision (ST/ESA/SER.A/420); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019; p. 125. Available online: https://www.un-ilibrary.org/content/books/9789210043144 (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y. How does urbanization affect public health? New evidence from 175 countries worldwide. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1096964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Health Organization (WHO). Urbanization and Health; Bulletin of the World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 88, p. 245. Available online: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2855604/ (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Flies, E.J.; Mavoa, S.; Zosky, G.R.; Mantzioris, E.; Williams, C.; Eri, R.; Brook, B.W.; Buettel, J.C. Urban-associated diseases: Candidate diseases, environmental risk factors, and a path forward. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, M.; Corso, M.; Chanel, O.; Declercq, C.; Badaloni, C.; Cesaroni, G.; Henschel, S.; Meister, K.; Haluza, D.; Martin-Olmedo, P.; et al. Assessing the public health impacts of urban air pollution in 25 European cities: Results of the Aphekom project. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 449, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khomenko, S.; Cirach, M.; Pereira-Barboza, E.; Mueller, N.; Barrera-Gómez, J.; Rojas-Rueda, D.; de Hoogh, K.; Hoek, G.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. Premature mortality due to air pollution in European cities: A health impact assessment. Lancet Planet. Health 2021, 5, e121–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester, J.; Quijal-Zamorano, M.; Méndez Turrubiates, R.F.; Pegenaute, F.; Herrmann, F.R.; Robine, J.M.; Basagaña, X.; Tonne, C.; Antó, J.M.; Achebak, H. Heat-related mortality in Europe during the summer of 2022. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1857–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.E.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Ambròs, A.; de Sá, T.H.; Mueller, N. The impact of urban environmental exposures on health: An assessment of the attributable mortality burden in Sao Paulo city, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, E.P.; Cirach, M.; Khomenko, S.; Iungman, T.; Mueller, N.; Barrera-Gómez, J.; Rojas-Rueda, D.; Kondo, M.; Niewenhuijsen, M. Green space and mortality in European cities: A health impact assessment study. Lancet Planet. Health 2021, 5, e718–e730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Regional Office for Europe. Urban Green Spaces and Health; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Soga, M.; Gaston, K.J.; Yamaura, Y. Gardening is beneficial for health: A meta-analysis. Prev. Med. Rep. 2017, 5, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bell, S.; White, M.; Griffiths, A.; Darlow, A.; Taylor, T.; Wheeler, B.; Lovell, R. Spending time in the garden is positively associated with health and wellbeing: Results from a national survey in England. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 200, 103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartig, T.; Kahn, P.H. Living in cities, naturally. Science 2016, 352, 938–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García de Jalón, S.; Chiabai, A.; Quiroga, S.; Suárez, C.; Ščasný, M.; Máca, V.; Zvěřinová, I.; Marques, S.; Craveiro, D.; Taylor, T. The influence of urban greenspaces on people’s physical activity: A population-based study in Spain. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 215, 104229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Sun, R.; Vejre, H. Links between green space and public health: A bibliometric review of global research trends and future prospects from 1901 to 2019. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, T.; Costa, J.; Santos, O.; Sousa, J.; Ribeiro, T.; Freire, E. Evidence on the contribution of community gardens to promote physical and mental health and well-being of non-institutionalized individuals: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratman, G.N.; Anderson, C.B.; Berman, M.G.; Cochran, B.; de Vries, S.; Flanders, J.; Folke, C.; Frunkim, H.; Gross, J.J.; Hartig, T.; et al. Nature and mental health: An ecosystem service perspective. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, 903–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, S.M.; Lindley, S.; Huck, J.J. Spatial dimensions of the influence of urban green-blue spaces on human health: A systematic review. Environ. Res. 2020, 180, 108869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.P.; Elliott, L.R.; Grellier, J.; Economou, T.; Bell, S.; Bratman, G.N.; Cirah, M.; Gascon, M.; Lima, M.L.; Lõhmus, M.; et al. Associations between green/blue spaces and mental health across 18 countries. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhambov, A.M.; Hartig, T.; Tilov, B.; Atanasova, V.; Makakova, D.R.; Dimitrova, D.D. Residential greenspace is associated with mental health via intertwined capacity-building and capacity-restoring pathways. Environ. Res. 2019, 178, 108708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soga, M.; Gaston, K.J. Extinction of experience: The loss of human–nature interactions. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation. Cities and Circular Economy for Food; Ellen MacArthur Foundation: Cowes, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO. Transforming food systems for food security, improved nutrition and affordable healthy diets for all. In The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World; Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, L.K.; Appel, L.J.; Franco, M.; Jones-Smith, J.C.; Nur, A.; Anderson, C.A.M. The relationship of the local food environment with obesity: A systematic review of methods, study quality, and results. Obesity 2015, 23, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinour, L.M.; Bergen, D.; Yeh, M.C. The Food Insecurity—Obesity Paradox: A Review of the Literature and the Role Food Stamps May Play. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 1952–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Ghadamgahi, F.; Jayedi, A.; Arzhang, P.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Azadbakht, L. The association between food insecurity and obesity, a body shape index and body roundness index among US adults. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Framework for the Urban Food Agenda; Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunapala, R.; Gangahagedara, R.; Wanasinghe, W.C.S.; Samaraweera, A.U.; Gamage, A.; Rathnayaka, C.; Hammed, Z.; Baki, Z.A.; Madhujith, T.; Merah, O. Urban agriculture: A strategic pathway to building resilience and ensuring sustainable food security in cities. Farming Syst. 2025, 3, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaño-López, F.; Biswas, A. Are heavy metals in urban garden soils linked to vulnerable populations? A case study from Guelph, Canada. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPMA—Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera. Normais Climatológicas. Available online: https://www.ipma.pt/pt/oclima/normais.clima/ (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Guitián, F.; Carballas, T. Técnicas De Análisis De Suelos, 2nd ed.; Pico Sacro: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1976; p. 288. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M. Determination of nitrogen in soils by the Kjeldahl method. J. Agric. Sci. 1960, 55, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, U.; Klee, J. Prüfung der Leistungsf¨ahigkeit von einigen wichtigeren Verfahren zur Bestimmung des Kohlen-stoffs mittels Chromschwefels¨ aure sowie Vorschlag einer neuen Schnellmethode. Z. Pflanzenern Ahrung Düngung Bodenkd. 1954, 64, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascomb, C.L. Distribution of pyrophosphate-extractable iron and organic carbon in soils of various groups. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1968, 19, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S. Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. In Circular No. 939; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Peech, M.; Alexander, L.T.; Dean, L.A.; Reed, J.F. Methods of Soil Analysis for Soil Fertility Investigations, USDA 575; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, G.W. Exchangeable Cations. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Page, A.L., Buxton, R.H., Miller Keeney, D.R., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 11466:1995(E); Soil Quality—Extraction of Trace Elements Soluble in Aqua Regia. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- DIN 38414-S4; German Standard Procedure for Water, Wastewater and Sediment Testing (Group S). Determination of Leachability by Water. Institutfür Normung: Berlin, Germany, 1984.
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol. Mar. Res. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Zhao, J.Z.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Solderland, L.; Liu, G.H. Impacts of sewage irrigation on heavy metal distribution and contamination in Beijing. China Environ. Int. 2005, 32, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APA—Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente. Valores de referência para solos (Revisão 3). In Solos Contaminados—Guia Técnico; Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente: Amadora, Portugal, 2022; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahim, G.M.S.; Parker, R.J. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machender, G.; Dhakate, R.; Prasanna, L.; Govil, P.K. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils around Balanagar industrial area, Hyderabad, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.H.; Khanam, D.; Adyel, T.M.; Islam, M.S.; Ahsan, M.A.; Akbor, M.A. Assessment of heavy metal contamination of agricultural soil around Dhaka Export Processing Zone (DEPZ), Bangladesh: Implication of seasonal variation and indices. Appl. Sci. 2012, 2, 584–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorfi, S.; Maleki, R.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Ahmadi, M. Pollution load index for heavy metals in Mian-Ab plain soil, Khuzestan, Iran. Data Brief 2017, 15, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaneev, A.I.; Brzhezinskiy, A.S.; Karandashev, V.K.; Ermolin, M.S.; Fedotov, P.S. Assessment of sources, environmental, ecological, and health risks of potentially toxic elements in urban dust of Moscow megacity, Russia. Chemosphere 2023, 321, 138142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, D.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. Ecological risk assessment and early warning of heavy metal cumulation in the soils near the Luanchuan molybdenum polymetallic mine concentration area, Henan Province, central China. China Geol. 2023, 6, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dahar, R.K.; Rabee, A.M.; Mohammed, R.J. Calculation of Soil Pollution Indices with Elements in Residential Areas of Baghdad City. Revis. Bionatura 2023, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Varennes, A. Productividade dos Solos e Ambiente; Escolar Editora: Lisboa, Portugal, 2003; ISBN 972-592-156-9. [Google Scholar]
- Veloso, A.; Sempiterno, C.; Calouro, F.; Rebelo, F.; Pedra, F.; Castro, I.V.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Marcelo, M.E.; Pereira, P.; Fareleira, P.; et al. Manual de Fertilização das Culturas, 3rd ed.; Instituto Nacional de Investigação Agrária e Veterinária, I.P.—INIAV: Oeiras, Portugal, 2022; ISBN 978-972-579-063-2. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, H.F.; Silva, N.F.; Oliveira, C.M.; Matos, M.J. Heavy Metals Contamination of Urban Soils—A Decade Study in the City of Lisbon, Portugal. Soil Syst. 2021, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachada, A.; Dias, A.C.; Pato, P.; Mieiro, C.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Pereira, M.E.; Ferreira da Silva, E.; Duarte, A.C. Major inputs and mobility of potentially toxic elements contamination in urban areas. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhou, X.; Chen, H.; Tang, M.; Xie, X. Cross-Talks Between Macro- and Micronutrient Uptake and Signaling in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 663477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, D.Y.; Li, C.; Chen, X.P.; Zou, C.Q. Accumulation, partitioning, and bioavailability of micronutrients in summer maize as affected by phosphorus supply. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 86, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barben, S.A.; Hopkins, B.G.; Jolley, V.D.; Webb, B.L.; Nichols, B.A. Phosphorus and Manganese Interactions and their relationships with Zn in chelator-buffered solution grown russet Burbank potato. J. Plant Nutr. 2010, 33, 752–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpiene, J.; Lagerkvist, A.; Maurice, C. Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments—A review. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larney, F.J.; Angers, D.A. The role of organic amendments in soil reclamation: A review. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 92, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.S.; Abreu, M.M.; Macías, F.; de Varennes, A. Chemical quality of leachates and enzymatic activities in Technosols with gossan and sulfide wastes from the São Domingos mine. J. Soil Sediments 2016, 16, 1366–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías, F.; Calvo de Anta, R. Niveles Genéricos de Referencia de Metales Pesados y Otros Elementos Traza en Suelos de Galicia; Xunta de Galicia: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2009; p. 232. ISBN 978-84-453-4664-8. [Google Scholar]
- Leitão, T.E.; Cameira, M.R.; Costa, H.D.; Pacheco, J.M.; Henriques, M.J.; Martins, L.L.; Mourato, M.P. Environmental Quality in Urban Allotment Gardens: Atmospheric Deposition, Soil, Water and Vegetable Assessment at LISBON City. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moitinho de Almeida, F. Carta Geológica do Concelho de Lisboa, Folha 1 2 3 e 4, Escala 1:10000; Serviços Geológicos de Portugal: Lisbon, Portugal, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Bidar, G.; Pelfrêne, A.; Schwartz, C.; Waterlot, C.; Sahmer, K.; Marot, F.; Douay, F. Urban kitchen gardens: Effect of the soil contamination and parameters on the trace element accumulation in vegetables—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriano, D. Trace Elements in Terrestrial Environments: Biogeochemistry, Bioavailability, and Risks of Metals, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Unit | Urban Kitchen Garden (n = 15) | Rural Kitchen Garden (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse fraction | % | 20.783 ± 9.863 22.598 | 23.547 ± 11.043 18.017 |
| Fine fraction | % | 79.217 ± 9.863 77.402 | 76.453 ± 11.043 81.983 |
| Humidity | % | 11.469 ± 10.329 8.255 | 22.424 ± 20.335 21.702 |
| pH (H2O) | - | 7.728 ± 0.406 7.770 | 7.504 ± 0.425 7.750 |
| pH (KCl) | - | 7.109 ± 0.324 * 7.240 | 6.700 ± 0.370 * 6.690 |
| EC 1 | µS/cm | 482.347 ± 264.457 391.000 | 589.500 ± 412.829 497.100 |
| Total C | g/kg | 34.095 ± 19.937 28.230 | 47.314 ± 42.054 32.270 |
| Organic C | g/kg | 18.237 ± 13.937 16.853 | 30.580 ± 33.325 12.781 |
| Labile C | g/kg | 6.175 ± 1.864 5.824 | 8.927 ± 6.958 6.307 |
| Total N | g/kg | 2.110 ± 1.079 2.012 | 3.049 ± 1.762 2.024 |
| Total S | g/kg | <2.500 | <2.500 |
| Total P | g/kg | 1.065 ± 0.490 * 0.970 | 1.792 ± 0.974 * 1.430 |
| Available P | mg/kg | 166.794 ± 224.455 90.335 | 204.550 ± 180.629 267.210 |
| CEC 2 | cmolc/kg | 44.699 ± 18.904 46.717 | 65.345 ± 58.749 36.013 |
| Exchange Ca | cmolc/kg | 39.327 ± 15.842 42.523 | 58.234 ± 56.338 28.816 |
| Exchange Mg | cmolc/kg | 3.222 ± 3.792 1.565 | 4.973 ± 2.827 3.925 |
| Exchange Na | cmolc/kg | 1.292 ± 0.728 1.405 | 0.904 ± 0.742 0.464 |
| Exchange K | cmolc/kg | 0.859 ± 0.420 0.760 | 1.234 ± 0.834 1.053 |
| Element | Unit | Urban Kitchen Garden (n = 15) | Rural Kitchen Garden (n = 5) | MAV [44] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Be | mg/kg | 0.820 (0.400–1.500) ** | 1.560 (0.900–1.900) ** | 2.500 |
| B | 9.300 (4.000–16.00) | 14.40 (9.000–23.00) | 36.00 | |
| V | 58.90 (11.00–219.0) | 110.8 (21.00–284.0) | 86.00 | |
| Cr | 53.20 (10.00–194.0) | 67.80 (20.00–228.0) | 67.00 | |
| Co | 15.88 (2.100–63.90) | 26.96 (5.500–75.80) | 19.00 | |
| Ni | 42.33 (5.500–191.0) | 49.30 (16.40–149.0) | 37.00 | |
| Cu | 35.34 (11.10–92.10) * | 58.82 (27.90–75.00) * | 62.00 | |
| Zn | 117.9 (44.00–348.0) | 131.4 (77.40–237.0) | 290.0 | |
| As | 5.640 (1.500–11.10) | 6.080 (1.900–13.20) | 11.00 | |
| Mo | 0.606 (0.230–1.370) | 0.786 (0.230–2.050) | 2.000 | |
| Ag | 0.192 (0.037–1.100) | 0.073 (0.049–0.120) | 0.500 | |
| Sb | 0.550 (0.160–1.280) | 0.426 (0.130–0.880) | 1.000 | |
| Cd | 0.168 (0.070–0.270) | 0.166 (0.100–0.340) | 1.000 | |
| Se | 0.470 (0.300–0.700) | 0.500 (0.300–0.700) | 1.200 | |
| Ta | <0.050 | <0.050 | 1.000 | |
| Pb | 29.13 (7.800–66.20) | 26.3 (7.800–55.90) | 45.00 | |
| U | 0.890 (0.500–1.700) | 0.920 (0.700–1.300) | 1.900 | |
| Hg | µg/kg | 73.00 (20.00–190.0) | 70.00 (30.00–100.0) | 160.0 |
| CD (n = 18) | mCD (n = 18) | PLI | PLI Zone | GER (n = 11) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UB1 | 5.34 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 23.23 | |
| UB2 | 6.42 | 0.36 | 0.19 | 30.61 | |
| UB3 | 8.31 | 0.46 | 0.23 | 44.47 | |
| UB4 | 7.39 | 0.41 | 0.24 | 44.15 | |
| UB5 | 7.02 | 0.39 | 0.23 | 38.03 | |
| UB6 | 8.19 | 0.46 | 0.26 | 46.66 | |
| UB7 | 16.60 | 0.92 | 0.27 | 67.25 | |
| UB8 | 3.68 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 26.65 | |
| UB9 | 4.54 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 27.36 | |
| UB10 | 5.09 | 0.28 | 0.17 | 20.06 | |
| UB11 | 7.72 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 28.00 | |
| UB12 | 18.35 | 1.02 | 0.40 | 24.24 | |
| UB13 | 6.62 | 0.37 | 0.20 | 35.09 | |
| UB14 | 6.29 | 0.35 | 0.20 | 77.24 | |
| UB15 | 7.64 | 0.42 | 0.22 | 80.01 | |
| Urban kitchen garden (n = 15) | 0.21 | ||||
| RU1 | 7.87 | 0.44 | 0.19 | 49.94 | |
| RU2 | 6.75 | 0.38 | 0.20 | 51.23 | |
| RU3 | 20.07 | 1.12 | 0.33 | 29.90 | |
| RU4 | 10.01 | 0.56 | 0.31 | 34.89 | |
| RU5 | 8.66 | 0.48 | 0.28 | 44.37 | |
| Rural kitchen garden (n = 5) | 0.26 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arán, D.; Santos, O.; Feteira-Santos, R.; Benhalima, Y.; Santos, E.S. Soil Quality and Trace Element Risk in Urban and Rural Kitchen Gardens: A Comparative Analysis. Toxics 2025, 13, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080697
Arán D, Santos O, Feteira-Santos R, Benhalima Y, Santos ES. Soil Quality and Trace Element Risk in Urban and Rural Kitchen Gardens: A Comparative Analysis. Toxics. 2025; 13(8):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080697
Chicago/Turabian StyleArán, Diego, Osvaldo Santos, Rodrigo Feteira-Santos, Yacine Benhalima, and Erika S. Santos. 2025. "Soil Quality and Trace Element Risk in Urban and Rural Kitchen Gardens: A Comparative Analysis" Toxics 13, no. 8: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080697
APA StyleArán, D., Santos, O., Feteira-Santos, R., Benhalima, Y., & Santos, E. S. (2025). Soil Quality and Trace Element Risk in Urban and Rural Kitchen Gardens: A Comparative Analysis. Toxics, 13(8), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080697










