Interactions of Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cd in Soil–Rice Systems: Implications for Reducing Cd Accumulation in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Treatment Condition and Sample Collection
2.3. Element Content Determination
2.4. Measurement of Soil pH, Available Metal Concentration
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Agronomic Traits and Accumulation of Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cd in Rice
3.2. Translocation of Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cd in Rice
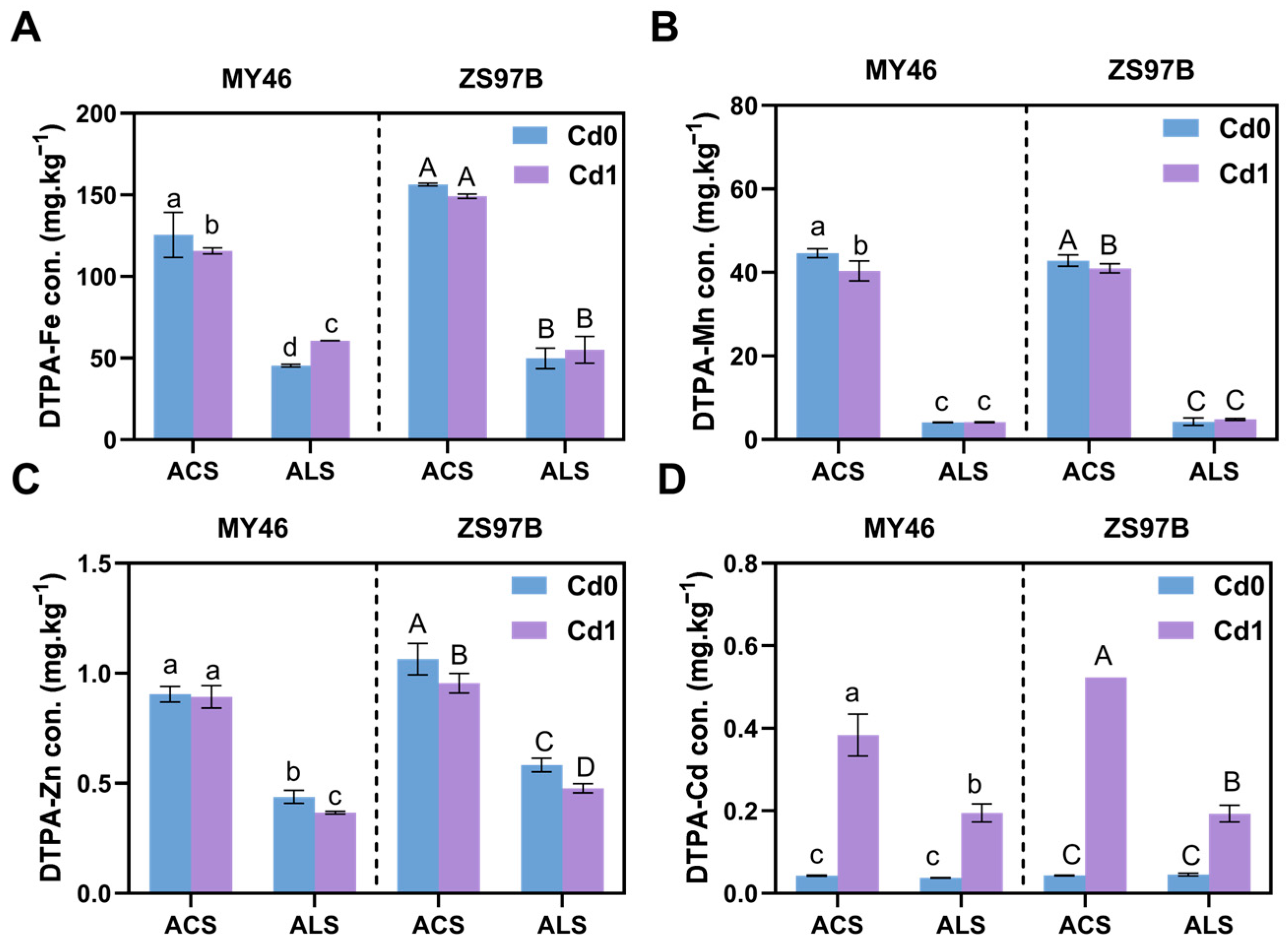
3.3. Availability of Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cd in Soils
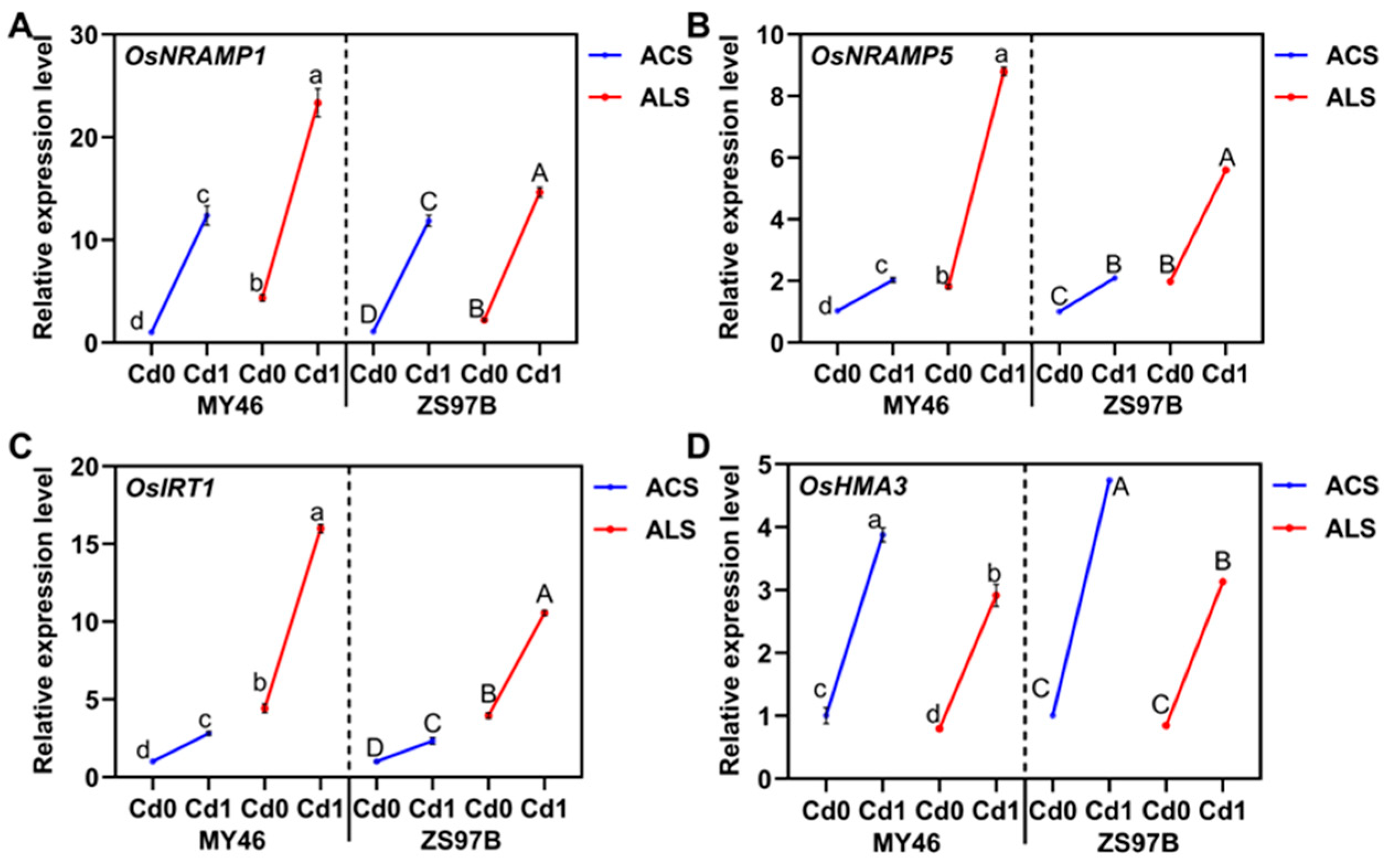
3.4. Expression Patterns of Transporter Genes in the Roots
3.5. Correlations of Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cd in Plants with Extractable Concentrations in Soils
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, F.J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Tang, Z.; McGrath, S.P. Soil contamination in China: Current status and mitigation strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, P.A.; Khan, M.S.; Zaidi, A. Impact of heavy metal toxicity on plant growth, symbiosis, seed yield and nitrogen and metal uptake in chickpea. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2007, 47, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.A.; Popova, L.P. Functions and toxicity of cadmium in plants: Recent advances and future prospects. Turk. J. Bot. 2013, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, Y.B.N.; Mao, W.F.; Sui, H.X.; Yong, L.; Yang, D.J.; Jiang, D.G.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Y.Y. Dietary cadmium exposure assessment among the Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, S.; Ma, J.F. Toxic heavy metal and metalloid accumulation in crop plants and foods. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhu, W.; Yang, W.T.; Gu, J.F.; Gao, Z.X.; Chen, L.W.; Du, W.Q.; Zhang, P.; Peng, P.Q.; Liao, B.H. Cadmium uptake, accumulation, and remobilization in iron plaque and rice tissues at different growth stages. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 152, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.B.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Naidu, R. Varietal variation and formation of iron plaques on cadmium accumulation in rice seedling. Environ. Adv. 2021, 5, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.B.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Naidu, R. Influences of soil pH, iron application and rice variety on cadmium distribution in rice plant tissues. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.S.; Chai, G.Q.; Lu, M.; Xiao, R.; Xie, Q.; Luo, L.Z. A new insight into the role of iron plaque in arsenic and cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 254, 114714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tang, Y.T.; Yao, A.J.; Cao, J.; Wu, Z.H.; Peng, Z.R.; Wang, S.Z.; Xiao, S.; Baker, A.J.M.; Qiu, R.L. Mitigation of Cd accumulation in paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.) by Fe fertilization. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wu, Q.T.; Lee, C.C.C.; Jiang, C.; Wei, Z. Evaluation of manganese application after soil stabilization to effectively reduce cadmium in rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, X.Y.; Guan, D.X.; Gao, J.L.; Yang, Q.; Chen, X.L.; Ma, L.Q. Manganese oxide application reduces cadmium bioavailability in rice rhizosphere: Insights from desorption kinetics and high-resolution imaging. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 373, 126110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, S.B.; Shi, H.D.; Liu, Y.B. Redox dependence of manganese controls cadmium isotope fractionation in a paddy soil-rice system under unsteady pe plus pH conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 15067. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Qin, L.Y.; Sun, X.Y.; Liu, J.X.; Chen, S.B. Mn loading on montmorillonite surfaces for Cd stabilization: Insights from density functional theory calculations and surface complexation modeling. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 154, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lei, J.; Tong, H.; Gu, M.; Fang, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, C. Effects of Mn(II) on the oxidation of Fe in soils and the uptake of cadmium by rice (Oryza sativa). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.N.; An, H.; Yang, Y.J.; Liang, Y.; Shao, G.S. Effects of Mn-Cd antagonistic interaction on Cd accumulation and major agronomic traits in rice genotypes by different Mn forms. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 82, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, M.F.; Sehar, S.; Ma, Z.X.; Tahira, K.; Askri, S.M.H.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Ahmad, A.; Zhou, F.R.; Zhao, P.; Shamsi, I.H. Insights into the alleviation of cadmium toxicity in rice by nano-zinc and Serendipita indica: Modulation of stress-responsive gene expression and antioxidant defense system activation. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 350, 123952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.X.; Ding, C.F.; Zhou, Z.G.; Zhang, T.L.; Wang, X.X. A tillering application of zinc fertilizer based on basal stabilization reduces Cd accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 167, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Li, X.; Fang, L.; Bai, J.; Gao, R.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Yin, H.; et al. Multifunctional roles of zinc in cadmium transport in soil-rice systems: Novel insights from stable isotope fractionation and gene expression. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 12467–12476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.E.; Yang, Y.; Chen, W.P. Manganese, zinc, and pH affect cadmium accumulation in rice grain under field conditions in southern China. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.L.; Chen, W.P.; Wang, M.E.; Wang, T.Q.; Dai, Y.T. Dynamic interactions between soil cadmium and zinc affect cadmium phytoavailability to rice and wheat: Regional investigation and risk modeling. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.Z.; Qin, M.L.; Lin, X.Y.; Zhu, Z.W.; Chen, M.X. Sulfur supply reduces cadmium uptake and translocation in rice grains (Oryza sativa L.) by enhancing iron plaque formation, cadmium chelation and vacuolar sequestration. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, Y.; Takahashi, R.; Bashir, K.; Shimo, H.; Senoura, T.; Sugimoto, K.; Ono, K.; Yano, M.; Ishikawa, S.; Arao, T.; et al. Characterizing the role of rice NRAMP5 in manganese, iron and cadmium transport. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Ishimaru, Y.; Nakanishi, H.; Nishizawa, N.K. Role of the iron transporter OsNRAMP1 in cadmium uptake and accumulation in rice. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 1813–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, R.; Ishimaru, Y.; Senoura, T.; Shimo, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Arao, T.; Nakanishi, H.; Nishizawa, N.K. The OsNRAMP1 iron transporter is involved in Cd accumulation in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4843–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, H.; Ogawa, I.; Ishimaru, Y.; Mori, S.; Nishizawa, N.K. Iron deficiency enhances cadmium uptake and translocation mediated by the Fe2+ transporters OsIRT1 and OsIRT2 in rice. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2006, 52, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyadate, H.; Adachi, S.; Hiraizumi, A.; Tezuka, K.; Nakazawa, N.; Kawamoto, T.; Katou, K.; Kodama, I.; Sakurai, K.; Takahashi, H.; et al. OsHMA3, a P-1B-type of ATPase affects root-to-shoot cadmium translocation in rice by mediating efflux into vacuoles. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.M.; Huang, S.; Che, J.; Yamaji, N.; Ma, J.F. The tonoplast-localized transporter OsHMA3 plays an important role in maintaining Zn homeostasis in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 2717–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh-Nagasawa, N.; Mori, M.; Nakazawa, N.; Kawamoto, T.; Nagato, Y.; Sakurai, K.; Takahashi, H.; Watanabe, A.; Akagi, H. Mutations in rice (Oryza sativa) heavy metal ATPase 2 (OsHMA2) restrict the translocation of zinc and cadmium. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraguchi, S.; Kamiya, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Kasai, K.; Sato, Y.; Nagamura, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Kyozuka, J.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, T. Low-affinity cation transporter (OsLCT1) regulates cadmium transport into rice grains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20959–20964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.S.; Feng, S.J.; Zhang, B.Q.; Wang, M.Q.; Cao, H.W.; Rono, J.K.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.M. OsZIP1 functions as a metal efflux transporter limiting excess zinc, copper and cadmium accumulation in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.T.; Qu, M.M.; Zhu, Y.X.; Peng, C.; Wang, J.R.; Gao, D.Y.; Chen, C.Y. ZINC TRANSPORTER5 and ZINC TRANSPORTER9 function synergistically in zinc/cadmium uptake. Plant Physiol. 2020, 183, 1235–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.T.; Zhu, Y.X.; Fan, T.; Peng, C.; Wang, J.R.; Sun, L.; Chen, C.Y. OsZIP7 functions in xylem loading in roots and inter-vascular transfer in nodes to deliver Zn/Cd to grain in rice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 512, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Lu, Y.S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.Z.; Chao, D.; Wang, Z.G.; Shi, M.X.; Chen, J.G.; Chao, D.Y.; Li, R.B.; et al. The ABC transporter ABCG36 is required for cadmium tolerance in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5909–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.L.; Xu, W.X.; Xie, J.Y.; Gao, Y.W.; Wu, L.L.; Sun, L.; Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Dai, C.H.; et al. Variation of a major facilitator superfamily gene contributes to differential cadmium accumulation between rice subspecies. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.T.; Wang, P.; Yan, T.Z.; Cao, B.B.; Xu, J.; Liu, D.F.; Luo, M.Z. The rice “fruit-weight 2.2-like” gene family member OsFWL4 is involved in the translocation of cadmium from roots to shoots. Planta 2018, 247, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A.; Yamaji, N.; Ma, J.F. Transporters involved in mineral nutrient uptake in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 3645–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.D.; Huang, S.; Yamaji, N.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J.F.; Zhao, F.J. OsNRAMP1 transporter contributes to cadmium and manganese uptake in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 2476–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A.; Yamaji, N.; Yokosho, K.; Ma, J.F. Nramp5 is a major transporter responsible for manganese and cadmium uptake in rice. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2155–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, K.; Dong, H.; Wang, D.; Zhao, F.J.; Huang, C.F.; et al. OsNRAMP5 contributes to manganese translocation and distribution in rice shoots. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4849–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bughio, N.; Yamaguchi, H.; Nishizawa, N.K.; Nakanishi, H.; Mori, S. Cloning an iron-regulated metal transporter from rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogo, Y.; Kakei, Y.; Itai, R.N.; Kobayashi, T.; Nakanishi, H.; Takahashi, H.; Nakazono, M.; Nishizawa, N.K. Spatial transcriptomes of iron-deficient and cadmium-stressed rice. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengel, Z. Availability of Mn, Zn and Fe in the rhizosphere. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2015, 15, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.A.; Shin, R.; Eide, D.J.; Schachtman, D.P. Differential metal selectivity and gene expression of two zinc transporters from rice. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Qayyum, M.F.; Ok, Y.S.; Adrees, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Zia-ur-Rehmand, M.; Farid, M.; Abbas, F. Effect of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on growth and physiology of globally important food crops: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Saifullah; Malhi, S.S.; Zia, M.H.; Naeem, A.; Bibi, S.; Farid, G. Role of mineral nutrition in minimizing cadmium accumulation by plants. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, M.F.; Sehar, S.; Han, Z.; Wa Lwalaba, J.L.; Jilani, G.; Zeng, F.; Chen, Z.H.; Shamsi, I.H. Zinc alleviates cadmium toxicity by modulating photosynthesis, ROS homeostasis, and cation flux kinetics in rice. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Tsadilas, C.D.; Rinklebe, J. A review of the distribution coefficients of trace elements in soils: Influence of sorption system, element characteristics, and soil colloidal properties. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 201–202, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Thangarajan, R.; Kumpiene, J.; Park, J.; Makino, T.; Kirkham, M.B.; Scheckel, K. Remediation of heavy metal(loid)s contaminated soils—To mobilize or to immobilize? J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 266, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, A.; Prasad, M.N.V. Cadmium minimization in rice. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.X.; Jiang, L.H.; Yang, J.J.; Guo, Z.W.; Li, K.W.; Peng, Y.L.; Ibrahim, N.; Liu, H.W.; Liang, Y.L.; Yin, H.Q.; et al. Transport behavior of Cd2+ in highly weathered acidic soils and shaping in soil microbial community structure. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 86, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Xue, Q.; Chen, H.H.; Li, W.T. Mechanistic study of lead desorption during the leaching process of ion-absorbed rare earths: pH effect and the column experiment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 12918–12926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.S.; Chen, S.B.; Wang, M.; Lei, X.Q.; Zheng, H.; Sun, X.Y.; Wang, L.F.; Han, Y. Iron fractions responsible for the variation of Cd bioavailability in paddy soil under variable pe plus pH conditions. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradl, H.B. Adsorption of heavy metal ions on soils and soils constituents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 277, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Nishizawa, N.K. Iron uptake, translocation, and regulation in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Itai, R.N.; Nishizawa, N.K. Iron deficiency responses in rice roots. Rice 2014, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Nozoye, T.; Nishizawa, N.K. Iron transport and its regulation in plants. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.F.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Q.; Manzoor, M.; Luo, J.; Guan, D.X. High-resolution chemical imaging to understand Cd activation in rice rhizosphere of karstic soils. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Rice Varieties | Types of Soil | Treatments | Tillering Stage | Maturity Stage | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeTFs/r | MnTFs/r | ZnTFs/r | CdTFs/r | FeTFs/r | MnTFs/r | ZnTFs/r | CdTFs/r | FeTFb/s | MnTFb/s | ZnTFb/s | CdTFb/s | |||
| MY46 | ACS | Cd0 | 0.24 ± 0.01 a | 8.21 ± 0.37 a | 0.45 ± 0.02 a | 0.29 ± 0.02 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 11.76 ± 0.58 a | 1.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.07 ± 0.02 c | 0.03 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 c | 0.41 ± 0.04 d | 0.65 ± 0.16 a |
| Cd1 | 0.16 ± 0.02 b | 6.58 ± 0.25 b | 0.40 ± 0.01 b | 0.13 ± 0.00 c | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 9.58 ± 0.36 b | 0.94 ± 0.06 b | 0.17 ± 0.02 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 c | 0.56 ± 0.01 c | 0.40 ± 0.03 b | ||
| ALS | Cd0 | 0.24 ± 0.02 a | 5.07 ± 0.28 c | 0.34 ± 0.03 bc | 0.17 ± 0.01 b | 0.11 ± 0.01 b | 3.49 ± 0.06 c | 0.63 ± 0.05 c | 0.13 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.73 ± 0.04 b | 0.38 ± 0.03 b | |
| Cd1 | 0.17 ± 0.03 b | 6.27 ± 0.60 b | 0.37 ± 0.04 c | 0.07 ± 0.00 d | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 4.67 ± 0.25 d | 0.81 ± 0.14 b | 0.08 ± 0.00 c | 0.02 ± 0.00 c | 0.03 ± 0.00 b | 1.12 ± 0.15 a | 0.67 ± 0.01 a | ||
| ZS97B | ACS | Cd0 | 0.26 ± 0.01 A | 17.41 ± 0.42 A | 0.87 ± 0.01 A | 0.15 ± 0.01 A | 0.05 ± 0.00 C | 11.95 ± 0.06 A | 2.91 ± 0.20 A | 0.24 ± 0.03 A | 0.02 ± 0.00 B | 0.02 ± 0.00 C | 0.30 ± 0.01 C | 0.38 ± 0.03 A |
| Cd1 | 0.25 ± 0.02 A | 14.35 ± 0.55 B | 0.69 ± 0.02 B | 0.15 ± 0.04 A | 0.06 ± 0.00 A | 9.60 ± 0.12 B | 1.90 ± 0.11 B | 0.27 ± 0.02 A | 0.02 ± 0.00 B | 0.02 ± 0.00 C | 0.51 ± 0.05 B | 0.26 ± 0.02 B | ||
| ALS | Cd0 | 0.25 ± 0.00 A | 5.30 ± 0.25 D | 0.56 ± 0.06 C | 0.14 ± 0.00 AB | 0.04 ± 0.00 D | 3.00 ± 0.06 D | 1.24 ± 0.08 C | 0.13 ± 0.01 B | 0.04 ± 0.00 A | 0.03 ± 0.00 B | 0.52 ± 0.03 B | 0.29 ± 0.02 B | |
| Cd1 | 0.21 ± 0.01 B | 6.20 ± 0.24 C | 0.67 ± 0.01 B | 0.11 ± 0.01 B | 0.06 ± 0.00 B | 4.89 ± 0.21 C | 1.27 ± 0.13 C | 0.07 ± 0.01 C | 0.04 ± 0.00 A | 0.04 ± 0.00 A | 0.60 ± 0.04 A | 0.36 ± 0.06 A | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Wang, H.; Yu, L.; Li, C.; Ding, L.; Shao, G. Interactions of Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cd in Soil–Rice Systems: Implications for Reducing Cd Accumulation in Rice. Toxics 2025, 13, 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080633
Zhang Y, Jiang S, Wang H, Yu L, Li C, Ding L, Shao G. Interactions of Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cd in Soil–Rice Systems: Implications for Reducing Cd Accumulation in Rice. Toxics. 2025; 13(8):633. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080633
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yan, Su Jiang, Han Wang, Linfei Yu, Chunfu Li, Liqun Ding, and Guosheng Shao. 2025. "Interactions of Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cd in Soil–Rice Systems: Implications for Reducing Cd Accumulation in Rice" Toxics 13, no. 8: 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080633
APA StyleZhang, Y., Jiang, S., Wang, H., Yu, L., Li, C., Ding, L., & Shao, G. (2025). Interactions of Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cd in Soil–Rice Systems: Implications for Reducing Cd Accumulation in Rice. Toxics, 13(8), 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080633





