Selenium Reduces Cadmium-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Modulating Oxidative Stress and the ROS/PARP-1/TRPM2 Signalling Pathway in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Groups of Experiments
Experimental Groups
- CON (Control): For five days, the rats in this group were fed regular pellet feed every day.
- CAD: For five days, the rats in this group received a gavage of 25 mg/kg CAD.
- SEL: For five days, this group received 25 mg/kg of CAD via gavage, and SEL was given intraperitoneally daily (0.5 mg/kg).
- 2-APB: For five days, this group received 25 mg/kg of CAD via gavage, and 2-APB was injected intraperitoneally daily (3 mg/kg).
- SEL+2-APB: For five days, this group received 25 mg/kg of CAD via gavage, and both SEL (0.5 mg/kg) and 2-APB (3 mg/kg) were given intraperitoneally daily.
2.2. Histopathological Analyses
2.3. Immunohistochemical Analyses
2.4. Biochemical Evaluation
2.5. Antioxidant/Oxidant Levels in Heart Tissues
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Histopathological Findings
3.2. Immunohistochemical Findings
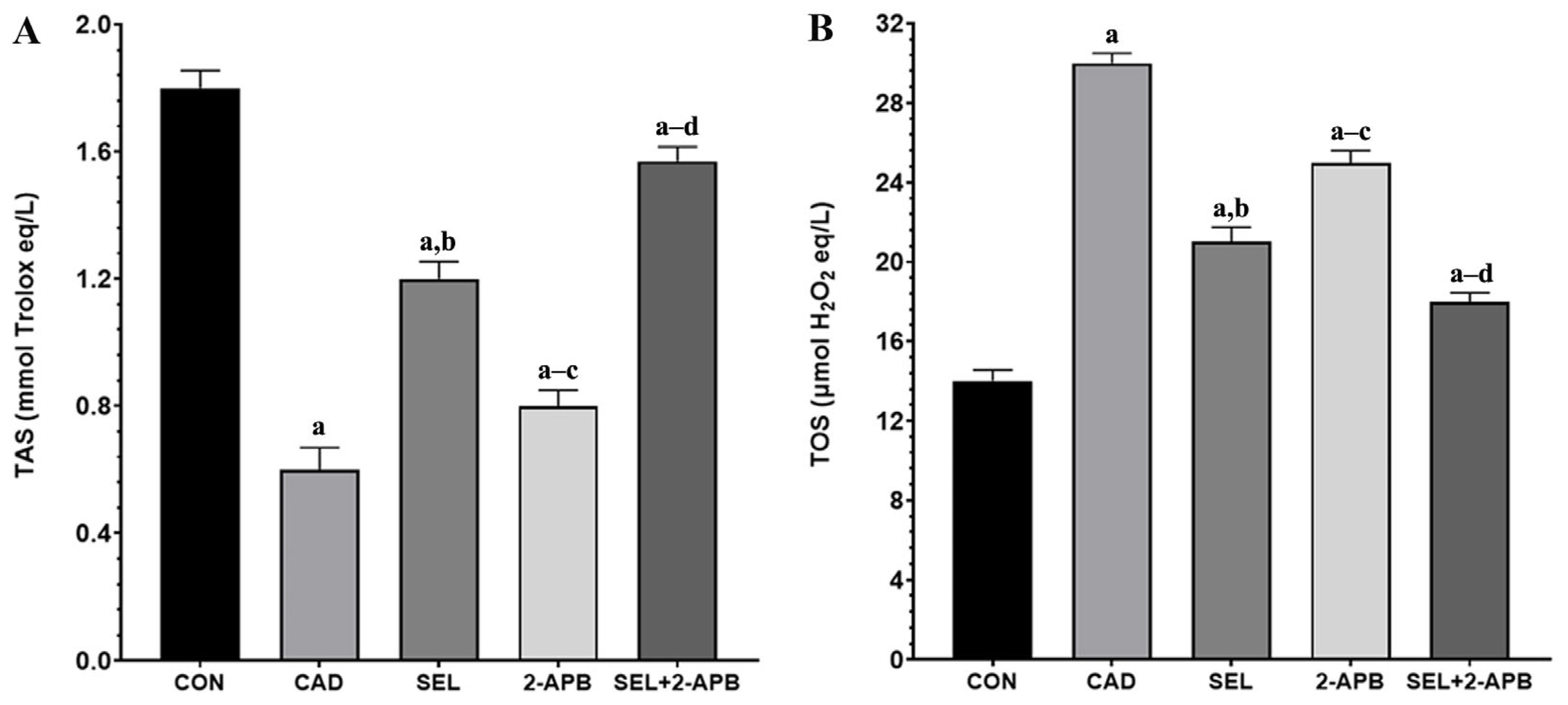
3.3. TAS and TOS Levels in CAD-Induced Heart Damage
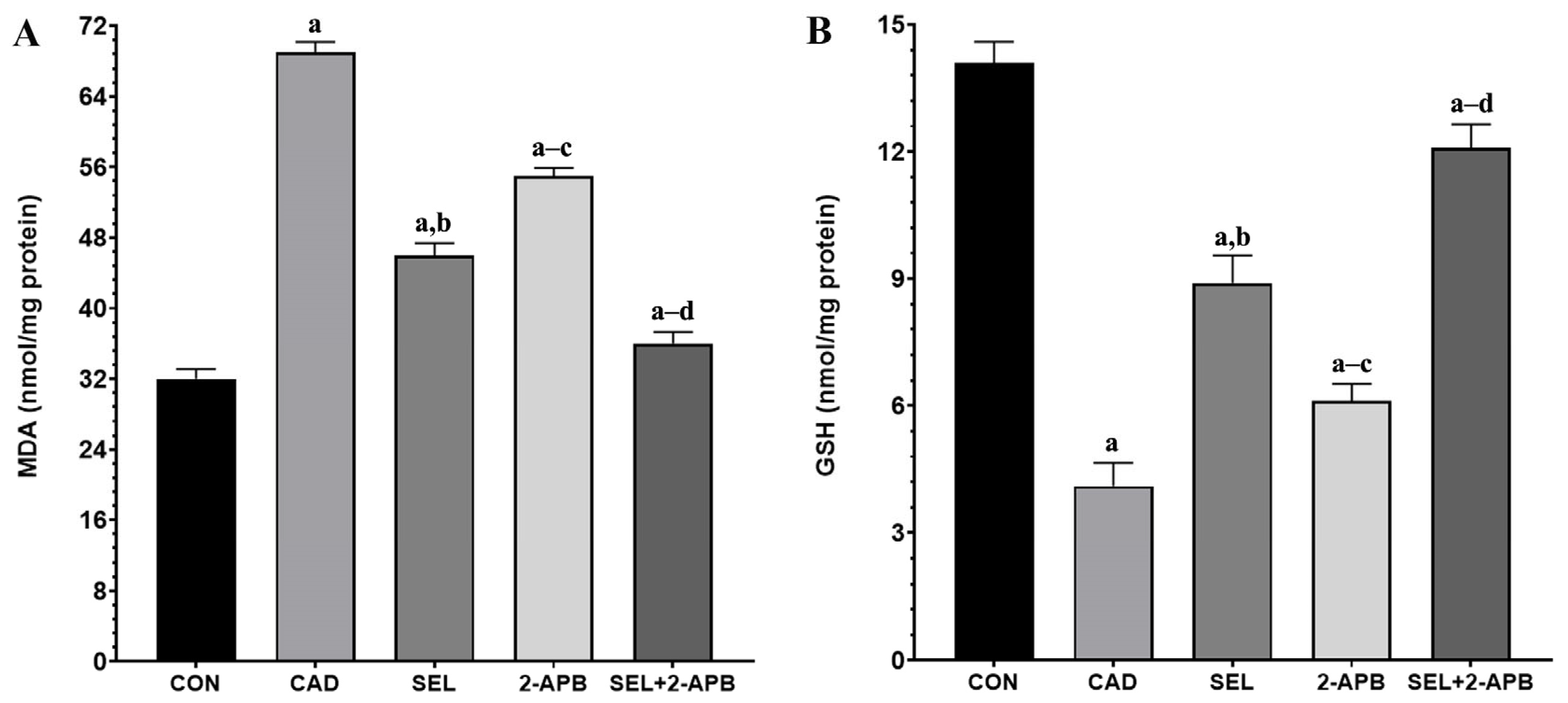
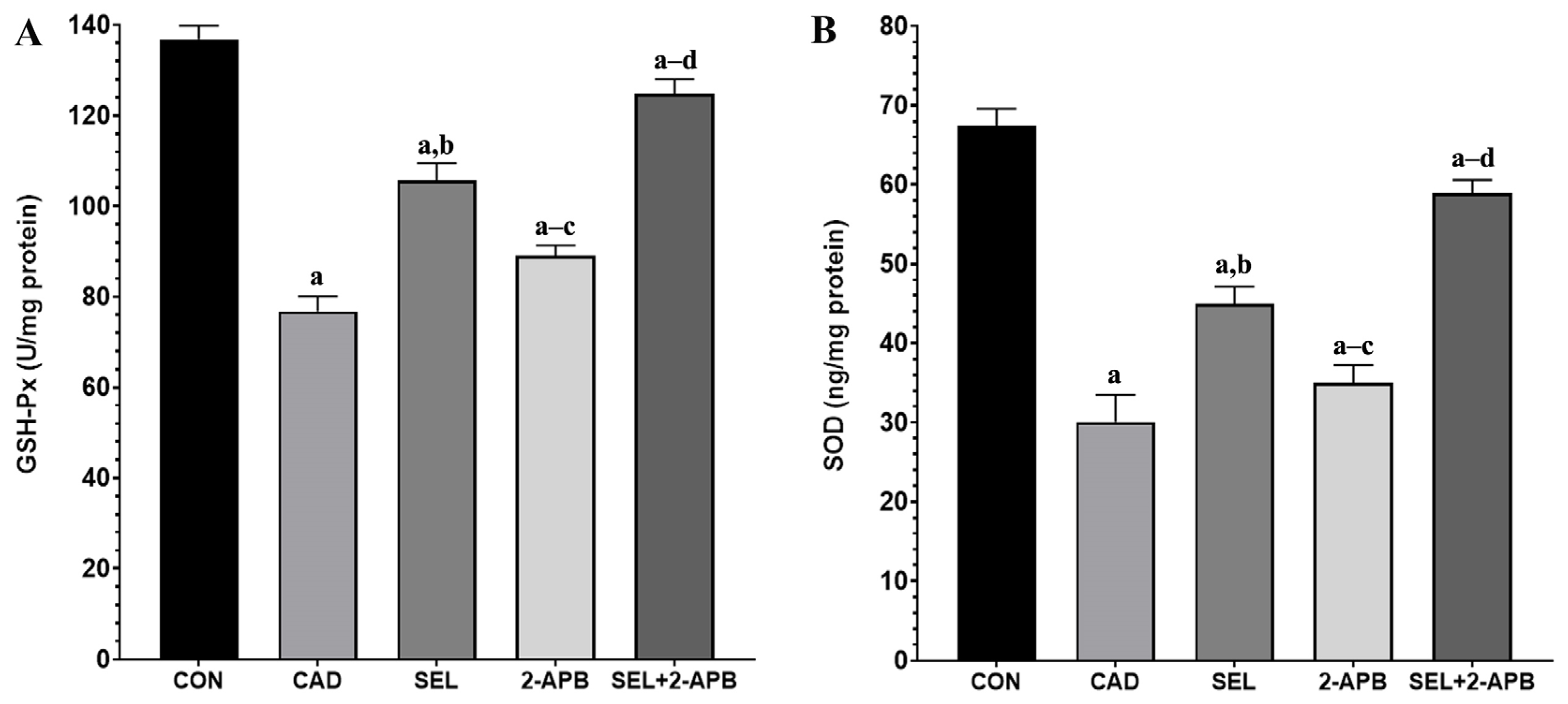
3.4. MDA, GSH, GSH-Px and SOD Levels in CAD-Induced Heart Damage
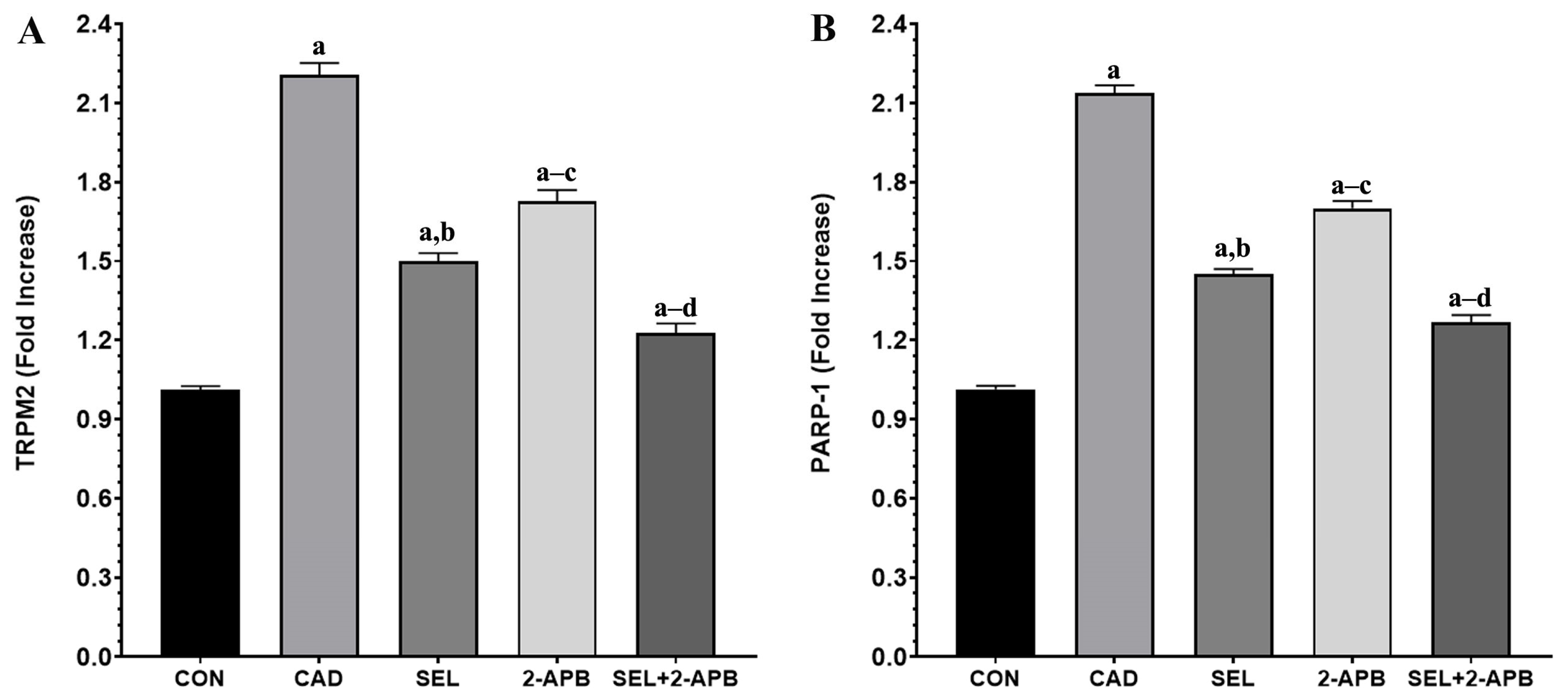
3.5. TRPM2 and PARP-1 Levels in CAD-Induced Heart Damage
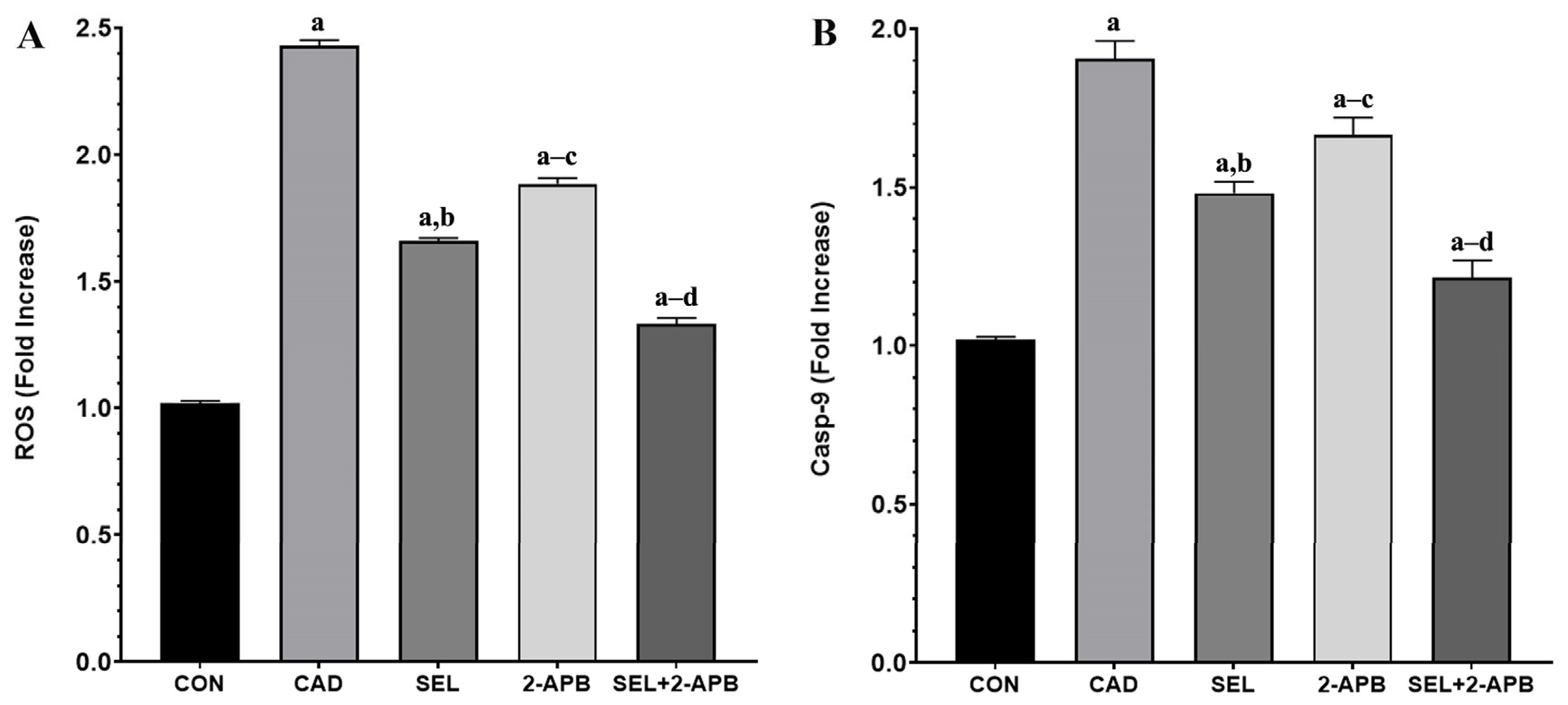
3.6. ROS and Casp-9 Levels in CAD-Induced Heart Damage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alruhaimi, R.S.; Hassanein, E.H.; Bin-Jumah, M.N.; Mahmoud, A.M. Cadmium cardiotoxicity is associated with oxidative stress and upregulated TLR-4/NF-kB pathway in rats; protective role of agomelatine. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 180, 114055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, B. Cardioprotective Effect of Eugenol Against Cd-Induced Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Dyslipidemia in Male Rats: An In Vivo and Molecular Docking Study. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2025, 203, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, G.; Wang, Y.; Howe, C.G.; Romano, M.E. Exposure to metal mixtures in association with cardiovascular risk factors and outcomes: A scoping review. Toxics 2022, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.C.; Varadharajan, K.; Shanmugakonar, M.; Al-Naemi, H.A. Chronic cadmium exposure alters cardiac matrix metalloproteinases in the heart of Sprague-Dawley rat. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 663048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazima, B.; Manoharan, V.; Miltonprabu, S. Oxidative stress induced by cadmium in the plasma, erythrocytes and lymphocytes of rats: Attenuation by grape seed proanthocyanidins. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 428–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajakumar, S.; Abhishek, A.; Selvam, G.S.; Nachiappan, V. Effect of cadmium on essential metals and their impact on lipid metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell Stress Chaperones 2020, 25, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidova, S.; Milushev, V.; Satchanska, G. The mechanisms of cadmium toxicity in living organisms. Toxics 2024, 12, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellez-Plaza, M.; Guallar, E.; Howard, B.V.; Umans, J.G.; Francesconi, K.A.; Goessler, W.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Devereux, R.B.; Navas-Acien, A. Cadmium exposure and incident cardiovascular disease. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malekmohammad, K.; Bezsonov, E.E.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Role of lipid accumulation and inflammation in atherosclerosis: Focus on molecular and cellular mechanisms. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 707529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, A.E.; Grabmann, G.; Gollmann-Tepeköylü, C.; Pechriggl, E.J.; Artner, C.; Türkcan, A.; Hartinger, C.G.; Fritsch, H.; Keppler, B.K.; Brenner, E. Chemical imaging and assessment of cadmium distribution in the human body. Metallomics 2019, 11, 2010–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.L.; Yan, X.; Xu, J.; Yin, X.; Zhang, X.; Arteel, G.E.; Barnes, G.N.; States, J.C.; Watson, W.H.; Kong, M. Cadmium and high-fat diet disrupt renal, cardiac and hepatic essential metals. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerzen, O.P.; Potoskueva, I.K.; Tzybina, A.E.; Myachina, T.A.; Nikitina, L.V. Cardiac myosin and thin filament as targets for lead and cadmium divalent cations. Biochemistry 2024, 89, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, D.; Li, T.; Tang, L.; Gong, T.; Su, J.; Liang, P. Modelling cadmium-induced cardiotoxicity using human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 4221–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yıldızhan, K.; Huyut, Z.; Altındağ, F. Involvement of TRPM2 channel on doxorubicin-induced experimental cardiotoxicity model: Protective role of selenium. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 2458–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, B.K.; Alfulaij, N.; Seale, L.A. The impact of selenium deficiency on cardiovascular function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; He, X.; Hu, L.; Zhao, J.; Su, K.; Lei, Y.; Li, Y. The relationship between plasma selenium, antioxidant status, inflammatory responses and ischemic cardiomyopathy: A case-control study based on matched propensity scores. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 5757–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mubarak, A.A.; van der Meer, P.; Bomer, N. Selenium, selenoproteins, and heart failure: Current knowledge and future perspective. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2021, 18, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benstoem, C.; Goetzenich, A.; Kraemer, S.; Borosch, S.; Manzanares, W.; Hardy, G. Stoppe, CSelenium and its supplementation in cardiovascular disease—What do we know? Nutrients 2015, 7, 3094–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanguy, S.; Rakotovao, A.; Jouan, M.G.; Ghezzi, C.; de Leiris, J.; Boucher, F. Dietary selenium intake influences Cx43 dephosphorylation, TNF-α expression and cardiac remodeling after reperfused infarction. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Guo, K.; Huang, Y.; Morse, P.D.; Zhang, C.; Lv, M.-W.; Li, J.-L. Comparison of antagonistic effects of nanoparticle-selenium, selenium-enriched yeast and sodium selenite against cadmium-induced cardiotoxicity via AHR/CAR/PXR/Nrf2 pathways activation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 105, 108992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazıroğlu, M. New molecular mechanisms on the activation of TRPM2 channels by oxidative stress and ADP-ribose. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 1990–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazğan, Y.; Nazıroğlu, M. Involvement of TRPM2 in the neurobiology of experimental migraine: Focus on oxidative stress and apoptosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 5581–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyuva, Y.; Nazıroğlu, M.; Yıldızhan, K. Selenium prevents interferon-gamma induced activation of TRPM2 channel and inhibits inflammation, mitochondrial oxidative stress, and apoptosis in microglia. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daldal, H.; Nazıroğlu, M. Selenium and resveratrol attenuated diabetes mellitus-mediated oxidative retinopathy and apoptosis via the modulation of TRPM2 activity in mice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yıldız, M.O.; Çelik, H.; Caglayan, C.; Genç, A.; Doğan, T.; Satıcı, E. Neuroprotective effects of carvacrol against cadmium-induced neurotoxicity in rats: Role of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Metab. Brain Dis. 2022, 37, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keleş, Ö.F.; Bayir, M.H.; Çiçek, H.A.; Ahlatcı, A.; Yıldızhan, K. The Effect of Selenium Against Cadmium-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats: The Role of the TRPM2 Channel. Toxics 2025, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapak, P.; Khare, P.; Bishnoi, M.; Sharma, S.S. Neuroprotective effect of 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl Borate (2-APB) in amyloid β-induced memory dysfunction: A mechanistic study. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yıldızhan, K.; Bayir, M.H.; Huyut, Z.; Altındağ, F. Effect of Hesperidin on Lipid Profile, Inflammation and Apoptosis in Experimental Diabetes. In Doklady Biochemistry and Biophysics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Çınar, R.; Yıldızhan, K. Curcumin protects against MPP+-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells by modulating the TRPV4 channel. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2025, 52, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhani, I.; Sahab, S.; Srivastava, V.; Singh, R.P. Impact of cadmium pollution on food safety and human health. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2021, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-C.; Hao, W.-M.; Chu, P.-H. Cadmium and cardiovascular disease: An overview of pathophysiology, epidemiology, therapy, and predictive value. Rev. Port. De Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 40, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Qiao, L.; Liu, H.; Bao, M.; Deng, H.; Jia, L.; Wen, X.; Deng, F.; Wan, P.; Lyu, Y. An untargeted metabolomics study of cardiac pathology damage in rats caused by low selenium diet alone or in combination with T-2 toxin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 189, 114759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyinloye, B.E.; Ajiboye, B.O.; Ojo, O.A.; Nwozo, S.O.; Kappo, A.P. Cardioprotective and antioxidant influence of aqueous extracts from Sesamum indicum seeds on oxidative stress induced by cadmium in wistar rats. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, S170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, L.B.; Baskaran, R.; Elangovan, P.; Dhivya, V.; Huang, C.-Y.; Padma, V.V. Tinospora cordifolia extract attenuates cadmium-induced biochemical and histological alterations in the heart of male Wistar rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Xu, S. Subacute cadmium exposure promotes M1 macrophage polarization through oxidative stress-evoked inflammatory response and induces porcine adrenal fibrosis. Toxicology 2021, 461, 152899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicek, B.; Hacimuftuoglu, A.; Yeni, Y.; Danisman, B.; Ozkaraca, M.; Mokhtare, B.; Kantarci, M.; Spanakis, M.; Nikitovic, D.; Lazopoulos, G. Chlorogenic acid attenuates doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress and markers of apoptosis in cardiomyocytes via Nrf2/HO-1 and dityrosine signaling. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirazi, L.F.; Bissett, J.; Romeo, F.; Mehta, J.L. Role of inflammation in heart failure. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoots, M.H.; Gordijn, S.J.; Scherjon, S.A.; van Goor, H.; Hillebrands, J.-L. Oxidative stress in placental pathology. Placenta 2018, 69, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, J.F.; Dressler, V.L.; Assmann, C.E.; Morsch, V.M.M.; Schetinger, M.R.C. Cadmium neurotoxicity: From its analytical aspects to neuronal impairment. In Advances in Neurotoxicology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 81–113. [Google Scholar]
- Yanchun, Z.; Xue, J.; SM, F.; Xue, W. Protective Effect of Ipomoea staphylina Against Cadmium-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Wistar Rats. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Choudhary, R.; Nirmalkar, U.; Singh, A.; Shree, J.; Vishwakarma, P.K.; Bodakhe, S.H. Magnesium taurate attenuates progression of hypertension and cardiotoxicity against cadmium chloride-induced hypertensive albino rats. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2019, 9, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çınar, R.; Nazıroğlu, M. TRPM2 channel inhibition attenuates amyloid β42-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress in the hippocampus of mice. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 43, 1335–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refaie, M.M.; Shehata, S.; Bayoumi, A.M.; El-Tahawy, N.F.G.; Abdelzaher, W.Y. The IL-6/STAT signaling pathway and PPARα are involved in mediating the dose-dependent cardioprotective effects of fenofibrate in 5-fluorouracil-induced cardiotoxicity. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2022, 36, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Feng, Z. The role of toll-like receptor signaling in the progression of heart failure. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 9874109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIlwain, D.R.; Berger, T.; Mak, T.W. Caspase functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.-B.; Ben-Moshe, T.; Varfolomeev, E.E.; Pewzner-Jung, Y.; Yogev, N.; Jurewicz, A.; Waisman, A.; Brenner, O.; Haffner, R.; Gustafsson, E. Caspase-8 serves both apoptotic and nonapoptotic roles. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2976–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refaie, M.M.; El-Hussieny, M.; Bayoumi, A.M.; Shehata, S. Mechanisms mediating the cardioprotective effect of carvedilol in cadmium induced cardiotoxicity. Role of eNOS and HO1/Nrf2 pathway. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 103198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaresan, S.; John, S.; Paneerselvam, G.; Andiapppan, R.; Christopher, G.; Selvam, G.S. Gallic acid attenuates cadmium mediated cardiac hypertrophic remodelling through upregulation of Nrf2 and PECAM-1signalling in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 103701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilhan, I.; Asci, H.; Tepebasi, M.Y.; Imeci, O.B.; Sevuk, M.A.; Temel, E.N.; Ozmen, O. Selenium exerts protective effects on inflammatory cardiovascular damage: Molecular aspects via SIRT1/p53 and Cyt-c/Cas-3 pathways. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikediobi, C.O.; Badisa, V.L.; Ayuk-Takem, L.T.; Latinwo, L.M.; West, J. Response of antioxidant enzymes and redox metabolites to cadmium-induced oxidative stress in CRL-1439 normal rat liver cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2004, 14, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casalino, E.; Sblano, C.; Landriscina, C. Enzyme activity alteration by cadmium administration to rats: The possibility of iron involvement in lipid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1997, 346, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
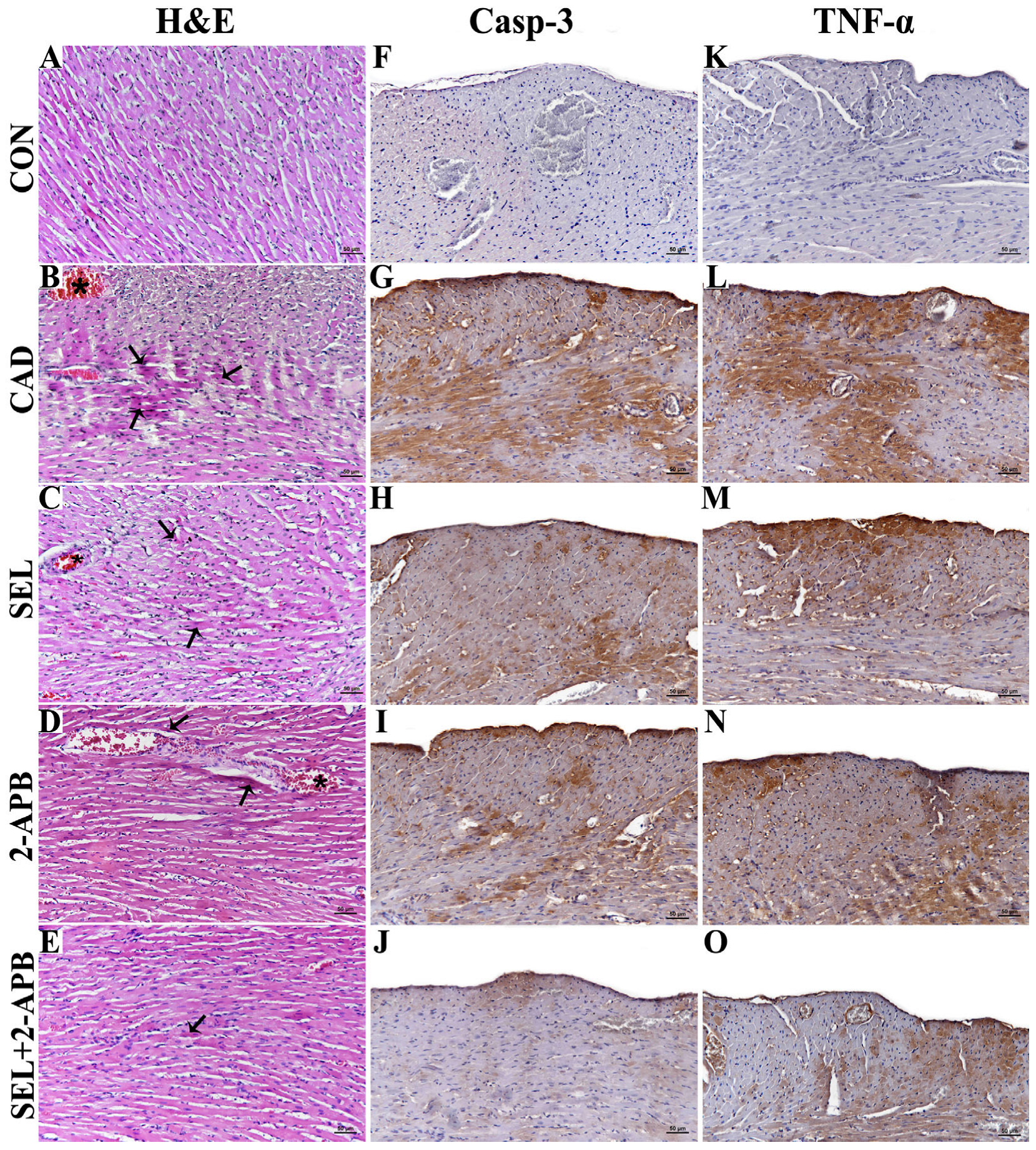
| Groups | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | CON | CAD | SEL | 2-APB | SEL+2-APB |
| Casp-3 | - | +++ | ++ | + | + |
| TNF-α | - | +++ | + | ++ | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yazğan, Y.; Keleş, Ö.F.; Bayir, M.H.; Çiçek, H.A.; Ahlatcı, A.; Yıldızhan, K. Selenium Reduces Cadmium-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Modulating Oxidative Stress and the ROS/PARP-1/TRPM2 Signalling Pathway in Rats. Toxics 2025, 13, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080611
Yazğan Y, Keleş ÖF, Bayir MH, Çiçek HA, Ahlatcı A, Yıldızhan K. Selenium Reduces Cadmium-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Modulating Oxidative Stress and the ROS/PARP-1/TRPM2 Signalling Pathway in Rats. Toxics. 2025; 13(8):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080611
Chicago/Turabian StyleYazğan, Yener, Ömer Faruk Keleş, Mehmet Hafit Bayir, Hacı Ahmet Çiçek, Adem Ahlatcı, and Kenan Yıldızhan. 2025. "Selenium Reduces Cadmium-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Modulating Oxidative Stress and the ROS/PARP-1/TRPM2 Signalling Pathway in Rats" Toxics 13, no. 8: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080611
APA StyleYazğan, Y., Keleş, Ö. F., Bayir, M. H., Çiçek, H. A., Ahlatcı, A., & Yıldızhan, K. (2025). Selenium Reduces Cadmium-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Modulating Oxidative Stress and the ROS/PARP-1/TRPM2 Signalling Pathway in Rats. Toxics, 13(8), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080611








