Ozone Pollution in the Western Yangtze River Delta During the 2020 and 2021 Warm Seasons: Roles of Meteorology and Air Mass Transport
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Observations
2.2. Backward-Trajectory and Concentration-Weighted Trajectory (CWT) Analysis
2.3. Observation-Based Box Model (OBM)
3. Results
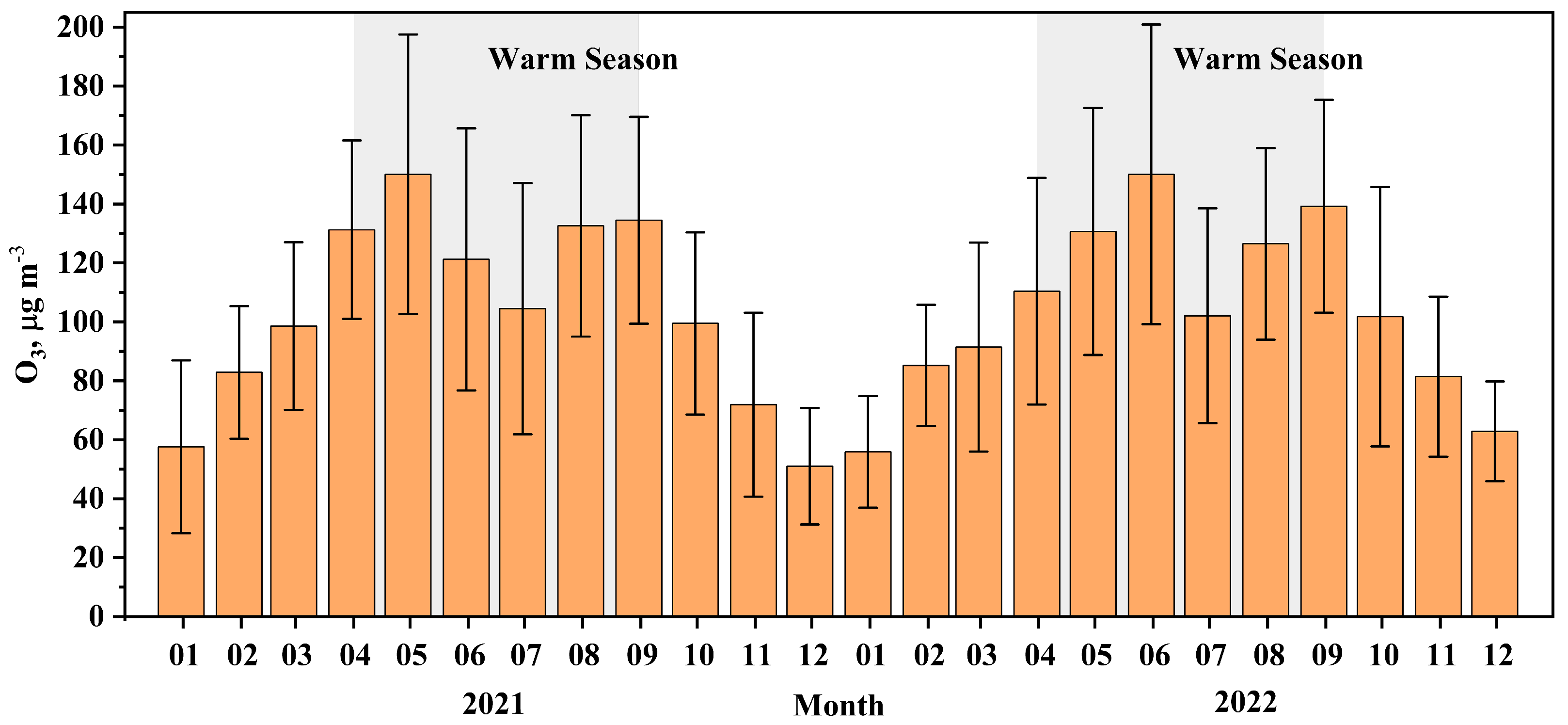
3.1. Variation of O3 and Its Precursors and Influence of Meterological Conditions
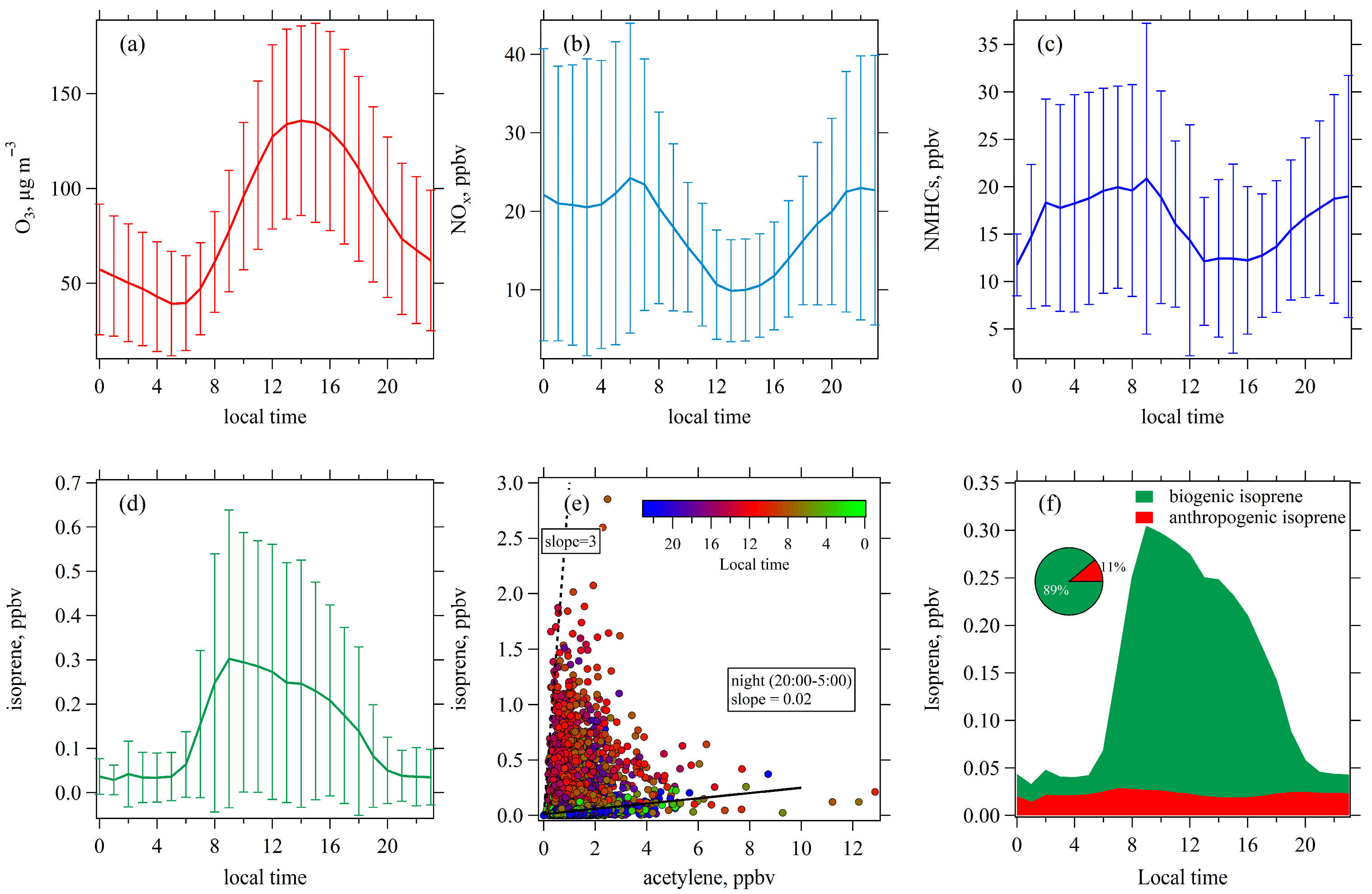
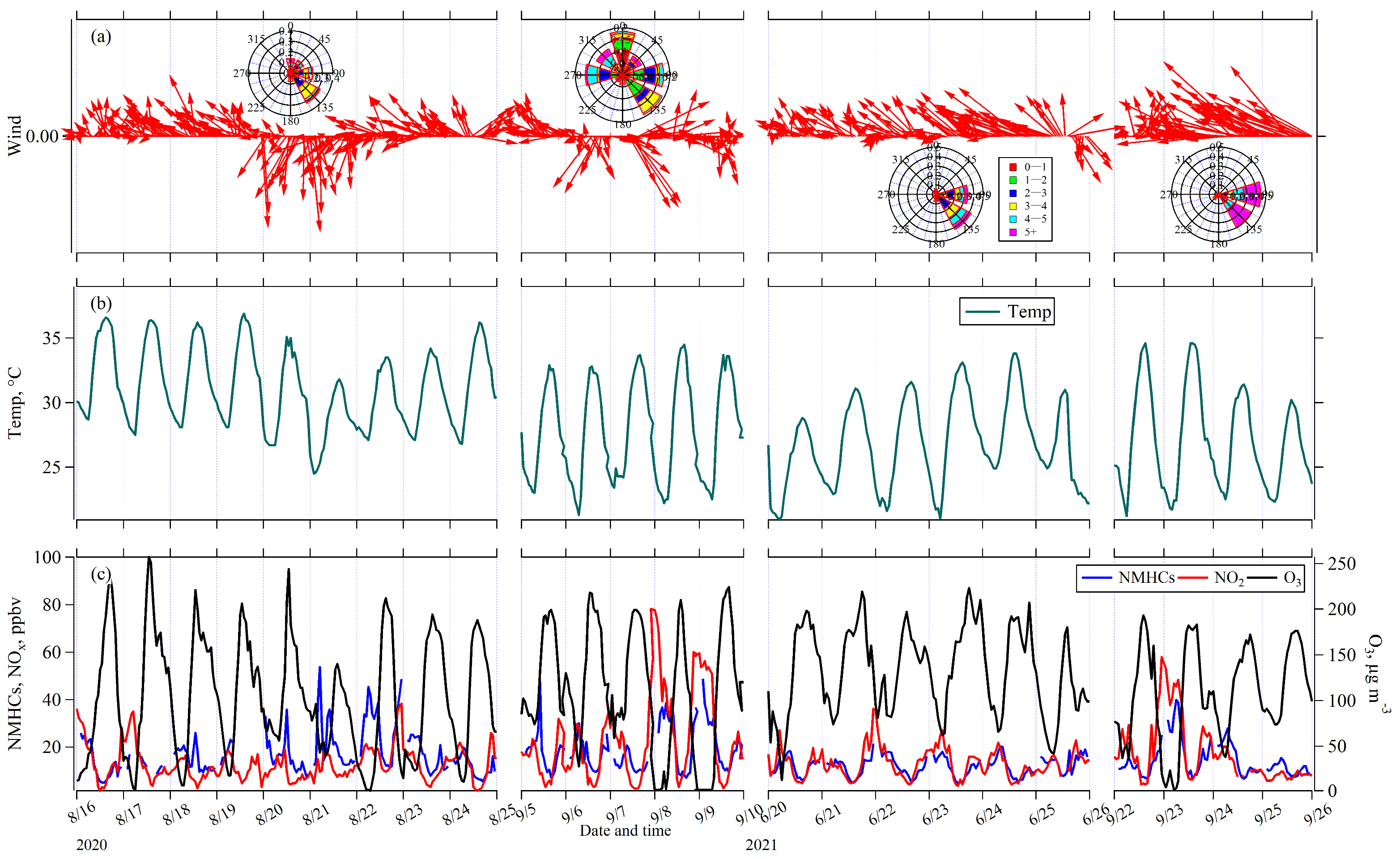
3.1.1. Diurnal Variations of O3 and Its Precursors Levels
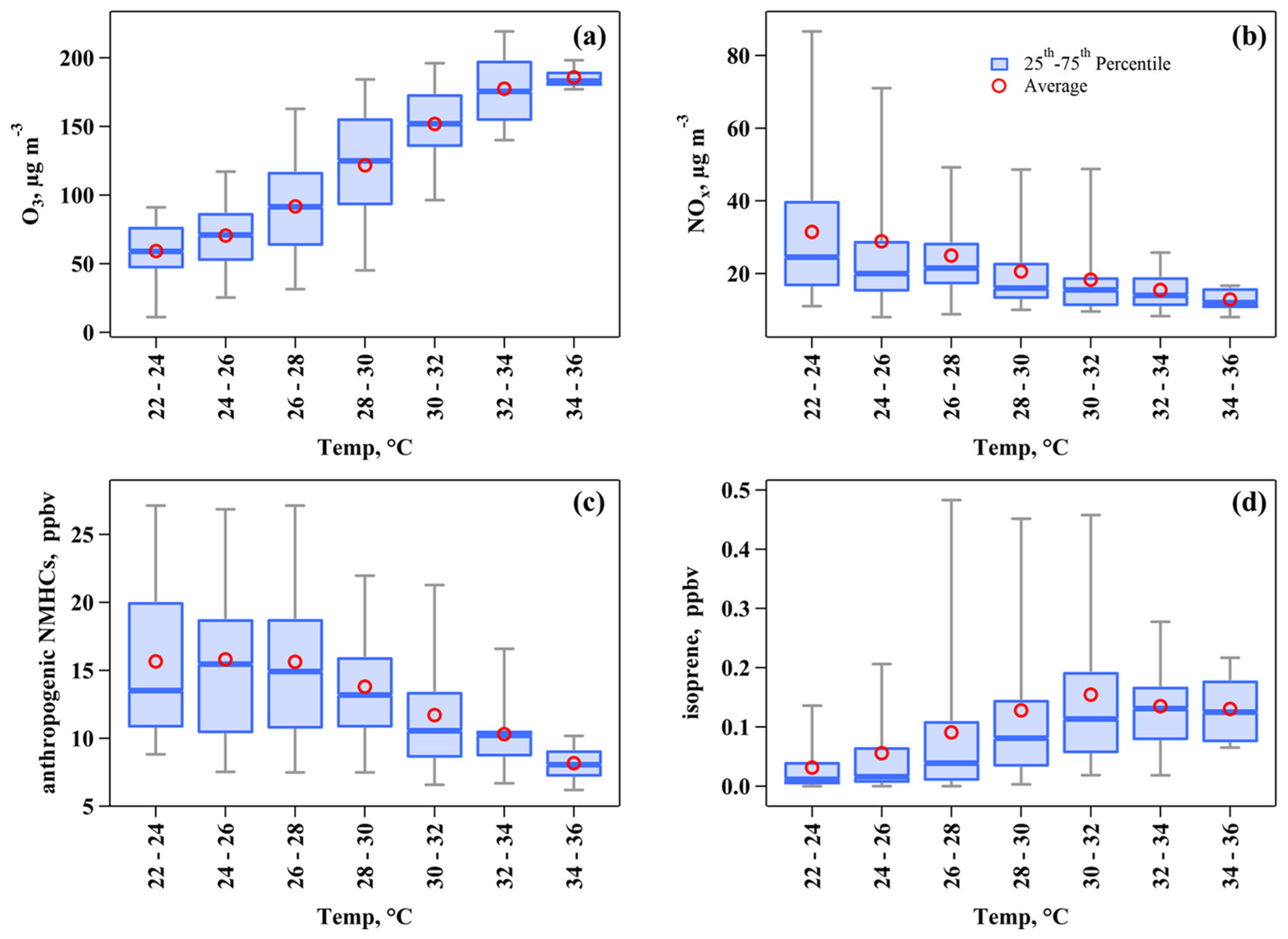
3.1.2. Influence of Temperature on O3 and Its Precursors Levels
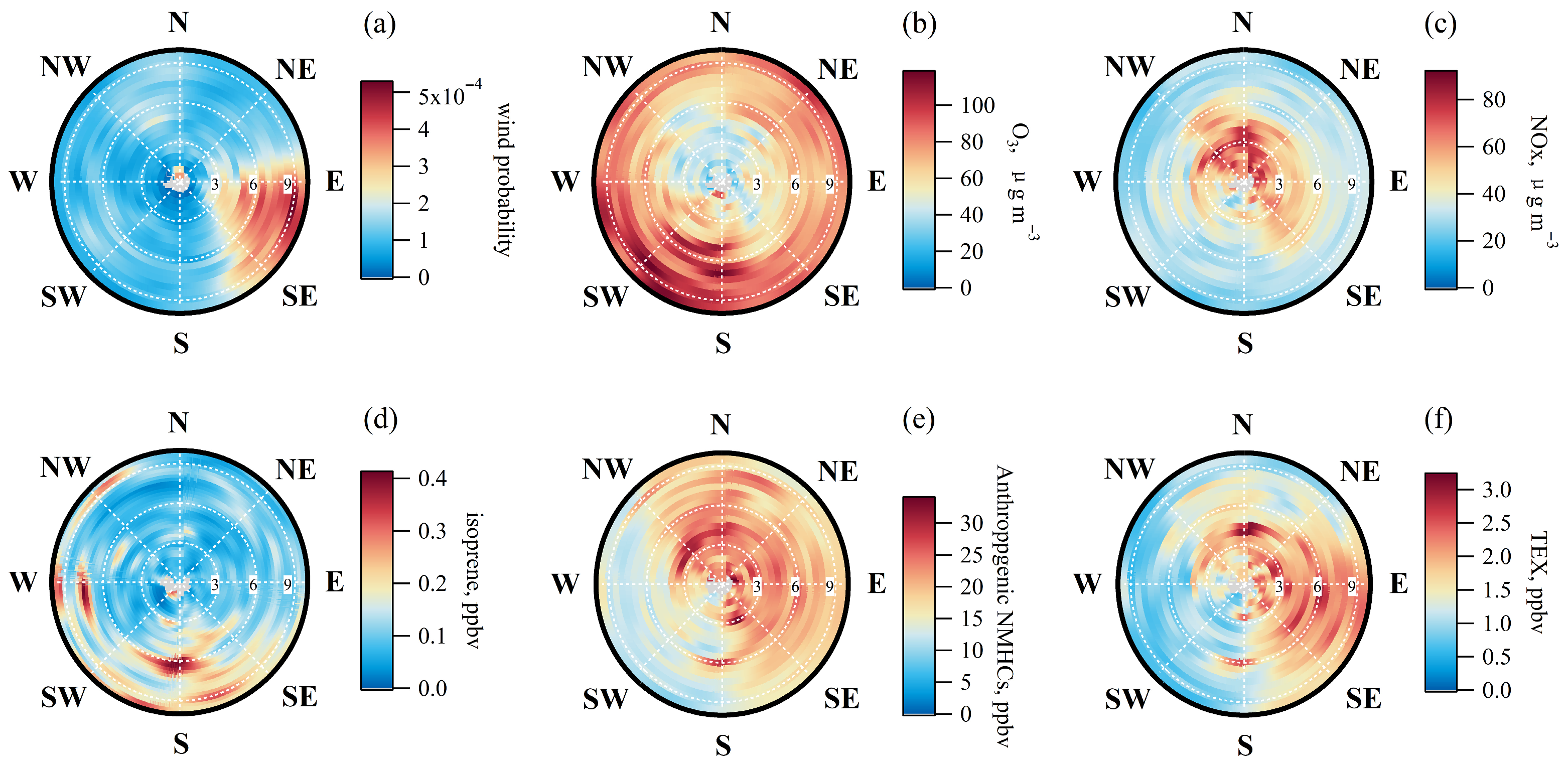
3.1.3. Wind Analysis of O3 and Its Precursors
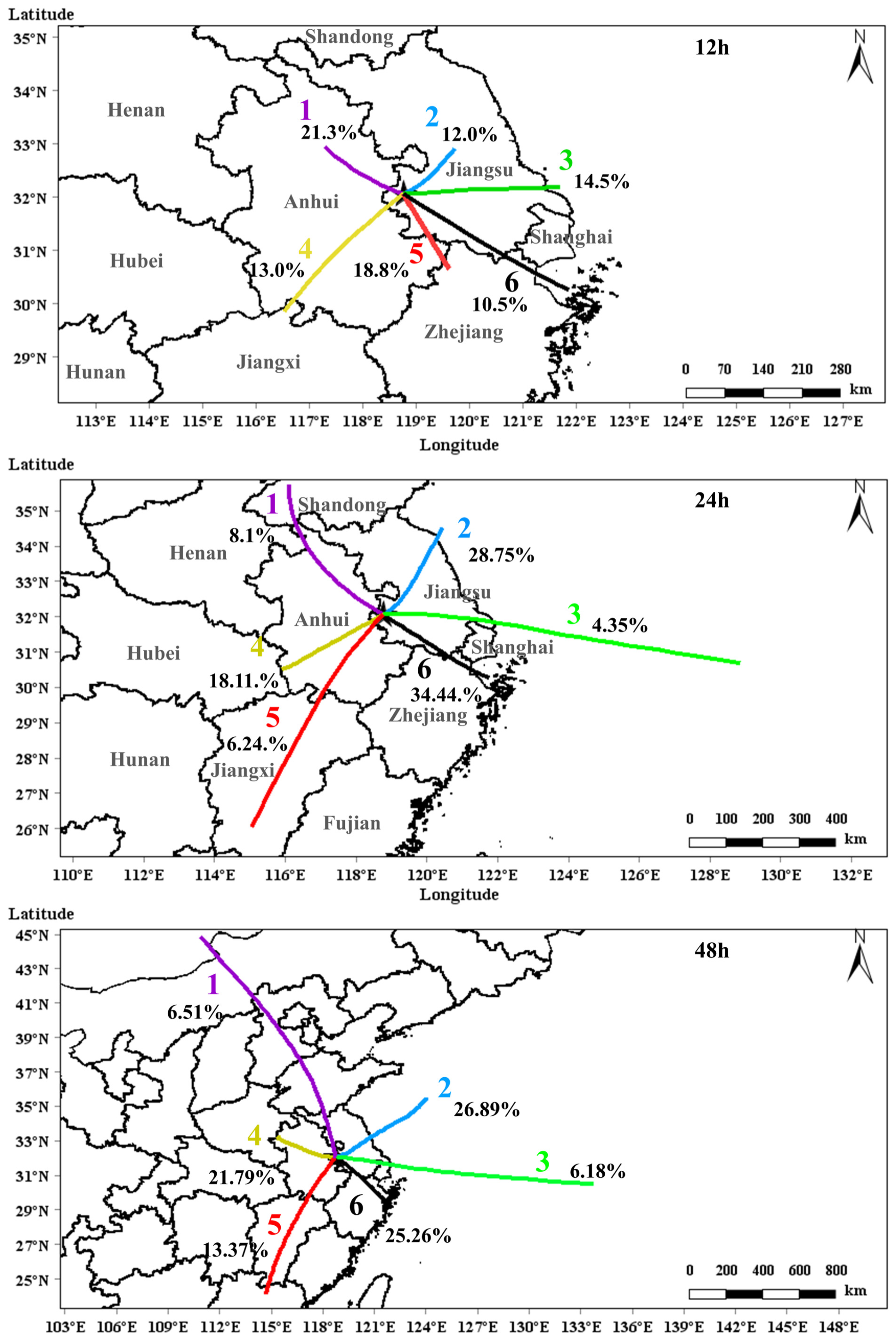
3.2. Air Mass Transport Pathways in Urban Nanjing
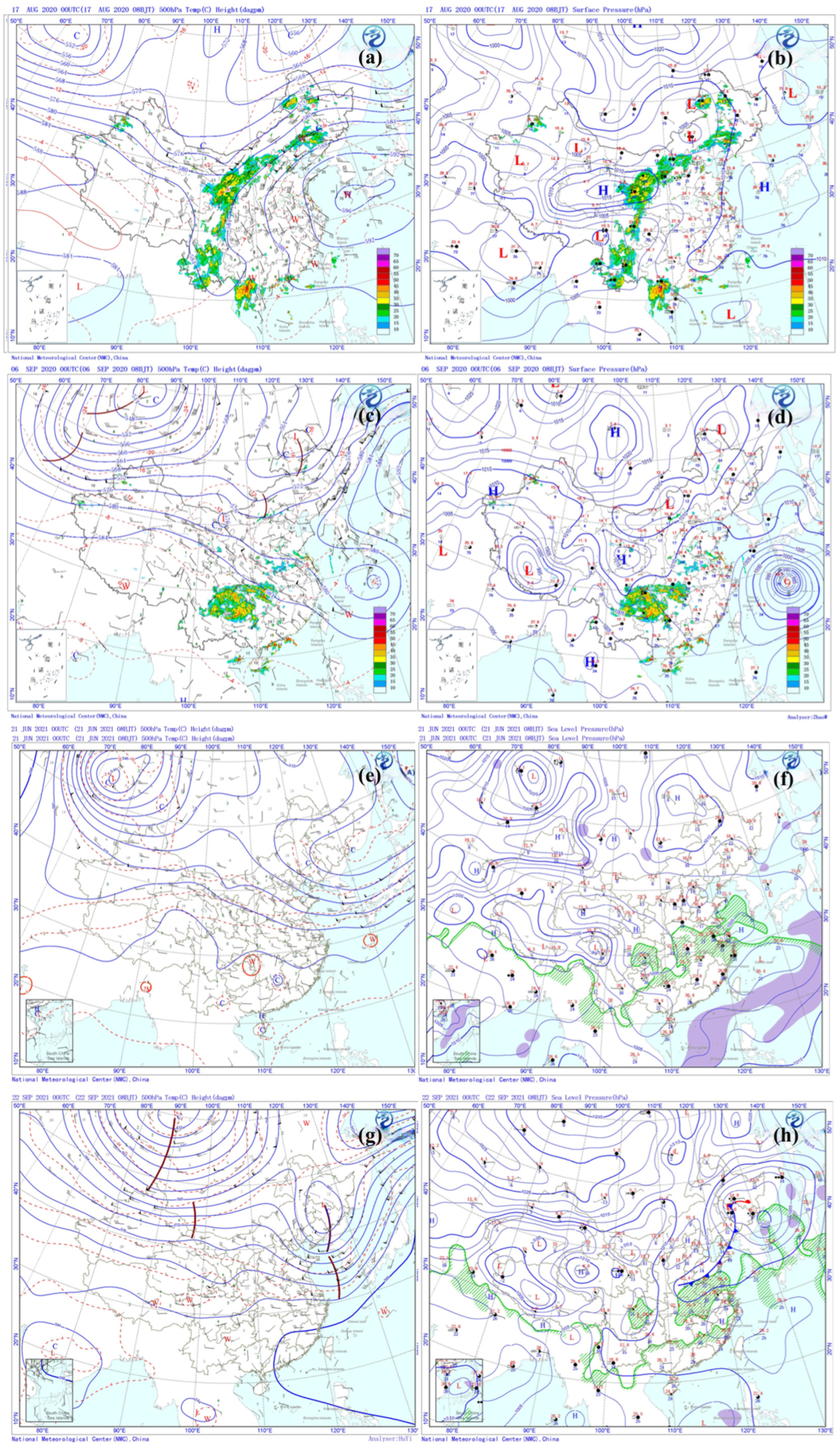
3.3. Characteristics of O3 and Its Precursors During Four O3 Pollution Episodes
3.3.1. Temporal Variations in Concentrations of O3 and Its Precursors
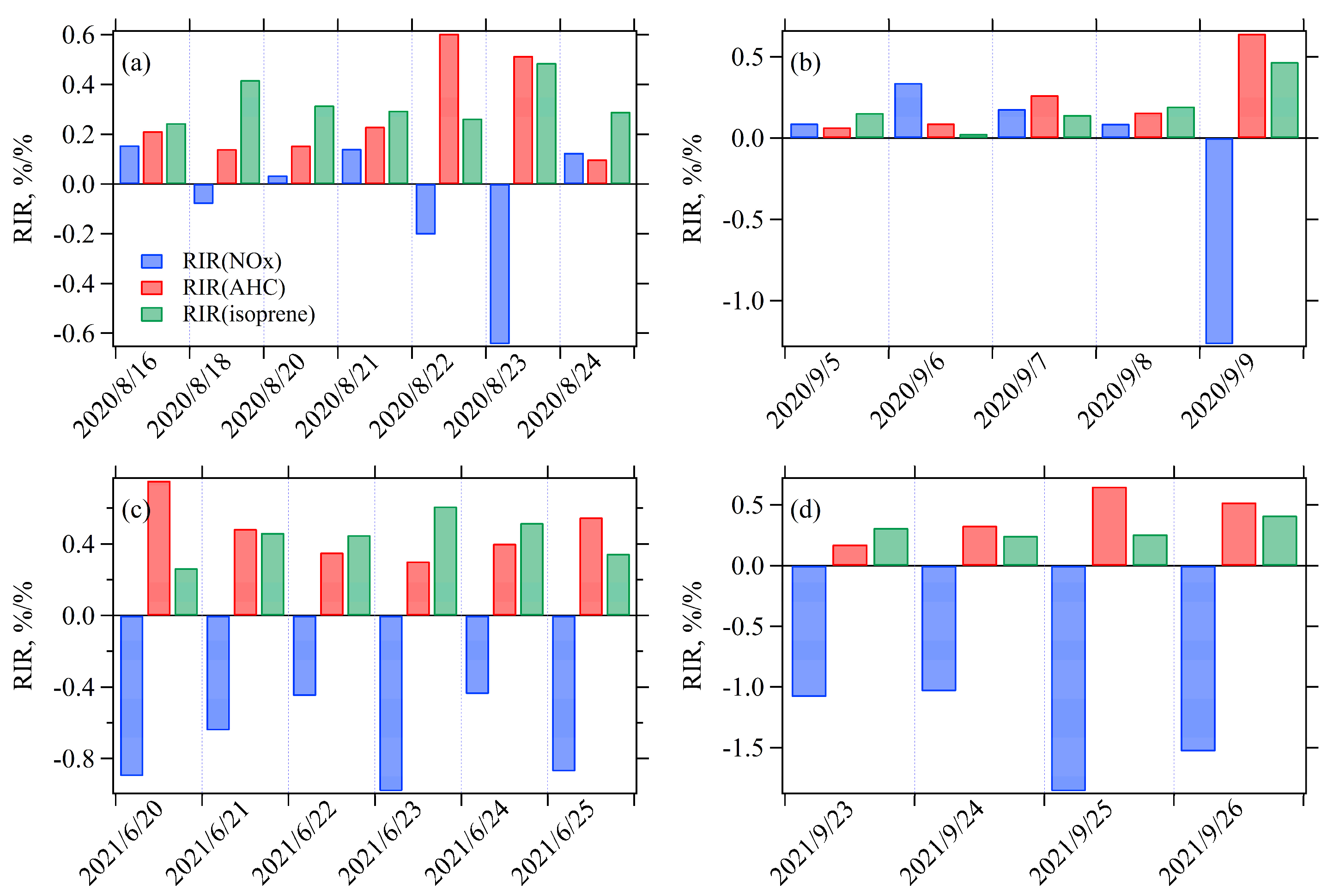
3.3.2. Sensitivity of O3 Formation to NMHCs and NOx
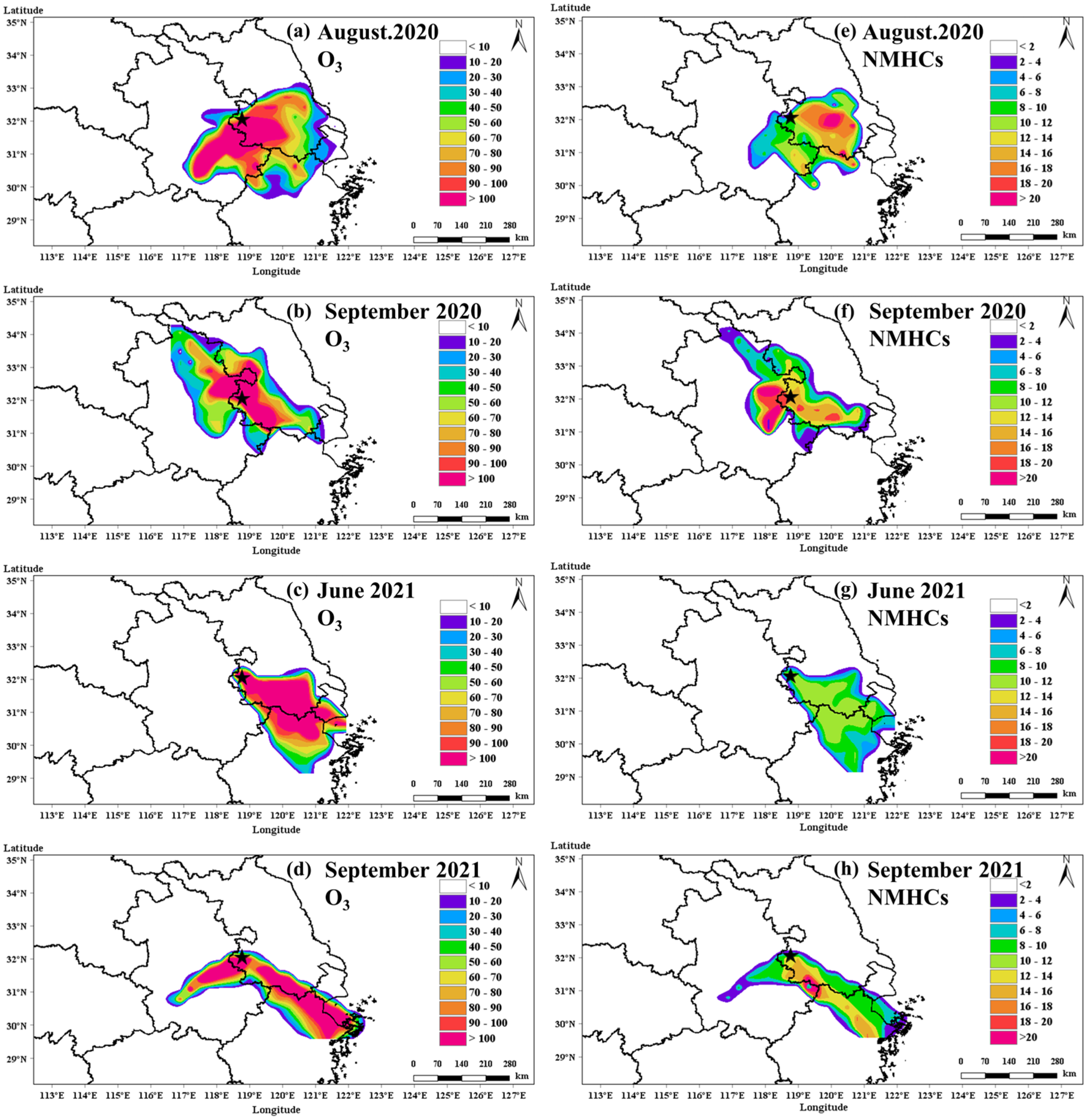
3.4. Potential Source Regions of O3 and NMHCs
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Air Mass Transport on O3 and Its Precursors Levels
4.2. Influence of Air Mass Transport on O3 Sensitivity to Its Precursors
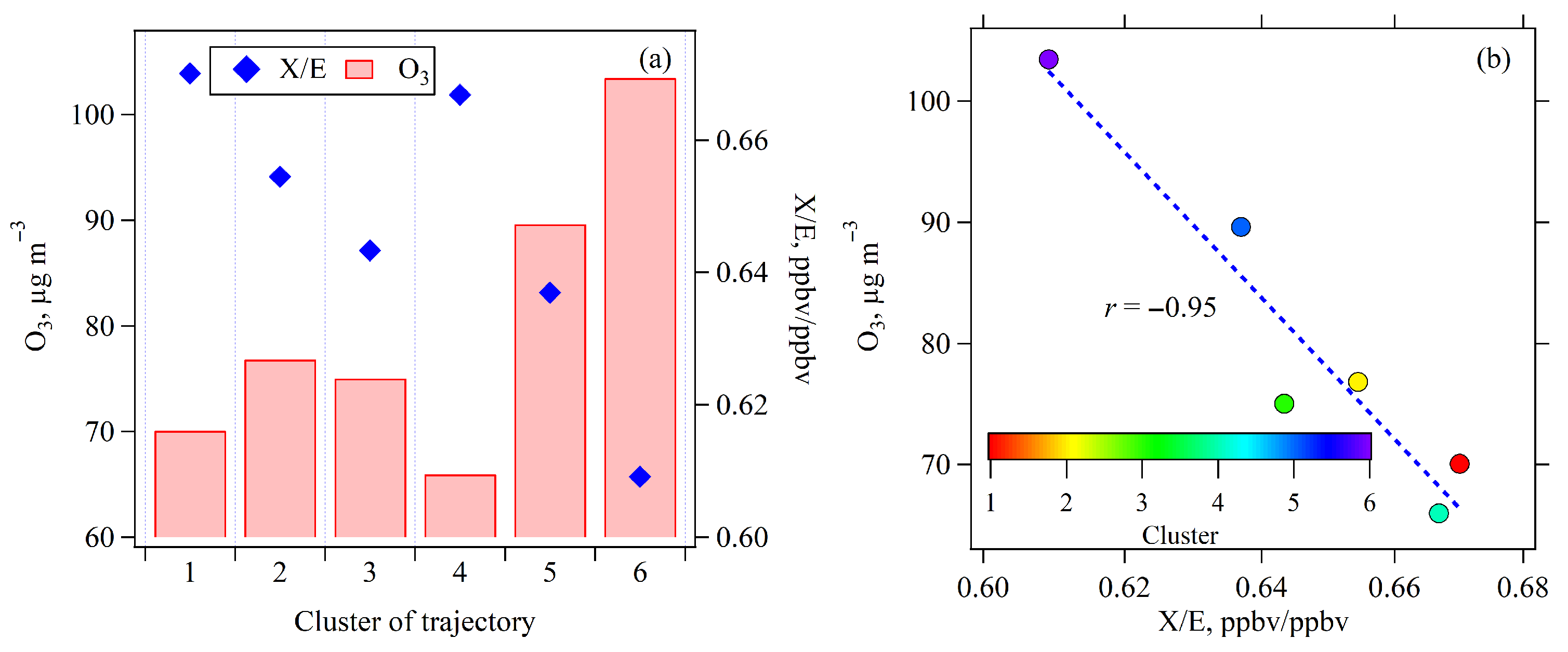
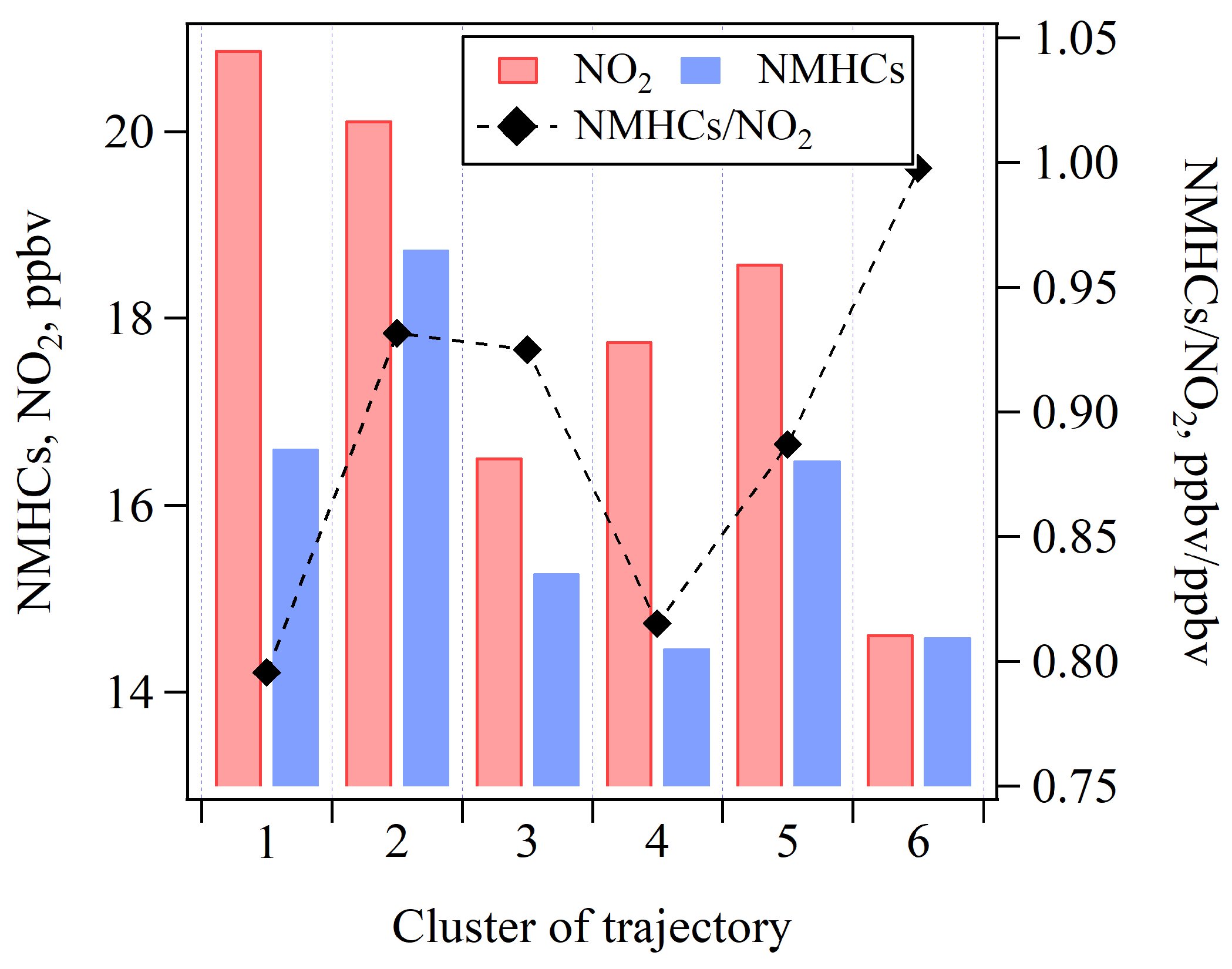
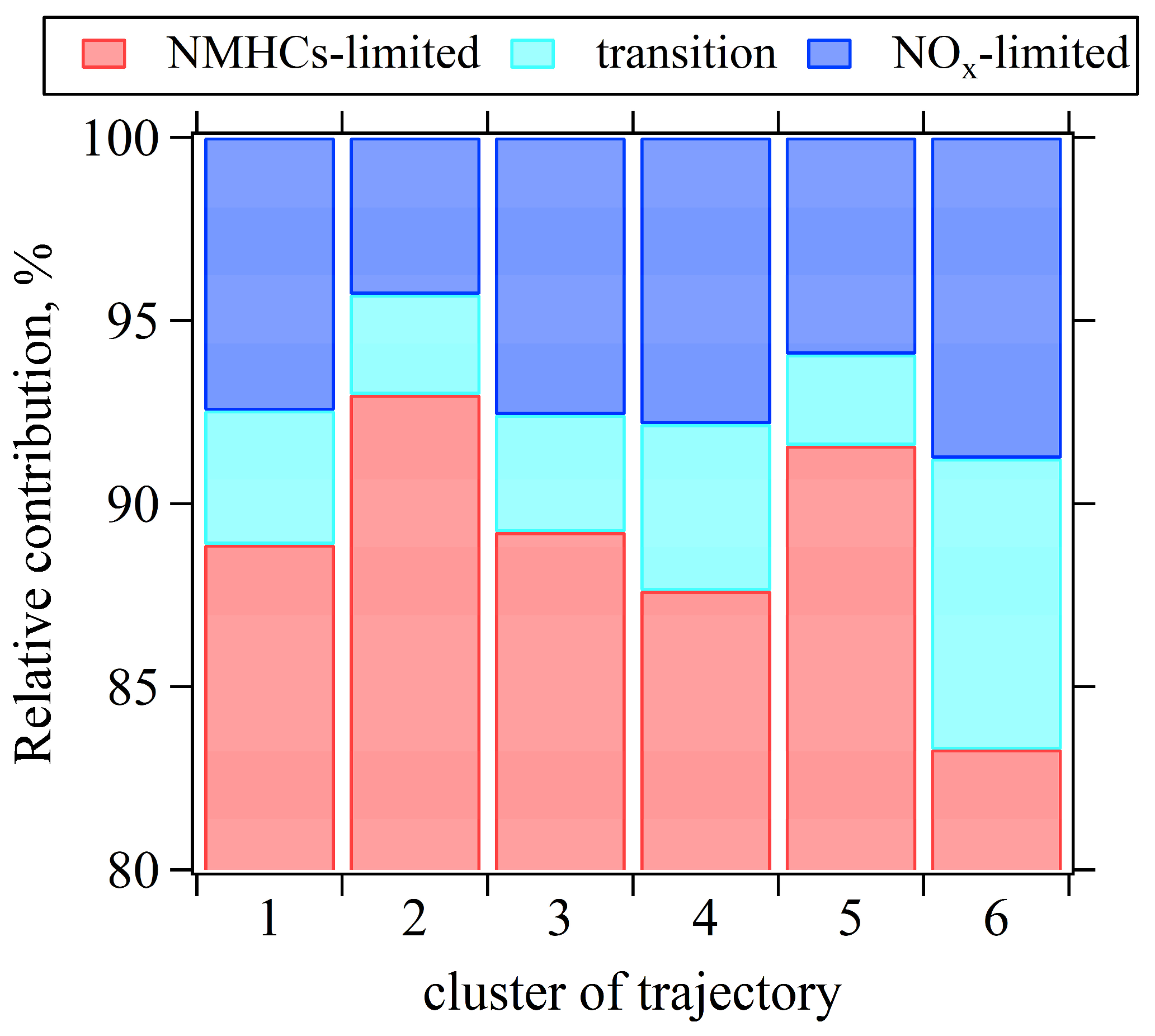
4.2.1. Comparison of O3 Sensitivity Across Six Trajectory Clusters
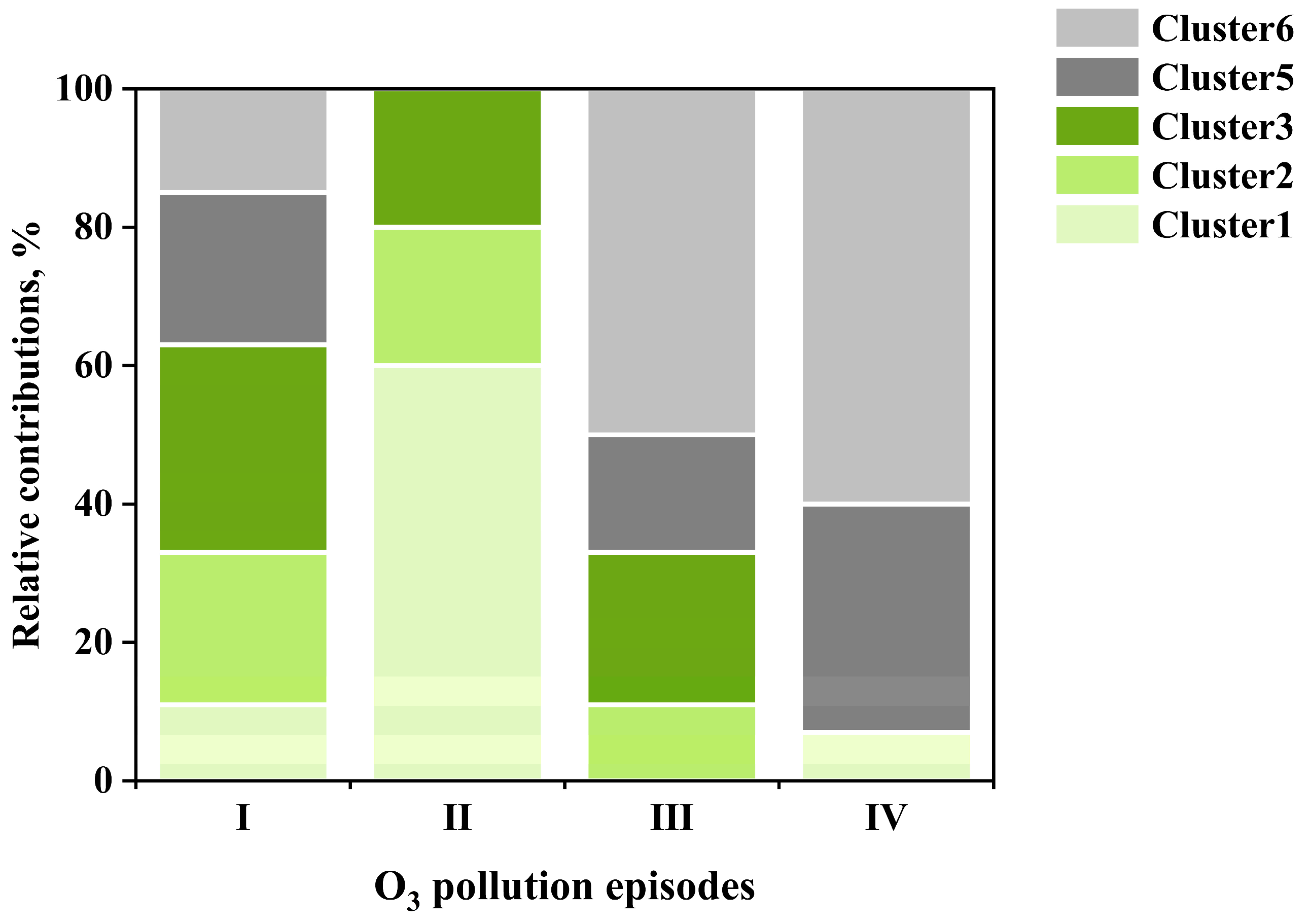
4.2.2. Air Mass Transport Influence on O3 Sensitivity During Four O3 Pollution Episodes
4.3. Limitations and Uncertainties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| O3 | ozone |
| SO2 | sulfur dioxide |
| VOCs | volatile organic compounds |
| NOx | nitrogen oxides |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| NO2 | nitrogen dioxide |
| CO | carbon monoxide |
| YRD | the Yangtze River Delta |
| PRD | the Pearl River Delta |
| CWT | concentration-weighted trajectory |
| OBM | observation-based box model |
| GC–MS | gas chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| GDAS | global data assimilation system |
| WCWT | weighted concentration-weighted trajectory |
| CB05 | carbon bond lumped chemical reaction mechanism |
| RIR | relative incremental reactivity |
| NMHCs | non-methane hydrocarbons |
| AHC | anthropogenic non-methane hydrocarbons |
| X/E | ratio of o-xylene to ethylbenzene |
| NJ | Nanjing |
| DMA-1h | daily maximum 1 h moving average |
| DMA-8h | daily maximum 8 h moving average |
| TUV | tropospheric ultraviolet–visible radiation |
| IOA | index of agreement |
| TEX | the sum of toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes |
| NWR | non-parametric wind regression |
| RH | relative humidity |
Appendix A
| Alkanes | Alkenes and Alkynes | Aromatics | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ethane | 2,4-dimethylpentane | ethene | benzene |
| propane | 2-methylhexane | propene | toluene |
| n-butane | 3-methylhexane | 1-butene | ethylbenzene |
| i-butane | cyclohexane | cis-2-butene | m,p-xylene |
| n-pentane | methylcyclopentane | trans-2-butene | o-xylene |
| i-pentane | n-octane | 1,3-butidene | styrene |
| cyclopentane | 2,2,4-trimethylpentane | 1-pentene | i-propylbenzene |
| n-hexane | 2,3,4-trimethylpentane | cis-2-pentene | n-propylbenzene |
| 2,2-dimethylbutane | methylcyclohexane | trans-2-pentene | 3-ethyltoluene |
| 2,3-dimethylbutane | 2-methylheptane | isoprene | 4-ethyltoluene |
| 2-methylpentane | 3-methylheptane | 1-hexene | 2-ethyltoluene |
| 3-methylpentane | n-nonane | acetylene | 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene |
| n-heptane | n-decane | 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene | |
| 2,3-dimethylpentane | n-undecane | 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene | |
| 1,3-diethylbenzene | |||
| 1,4-diethylbenzene | |||
References
- Jin, Y.; Andersson, H.; Zhang, S. Air pollution control policies in China: A retrospective and prospects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1219–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhuang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Li, S.; Xie, M.; Li, M.; Chen, P.; Zhao, M. Characteristics of ozone and particles in the near-surface atmosphere in the urban area of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 4153–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Palmer, P.; Zhang, L.; Lu, K.D.; Li, K.; Nagashima, T.; Koo, J.H.; Tanimoto, H.; Wang, H.C.; et al. Deciphering decadal urban ozone trends from historical records since 1980. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwae369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Parrish, D.; Ni, R.; Tan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. Ozone pollution mitigation strategy informed by long-term trends of atmospheric oxidation capacity. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 17, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraufnagel, D.E.; Balmes, J.R.; Matteis, S.D.; Hoffman, B.; Kim, W.J.; Perez-Padilla, R.; Rice, M.; Sood, A.; Vanker, A.; Wuebbles, D.J. Health Benefits of Air Pollution Reduction. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Xue, B.; Lv, Z.; Meng, Z.; Yang, X.; Xue, T.; Yu, Q.; He, K. Ground-level ozone pollution and its health impacts in China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 173, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hanaoka, T.; Masui, T. Comparison of health and economic impacts of PM2.5 and ozone pollution in China. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Feng, Z.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y. Ground-level ozone pollution in China: A synthesis of recent findings on influencing factors and impacts. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 063003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.F.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, B.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.M.; Lin, J.T.; Fu, T.M.; Zhang, Q. Exploring 2016–2017 surface ozone pollution over China: Source contributions and meteorological influences. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8339–8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Xing, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Nielsen, C.P. Sustained emission reductions have restrained the ozone pollution over China. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Liu, J.; Zhao, T.; Xu, X.; Han, H.; Wang, H.; Shu, Z. Atmospheric transport drives regional interactions of ozone pollution in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiang, F.; Feng, S.; Cai, Z.; Shen, Y.; Ying, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q. Long-range transport of ozone across the eastern China seas: A case study in coastal cities in southeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Xie, S. Spatial distribution of ozone formation in China derived from emissions of speciated volatile organic compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2574–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xie, J.; Zhang, R.; Ma, M.; Li, X.; Gong, P. Recent advances in different catalysts for synergistic removal of NOx and VOCs: A minor review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, S.; Rodríguez, A.; Taboada, J.J.; Souto, J.A.; Casares, J.J. Synoptic patterns and air mass transport during ozone episodes in northwestern Iberia. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 441, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghani, M.; Archer, C.L.; Mirzakhalili, A. The importance of transport to ozone pollution in the U.S. Mid-Atlantic. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Liao, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, L.; Zhu, J. Meteorological influences on daily variation and trend of summertime surface ozone over years of 2015–2020: Quantification for cities in the Yangtze River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, S.K.; Liu, S.; Liu, S.; Ding, D.; Xing, J. Ozone pollution in China: Background and transboundary contributions to ozone concentration & related health effects across the country. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 144131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Liao, H.; Zhang, L.; Yue, X.; Dang, R.; Yang, Y. Persistent ozone pollution episodes in North China exacerbated by regional transport. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fan, G.; Lou, S.; Yuan, B.; Wang, X.; Shao, M. Transport and boundary layer interaction contribution to extremely high surface ozone levels in eastern China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, B.; Yang, S.; Peng, Y.; Chen, W.; Xie, Q.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Quantifying the contributions of meteorology, emissions, and transport to ground-level ozone in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 932, 173011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Hong, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, L.; Chen, J.; Bian, Y.; Yang, C.; Dan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, L.; et al. Atmospheric oxidation capacity and ozone pollution mechanism in a coastal city of southeastern China: Analysis of a typical photochemical episode by an observation-based model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 2173–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Qin, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xie, X. Ozone pollution characteristics and sensitivity analysis using an observation-based model in Nanjing, Yangtze River Delta Region of China. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 93, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatani, S.; Shimadera, H.; Itahashi, S.; Yamaji, K. Comprehensive analyses of source sensitivities and apportionments of PM2.5 and ozone over Japan via multiple numerical techniques. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 10311–10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, R.; Xie, S. Characteristics of volatile organic compounds, NO2, and effects on ozone formation at a site with high ozone level in Chengdu. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 75, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, P.; Khare, M. Photo-chemical transport modelling of tropospheric ozone: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 159, 34–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lewis, A.C.; Hopkins, J.R.; Andrews, S.J.; Murrells, T.; Passant, N.; Richmond, B.; Hou, S.; Bloss, W.J.; Harrison, R.M.; et al. The impact of multi-decadal changes in VOC speciation on urban ozone chemistry: A case study in Birmingham, United Kingdom. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 6219–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavinezhad, S.; Choi, Y.; Pouyaei, A.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Nelson, D.L. A comprehensive investigation of surface ozone pollution in China, 2015–2019: Separating the contributions from meteorology and precursor emissions. Atmos. Res. 2021, 257, 105599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, K.; Tan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, F.; He, C. Transmission paths and source areas of near-surface ozone pollution in the Yangtze River delta region, China from 2015 to 2021. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ma, J.; Tao, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H. Regional source contributions to summertime ozone in the Yangtze River Delta. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 338, 120822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, M.; Ding, F.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, K. Changes in O3-VOCs-NOx sensitivity and VOCs sources at an urban site of Nanjing between 2020 and 2021. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 144–154. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Zeng, L.; Lu, S.; Shao, M.; Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Chen, W.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, M.; et al. Development and validation of a cryogen-free automatic gas chromatograph system (GC-MS/FID) for online measurements of volatile organic compounds. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 9424–9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. MeteoInfo: GIS software for meteorological data visualization and analysis. Meteorol. Appl. 2014, 21, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Bian, J. An analysis of regional ozone pollution generation and intercity transport characteristics in the Yangtze River Delta. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, W.; Lv, L.; Dong, Y.; Fan, G.; Ou, J.; Zhang, T. Vertical profiles and regional transport of ozone and aerosols in the Yangtze River Delta during the 2016 G20 summit based on multiple lidars. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 259, 118506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Hong, X.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T.; Qin, Z.; Ou, J. Vertical profiles and regional transport of ozone in typical area of Yangtze-Huaihe River Basin during the autumn base on multiple lidars. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 101983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y. Contrasting the effect of aerosol properties on the planetary boundary layer height in Beijing and Nanjing. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 308, 119861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardelino, C.A.; Chameides, W.L. An observation-based model for analyzing ozone precursor relationships in the urban atmosphere. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1995, 45, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhao, K.; Liu, X.; Duan, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Jing, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Multi-factor reconciliation of discrepancies in ozone-precursor sensitivity retrieved from observation- and emission-based models. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, M.; She, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Chang, Y.; Tan, Z.; An, J.; Huang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Lu, J.; et al. Increased urban ozone in heatwaves due to temperature-induced emissions of anthropogenic volatile organic compounds. Nat. Geosci. 2025, 18, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, F.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S.; Dai, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Shu, Z.; Yan, H.; Ge, X.; et al. Impact of temperature on the biogenic volatile organic compound (BVOC) emissions in China: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.E.; Favez, O.; Albinet, A.; Canonaco, F. A user-friendly tool for comprehensive evaluation of the geographical origins of atmospheric pollution: Wind and trajectory analyses. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2017, 88, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Shao, M.; Lu, S.; Wang, B. Source profiles of volatile organic compounds associated with solvent use in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Lu, K.; Jiang, M.; Su, R.; Wang, H.; Lou, S.; Fu, Q.; Zhai, C.; Tan, Q.; Yue, D.; et al. Daytime atmospheric oxidation capacity in four Chinese megacities during the photochemically polluted season: A case study based on box model simulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3493–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Shen, L. Meteorology and climate influences on tropospheric ozone: A review of natural sources, chemistry, and transport patterns. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2019, 5, 238–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Tang, J.; Liu, G.; Wu, J. Effects of vegetation fraction: Variation on regional climate simulation over Eastern China. Glob. Planet. Change 2019, 175, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Yan, R.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Jing, S.a.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Emission inventory of air pollutants and chemical speciation for specific anthropogenic sources based on local measurements in the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 2003–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gouw, J.A.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Warneke, C.; Goldan, P.D.; Kuster, W.C.; Roberts, J.M.; Fehsenfeld, F.C.; Worsnop, D.R.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Pszenny, A.A.P.; et al. Budget of organic carbon in a polluted atmosphere: Results from the New England Air Quality Study in 2002. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D16305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, M.; Kuster, W.C.; Goldan, P.D.; Li, X.H.; Lu, S.H.; De Gouw, J.A. Source identification of reactive hydrocarbons and oxygenated VOCs in the Summertime in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickly, P.S.; Coggon, M.M.; Aikin, K.C.; Alvarez, R.J., II; Baidar, S.; Gilman, J.B.; Gkatzelis, G.I.; Harkins, C.; He, J.; Lamplugh, A.; et al. Influence of wildfire on urban ozone: An observationally constrained box modeling study at a site in the Colorado Front Range. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Huang, L.; Lu, G.; Kasemsan, M.; Yaluk, E.A.; Liu, H.; Liao, J.; Bian, J.; Zhang, K.; et al. Differences between VOCs and NOx transport contributions, their impacts on O3, and implications for O3 pollution mitigation based on CMAQ simulation over the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Gong, K.; Wang, X.; Ying, Q.; Qin, M.; Liao, H.; Guo, S.; Hu, M.; et al. Modelling air quality during the EXPLORE-YRD campaign—Part II. Regional source apportionment of ozone and PM2.5. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 247, 118063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, T.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.-M.; Liu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, J.; Chang, L. An important mechanism of regional O3 transport for summer smog over the Yangtze River Delta in eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16239–16251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Ding, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L. Ozone Pollution in the Western Yangtze River Delta During the 2020 and 2021 Warm Seasons: Roles of Meteorology and Air Mass Transport. Toxics 2025, 13, 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080670
Wang Y, Wang M, Ding F, Chen X, Zhang L. Ozone Pollution in the Western Yangtze River Delta During the 2020 and 2021 Warm Seasons: Roles of Meteorology and Air Mass Transport. Toxics. 2025; 13(8):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080670
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuchen, Ming Wang, Feng Ding, Xueqi Chen, and Liangyu Zhang. 2025. "Ozone Pollution in the Western Yangtze River Delta During the 2020 and 2021 Warm Seasons: Roles of Meteorology and Air Mass Transport" Toxics 13, no. 8: 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080670
APA StyleWang, Y., Wang, M., Ding, F., Chen, X., & Zhang, L. (2025). Ozone Pollution in the Western Yangtze River Delta During the 2020 and 2021 Warm Seasons: Roles of Meteorology and Air Mass Transport. Toxics, 13(8), 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080670







