Assessment of Potentially Toxic Element Pollution in Surface Soils of the Upper Ohře River Basin
Highlights
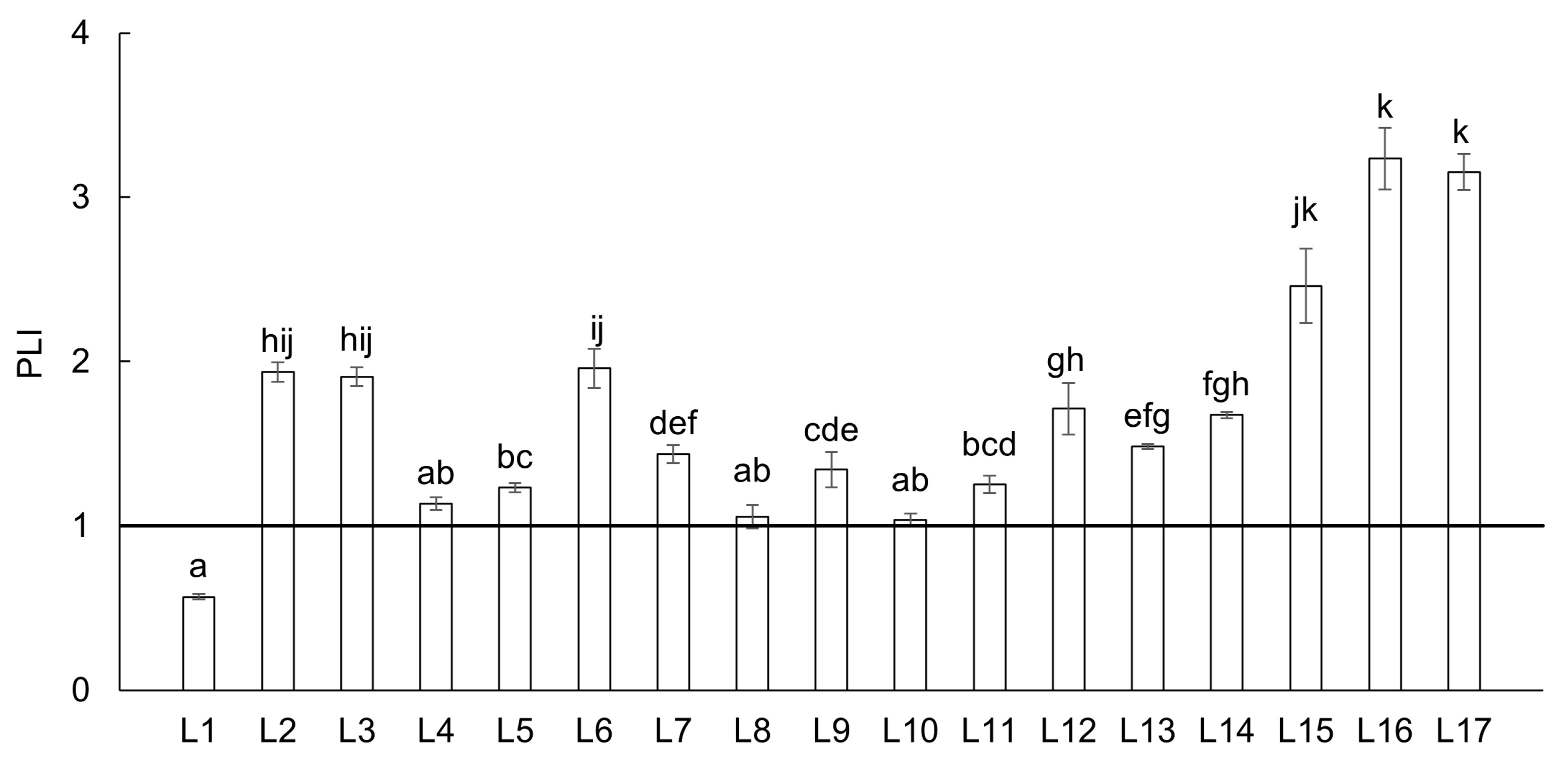
- The pollution load index indicated that 16 out of the 17 studied locations in the upper Ohře River basin were polluted.
- Health risk evaluations indicate a significant non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risk associated with surface soil exposure in children.
- They emphasized the significance of the pollution load index in assessing soil quality and contamination.
- They demonstrated that oral ingestion is a pathway with a high risk to human health, particularly for children.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
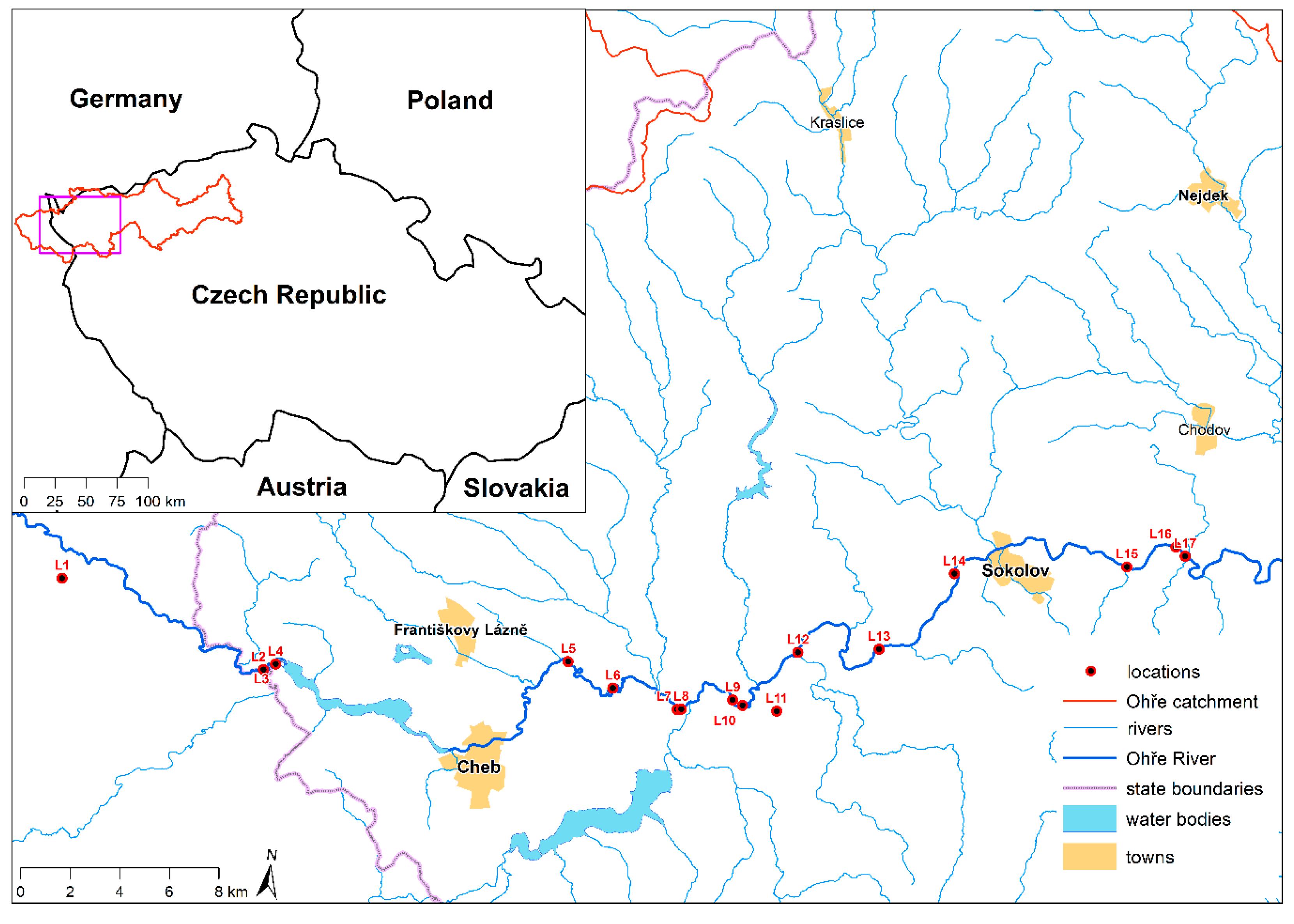
2.1. Study Area, Sampling, and Laboratory Analysis
2.2. Pollution Indices
2.2.1. Geo-Accumulation Index
2.2.2. Contamination Factor and Pollution Load Index
2.2.3. Ecological Risk Factor and Potential Ecological Risk Index
2.3. Human Health Risk Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analyses
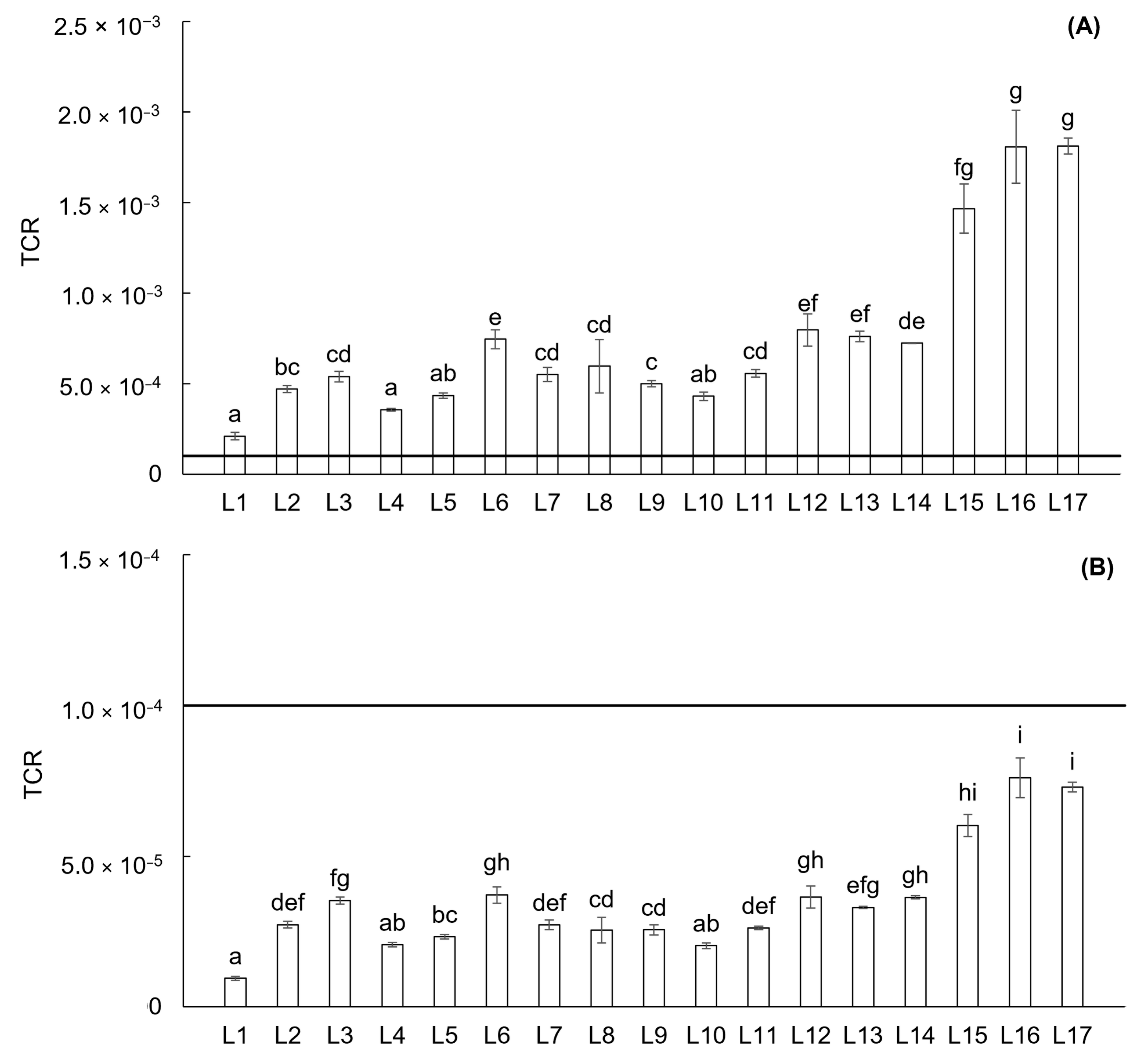
3. Results
4. Discussion
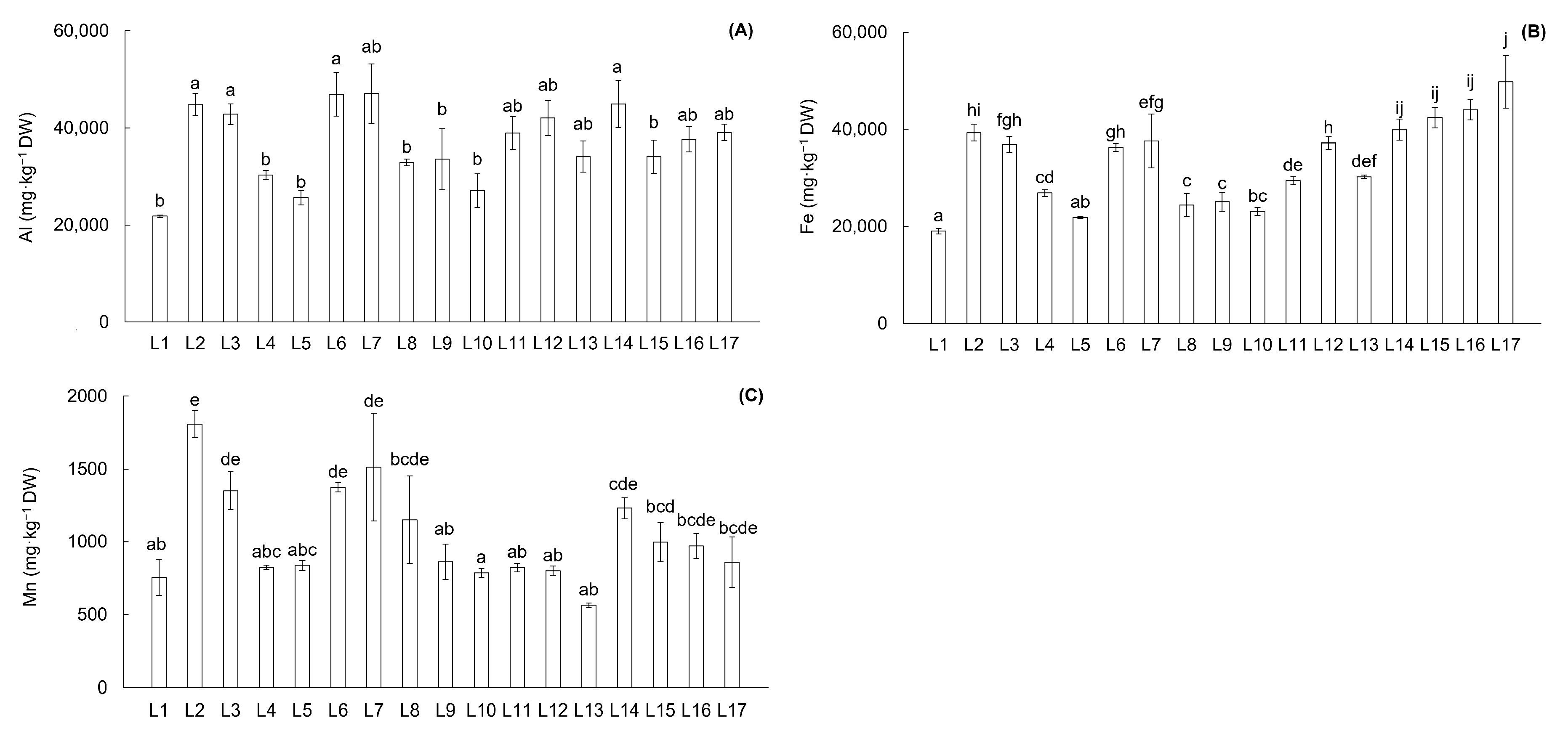
4.1. Content of Potentially Toxic Elements in the Soil of the Upper Ohře River Basin
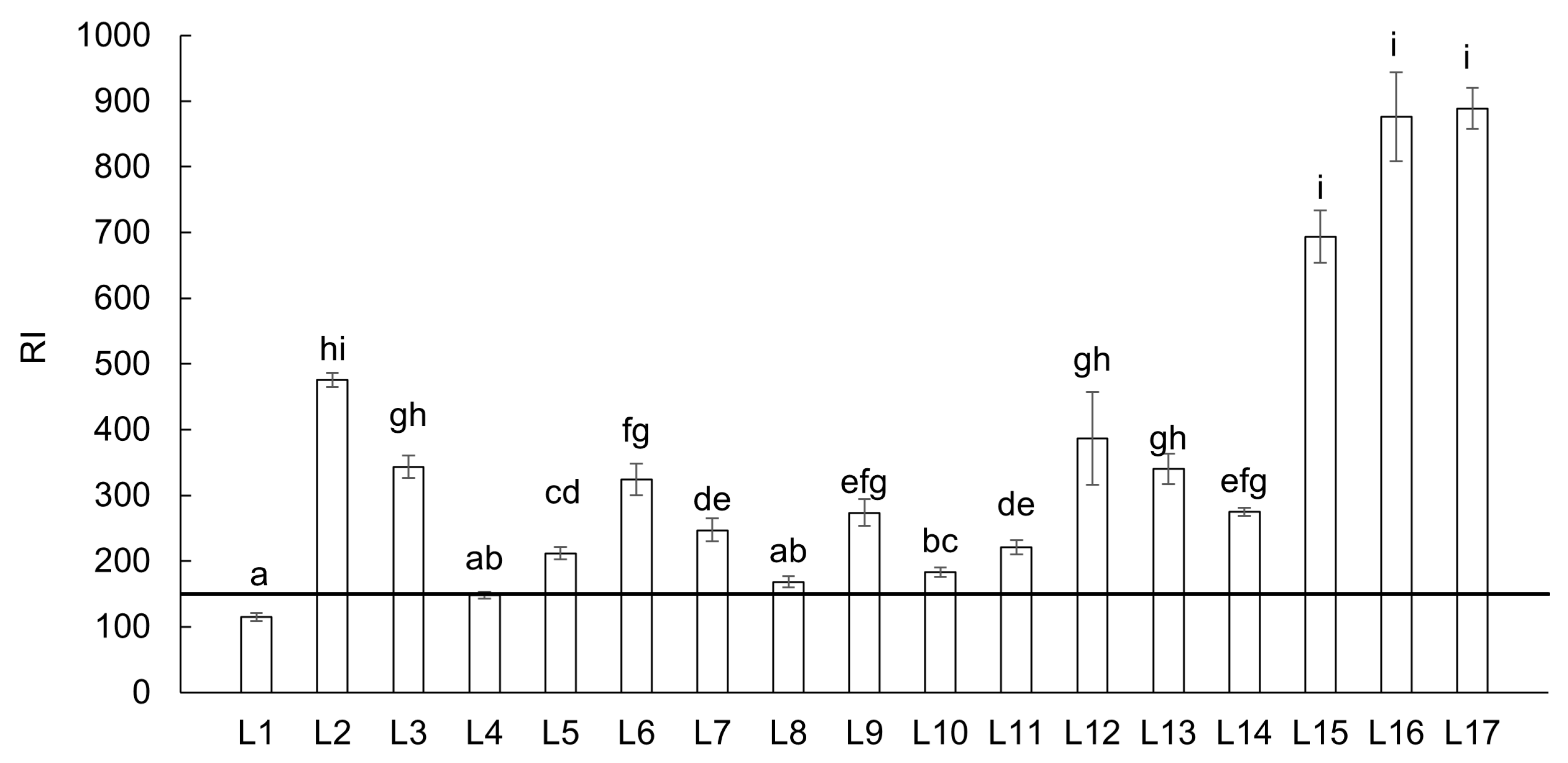
4.2. Ecological Risk Assessment
4.3. Potential Human Health Risk
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jianfei, C.; Chunfang, L.; Lixia, Z.; Quanyuan, W.; Jianshu, L. Source apportionment of potentially toxic elements in soils using APCS/MLR, PMF and geostatistics in a typical industrial and mining city in Eastern China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, M.; Cai, B.; Song, X.; Tang, R.; Huang, X.; Huang, H.; Huang, J.; Fan, Z. Risk assessment and driving factors of trace metal(loid)s in soils of China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoque, M.M.; Islam, A.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Pal, S.C.; Mahammad, S.; Alam, E. Assessment of soil heavy metal pollution and associated ecological risk of agriculture dominated mid-channel bars in a subtropical river basin. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Li, J.; Liu, R.; Lei, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Exposure to arsenic and other potentially toxic elements: Health risk assessment and source analysis in the Wuming Basin, Guangxi Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Tulcan, R.X.S.; Yan, L.; Lin, C.; Pan, J. Priority sources identification and risks assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils of a typical antimony mining watershed. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goren, A.Y.; Genisoglu, M.; Kazancl, Y.; Sofuoglu, S.C. Countrywide spatial variation of potentially toxic element contamination in soils of Turkey and assessment of population health risks for nondietary ingestion. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 36457–36467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyeman, P.C.; John, K.; Kebonye, N.M.; Borůvka, L.; Vašát, R.; Drábek, O.; Němeček, K. Human health risk exposure and ecological risk assessment of potentially toxic element pollution in agricultural soils in the district of Frydek Mistek, Czech Republic: A sample location approach. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, I.; Salman, S.A.E.R.; Samy, Y.; Awad, S.A.; Melegy, A.; Hursthouse, A.S. Environmental factors controlling potentially toxic element behaviour in urban soils, El Tebbin, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmonov, O.; Sobala, M.; Środek, D.; Karkosz, D.; Pytel, S.; Rahmonov, M. The spatial distribution of potentially toxic elements in the mountain forest topsoils (the Silesian Beskids, southern Poland). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniran, A.O.; Balgobind, A.; Pillay, B. Bioavailability of heavy metals in soil: Impact on microbial biodegradation of organic compounds and possible improvement strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10197–10228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, X.; Tu, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.C.; Fang, H.; Huo, H.; Lin, C. Relationships between soil properties and the accumulation of heavy metals in different Brassica campestris L. growth stages in a Karst mountainous area. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicińska, A.; Pomykała, R.; Izquierdo-Diaz, M. Changes in soil pH and mobility of heavy metals in contaminated soils. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2022, 73, e13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Li, J.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Yan, M.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Liang, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. Effects of redox potential on soil cadmium solubility: Insight into microbial community. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 75, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbulut, S.; Grieken, R.; Kilic, M.A.; Cevik, U.; Rotondo, G.G. Identification of heavy metal origins related to chemical and morphological soil properties using several non-destructive X-ray analytical methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 2377–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyeman, P.C.; Ahado, S.K.; Kingsley, J.; Kebonye, N.M.; Biney, J.K.M.; Borůvka, L.; Vasat, R.; Kocarek, M. Source apportionment, contamination levels, and spatial prediction of potentially toxic elements in selected soils of the Czech Republic. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gąsiorek, M.; Zaleski, T. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination–A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2395–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.J.; Deng, J.; Xiang, Y.C.; Wang, Q.F.; Yang, L.Q. Calculating pollution indices by heavy metals in ecological geochemistry assessment and a case study in parks of Beijing. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2008, 19, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majerová, L.; Bábek, O.; Navrátil, T.; Nováková, T.; Štojdl, J.; Elznicová, J.; Hron, K.; Matys Grygar, T. Dam reservoirs as an efficient trap for historical pollution: The passage of Hg and Pb through the Ohře River, Czech Republic. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matys Grygar, T.; Elznicová, J.; Kiss, T.; Smith, H.G. Using sedimentary archives to reconstruct pollution history and sediment provenance: The Ohře River, Czech Republic. Catena 2016, 144, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matys Grygar, T.; Elznicová, J.; Lelková, T.; Kiss, T.; Balogh, M.; Strnad, L.; Navrátil, T. Sedimentary archive of contamination in the confined channel of the Ohře River, Czech Republic. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 2596–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fikarová, J.; Kenecká, S.; Elznicová, J.; Faměra, M.; Lelková, T.; Matkovič, J.; Matys Grygar, T. Spatial distribution of organic pollutants (PAHs and polar pesticides) in the floodplain of the Ohře (Eger) River, Czech Republic. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elznicová, J.; Kiss, T.; Sipos, G.; Faměra, M.; Štojdl, J.; Váchová, V.; Matys Grygar, T. A central European alluvial river under anthropogenic pressure: The Ohře River, Czechia. Catena 2021, 201, 105218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlich, A. Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: A modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plan. Anal. 1984, 15, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbíral, J.; Malý, S.; Váňa, M.; Čuhel, J.; Fojtlová, E.; Čižmár, D.; Žalmanová, A.; Srnková, J.; Obdržálková, E. Jednotné pracovní postupy: Analýza půd III (In Czech). In Central Institute for Supervising and Testing in Agriculture; ÚKZÚZ Brno: Brno, Czech Republic, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Deng, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhan, F.; He, Y.; He, L.; Li, Y. Contamination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil and ditch sediments in long-term mine wastes area. Toxics 2022, 10, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, W.; Alharthy, R.D.; Zubair, M.; Ahmed, M.; Hameed, A.; Rafique, S. Toxic and heavy metals contamination assessment in soil and water to evaluate human health risk. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, N.; Upadhyay, M.K.; Majumdar, A.; Pathak, S.K.; Giri, B.; Jaiswal, M.K.; Srivastava, S. An assessment of various potentially toxic elements and associated health risks in agricultural soil along the middle Gangetic basin, India. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic. Pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoto, R.; Anning, A.K. Heavy metal enrichment and potential ecological risks from different solid mine wastes at a mine site in Ghana. Environ. Adv. 2021, 3, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlillah, L.N.; Utami, S.; Rachmawati, A.A.; Jayanto, G.D.; Widyastuti, M. Ecological risk and source identifications of heavy metals contamination in the water and surface sediments from anthropogenic impacts of urban river, Indonesia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Sun, L.; Sun, Y.; Song, K.; Qin, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Xue, Y. Towards an integrated health risk assessment framework of soil heavy metals pollution: Theoretical basis, conceptual model, and perspectives. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhu, X.; Cui, X. Heavy metals in soil, water sediment, and ambient PM2.5 across the Yangtze River economic belt: Integrated environment risk identification and countermeasures. J. Water Clim. Change 2021, 12, 2920–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Exposure Factors Handbook, Final ed.; U.S. Environment Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Taylor, A.A.; Tsuji, J.S.; McArdle, M.E.; Adams, W.J.; Goodfellow, W.L., Jr. Recommended reference values for risk assessment of oral exposure to copper. Risk Anal. 2023, 43, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezez, D.; Birhanu, H.; Shamena, S.; Engidaw, S. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals, assessment of carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic health risk in various spices. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 15, 100441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, R.E.; Fontes, M.P.F.; Tucci, C.A.F.; Lima, H.N.; da Silva Ferreira, M. Health risk assessment and quality reference values of potentially toxic elements in soils of the Southwestern Amazonas State—Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, H.; Yang, X. Quantifying ecological and human health risks of heavy metals from different sources in farmland soils within a typical mining and smelting industrial area. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 5669–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xu, L.; Hao, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, M.; Zhu, P.; Fu, S.; Liang, Y.; Yin, H.; et al. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in contaminated paddy fields—A case study in Xiangtan City, southern China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vácha, R.; Sáňka, M.; Sáňka, O.; Skála, J.; Čechmánková, J. The Fluvisol and sediment trace element contamination level as related to their geogenic and anthropogenic source. Plant Soil. Environ. 2013, 59, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F. Plant root responses to three abundant soil minerals: Silicon, aluminum and iron. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2005, 24, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, C.; Palumbo, G.; He, J.Z.; Pinton, R.; Cesco, S. Review on iron availability in soil: Interaction of Fe minerals, plants, and microbes. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; Fabian, K.; Birke, M.; Filzmoser, P.; Demetriades, A.; Négrel, P.; Oorts, K.; Matschullat, J.; de Caritat, P.; Albanese, S.; et al. GEMAS: Establishing geochemical background and threshold for 53 chemical elements in European agricultural soil. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 88, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skála, J.; Vácha, R.; Hofman, J.; Horváthová, V.; Sáňka, M.; Čechmánková, J. Spatial differentiation of ecosystem risks of soil pollution in floodplain areas of the Czech Republic. Soil. Water Res. 2017, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matys Grygar, T.; Bábek, O.; Sedláček, J.; Lenďáková, Z.; Faměra, M.; Štojdl, J.; Pacina, J.; Tolaszová, J.; Kříženecká, S. Segregation and retention of As, potentially toxic metals, and organic pollutants in a reservoir from the Ohře River (the Czech Republic). J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2931–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.K.; Vaid, U.; Sharma, S.K.; Singh, S. Assessment of potentially toxic elements’ contamination in surface soils of Kulsi River Basin in North East India. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Hernández, J.R.; Alvarado-Zambrano, D.; Gonzalez, L.A.; Green-Ruiz, C.R. Subtotal content and geochemical fractionation of potential toxic elements in agricultural soils from Mocorito River basin in NW Mexico: Environmental and health implications. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2021, 31, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Singh, A.K. Human health risk assessment due to dietary intake of heavy metals through rice in the mining areas of Singhbhum Copper Belt, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14945–14956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, T.O.; Olatunji, A.S.; Jimoh, M.T.; Fajemila, O.T. Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk assessment in soils and sediments of an industrial area in Southwestern Nigeria. J. Health Pollut. 2018, 8, 180906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugoša, B.; Ðurović, D.; Nedović-Vuković, M.; Barjaktarović-Labović, S.; Vrvić, M. Assessment of ecological risk of heavy metal contamination in coastal municipalities of Montenegro. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, M.; Li, C. Soil heavy metal contamination assessment in the Hun-Taizi River watershed, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vácha, R.; Skála, J.; Čechmánková, J.; Horváthová, V.; Hladík, J. Toxic elements and persistent organic pollutants derived from industrial emissions in agricultural soils of the Northern Czech Republic. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 1813–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Dong, K. Ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in the soils of a lead-zinc mining watershed area. Water 2023, 15, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jia, Z.; Li, S.; Hu, J. Assessment of heavy metal pollution, distribution and quantitative source apportionment in surface sediments along a partially mixed estuary (Modaomen, China). Chemosphere 2019, 225, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Fang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Su, B.; Li, D.; Xiang, B. Potentially toxic element pollution levels and risk assessment of soils and sediments in the upstream river, Miyun Reservoir, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiriou, I.; Gasparatos, D.; Megremi, I.; Ioannou, D.; Massas, I.; Economou-Eliopoulos, M. Assessment of potentially toxic element contamination in the Philippi Peatland, Eastern Macedonia, Greece. Minerals 2022, 12, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Igeo | Level | CF | Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Igeo < 0 | Non-contamination | CF < 1 | Low contamination |
| 0 < Igeo < 1 | Slight contamination | 1 ≤ CF < 3 | Moderate contamination |
| 1 ≤ Igeo < 2 | Low contamination | 3 ≤ CF < 6 | Considerable contamination |
| 2 ≤ Igeo < 3 | Moderate contamination | CF ≥ 6 | Very high contamination |
| 3 ≤ Igeo < 4 | Heavy contamination | ||
| 4 ≤ Igeo < 5 | High contamination | ||
| Igeo ≥ 5 | Extreme contamination | ||
| Er | Level | RI | Level |
| Er < 40 | Low potential ecological risk | RI < 90 | Low potential ecological risk |
| 40 ≤ Er < 80 | Moderate potential ecological risk | 90 ≤ RI < 180 | Moderate potential ecological risk |
| 80 ≤ Er < 160 | Considerable potential ecological risk | 180 ≤ RI < 360 | Strong potential ecological risk |
| 160 ≤ Er < 320 | High potential ecological risk | 360 ≤ RI < 720 | Very strong potential ecological risk |
| Er ≥ 320 | Very high potential ecological risk | RI ≥ 720 | Highly strong potential ecological risk |
| Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD | CV | Limit Value a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 21,505.34 | 53,222.06 | 36,228.40 | 36,944.41 | 7974.53 | 22.01 | - |
| As | 6.57 | 89.14 | 26.08 | 17.38 | 22.15 | 84.94 | 20 |
| Cd | 0.20 | 1.42 | 0.59 | 0.48 | 0.36 | 59.99 | 0.5 |
| Co | 6.98 | 22.68 | 14.71 | 13.52 | 4.00 | 27.23 | 30 |
| Cr | 8.54 | 74.93 | 34.30 | 33.03 | 10.25 | 29.88 | 90 |
| Cu | 0.93 | 185.91 | 36.69 | 19.55 | 43.86 | 119.52 | 60 |
| Fe | 18,658.60 | 46,082.50 | 32,076.07 | 30,654.11 | 8064.81 | 25.14 | - |
| Mn | 555.63 | 1875.64 | 1016.50 | 863.13 | 318.44 | 31.33 | - |
| Ni | 5.78 | 42.15 | 21.99 | 19.67 | 7.98 | 36.29 | 50 |
| Pb | 14.42 | 177.69 | 53.28 | 39.07 | 35.71 | 67.01 | 60 |
| Zn | 49.16 | 321.39 | 128.51 | 110.74 | 64.54 | 50.22 | 120 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zemanová, V.; Menšík, L.; Hangen, E.; Schilling, B.; Hlisnikovský, L.; Kunzová, E. Assessment of Potentially Toxic Element Pollution in Surface Soils of the Upper Ohře River Basin. Toxics 2025, 13, 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080644
Zemanová V, Menšík L, Hangen E, Schilling B, Hlisnikovský L, Kunzová E. Assessment of Potentially Toxic Element Pollution in Surface Soils of the Upper Ohře River Basin. Toxics. 2025; 13(8):644. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080644
Chicago/Turabian StyleZemanová, Veronika, Ladislav Menšík, Edzard Hangen, Bernd Schilling, Lukáš Hlisnikovský, and Eva Kunzová. 2025. "Assessment of Potentially Toxic Element Pollution in Surface Soils of the Upper Ohře River Basin" Toxics 13, no. 8: 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080644
APA StyleZemanová, V., Menšík, L., Hangen, E., Schilling, B., Hlisnikovský, L., & Kunzová, E. (2025). Assessment of Potentially Toxic Element Pollution in Surface Soils of the Upper Ohře River Basin. Toxics, 13(8), 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080644








