Toxic Effects of p-Chloroaniline on Cells of Fungus Isaria fumosorosea SP535 and the Role of Cytochrome P450
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Growth Medium
2.2. Preparation of Fungal Conidia Inoculum
2.3. Determination of PCA Degradation Capacity by Isaria fumonorosea SP535
2.4. Optimization Studies of Isolated Isaria fumosorosea SP535
2.5. Estimation of Biomass
2.6. Determination of Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenase
2.7. Sample Preparation for Scanning Electron Microscopy and Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.8. Chemical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
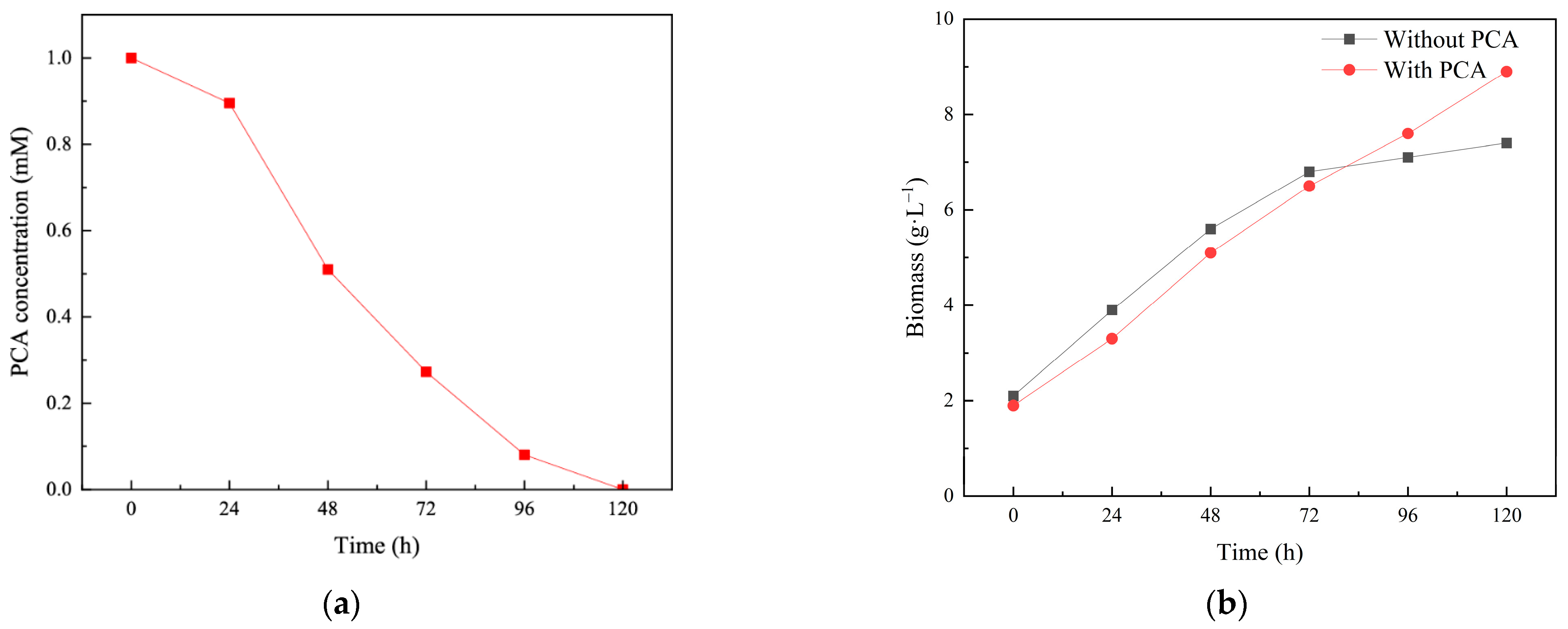
3.1. The PCA Biodegradation by SP353
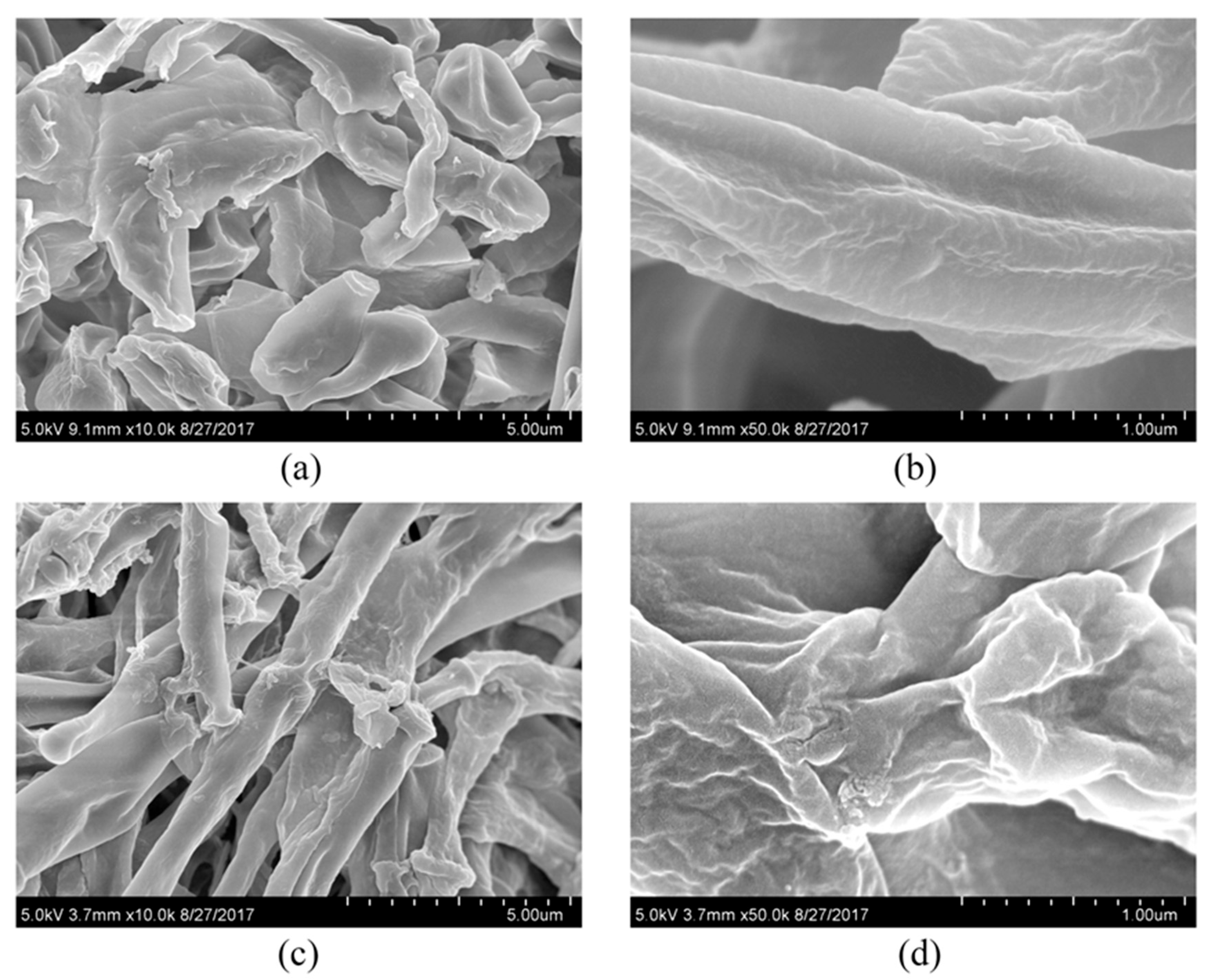
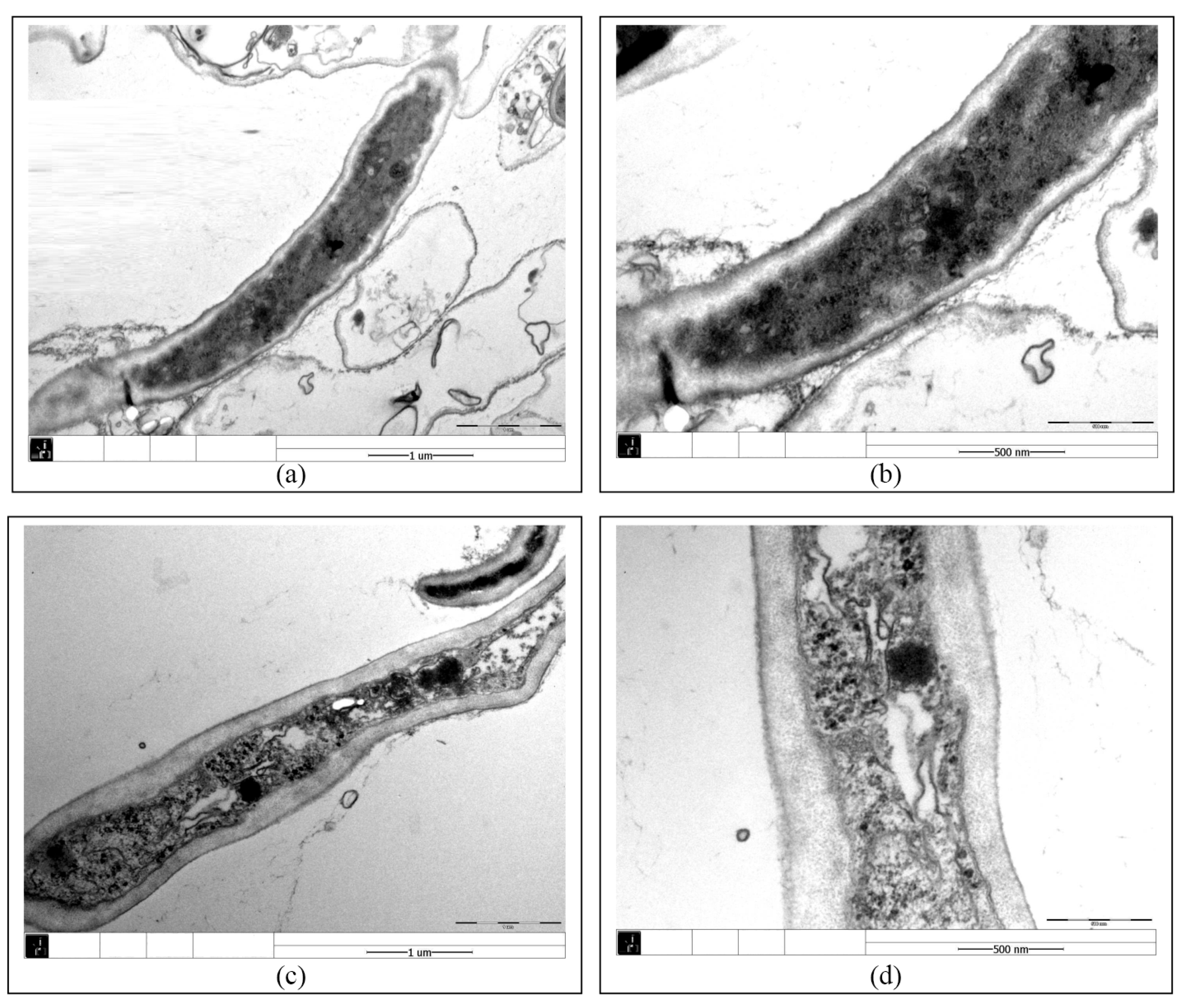
3.2. Effect of PCA on the Growth and Cellular Structure of Isaria fumosorosea SP535
3.3. Factors Affecting PCA Degradation by SP353
3.3.1. Effects of Initial PCA Concentrations on Biodegradation
3.3.2. Effects of pH on Biodegradation
3.3.3. Effects of Temperature on Biodegradation
3.4. Potential Mechanism of PCA Degradation by Isaria fumosorosea SP535
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khusnun, N.F.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; N. Jusoh, W.C.; Johariab, A.; Kidamab, K. Interaction between copper and carbon nanotubes triggers their mutual role in the enhanced photodegradation of p-chloroaniline. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 12323–12331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silambarasan, S.; Vangnai, A.S. Biodegradation of 4-nitroaniline by plant-growth promoting Acinetobacter sp. AVLB2 and toxicological analysis of its biodegradation metabolites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Dai, X.; Xu, X.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Zhu, L. Evolution and functional analysis of extracellular polymeric substances during the granulation of aerobic sludge used to treat p-chloroaniline wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongarun, R.; Luepromchai, E.; Vangnai, A.S. Natural attenuation, biostimulation, and bioaugmentation in 4-chloroaniline-contaminated soil. Curr. Microbiol. 2008, 56, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Lv, M.; Dai, X.; Xu, X.; Qi, H.; Yu, Y. Reaction kinetics of the degradation of chloroanilines and aniline by aerobic granule. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 68, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzger, D.D.; Jonsson, C.M.; Aoyama, H. Mixtures of diflubenzuron and p-chloroaniline changes the activities of enzymes biomarkers on tilapia fish (Oreochromis niloticus) in the presence and absence of soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisana, N.; Oku, S.; Kudo, D.; Nakashimada, Y.; Tajima, T.; Vangnai, A.S.; Kato, J. Degradation of chloroanilines by toluene dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida T57. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 117, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Mahajan, R.; Saini, H.S. Evaluating metabolic potential of Thauera sp. M9 for the transformation of 4-chloroaniline (4-CA). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 101768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Miao, J.; Pan, L.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wu, J. Toxicity effects of p-choroaniline on the growth, photosynthesis, respiration capacity and antioxidant enzyme activities of a diatom, Phaeodactylum tricornutu. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, G. Cometabolic degradation of p-chloroaniline by the genus Brevibacillus bacteria with extra carbon sources. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolin, C.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Chitra, B.; Jackulin, C.F.; Ramamurthy, R. Stimulation of Bacillus sp. by lipopeptide biosurfactant for the degradation of aromatic amine 4-Chloroaniline. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleine, C.; Stajich, J.E.; Selbmann, L. Fungi are key players in extreme ecosystems. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2023, 37, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.K.; Raut, S.; Bandyopadhyay, P.; Raut, S. Fungal decolouration and degradation of azo dyes: A review. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2016, 30, 112–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Megharaj, M.; Wu, C.; Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Dai, C. Endophyte-assisted phytoremediation: Mechanisms and current application strategies for soil mixed pollutants. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Kong, D.; Ma, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Z.; Parales, R.E.; Ruan, Z. Biodegradation of tetracycline antibiotics by the yeast strain Cutaneotrichosporon dermatis M503. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Lai, B.; Niu, D.; Wang, Z.; Hardie, W.J.; Zhi, J.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Taoli, H.; Li, Z.; et al. Characterization of erythromycin-degrading strain Aspergillus sydowii W1 revealed by transcriptome analyses. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2023, 178, 105545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čvančarov, M.; Křesinov, Z.; Filipová, l.; Covino, S.; Cajthaml, T. Biodegradation of PCBs by ligninolytic fungi and characterization of the degradation products. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Črešnar, B.; Petrič, Š. Cytochrome P450 enzymes in the fungal kingdom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1814, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, G.A.L.; Magrini, M.J.; Bonugli-Santos, R.C.; Rodrigues, M.V.N.; Sette, L.D. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degradation by marine-derived basidiomycetes: Optimization of the degradation process. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho-Moreira, J.S.; Bracht, A.; Souza, A.C.S.; Oliveira, R.F.; Sá-Nakanishi, A.B.; Souza, C.G.M.; Peralta, R.M. Degradation of diuron by Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Role of ligninolytic enzymes and cytochrome P450. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 251354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Karuppiah, V.; Li, Y.; Pandian, S.; Kumaran, S.; Chen, J. Role of cytochrome P450 genes of Trichoderma atroviride T23 on the resistance and degradation of dichlorvos. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J. Studies on the Extraction, Characterization and Toxicity of Toxins Produced by Different Isolates of Entomopathogenic Fungus Isaria fumosorosea. Master’s Thesis, South China Agriculture University, Guangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Różalska, S.; Szewczyk, R.; Długoński, J. Biodegradation of 4-n-nonylphenol by the non-ligninolytic filamentous fungus Gliocephalotrichum simplex: A proposal of a metabolic pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Huang, Z.; Ren, S. Media composition influences on growth, enzyme activity, and virulence of the entomopathogen hyphomycete Isaria fumosorosea. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2009, 131, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Bashir, M.H.; Ren, S.; Huang, Z. The effect of alkanes on the physiology and metabolism of the entomopathogenic fungus, Isaria fumosorosea. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováč, L.; Bednárová, H.; Greksák, M. Oxidative phosphorylation in yeast I. Isolation and properties of phosphorylating mitochondria from stationary phase cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1968, 153, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauersberger, S.; Matyashova, R.N.; Müller, H.G.; Losinov, A.B. Influence of the growth substrate and the oxygen concentration in the medium on the cytochrome P-450 content in Candida guilliermondii. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1980, 9, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estabrook, R.W.; Werringloer, J. The measurement of difference spectra: Application to the cytochromes of microsomes. Methods Enzymol. 1978, 52, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, E.S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 17, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różalska, S.; Glińska, S.; Długoński, J. Metarhizium robertsii morphological flexibility during nonylphenol removal. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 95, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Du, X. Degradation of p-chloroaniline by persulfate activated with zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 203, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, D.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y. Biodegradation of 2-chloroaniline, 3-chloroaniline, and 4-chloroaniline by a novel strain Delftia tsuruhatensis H1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongsawat, P.; Vangnai, A.S. Biodegradation pathways of chloroanilines by Acinetobacter baylyi strain GFJ2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzikova, I.; Rybalchenko, O.; Kurashov, E.; Krylova, Y.; Safronova, V.; Medvedeva, N. Defense responses of the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus tubingensis to alkylphenols stress. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2020, 231, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soboń, A.; Szewczyk, R.; Różalska, S.; Długoński, J. Metabolomics of the recovery of the filamentous fungus Cunninghamella echinulata exposed to tributyltin. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 127, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sang, C.; Xie, S.; Huang, J. Toxicity of perfluorooctane sulfonate on Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Growth, pollutant degradation and transcriptomics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncic, M.K.; Kogej, T.; Drobne, D.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Morphological response of the halophilic fungal genus Wallemia to high salinity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vangnai, A.S.; Petchkroh, W. Biodegradation of 4-chloroaniline by bacteria enriched from soil. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 268, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, X.; Shen, L.; Li, J.; Yu, R.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, G.; Zeng, W. Whole genome sequencing and comparative genomics analyses of Pandoraea sp. XY-2, a new species capable of biodegrade tetracycline. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Li, Z.; Yan, J. Isolation, identification and degradation characterization of a p-chloroaniline degrading strain. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 86, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkie, M.P.; Tessier, L.R.; Boogaard, M.; O’Connor, L.; Birceanu, O.; Steeves, T.B.; Sullivan, W.P. Lampricide bioavailability and toxicity to invasive sea lamprey and non-target fishes: The importance of alkalinity, pH, and the gill microenvironment. J. Great Lakes Res. 2021, 47, S407–S420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Zhao, D.; Wang, H.; Wei, T. Residues and bioavailability of neonicotinoid pesticide in shaanxi agricultural soil. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2023, 234, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Suo, Y.; Li, C. Impacts of elevated temperature on morphology, oxidative stress levels, and testosterone synthesis in ex vivo cultured porcine testicular tissue. Theriogenology 2023, 212, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gorcom, R.F.M.; van den Hondel, C.A.; Punt, P.J. Cytochrome P450 enzyme systems in fungi. Fungal Genet. Biol. 1988, 23, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lah, L.; Krasevec, N.; Trontelj, P.; Komel, R. High diversity and complex evolution of fungal cytochrome P450 reductase: Cytochrome P450 systems. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2008, 45, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrendorff, J.B.Y.H. Reductive cytochrome P450 reactions and their potential role in bioremediation. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 649273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hawash, A.B.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Ghalib, H.B.; Zhang, X.; Ma, F. Biodegradation of n-hexadecane by Aspergillus sp. RFC-1 and its mechanism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Lin, C.; Chen, S.; Chuang, C.; Chou, T.; Ko, C.; Chou, P.; Liu, C.; Shih, Y. The degradation mechanisms of Rhodopseudomonas palustris toward hexabromocyclododecane by time-course transcriptome analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 130489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Xie, L.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; Han, Z.; Wu, X.; Mo, W.; Wen, C.; Gao, Y.; Wan, T.; et al. The removal of butachlor from soil by wastewater-derived Rhodopseudomonas marshes. Soil. Use Manag. 2012, 36, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Cell-Free Extract | Microsomal Fraction |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.02 ± 0.00 b | 0.03 ± 0.01 b |
| PCA | 0.31 ± 0.02 a | 0.84 ± 0.04 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; Gao, J.; Zhou, L.; Gao, L.; Song, M.; Zeng, Q. Toxic Effects of p-Chloroaniline on Cells of Fungus Isaria fumosorosea SP535 and the Role of Cytochrome P450. Toxics 2025, 13, 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060506
Huang S, Gao J, Zhou L, Gao L, Song M, Zeng Q. Toxic Effects of p-Chloroaniline on Cells of Fungus Isaria fumosorosea SP535 and the Role of Cytochrome P450. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):506. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060506
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shicong, Jiahui Gao, Lin Zhou, Liujian Gao, Mengke Song, and Qiaoyun Zeng. 2025. "Toxic Effects of p-Chloroaniline on Cells of Fungus Isaria fumosorosea SP535 and the Role of Cytochrome P450" Toxics 13, no. 6: 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060506
APA StyleHuang, S., Gao, J., Zhou, L., Gao, L., Song, M., & Zeng, Q. (2025). Toxic Effects of p-Chloroaniline on Cells of Fungus Isaria fumosorosea SP535 and the Role of Cytochrome P450. Toxics, 13(6), 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060506





