Utilizing Molecular Descriptor Importance to Enhance Endpoint Predictions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Counter-Propagation Artificial Neural Networks
2.3. Algorithm for the Estimation of Descriptor Importance
2.4. Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
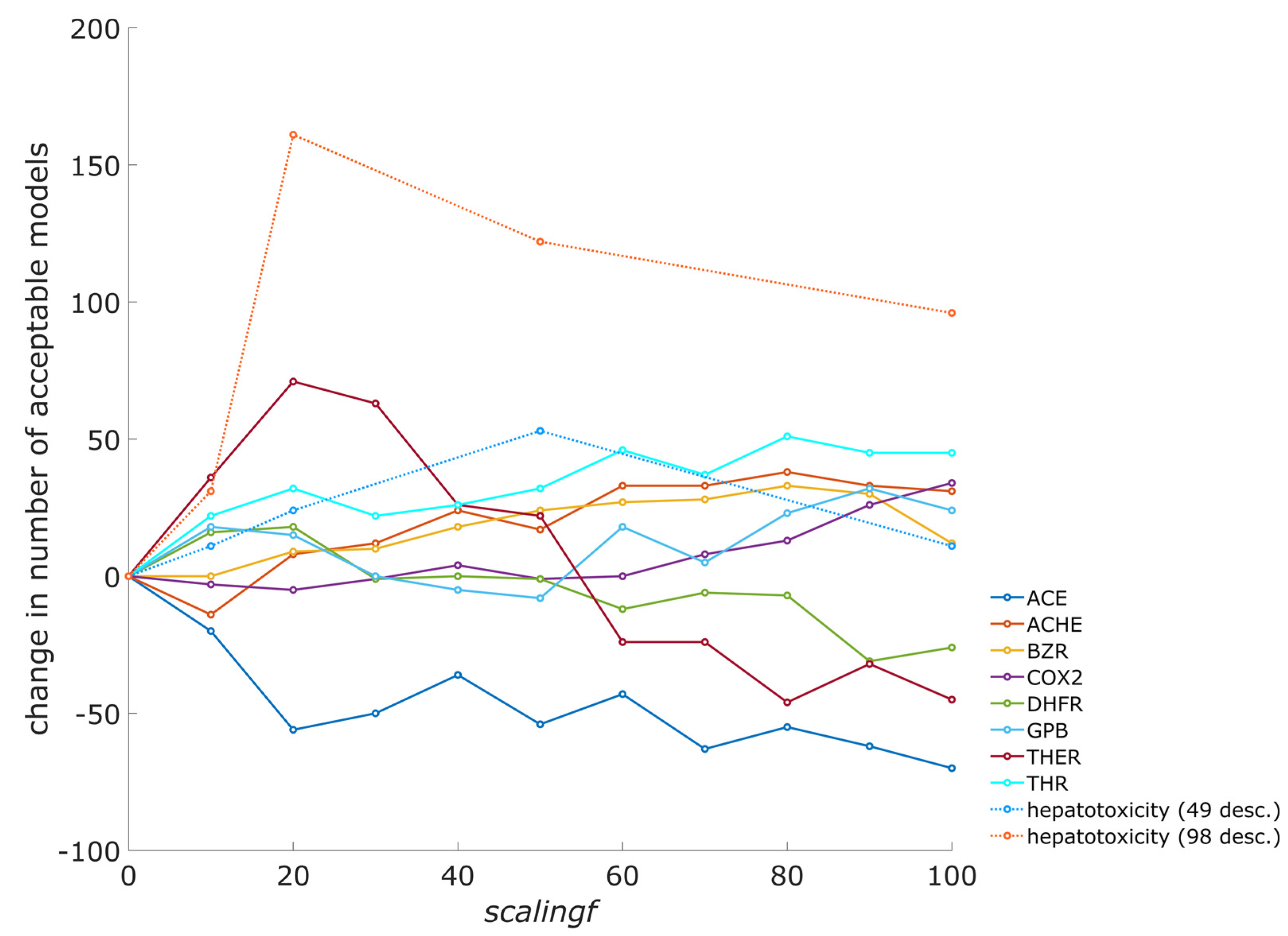
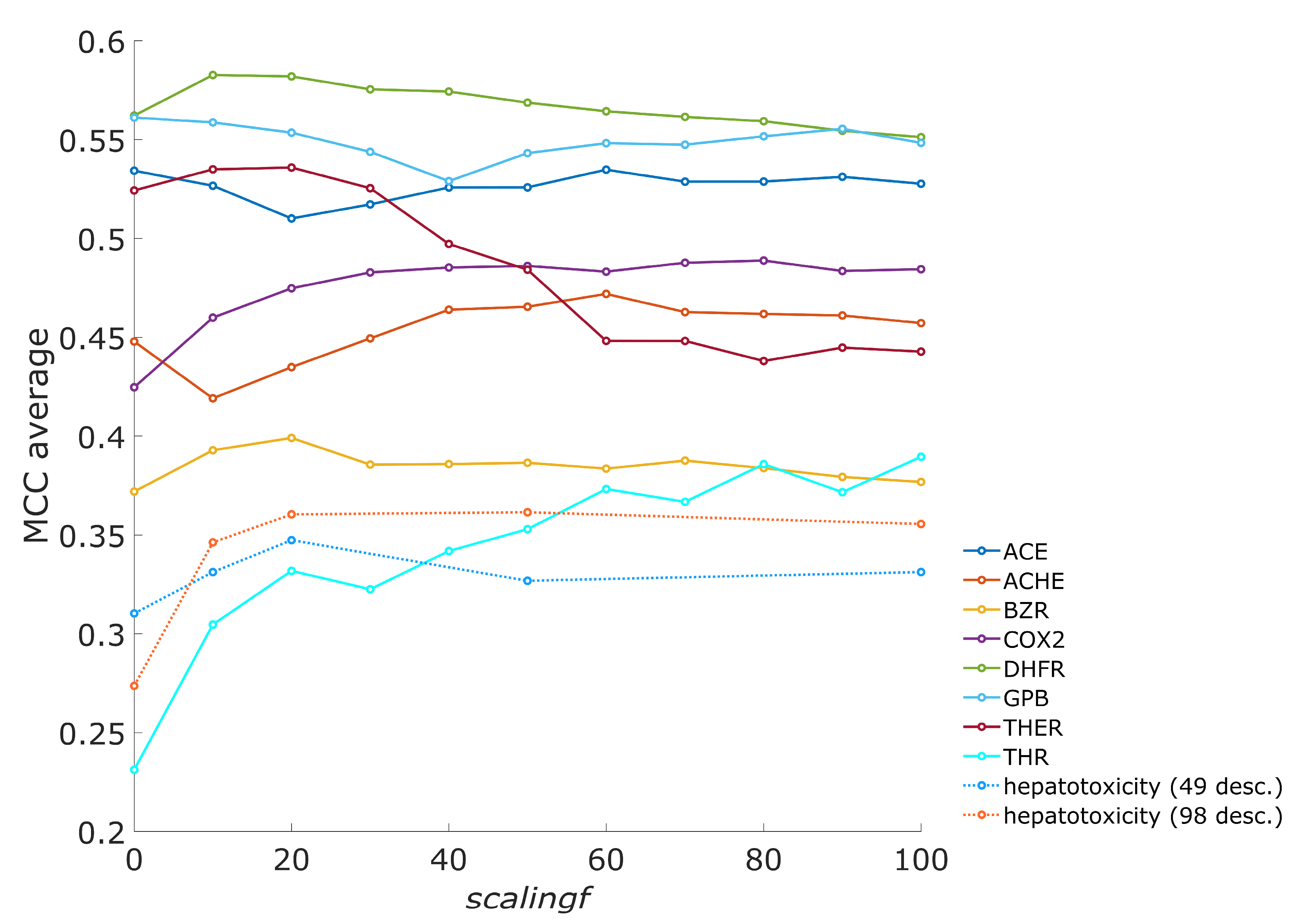
3.1. The Influence of Scaling Factor on the Number of Acceptable Models
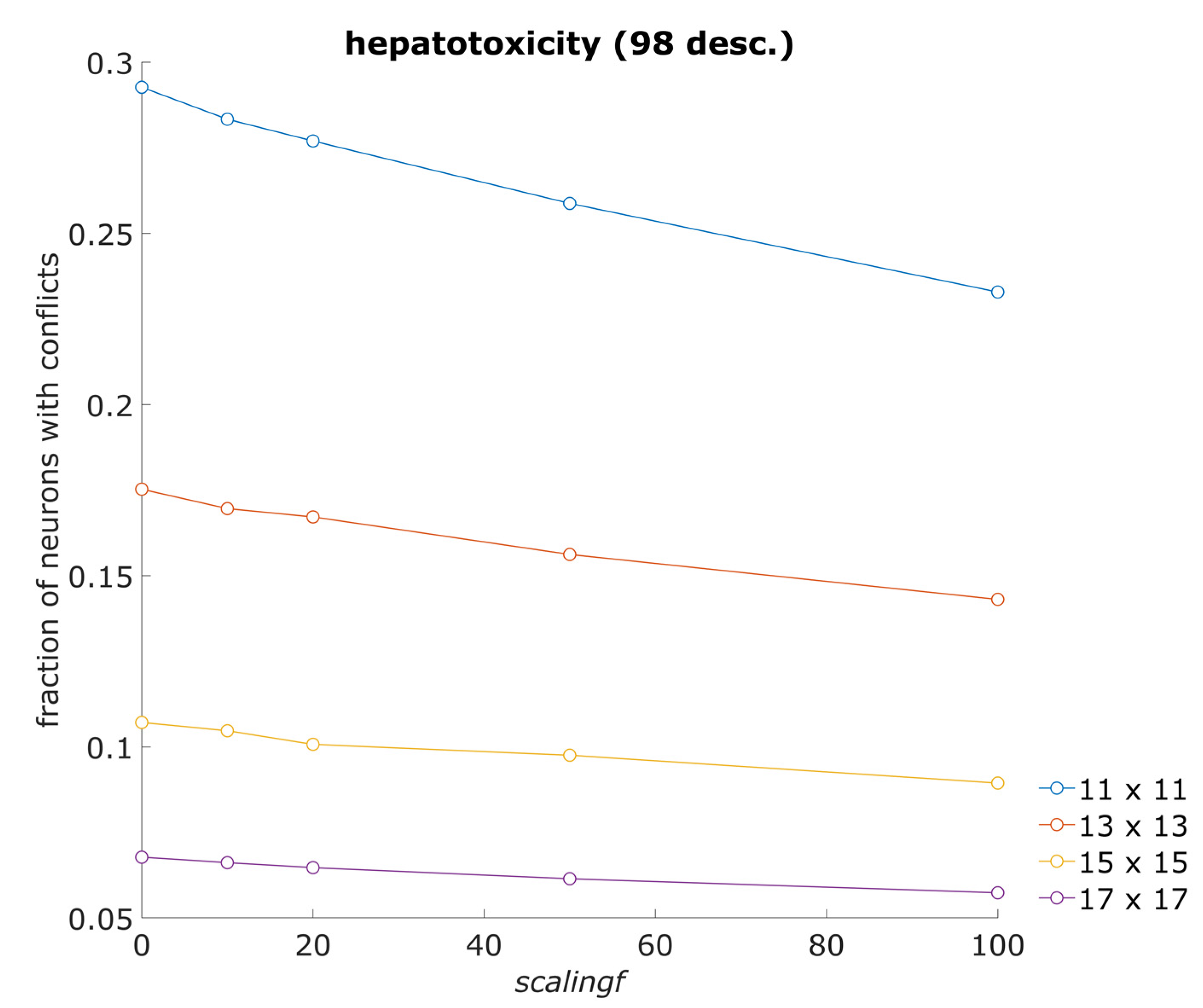
3.2. Average Fraction of Neurons with Conflicts
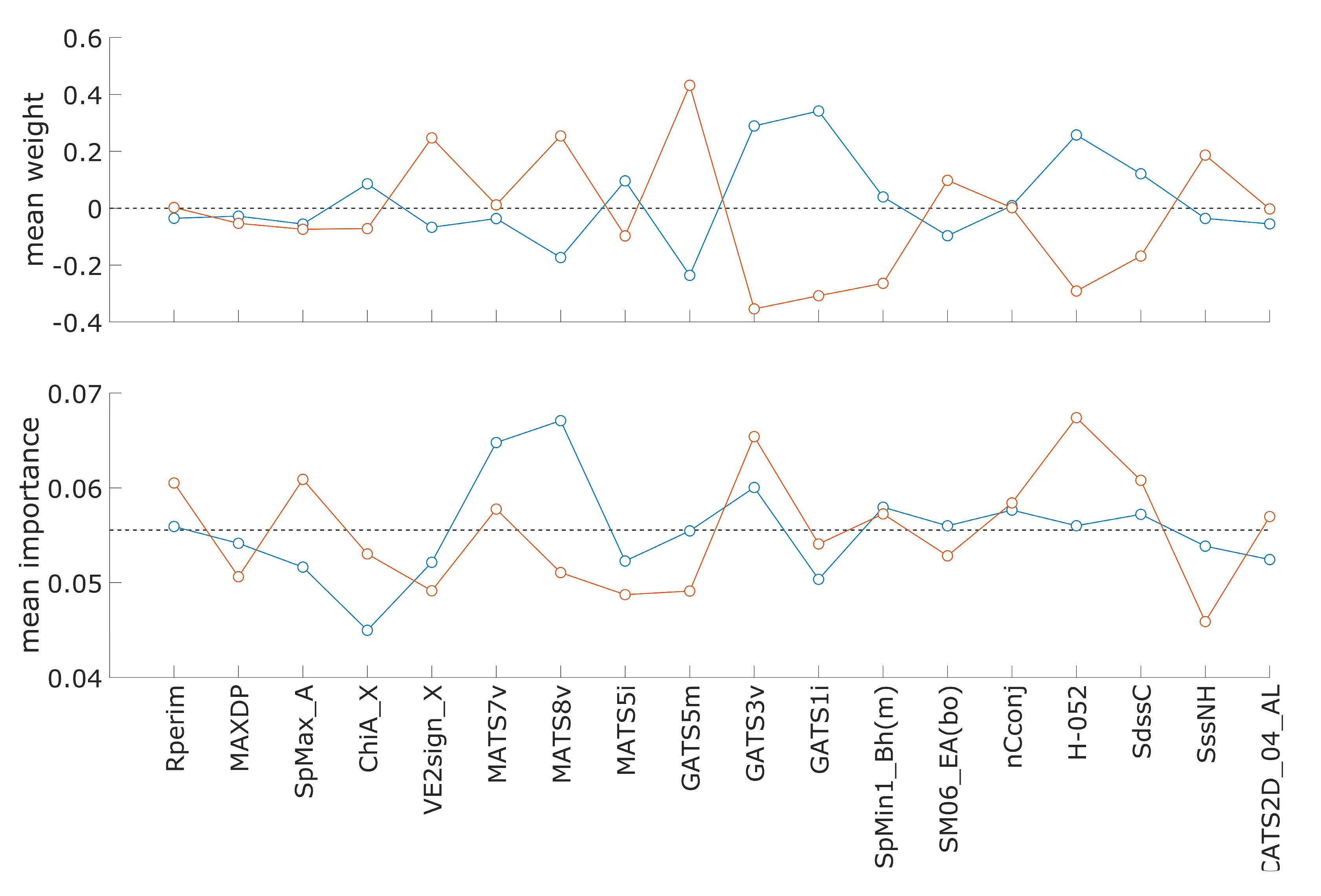
3.3. Descriptor Weights and Importance in Hepatotoxicity Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polishchuk, P. Interpretation of Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship Models: Past, Present, and Future. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 2618–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amgoud, L. Explaining Black-Box Classifiers: Properties and Functions. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2023, 155, 40–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.; DiMaio, F.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Lee, G.R.; Wang, J.; Cong, Q.; Kinch, L.N.; Schaeffer, R.D.; et al. Accurate Prediction of Protein Structures and Interactions Using a Three-Track Neural Network. Science 2021, 373, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; He, X.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Bi, R.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Shen, X.; Meng, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Ab Initio Characterization of Protein Molecular Dynamics with AI2BMD. Nature 2024, 635, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secor, M.; Soudackov, A.V.; Hammes-Schiffer, S. Artificial Neural Networks as Propagators in Quantum Dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 10654–10662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Li, B.; Chen, H. Application of Message Passing Neural Networks for Molecular Property Prediction. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2023, 81, 102616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieder, O.; Kuenemann, M.; Wieder, M.; Seidel, T.; Meyer, C.; Bryant, S.D.; Langer, T. Improved Lipophilicity and Aqueous Solubility Prediction with Composite Graph Neural Networks. Molecules 2021, 26, 6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Wu, C. Pre-Training Molecular Representation Model with Spatial Geometry for Property Prediction. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2024, 109, 108023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Milthorpe, B.K.; Jones, A.S. Direct Neural Network Application for Automated Cell Recognition. Cytometry A 2004, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingman, I.; Stierstorfer, B.; Lempp, C.; Heinemann, F. Learning Image Representations for Anomaly Detection: Application to Discovery of Histological Alterations in Drug Development. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 92, 103067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Wu, H. Variable Importance Evaluation with Personalized Odds Ratio for Machine Learning Model Interpretability with Applications to Electronic Health Records-based Mortality Prediction. Stat. Med. 2023, 42, 761–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. Anchors: High-Precision Model-Agnostic Explanations. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why Should I Trust You?”: Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD’16), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, A.; Rudin, C.; Dominici, F. All Models Are Wrong, but Many Are Useful: Learning a Variable’s Importance by Studying an Entire Class of Prediction Models Simultaneously. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2019, 20, 177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’17), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Guyon, I., Fergus, R., Wallach, H., Wallach, H., Guyon, I., Vishwanathan, S.V.N., von Luxburg, U., Garnett, R., Vishwanathan, S.V.N., Bengio, S., et al., Eds.; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation. Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 2017-December, pp. 4766–4775. [Google Scholar]
- Štrumbelj, E.; Kononenko, I. Explaining Prediction Models and Individual Predictions with Feature Contributions. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2014, 41, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveieva, M.; Polishchuk, P. Benchmarks for Interpretation of QSAR Models. J. Cheminform. 2021, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadaleta, D.; Spînu, N.; Roncaglioni, A.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Benfenati, E. Prediction of the Neurotoxic Potential of Chemicals Based on Modelling of Molecular Initiating Events Upstream of the Adverse Outcome Pathways of (Developmental) Neurotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, A.; Manganaro, A.; Arning, J.; Benfenati, E. Development of New QSAR Models for Water, Sediment, and Soil Half-Life. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Guidance Document on the Validation of (Quantitative) Structure-Activity Relationship [(Q)SAR] Models; OECD Series on Testing and Assessment, No. 69; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fjodorova, N.; Novič, M. Integration of QSAR and SAR methods for the mechanistic interpretation of predictive models for carcinogenicity. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2012, 1, e201207003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, C.; Manganaro, A.; Raitano, G.; Marzo, M.; Gadaleta, D.; Baderna, D.; Roncaglioni, A.; Kramer, N.; Benfenati, E. QSAR Models for Human Carcinogenicity: An Assessment Based on Oral and Inhalation Slope Factors. Molecules 2020, 26, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmanovski, I.; Novič, M.; Trpkovska, M. Automatic Adjustment of the Relative Importance of Different Input Variables for Optimization of Counter-Propagation Artificial Neural Networks. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 642, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drgan, V.; Bajželj, B. Application of Supervised SOM Algorithms in Predicting the Hepatotoxic Potential of Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012.
- Sutherland, J.J.; O’Brien, L.A.; Weaver, D.F. A Comparison of Methods for Modeling Quantitative Structure−Activity Relationships. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 5541–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajželj, B.; Drgan, V. Hepatotoxicity Modeling Using Counter-Propagation Artificial Neural Networks: Handling an Imbalanced Classification Problem. Molecules 2020, 25, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupan, J.; Gasteiger, J. Neural Networks in Chemistry and Drug Design, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1999; ISBN 3-527-29778-2. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, V.; Gasteiger, J.; Zupan, J. A Combined Application of Two Different Neural Network Types for the Prediction of Chemical Reactivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 9148–9159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bajželj, B.; Novič, M.; Drgan, V. Utilizing Molecular Descriptor Importance to Enhance Endpoint Predictions. Toxics 2025, 13, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050383
Bajželj B, Novič M, Drgan V. Utilizing Molecular Descriptor Importance to Enhance Endpoint Predictions. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050383
Chicago/Turabian StyleBajželj, Benjamin, Marjana Novič, and Viktor Drgan. 2025. "Utilizing Molecular Descriptor Importance to Enhance Endpoint Predictions" Toxics 13, no. 5: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050383
APA StyleBajželj, B., Novič, M., & Drgan, V. (2025). Utilizing Molecular Descriptor Importance to Enhance Endpoint Predictions. Toxics, 13(5), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050383





