Children and Adolescents’ Susceptibility to Domoic Acid in Southern China: Preliminary Evidence Revealing Baseline Exposure Profiles and Multidimensional Influencing Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Sample Collection
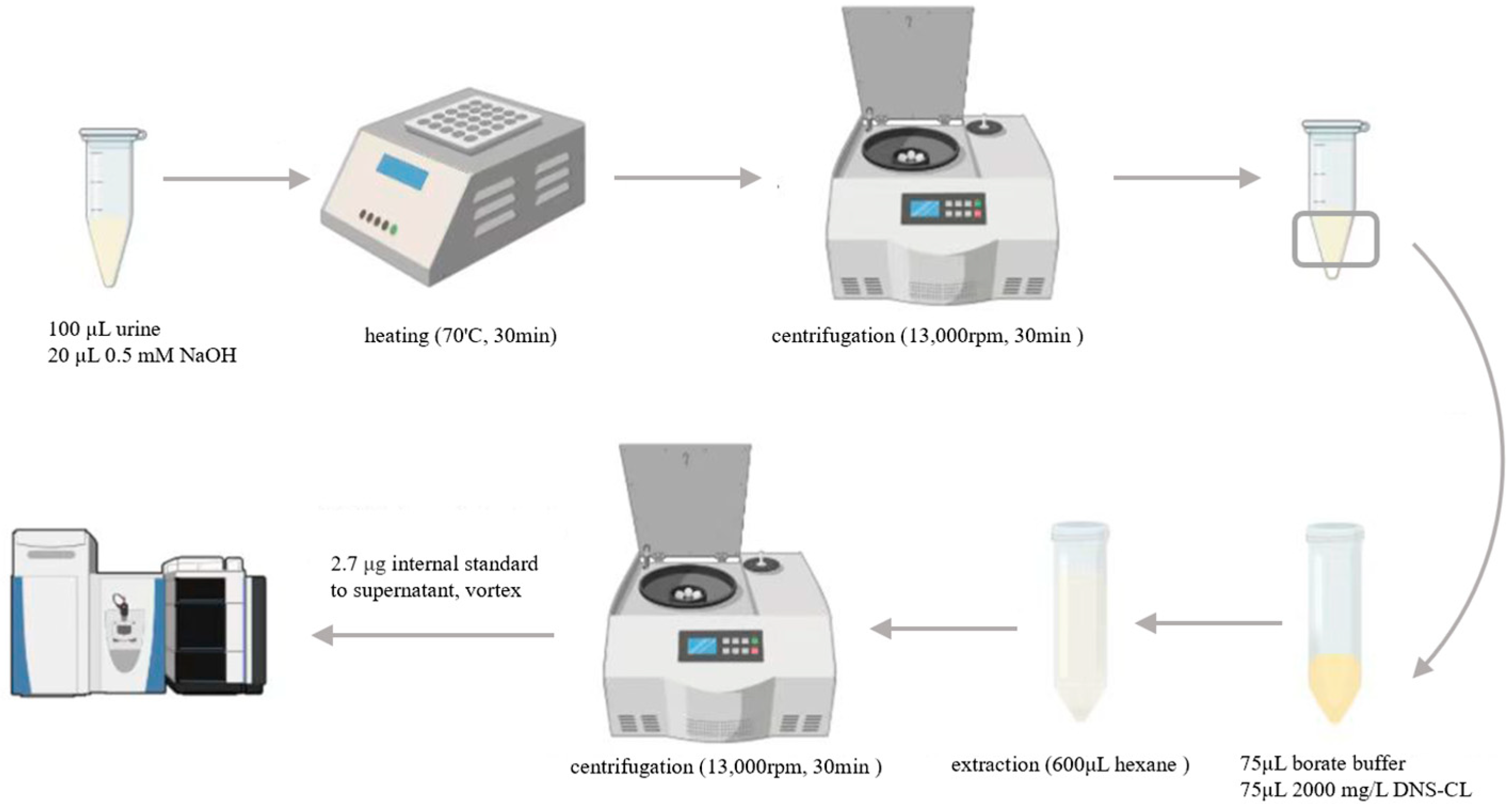
2.3. Urine Sample Preparation
2.4. HPLC–MS/MS Analysis
2.5. Method Validation
2.6. Exposure Risk Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
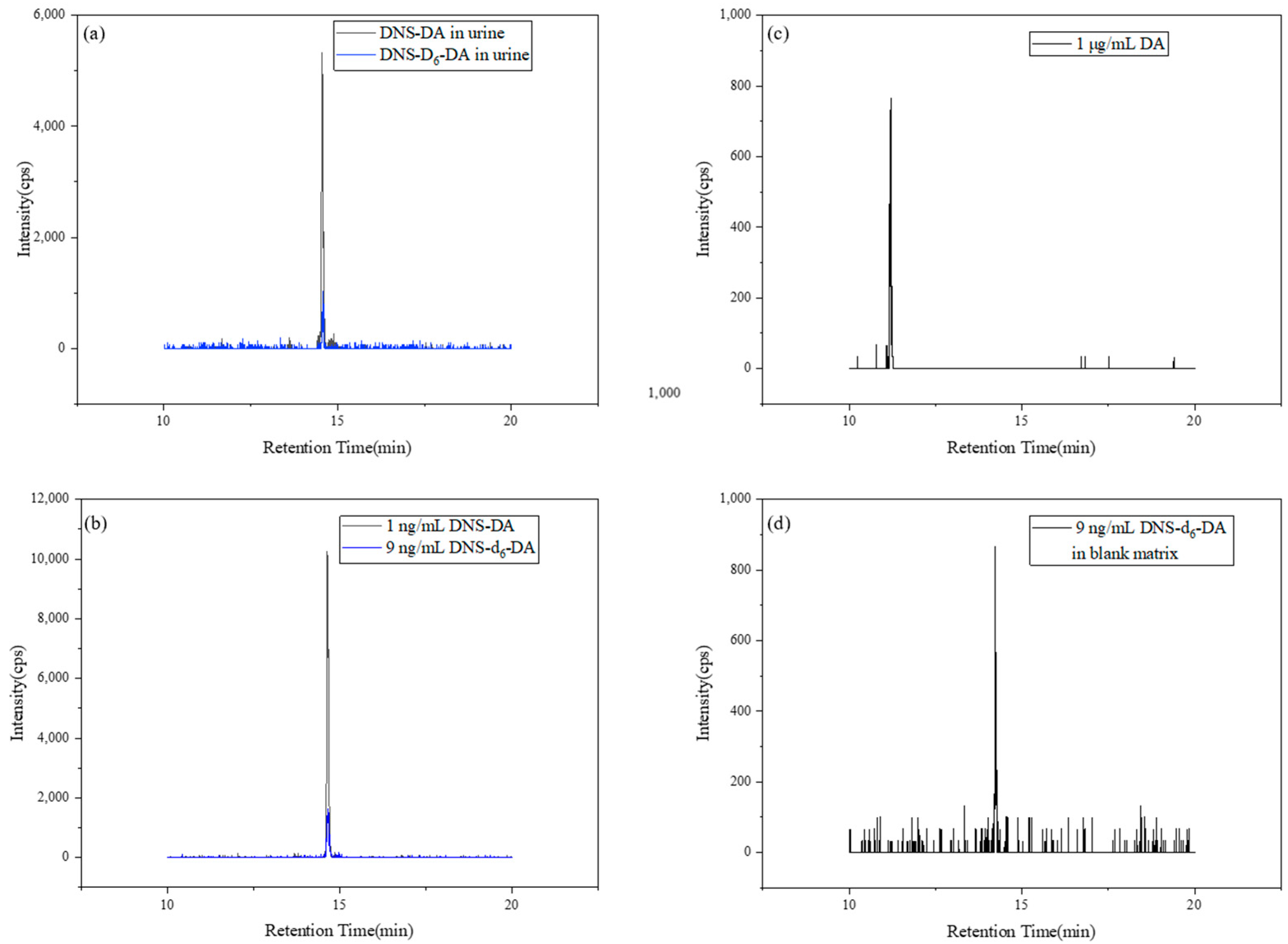
3.1. Method Validation
3.2. Levels of DA in Urine Samples
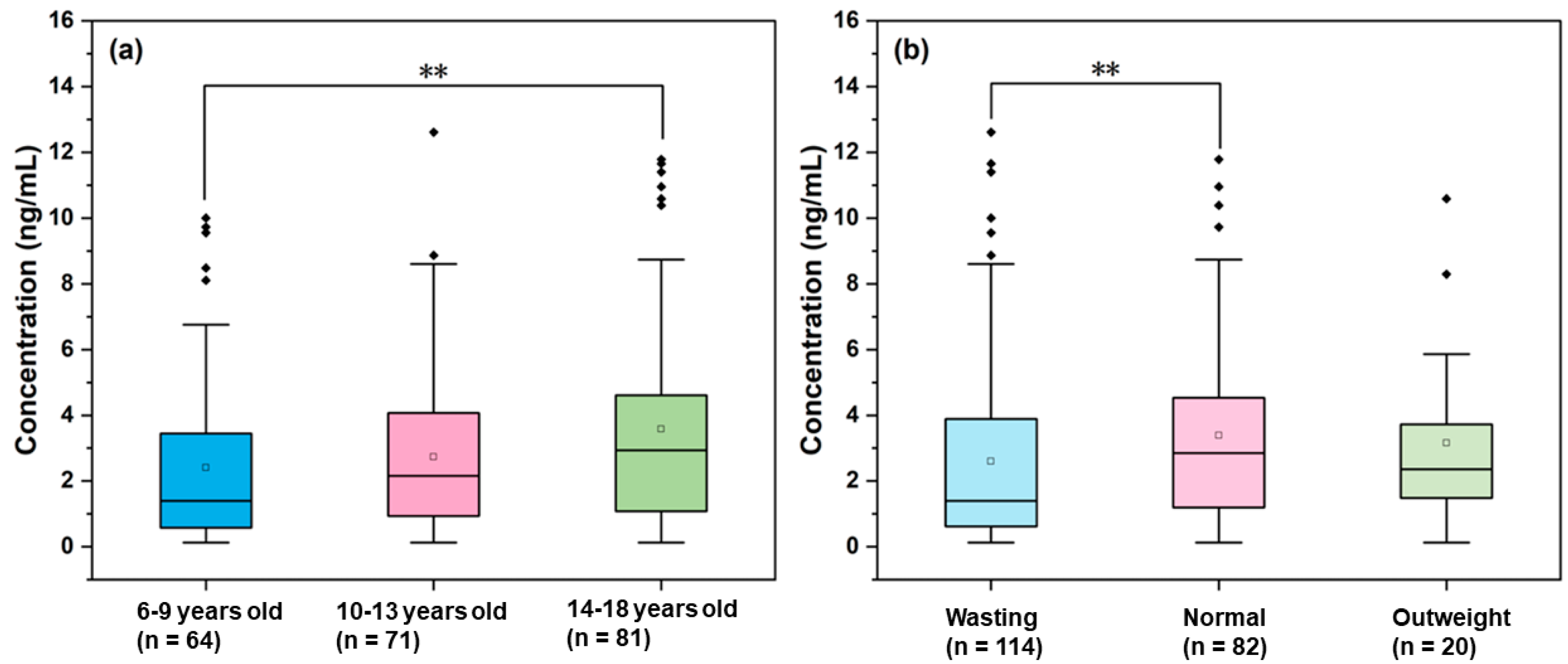
3.3. Effect of Gender
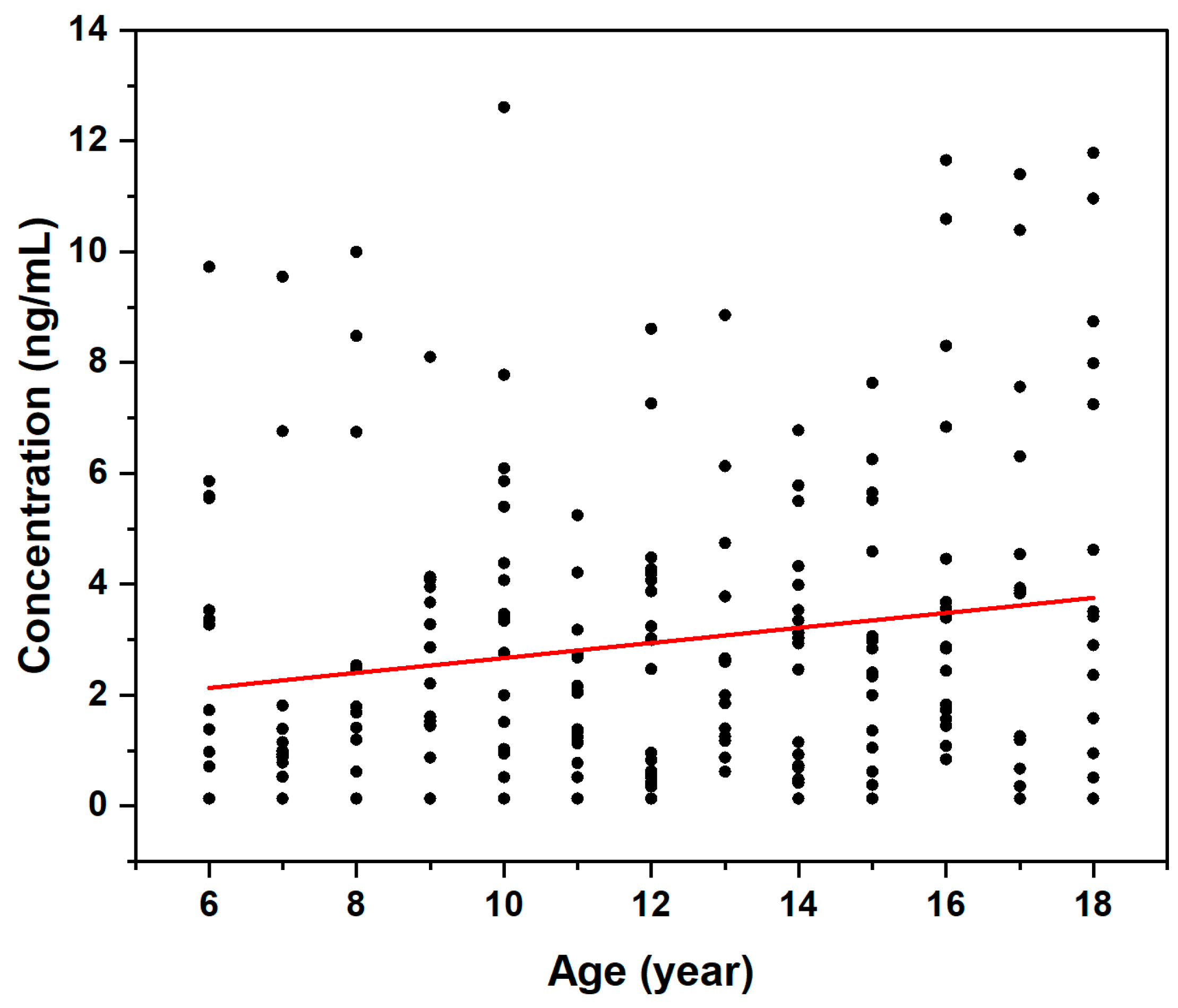
3.4. Effect of Age
3.5. Effect of BMI
3.6. Estimated Daily Intake and Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DA | Domoic acid |
| DNS-Cl | Dansyl-chloride |
| HPLC–MS/MS | High-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| EDI | Estimated daily intake |
| DF | Detect frequency |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
References
- Percopo, I.; Ruggiero, M.V.; Sarno, D.; Longobardi, L.; Rossi, R.; Piredda, R.; Zingone, A. Phenological segregation suggests speciation by time in the planktonic diatom Pseudo-nitzschia allochrona sp. nov. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.N.; Teng, S.T.; Lim, H.C.; Kotaki, Y.; Bates, S.S.; Leaw, C.P.; Lim, P.T. Diatom Nitzschia navis-varingica (Bacillariophyceae) and its domoic acid production from the mangrove environments of Malaysia. Harmful Algae 2016, 60, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, M.A.; Murphy, S.R.; Klasing, S.A.; Niknam, Y.; Iyer, P.; Stanton, B.; Zeise, L. Life Course Considerations in Environmental Health: Developmental Neurotoxicity of Domoic Acid at Doses Below Acute Effect Levels in Adult Humans. Birth Defects Res. 2024, 116, e2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Robertson, A. Domoic acid and human exposure risks: A review. Toxicon 2010, 56, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroff, R.; Hendrix, A.; Shum, S.; Grant, K.S.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Burbacher, T.M. Public health risks associated with chronic, low-level domoic acid exposure: A review of the evidence. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 227, 107865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKibben, S.M.; Peterson, W.; Wood, A.M.; Trainer, V.L.; Hunter, M.; White, A.E. Climatic regulation of the neurotoxin domoic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajski, G.; Gerić, M.; Baričević, A.; Smodlaka Tanković, M. Domoic Acid: A Review of Its Cytogenotoxicity Within the One Health Approach. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.; Olesen, A.J.; Hatfield, R.G.; Krock, B.; Lundholm, N. Extensive Variation in Thermal Responses and Toxin Content Among 40 Strains of the Cold-Water Diatom Pseudo-nitzschia seriata—In a Global Warming Context. Toxins 2025, 17, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burbacher, T.M.; Grant, K.S.; Petroff, R.; Shum, S.; Crouthamel, B.; Stanley, C.; McKain, N.; Jing, J.; Isoherranen, N. Effects of oral domoic acid exposure on maternal reproduction and infant birth characteristics in a preclinical nonhuman primate model. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2019, 72, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramya, E.M.; Kumar, G.P.; Anand, T.; Anilakumar, K.R. Modulatory effects of Terminalia arjuna against domoic acid induced toxicity in Caco-2 cell line. Cytotechnology 2017, 69, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, P.K.; Gulati, A.; Mahesh, A.K.; Sharma, B.; Malik, G.; Dhawan, K. Maturity of blood brain barrier in children. Indian J. Med. Res. 1987, 85, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Atiyeh, B.A.; Dabbagh, S.S.; Gruskin, A.B. Evaluation of renal function during childhood. Pediatr. Rev. 1996, 17, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasner, A.E.; Martinez, M.E.; Field, C.L.; Fire, S.E. The Toxic Effects of Environmental Domoic Acid Exposure on Humans and Marine Wildlife. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemoto, T.; Daigo, K. On the constituents of Chondria armata and their pharmacological effect. Arch. Pharm. Berichte Dtsch. Pharm. Ges. 1960, 293, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Fan, S.; He, X.; Tan, L.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal variations of domoic acid: New findings in the sedimentary environment of a typical nearshore mariculture bay, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 261, 119646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Wu, H.; Che, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, J.; Guo, M.; Tan, Z. Residue Analysis and Assessment of the Risk of Dietary Exposure to Domoic Acid in Shellfish from the Coastal Areas of China. Toxins 2022, 14, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Xia, C.; Wang, H.-F.; Tang, C. Recent advances in electrocatalytic oxygen reduction for on-site hydrogen peroxide synthesis in acidic media. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 67, 432–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, F.; Truelove, J. Toxicology and seafood toxins: Domoic acid. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Marine biotoxins in shellfish—Summary on regulated marine biotoxins. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzillo, F.; Pomeroy, C.; Kuo, J.; Ramondi, P.; Prado, R.; Silver, M. Angler exposure to domoic acid via consumption of contaminated fishes. Aquat. Biol. 2010, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesp, B.R.; Clarkson, A.N.; Sawant, P.M.; Kerr, D.S. Domoic acid preconditioning and seizure induction in young and aged rats. Epilepsy Res. 2007, 76, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, A.W.; Rushton, S.P.; Rens, N.; Morris, C.M.; Blain, P.G.; Judge, S.J. Sex differences in effects of low level domoic acid exposure. NeuroToxicology 2013, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Z. Progresses of the Influencing Factors and Detection Methods of Domoic Acid. Processes 2023, 11, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shum, S.; Kirkwood, J.S.; Jing, J.; Petroff, R.; Crouthamel, B.; Grant, K.S.; Burbacher, T.M.; Nelson, W.L.; Isoherranen, N. Validated HPLC-MS/MS Method To Quantify Low Levels of Domoic Acid in Plasma and Urine after Subacute Exposure. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12079–12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvrgić, K.; Lešić, T.; Džafić, N.; Pleadin, J. Occurrence and Seasonal Monitoring of Domoic Acid in Three Shellfish Species from the Northern Adriatic Sea. Toxins 2022, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beach, D.; Liu, H.; Quilliam, M. Sensitive determination of domoic acid in mussel tissue using dansyl chloride derivatization and liquid chromatography—Mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckford, K.; Grimes, C.A.; Margerison, C.; Riddell, L.J.; Skeaff, S.A.; West, M.L.; Nowson, C.A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of 24-h urinary output of children and adolescents: Impact on the assessment of iodine status using urinary biomarkers. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3113–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, C.A.M.; Hierlihy, S.L. Renal clearance of domoic acid in the rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1993, 31, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomov, D.G.; Bocheva, G.; Divarova, V.; Kasabova, L.; Svinarov, D. Fazno deljenje ekstrakcije tečno-tečno za kvantifikaciju 8-izo-prostaglandina F2a u ljudskoj plazmi pomoću LC-MS/MS metode. J. Med. Biochem. 2021, 40, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Niu, B.; et al. Spatial distribution and source of biotoxins in phytoplankton from the South China Sea, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Che, H.; Wu, H.; Cheng, L.; Deng, Y.; Guo, M.; Peng, J.; Liu, L.; Tan, Z. Risk characteristics of shellfish toxins in Mytilus unguiculatus around the Zhoushan Islands, East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 115955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Xie, C.; Tang, T.; Chen, J.; Ji, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T. Annual variation in domoic acid in phytoplankton and shellfish samples from Daya Bay of the South China Sea. Harmful Algae 2023, 127, 102438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Yan, G.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Tang, Z.; Yan, Y.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, L.; Pan, W.; Fu, Y.; et al. Prevalence and distribution of domoic acid and cyclic imines in bivalve mollusks from Beibu Gulf, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P. Ontogenic differences in the concentration of domoic acid in the digestive gland of male and female Octopus vulgaris. Aquat. Biol. 2010, 9, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen SOJFQ, Preference. Understanding the relationship between age and seafood consumption: The mediating role of attitude, health involvement and convenience. Food Qual. Prefer. 2003, 14, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.Z. Pharmacokinetics and Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Xenobiotic Disposition in Special Populations. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, J.; Petroff, R.; Shum, S.; Crouthamel, B.; Topletz, A.R.; Grant, K.S.; Burbacher, T.M.; Isoherranen, N. Toxicokinetics and Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling of the Shellfish Toxin Domoic Acid in Nonhuman Primates. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffa, R.; Baali, A.; Lahmam, A.; Amor, H.; Zouini, M.; Floris, G.; Racugno, W.; DomíNguez-Bello, M.G.; Marini, E. Assessment of nutritional status in the Amazigh children of Amizmiz (Azgour Valley, High Atlas and Morocco). J. Trop. Pediatr. 2009, 55, 406–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, C.L.; Ferdin, M.; Busman, M.; Kvitek, R.G.; Doucette, G.J. Development of a protocol for determination of domoic acid in the sand crab (Emerita analoga): A possible new indicator species. Toxicon 2002, 40, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabaglo, K.; Chrapusta, E.; Bober, B.; Kaminski, A.; Adamski, M.; Bialczyk, J. Environmental roles and biological activity of domoic acid: A review. Algal Res. 2016, 13, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafra, L.L.; Léger, C.; Bates, S.S.; Quilliam, M.A. Analysis of trace levels of domoic acid in seawater and plankton by liquid chromatography without derivatization, using UV or mass spectrometry detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 6003–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, E.C.; Peng, Y.-G.; Means, L.W.; Ramsdell, J.S. Working memory deficits induced by single but not repeated exposures to domoic acid. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, B.F.; Pinsky, C.; Standish, N.M.; Bose, R.; Glavin, G. Parenteral domoic acid impairs spatial learning in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1992, 41, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, B.; Barlow, T.; Moizer, K.; Paul, S.; Boyle, C. Amnesic shellfish poison. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Groups | n | n (<LOD) | Concentration (ng/mL) | DF | EDI (ng/kg/day) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 25th–75th Percentiles | ||||||
| All | 216 | 28 | 2.17 | 0.87–4.08 | 87.0% | 1.73–374 | |
| Gender | Male | 113 | 11 | 2.44 | 1.03–4.07 | 90.3% | 1.73–374 |
| Female | 103 | 17 | 2.0 | 0.6–4.19 | 83.5% | 2.16–321 | |
| Age (years) | 6–9 years | 64 | 15 | 1.40 | 0.55–3.49 | 76.6% | 1.73–321 |
| 10–13 years | 71 | 6 | 2.16 | 0.94–4.07 | 91.6% | 2.16–374 | |
| 14–18 years | 81 | 7 | 2.93 | 1.06–5.06 | 91.4% | 2.21–244 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ≤18.5 | 114 | 27 | 1.39 | 0.61–3.90 | 76.3% | 2.65–374 |
| 18.5–25 | 82 | 0 | 2.85 | 1.18–4.56 | 100% | 2.16–307 | |
| ≥25 | 20 | 1 | 2.36 | 1.44–3.75 | 95.0% | 1.73–141 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Long, T.; Zou, S.; Hua, R.; Ye, M.; Ma, S.; Peng, B. Children and Adolescents’ Susceptibility to Domoic Acid in Southern China: Preliminary Evidence Revealing Baseline Exposure Profiles and Multidimensional Influencing Factors. Toxics 2025, 13, 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080628
Lin Y, Long T, Zou S, Hua R, Ye M, Ma S, Peng B. Children and Adolescents’ Susceptibility to Domoic Acid in Southern China: Preliminary Evidence Revealing Baseline Exposure Profiles and Multidimensional Influencing Factors. Toxics. 2025; 13(8):628. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080628
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yuxin, Tingze Long, Siyi Zou, Rui Hua, Meixia Ye, Shengtao Ma, and Bo Peng. 2025. "Children and Adolescents’ Susceptibility to Domoic Acid in Southern China: Preliminary Evidence Revealing Baseline Exposure Profiles and Multidimensional Influencing Factors" Toxics 13, no. 8: 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080628
APA StyleLin, Y., Long, T., Zou, S., Hua, R., Ye, M., Ma, S., & Peng, B. (2025). Children and Adolescents’ Susceptibility to Domoic Acid in Southern China: Preliminary Evidence Revealing Baseline Exposure Profiles and Multidimensional Influencing Factors. Toxics, 13(8), 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080628







