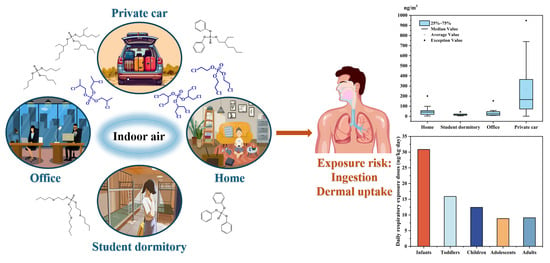
Concentrations, Compositions and Human Exposure Risks to Organophosphate Esters in Indoor Air from Various Microenvironments in Guangzhou, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Collection
2.2. Chemicals and Materials
2.3. Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.4. Quality Assurance/Quality Control
2.5. Exposure and Risk Assessment
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Total Concentrations and Profiles of OPEs in Indoor Air from China Homes, Offices, and Student Dormitories
3.2. Total Concentrations and Profiles of OPEs in Indoor Air of Private Cars from China
3.3. Exposure Levels and Health Risks of OPEs in Four Indoor Environments for Different Populations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, J.; Ye, L.; Fang, M.; Su, G. Industrial Production of Organophosphate Flame Retardants (OPFRs): Big Knowledge Gaps Need to Be Filled? Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekele, T.G.; Zhao, H.; Yang, J.; Chegen, R.G.; Chen, J.; Mekonen, S.; Qadeer, A. A review of environmental occurrence, analysis, bioaccumulation, and toxicity of organophosphate esters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 49507–49528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Fu, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Ye, T.; Gao, K.; Pan, W.; Zhang, A.; Fu, J. Long-Range Transport, Trophic Transfer, and Ecological Risks of Organophosphate Esters in Remote Areas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10192–10209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Guo, C.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Sun, S.; Xu, J. Spatial distribution, receptor modelling and risk assessment of organophosphate esters in surface water from the largest freshwater lake in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 238, 113618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, S.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y. Critical review on organophosphate esters in water environment: Occurrence, health hazards and removal technologies. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 343, 123218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Shen, C. Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Organophosphate Esters in Surface Soils of China. Toxics 2024, 12, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Jimenez, J.; Cuny, P.; Militon, C.; Sylvi, L.; Royer, F.; Papillon, L.; Sempere, R. Effective degradation of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in coastal sediments under high urban pressure. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Castro-Jimenez, J.; Kallenborn, R.; Liao, C.; Mi, W.; Lohmann, R.; Vila-Costa, M.; Dachs, J. Organophosphate ester pollution in the oceans. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, S.; Medley, E.A.; Naidu, M.; Trasande, L.; Ghassabian, A. Exposure to organophosphate esters and maternal-child health. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, A.; Alhujaily, M. Molecular Mechanism of Indoor Exposure to Airborne Halogenated Flame Retardants TCIPP (Tris(1,3-Dichloro-2-Propyl) Phosphate) and TCEP Tris(2-chloroethyl) Phosphate and Their Hazardous Effects on Biological Systems. Metabolites 2024, 14, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, C.; Sun, H.; Matsiko, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Meng, W.; et al. Temporal variations of PM2.5-bound organophosphate flame retardants in different microenvironments in Beijing, China, and implications for human exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharska, A.; Cequier, E.; Thomsen, C.; Becher, G.; Covaci, A.; Voorspoels, S. Assessment of human hair as an indicator of exposure to organophosphate flame retardants. Case study on a Norwegian mother-child cohort. Environ. Int. 2015, 83, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Guo, J.-Q.; Liu, L.-Y.; Sverko, E.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, C.-G.; Huo, C.-Y.; Li, H.-L.; Ma, W.-L.; Zhang, Z.-F.; et al. Seasonal variation and influence factors of organophosphate esters in air particulate matter of a northeastern Chinese test home. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, U.-J.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of and human exposure to organophosphate flame retardants/plasticizers in indoor air and dust from various microenvironments in the United States. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergh, C.; Torgrip, R.; Emenius, G.; Ostman, C. Organophosphate and phthalate esters in air and settled dust—A multi-location indoor study. Indoor Air 2011, 21, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, R.E.; Van den Eede, N.; Covaci, A.; Perovich, L.J.; Brody, J.G.; Rudel, R.A. Urinary Biomonitoring of Phosphate Flame Retardants: Levels in California Adults and Recommendations for Future Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13625–13633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.-W.; Li, Y.-Z.; Xiang, P.; Li, C.; Cui, X.-Y.; Ma, L.Q. Impact of particle size on distribution and human exposure of flame retardants in indoor dust. Environ. Res. 2018, 162, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Van den Eede, N.; Dirtu, A.C.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Assessment of human exposure to indoor organic contaminants via dust ingestion in Pakistan. Indoor Air 2012, 22, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brommer, S.; Harrad, S. Sources and human exposure implications of concentrations of organophosphate flame retardants in dust from UK cars, classrooms, living rooms, and offices. Environ. Int. 2015, 83, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandsma, S.H.; de Boer, J.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Leonards, P.E.G. Organophosphorus flame retardants (PFRs) and plasticizers in house and car dust and the influence of electronic equipment. Chemosphere 2014, 116, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddam, A.; Herkert, N.; Stapleton, H.M.; Volz, D.C. Partial dust removal in vehicles does not mitigate human exposure to organophosphate esters. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yang, K.; Li, J.; Zeng, X.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, G. An assessment of polyurethane foam passive samplers for atmospheric metals compared with active samplers. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J. Theory and Concentration Calculations of PUF Atmospheric Passive Sampling Technique for Persistent Organic Pollutants. Environ. Monit. China 2012, 28, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, G.; Chen, Z.; Feng, J.; Ji, W.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, K.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, X. Organophosphate esters in total suspended particulates of an urban city in East China. Chemosphere 2016, 164, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Yue, C.; Tang, J.; Lin, M.; Zhuo, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; An, T. Occurrence and distribution of typical semi-volatile organic chemicals (SVOCs) in paired indoor and outdoor atmospheric fine particle samples from cities in southern China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, F.; Rodgers, T.F.M.; Hou, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, X. Ornamental houseplants as potential biosamplers for indoor pollution of organophosphorus flame retardants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Hiltscher, M.; Gruber, D.; Puettmann, W. Organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs) in indoor and outdoor air in the Rhine/Main area, Germany: Comparison of concentrations and distribution profiles in different microenvironments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 10992–11005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staaf, T.; Ostman, C. Organophosphate triesters in indoor environments. J. Environ. Monit. 2005, 7, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, I.C.; Devi, N.L.; Kumar, A.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Airborne brominated, chlorinated and organophosphate ester flame retardants inside the buildings of the Indian state of Bihar: Exploration of tag source and human exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, M.A.; Lohmann, R. Organophosphate flame retardants in the indoor and outdoor dust and gas-phase of Alexandria, Egypt. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wang, X.; Phong, T.; Baduel, C.; Gallen, C.; Banks, A.; Bainton, P.; English, K.; Mueller, J.F. Organophosphate and brominated flame retardants in Australian indoor environments: Levels, sources, and preliminary assessment of human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okeme, J.O.; Yang, C.; Abdollahi, A.; Dhal, S.; Harris, S.A.; Jantunen, L.M.; Tsirlin, D.; Diamond, M.L. Passive air sampling of flame retardants and plasticizers in Canadian homes using PDMS, XAD-coated PDMS and PUF samplers. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.; Xie, Z.; Song, T.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mi, W.; Peng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, S.; Ebinghaus, R. Occurrence and dry deposition of organophosphate esters in atmospheric particles over the northern South China Sea. Chemosphere 2015, 127, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, F.; Li, Q.; Zhao, H.; Xie, Q.; Chen, J. Polyurethane heat preservation materials: The significant sources of organophosphorus flame retardants. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumura, M.; Hatayama, R.; Tatsu, K.; Naito, T.; Takeda, T.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Masunaga, S. Organophosphate flame retardants in the indoor air and dust in cars in Japan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, P.C.; Bürgi, D.; Giger, W. Organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in indoor air. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Lv, K.; Gao, W.; Fu, J.; Wu, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G. Presence and human exposure assessment of organophosphate flame retardants (OPEs) in indoor dust and air in Beijing, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compounds | DF (%) | Mean | Percentile | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 25th | 50th | 75th | 90th | Max | |||
| TBP | 45.2 | 0.95 | ND | <MDL | <MDL | 1.02 | 2.59 | 16.15 |
| TCEP | 100 | 18.01 | 0.27 | 2.16 | 11.71 | 30.92 | 42.65 | 92.20 |
| TCPP | 100 | 14.52 | 0.10 | 3.74 | 7.26 | 13.90 | 36.26 | 108.36 |
| TDCPP | 88.7 | 0.96 | ND | 0.67 | 0.85 | 1.11 | 1.61 | 6.86 |
| TBEP | 25.8 | 0.29 | ND | <MDL | <MDL | 0.50 | 1.01 | 3.39 |
| TPHP | 98.4 | 2.61 | ND | 0.31 | 1.26 | 2.51 | 6.06 | 43.18 |
| DPEHP | 98.4 | 0.58 | ND | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.40 | 0.94 | 11.51 |
| TEHP | 62.9 | 0.70 | ND | <MDL | 0.36 | 0.52 | 1.84 | 8.79 |
| Σ8OPEs | 100 | 38.62 | 2.99 | 14.88 | 32.78 | 52.11 | 71.12 | 200.76 |
| Compounds | DF (%) | Mean | Percentile | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 25th | 50th | 75th | 90th | Max | |||
| TBP | 75% | 12.12 | ND | 0.0076 | 3.68 | 12.95 | 37.73 | 89.6 |
| TCEP | 95% | 22.36 | ND | 9.25 | 14.04 | 33.24 | 47.82 | 105.99 |
| TCPP | 100% | 180.33 | 0.06 | 17.78 | 75.52 | 242.96 | 540.17 | 1087.38 |
| TDCPP | 91.7% | 30.84 | ND | 1.19 | 3.66 | 7.05 | 15.00 | 827.49 |
| TBEP | 21.7% | 7.36 | ND | <MDL | <MDL | <MDL | 38.60 | 72.86 |
| TPHP | 93.3% | 5.65 | ND | 0.64 | 1.85 | 5.07 | 10.03 | 108.8 |
| DPEHP | 73.7% | 3.30 | ND | <MDL | 0.83 | 8.60 | 8.87 | 22.94 |
| TEHP | 71.7% | 2.61 | ND | <MDL | 0.87 | 2.99 | 4.16 | 70.21 |
| TPEP | 11.7% | 0.31 | ND | <MDL | <MDL | <MDL | 1.25 | 3.81 |
| Σ9OPEs | 100% | 264.89 | 1.22 | 71.79 | 165.58 | 369.65 | 702.25 | 1288.81 |
| Infants | TBP | TCEP | TCPP | TDCPP | TPHP | DPEHP | TEHP | ΣOPEs |
| Mean | 0.73 | 15.13 | 11.26 | 0.76 | 0.29 | 2.35 | 0.5 | 30.85 |
| P5 | 0.02 | 2.78 | 1.15 | 0.16 | 0 | 0.75 | 0.02 | 7.42 |
| P50 | 0.26 | 10.66 | 6.32 | 0.51 | 0.01 | 1.97 | 0.18 | 23.15 |
| P95 | 2.71 | 42.13 | 37.08 | 1.62 | 0.74 | 5.17 | 1.96 | 79.18 |
| Toddlers | TBP | TCEP | TCPP | TDCPP | TPHP | DPEHP | TEHP | ΣOPEs |
| Mean | 0.39 | 7.77 | 5.61 | 0.38 | 0.15 | 1.19 | 0.27 | 15.89 |
| P5 | 0.01 | 1.54 | 0.63 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.44 | 0.01 | 4.25 |
| P50 | 0.14 | 5.61 | 3.32 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 1.03 | 0.09 | 12.05 |
| P95 | 1.45 | 21.09 | 17.85 | 0.77 | 0.41 | 2.48 | 1.02 | 39.91 |
| Children | TBP | TCEP | TCPP | TDCPP | TPHP | DPEHP | TEHP | ΣOPEs |
| Mean | 0.45 | 2.69 | 7.55 | 0.94 | 0.44 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 12.41 |
| P5 | 0.09 | 0.97 | 2.08 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 4.74 |
| P50 | 0.31 | 2.24 | 5.79 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 10.34 |
| P95 | 1.25 | 5.94 | 18.92 | 1.66 | 0.96 | 0.36 | 0.35 | 27.39 |
| Adolescents | TBP | TCEP | TCPP | TDCPP | TPHP | DPEHP | TEHP | ΣOPEs |
| Mean | 0.32 | 1.94 | 5.55 | 0.66 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 8.86 |
| P5 | 0.06 | 0.71 | 1.53 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 3.43 |
| P50 | 0.22 | 1.6 | 4.2 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.1 | 0.06 | 7.37 |
| P95 | 0.86 | 4.26 | 13.6 | 1.18 | 0.68 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 19.12 |
| Adults | TBP | TCEP | TCPP | TDCPP | TPHP | DPEHP | TEHP | ΣOPEs |
| Mean | 0.29 | 3.37 | 4.27 | 0.48 | 0.18 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 9.1 |
| P5 | 0.06 | 1.16 | 1.09 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 3.63 |
| P50 | 0.2 | 2.78 | 3.28 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 7.9 |
| P95 | 0.8 | 7.51 | 10.69 | 0.81 | 0.46 | 0.76 | 0.39 | 18.59 |
| Compounds | Non-Carcinogenic Risk Quotient a (×10−4) | Carcinogenic Risk Index b (×10−6) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infants | Toddlers | Children | Adolescents | Adults | Infants | Toddlers | Children | Adolescents | Adults | |
| TBP | 0.73 | 0.39 | 0.45 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.0066 | 0.0035 | 0.0041 | 0.0029 | 0.0026 |
| TCEP | 21.61 | 11.10 | 3.84 | 2.77 | 4.81 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.054 | 0.039 | 0.067 |
| TCPP | 11.26 | 5.61 | 7.71 | 5.55 | 4.27 | - | - | - | - | - |
| TDCPP | 0.38 | 0.19 | 0.47 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 0.024 | 0.012 | 0.029 | 0.020 | 0.015 |
| TPHP | 0.041 | 0.021 | 0.063 | 0.044 | 0.026 | - | - | - | - | - |
| TEHP | 0.050 | 0.027 | 0.013 | 0.009 | 0.013 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Σ6OPEs | 34.08 | 17.34 | 12.55 | 9.02 | 9.65 | 0.33 | 0.17 | 0.087 | 0.062 | 0.085 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Y.; Xu, M.; Ouyang, M.; Wu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zheng, K.; Ren, G. Concentrations, Compositions and Human Exposure Risks to Organophosphate Esters in Indoor Air from Various Microenvironments in Guangzhou, China. Toxics 2025, 13, 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070531
Cai Y, Xu M, Ouyang M, Wu Y, Wang R, Zheng K, Ren G. Concentrations, Compositions and Human Exposure Risks to Organophosphate Esters in Indoor Air from Various Microenvironments in Guangzhou, China. Toxics. 2025; 13(7):531. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070531
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Yunmei, Maoyuan Xu, Minghui Ouyang, Yusheng Wu, Ruijie Wang, Kewen Zheng, and Guofa Ren. 2025. "Concentrations, Compositions and Human Exposure Risks to Organophosphate Esters in Indoor Air from Various Microenvironments in Guangzhou, China" Toxics 13, no. 7: 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070531
APA StyleCai, Y., Xu, M., Ouyang, M., Wu, Y., Wang, R., Zheng, K., & Ren, G. (2025). Concentrations, Compositions and Human Exposure Risks to Organophosphate Esters in Indoor Air from Various Microenvironments in Guangzhou, China. Toxics, 13(7), 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070531