Evaluation of Leaching Characteristics of Heavy Metal Ions from Red Mud–Graphite Tailings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Specimen Preparation
2.3. Test Methods
2.3.1. Chemical Composition
2.3.2. Microstructure Characterization
2.3.3. Heavy Metal Leaching Tests
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Leaching Models
3.1. Unreacted Shrinking Core Model (USCM)
3.2. Double-Exponential Model
3.3. Elovich Equation
3.4. Avrami Model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Elemental Composition
4.2. Mineral Composition
4.3. Microstructure Characteristics
4.4. Leaching Characteristics
4.4.1. Leachability of Cr, Pb, and Cu
4.4.2. Leaching Kinetics and Mechanisms
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- ISS significantly reduced the leaching of heavy metals. The specific mechanism through which ISS influences lead leaching in deionized water requires additional investigation.
- (2)
- The experiments indicated that the leaching of Cr, Pb, and Cu follows the Elovich model and the double constant equation. The leaching behavior of Cr was also described by the Avrami equation. In line with the shrinkage core model, the leaching mechanism of heavy metal ions encompasses diffusion control, which is partly governed by a combination of internal diffusion and surface chemical reactions.
- (3)
- Evaluation of the LX values of Cr, Pb, and Cu in the test samples indicated the potential reuse of red mud–graphite tailings. Thus, their application is environmentally sound and supports sustainable development efforts.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaza, S.; Yao, L.C.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Van Woerden, F. What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-4648-1329-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.X.; Zhou, F.S.; Evelina, L.M.A.; Liu, J.L.; Zhou, Y. A Review on the Industrial Solid Waste Application in Pelletizing Additives: Composition, Mechanism and Process Characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, Q.; Choi, G. Efficiency Assessment of Industrial Solid Waste Generation and Treatment Processes with Carry-over in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Xue, B.; Wang, G.; Zhu, G.; Gou, W.; Yang, D. Potential of Artificial Soil Preparation for Vegetation Restoration Using Red Mud and Phosphogypsum. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 941, 173553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Liu, D.Y. Physical and Chemical Properties of Sintering Red Mud and Bayer Red Mud and the Implications for Beneficial Utilization. Materials 2012, 5, 1800–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damayanti, R.; Khareunissa, H. Composition and Characteristics of Red Mud: A Case Study on Tayan Bauxite Residue from Alumina Processing Plant at West Kalimantan. Indones. Min. J. 2017, 19, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.H.; Li, Y.S.; Luo, X.L. Characteristics and reserve prospect of graphite resources in China. China Min. Mag. 2016, 25, 5–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, P.; Zhang, G. Principles of Polymer Film in Tile Adhesive Mortars at Early Ages. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 6, 025317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bai, Q.; Ma, H.; Xin, Z.; Deng, S.; Jiang, C. Research on the Preparation of Eco-Economical Ultra-High Performance Concrete Utilizing Graphite Tailings Resources. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 438, 137102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.S.G.; Bin Mahmud, H.; Ghuan, T.C.; Chin, A.B.; Kuenzel, C.; Ranjbar, N. Safe Disposal of Coal Bottom Ash by Solidification and Stabilization Techniques. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.M.; Sollars, C.J.; Perry, R. Cement-Based Solidification for the Safe Disposal of Heavy Metal Contaminated Sewage Sludge. Waste Manag. Res. 1988, 6, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhang, P.; Elmaadawy, K.; Ke, Y.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Hu, J.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; et al. Microwave Enhanced Solidification/Stabilization of Lead Slag with Fly Ash Based Geopolymer. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Liu, R. Study on Solidification Mechanism of Magnesium Phosphate Cement on Heavy Metals Cu2+. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kindi, G.Y.; Al-Haidri, H.A. Solidification/Stabilization Remediation of Heavy Metal from Petroleum Al-Dura Sludge with Portland Cement. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2022, 26, 7841–7856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.W.; Mallampati, S.R.; Park, H.S. Novel Synthesis and Applications of Thiomer Solidification for Heavy Metals Immobilization in Hazardous ASR/ISW Thermal Residue. Waste Manag. 2016, 49, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, A.; Asjadi, F.; Safari, A.A. Effect of Sulfide and Hydroxide on the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Hydrometallurgical Zinc Effluent. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 104, 6370–6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Jiang, N.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, X.; Cheng, L. Heavy Metals Remediation through Bio-Solidification: Potential Application in Environmental Geotechnics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Kang, B.; Zha, F.; Chen, X. Synergistic Solidification of Heavy Metal Tailings by Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) and Microorganisms. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 36, 103788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; Lin, M.; Tang, P.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Z. Cement and Zeolite Stabilization/Solidification of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Sediments: 841-Day Leaching Characteristics, Mechanisms, and Microstructure. Waste Manag. 2024, 190, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Tyrer, M.; Hills, C.D.; Yang, X.M.; Carey, P. Immobilisation of Heavy Metal in Cement-Based Solidification/Stabilisation: A Review. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.J.; Wei, M.L.; Reddy, K.R.; Liu, Z.P.; Jin, F. Effect of Acid Rain PH on Leaching Behavior of Cement Stabilized Lead-Contaminated Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 271, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Li, Y.; Yu, B.; Liu, L.; Xue, Q.; Du, Y. Assessment of Semi-Dynamic Leaching Characteristics of Lead and Zinc from Stabilized Contaminated Soil Using Sustainable Phosphate-Based Binder after Carbonation. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 332, 130126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, D.; Liu, Q.; Peng, C.; Li, F.; Gu, Q. An Innovative Method for the Solidification/Stabilization of PAHs-Contaminated Soil Using Sulfonated Oil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, L.; Xie, X. Effects of Organic Matter Components and Incubation on the Cement-Based Stabilization/Solidification Characteristics of Lead-Contaminated Soil. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wen, D.; Guo, X.; Fu, R.; Chen, S.; Xu, D. Synchronous Stabilization of Multi-Metal in Pb/Zn Smelter-Contaminated Soil by Dithiocarbamate. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 194, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Xu, J.; Jiang, X.; Liu, C.; McCall, W.; Lu, J. Stabilization of Heavy Metals in Soil Using Two Organo-Bentonites. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Xiong, K.; Yang, K.; Feng, D. Experimental Study on Solidification/Stabilization of Heavy Metal Lead and Chromium Sludge Solidified by Cement-Based Materials. MATEC Web Conf. 2023, 382, 01008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Wu, W.; Feng, T.; Zhong, K. Cement-SG Curing Agent for Solidification of Mucky Soils. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y. Application of Chitosan in EICP Treatment for Stabilization of Red Mud against Wind Erosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 465, 140164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Lu, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, X. Effect of Ionic Soil Stabilizer on the Properties of Lime and Fly Ash Stabilized Iron Tailings as Pavement Base. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 450, 138558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Kong, D.; Li, Y.; Fu, X.; Ren, C.; Chen, M. Investigation of the Properties and Microscopic Mechanism of Red Mud-Phosphogypsum-Based Composite Cementitious Materials. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 101, 111962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Jia, C.; Tao, D. Freeze-Thaw Cycle Characteristics of Graphite Tailing Concrete and Steel Fiber Reinforced-Graphite Tailing Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 462, 140006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E51-2009; Test Methods of Materials Stabilized with Inorganic Binders for Highway Engineering. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- EPA—U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Draft Method 1315—Mass Transfer Rates of Constituents in Monoliths or Compacted Granular Materials Using a Semi-dynamic Tank Leaching Test. Pre-Release Draft for Comment, October 2009. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2017-10/documents/method_1315_-_final_8-3-17.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Dong, L.; Dong, H.; Fujita, T.; Geng, Y.; Fujii, M. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of China’s Sulfur Dioxide Control Strategy at the Regional Level: Regional Disparity, Inequity and Future Challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 90, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, G.; van der Sloot, H. Determination of Leaching Characteristics of Waste Materials Leading to Environmental Product Certification. In Stabilization and Solidification of Hazardous, Radioactive, and Mixed Wastes: 2nd Volume; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1992; pp. 149–170. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Mei, B.; Deng, X.; Sun, Z. Influence of Thermal Condition on the Shrinkage and Bond Strength of Polymer-Modified Ceramic Tile Adhesive. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2024, 130, 103647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydogan, S. Dissolution Kinetics of Sphalerite with Hydrogen Peroxide in Sulphuric Acid Medium. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 123, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, C.F.; Heal, G.R. Solid–liquid Diffusion Controlled Rate Equations. Thermochim. Acta 1999, 340, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalai, R.C. Desorption of Soil Phosphate by Anion-Exchange Resin. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1974, 5, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. Characteristics of Elovich Equation Used for the Analysis of Adsorption Kinetics in Dye-Chitosan Systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Zou, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, F.; Liu, S.; Tu, J.; Fedorova, I.V. Influence of vegetation on heavy metal Cr release process from bottom sediment under unidirectional flows and regular waves. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 204, 116535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L.; Jardine, P.M. Comparison of kinetic equations to describe potassium-calcium exchange in pure and in mixed systems. Soil Sci. 1984, 138, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Q.; Chen, S.; Yang, F.H.; Wang, A. min Study on Properties of Representative Ordinary Portland Cement: Heavy Metal Risk Assessment, Leaching Release Kinetics and Hydration Coupling Mechanism. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 385, 131507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, A.J.; Fall, M. Thermally Induced Changes in Metalloid Leachability of Cemented Paste Backfill That Contains Blast Furnace Slag. Miner. Eng. 2020, 156, 106520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; He, X.; Lou, X.; Jiao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Luo, X.; Sun, S.; Guan, J.; Yuan, H. A Citric Acid/Na2S2O3 System for the Efficient Leaching of Valuable Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. JOM 2019, 71, 3673–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, S.; Akgün, D. Leaching Kinetics of Mo, Ni, and Al Oxides from Spent Nickel–Molybdenum Hydrodesulfurization Catalyst in H2SO4 Solution. J. Sustain. Metall. 2021, 7, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Min, X.; Ke, Y.; Liu, D.; Tang, C. Preparation of Red Mud-Based Geopolymer Materials from MSWI Fly Ash and Red Mud by Mechanical Activation. Waste Manag. 2019, 83, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S.; Liu, H. Investigations on Influencing Factors of Resistivity Measurement for Graphite Tailings Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 123, 104206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Wu, J. Experimental Study on Ionic Soil Stabilizer Combined with Vacuum Preloading to Solidify Sludge. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB5085.3-2007; Hazardous Waste Identification Criteria: Leaching Toxicity Identification. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Xue, Q.; Wang, P.; Li, J.S.; Zhang, T.T.; Wang, S.Y. Investigation of the Leaching Behavior of Lead in Stabilized/Solidified Waste Using a Two-Year Semi-Dynamic Leaching Test. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Ai, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J. Impact of Acid Rain on Release Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Low-Sulfur Tailings with Strong Acid Neutralization Capacity: A Case Study from Northern Guangxi, China. Processes 2024, 12, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Qiu, S.; Zhou, B.; Li, Q.; Chen, M. Leaching of Heavy Metals from Tungsten Mining Tailings: A Case Study Based on Static and Kinetic Leaching Tests. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 342, 123055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; He, B.; Chu, D.; Wang, L.; Peng, X.; Nie, X.; Ma, F.; Han, P.; Bai, X. Synergy between Fenton Reagent and Solid Waste-Based Solidifying Agents during the Solidification/Stabilization of Lead(II) and Arsenic(III) Contaminated Soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermatas, D.; Moon, D.H.; Menounou, N.; Meng, X.; Hires, R. An Evaluation of Arsenic Release from Monolithic Solids Using a Modified Semi-Dynamic Leaching Test. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 116, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-J.; Lin, M.-F. Influence of Redox Potential on Leaching Behavior of a Solidified Chromium Contaminated Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, N.; Jiang, P.; Zhou, A.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, P. Study on Semi-Dynamic Leaching and Microstructure Characteristics of MSWI Fly Ash Solidified Sediment. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wan, X.; Qiu, J.; Wu, P.; Sun, X. Stabilization/Solidification of Lead- and Cadmium-Containing Tailings for Cemented Paste Backfill by Using Clinker-Free Binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 359, 129469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, R.; Chaudhary, R. Evaluation of Leaching Characteristics and Environmental Compatibility of Solidified/Stabilized Industrial Waste. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2006, 8, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, D.H.; Dermatas, D.; Menounou, N. Arsenic Immobilization by Calcium-Arsenic Precipitates in Lime Treated Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 330, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchinadham, S.B.K.; Narasimman, L.M.; Pedaballe, V.; Kalyanaraman, C. Diffusion and Leachability Index Studies on Stabilization of Chromium Contaminated Soil Using Fly Ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Potential Risk, Leaching Behavior and Mechanism of Heavy Metals from Mine Tailings under Acid Rain. Chemosphere 2024, 350, 140995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
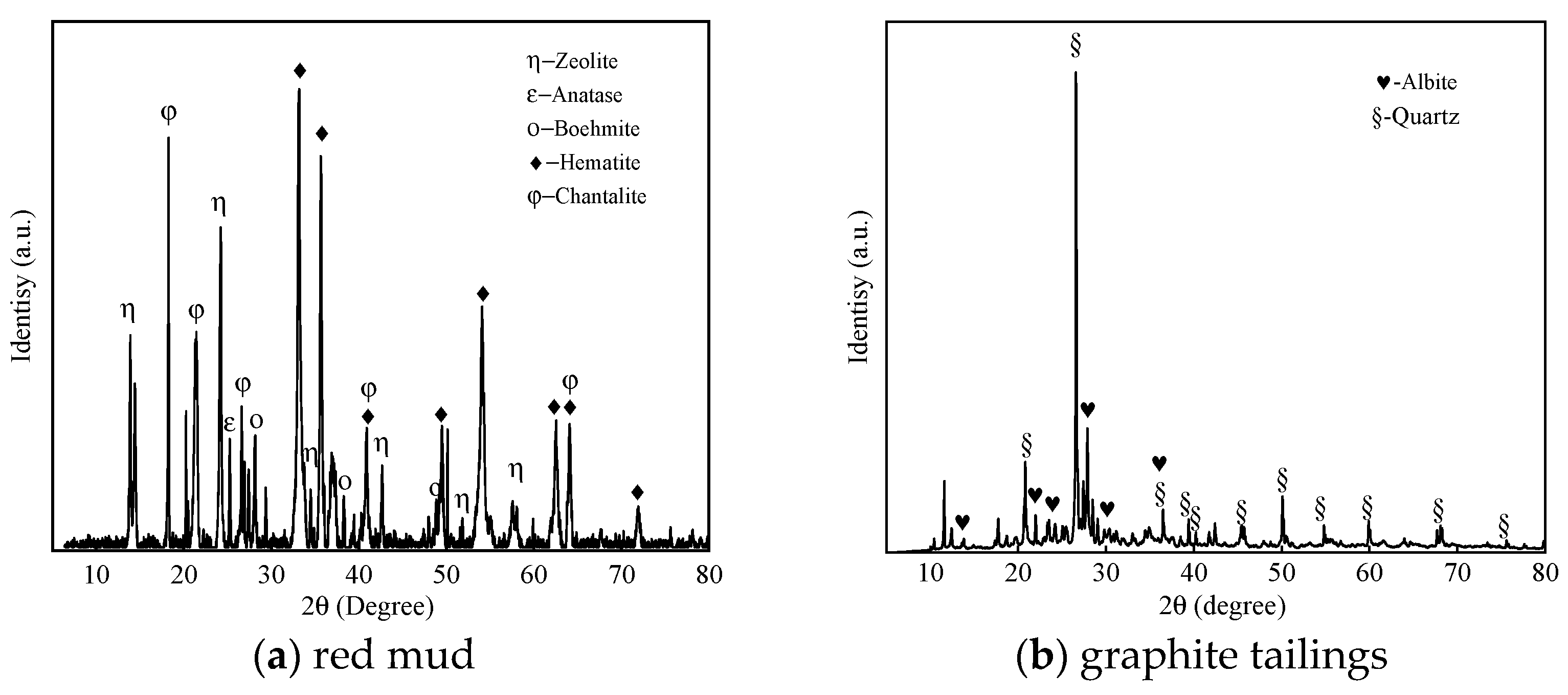
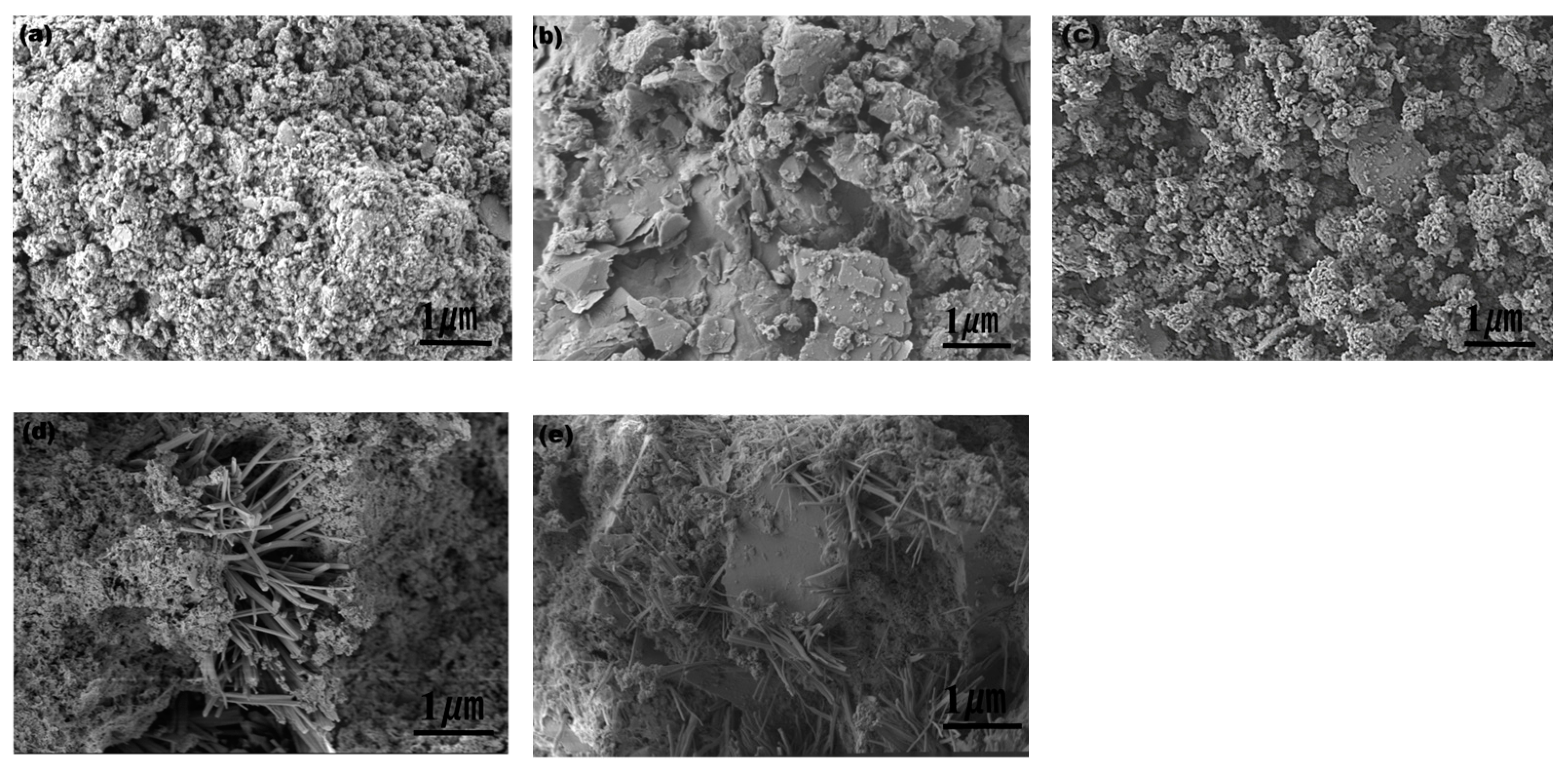

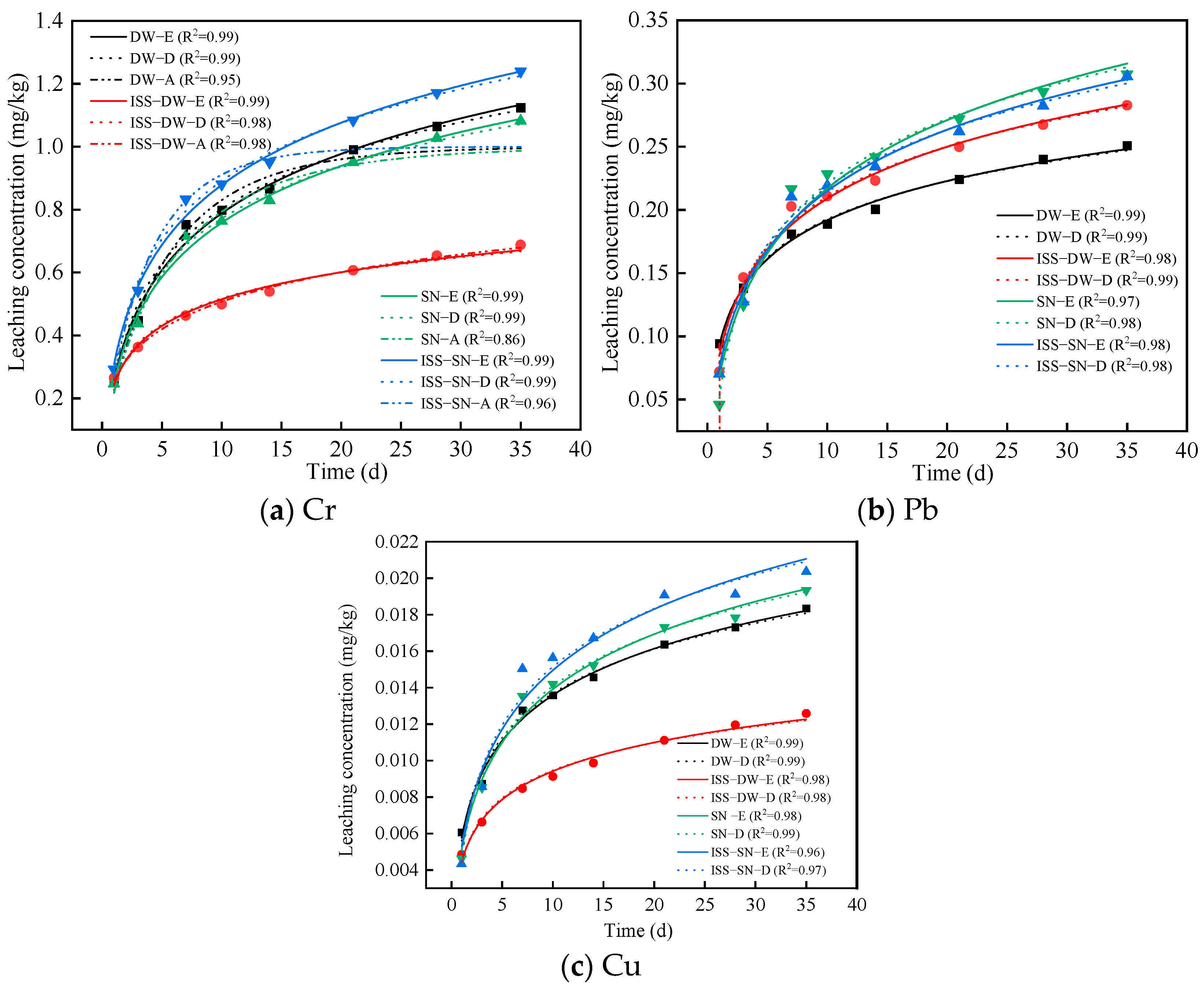

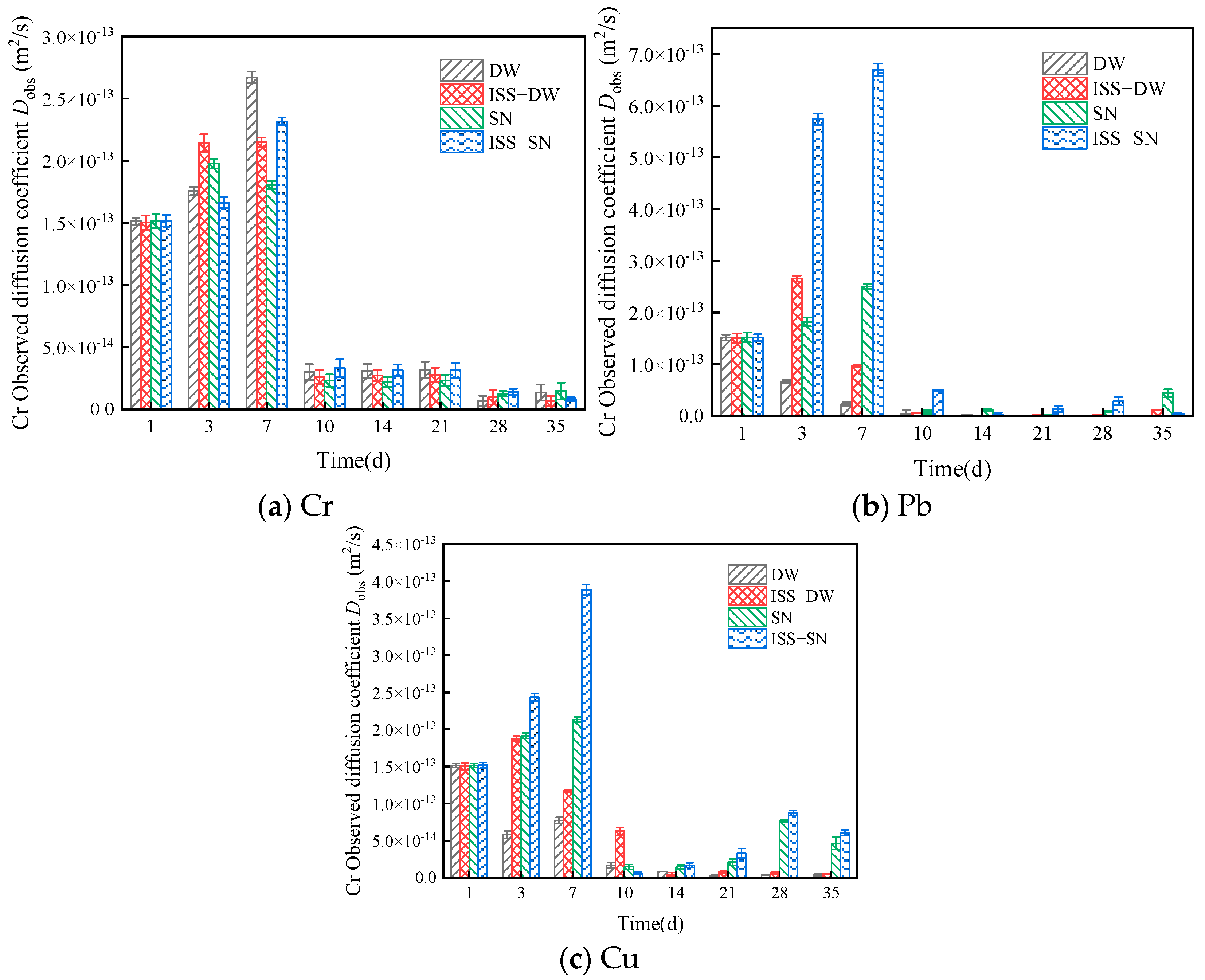


| Element | Mass Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Red Mud | Graphite Tailings | |
| Ca | 1.12 | 0.02 |
| Na | 8.64 | 0.74 |
| Al | 22.91 | 11.87 |
| Si | 11.62 | 39.37 |
| Fe | 36.6 | 11.55 |
| Ti | 6.45 | 0.74 |
| Mg | 0.08 | 4.52 |
| Cr | 1.12 | 0.02 |
| Cu | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Sr | 0.004 | 0.02 |
| Zr | 0.19 | 0.03 |
| Ti | 6.45 | 0.73 |
| Pb | 0.01 | 0.006 |
| Element | Type | Mechanism | Correlation | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | DW | internal diffusion | 0.98 | k = 0.00886 |
| ISS-DW | mixture of interfacial chemistry and diffusion | 0.98 | k = 0.00255 | |
| SN | internal diffusion | 0.97 | k = 0.00881 | |
| ISS-SN | internal diffusion | 0.98 | k = 0.00886 | |
| Pb | DW | mixture of interfacial chemistry and diffusion | 0.85 | k = 1.69484 × 104 |
| ISS-DW | 0.88 | k = 2.18592 × 104 | ||
| SN | 0.90 | k = 2.64448 × 104 | ||
| ISS-SN | 0.92 | k = 2.47926 × 104 | ||
| Cu | DW | mixture of interfacial chemistry and diffusion | 0.84 | k = 6.84286 × 107 |
| ISS-DW | 0.85 | k = 3.18006 × 107 | ||
| SN | 0.85 | k = 7.49356 × 107 | ||
| ISS-SN | 0.80 | k = 8.8319 × 107 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Lu, X.; Jiang, C.; Wang, D.; Zhu, J.; Xu, M.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, X. Evaluation of Leaching Characteristics of Heavy Metal Ions from Red Mud–Graphite Tailings. Toxics 2025, 13, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030211
Li K, Lu X, Jiang C, Wang D, Zhu J, Xu M, Zhang L, Cheng X. Evaluation of Leaching Characteristics of Heavy Metal Ions from Red Mud–Graphite Tailings. Toxics. 2025; 13(3):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030211
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kangli, Xiaolei Lu, Congcong Jiang, Dan Wang, Jiang Zhu, Meiling Xu, Lina Zhang, and Xin Cheng. 2025. "Evaluation of Leaching Characteristics of Heavy Metal Ions from Red Mud–Graphite Tailings" Toxics 13, no. 3: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030211
APA StyleLi, K., Lu, X., Jiang, C., Wang, D., Zhu, J., Xu, M., Zhang, L., & Cheng, X. (2025). Evaluation of Leaching Characteristics of Heavy Metal Ions from Red Mud–Graphite Tailings. Toxics, 13(3), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030211







