Effects of Aging Biodegradable Agricultural Films on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Heavy Metal Speciation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials for Testing
2.2. Residual Film Preparation and Characterization
2.3. Soil Sample Collection
2.4. Biomass Preparation
2.5. Soil pH Determination
2.6. Measurement of Soil Enzyme Activity
2.7. Soil DOM Extraction and Characterization
2.7.1. Soil DOM Extraction
2.7.2. Extraction of DOM from Mulch Leachate
2.7.3. Fluorescent Composition Analysis of DOM
2.8. Speciation Analysis of Heavy Metals in Soils
2.9. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
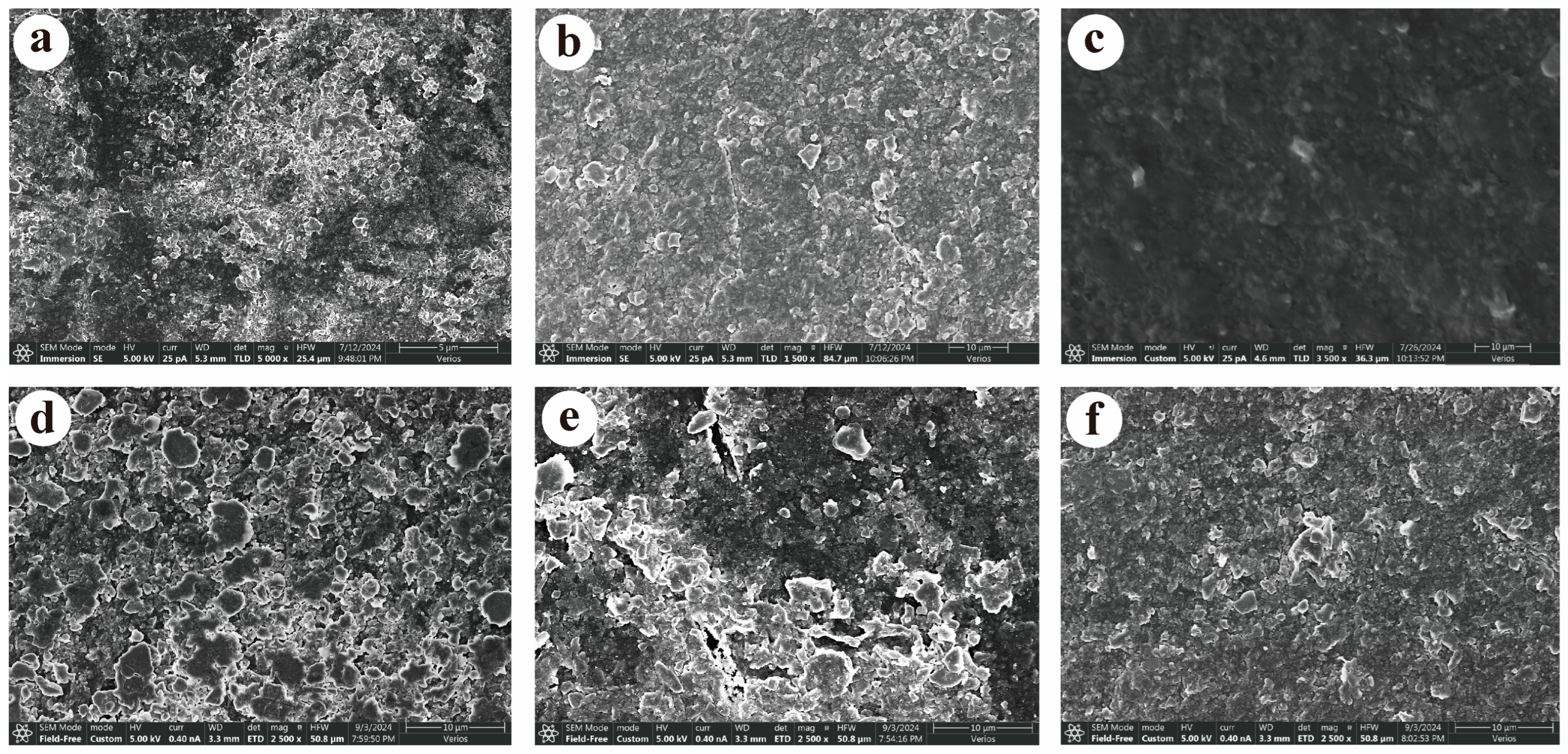
3.1. Changes in Surface Morphology of Biodegradable Film Agro-Film of Different Vintages
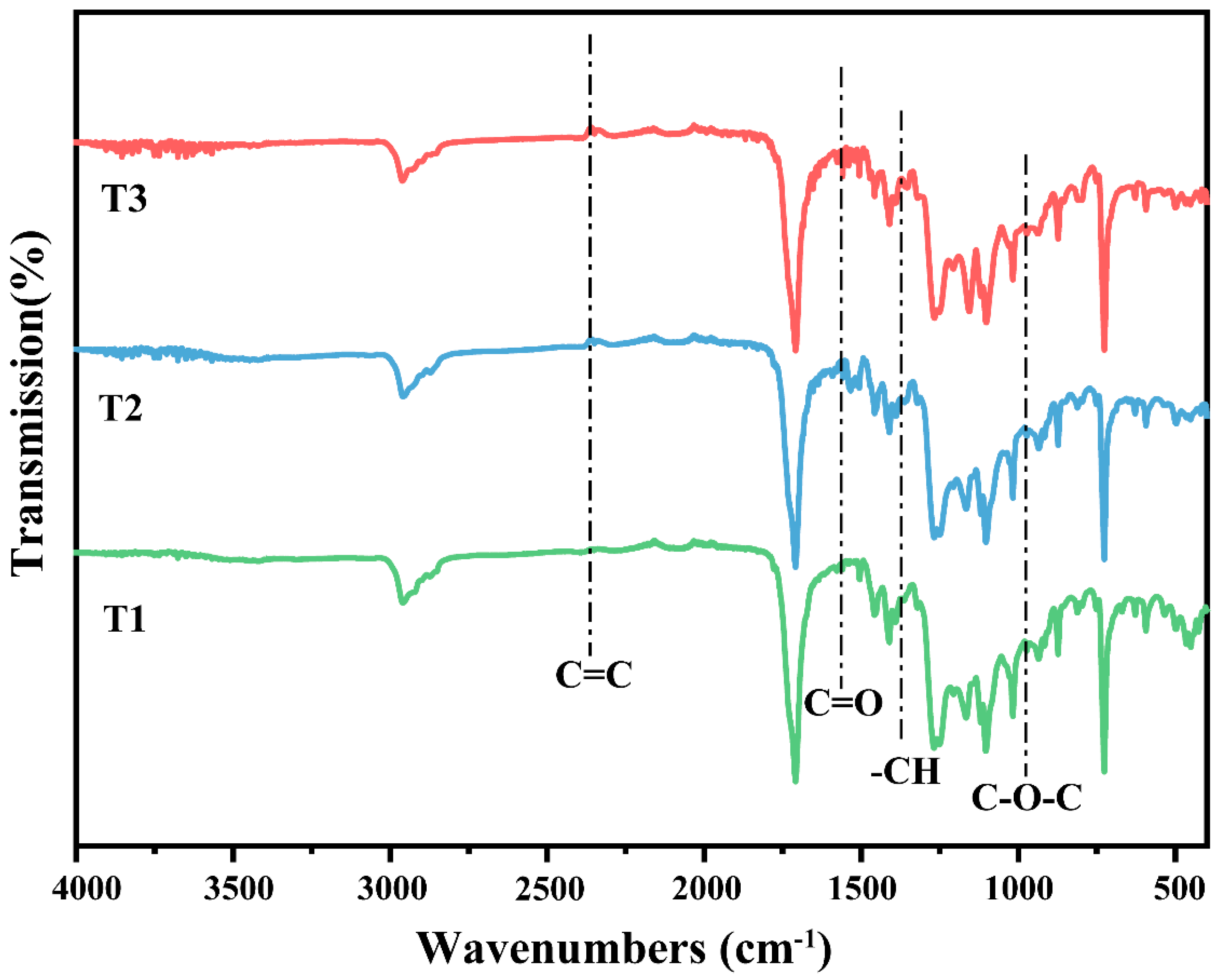
3.2. FTIR Spectral Analysis of Biodegradable Agricultural Films from Three Different Years
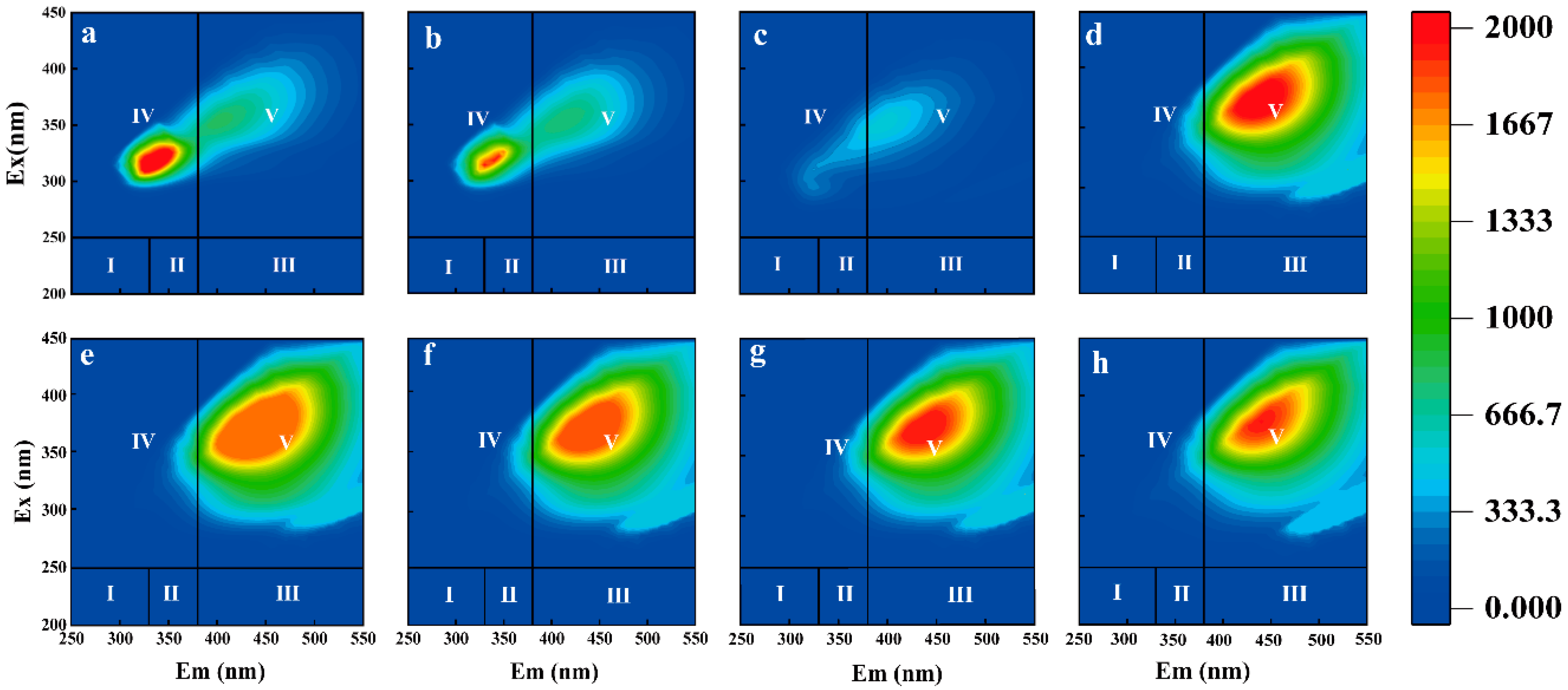
3.3. DOM Spectral Analysis of Leachate from Biodegradable Agricultural Films from Three Different Years
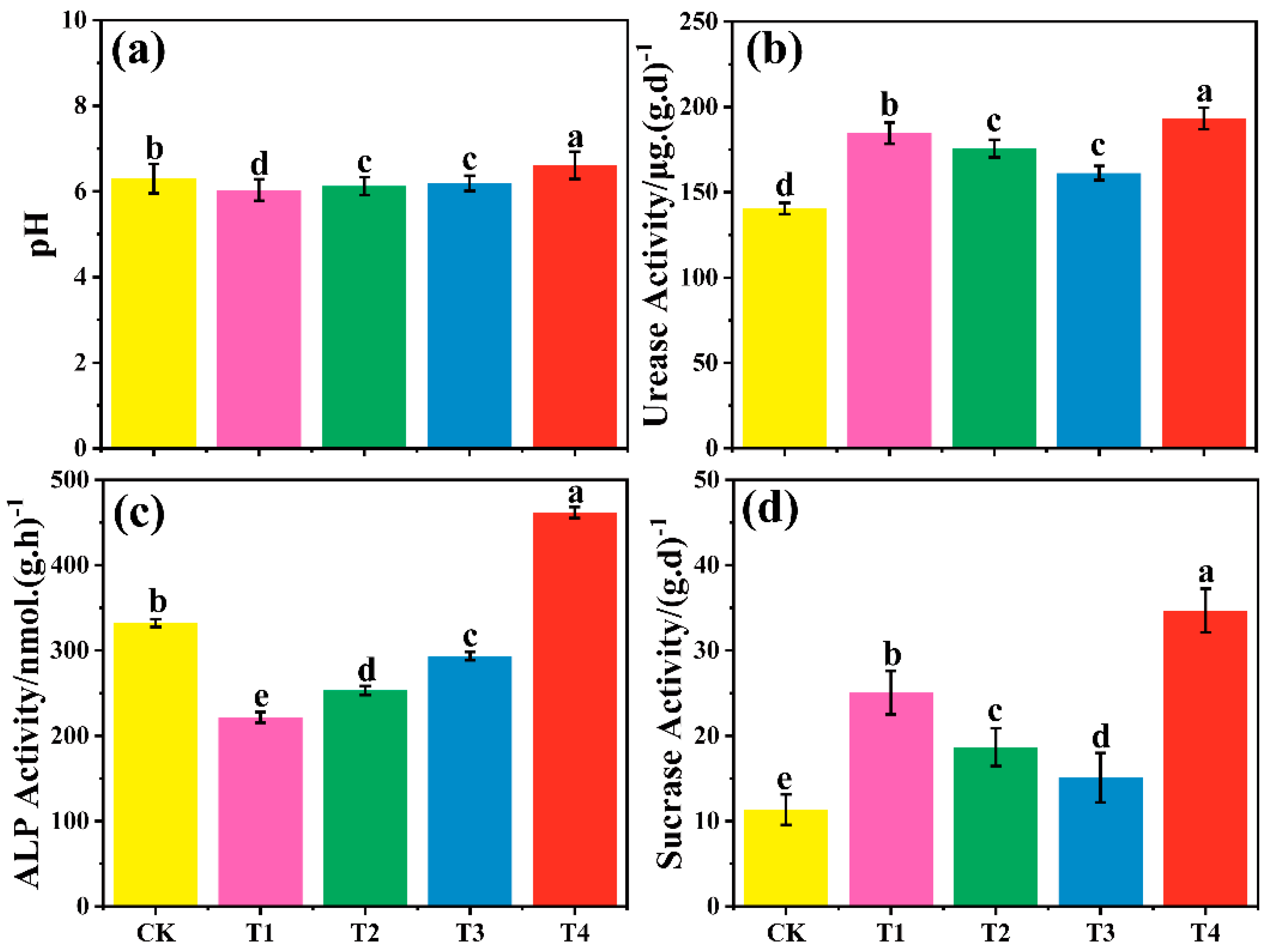
3.4. Effect of Different Treatment Groups on Soil pH
3.5. Effect of Different Treatment Groups on Soil Enzyme Activities
3.6. Effect of Different Treatment Groups on Soil DOM: Comparative Analysis with DOM Spectral Characteristics of Leachate
3.6.1. Comparative Analysis of DOM Fluorescence Characteristics Between Leachate and Soil Systems
3.6.2. Mechanism Linking Aged Films and Soil DOM Humification
3.6.3. Synergistic Effects of DOM and Heavy Metal Speciation
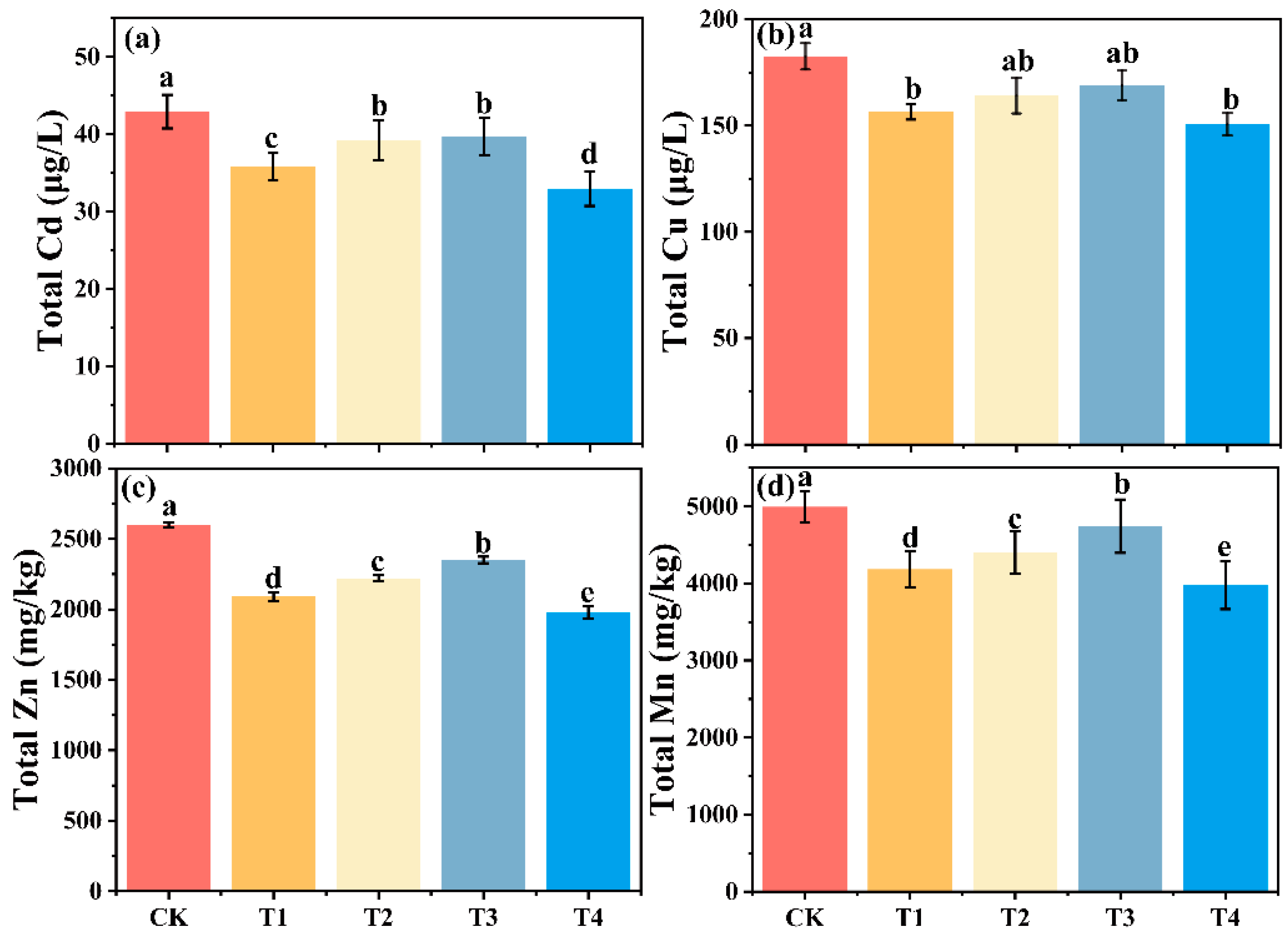
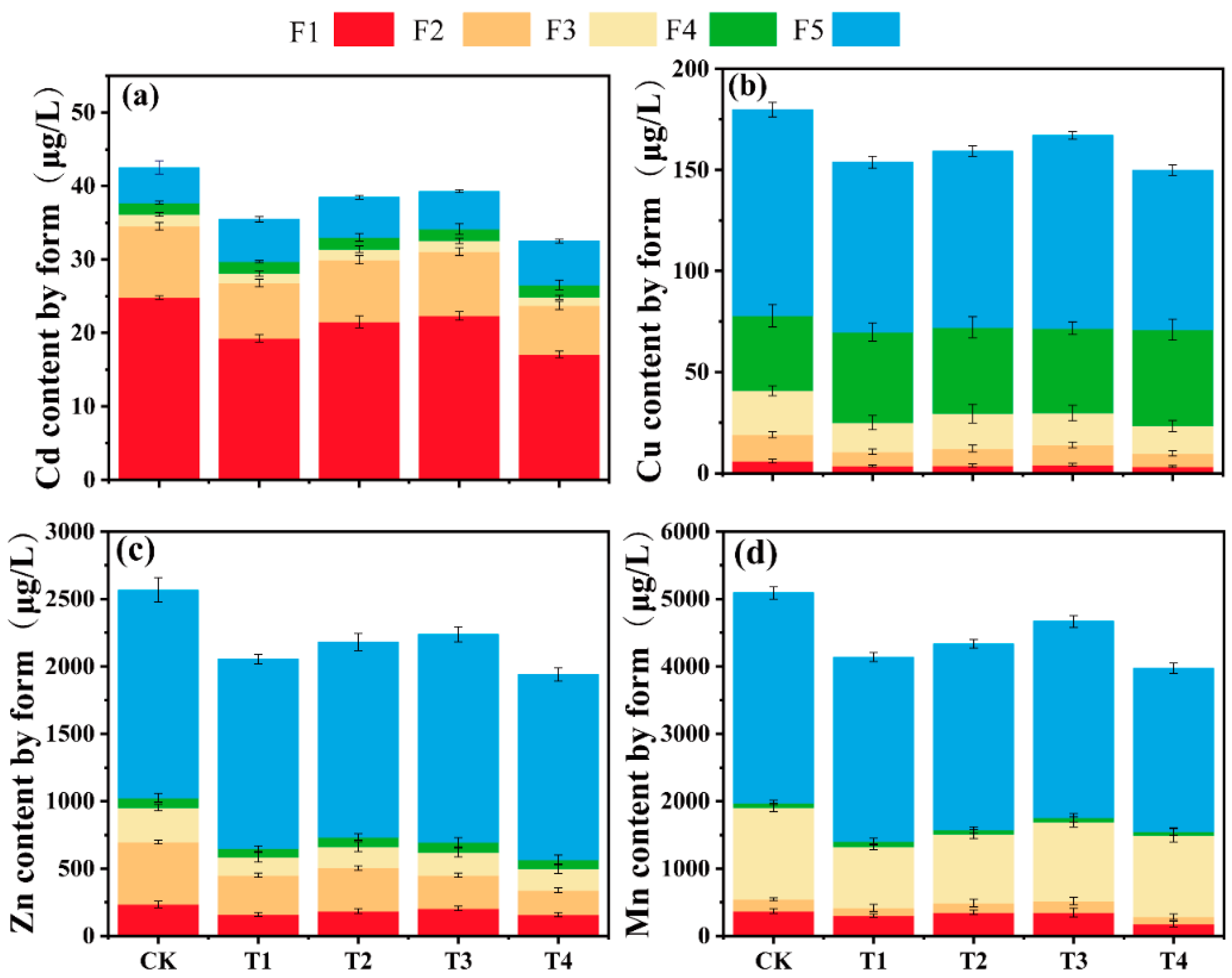
3.7. Speciation Analysis of Soil Heavy Metals in Different Treatment Groups
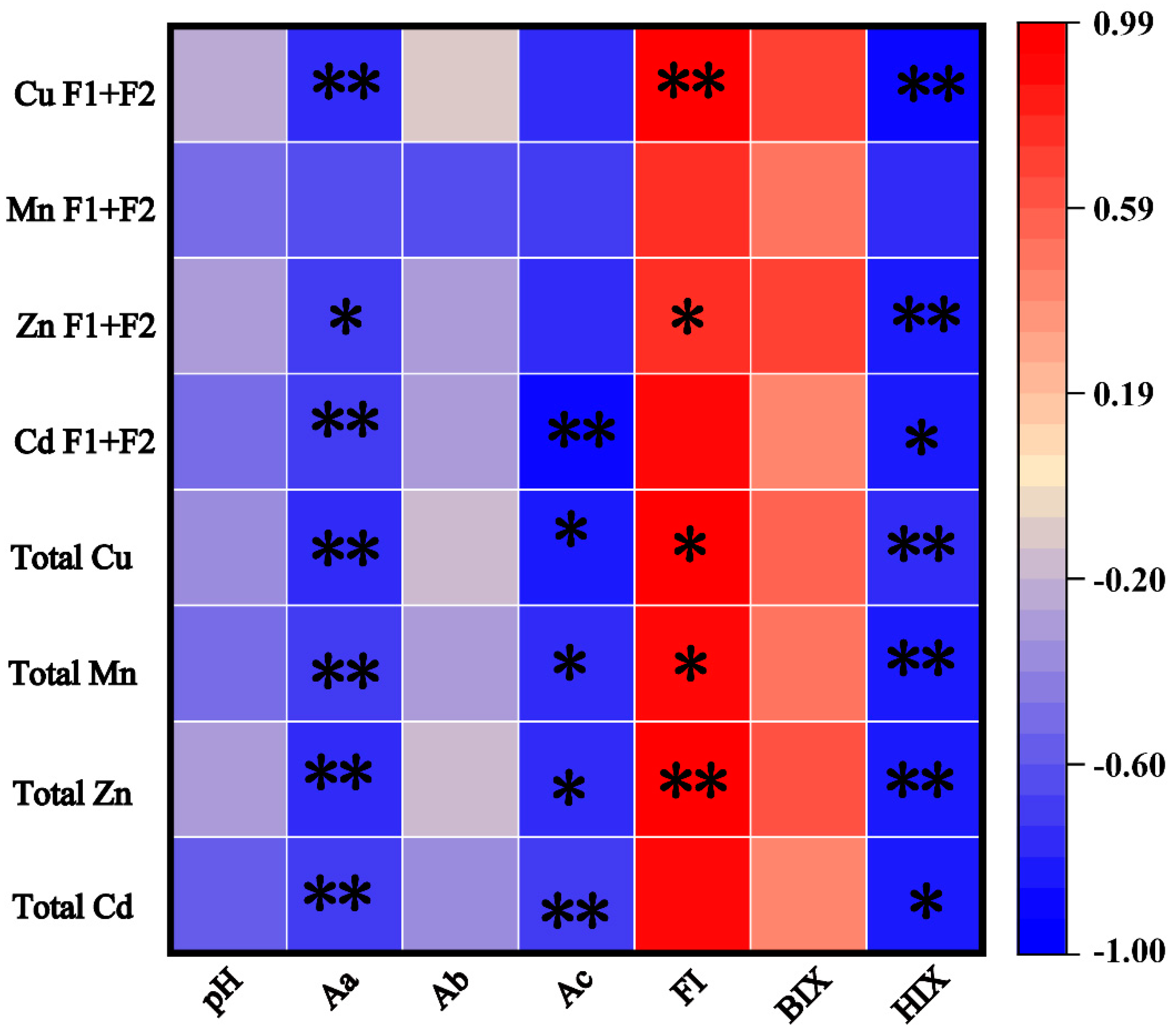
3.8. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Luo, Y.; Li, R.; Zhou, Q.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Yin, N.; Yang, J.; Tu, C.; Zhang, Y. Effective uptake of submicrometre plastics by crop plants via a crack-entry mode. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 929–937. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Q. A review of the occurrence and degradation of biodegradable microplastics in soil environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166855. [Google Scholar]
- Law, K.L.; Narayan, R. Reducing environmental plastic pollution by designing polymer materials for managed end-of-life. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 104–116. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, A.A.d.S.; Lau, C.W.; Till, J.; Kloas, W.; Lehmann, A.; Becker, R.; Rillig, M.C. Impacts of Microplastics on the Soil Biophysical Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9656–9665. [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield, L.M.; Graf, M.; Rengaraj, S.; Bargiela, R.; Williams, G.; Golyshin, P.N.; Chadwick, D.R.; Jones, D.L. Field response of N2O emissions, microbial communities, soil biochemical processes and winter barley growth to the addition of conventional and biodegradable microplastics. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 336, 108023. [Google Scholar]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoellein, T. The global odyssey of plastic pollution. Science 2020, 368, 1184–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Chia, R.W.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, H.; Jang, J. Microplastic pollution in soil and groundwater: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 4211–4224. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, G.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Zhong, W.; Qiu, R.; Song, K.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Han, L. Solvent-free upcycling of agricultural plastic waste using in situ self-assembly metal nanoparticles co-doped microporous carbocatalyst for advanced transportation fuels. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 486, 137086. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Teng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, W.; Wang, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Christie, P. Soil Type Driven Change in Microbial Community Affects Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Degradation Potential. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4648–4657. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, N.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Feng, H.; Dong, Q.g. Effects of different plastic film mulching on soil hydrothermal conditions and grain-filling process in an arid irrigation district. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148886. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Zou, Y.; Geng, N.; Liu, J.; Hou, J.; Li, D.; Yang, C.; Li, Y. Investigation on the adsorption and desorption behaviors of antibiotics by degradable MPs with or without UV ageing process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123363. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yu, F.; Ma, J. Sorption behavior and mechanism of hydrophilic organic chemicals to virgin and aged microplastics in freshwater and seawater. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wangjin, X.; Wang, Y.; Meng, G.; Chen, Y. The adsorption behavior of metals in aqueous solution by microplastics effected by UV radiation. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 87, 272–280. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Cui, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, F. Effects of microplastics and carbon nanotubes on soil geochemical properties and bacterial communities. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128826. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Li, C.; Gao, X.; Cai, Y.; Song, X.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Zhao, X. Agricultural soil plastic as a hidden carbon source stimulates microbial activity and increases carbon dioxide emissions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 198, 107151. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, M.; Chen, C.; Song, B.; Shen, M.; Cao, W.; Yang, H.; Zeng, G.; Gong, J. A review of biodegradable plastics to biodegradable microplastics: Another ecological threat to soil environments? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127816. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Li, S.; Xue, J.; Liao, J.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Liu, P.; Hu, S.; Guo, X.; et al. Dissolved organic matter derived from biodegradable microplastic promotes photo-aging of coexisting microplastics and alters microbial metabolism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130564. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, M.; Hu, W.; Chen, L.; Ai, S. Speciation of heavy metals in soils and their immobilization at micro-scale interfaces among diverse soil components. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153862. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ren, S.; Xu, W.; Liang, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Jones, D.L.; Chadwick, D.R.; et al. Effects of plastic residues and microplastics on soil ecosystems: A global meta-analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129065. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Yang, X.; Pelaez, A.M.; Huerta Lwanga, E.; Beriot, N.; Gertsen, H.; Garbeva, P.; Geissen, V. Macro- and micro- plastics in soil-plant system: Effects of plastic mulch film residues on wheat (Triticum aestivum) growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Huang, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, M.; Xue, S.; Tang, D.; Cheng, W.; Fan, T.; Yang, X. Effects of plastic particles on germination and growth of soybean (Glycine max): A pot experiment under field condition. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 116418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bo, L.; Shukla, M.K.; Mao, X. Long-term plastic film mulching altered soil physicochemical properties and microbial community composition in Shiyang River Basin, Northwest China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 193, 105108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J.; Khan, M.A.; Guo, G.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S.; Jin, F.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y. Dissolved organic carbon drives nutrient cycling via microbial community in paddy soil. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131472. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, H.; Liu, M.; Liu, C.-Q.; Lang, Y.; Xue, H.; Li, S.; La, W.; Han, X.; Ding, H. Differences in the spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter binding to Cu(II) in wetland soils with moisture gradients. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162509. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Zou, L.; Guan, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, H. Molecular weight-dependent spectral and metal binding properties of sediment dissolved organic matter from different origins. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 828–835. [Google Scholar]
- Huguet, A.; Vacher, L.; Relexans, S.; Saubusse, S.; Froidefond, J.M.; Parlanti, E. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 706–719. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wei, S.; Zhou, Y.; Mašek, O.; Khan, M.A.; Li, D.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lu, W.; Su, X.; et al. Rhizosphere effect on the relationship between dissolved organic matter and functional genes in contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118118. [Google Scholar]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar]
- GBW(E)070235[S]; National Certified Reference Materials Committee. Certified Reference Material for Polluted Soil Composition Analysis. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 3–5.
- Shen, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xing, B. Aging characteristics of degradable and non-biodegradable microplastics and their adsorption mechanism for sulfonamides. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 166452. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Jiang, G.; Xie, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Fan, X. Effect of oxygen-containing functional groups on the micromechanical behavior of biodegradable plastics and their formation of microplastics during aging. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 463, 132911. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Guo, J.; Fei, B.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Gu, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, S. Synthesis of a novel polyhydroxy triazine-based charring agent and its effects on improving the flame retardancy of polypropylene with ammonium polyphosphate and zinc borate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 175, 109123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Hong, S.; Hur, J. A fluorescence indicator for source discrimination between microplastic-derived dissolved organic matter and aquatic natural organic matter. Water Res. 2021, 207, 117833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnuolo, M.L.; Marini, F.; Sarabia, L.A.; Ortiz, M.C. Migration test of Bisphenol A from polycarbonate cups using excitation-emission fluorescence data with parallel factor analysis. Talanta 2017, 167, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, J.; Ding, L.; Li, L.; Jia, H.; Wang, T.; Guo, X.; Gao, S. Microplastics-derived dissolved organic matters accelerate photodegradation of sulfamethazine in wastewater ultraviolet disinfection process. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, W.; Li, W.; Xu, S.; Sun, Y.; Xu, G.; Wang, F. Effects of microplastics on cadmium accumulation by rice and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in cadmium-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczak, K.; Hrynkiewicz, K.; Znajewska, Z.; Dąbrowska, G. Use of rhizosphere microorganisms in the biodegradation of PLA and PET polymers in compost soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 130, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, N.; An, N. Effects of biochar and straw application on the physicochemical and biological properties of paddy soils in Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tang, S.; Pan, W.; Liu, X.; Han, K.; Si, L.; Ma, Q.; Mao, X.; Fu, H.; Wu, L. Long-term non-flooded cultivation with straw return maintains rice yield by increasing soil pH and soil quality in acidic soil. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 159, 127208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Wu, H. Discrepant responses of bacterial community and enzyme activities to conventional and biodegradable microplastics in paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Lv, J.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Wang, X. Microplastic presence significantly alters soil nitrogen transformation and decreases nitrogen bioavailability under contrasting temperatures. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Yao, B.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Nizzetto, L.; Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Räty, M.; Long, J.; et al. Microplastic effects on soil nitrogen cycling enzymes: A global meta-analysis of environmental and edaphic factors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 484, 136677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futa, B.; Oleszczuk, P.; Andruszczak, S.; Kwiecińska-Poppe, E.; Kraska, P. Effect of natural aging of biochar on soil enzymatic activity and physicochemical properties in long-term field experiment. Agronomy 2020, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, H.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, J. Effects of microplastics pollution on plant and soil phosphorus: A meta-analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132705. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Feng, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, B. Microplastics effects on soil biota are dependent on their properties: A meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 178, 108940. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, D.; Peng, Y.; Li, B.; Shao, F.; Li, K.; Cai, Y.; Guo, T.; Zhang, H. Microplastic formation and simultaneous release of phthalic acid esters from residual mulch film in soil through mechanical abrasion. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164821. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Song, J.; Xu, W.; Gao, G.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Hao, J.; Yang, G.; Ren, G.; et al. Straw return with fertilizer improves soil CO2 emissions by mitigating microbial nitrogen limitation during the winter wheat season. Catena 2024, 241, 108050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Martinez, V.; Tabatabai, M. Enzyme activities in a limed agricultural soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 31, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Qi, C.; Yang, J.; Ni, Y.; Guo, Y. The cuticular wax on sorghum straw influenced soil microbial diversity and straw degradation in soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 195, 105272. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Han, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tsui, T.-H.; Wang, Q. Elucidating the characteristic of leachates released from microplastics under different aging conditions: Perspectives of dissolved organic carbon fingerprints and nano-plastics. Water Res. 2023, 233, 119786. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Shen, J.; Riaz, M.; Jiang, C.; Zu, C.; Jiang, C.; Liu, B. Effects of biochar and straw amendment on soil fertility and microbial communities in paddy soils. Plants 2024, 13, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, X.; Wu, D.; Peng, L.; Fan, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Ge, C. Addition of biodegradable microplastics alters the quantity and chemodiversity of dissolved organic matter in latosol. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, P.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. Metal type and aggregate microenvironment govern the response sequence of speciation transformation of different heavy metals to microplastics in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Habibul, N.; Liu, X.-Y.; Sheng, G.-P.; Yu, H.-Q. FTIR and synchronous fluorescence heterospectral two-dimensional correlation analyses on the binding characteristics of copper onto dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2052–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zou, D.; Zeng, X.; Li, L.; Wang, A.; Liu, F.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Xiao, Z. Effect of the direct use of biomass in agricultural soil on heavy metals __ activation or immobilization? Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Hou, J.; Dang, Q.; Cui, D.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. Decrease in bioavailability of soil heavy metals caused by the presence of microplastics varies across aggregate levels. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Han, B.; Sun, Y.; Wang, F. Microplastics influence the adsorption and desorption characteristics of Cd in an agricultural soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Quan, G.; Ding, C. Effects of the combined pollution of lead and cadmium on soil urease activity and nitrification. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungur, A.; Soylak, M.; Ozcan, H. Investigation of heavy metal mobility and availability by the BCR sequential extraction procedure: Relationship between soil properties and heavy metals availability. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2014, 26, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Shi, L.; Yi, K.; Zhang, C.; Pang, H.; Li, J.; Li, S. Investigation of the adsorption behavior of Pb(II) onto natural-aged microplastics as affected by salt ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Experimental Sample | Treatment Number |
|---|---|
| Initial soil | CK |
| Add 2022 residual film 0.4% (w/w) | T1 |
| Add 2023 residual film 0.4% (w/w) | T2 |
| Add 2024 residual film 0.4% (w/w) | T3 |
| Add biomass 0.4% (w/w) | T4 |
| Region | Fluorescence Peak | Fluorescence Integral Region | Type of Fluorescent Substance |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | B | λex: 220–250 nm, λem: 280–330 nm | Tyrosine-like |
| II | T | λex: 220–250 nm, λem: 330–380 nm | Tryptophan-like |
| III | A | λex: 220–250 nm, λem: 380–480 nm | Fulvic acids |
| IV | D | λex: 250–360 nm, λem: 280–380 nm | Dissolved microbial by-products |
| V | C | λex: 250–420 nm, λem: 380–520 nm | Humic acids |
| Fluorescence Spectral Parameters | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| FI | The ratio of fluorescence emission spectral intensity at 450 nm to 500 nm for an excitation wavelength of 370 nm | Humus-like sources in DOM can be characterized, where FI > 1.9 indicates that DOM is mainly derived from microbial activities, and FI < 1.4 denotes DOM is mainly derived from terrestrial plants and soil organic matter, which are exogenous inputs |
| BIX | The ratio of fluorescence emission spectral intensity at 380 nm to 430 nm for an excitation wavelength of 310 nm | BIX > 1 means DOM mainly caused by organisms or bacteria; BIX 0.6–0.7 means DOM imported by terrestrial sources or strongly influenced by humans |
| HIX | The ratio of the spectral area in the fluorescence emission spectrum with emission wavelengths in the band of 435–480 nm to 300–345 nm at an excitation wavelength of 254 nm | HIX characterizes the degree of humification or maturity of DOM; HIX < 4 indicates that DOM is weakly humified, and HIX between 10 and 16 indicates that DOM has significant humus characteristics |
| Treatment | FI | BIX | HIX |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.64 ± 0.05 a | 0.82 ± 0.01 a | 5.53 ± 0.06 c |
| T1 | 1.29 ± 0.03 b | 0.60 ± 0.02 bc | 9.20 ± 0.28 b |
| T2 | 1.33 ± 0.02 b | 0.58 ± 0.04 bc | 8.87 ± 0.33 b |
| T3 | 1.38 ± 0.03 b | 0.54 ± 0.02 c | 8.26 ± 0.26 b |
| T4 | 1.28 ± 0.03 b | 0.65 ± 0.06 b | 10.43 ± 0.39 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.; Peng, T.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, F.; Guo, P.; Lyu, M.; Yin, J.; Liu, Q.; Gouda, S.; et al. Effects of Aging Biodegradable Agricultural Films on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Heavy Metal Speciation. Toxics 2025, 13, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040245
Wu H, Peng T, Li X, Zhao Y, Huang F, Guo P, Lyu M, Yin J, Liu Q, Gouda S, et al. Effects of Aging Biodegradable Agricultural Films on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Heavy Metal Speciation. Toxics. 2025; 13(4):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040245
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Hao, Tianmu Peng, Xueya Li, Yang Zhao, Fengshuo Huang, Peng Guo, Mingfu Lyu, Junhua Yin, Qin Liu, Shaban Gouda, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Aging Biodegradable Agricultural Films on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Heavy Metal Speciation" Toxics 13, no. 4: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040245
APA StyleWu, H., Peng, T., Li, X., Zhao, Y., Huang, F., Guo, P., Lyu, M., Yin, J., Liu, Q., Gouda, S., Mohamed, I., Huang, Q., & Wang, X. (2025). Effects of Aging Biodegradable Agricultural Films on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Heavy Metal Speciation. Toxics, 13(4), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040245








