Biogeochemical Mechanisms of HCO3–Ca Water and NO3− Pollution in a Typical Piedmont Agricultural Area: Insights from Nitrification and Carbonate Weathering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
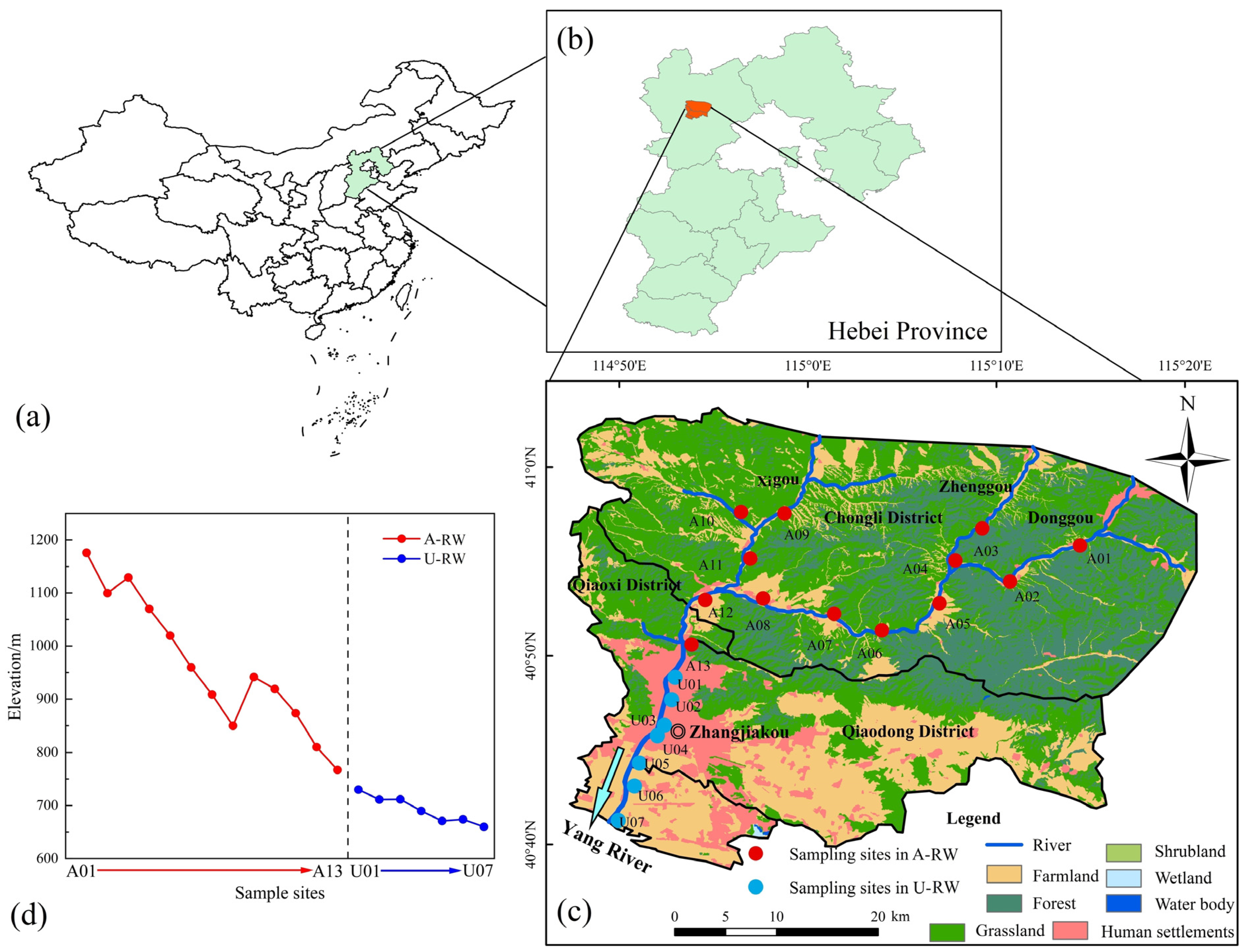
2.1. Site Information and Sampling Campaign
2.2. Hydrochemical, Isotopic and Microbial Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overall Riverine Hydrochemistry
3.2. Isotopic Parameters
3.3. Microbial Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. Environmental Factors
4.1.1. Evaporation and Recharge Processes
4.1.2. Topography and Channel Structure
4.2. Mineral Dissolution Dominated by Carbonate Rocks
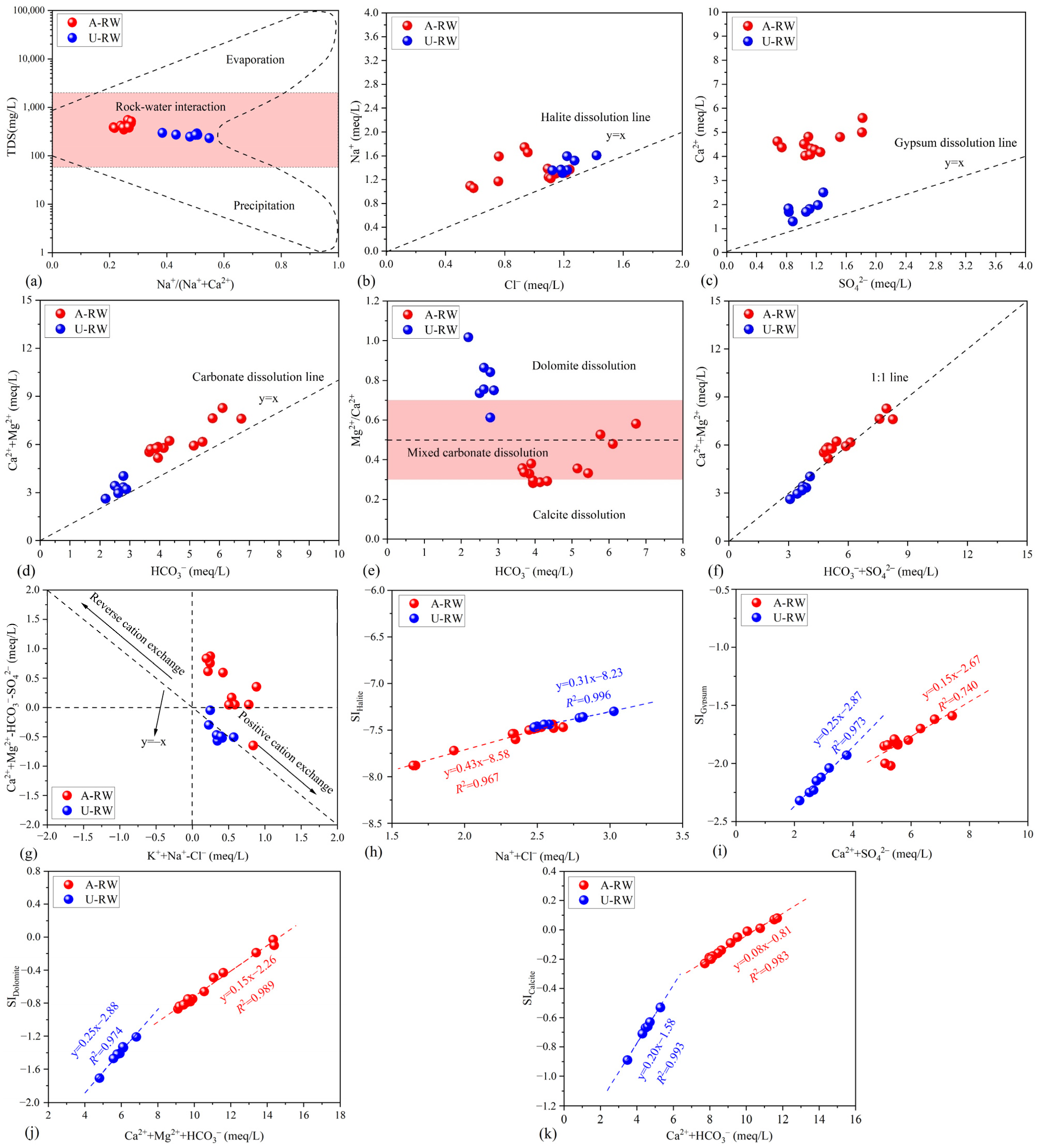
4.2.1. Hydrochemical Indicators
4.2.2. Saturation Index
4.2.3. Forward Model
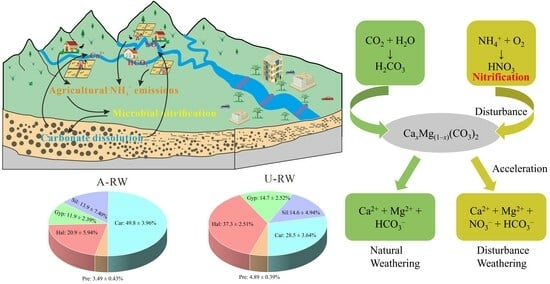
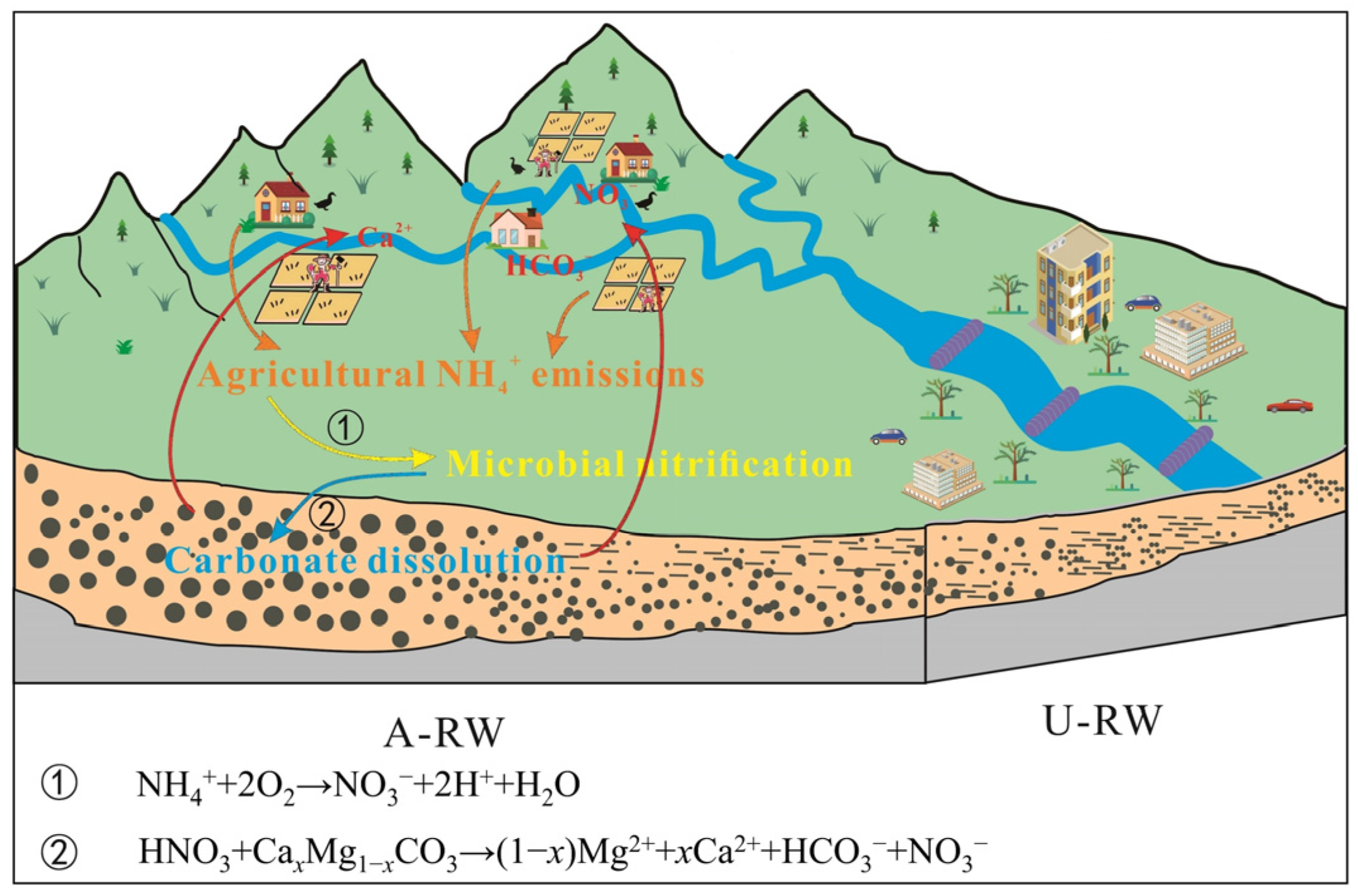
4.3. Agricultural NH4+ Emissions
4.4. Biogeochemical Mechanisms
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stringer, L.C.; Mirzabaev, A.; Benjaminsen, T.A.; Harris, R.M.B.; Jafari, M.; Lissner, T.K.; Stevens, N.; Tirado-von Der Pahlen, C. Climate change impacts on water security in global drylands. One Earth 2021, 4, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Fakhreddine, S.; Rateb, A.; de Graaf, I.; Famiglietti, J.; Gleeson, T.; Grafton, R.Q.; Jobbagy, E.; Kebede, S.; Kolusu, S.R.; et al. Global water resources and the role of groundwater in a resilient water future. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Li, P.; He, X.; Zhang, Q. Tracing the sources and evaporation fate of surface water and groundwater using stable isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Deng, L.; Jin, Z. Characteristics, sources, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in river water and well water in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Chai, N.; Jin, Z. Controlling mechanism and water quality assessment of arsenic in China’s Yellow River Basin. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 137953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gençer, E.; Başaran, C. Water quality assessment and pollution of Akarçay River, Türkiye. Kuwait J. Sci. 2024, 51, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Liu, C.; Wu, X.; He, W.; Kong, Y.; Degefu, D.M.; Ramsey, T.S. A set pair analysis method for assessing and forecasting water conflict risk in transboundary river basins. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 38, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borysenko, K.; Hutchinson, S.M.; Sinchuk, D. Manifestations and consequences of water conflicts: Case study of the Pechenihy reservoir, Kharkiv region, Ukraine. Visnyk V. N. Karazin Kharkiv Natl. Univ. Ser. Geology. Geography. Ecol. Quot 2024, 60, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Lv, G.; Chai, N.; Hu, J.; Jin, Z. Hydrochemistry and source apportionment of boron, sulfate, and nitrate in the Fen River, a typical loess covered area in the eastern Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.; Xiao, J.; Li, S.; Li, Z. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and their controlling factors in the Fen River of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, G.; Zhu, D.; Xie, H.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, L.; Zou, S. Hydrogeochemistry of karst groundwater for the environmental and health risk assessment: The case of the suburban area of Chongqing (Southwest China). Geochemistry 2022, 82, 125866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, J.; Xue, Z.; Guan, J.; Lang, Y.; Ding, H.; Li, L. Evaluation of nitrate source in surface water of southwestern China based on stable isotopes. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H. Assessment of sources and transformation of nitrate in the alluvial-pluvial fan region of north China using a multi-isotope approach. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 89, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Past´en-Zapata, E.; Ledesma-Ruiz, R.; Harter, T.; Ramírez, A.I.; Mahlknecht, J. Assessment of sources and fate of nitrate in shallow groundwater of an agricultural area by using a multi-tracer approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y. Assessing nitrate and ffuoride contaminants in drinking water and their health risk of rural residents living in a semiarid region of Northwest China. Expo. Health 2017, 9, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Fei, Y.; Tian, X.; Cui, X.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, R.; Li, Y. Determining the origin and fate of nitrate in the Nanyang Basin, Central China, using environmental isotopes and the Bayesian mixing model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 48343–48361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Li, J. Distribution characteristics and formation mechanism of main hydrochemical ions in Qingshui River. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 337–348. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Qian, P.; Li, J.; Yu, S.; Miao, X.; Guo, Y.; Huang, F.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, L. Response of weathering carbon sink effect to anthropogenic sulfuric acid in different lithological catchments: A case study from Southwest China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2024, 270, 106195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Ding, Q. Hydrogeochemical evidence for fluoride sources and enrichment in desert groundwater: A case study of Cherchen River Basin, northwestern China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2023, 259, 104270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, Y.; Qian, H.; Ren, W.; Qu, W. Hydrogeochemical evidence for fluoride behavior in groundwater and the associated risk to human health for a large irrigation plain in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Q.; Tian, X.; Xie, H.; Gong, Z.; Lin, Y.; Dang, Z.; Li, J.; Zou, S.; Zhu, T. Hydrogeochemical characteristics, driving factors, and health risk assessment of karst groundwater in Southwest Hubei Province, China. Water Environ. Res. 2024, 96, e11069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Pan, X.; Yuan, D.; Zeng, J.; Liang, J.; Peng, C. Nitrate sources and nitrogen dynamics in a karst aquifer with mixed nitrogen inputs (Southwest China): Revealed by multiple stable isotopic and hydro-chemical proxies. Water Res. 2022, 210, 118000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Han, G. Effects of chemical weathering and CO2 outgassing on δ13CDIC signals in a karst watershed. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, D.; Cui, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Cao, M. Source and flux of anthropogenically enhanced dissolved inorganic carbon: A comparative study of urban and forest karst catchments in Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, H.; Li, J.; Yang, G.; Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, C.; Zou, S. Influences of anthropogenic acids on carbonate weathering and CO2 sink in an agricultural karst wetland (South China). Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, J.; Strebel, O.; Voerkelius, S.; Schmidt, H.L. Using isotope fractionation of nitrate-nitrogen and nitrate-oxygen for evaluation of microbial denitrification in a sandy aquifer. J. Hydrol. 1990, 114, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Shi, B.; Jia, Z.; Liu, D.; Hu, W.; Feng, C.; Li, R. Tracing the impacts of ecological water replenishment on the sources and transformation of groundwater nitrate through isotope and microbial analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 928, 172248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Pei, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, G.; Xie, Y.; Cao, S.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Zhang, H. Coupled processes involving ammonium inputs, microbial nitrification, and calcite dissolution control riverine nitrate pollution in the piedmont zone (Qingshui River, China). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, F.J.; Li, S.L.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Ding, H. Tracing nitrate sources with dual isotopes and long term monitoring of nitrogen species in the Yellow River. China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, M.S.; Rhee, H.P.; Hur, J.; Shin, K.H. Systematic tracing of nitrate sources in a complex river catchment: An integrated approach using stable isotopes and hydrological models. Water Res. 2023, 235, 119755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Huang, F.; Yang, H.; Yu, S. Role of anthropogenic sulfuric and nitric acids in carbonate weathering and associated carbon sink budget in a karst catchment (Guohua), southwestern China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 599, 126287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Fan, M.; Wei, X.; Cao, J. Overestimating the involvement of nitric acid derived from nitrification in carbonate dissolution under a calcareous soil system. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 35, 103692. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Liang, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, L.; Yu, Q. Fundamentals of Hydrogeology, 7th ed.; Geology Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Lu, K.; Shen, C.; Song, X.; Hu, B.; Liu, G. Human health risk assessment of groundwater nitrate at a two geomorphic units transition zone in northern China. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 110, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, M.Z.M.; Hu, A.; Feng, C.; Maeda, T.; Shirai, Y.; Hassan, M.A.; Yu, C.P. Influence of pretreated activated sludge for electricity generation in microbial fuel cell application. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 145, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupré, B.; Louvat, P.; Allègre, C.J. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; Incorporating the First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y. Tracing nitrate origins and transformation processes in groundwater of the Hohhot Basin’s Piedmont strong runoff zone through dual isotopes and hydro-chemical analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocca, D.; Lasagna, M.; Debernardi, L.; Destefanis, E.; De Luca, D.A. Hydrogeochemistry of the shallow aquifer in the western Po Plain (Piedmont, Italy): Spatial and temporal variability. J. Maps 2024, 20, 2329164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Su, H.; Xiao, J.; Han, F.; Li, Z. Spatial and seasonal variability, control factors and health risk of fluoride in natural water in the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahlknecht, J.; Daessle, L.; Esteller, M.; Torres-Martinez, J.; Mora, A. Groundwater flow processes and human impact along the arid US-Mexican border, evidenced by environmental tracers: The case of Tecate, Baja California. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Mora, A.; Mahlknecht, J.; Daesslé, L.W.; Cervantes-Avilés, P.A.; Ledesma-Ruiz, R. Estimation of nitrate pollution sources and transformations in groundwater of an intensive livestock-agricultural area (Comarca Lagunera), combining major ions, stable isotopes and MixSIAR. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 115445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, C. Enrichment mechanism and health risk assessment of fluoride in groundwater in the oasis zone of the Tarim Basin in Xinjiang, China. Expo. Health 2024, 16, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Chetelat, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, F. Assessment of the sources of nitrate in the Changjiang river, China using a nitrogen and oxygen isotopic approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, S.; Dong, G. Groundwater geochemical signatures and implication for sustainable development in a typical endorheic watershed on Tibetan plateau. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 48312–48329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, L.; Lan, F.; Li, J.; Hou, S. Hydrogeochemistry characteristics of groundwater in the Nandong karst water system, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Zhou, J. Hydrochemical evolution characteristics, controlling factors, and high nitrate hazards of shallow groundwater in a typical agricultural area of Nansi Lake Basin, North China. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Wei, X.; Zeng, Y.; Sun, Y. Identifying the factors controlling surface water and groundwater chemical characteristics and irrigation suitability in the Yarkant River Basin, northwest China. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshetrimayum, K.S. Hydrochemical evaluation of shallow groundwater aquifers: A case study from a semiarid Himalayan foothill river basin, northwest India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 7187–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.B. Carbonate minerals in the global carbon cycle. Chem. Geol. 2017, 449, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Huh, Y.; Qin, J.; Ellis, A. Chemical weathering in the Three Rivers region of Eastern Tibet. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 1857–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyilitya, B.; Mureithi, S.; Bauters, M.; Boeckx, P. Nitrate source apportionment in the complex Nyando tropical river basin in Kenya. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadhullah, W.; Yaccob, N.S.; Syakir, M.I.; Muhammad, S.A.; Yue, F.J.; Li, S.L. Nitrate sources and processes in the surface water of a tropical reservoir by stable isotopes and mixing model. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 700, 134517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddau, R.; Dore, E.; Pelo, S.D.; Lorrai, M.; Botti, P.; Testa, M.; Cidu, R. Geochemistry, stable isotopes and statistic tools to estimate threshold and source of nitrate in groundwater (Sardinia, Italy). Water Res. 2023, 232, 119663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semhi, K.; Suchet, P.A.; Clauer, N.; Probst, J. Impact of nitrogen fertilizers on the natural weathering-erosion processes and fluvial transport in the Garonne basin. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husic, A.; Fox, J.; Al Aamery, N.; Ford, W.; Pollock, E.; Backus, J. Seasonality of recharge drives spatial and temporal nitrate removal in a karst conduit as evidenced by nitrogen isotope modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2021, 126, e2021JG006454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Liu, Z.; Dong, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C. The fates of CO2 generated by H2SO4 and/or HNO3 during the dissolution of carbonate and their influences on the karst-related carbon cycle. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 125746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; Lewis Press: Boca Raton, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Wu, X.; Ge, J.; Liu, F.; Zhao, W.; Wu, C. Influence of mining activities on groundwater hydrochemistry and heavy metal migration using a self-organizing map (SOM). J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Bao, Q.; Wei, Y.; Chen, C.; Sun, H. Lake metabolic processes and their effects on the carbonate weathering CO2 sink: Insights from diel variations in the hydrochemistry of a typical karst lake in SW China. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Parameters | Unit | A-RW (n = 13) | U-RW (n = 7) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Min. | Max. | SD | CV | Mean | Min. | Max. | SD | CV | ||
| pH | / | 8.48 | 7.75 | 8.75 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 8.86 | 8.46 | 9.18 | 0.25 | 0.03 |
| DO | mg/L | 10.1 | 8.40 | 13.7 | 1.45 | 0.14 | 10.6 | 3.79 | 15.0 | 4.26 | 0.40 |
| T | °C | 15.0 | 12.1 | 18.4 | 2.20 | 0.15 | 20.0 | 18.0 | 22.2 | 1.37 | 0.07 |
| ORP | mV | −76.4 | −92.7 | −33.7 | 16.0 | 0.21 | −100 | −123 | −75.2 | 17.4 | 0.17 |
| TDS | mg/L | 415 | 346 | 546 | 58.9 | 0.14 | 267 | 230 | 296 | 22.8 | 0.09 |
| K+ | mg/L | 3.33 | 0.37 | 5.07 | 1.38 | 0.41 | 5.86 | 4.30 | 7.72 | 1.22 | 0.21 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 30.9 | 24.3 | 40.1 | 4.81 | 0.16 | 33.2 | 30.1 | 37.0 | 2.87 | 0.09 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 90.9 | 80.6 | 112 | 8.63 | 0.09 | 36.5 | 25.9 | 50.0 | 7.30 | 0.20 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 20.6 | 13.6 | 33.5 | 6.93 | 0.34 | 17.0 | 15.3 | 18.4 | 1.21 | 0.07 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 34.0 | 19.9 | 43.4 | 8.18 | 0.24 | 43.2 | 39.3 | 49.7 | 3.32 | 0.08 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 57.1 | 32.7 | 87.3 | 16.6 | 0.29 | 49.6 | 39.7 | 62.1 | 9.06 | 0.18 |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 285 | 223 | 411 | 63.6 | 0.22 | 160 | 134 | 176 | 14.2 | 0.09 |
| NO3− | mg/L | 35.6 | 3.08 | 52.8 | 12.5 | 0.35 | 1.12 | 0.52 | 2.86 | 1.16 | 1.03 |
| NO2− | mg/L | / | BDL | BDL | / | / | 1.38 | 1.03 | 1.69 | 0.35 | 0.26 |
| NH4+ | mg/L | / | BDL | 0.16 | / | / | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.21 |
| F− | mg/L | / | BDL | 0.03 | / | / | / | BDL | BDL | / | / |
| δ2H-H2O | ‰ | −73.2 | −80.0 | −63.0 | 5.18 | 0.07 | −53.3 | −66.0 | −43.0 | 7.89 | 0.15 |
| δ18O-H2O | ‰ | −9.90 | −10.8 | −8.20 | 0.84 | 0.08 | −6.66 | −8.70 | −4.50 | 1.41 | 0.21 |
| d-excess | ‰ | 6.05 | 2.60 | 7.80 | 1.74 | 0.29 | −0.03 | −7.00 | 3.60 | 3.62 | / |
| δ13C-DIC | ‰ | −10.6 | −12.0 | −8.60 | 1.14 | 0.11 | −5.01 | −7.12 | −3.88 | 1.08 | 0.22 |
| Regions | NH4+-Containing Pollutants | References |
|---|---|---|
| Comarca Lagunera, Mexico | Manure from concentrated animal-feeding operations (~48%), urban sewage (~43%), soil organic nitrogen (~4%), NH4+-synthetic fertilizers (~3%) and atmospheric deposition (~1%). | [45] |
| Huixian karst wetland, China | Atmospheric nitrogen deposition (3.44%), synthetic NH4+ fertilizer (36.6%), soil organic nitrogen (28.0%), domestic sewage and manure (15.1%). | [25] |
| Hohhot Basin’s Piedmont, China | Manure (20.5%), soil nitrogen (63.8%) and ammonia fertilizer (28.8%). | [40] |
| Nyando tropical river basin, Kenya | Ammonium in fertilizer/rain (10%), soil nitrogen (18–41%), manure and sewage (46–70%). | [56] |
| Bukit Merah Reservoir, Malaysia | Atmospheric deposition (23–29%), soil nitrogen (25–26%), manure and sewage (25–33%), | [57] |
| Sardinia, Italy | NH4+ fertilizers (2.13%), soil organic nitrogen (0.55%), sewage and manure (58.5%). | [58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Xin, B.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Yang, G.; Hao, G. Biogeochemical Mechanisms of HCO3–Ca Water and NO3− Pollution in a Typical Piedmont Agricultural Area: Insights from Nitrification and Carbonate Weathering. Toxics 2025, 13, 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050394
Xu L, Xin B, Liu W, Liu H, Yang G, Hao G. Biogeochemical Mechanisms of HCO3–Ca Water and NO3− Pollution in a Typical Piedmont Agricultural Area: Insights from Nitrification and Carbonate Weathering. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050394
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Li, Bo Xin, Wei Liu, Haoyang Liu, Guoli Yang, and Guizhen Hao. 2025. "Biogeochemical Mechanisms of HCO3–Ca Water and NO3− Pollution in a Typical Piedmont Agricultural Area: Insights from Nitrification and Carbonate Weathering" Toxics 13, no. 5: 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050394
APA StyleXu, L., Xin, B., Liu, W., Liu, H., Yang, G., & Hao, G. (2025). Biogeochemical Mechanisms of HCO3–Ca Water and NO3− Pollution in a Typical Piedmont Agricultural Area: Insights from Nitrification and Carbonate Weathering. Toxics, 13(5), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050394