Environmental Risk Assessment of Metals in Groundwater in an Area of Jiujiang City, Jiangxi Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Measurement Methods and Instruments
2.4. Evaluation Method
2.4.1. Single-Factor Pollution Index Method
2.4.2. Nemerow Comprehensive Pollution Index Method
2.4.3. Potential Ecological Hazard Index Method
2.4.4. Correlation Analysis
2.4.5. Principal Component Analysis
2.5. Data Statistics and Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Metal Content in Site Groundwater
3.2. Evaluation of Metal Pollution in Groundwater
3.2.1. Single-Factor and Nemerow Comprehensive Pollution Index Methods
3.2.2. Potential Ecological Hazard Index Method in Groundwater
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Metal Elements in Groundwater
3.4. Principal Component Analysis
3.5. Comparison with Heavy Metals in Groundwater from Other Places
4. Conclusions
5. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, R.; Xin, C.; Yu, S.; Li, X. Analysis of Metals Sources in Groundwater and Assessment of Health Risks: An Example from the Southwest Sub-basin of the Shiqi River. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, J.; Xi, B.; Yang, Y.; Lu, H.; Shi, J. Groundwater Pollution Prevention and Control in China: Current Status and Countermeasures. Strateg. Study CAE Sci. 2022, 24, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kennedy, C. Determination of sustainable yield in urban groundwater systems: Beijing, china. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2006, 11, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Pan, Y.; Zeng, M.; Huang, C.; Hou, Q.; Pi, P.; Peng, H. Source Analysis and Health Risk Assessment of Metals in Groundwater of Leizhou Peninsula. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 4246–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; An, R.; Shi, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, A. Metals Pollution and Influencing Factors of Agricultural Land in a Typical Watershed in Hunan Province. Res. Environ. Sci. 2021, 34, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Ma, Z.; Pan, L. Analysis of relations of metals accumulation with land utilization using the positive and negative association rule method. Math. Comput. Model. 2011, 54, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Research progress of water ecological health assessment at home and abroad. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2022, 12, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Tang, L.; Xie, Y.; Gao, W.; Tan, X.; Zeng, J. Groundwater heavy metal(loid)s risk prediction based on topsoil contamination and aquifer vulnerability at a zinc smelting site. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; da Silva, J.B.; dos Santos, I.F.; de Oliveira, O.M.C.; Cerda, V.; Queiroz, A.F.S. Use of pollution indices and ecological risk in the assessment of contamination from chemical elements in soils and sediments—Practical aspects. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 35, e00169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eziz, M.; Sidikjan, N.; Zhong, Q.; Rixit, A.; Li, X. Distribution, pollution levels, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater in the main pepper production area of china. Open Geosci. 2023, 15, 20220491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogwu, M.; Izah, S.; Sawyer, W.; Amabie, T. Environmental Risk Assessment of Trace Metal Pollution: A Statistical Perspective. Env. Geochem. Health 2025, 47, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, C.; Zhou, G.; Zhou, P. State of the art and future directions in groundwater contamination risk assessment. Coal Geol. Explor. 2024, 52, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Bao, X.; Zhang, P. Prospect of groundwater pollution remediation methods and technologies in China. Geol. China 2022, 49, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Meng, F. Remote sensing inversion on heavy metal content in salinized soil of Yellow River Delta based on Random Forest Regression—A case study of Gudao Town. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Lin, M.; Mao, K.; Hao, S. Analysis of TDS and Heavy Metal Pollution Characteristics in Groundwater of Typical Antimony Mining Areas in Hunan. Water 2024, 16, 3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Niu, B.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Water Quality Assessment and Pollution Source Analysis of the Dawen River. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2021, 28, 176–185, 195. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yan, Z.; Xu, D.; Wang, S. Application of Improved Nemerow Index Method in Reservoir Water Quality Evaluation. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 20, 13079–13084. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 14848-2017; Groundwater Quality Standards. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Yu, J.; Li, B.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Lei, M. Pollution and risk assessment of metals in agricultural soil around an abandon mine site in Hunan Province. Environ. Chem. 2020, 4, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, D.; Cui, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, L. Distribution patterns and potential ecological risk evaluation of metals in the surface sediments of Beibu Gulf. Geol. Surv. China 2020, 7, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, B. Geochemical Background and Element Distribution in Soil in Chengdu, Sichuan. J. Sichuan Geol. 2004, 24, 159–164. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ji, D.; Ma, J.; Xue, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Wei, S. Identifying groundwater characteristics and controlling factors in Jiaozhou Bay’s northern coastal region, China: A combined approach of multivariate statistics, isotope analysis, and field empirical investigations. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, M.; Ahmad, M.; Laiq, M.; Nabi, M. Geostatistical analysis and multivariate assessment of groundwater quality. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; He, J.; He, B.; Chu, Y.; Xia, Q. A new approach combining principal component factor analysis and k-means for identifying natural background levels of NO3-N in shallow groundwater of the huaihe river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Bao, B.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F.; Yu, X. Assessment of Metals Pollution and Human Health Risk of Surface Waters in the City of Ningbo, China. Environ. Sci. 2018, 39, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; Meng, X.; Wen, X.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.; Wu, M. Contamination characteristics, source identification, and source-specific health risks of metals(loid)s in groundwater of an arid oasis region in northwest china. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, X.; Fan, P.; Yu, B.; Wang, L.; Lei, K.; Zuo, L. Multi-element features and trace metal sources of road sediment from a mega heavy industrial city in north china. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Khurshid, S.; Qureshi, F.; Hussain, A.; Bhattacharya, A. Heavy metals and geo-accumulation index development for groundwater of Mathura city, Uttar Pradesh. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 138, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Peng, H.; Pan, Y.; Zeng, M.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, R. Source Determination and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Groundwater of Guangzhou. Environ. Sci. 2025, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Yang, F. Heavy Metal Pollution Sources Analysis and Health Risk Assessment of Groundwater in Lingjiang Basin. Resour. Environ. Eng. 2025, 1–10. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/42.1736.P.20250114.1436.006 (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Triassi, M.; Cerino, P.; Montuori, P.; Pizzolante, A.; Trama, U.; Nicodemo, F.; D’Auria, J.L.; Vita, S.D.; Rosa, E.D.; Limone, A. Heavy Metals in Groundwater of Southern Italy: Occurrence and Potential Adverse Effects on the Environment and Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

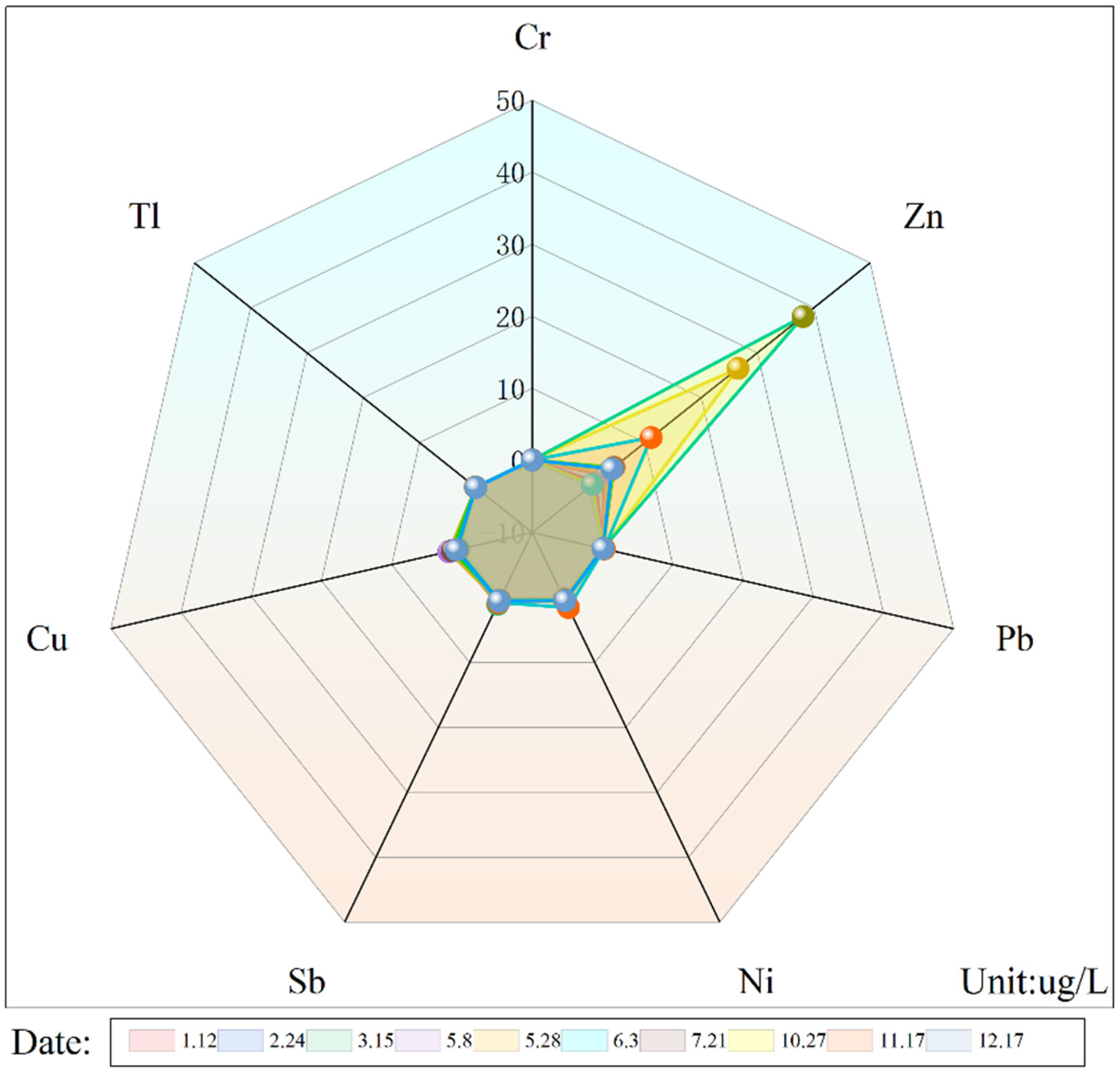
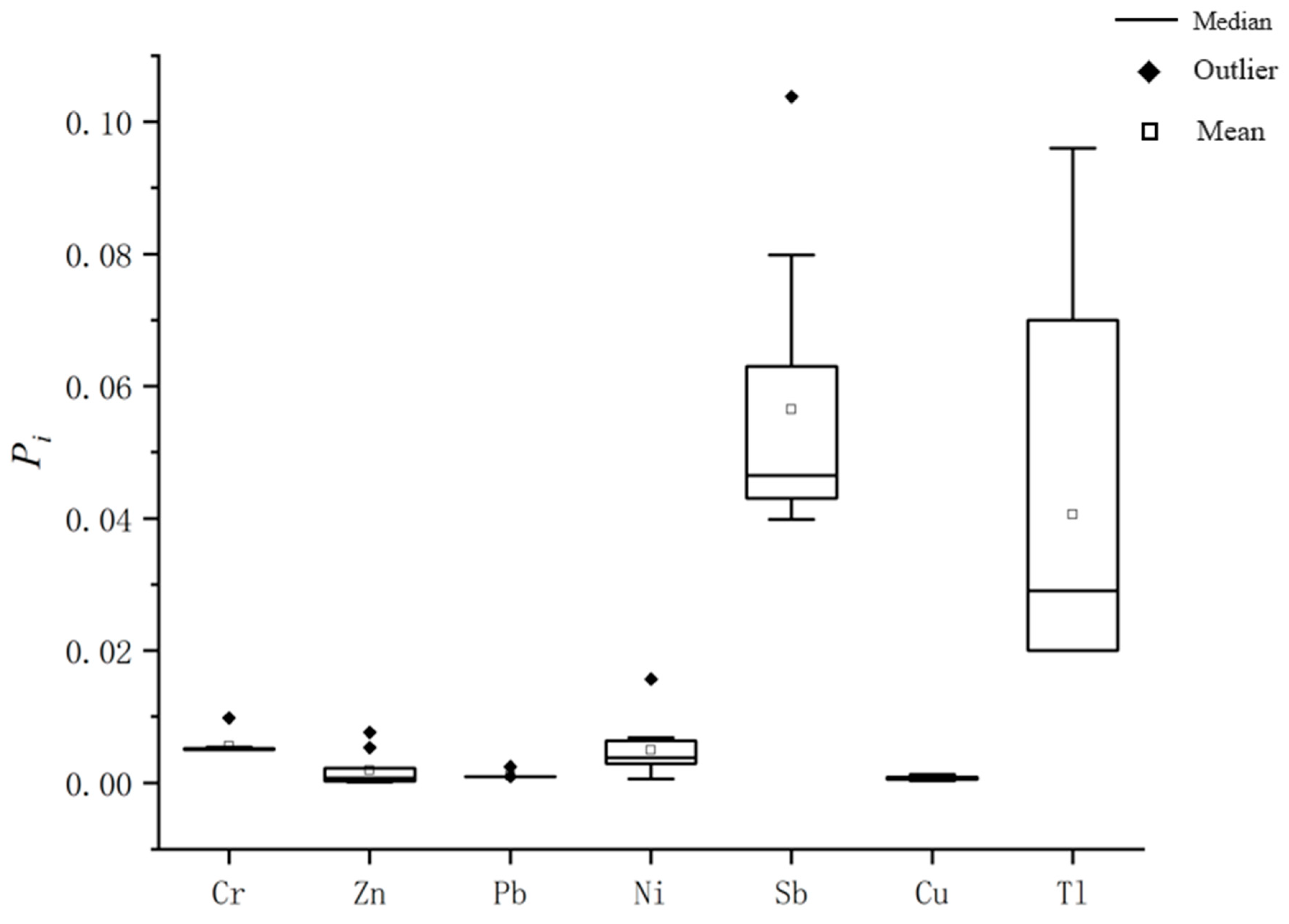

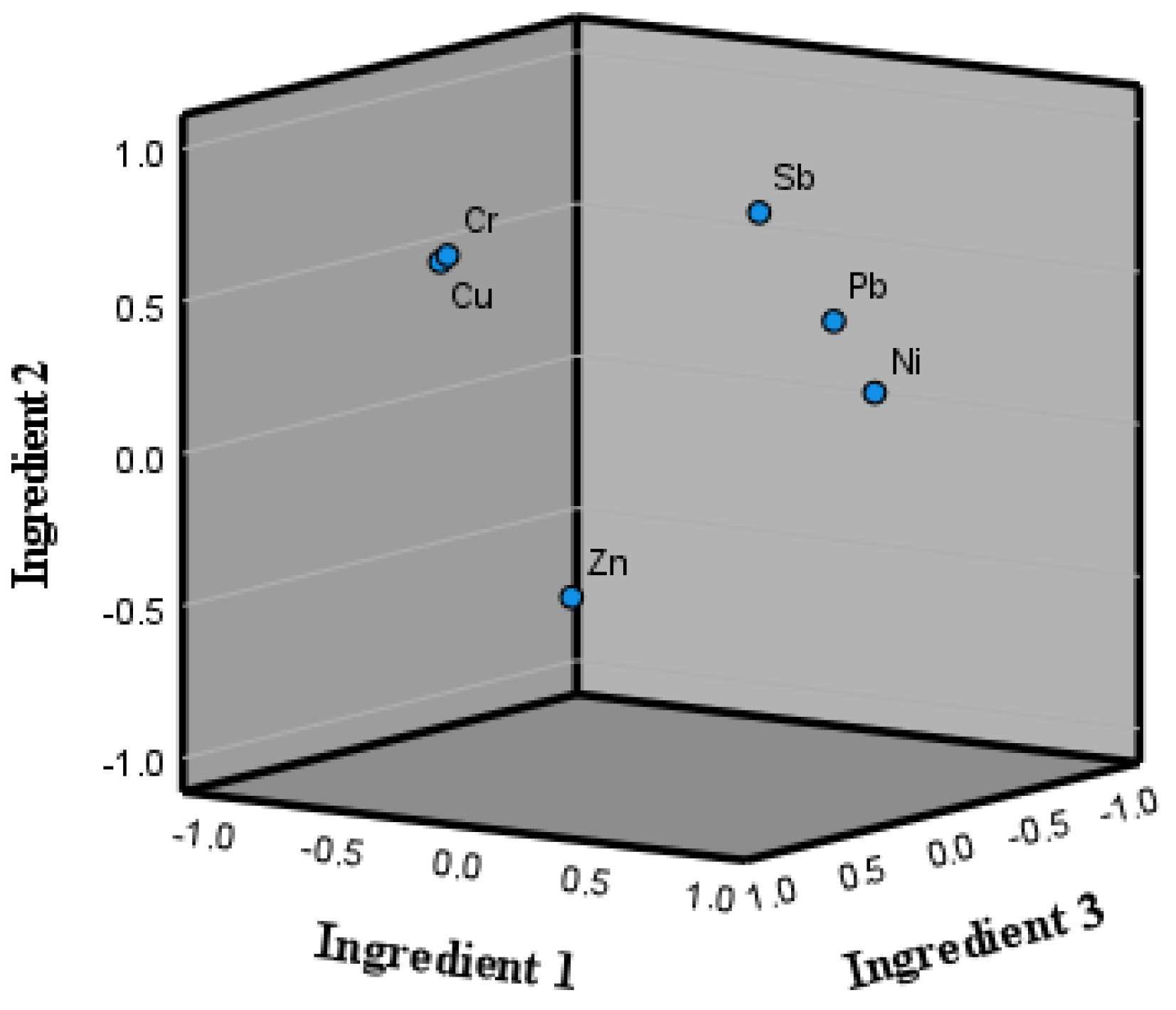
| Unit: μg/L | Detection Limit | Quantitation Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Cr | 0.015 | 0.045 |
| Zn | 0.0521 | 0.156 |
| Pb | 0.0186 | 0.0558 |
| Ni | 0.0045 | 0.0135 |
| Sb | 0.00494 | 0.0148 |
| Cu | 0.018 | 0.054 |
| Tl | 0.002 | 0.006 |
| Unit: μg/L | Internal Standard Elements and Concentration Range of Multi-Element Standard Solution Used (μg/L) | Correction Curve Equation | Correction Correlation Coefficient r |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Sc (5~100) | y = 0.207x + 0.287 | 0.9999 |
| Zn | Ge (5~500) | y = 0.036x − 0.058 | 1.0000 |
| Pb | Bi (5~500) | y = 0.209x + 0.032 | 1.0000 |
| Ni | Ge (5~500) | y = 0.182x − 0.261 | 0.9999 |
| Sb | Rh (5~500) | y = 0.002x + 0.006 | 0.9999 |
| Cu | Ge (5~500) | y = 0.500x + 0.219 | 1.0000 |
| Tl | Bi (5~500) | y = 0.032x + 0.295 | 0.9995 |
| Single-Factor Pollution Index | Grade | Nemerow Comprehensive Pollution Index | Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pi ≤ 1 | Class I, no contamination | P Synthetic ≤ 0.7 | Class I, no contamination |
| Pi ∈ (1, 2] | Class II, slightly contaminated | P Synthesis ∈ (0.7, 1.0] | Class II, slightly contaminated |
| Pi ∈ (2, 3] | Class III, lightly contaminated | P Synthesis ∈ (1.0, 2.0) | Class III, lightly contaminated |
| Pi ∈ (3, 5] | Class IV, moderately contaminated | P Synthesis ∈ (2.0, 3.0) | Class IV, moderately contaminated |
| Pi > 5 | Class V, heavily polluted | P Overall > 3.0 | Class V, heavily polluted |
| Element | Cr | Zn | Pb | Ni | Sb | Cu | Tl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background content (μg/L) | 10 | 5000 | 100 | 100 | 10 | 1500 | 1 |
| Toxicity coefficient | 2 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 10 |
| Metals | Minimum (µg/L) | Maximum (µg/L) | Mean (µg/L) n = 10 | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation (%) | Screening Value (µg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 0.05 | 0.098 | 0.0554 | 0.0150 | 27.08 | 10 |
| Zn | 0.67 | 38.08 | 9.312 | 12.781 | 137.25 | 5000 |
| Pb | 0.09 | 0.342 | 0.1056 | 0.0479 | 45.45 | 100 |
| Ni | 0.06 | 1.566 | 0.4896 | 0.431 | 88.03 | 100 |
| Sb | 0.398 | 1.038 | 0.565 | 0.208 | 36.81 | 10 |
| Cu | 0.498 | 1.9 | 1.061 | 0.4299 | 40.53 | 1500 |
| Tl | 0.02 | 0.096 | 0.0406 | 0.0279 | 68.97 | 1 |
| Cr (µg/L) | Zn (µg/L) | Pb (µg/L) | Ni (µg/L) | Sb (µg/L) | Cu (µg/L) | Tl (µg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GW1 | 0.051 | 10.085 | 0.095 | 0.484 | 0.661 | 1.188 | 0.049 |
| GW2 | 0.074 | 164.656 | 0.090 | 0.405 | 0.523 | 1.15 | 0.041 |
| GW3 | 0.050 | 14.832 | 0.101 | 0.532 | 0.59 | 1.0574 | 0.038 |
| GW4 | 0.051 | 11.80 | 0.151 | 0.632 | 0.545 | 1.106 | 0.038 |
| GW5 | 0.051 | 8.616 | 0.091 | 0.395 | 0.506 | 0.802 | 0.037 |
| Metal Elements | Single-Factor Contamination Index Range | Single-Factor Pollution Index Average | Pollution Index | Comprehensive Pollution Index | Contamination Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 0.05–0.0098 | 0.00554 | No pollution | 0.01588 | No pollution |
| Zn | 0.000134–0.007616 | 0.001862 | No pollution | ||
| Pb | 0.0009–0.00242 | 0.001056 | No pollution | ||
| Ni | 0.0006–0.01566 | 0.004896 | No pollution | ||
| Sb | 0.0398–0.1038 | 0.0565 | No pollution | ||
| Cu | 0.000332–0.001267 | 0.000707 | No pollution | ||
| Tl | 0.02–0.096 | 0.0406 | No pollution |
| Principal Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Sum of Squared Loadings for Extraction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum | Percentage of Variance | Accumulation % | Total | Percentage of Variance | Accumulation % | |
| 1 | 2.450 | 40.826 | 40.826 | 2.450 | 40.826 | 40.826 |
| 2 | 1.651 | 27.523 | 68.349 | 1.651 | 27.523 | 68.349 |
| 3 | 0.968 | 16.130 | 84.479 | 0.968 | 16.130 | 84.479 |
| 4 | 0.586 | 9.762 | 94.241 | |||
| 5 | 0.266 | 4.441 | 98.681 | |||
| 6 | 0.079 | 1.319 | 100.000 | |||
| Metals | Component 1 | Component 2 | Component 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | −0.019 | 0.913 | −0.004 |
| Zn | 0.058 | −0.050 | 0.951 |
| Pb | 0.934 | −0.104 | 0.082 |
| Ni | 0.880 | −0.356 | 0.151 |
| Sb | 0.650 | 0.258 | −0.408 |
| Cu | −0.171 | 0.898 | −0.133 |
| Place | Cr | Zn | Pb | Ni | Cu | Tl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study | 0.0554 | 9.31196 | 0.1056 | 0.4896 | 0.565 | 1.0606 |
| Mathura, India [29] | 1900 | 105 | 2290 | 3373 | 400 | / |
| Guangzhou [30] | 3.3 | 27.99 | 1.61 | / | 1.87 | / |
| Lingjiang, Zhejiang [31] | 7.21 | 37 | 4.45 | 1.91 | 4.00 | / |
| Campania Plain, Southern Italy [32] | 12.8 | 1.22 | 3.66 | 3.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, M.; Xue, S.; Hui, F.; Cao, W.; Zhang, P. Environmental Risk Assessment of Metals in Groundwater in an Area of Jiujiang City, Jiangxi Province, China. Toxics 2025, 13, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030197
Tian M, Xue S, Hui F, Cao W, Zhang P. Environmental Risk Assessment of Metals in Groundwater in an Area of Jiujiang City, Jiangxi Province, China. Toxics. 2025; 13(3):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030197
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Minghao, Shihan Xue, Fujiang Hui, Weiyuan Cao, and Ping Zhang. 2025. "Environmental Risk Assessment of Metals in Groundwater in an Area of Jiujiang City, Jiangxi Province, China" Toxics 13, no. 3: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030197
APA StyleTian, M., Xue, S., Hui, F., Cao, W., & Zhang, P. (2025). Environmental Risk Assessment of Metals in Groundwater in an Area of Jiujiang City, Jiangxi Province, China. Toxics, 13(3), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030197







