The Significant Impact of Biomass Burning Emitted Particles on Typical Haze Pollution in Changsha, China
Highlights
- Biomass burning (BB) particles accounted for up to 67% of ambient fine particles during severe haze episodes.
- Single-particle mixing state analysis revealed that BB particles originated from both regional crop residue burning sources and local nocturnal cooking emissions.
- Aged BB particles developed ammonium sulfate coatings through atmospheric aging.
- The mitigation of open crop residue burning is crucial for reducing the occurrence of local haze pollution events.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sampling and Data Analysis
2.1. Sampling and Measurements
2.2. SPAMS Measurement and Clustering Algorithm
2.3. The Identification of Biomass Burning Particles
3. Results and Discussions
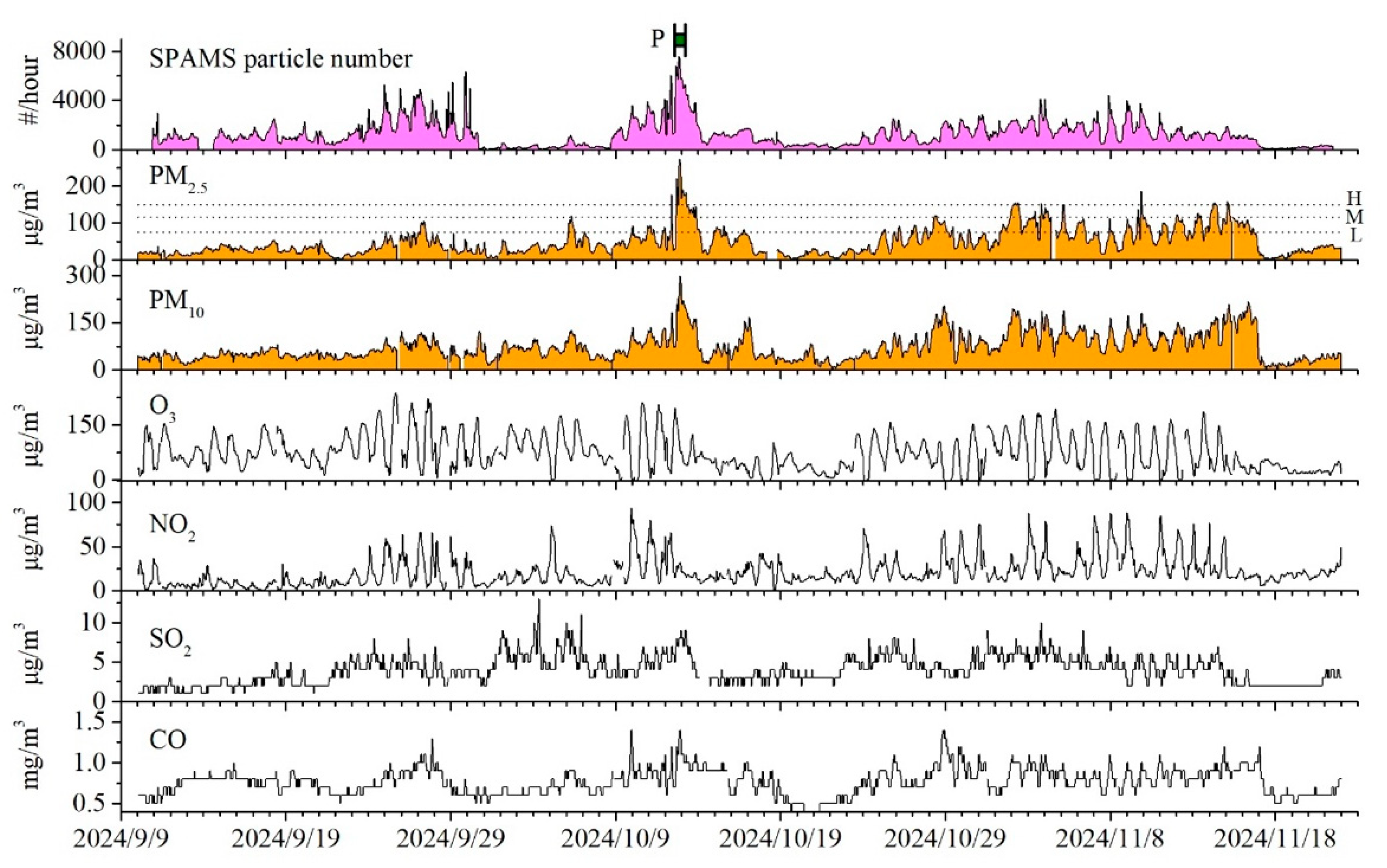
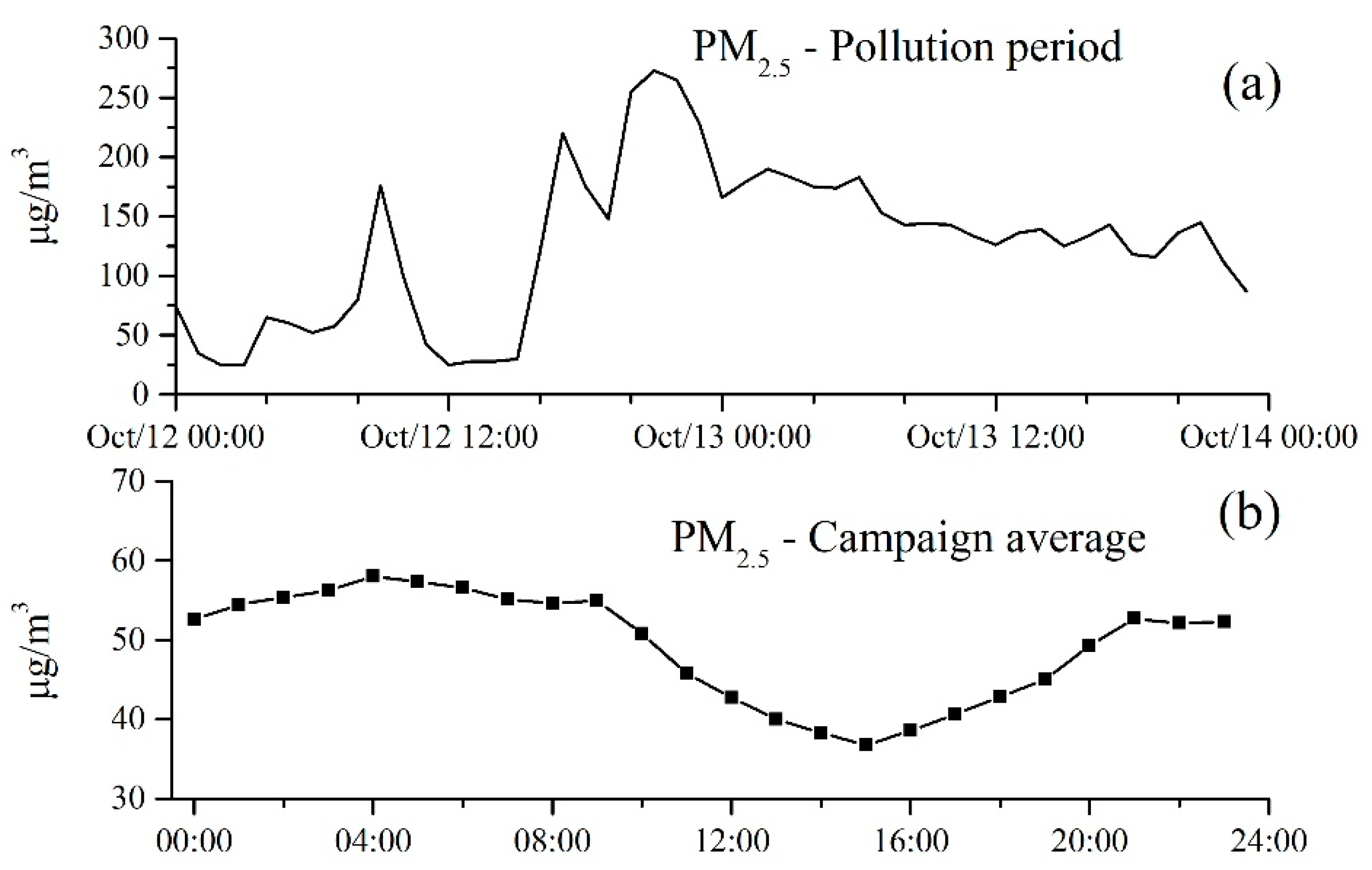
3.1. Overview of Campaign
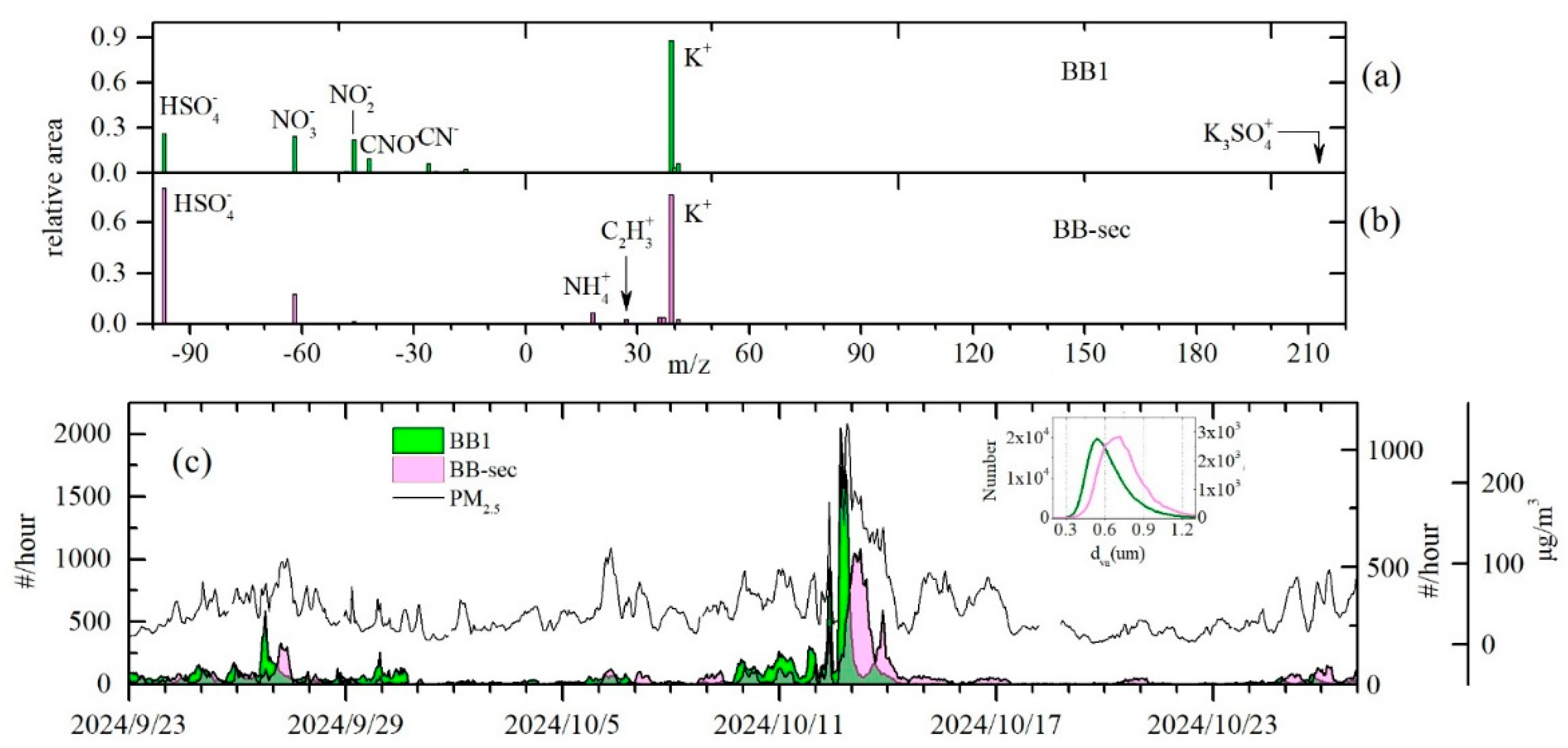
3.2. Mass Spectra of Biomass Burning Particles
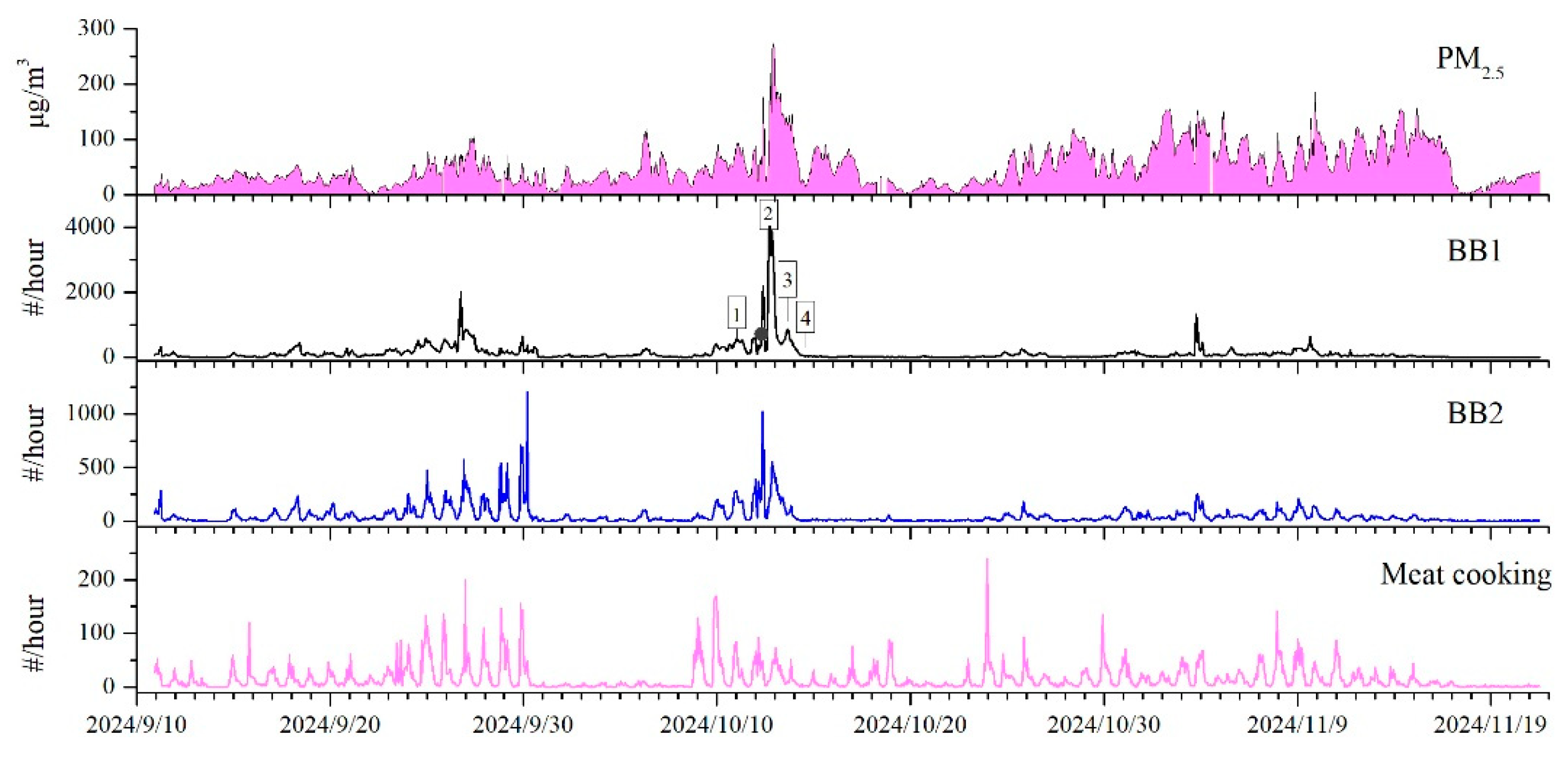
3.3. Distribution of Biomass Burning Particles
3.4. Source Analysis of Biomass Burning Particles
3.4.1. Source Analysis of BB1 Type Particles
3.4.2. Source Analysis of BB2 Type Particles
3.5. Aging Process of Biomass Burning Particles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BB | Biomass burning |
| SPAMS | Single-particle aerosol mass spectrometry |
| PM2.5 | Atmospheric fine particulate matter |
| BB1 | BB particles originated from straw burning emissions |
| BB2 | BB particles related to local nighttime cooking emissions |
| BB-lab | BB particles derived from laboratory |
| BB-sec | Secondarily processed BB particles |
| PAHs | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| OA | Organic aerosol |
| AMS | Aerosol mass spectrometry |
| FIRMS | Resource Management System |
| HYSPLIT | Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory |
References
- Lelieveld, J.; Crutzen, P.J.; Ramanathan, V.; Andreae, M.O.; Brenninkmeijer, C.A.M.; Campos, T.; Cass, G.R.; Dickerson, R.R.; Fischer, H.; de Gouw, J.A.; et al. The Indian Ocean Experiment: Widespread air pollution from South and Southeast Asia. Science 2001, 291, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Weber, R.J.; Lee, Y.N.; Orsini, D.A.; Maxwell-Meier, K.; Thornton, D.C.; Bandy, A.R.; Clarke, A.D.; Blake, D.R.; Sachse, G.W.; et al. Characteristics and influence of biosmoke on the fine-particle ionic composition measured in Asian outflow during the Transport and Chemical Evolution Over the Pacific (TRACE-P) experiment. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2003, 108, 8816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.J.; Fu, C.B.; Yang, X.Q.; Sun, J.N.; Petäjä, T.; Kerminen, V.M.; Wang, T.; Xie, Y.; Herrmann, E.; Zheng, L.F.; et al. Intense atmospheric pollution modifies weather: A case of mixed biomass burning with fossil fuel combustion pollution in eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10545–10554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zauscher, M.D.; Wang, Y.; Moore, M.J.K.; Gaston, C.J.; Prather, K.A. Air Quality Impact and Physicochemical Aging of Biomass Burning Aerosols during the 2007 San Diego Wildfires. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7633–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Zhu, T.; Xu, X.; Ge, S.; Sun, H.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J.; Ji, Y.; et al. Atmospheric sulfate aerosol formation enhanced by interfacial anions. PNAS Nexus 2025, 4, pgaf058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, T.R.; Lutes, C.C.; Doorn, M.R.J.; Fuchsman, P.C.; Timmenga, H.J.; Crouch, R.L. Aquatic ecological risks due to cyanide releases from biomass burning. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Bin, Y.; E, Z.; Chen-shuo, Y.; Si-hang, W.; Xian-jun, H.; Xiao-xiao, Z.; Shan, H.; Wei-wei, H.; Min, S. Contribution of autumn biomass burning to organic aerosol in the Pearl River Delta region. China Enviromental Sci. 2023, 43, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.K.; Liu, X.D.; Yu, T.; Cachier, H. Identification and estimate of biomass burning contribution to the urban aerosol organic carbon concentrations in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Engling, G.; He, K.B.; Duan, F.K.; Ma, Y.L.; Du, Z.Y.; Liu, J.M.; Zheng, M.; Weber, R.J. Biomass burning contribution to Beijing aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7765–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Huang, R.-J.; Duan, J.; Lin, C.; Gu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; et al. Seasonal variations in the sources of organic aerosol in Xi’an, Northwest China: The importance of biomass burning and secondary formation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wen, T.; Zhang, X.; Si, R.; Wu, X.; Li, A.; Liu, G.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xin, J. Component and Source Analyses of PM2.5 in Typical Agricultural Regions of North China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 45, 819–832. [Google Scholar]
- Casotto, R.; Skiba, A.; Rauber, M.; Strähl, J.; Tobler, A.; Bhattu, D.; Lamkaddam, H.; Manousakas, M.I.; Salazar, G.; Cui, T.; et al. Organic aerosol sources in Krakow, Poland, before implementation of a solid fuel residential heating ban. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltsonoudis, C.; Florou, K.; Kodros, J.K.; Jorga, S.D.; Vasilakopoulou, C.N.; Baliaka, H.D.; Matrali, A.; Aktypis, A.; Georgopoulou, M.P.; Nenes, A.; et al. Significant contributions of fresh and aged biomass burning organic aerosol from residential burning in a wintertime urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 2025, 343, 121018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.J.; Liu, D.Y.; Noble, C.A.; Prather, K.A. Size and chemical characterization of individual particles resulting from biomass burning of local Southern California species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 3068–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.H.; Zhang, G.H.; Li, L.; Wang, X.M.; Li, M.; Sheng, G.Y.; Fu, J.M.; Zhou, Z. Mixing state of biomass burning particles by single particle aerosol mass spectrometer in the urban area of PRD, China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3447–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Mi, T.; Cao, J.; Shi, G.; Huang, R.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Lou, S.; Wang, Q. Characterizing the composition and evolution of and urban particles in Chongqing (China) during summertime. Atmos. Res. 2017, 187, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wu, X.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, J.; Hong, Y.; Chen, J. Composition, mixing state, and size distribution of single submicron particles during pollution episodes in a coastal city in southeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 1464–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yin, Y.; Kong, S.; Xiao, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, A. Size-resolved chemical composition of atmospheric particles during a straw burning period at Mt. Huang (the Yellow Mountain) of China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 84, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Dong, J.; Li, M.; Gao, W.; Nian, H.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Bi, X.; Cheng, P.; et al. Real time bipolar time-of-flight mass spectrometer for analyzing single aerosol particles. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 303, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.H.; Hopke, P.K.; Fergenson, D.P.; Prather, K.A. Classification of single particles analyzed by ATOFMS using an artificial neural network, ART-2A. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.S.; Tullin, C.; Leckner, B.; Sjövall, P. Particle emissions from biomass combustion in small combustors. Biomass Bioenergy 2003, 25, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ge, P.; Chen, M.; Tang, J.; Cao, M.; Cui, Y.; Hu, K.; Nie, D. Tracers from Biomass Burning Emissions and Identification of Biomass Burning. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, K.A.; Murphy, S.M.; Subramanian, R.; DeMott, P.J.; Kok, G.L.; Campos, T.; Rogers, D.C.; Prenni, A.J.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Seinfeld, J.H.; et al. Flight-based chemical characterization of biomass burning aerosols within two prescribed burn smoke plumes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12549–12565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pósfai, M.; Hobbs, P.V.; Buseck, P.R. Individual aerosol particles from biomass burning in southern Africa: 2, Compositions and aging of inorganic particles. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, SAF 20-1–SAF 20-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffet, R.C.; de Foy, B.; Molina, L.T.; Molina, M.J.; Prather, K.A. Measurement of ambient aerosols in northern Mexico City by single particle mass spectrometry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 4499–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Harrison, R.M. Urban organic aerosols measured by single particle mass spectrometry in the megacity of London. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 4127–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Wang, X.; Tian, C.; Chen, Y.; Qu, L.; Ji, L.; Zhi, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Source apportionment of PM2.5 at a regional background site in North China using PMF linked with radiocarbon analysis: Insight into the contribution of biomass burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11249–11265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Bai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; et al. Wintertime aerosol chemistry in Beijing during haze period: Significant contribution from secondary formation and biomass burning emission. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casquero-Vera, J.A.; Lyamani, H.; Titos, G.; Minguillón, M.C.; Dada, L.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Petäjä, T.; Olmo, F.J.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Quantifying traffic, biomass burning and secondary source contributions to atmospheric particle number concentrations at urban and suburban sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 145282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; LI, M.; Wu, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liao, Q.; Hunag, B. Characterizing Single Particle Aerosols during the Formation and Removal of A Haze Event in the Autumn of Guangzhou. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 25, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Yu, G.; Xuehui, C.; Xinyu, W.; Yanju, S.; Man, X.; Yufei, C.; Yongli, T.; Bo, H. Biomass burning related single-particle characteristics during a typical month in Hohhot City. Geochimica 2025, 54, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Saxena, V.K.; Zhao, Z. A comparison of signals of regional aerosol-induced forcing in eastern China and the southeastern United States. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Y. Emission inventories of atmospheric pollutants discharged from biomass burning in China. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2011, 31, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, L.E.; Pratt, K.A.; Huffman, J.A.; Jimenez, J.L.; Prather, K.A. Impacts of Aerosol Aging on Laser Desorption/Ionization in Single-Particle Mass Spectrometers. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Ho, K.F.; Han, J.; Dai, W.; Wu, C.; Cao, C.; Liu, L. In-vitro oxidative potential and inflammatory response of ambient PM2.5 in a rural region of Northwest China: Association with chemical compositions and source contribution. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, M.; Song, W.; Yu, D. Emissions of Toxic Substances from Biomass Burning: A Review of Methods and Technical Influencing Factors. Processes 2023, 11, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samburova, V.; Connolly, J.; Gyawali, M.; Yatavelli, R.L.N.; Watts, A.C.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Zielinska, B.; Moosmüller, H.; Khlystov, A. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in biomass-burning emissions and their contribution to light absorption and aerosol toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.; Li, C.; Fang, Z.; Levin-Zaidman, S.; Dezorella, N.; Czech, H.; Martens, P.; Käfer, U.; Gröger, T.; Rüger, C.P.; et al. Toxicity of Water- and Organic-Soluble Wood Tar Fractions from Biomass Burning in Lung Epithelial Cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 1588–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Heuvel, R.; Staelens, J.; Koppen, G.; Schoeters, G. Toxicity of Urban PM10 and Relation with Tracers of Biomass Burning. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Peng, Z.; Lv, J.; Peng, Q.; He, K.; Xu, H.; Sun, J.; Shen, Z. Gas Particle Partitioning of PAHs Emissions from Typical Solid Fuel Combustions as Well as Their Health Risk Assessment in Rural Guanzhong Plain, China. Toxics 2023, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.S.; Huang, W.; Shen, G.; Pang, Y.; Tang, M.; Li, W.; Zhao, Z.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Xie, L.; et al. Source differences in the components and cytotoxicity of PM2.5 from automobile exhaust, coal combustion, and biomass burning contributing to urban aerosol toxicity. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ma, H.; Li, J.; Jiang, H.; Chen, W.; Wan, C.; Jiang, B.; Dong, G.; Zeng, X.; Chen, D.; et al. Nitroaromatic Compounds from Secondary Nitrate Formation and Biomass Burning Are Major Proinflammatory Components in Organic Aerosols in Guangzhou: A Bioassay Combining High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 21570–21580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Type | Min | P25 | P50 | P75 | Max | Mean | Std |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BB1 | 0.0 | 2.1 | 5.6 | 12.0 | 64.0 | 8.2 | 8.3 |
| BB2 | 0.0 | 1.4 | 2.5 | 4.4 | 24.1 | 3.3 | 2.7 |
| BB1 + BB2 | 0.0 | 3.9 | 8.6 | 16.6 | 66.9 | 11.5 | 9.8 |
| BB-sec | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 1.6 | 11.8 | 1.3 | 1.6 |
| Total | 0.0 | 5.1 | 10.0 | 18.1 | 68.5 | 12.8 | 10.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Q.; Guo, H.; Tan, J.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Jin, H.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Cheng, C.; Huang, B.; et al. The Significant Impact of Biomass Burning Emitted Particles on Typical Haze Pollution in Changsha, China. Toxics 2025, 13, 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080691
Xiao Q, Guo H, Tan J, Wang Z, Xie Y, Jin H, Yang M, Wang X, Cheng C, Huang B, et al. The Significant Impact of Biomass Burning Emitted Particles on Typical Haze Pollution in Changsha, China. Toxics. 2025; 13(8):691. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080691
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Qu, Hui Guo, Jie Tan, Zaihua Wang, Yuzhu Xie, Honghong Jin, Mengrong Yang, Xinning Wang, Chunlei Cheng, Bo Huang, and et al. 2025. "The Significant Impact of Biomass Burning Emitted Particles on Typical Haze Pollution in Changsha, China" Toxics 13, no. 8: 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080691
APA StyleXiao, Q., Guo, H., Tan, J., Wang, Z., Xie, Y., Jin, H., Yang, M., Wang, X., Cheng, C., Huang, B., & Li, M. (2025). The Significant Impact of Biomass Burning Emitted Particles on Typical Haze Pollution in Changsha, China. Toxics, 13(8), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080691








