Oral Supplementation with Modified Natural Clinoptilolite Protects Against Cadmium Toxicity in ICR (CD-1) Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinoptilolite
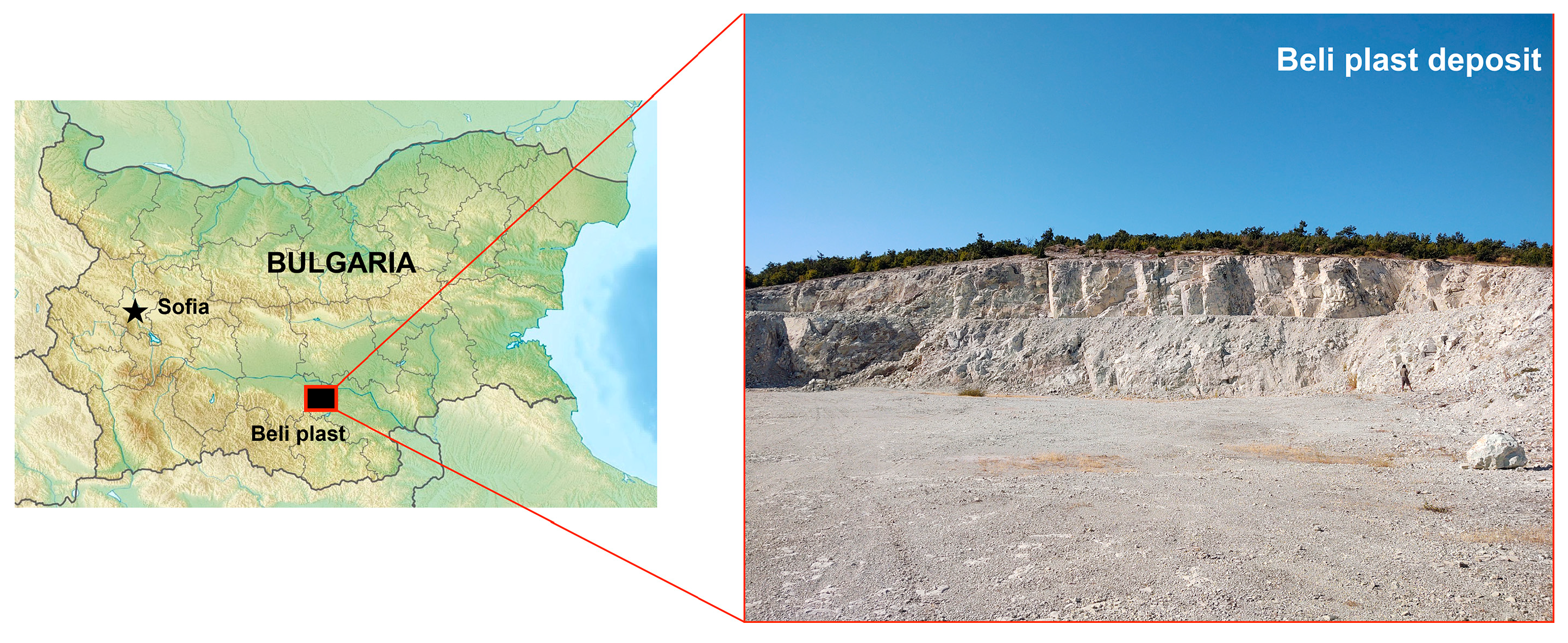
2.1.1. Sample Collection
2.1.2. Preparation of Na-Exchanged Clinoptilolite Sorbent
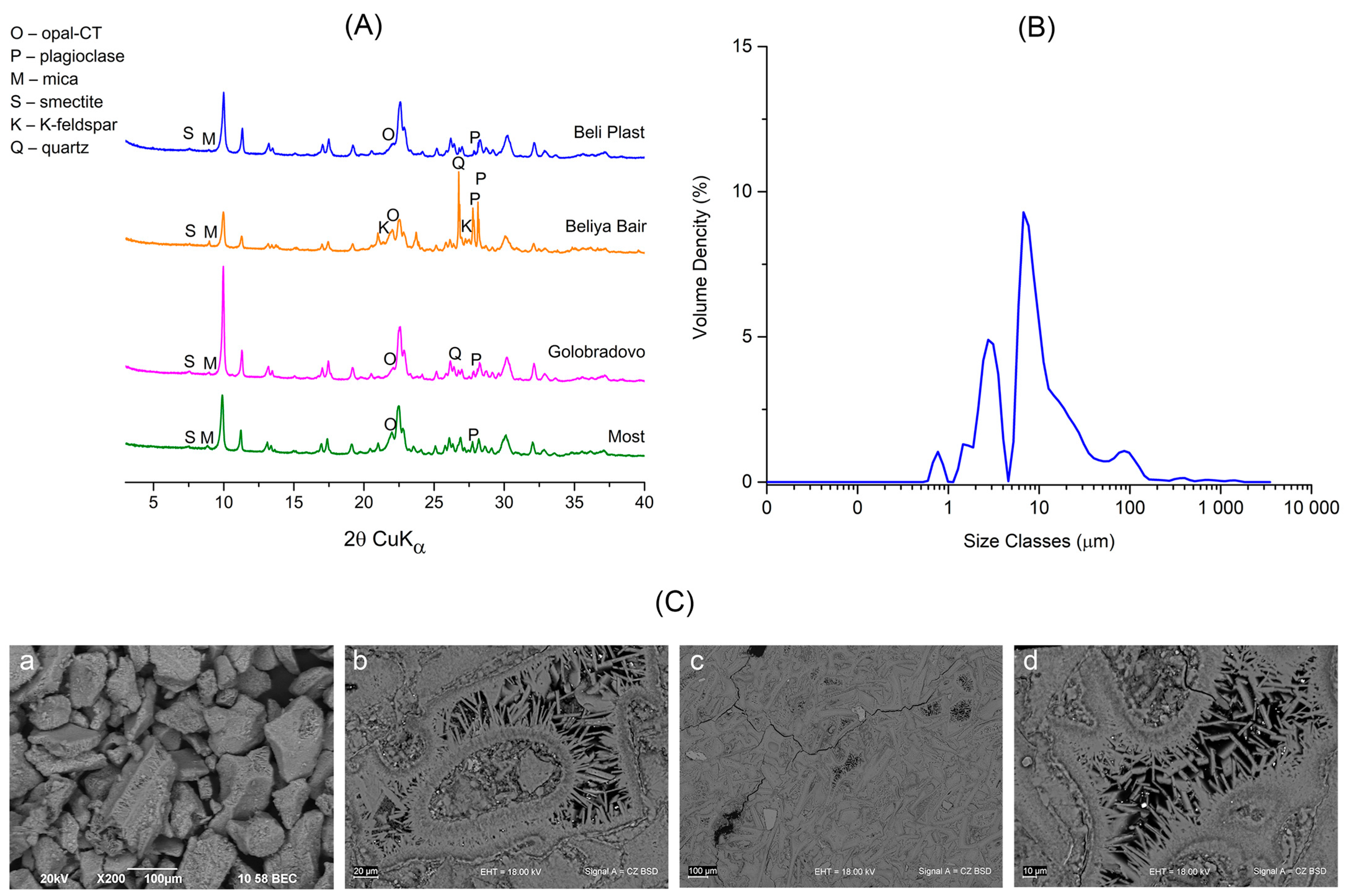
2.1.3. Characterization Methods
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Experimental Animals and Husbandry
2.4. Heavy Metal Loading
2.5. Weight and Organ Index Assays
2.6. Hematology
2.7. Oxidative Stress Markers
2.8. Micronucleus Test
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Natural and Na-Exchanged Clinoptilolite Tuff
3.2. Cadmium Bioaccumulation
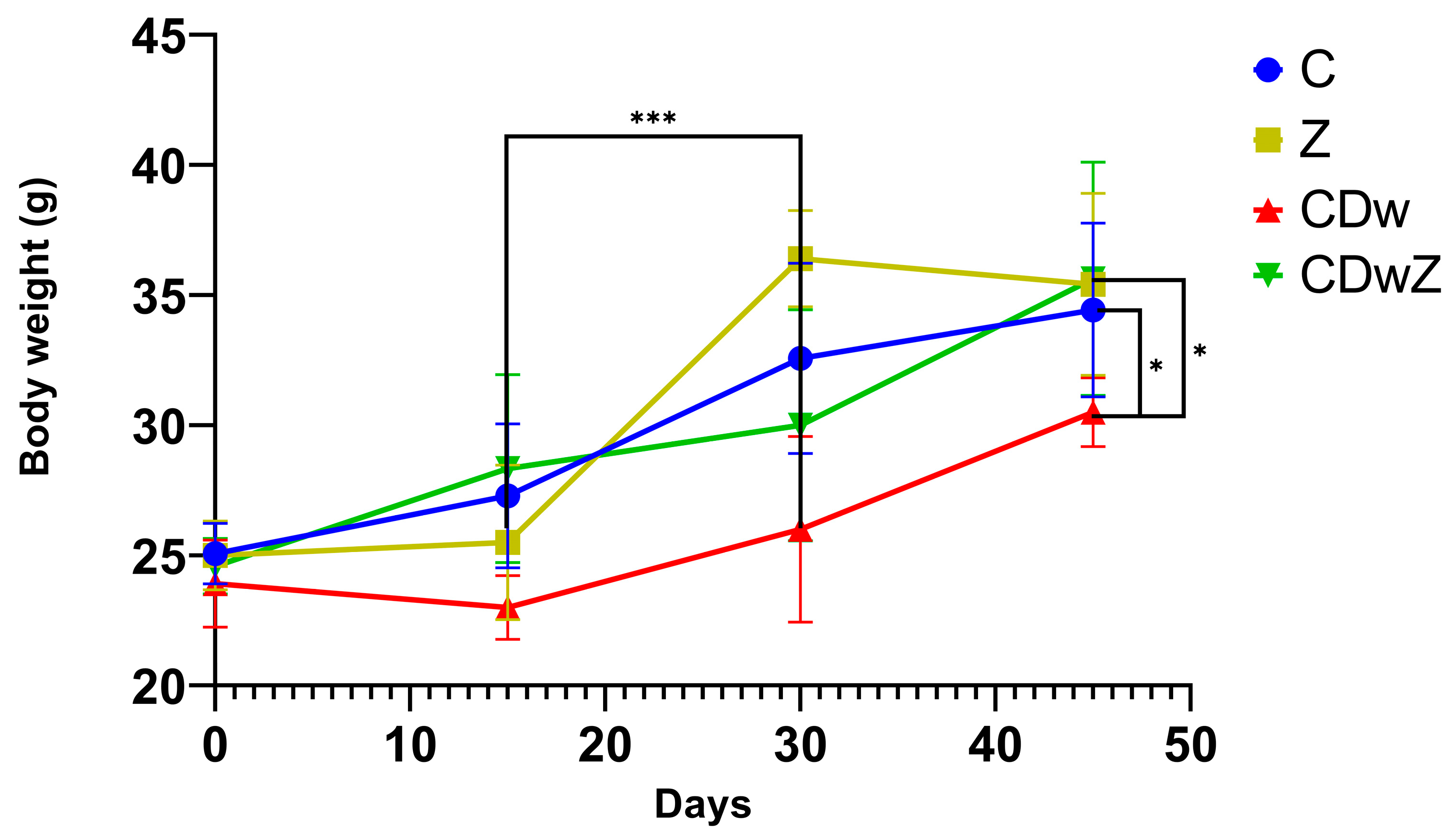
3.3. Growth Rate
3.4. Organ Index Changes
3.5. Hematology
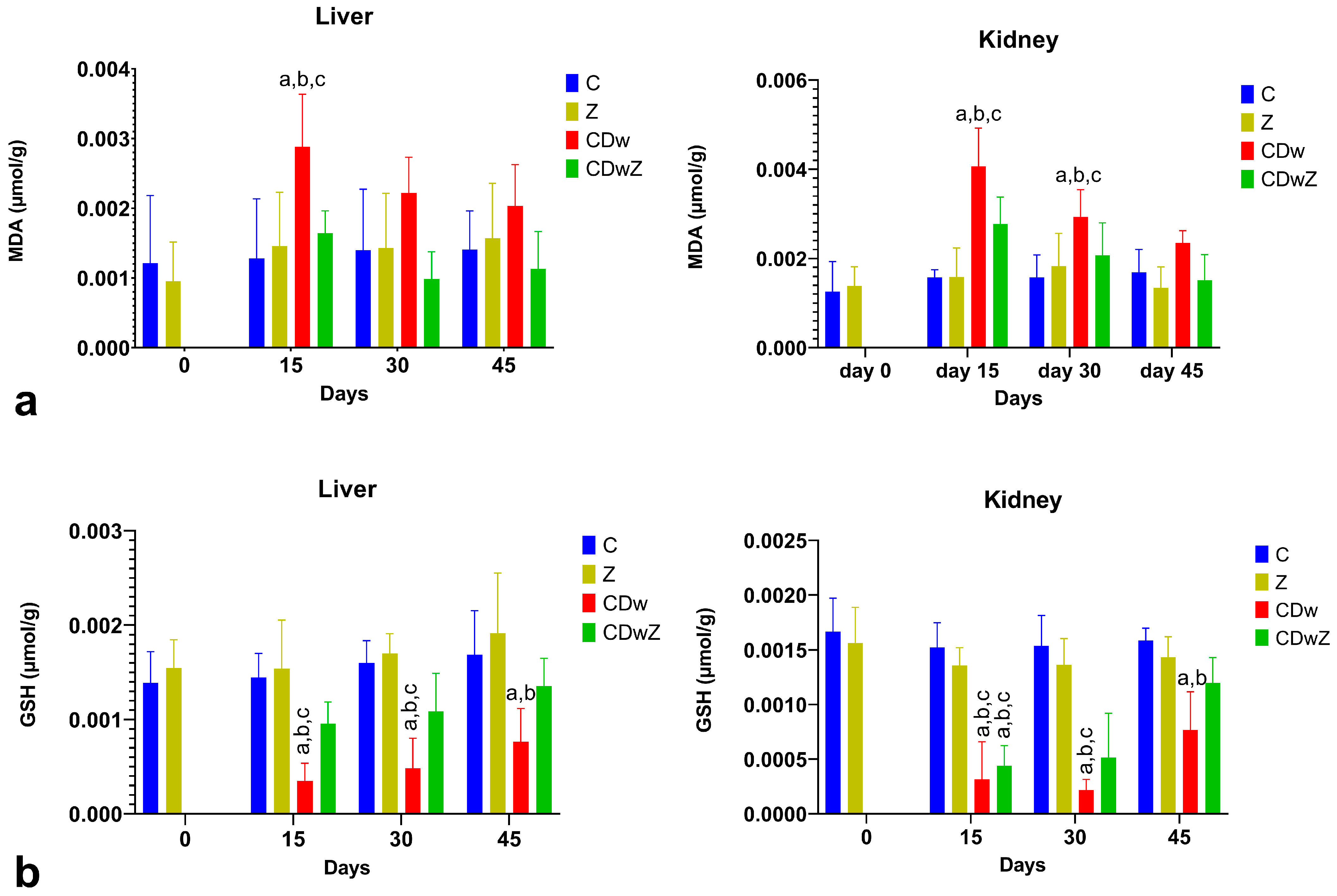
3.6. Oxidative Stress
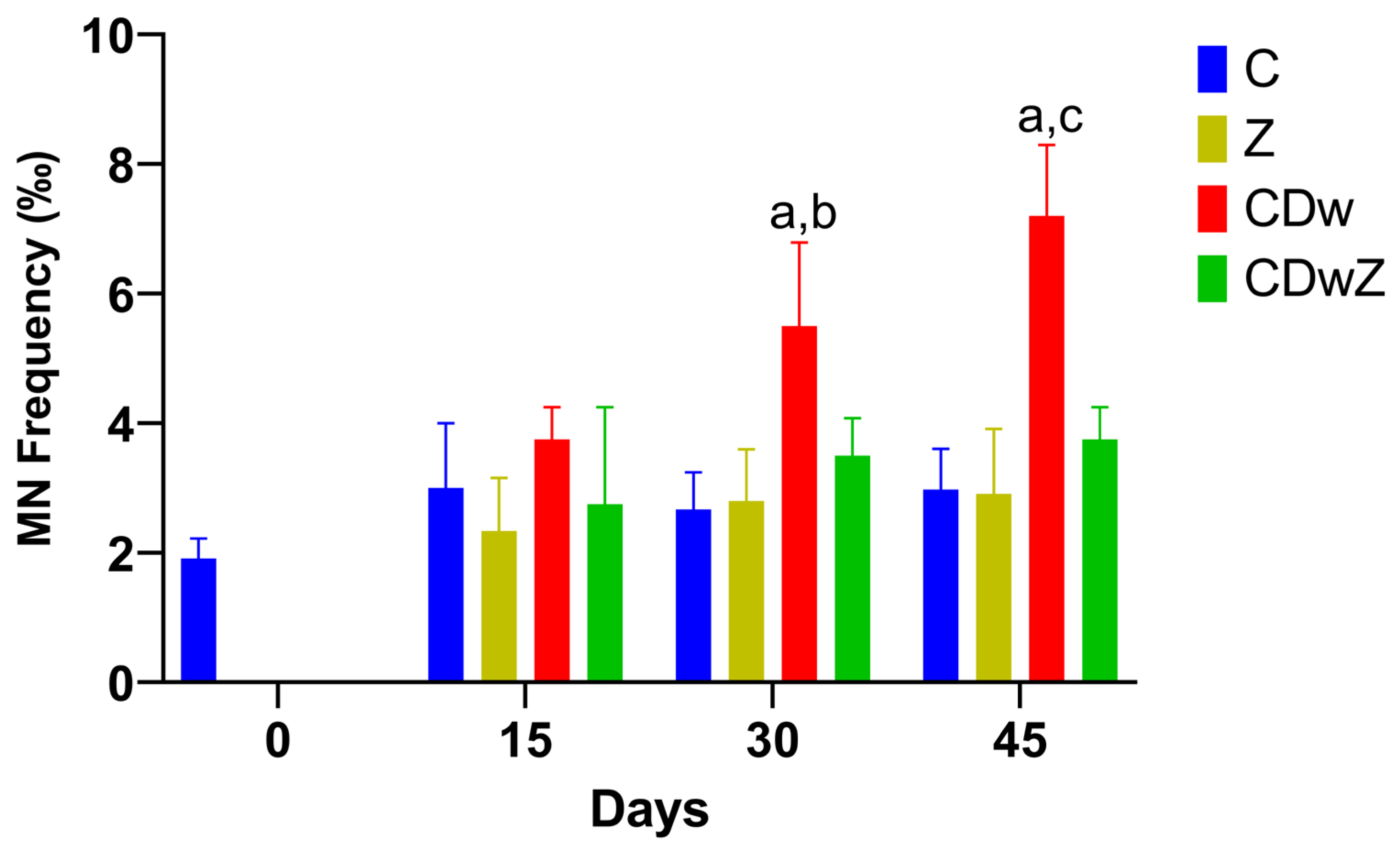
3.7. Micronucleus Test
4. Discussion
4.1. Sorption Properties of Modified Natural Clinoptilolite
4.2. Cadmium Toxicity and Bioaccumulation
4.3. Growth Rate
4.4. Hematology
4.5. Oxidative Stress
4.6. Genotoxic Effects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez-Morata, I.; Sobel, M.; Tellez-Plaza, M.; Navas-Acien, A.; Howe, C.G.; Sanchez, T.R. A State-of-the-Science Review on Metal Biomarkers. Curr. Env. Health Rep. 2023, 10, 215–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumpton, F.A. La Roca Magica: Uses of Natural Zeolites in Agriculture and Industry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3463–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bish, D.L.; Ming, D. Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry: Occurrence, Properties, Applications. Nat. Zeolites 2001, 45, 1521–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Coombs, D.S.; Alberti, A.; Armbruster, T.; Artioli, G.; Colella, C.; Galli, E.; Grice, J.D.; Liebau, F.; Mandarino, J.A.; Minato, H.; et al. Recommended Nomenclature for Zeolite Minerals: Report of the Subcommittee on Zeolites of the International Mineralogical Association, Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names. Miner. Mag. 1998, 62, 533–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebelin, N.; Armbruster, T. Stepwise Dehydration and Change of Framework Topology in Cd-Exchanged Heulandite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 61, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, A.B.; Slaughter, M. Determination and Refinement of the Structure of Heulandite. Am. Mineral. J. Earth Planet. Mater. 1968, 53, 1120–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Alberti, A. The Crystal Structure of Two Clinoptilolites. TMPM Tschermaks Mineral. Und Petrogr. Mitteilungen 1975, 22, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, K.; Takeuchi, Y. Clinoptilolite: The Distribution of Potassium Atoms and Its Role in Thermal Stability. Z. Krist. Cryst. Mater. 1977, 145, 216–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, J.W.; Bish, D.L. Equilibrium in the Clinoptilolite-H2O System. Am. Mineral. 1996, 81, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, T.; Gunter, M.E. Stepwise Dehydration of Heulandite-Clinoptilolite from Succor Creek, Oregon, USA: A Single-Crystal X-Ray Study at 100 K. Am. Mineral. 1991, 76, 1872–1888. [Google Scholar]
- Langella, A.; Pansini, M.; Cappelletti, P.; de Gennaro, B.; de’ Gennaro, M.; Colella, C. Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ Exchange for Na+ in a Sedimentary Clinoptilolite, North Sardinia, Italy. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 37, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksiev, B.; Djourova, E.G. On the Origin of Zeolite Rocks. C. R. Acad. Bulg. Sci. 1975, 28, 517–520. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksiev, B.; Djourova, E.G. Mordenite Zeolitites from the Northeastern Rhodopes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 29, 865–867. [Google Scholar]
- Yanev, Y.; Cochemé, J.J.; Ivanova, R.; Grauby, O.; Burlet, E.; Pravchanska, R. Zeolites and Zeolitization of Acid Pyroclastic Rocks from Paroxysmal Paleogene Volcanism, Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria. Neues Jahrb. Für Mineral.-Abh. 2006, 182, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanev, Y.; Ivanova, R. Mineral Chemistry of the Collision-Related Acid Paleogene Volcanic Rocks of the Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria. Geochem. Mineral. Petrol. 2010, 48, 39–65. [Google Scholar]
- Dolanc, I.; Ferhatović Hamzić, L.; Orct, T.; Micek, V.; Šunić, I.; Jonjić, A.; Jurasović, J.; Missoni, S.; Čoklo, M.; Pavelić, S.K. The Impact of Long-Term Clinoptilolite Administration on the Concentration Profile of Metals in Rodent Organisms. Biology 2023, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltcheva, M.; Metcheva, R.; Popov, N.; Teodorova, S.E.; Heredia-Rojas, J.A.; Rodríguez-de la Fuente, A.O.; Rodríguez-Flores, L.E.; Topashka-Ancheva, M. Modified Natural Clinoptilolite Detoxifies Small Mammal’s Organism Loaded with Lead I. Lead Disposition and Kinetic Model for Lead Bioaccumulation. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 147, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topashka-Ancheva, M.; Beltcheva, M.; Metcheva, R.; Rojas, J.A.H.; Rodriguez-De la Fuente, A.O.; Gerasimova, T.; Rodríguez-Flores, L.E.; Teodorova, S.E. Modified Natural Clinoptilolite Detoxifies Small Mammal’s Organism Loaded with Lead II: Genetic, Cell, and Physiological Effects. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 147, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltcheva, M.; Metcheva, R.; Topashka-Ancheva, M.; Popov, N.; Teodorova, S.; Heredia-Rojas, J.A.; Rodríguez-de la Fuente, A.O.; Rodríguez-Flores, L.E. Zeolites versus Lead Toxicity. J. Bioequivalence Bioavailab. 2015, 7, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraljević Pavelić, S.; Simović Medica, J.; Gumbarević, D.; Filošević, A.; Pržulj, N.; Pavelić, K. Critical Review on Zeolite Clinoptilolite Safety and Medical Applications in Vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Ahmad, H.; Wang, T. Effects of Clinoptilolite on Growth Performance and Antioxidant Status in Broilers. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 155, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montinaro, M.; Uberti, D.; Maccarinelli, G.; Bonini, S.A.; Ferrari-Toninelli, G.; Memo, M. Dietary Zeolite Supplementation Reduces Oxidative Damage and Plaque Generation in the Brain of an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Life Sci. 2013, 92, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trottier, B.; Athot, J.; Ricard, A.C.; Lafond, J. Maternal–Fetal Distribution of Cadmium in the Guinea Pig Following a Low Dose Inhalation Exposure. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 129, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Xu, S. Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress Promotes Apoptosis and Necrosis through the Regulation of the MiR-216a-PI3K/AKT Axis in Common Carp Lymphocytes and Antagonized by Selenium. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Nie, G.; Yang, F.; Chen, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Dai, X.; Liao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Cao, H.; Xing, C.; et al. Molybdenum and Cadmium Co-Induce Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis through Mitochondria-Mediated Pathway in Duck Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Song, W.; Hong, D.; Huang, L.; Li, Y. A Review on Cadmium Exposure in the Population and Intervention Strategies Against Cadmium Toxicity. Bull. Env. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Reynolds, M. Cadmium Exposure in Living Organisms: A Short Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Env. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, F.M.; Caglayan, C.; Darendelioğlu, E.; Küçükler, S.; İzol, E.; Kandemir, Ö. Modulatory Effects of Carvacrol against Cadmium-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity by Molecular Targeting Regulation. Life Sci. 2021, 277, 119610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, C.D.; Liu, J.; Diwan, B.A. Metallothionein Protection of Cadmium Toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, H.; Aziz, A.T.; Saggu, S.; VanWert, A.L.; Zidan, N.; Saggu, S. Additive Toxic Effect of Deltamethrin and Cadmium on Hepatic, Hematological, and Immunological Parameters in Mice. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2017, 33, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saggu, S.; Rehman, H.; Aziz, A.T.; Alzeibr, F.M.A.; Oyouni, A.A.A.; Zidan, N.; Panneerselvam, C.; Trivedi, S. Cymbopogon Schoenanthus (Ethkher) Ameliorates Cadmium Induced Toxicity in Swiss Albino Mice. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sani, A.; Darma, A.I.; Abdullahi, I.L.; Musa, B.U.; Imam, F.A. Heavy Metals Mixture Affects the Blood and Antioxidant Defense System of Mice. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 11, 100340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bist, P.; Singh, D.; Choudhary, S. Blood Metal Levels Linked with Hematological, Oxidative, and Hepatic-Renal Function Disruption in Swiss Albino Mice Exposed to Multi-Metal Mixture. Comp. Clin. Path 2023, 32, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amedu, N.O.; Omotoso, G.O. Evaluating the Role of Vitexin on Hematologic and Oxidative Stress Markers in Lead-Induced Toxicity in Mice. Toxicol. Env. Health Sci. 2020, 12, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Bashir, S.; Mumtaz, S.; Shakir, H.A.; Ara, C.; Ahmad, F.; Tahir, H.M.; Faheem, M.; Irfan, M.; Masih, A.; et al. Evaluation of Cadmium Chloride-Induced Toxicity in Chicks Via Hematological, Biochemical Parameters, and Cadmium Level in Tissues. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 3457–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matović, V.; Buha, A.; Ðukić-Ćosić, D.; Bulat, Z. Insight into the Oxidative Stress Induced by Lead and/or Cadmium in Blood, Liver and Kidneys. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q. Protective Effect of Melatonin against Chronic Cadmium-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Suppressing Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Mice. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2021, 228, 112947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, R.K.; Anderson, M.E.; Meister, A. Glutathione, a First Line of Defense against Cadmium Toxicity. FASEB J. 1987, 1, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupina, K.; Goginashvili, A.; Cleveland, D.W. Causes and Consequences of Micronuclei. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2021, 70, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapisso, J.T.; Marques, C.C.; Mathias, M.d.L.; Ramalhinho, M.d.G. Induction of Micronuclei and Sister Chromatid Exchange in Bone-Marrow Cells and Abnormalities in Sperm of Algerian Mice (Mus Spretus) Exposed to Cadmium, Lead and Zinc. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2009, 678, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitkovska, V.I.; Dimitrov, H.A.; Chassovnikarova, T.G. Chronic Exposure to Lead and Cadmium Pollution Results in Genomic Instability in a Model Biomonitor Species (Apodemus Flavicollis Melchior, 1834). Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2020, 194, 110413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çelik, A.; Mazmanci, B.; Çamlica, Y.; Aşkin, A.; Çömelekoğlu, Ü. Induction of Micronuclei by Lambda-Cyhalothrin in Wistar Rat Bone Marrow and Gut Epithelial Cells. Mutagenesis 2005, 20, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, A.; Büyükakilli, B.; Çimen, B.; Taşdelen, B.; Öztürk, M.İ.; Eke, D. Assessment of Cadmium Genotoxicity in Peripheral Blood and Bone Marrow Tissues of Male Wistar Rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2009, 19, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, M.A.; Aly, F.A. In Vivo and in Vitro Studies on the Genotoxicity of Cadmium Chloride in Mice. J. Appl. Toxicol. Int. J. 2000, 20, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belliardo, C.; Di Giorgio, C.; Chaspoul, F.; Gallice, P.; Bergé-Lefranc, D. Direct DNA Interaction and Genotoxic Impact of Three Metals: Cadmium, Nickel and Aluminum. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2018, 125, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltcheva, M.; Ostoich, P.; Aleksieva, I.; Metcheva, R. Natural Zeolites as Detoxifiers and Modifiers of the Biological Effects of Lead and Cadmium in Small Rodents: A Review. BioRisk 2022, 17, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Economic Area. Heavy Metal Emissions in Europe. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/analysis/indicators/heavy-metal-emissions-in-europe (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- Ramezani, M.; Enayati, M.; Ghorbani, A. A Study of Different Strategical Views into Heavy Metal(Oid) Removal in the Environment. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, D.; Maiti, S.K. Sources, Bioaccumulation, Health Risks and Remediation of Potentially Toxic Metal(Loid)s (As, Cd, Cr, Pb and Hg): An Epitomised Review. Env. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union (EU). Commission Regulation (EU) No 744/2012 Annexes I and II to Directive 2002/32/EC of the European Parliament and the Council as Regards Maximum Levels for Arsenic, Fluorine, Lead, Mercury, Endosulfan, Dioxins, Ambrosia Spp., Diclazuril and Lasalocid A Sodium and Action Thresholds for Dioxins. Off. J. Eur. Union 2012, 219, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- European Union (EU). Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 651/2013 The Authorisation of Clinoptilolite of Sedimentary Origin as a Feed Additive for All Animal Species and Amending Regulation (EC) No 1810/2005. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013, 189, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanova, I.; Djurova, E.; Gradev, G. Sorption of Zinc and Cadmium on Zeolite Rocks. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. Lett. 1988, 128, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO Standard No 13320:2020; Particle Size Analysis—Lazer Diffraction Methods. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Benoff, S.; Auborn, K.; Marmar, J.L.; Hurley, I.R. Link between Low-Dose Environmentally Relevant Cadmium Exposures and Asthenozoospermia in a Rat Model. Fertil. Steril. 2008, 89, e73–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caflisch, C.R. Effect of Orally Administered Cadmium on in Situ PH, PCO 2, and Bicarbonate Concentration in Rat Testis and Epididymis. J. Toxicol. Env. Health 1994, 42, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Nam, J.H.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, K.S.; Hwang, D.Y. Annual Tendency of Research Papers Used ICR Mice as Experimental Animals in Biomedical Research Fields. Lab. Anim. Res. 2017, 33, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and Council of the European Union. Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes (Directive 2010/63/EU). Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, L 276, 33–79. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2010/63/oj/eng (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Friberg, L. Cadmium and the Kidney. Env. Health Perspect. 1984, 54, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şehirli, Ö.; Tozan, A.; Omurtag, G.Z.; Cetinel, S.; Contuk, G.; Gedik, N.; Şener, G. Protective Effect of Resveratrol against Naphthalene-Induced Oxidative Stress in Mice. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2008, 71, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; MacGregor, J.T.; Gatehouse, D.G.; Adler, I.-D.; Blakey, D.H.; Dertinger, S.D.; Krishna, G.; Morita, T.; Russo, A.; Sutou, S. In Vivo Rodent Erythrocyte Micronucleus Assay. II. Some Aspects of Protocol Design Including Repeated Treatments, Integration with Toxicity Testing, and Automated Scoring. Env. Mol. Mutagen. 2000, 35, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the Continental Crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Tzvetanova, Y.; Tacheva, E.; Dimowa, L.; Tsvetanova, L.; Nikolov, A. Trace Elements in the Clinoptilolite Tuffs from Four Bulgarian Deposits, Eastern Rhodopes. Rev. Bulg. Geol. Soc. 2023, 84, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apreutesei, R.E.; Catrinescu, C.; Teodosiu, C. Surfactant-modified natural zeolites for environmental applications in water purification. Env. Eng. Manag. J. 2008, 7, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraljević Pavelić, S.; Micek, V.; Filošević, A.; Gumbarević, D.; Žurga, P.; Bulog, A.; Orct, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Preočanin, T.; Plavec, J.; et al. Novel, Oxygenated Clinoptilolite Material Efficiently Removes Aluminium from Aluminium Chloride-Intoxicated Rats in Vivo. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 249, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances Used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP). Scientific Opinion on the Safety and Efficacy of Clinoptilolite of Sedimentary Origin for All Animal Species. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltcheva, M.; Tzvetanova, Y.; Todorova, T.; Tsvetanova, L.; Aleksieva, I.; Gerasimova, T.; Chassovnikarova, T. Does Natural Clinoptilolite Induce Toxicity in Small Mammals? Acta Zool. Bulg. 2024, 76, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Kalinin, I.; Tomchuk, V. Removal of Heavy Metals Using Sorbents and Biochemical Indexes in Rats. Ukr. J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 14, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkuna, O.; Leboda, R.; Skubiszewska-Zie¸ba, J.; Vrublevs’ka, T.; Gun’ko, V.M.; Ryczkowski, J. Structural and Physicochemical Properties of Natural Zeolites: Clinoptilolite and Mordenite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 87, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Iznaga, I.; Shelyapina, M.G.; Petranovskii, V. Ion Exchange in Natural Clinoptilolite: Aspects Related to Its Structure and Applications. Minerals 2022, 12, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelić, K.H.M. Medical Applications of Zeolites. In Handbook of Zeolite Science and Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 1453–1491. [Google Scholar]
- Kristo, A.S.; Tzanidaki, G.; Lygeros, A.; Sikalidis, A.K. Bile Sequestration Potential of an Edible Mineral (Clinoptilolite) under Simulated Digestion of a High-Fat Meal: An in Vitro Investigation. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3818–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.E.; Olin, T.J.; Bricka, R.M.; Adrian, D.D. A Review of Potentially Low-Cost Sorbents for Heavy Metals. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizidou, M.; Townsend, R.P. Exchange of Cadmium into the Sodium and Ammonium Forms of the Natural Zeolites Clinoptilolite, Mordenite, and Ferrierite. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1987, 1911–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.J. Zeolites: Physical Aspects and Environmental Applications. Annu. Rep. Sect. “C” (Phys. Chem.) 2007, 103, 287–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haemmerle, M.M.; Fendrych, J.; Matiasek, E.; Tschegg, C. Adsorption and Release Characteristics of Purified and Non-Purified Clinoptilolite Tuffs towards Health-Relevant Heavy Metals. Crystals 2021, 11, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, C.D.; Liu, J.; Choudhuri, S. METALLOTHIONEIN: An Intracellular Protein to Protect Against Cadmium Toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1999, 39, 267–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Shu, Y. Cadmium Transporters in the Kidney and Cadmium-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsenhans, B.; Strugala, G.; Schäfer, S. Small-Intestinal Absorption of Cadmium and the Significance of Mucosal Metallothionein. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 1997, 16, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmańczuk, A.; Markiewicz, W.; Burmańczuk, A.; Kowalski, C.; Roliński, Z.; Burmańczuk, N. Possibile Use of Natural Zeolites in Animal Production and Environment Protection. J. Elem. 2015, 20, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bist, R.B.; Subedi, S.; Chai, L.; Regmi, P.; Ritz, C.W.; Kim, W.K.; Yang, X. Effects of Perching on Poultry Welfare and Production: A Review. Poultry 2023, 2, 134–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, D.; Katsoulos, P.D.; Panousis, N.; Karatzias, H. The Role of Natural and Synthetic Zeolites as Feed Additives on the Prevention and/or the Treatment of Certain Farm Animal Diseases: A Review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 84, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.M.; Al-Baadani, H.H.; Qaid, M.M.; Al-Garadi, M.A.; Suliman, G.M.; Alobre, M.M.; Al-Mufarrej, S.I. Using natural zeolite as a feed additive in broilers’ diets for enhancing growth performance, carcass characteristics, and meat quality traits. Life 2023, 13, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraljević Pavelić, S.; Saftić Martinović, L.; Simović Medica, J.; Žuvić, M.; Perdija, Ž.; Krpan, D.; Eisenwagen, S.; Orct, T.; Pavelić, K. Clinical Evaluation of a Defined Zeolite-Clinoptilolite Supplementation Effect on the Selected Blood Parameters of Patients. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 851782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świergosz-Kowalewska, R. Cadmium Distribution and Toxicity in Tissues of Small Rodents. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2001, 55, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, C.P.; Lill, A.; Reina, R.D. Use of Erythrocyte Indicators of Health and Condition in Vertebrate Ecophysiology: A Review and Appraisal. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powolny, T.; Scheifler, R.; Raoul, F.; Coeurdassier, M.; Fritsch, C. Effects of Chronic Exposure to Toxic Metals on Haematological Parameters in Free-Ranging Small Mammals. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçak, M.; Akçıl, E. The Effects of Chronic Cadmium Toxicity on the Hemostatic System. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2006, 35, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazima, B.; Manoharan, V.; Miltonprabu, S. Oxidative Stress Induced by Cadmium in the Plasma, Erythrocytes and Lymphocytes of Rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 428–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, D.; Valberg, L. Relationship between Cadmium and Iron Absorption. Am. J. Physiol.-Leg. Content 1974, 227, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, H.; Teranishi, H.; Niiya, K.; Aoshima, K.; Katoh, T.; Sakuragawa, N.; Kasuya, M. Hypoproduction of Erythropoietin Contributes to Anemia in Chronic Cadmium Intoxication: Clinical Study on Itai-Itai Disease in Japan. Arch. Toxicol. 1994, 68, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolanjiappan, K.; Manoharan, S.; Kayalvizhi, M. Measurement of Erythrocyte Lipids, Lipid Peroxidation, Antioxidants and Osmotic Fragility in Cervical Cancer Patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2002, 326, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minetti, M.; Pietraforte, D.; Straface, E.; Metere, A.; Matarrese, P.; Malorni, W. Red Blood Cells as a Model to Differentiate between Direct and Indirect Oxidation Pathways of Peroxynitrite. Methods Enzymol. 2008, 440, 253–272. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, H.; Kanter, M.; Coskun, O.; Uz, Y.H.; Koc, A.; Yildiz, A. Effect of Black Cumin (Nigella Sativa) on Heart Rate, Some Hematological Values, and Pancreatic β-Cell Damage in Cadmium-Treated Rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2006, 110, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boshy, M.E.; Risha, E.F.; Abdelhamid, F.M.; Mubarak, M.S.; Hadda, T. Ben Protective Effects of Selenium against Cadmium Induced Hematological Disturbances, Immunosuppressive, Oxidative Stress and Hepatorenal Damage in Rats. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 29, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donmez, H.H.; Donmez, N.; Kısadere, I.; Undag, I. Protective Effect of Quercetin on Some Hematological Parameters in Rats Exposed to Cadmium. Biotech. Histochem. 2019, 94, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karuppasamy, R.; Subathra, S.; Puvaneswari, S. Haematological Responses to Exposure to Sublethal Concentration of Cadmium in Air-Breathing Fish, Channa Punctatus (Bloch). J. Env. Biol. 2005, 26, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Morsy, A.S.; Manal, M.; Gad-El-Moula, H.; Dooa, O.; Hassan, M.S.; Nagwa, A.A. Blood picture, metabolites and minerals of rabbits as influenced by drinking saline water in Egypt. Glob. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 3, 1008–1017. Available online: http://gjar.org/publishpaper/vol3issue11/d628r62.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Martin-Kleiner, I.; Flegar-Meštrić, Z.; Zadro, R.; Breljak, D.; Stanović Janda, S.; Stojković, R.; Marušić, M.; Radačić, M.; Boranić, M. The Effect of the Zeolite Clinoptilolite on Serum Chemistry and Hematopoiesis in Mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2001, 39, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojzis, J.; Nistiar, F.; Kovac, G.; Mojzisova, G. Preventive Effect of Zeolite in VX Poisoning in Rats. Vet. Med. 1994, 39, 443–449. [Google Scholar]
- Waisberg, M.; Joseph, P.; Hale, B.; Beyersmann, D. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Cadmium Carcinogenesis. Toxicology 2003, 192, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, W.G.; Ming, D.W.; Mumpton, F.A. Zeolites in animal nutrition and health: A review. Nat. Zeolites 1995, 93, 449. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Qu, W.; Kadiiska, M.B. Role of Oxidative Stress in Cadmium Toxicity and Carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Liu, S.; Luo, Y.; Pu, J.; Deng, X.; Zhou, W.; Dong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, F.; et al. Procyanidin B2 Alleviates Uterine Toxicity Induced by Cadmium Exposure in Rats: The Effect of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2023, 263, 115290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Morris, H.; Cronin, M. Metals, Toxicity and Oxidative Stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1161–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Qi, K.; Zhang, L.; Bai, Z.; Ren, C.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X. Glutathione Might Attenuate Cadmium-Induced Liver Oxidative Stress and Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 191, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Singh, R.; Shekhar, A. Oxidative Stress in Cadmium Toxicity in Animals and Its Amelioration. In Cadmium Toxicity Mitigation; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 391–411. [Google Scholar]
- Souza-Arroyo, V.; Fabián, J.J.; Bucio-Ortiz, L.; Miranda-Labra, R.U.; Gomez-Quiroz, L.E.; Gutiérrez-Ruiz, M.C. The Mechanism of the Cadmium-Induced Toxicity and Cellular Response in the Liver. Toxicology 2022, 480, 153339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saribeyoglu, K.; Aytac, E.; Pekmezci, S.; Saygili, S.; Uzun, H.; Ozbay, G.; Aydin, S.; Seymen, H.O. Effects of Clinoptilolite Treatment on Oxidative Stress after Partial Hepatectomy in Rats. Asian J. Surg. 2011, 34, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-El-Zahab, H.S.H.; Hamza, R.Z.; Montaser, M.M.; El-Mahdi, M.M.; Al-Harthi, W.A. Antioxidant, Antiapoptotic, Antigenotoxic, and Hepatic Ameliorative Effects of L-Carnitine and Selenium on Cadmium-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Alterations in Liver Cell Structure in Male Mice. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2019, 173, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; He, C.; Shen, C.; Guo, J.; Mubeen, S.; Yuan, J.; Yang, Z. Toxicity of Cadmium and Its Health Risks from Leafy Vegetable Consumption. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1373–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Li, Y.; Shi, L.; Hussain, R.; Mehmood, K.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, H. Heavy Metals Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Animals: Molecular Mechanism of Toxicity. Toxicology 2022, 469, 153136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, T.; Alexieva, I.; Ostoich, P.; Dimitrova, M.; Boyadzhiev, K.; Lyubomirova, L.; Beltcheva, M. Different Lead- and Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress Profiles in the Liver and Kidneys of Subchronically-Exposed Mice. Acta Zool. Bulg. 2023, 75, 343–349. [Google Scholar]
- Mabbott, N.A.; Donaldson, D.S.; Ohno, H.; Williams, I.R.; Mahajan, A. Microfold (M) Cells: Important Immunosurveillance Posts in the Intestinal Epithelium. Mucosal Immunol. 2013, 6, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaiotov, S.; Tancheva, L.; Kalfin, R.; Petkova-Kirova, P. Zeolite and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2024, 29, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Zheng, W. Cadmium Exposure: Mechanisms and Pathways of Toxicity and Implications for Human Health. Toxics 2024, 12, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Du, J.; Ge, J.; Liu, S.-B. DNA Damage-Inducing Endogenous and Exogenous Factors and Research Progress. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2024, 43, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.; Cavalie, I.; Camilleri, V.; Gilbin, R.; Adam-Guillermin, C. Comparative Genotoxicity of Aluminium and Cadmium in Embryonic Zebrafish Cells. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2013, 750, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viau, M.; Sonzogni, L.; Ferlazzo, M.L.; Berthel, E.; Pereira, S.; Bodgi, L.; Granzotto, A.; Devic, C.; Fervers, B.; Charlet, L.; et al. DNA Double-Strand Breaks Induced in Human Cells by Twelve Metallic Species: Quantitative Inter-Comparisons and Influence of the ATM Protein. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popović-Bubujuk, S.; Đelić, N.; Muster, A.; Kataranovski, D.; Anđelković, M. Influence of cadmium chloride on the frequency of micronuclei in da and AO rats. Genetika 2018, 50, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 (t) | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | SO3 | LOI | H2O | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural clinoptilolite tuff | 71.08 | 0.12 | 10.88 | 0.96 | 0.09 | 1.03 | 2.78 | 0.31 | 2.76 | 0.15 | 9.3 | 2.31 | 101.77 |
| Na- exchanged sample | 69.42 | 0.14 | 10.63 | 0.82 | 0.08 | 0.58 | 0.9 | 4.26 | 2.46 | 0 | 9.13 | 3.56 | 101.98 |
| Samples Oxides | P1-17 | P1-19 | P1-12 | P1-13 | P1-14 | P1-15 | P1-16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 69.07 | 70.74 | 66.90 | 68.19 | 66.97 | 67.88 | 68.46 |
| Al2O3 | 12.70 | 12.82 | 13.44 | 13.38 | 13.38 | 12.31 | 12.34 |
| MgO | 0.82 | 0.90 | 0.84 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.81 |
| CaO | 3.86 | 3.93 | 4.51 | 4.52 | 4.54 | 3.76 | 3.89 |
| Na2O | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.09 |
| K2O | 3.06 | 2.92 | 2.66 | 2.59 | 2.52 | 2.83 | 2.84 |
| Total | 89.69 | 91.45 | 88.50 | 89.66 | 88.39 | 87.77 | 88.43 |
| Atoms per formula unit (apfu) | |||||||
| Si | 29.588 | 29.664 | 29.106 | 29.235 | 29.136 | 29.661 | 29.691 |
| Al | 6.412 | 6.337 | 6.892 | 6.761 | 6.861 | 6.340 | 6.308 |
| Mg | 0.524 | 0.563 | 0.545 | 0.562 | 0.590 | 0.573 | 0.524 |
| Ca | 1.772 | 1.766 | 2.103 | 2.076 | 2.116 | 1.760 | 1.808 |
| Na | 0.150 | 0.114 | 0.127 | 0.083 | 0.059 | 0.093 | 0.076 |
| K | 1.672 | 1.562 | 1.476 | 1.416 | 1.398 | 1.577 | 1.571 |
| Days | Organs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDw ( ± SD) | CDwZ ( ± SD) | |||||
| Liver | Kidneys | Feces | Liver | Kidneys | Feces | |
| 0 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0 |
| 15 | 56.2 ± 1.1 a,d | 53.1 ± 1.8 a | 113.0 ± 2.8 a | 44.2 ± 1.6 a | 39.1 ± 0.9 a | 156.0 ± 3.2 a |
| 30 | 96.0 ± 3.6 a,b,d | 104.0 ± 12.6 a,b | 153.0 ± 13.4 a,b,d | 78.0 ± 12.1 a,b | 74.6 ± 11.8 a,b | 200.0 ± 22.1 a,b |
| 45 | 173.0 ± 11.9 a,c,d | 260.0 ± 23.1 a,b,c | 177.0 ± 13.1 a,b,c,d | 90.0 ± 12.3 a,b,c | 100.0 ± 12.4 a,b,c | 276.0 ± 22.6 a,b,c |
| Parameters | WBC (g/L) | LYM (109/L) | GR (109/L) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | C | Z | CDw | CDwZ | C | Z | CDw | CDwZ | C | Z | CDw | CDwZ | |
| Days | |||||||||||||
| 0 | 4.3 ± 1.7 | 4.3 ± 1.7 | - | - | 3.1 ± 1.2 | 3.2 ± 1.2 | - | - | 2.2 ± 0.8 | 2.6 ± 0.9 | - | - | |
| 15 | 3.7 ± 1.5 | 3.6 ± 1.7 | 9.6± 1.9 b,c | 4.6± 2.0 | 3.8 ± 0.8 | 2.1 ± 1.2 | 3.8 ± 1.2 | 2.2 ± 1.3 | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 0.8 ± 0.5 | |
| 30 | 6.0 ± 1.3 | 7.2 ± 2.2 | 11.7± 2.5 b,c | 6.0± 1.3 c | 3.5 ± 1.4 | 3.8 ± 1.5 | 2.5 ± 1.8 | 2.8 ± 1.4 | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 2.7 ± 0.6 * | 1.0 ± 0.6 b | 1.5 ± 0.7 * | |
| 45 | 6.6 ± 3.2 | 7.8 ± 2.1 * | 8.1 ± 3.1 | 10.1 ± 7.4 * | 4.2 ± 2.7 | 4.4 ± 1.4 | 3.3 ± 2.5 | 4.2 ± 1.0 | 4.0 ± 2.9 * | 2.7 ± 0.8 * | 1.9 ± 1.5 | 3.2 ± 1.2 *,a | |
| MO (109/L) | RBC (1012/L) | Hb (g/L) | |||||||||||
| 0 | 2.6 ± 0.14 | 2.8 ± 0.19 | - | - | 3.3 ± 1.3 | 3.7 ± 1.0 | - | - | 69.6 ± 22.1 | 68.3 ± 19.8 | - | - | |
| 15 | 1.1 ± 0.03 | 1.0 ± 0.05 | 12.9 ± 0.22 b | 2.1 ± 0.06 b | 3.7 ± 0.6 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 2.3 ± 1.5 | 5.6 ± 1.2 | 54.4 ± 12.9 | 70.0 ± 43.5 | 36.3 ± 24.0 b,c | 45.0 ± 5.9 | |
| 30 | 2.6 ± 0.14 | 0.9 ± 0.01 | 10.4 ± 0.62 b | 1.7 ± 0.03 b | 5.3 ± 2.0 | 3.9 ± 1.4 | 3.1 ± 1.9 * | 5.7 ± 3.8 | 81.1 ± 29.5 | 79.3 ± 28.3 | 28.3 ± 16.6 b,c | 56.0 ± 25.2 | |
| 45 | 4.1 ± 0.26 | 1.1 ± 0.07 | 12.4 ± 0.18 *,a | 2.2 ± 0.06 | 0.9 ± 2.6 * | 4.2 ± 1.3 | 1.8 ± 1.2 *,a,b,c | 5.3 ± 3.5 | 82.9 ± 37.3 | 89.3 ± 10.6 | 22.7 ± 11.7 *,b | 69.9 ± 14.4 b | |
| Hct (L/L) | MCV (fL) | MCH (pg) | |||||||||||
| 0 | 0.25 ± 0.09 | 0.24 ± 0.09 | - | - | 46.8 ± 1.6 | 46.8 ± 1.6 | - | - | 15.3 ± 1.0 | 15.3 ± 1.0 | - | - | |
| 15 | 0.26 ± 0.08 | 0.19 ± 0.06 | 0.22 ± 0.06 | 0.12 ± 0.07 | 48.7 ± 5.4 | 48.8 ± 6.5 | 42.2 ± 2.4 c | 50.0 ± 4.4 | 15.6 ± 1.5 | 15.1 ± 1.6 | 12.5 ± 0.3 b,c | 15.5 ± 1.0 c | |
| 30 | 0.25 ± 0.12 | 0.19 ± 0.07 | 0.23 ± 0.14 | 0.27 ± 0.09 | 46.8 ± 1.6 | 48.2 ± 3.0 | 41.7 ± 4.1 | 44.4 ± 3.0 | 15.3 ± 1.0 | 14.0 ± 1.2 | 13.0 ± 1.1 b | 13.7 ± 0.7 | |
| 45 | 0.26 ± 011 | 0.21 ± 0.05 | 0.24 ± 0.15 | 0.07 ± 0.04 a | 44.0 ± 4.5 | 50.4 ± 1.3 | 44.7 ± 3.5 | 41.9 ± 2.7 b | 14.0 ± 1.8 | 14.9 ± 0.5 | 13.5 ± 3.0 | 14.2 ± 1.3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beltcheva, M.; Tzvetanova, Y.; Ostoich, P.; Aleksieva, I.; Chassovnikarova, T.; Tsvetanova, L.; Rusew, R. Oral Supplementation with Modified Natural Clinoptilolite Protects Against Cadmium Toxicity in ICR (CD-1) Mice. Toxics 2025, 13, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050350
Beltcheva M, Tzvetanova Y, Ostoich P, Aleksieva I, Chassovnikarova T, Tsvetanova L, Rusew R. Oral Supplementation with Modified Natural Clinoptilolite Protects Against Cadmium Toxicity in ICR (CD-1) Mice. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050350
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeltcheva, Michaela, Yana Tzvetanova, Peter Ostoich, Iliana Aleksieva, Tsenka Chassovnikarova, Liliya Tsvetanova, and Rusi Rusew. 2025. "Oral Supplementation with Modified Natural Clinoptilolite Protects Against Cadmium Toxicity in ICR (CD-1) Mice" Toxics 13, no. 5: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050350
APA StyleBeltcheva, M., Tzvetanova, Y., Ostoich, P., Aleksieva, I., Chassovnikarova, T., Tsvetanova, L., & Rusew, R. (2025). Oral Supplementation with Modified Natural Clinoptilolite Protects Against Cadmium Toxicity in ICR (CD-1) Mice. Toxics, 13(5), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050350







