Spatial Variation Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Derivatives in Surface Water of Suzhou City: Occurrence, Sources, and Risk Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Reagents and Instruments
2.3. Pretreatment and Instrumental Conditions
2.3.1. Water Sample Pretreatment
2.3.2. Instrumental Parameters
2.4. Quality Assurance and Control
2.5. Source Identification and Risk Assessment
2.5.1. PCA and Isomer Ratios
2.5.2. Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
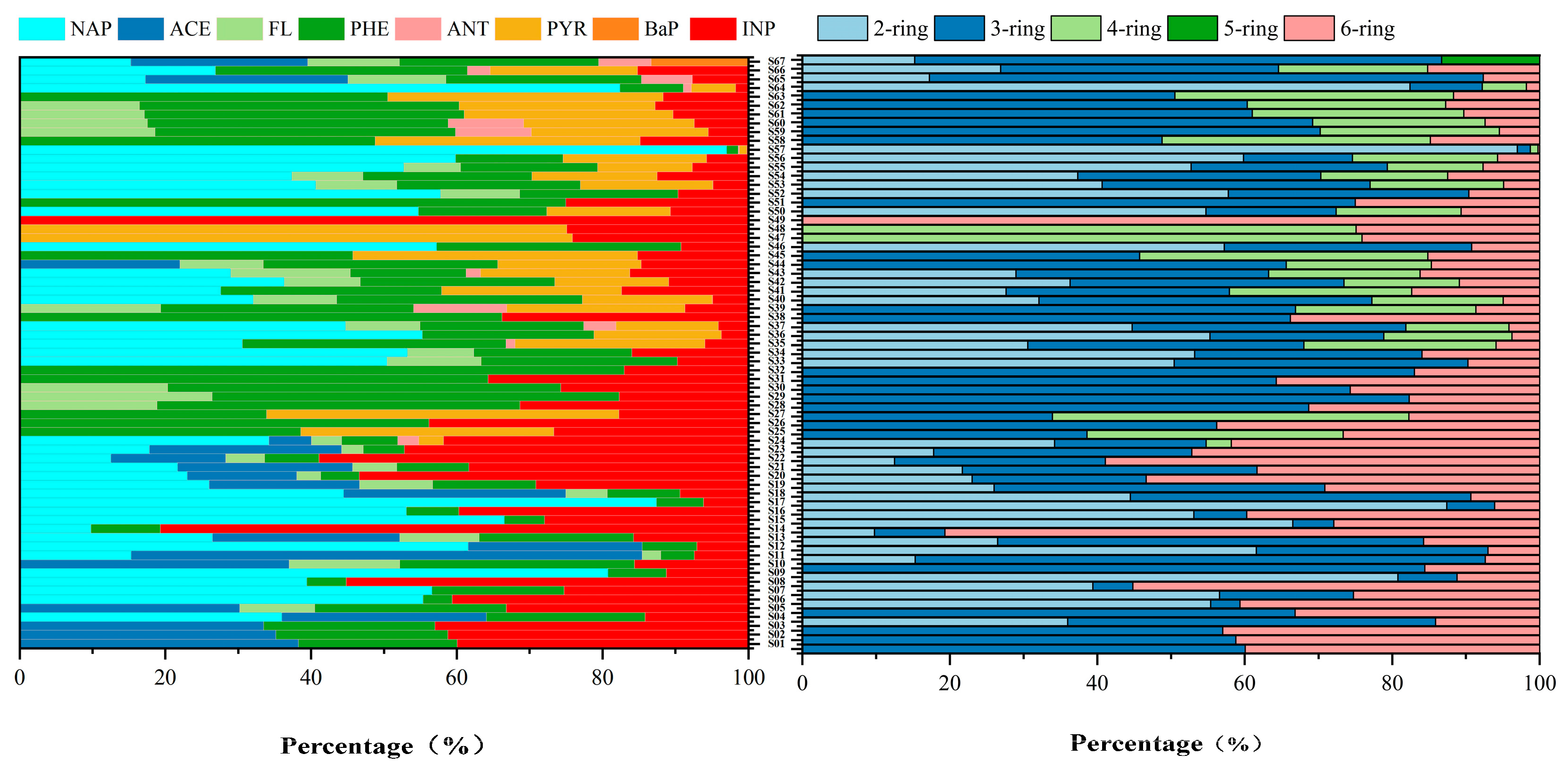
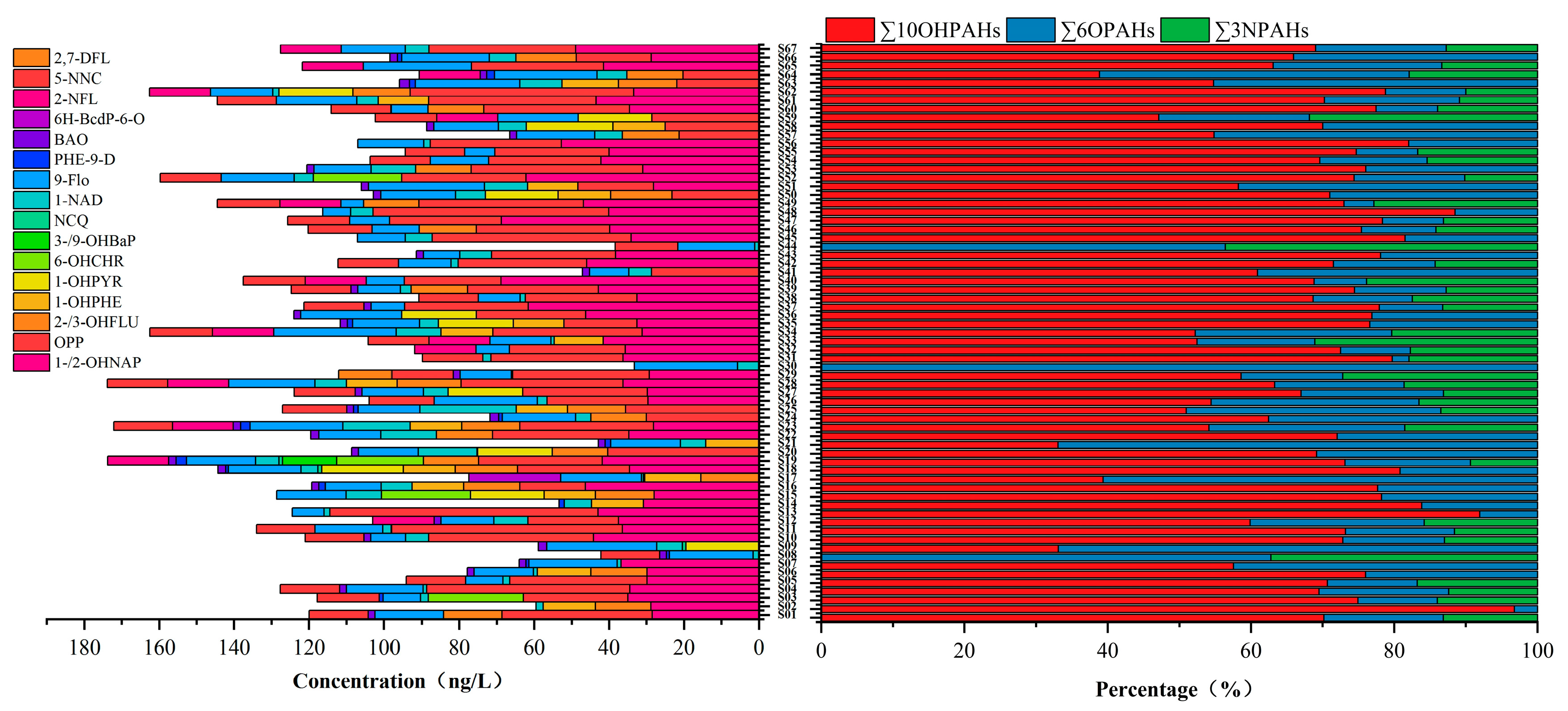
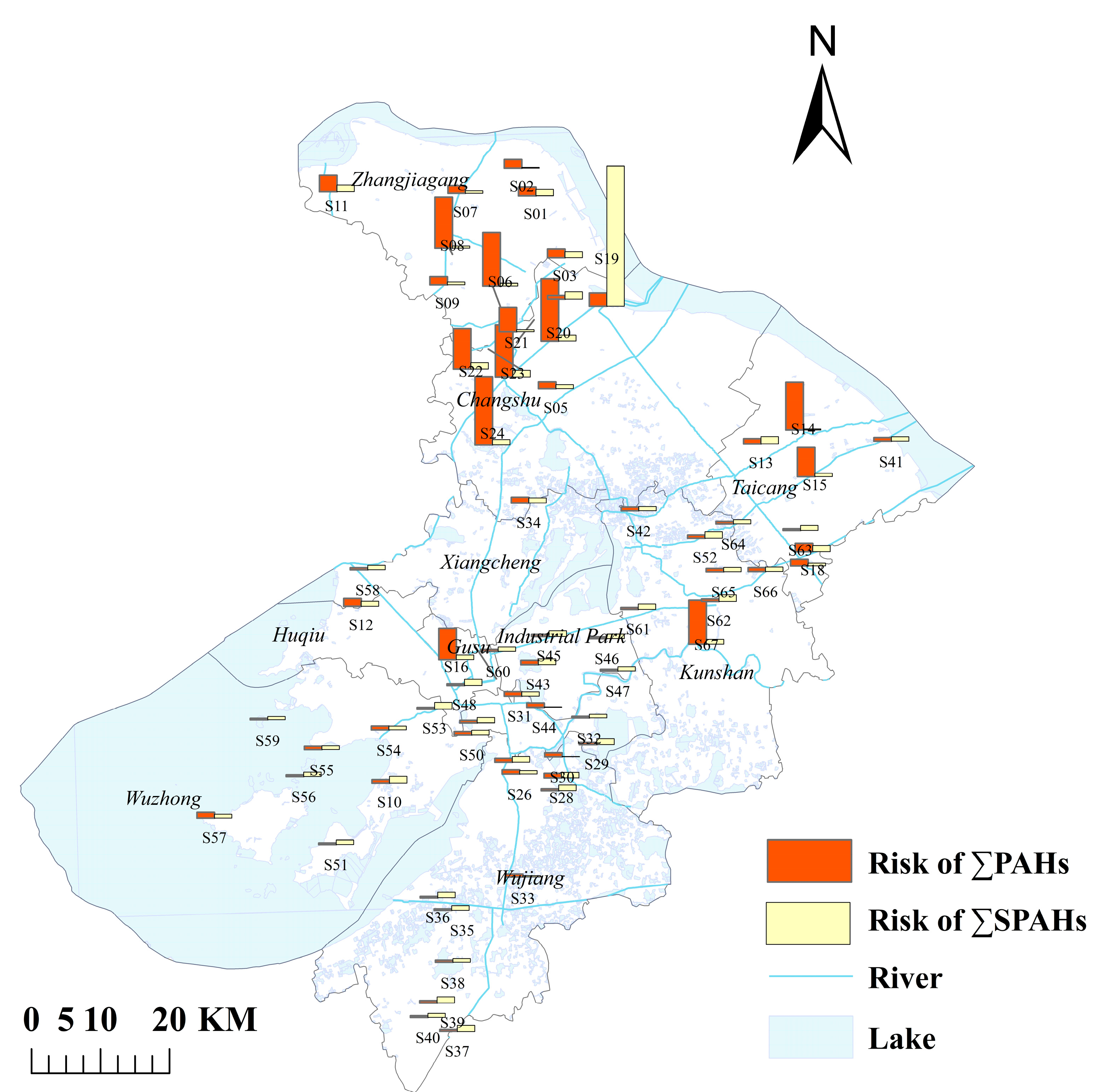
3.1. Occurrence and Spatial Distribution of PAHs and SPAHs in Surface Water
3.2. Compositional Characteristics of PAHs and SPAHs
3.3. Source Apportionment of PAHs and SPAHs
3.3.1. PCA
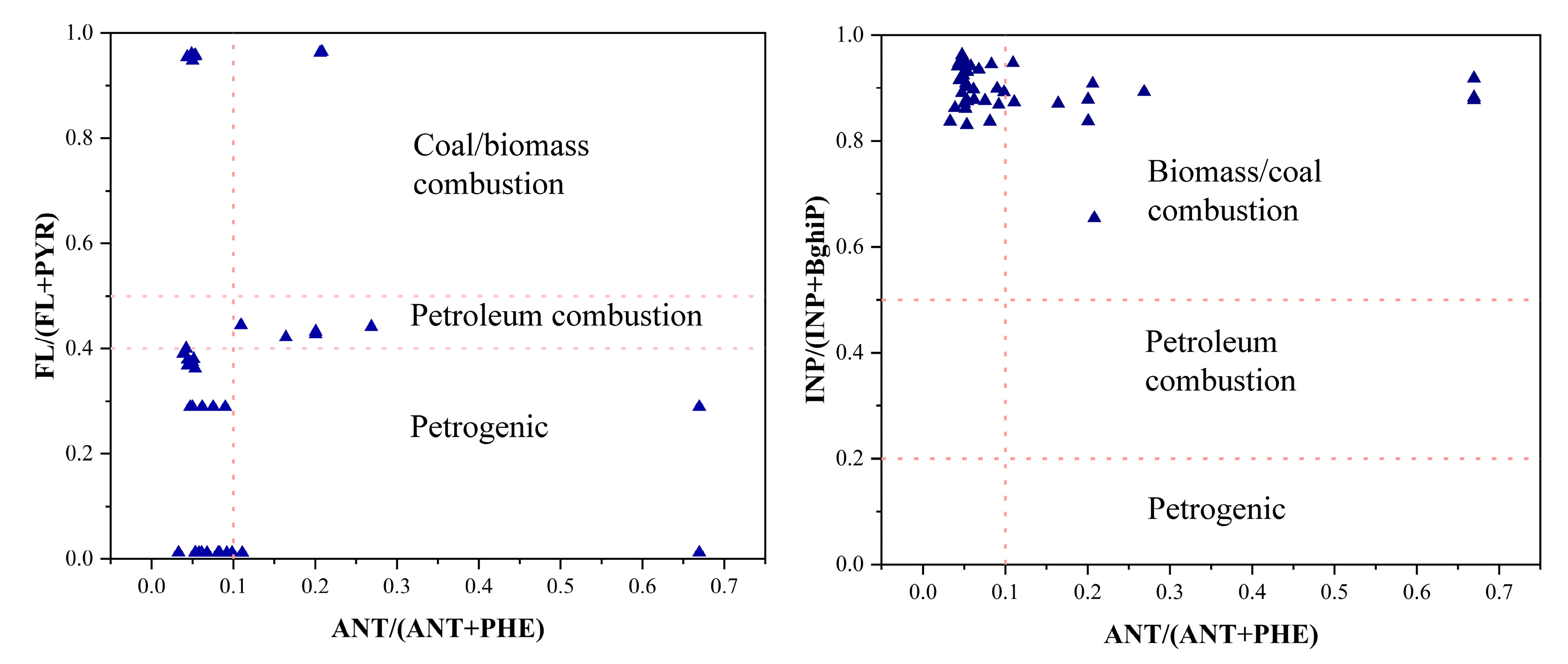
3.3.2. Diagnostic Ratio
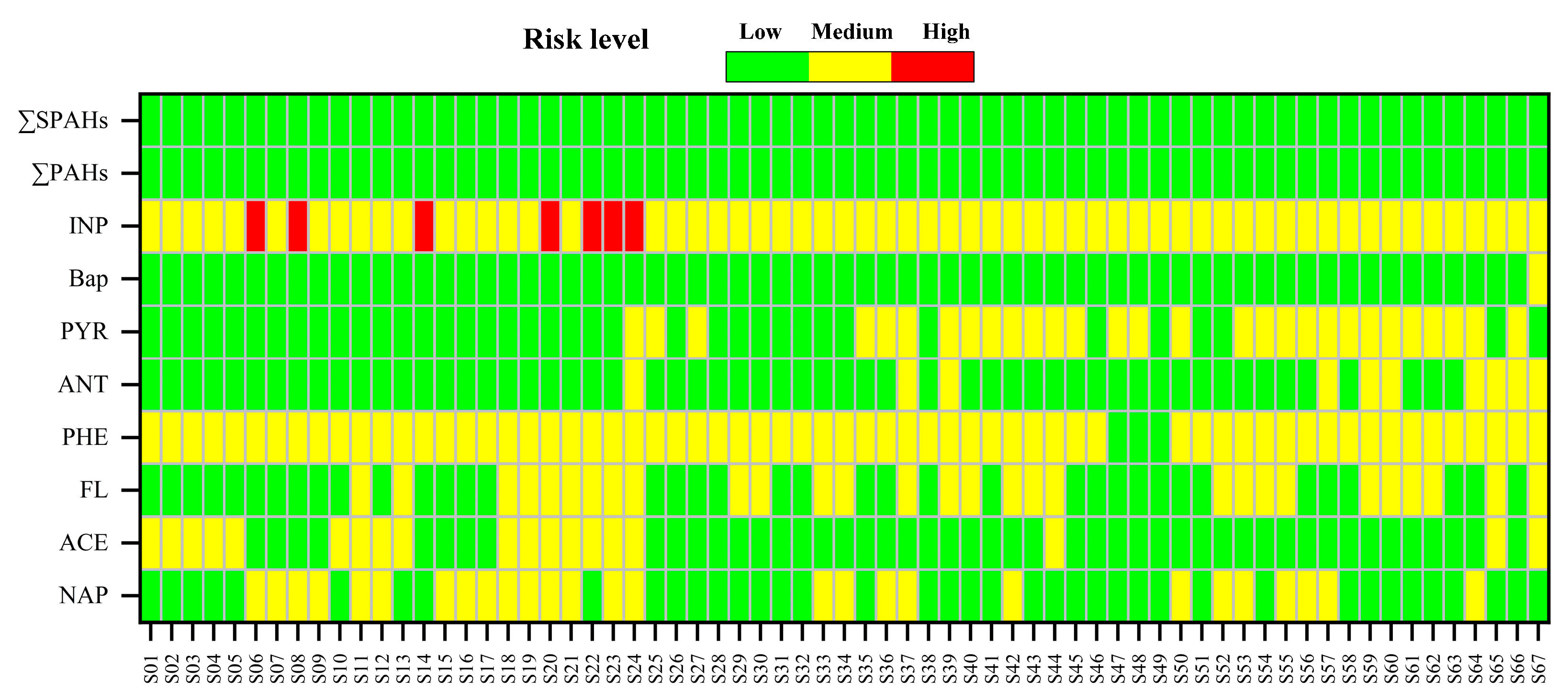
3.4. Ecological and Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Time (min) | Left Pump | Right Pump | Position | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 (%) | B1 (%) | Flow Rate (mL/min) | A2 (%) | B2 (%) | Flow Rate (mL/min) | ||
| −6.0 | 100 | 0 | 4.0 | 60 | 40 | 0.4 | 1 |
| 0.0 | 100 | 0 | 4.0 | 60 | 40 | 0.4 | 1 |
| 0.1 | 98 | 2 | 0.5 | 60 | 40 | 0.4 | 1 |
| 5.0 | 98 | 2 | 0.5 | 60 | 40 | 0.4 | 2 |
| 12.0 | 95 | 5 | 0.5 | - | - | - | 1 |
| 12.5 | 5 | 95 | 2.0 | - | - | - | 1 |
| 18.0 | 5 | 95 | 2.0 | 0 | 100 | 0.4 | 1 |
| 25.0 | 5 | 95 | 2.0 | 0 | 100 | 0.4 | 1 |
| 25.1 | 100 | 0 | 4.0 | 60 | 40 | 0.4 | 1 |
| 29.0 | 100 | 0 | 4.0 | 60 | 40 | 0.4 | 1 |
| PAHs | Water (ng/L) | |
|---|---|---|
| CQV(NCS) | CQV(MPCS) | |
| Nap | 12 | 1200 |
| Ace | 0.7 | 70 |
| Fl | 0.7 | 70 |
| Phe | 3 | 300 |
| Ant | 0.7 | 70 |
| Flu | 3 | 300 |
| Pyr | 0.7 | 70 |
| BaA | 0.1 | 10 |
| ChR | 3.4 | 340 |
| BbF | 0.1 | 10 |
| BkF | 0.4 | 40 |
| BaP | 0.5 | 50 |
| Inp | 0.4 | 40 |
| DBA | 0.5 | 50 |
| Bghip | 0.3 | 30 |
| Individual PAHs | ∑PAHs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Level | RQ(NCS) | RQ(MPCs) | Risk Level | RQ(NCS) | RQ(MPCs) |
| Low risk | 0 | <1 | No risk | 0 | <1 |
| Low risk | 1–800 | <1 | |||
| Medium risk | ≥1 | <1 | Medium risk 1 | ≥800 | <1 |
| Medium risk 2 | <800 | ≥1 | |||
| High risk | ≥1 | High risk | ≥800 | ≥1 | |
| PAH | TEF | PNEC (ng/L) | SF | SPAH | PNEC (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BaP | 1.0 | 0.7 | 7.3 | 1-/2-OHNAP | 100.0 |
| OPP | 50 | ||||
| INP | 0.1 | 3.0 | 0.73 | 2-/3-OHFLU | 200.0 |
| 1-OHPHE | 150.0 | ||||
| ACE | 0.01 | 50.0 | 0.073 | 6-OHCHR | 80.0 |
| 1-OHPYR | 50.0 | ||||
| PHE | 0.001 | 100.0 | 0.0073 | 3-/9-OHBaP | 1.0 |
| 9-FLo | 80.0 | ||||
| ANT | 0.01 | 80.0 | 0.073 | PHE-9-D | 200.0 |
| 6H-BcdP-6-O | 10.0 | ||||
| PYR | 0.001 | 150.0 | 0.0073 | 5-NNC | 20.0 |
| 2-NFL | 25.0 | ||||
| FL | 0.001 | 600.0 | 0.00073 | 2,7-DFL | 15.0 |
| 1-NAD | 300.0 | ||||
| NAP | 0.001 | 1000.0 | 0.00073 | NCQ | 500.0 |
| BAO | 50.0 |
| Compound | Minimum (ng/L) | Maximum (ng/L) | Mean (ng/L) | Detection Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAP | ND | 498.53 | 22.07 | 59.70 |
| ACE | ND | 86.95 | 4.41 | 28.36 |
| FL | ND | 7.19 | 1.76 | 47.76 |
| PHE | ND | 13.35 | 6.61 | 95.52 |
| ANT | ND | 4.98 | 0.33 | 17.91 |
| PYR | ND | 5.92 | 2.32 | 42.28 |
| BaP | ND | 4.59 | 0.07 | 1.49 |
| INP | ND | 72.43 | 10.48 | 98.51 |
| 1-/2-OHNAP | ND | 68.81 | 29.59 | 76.12 |
| OPP | ND | 71.45 | 28.82 | 82.09 |
| 2-/3-OHFLU | ND | 17.07 | 5.73 | 37.31 |
| 1-OHPHE | ND | 15.06 | 3.93 | 28.36 |
| 1-OHPYR | ND | 23.15 | 3.32 | 16.42 |
| 6-OHCHR | ND | 25.33 | 1.42 | 5.97 |
| 3-/9-OHBaP | ND | 14.49 | 0.22 | 1.49 |
| NCQ | ND | 1.00 | 0.05 | 7.46 |
| 1-NAD | ND | 25.72 | 4.91 | 80.60 |
| 9-Flo | ND | 32.64 | 16.69 | 95.52 |
| PHE-9-D | ND | 2.82 | 0.32 | 22.39 |
| BAO | ND | 2.64 | 0.95 | 49.25 |
| 6H-BcdP-6-O | ND | 24.52 | 0.37 | 1.49 |
| 2-NFL | ND | 16.34 | 3.40 | 20.90 |
| 5-NNC | ND | 17.19 | 7.49 | 46.27 |
| 2,7-DFL | ND | 14.12 | 0.21 | 1.49 |
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Variance % | Cumulative % | Total | Variance % | Cumulative % | Total | Variance % | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 2.309 | 28.868 | 28.868 | 2.309 | 28.868 | 28.868 | 1.798 | 22.473 | 22.473 |
| 2 | 1.567 | 19.581 | 48.449 | 1.567 | 19.581 | 48.449 | 1.243 | 15.532 | 38.006 |
| 3 | 1.163 | 14.537 | 62.986 | 1.163 | 14.537 | 62.986 | 1.120 | 13.994 | 52.000 |
| 4 | 0.955 | 11.942 | 74.928 | 0.955 | 11.942 | 74.928 | 1.068 | 13.355 | 65.355 |
| 5 | 0.775 | 9.685 | 84.613 | 0.775 | 9.685 | 84.613 | 1.062 | 13.270 | 78.625 |
| 6 | 0.578 | 7.224 | 91.837 | 0.578 | 7.224 | 91.837 | 1.057 | 13.212 | 91.837 |
| 7 | 0.349 | 4.358 | 96.195 | ||||||
| 8 | 0.304 | 3.805 | 100.000 | ||||||
| Rotated component matrix a | |||||||||
| Component | |||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||||
| NAP | 0.007 | −0.010 | 0.049 | 0.004 | 0.056 | 0.984 | |||
| ACE | 0.057 | 0.016 | −0.141 | 0.971 | 0.088 | 0.006 | |||
| FL | 0.821 | 0.130 | 0.052 | 0.279 | 0.100 | −0.220 | |||
| PHE | 0.902 | 0.100 | 0.059 | −0.126 | −0.015 | 0.177 | |||
| ANT | 0.527 | 0.563 | 0.427 | −0.004 | 0.266 | 0.039 | |||
| PYR | 0.090 | −0.103 | 0.930 | −0.152 | −0.181 | 0.051 | |||
| BaP | 0.125 | 0.940 | −0.147 | 0.023 | −0.122 | −0.022 | |||
| INP | 0.074 | −0.067 | −0.149 | 0.092 | 0.960 | 0.058 | |||
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Variance % | Cumulative % | Total | Variance % | Cumulative % | Total | Variance % | Cumulative % | ||||
| 1 | 3.883 | 22.839 | 22.839 | 3.883 | 22.839 | 22.839 | 2.182 | 12.833 | 12.833 | |||
| 2 | 2.228 | 13.109 | 35.947 | 2.228 | 13.109 | 35.947 | 1.898 | 11.167 | 24.000 | |||
| 3 | 1.474 | 8.672 | 44.620 | 1.474 | 8.672 | 44.620 | 1.876 | 11.035 | 35.034 | |||
| 4 | 1.315 | 7.734 | 52.354 | 1.315 | 7.734 | 52.354 | 1.371 | 8.066 | 43.100 | |||
| 5 | 1.174 | 6.905 | 59.260 | 1.174 | 6.905 | 59.260 | 1.247 | 7.333 | 50.433 | |||
| 6 | 1.113 | 6.545 | 65.804 | 1.113 | 6.545 | 65.804 | 1.197 | 7.041 | 57.475 | |||
| 7 | 1.009 | 5.936 | 71.740 | 1.009 | 5.936 | 71.740 | 1.155 | 6.794 | 64.269 | |||
| 8 | 0.908 | 5.339 | 77.079 | 0.908 | 5.339 | 77.079 | 1.136 | 6.685 | 70.954 | |||
| 9 | 0.843 | 4.958 | 82.037 | 0.843 | 4.958 | 82.037 | 1.132 | 6.660 | 77.614 | |||
| 10 | 0.706 | 4.155 | 86.192 | 0.706 | 4.155 | 86.192 | 1.065 | 6.266 | 83.880 | |||
| 11 | 0.637 | 3.746 | 89.938 | 0.637 | 3.746 | 89.938 | 1.030 | 6.058 | 89.938 | |||
| 12 | 0.566 | 3.329 | 93.266 | |||||||||
| 13 | 0.382 | 2.247 | 95.513 | |||||||||
| 14 | 0.333 | 1.960 | 97.473 | |||||||||
| 15 | 0.268 | 1.574 | 99.047 | |||||||||
| 16 | 0.162 | 0.953 | 100.000 | |||||||||
| 17 | 2.993 × 10−5 | 0.000 | 100.000 | |||||||||
| Rotated component matrix a | ||||||||||||
| Component | ||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | ||
| OHNAP1 | 0.945 | −0.002 | −0.152 | 0.138 | −0.061 | −0.093 | 0.069 | 0.066 | −0.142 | 0.096 | −0.013 | |
| OHNAP2 | 0.945 | −0.002 | −0.151 | 0.138 | −0.061 | −0.093 | 0.069 | 0.066 | −0.142 | .0096 | −0.012 | |
| OPP | 0.321 | −0.092 | 0.156 | 0.847 | −0.075 | 0.020 | 0.096 | −0.028 | −0.034 | 0.097 | 0.049 | |
| OHFLU | −0.196 | 0.269 | 0.748 | 0.049 | 0.199 | 0.065 | 0.061 | −0.097 | −0.211 | 0.011 | −0.080 | |
| OHPHE1 | 0.032 | −0.153 | 0.578 | −0.666 | 0.181 | 0.182 | 0.051 | 0.017 | 0.123 | −0.047 | 0.004 | |
| OHPYR1 | −0.164 | 0.074 | 0.047 | −0.044 | −0.097 | 0.929 | −0.019 | 0.025 | 0.079 | −0.118 | −0.018 | |
| OHCHR6 | 0.099 | 0.266 | 0.029 | −0.045 | −0.025 | 0.034 | −0.029 | 0.917 | −0.018 | 0.037 | −0.011 | |
| OHBap | 0.049 | 0.797 | 0.044 | 0.065 | −0.056 | −0.140 | 0.189 | 0.363 | −0.023 | −0.078 | 0.011 | |
| NCQ | −0.012 | 0.795 | 0.019 | −0.045 | 0.226 | 0.350 | −0.049 | 0.037 | 0.126 | −0.076 | −0.025 | |
| NAD1 | −0.203 | −0.102 | 0.739 | 0.055 | −0.208 | −0.034 | −0.059 | 0.146 | 0.333 | −0.212 | −0.049 | |
| FLO9 | −0.244 | 0.101 | 0.055 | −0.083 | 0.056 | 0.089 | 0.115 | −0.032 | 0.894 | −0.013 | −0.034 | |
| PHE9D | −0.121 | 0.506 | 0.435 | −0.342 | −0.281 | −0.321 | 0.114 | 0.133 | 0.100 | −0.089 | −0.007 | |
| BAO | −0.225 | 0.372 | 0.383 | −0.061 | −0.329 | 0.041 | −0.385 | −0.316 | 0.268 | −0.248 | 0.175 | |
| HBCDP | −0.117 | 0.072 | 0.034 | −0.122 | 0.926 | −0.079 | −0.045 | −0.024 | 0.048 | −0.059 | 0.008 | |
| NFL2 | 0.095 | 0.114 | 0.036 | 0.044 | −0.055 | −0.022 | 0.954 | −0.026 | 0.111 | 0.006 | −0.020 | |
| NNC5 | 0.156 | −0.127 | −0.123 | 0.103 | −0.059 | −0.121 | 0.016 | 0.037 | −0.020 | 0.941 | 0.074 | |
| DFL27 | −0.018 | −0.005 | −0.065 | 0.036 | 0.003 | −0.018 | −0.029 | −0.014 | −0.028 | 0.063 | 0.990 | |
References
- Alegbeleye, O.O.; Opeolu, B.O.; Jackson, V.A. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: A Critical Review of Environmental Occurrence and Bioremediation. Environ. Manag. 2017, 60, 758–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reizer, E.; Viskolcz, B.; Fiser, B. Formation and growth mechanisms of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A mini-review. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, F.; Rocha, B.A.; Souza, M.C.O.; Bocato, M.Z.; Azevedo, L.F.; Adeyemi, J.A.; Santana, A.; Campiglia, A.D. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): Updated aspects of their determination, kinetics in the human body, and toxicity. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health-Part B-Crit. Rev. 2023, 26, 28–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Xu, D.; Yang, X.; Hu, J. Microplastics and PAHs mixed contamination: An in-depth review on the sources, co-occurrence, and fate in marine ecosystems. Water Res. 2024, 257, 121622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, O.; Semple, K.T.; Ramadass, K.; O’Connor, W.; Hansbro, P.; Thavamani, P. Beyond the obvious: Environmental health implications of polar polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.; Varshney, J.G.; Agarwal, T. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons’ formation and occurrence in processed food. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 768–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wnorowski, A.; Harnish, D.; Jiang, Y.; Celo, V.; Dabek-Zlotorzynska, E.; Charland, J.-P. Assessment and Characterization of Alkylated PAHs in Selected Sites across Canada. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Dong, Q.; Li, F.; Wang, T.; Qiu, X.; Zhu, T. A Systematic Review of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Derivatives: Occurrences, Levels, Biotransformation, Exposure Biomarkers, and Toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 15314–15335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacic, P.; Somanathan, R. Nitroaromatic compounds: Environmental toxicity, carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, therapy and mechanism. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 810–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Gan, J.; Liu, C.; Shu, X.; Shu, J. Nitration of particle-associated PAHs and their derivatives (nitro-, oxy-, and hydroxy-PAHs) with NO3 radicals. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2515–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Qin, R.; Luo, W. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Bohai Sea: A review of their distribution, sources, and risks. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2022, 18, 1705–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samburova, V.; Zielinska, B.; Khlystov, A. Do 16 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Represent PAH Air Toxicity? Toxics 2017, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, S.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y. A novel biomass pyrogenic index and its application coupled with black carbon for improving polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon source identification. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, E.; Walker, T.R.; Adams, M.; Willis, R.; Norris, G.A.; Henry, R.C. Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in small craft harbor (SCH) surficial sediments in Nova Scotia, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gao, X.; Zhu, S.; Liang, H. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coal preparation plant products: A contributor to environmental pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, K.; Athanasiou, D.; Edwards, M. Evaluation of Generic PAH Profiles Commonly Used in Receptor Models: Implications for Source Control Policy. Environ. Forensics 2024, 25, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, M.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Su, G. The importance of compound-specific radiocarbon analysis in source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 937–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiyeh, L.; Chen, K.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, C.; Lv, J.; Tang, Y.-T.; Yu, H.; Snape, C.; et al. A review on analysis methods, source identification, and cancer risk evaluation of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, T.; Russell, J.; Zhang, F.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Guan, M.; Han, Q. Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in continental shelf of the East China Sea with dual compound-specific isotopes (δ13C and δ2H). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Ahad, J.M.E.; Cooke, C.A. Optimized sample cleanup for compound-specific isotope analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in complex environmental samples. Org. Geochem. 2025, 203, 104966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, M.; Ragone, R.; Dell’Anna, M.M.; Romanazzi, G.; Damiani, L.; Mastrorilli, P. Improved identification of pollution source attribution by using PAH ratios combined with multivariate statistics. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Han, Y.; Duan, Y.; Lai, X.; Fu, R.; Liu, S.; Leong, K.H.; Tu, Y.; Zhou, L. Review on the contamination and remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coastal soil and sediments. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenov, M.; Marinaite, I.; Golobokova, L.; Khodzher, T. Factors affecting the source identification and distribution of polycyclic aromatic compounds in environmental compartments of the Lake Baikal area. Chem. Ecol. 2025, 41, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Yu, H.; Cao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Hu, L.; Duan, L.; Sun, X.; Lin, T. Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of the East China marginal seas: Significance of the terrestrial input and shelf mud deposition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 115920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koudryashova, Y.; Chizhova, T.; Zadorozhny, P.; Ponomareva, A.; Eskova, A. Occurrence and Sources of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Factors Influencing Their Accumulation in Surface Sediment of a Deep-Sea Depression, Namely, the Tatar Trough (Tatar Strait, the Sea of Japan). Water 2023, 15, 4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Liang, H. Profiles and source apportionment of PAHs in particulate matter from resuspended dust in coal mining areas: Implications for atmospheric pollution. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2025, 16, 102434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, S.; Liu, R.; Liu, D.; Fang, Y. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of surface soil’s polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Yangtze River Delta. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Tian, Y.; Yao, Q.; Shi, Y. Structural Characteristics of Intergovernmental Water Pollution Control Cooperation Networks Using Social Network Analysis and GIS in Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, T.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Ye, M.; Zhao, Z. Environmental characteristics of antibiotics and antibiotic-resistance genes in the Suzhou River of Shanghai, China. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, X.; Jin, W.; Chen, M.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, P. Quantifying pollution contributions across a reticular river network: Insights from water quantity composition analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaibu, N.S.; Qin, C.; Chu, F.; Ismail, B.B.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Indabawa, M.G.; Abdalmohammed, S.A.A.; Zhao, G.; Wang, X. Traceability tagging of volatile organic compound sources and their contributions to ozone formation in Suzhou using vehicle-based portable single-photon ionization mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2024, 36, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wu, X.; He, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Z. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Urban Stream Sediments from Suzhou Industrial Park in China: Occurrence and Potential Risk. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Qi, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Lv, J.; Zong, L.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, H.; Jia, Z.; Mei, S.; et al. Shallow Groundwater Quality Assessment and Pollution Source Apportionment: Case Study in Wujiang District, Suzhou City. Water 2024, 16, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Yin, Y.; Cao, C. Carbon Emission Peak Paths Under Different Scenarios Based on the LEAP Model-A Case Study of Suzhou, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 905471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Rao, Z.; Zhan, N.; Li, G.-h.; Guo, X.-c.; Liu, C.; Yang, Z.-p.; Song, S.-j.; Zuo, X.-l. An automatic and sensitive method for simultaneous determination of sixteen polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and four derivatives by online solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with online solvent filtration. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 7721–7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Hou, M.; Zhou, S.; Shi, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Ni, S.; Wang, R. Geographical impact on the distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in hilly terrain topsoil: A case study at Chongqing, SW, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuyet Nam Thi, N.; Jung, K.-S.; Son, J.M.; Kwon, H.-O.; Choi, S.-D. Seasonal variation, phase distribution, and source identification of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at a semi-rural site in Ulsan, South Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, D.; Lv, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Huang, L.; Zhu, L. Ecological and health risk assessments of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soils around a petroleum refining plant in China: A quantitative method based on the improved hybrid model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.; Souza, M.R.R.; Vilela Junior, A.R.; Soares, L.S.; Frena, M.; Alexandre, M.R. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in superficial water from a tropical estuarine system: Distribution, seasonal variations, sources and ecological risk assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Wu, F.; He, J.; Sun, Y.; Qin, N.; Sun, F.; Su, H.; Wang, B. Spatiotemporal distributions and ecological risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surface seawater of Laizhou Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 12131–12143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, T.K.; Kumar, A.; Mahto, D.K.; Das, K.C.; Narayan, P.; Fukate, M.; Awachat, P.; Padghan, D.; Mohammad, F.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.A.; et al. The Health Risk and Source Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Soil of Industrial Cities in India. Toxics 2023, 11, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Song, Y.; He, F.; Jing, M.; Tang, J.; Liu, R. A review of human and animals exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Health risk and adverse effects, photo-induced toxicity and regulating effect of microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.-j.; Chen, S.-j.; Yu, M.; Mai, B.-x.; Sheng, G.-y.; Fu, J.-m. Distribution and Partition of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Water from the Pearl River Estuary. Huanjing Kexue 2008, 29, 2385–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Yan, L.; Luo, J.; Jones, K.C. Occurrence and distribution of PAHs in the Yangtze River and urban river waters of Nanjing, China: Insights from in situ DGT measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 371, 125921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, A.; Yang, Z.; Wei, C.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y. Distribution characteristics, source analysis and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of Kuye River: A river in a typical energy and chemical industry zone. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, C.; Yao, Q.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Q.; Chen, L. Unveiling polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution dynamics in river-lake sediments: Insights for energy transition. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 378, 124737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Han, M.; Cao, X.; Cheng, X.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Sun, C.; He, H. Sedimentary spatial variation, source identification and ecological risk assessment of parent, nitrated and oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a large shallow lake in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Yan, S.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ran, C.; Chen, X.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; He, H. Quantitative source apportionment and health risk assessment for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and their derivatives in indoor dust from housing and public buildings of a mega-city in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 486, 137057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Yang, B.; Cheng, L.; Li, Y.; Qadeer, A. Levels, sources and risk assessment of PAHs in multi-phases from urbanized river network system in Shanghai. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Niu, J.; Wang, J. Characterization, ecological risk assessment and source diagnostics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water column of the Yellow River Delta, one of the most plenty biodiversity zones in the world. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Wang, L.; Lei, K.; Nan, B. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Daliao River estuary and the adjacent area, China. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarria-Villa, R.; Ocampo-Duque, W.; Paez, M.; Schuhmacher, M. Presence of PAHs in water and sediments of the Colombian Cauca River during heavy rain episodes, and implications for risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srogi, K. Monitoring of environmental exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2007, 5, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyte, I.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Lammel, G. Chemical reactivity and long-range transport potential of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons—A review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 9333–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhu, D.; Li, W.; Shen, G.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; et al. Global Atmospheric Emissions of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from 1960 to 2008 and Future Predictions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6415–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Han, M.; Liu, Y.; He, H.; Gao, Z.; Xian, Q.; Yang, S.; Sun, C.; Lie, S.; Zhang, L. Analysis of trace-level nitrated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples by solid-phase microextraction with gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 2681–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Qi, W.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Oxygenated, nitrated, methyl and parent polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rivers of Haihe River System, China: Occurrence, possible formation, and source and fate in a water-shortage area. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, Z.; Wu, P.; Zhu, S.; Liang, H. Native polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coal and its preparation products-A mixed source of environmental contamination. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 361, 124894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, T.; Guo, W.; Liu, W.; Xing, Y.; Lei, R.; Wu, X.; Sun, S. Spatial distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the water-sediment system near chemical industry parks in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhen, Q.; Han, F.; Zhang, X. Distribution, Origins and Hazardous Effects of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Topsoil Surrounding Oil Fields: A Case Study on the Loess Plateau, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, J.D.; Bernal, S.; Meredith, W.; Schumer, R.; Marti, E. Stream Hydrology Controls the Longitudinal Bioreactive Footprint of Urban-Sourced Fine Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 9083–9091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Yuan, J.; Geng, S.; Zou, J.; Dou, J.; Fan, F. Oxygenated and Nitrated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Sources, Quantification, Incidence, Toxicity, and Fate in Soil-A Review Study. Processes 2023, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.; Du, W.; Shen, G.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Cheng, H.; Xing, B.; Tao, S. Estimating relative contributions of primary and secondary sources of ambient nitrated and oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 159, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.V.F.; Santos, F.R.; Oliveira, A.H.B.; Nascimento, R.F.; Cavalcante, R.M. Influence of sediment parameters on the distribution and fate of PAHs in an estuarine tropical region located in the Brazilian semi-arid (Jaguaribe River, Ceara coast). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Wang, S. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediment of Wei River. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ya, M.; Li, Y.; Hong, H. Seasonal variation and spatial transport of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water of the subtropical Jiulong River watershed and estuary, Southeast China. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strotmann, U.; Durand, M.-J.; Thouand, G.; Eberlein, C.; Heipieper, H.J.; Gartiser, S.; Pagga, U. Microbiological toxicity tests using standardized ISO/OECD methods-current state and outlook. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, D.; Entwistle, J.A.; Cave, M.; Dean, J.R. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban street dust: Implications for human health. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, A.; Wang, P.; Tuo, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, P.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, T.; et al. Temporal profiles, source analysis, and health risk assessments of parent polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PPAHs) and their derivatives (NPAHs, OPAHs, ClPAHs, and BrPAHs) in PM2.5 and PM1.0 from the eastern coastal region of China: Urban coastal area versus coastal background area. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrychowski, W.A.; Perera, F.P.; Camann, D.; Spengler, J.; Butscher, M.; Mroz, E.; Majewska, R.; Flak, E.; Jacek, R.; Sowa, A. Prenatal exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and cognitive dysfunction in children. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3631–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
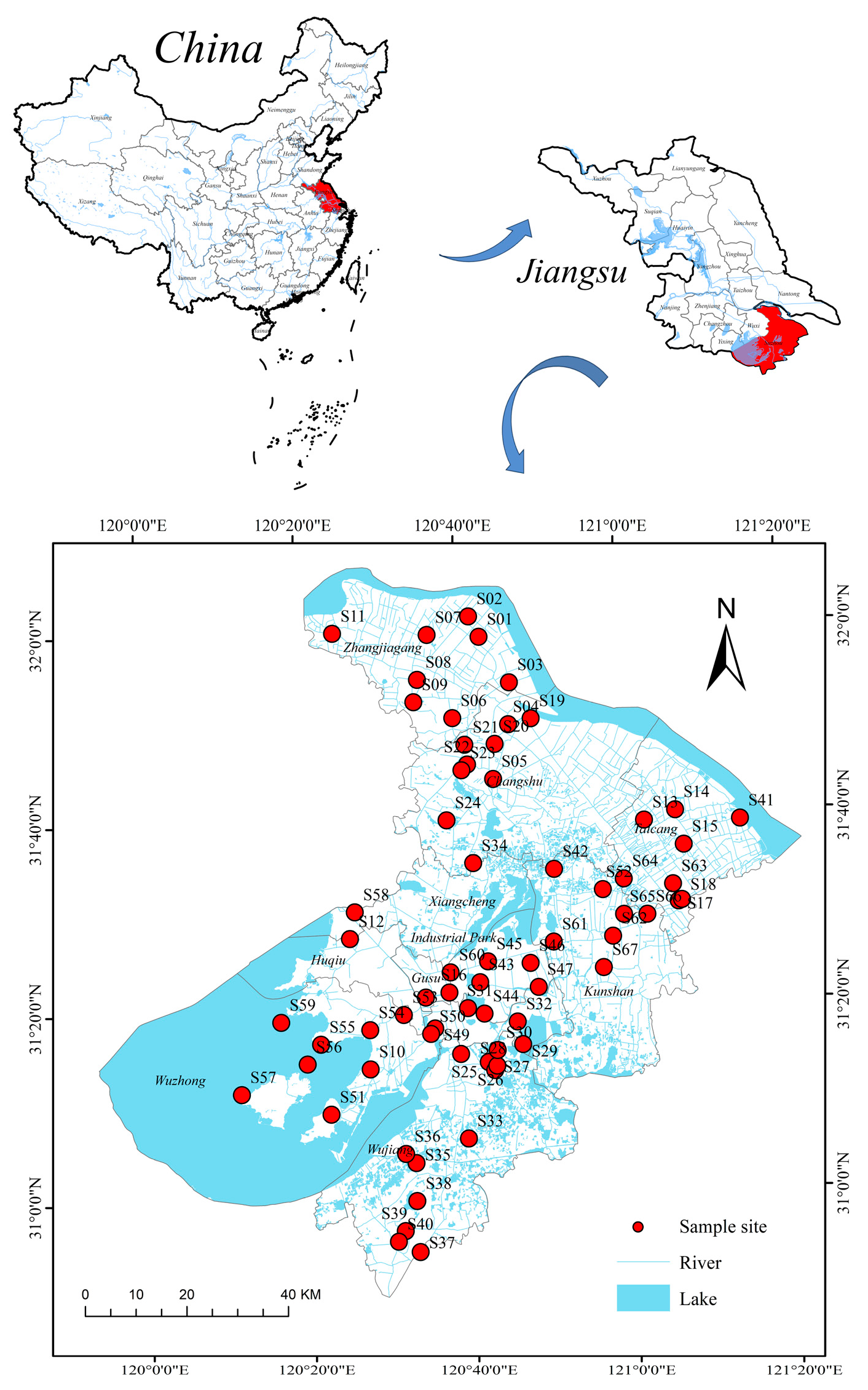


| 15 abbreviations for PAHs | |||||
| Naphthalene | NAP | Chrysene | CHR | Benz[a]anthracene | BaA |
| Acenaphthene | ACE | Fluoranthene | FLU | Dibenz[a,h]anthracene | DBA |
| Anthracene | ANT | Pyrene | PYR | Benzo[a]pyrene | BaP |
| Phenanthrene | PHE | Benzo[k]fluoranthene | BkF | Benzo[g,h,i]perylene | BghiP |
| Fluorene | FL | Benzo[b]fluoranthene | BbF | Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene | INP |
| 19 abbreviations for SPAHs | |||||
| 1-Naphthol | 1-OHNAP | 1-Hydroxypyrene | 1-OHPYR | 9-Fluorenone | 9-FLo |
| 2-Naphthol | 2-OHNAP | 3-Hydroxybenzo(a)pyrene | 3-OHBaP | 9-Phenanthraldehyde | PHE-9-D |
| 2-Phenylphenol | OPP | 9-Hydroxybenzo(a)pyrene | 9-OHBaP | 6H-Benzo[c,d]pyren-6-one | 6H-BcdP-6-O |
| 2-Hydroxyfluorene | 2-OHFLU | 1-Naphthaldehyde | 1-NAD | 5-Nitroacenaphthene | 5-NNC |
| 3-Hydroxyfluorene | 3-OHFLU | Acenaphthenequinone | NCQ | 2-Nitrofluorene | 2-NFL |
| 1-Hydroxyphenanthrene | 1-OHPHE | Benzanthrone | BAO | 2,7-Dinitrofluorene | 2,7-DFL |
| 6-Hydroxychrysene | 6-OHCHR | ||||
| Water (ng/L) | Location | Country | Number of PAHs | Sampling Sites | Range, ΣPAHs | Mean, ∑PAHs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suzhou | China | 15 | 67 | 2.65–514.16 | 48.05 | This study | |
| Bohai Sea | China | 16 | 200 | 71.1–4260 | - | [11] | |
| Pearl River Estuary | China | 5 | 11 | 15.9–182.4 | - | [43] | |
| Rivers in Shanghai | China | 16 | 47 | 46.53–221.54 | 112.92 | [49] | |
| Yellow River Delta | China | 15 | 42 | 64.8–334.6 | 121.3 | [50] | |
| Daliao River | China | 16 | 27 | 71.12–4255.43 | 748.76 | [51] | |
| Cauca | Colombia | 12 | 8 | 52.1–12,888.2 | 2344.5 | [52] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, J.; Jing, Z.; Guo, F.; Jia, J.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Song, X. Spatial Variation Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Derivatives in Surface Water of Suzhou City: Occurrence, Sources, and Risk Assessment. Toxics 2025, 13, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050403
Fan J, Jing Z, Guo F, Jia J, Jiang Y, Cai X, Wang S, Zhao H, Song X. Spatial Variation Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Derivatives in Surface Water of Suzhou City: Occurrence, Sources, and Risk Assessment. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050403
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Jinxu, Zhangwei Jing, Feng Guo, Jing Jia, Yu Jiang, Xiaoyu Cai, Shuting Wang, Hu Zhao, and Xianjing Song. 2025. "Spatial Variation Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Derivatives in Surface Water of Suzhou City: Occurrence, Sources, and Risk Assessment" Toxics 13, no. 5: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050403
APA StyleFan, J., Jing, Z., Guo, F., Jia, J., Jiang, Y., Cai, X., Wang, S., Zhao, H., & Song, X. (2025). Spatial Variation Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Derivatives in Surface Water of Suzhou City: Occurrence, Sources, and Risk Assessment. Toxics, 13(5), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050403





